Psyc 100 Chap 2
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
frontal lobe
complex thought, planning, movement
perfrontal cortex
personality, emotional behavior , mood
nervous system
billions of cells in brain that receive process and respond to information.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body (2)
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
voluntary nerves, senses, behavior
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
controls gland, muscles, organs, AUTO BEHAVIOR
Neuron
cells in nervous system that sends and receives information thru body
sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. body-brain
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. brain -body
Soma
cell body
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
myelin sheath
covers the ____ to make faster and protect
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
terminal buttons
Small knobs at the end of axons that secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
neurtransmitters
chemical messengers
excitatory message
increases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will activate.
inhibitory message
decreases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will activate
all or nothing
need enough messages to either fire or no.
lightswitch
Broca's area
speech production
Forebrain
motivation, emotion, complex thought (4)
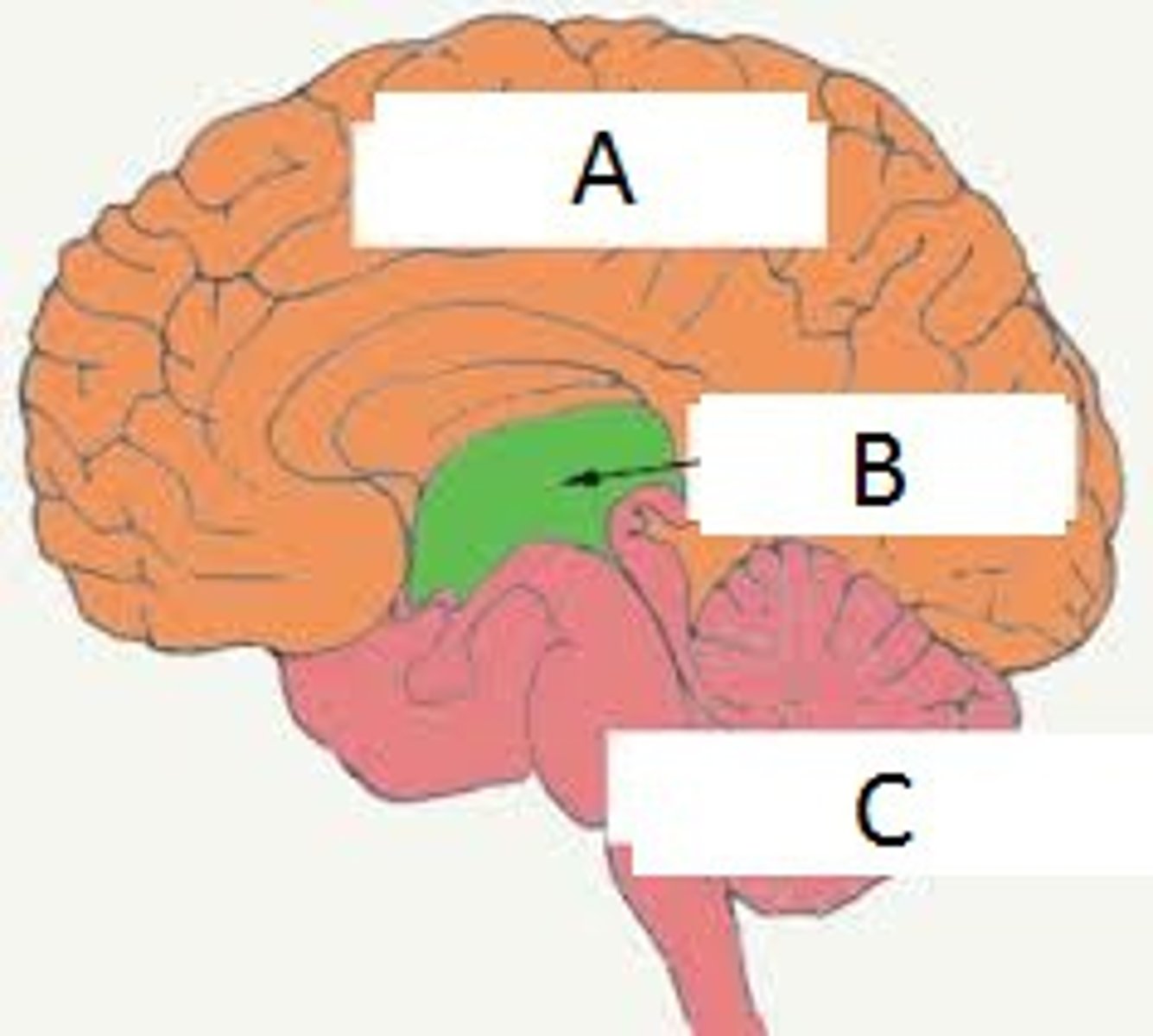
Thalamus
sensory switchboard
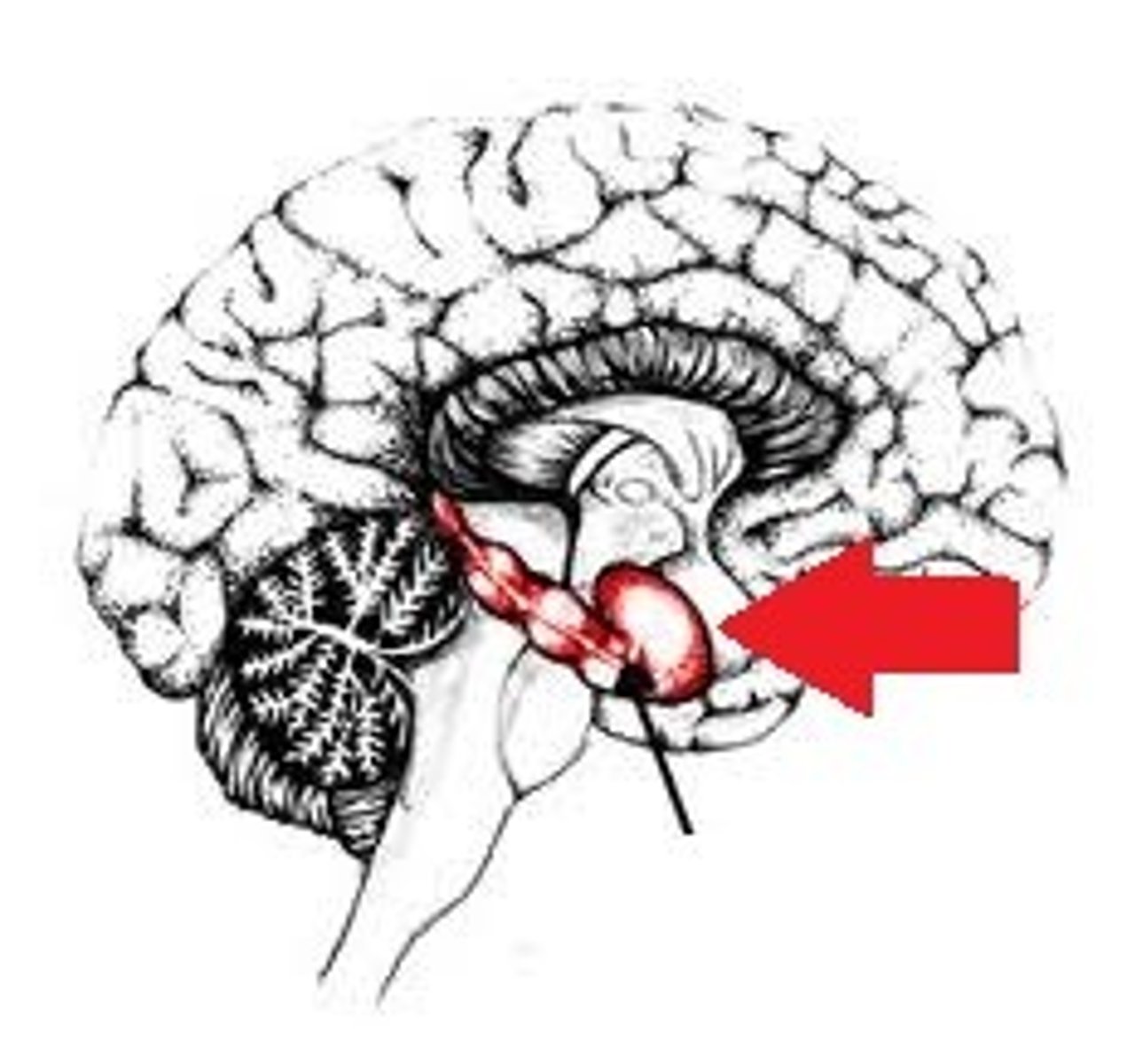
Amgydala
emotions, fear
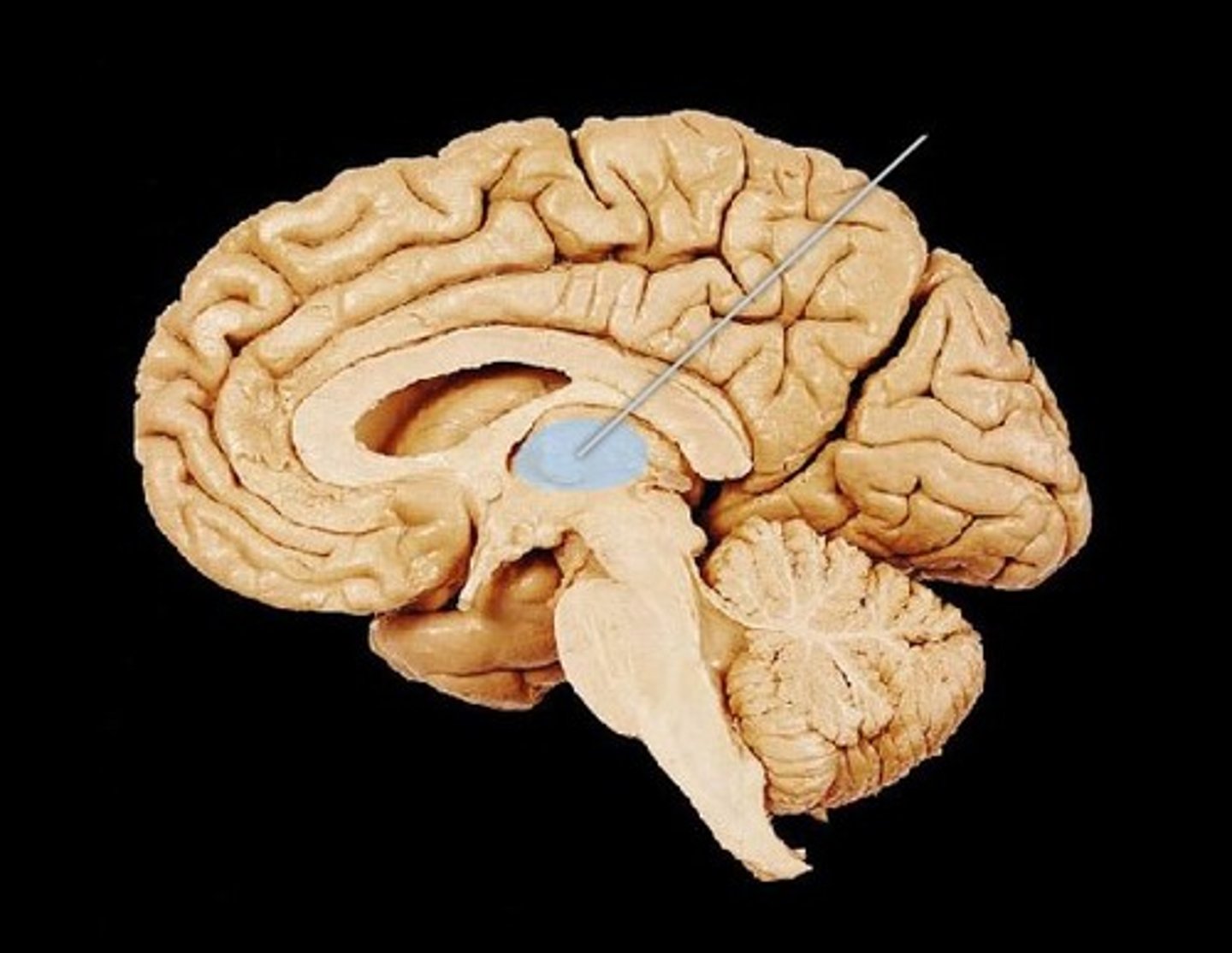
Hippocampus
memory formation and new
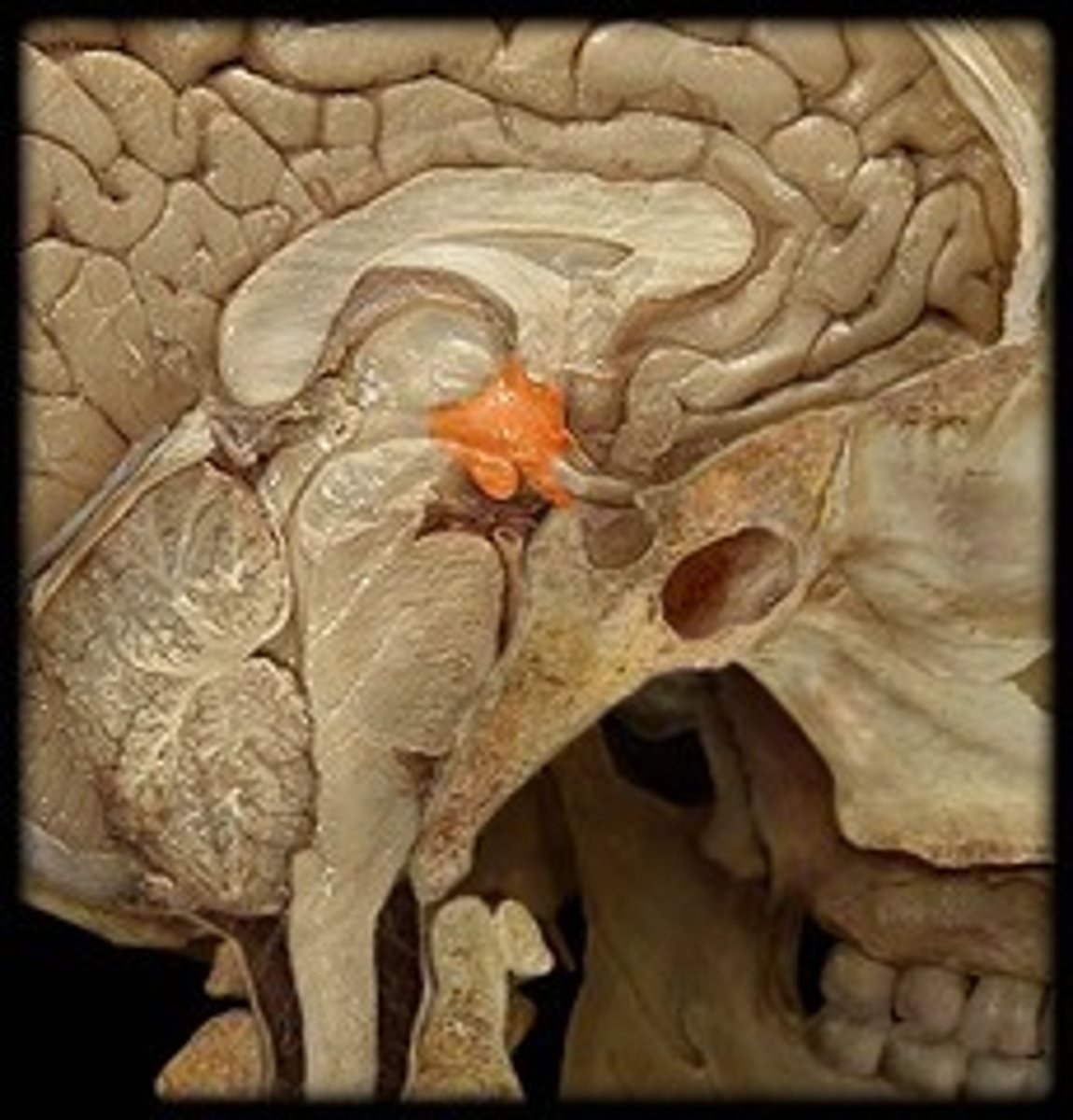
Hypothalamus
regulates survival, body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior
Midbrain
movement
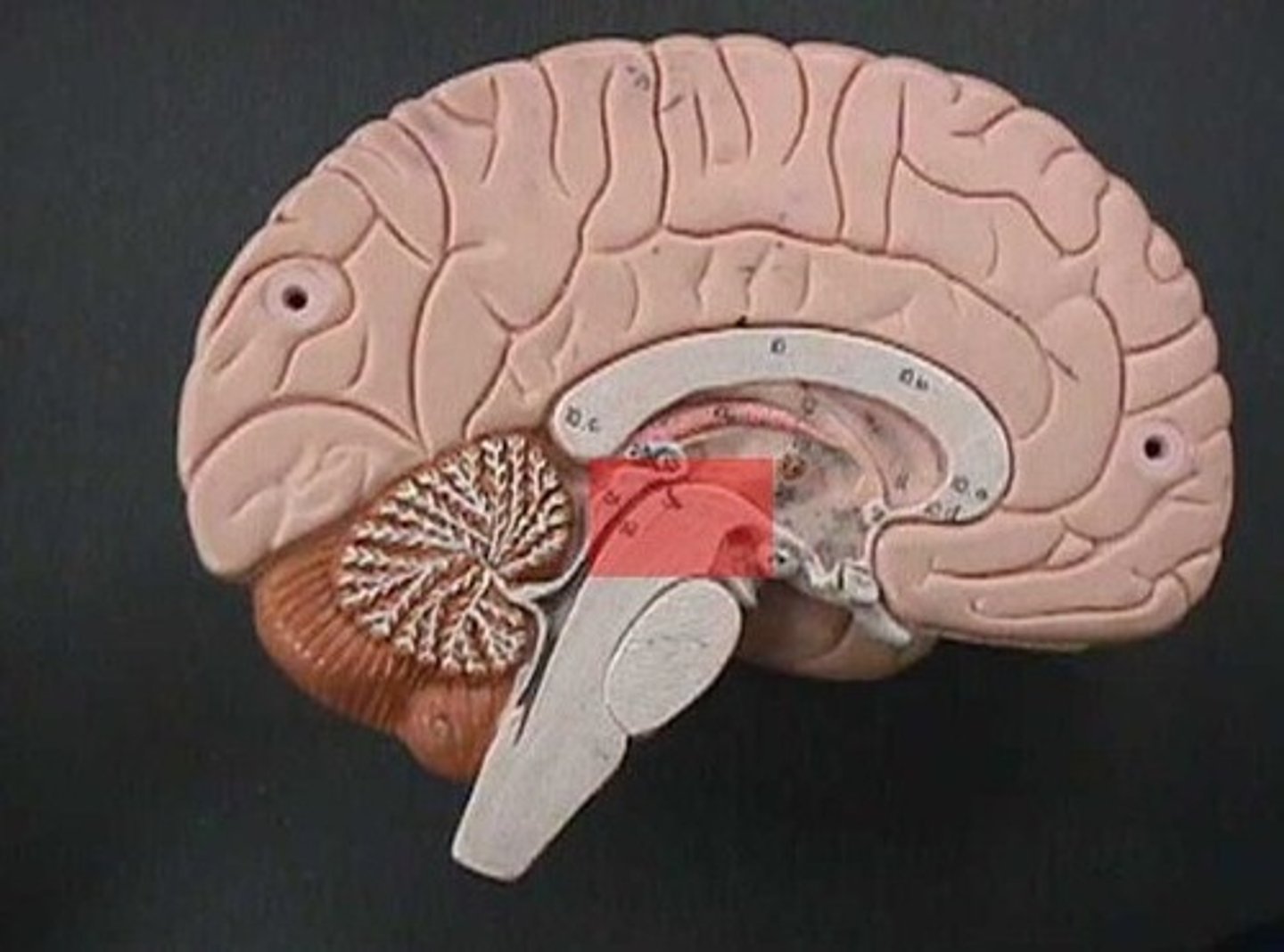
substantia nigra
midbrain structure where dopamine is produced; involved initiation movement
Hindbrain
survival functions, movement (3)
Cerebellum (little brain)
Balance, coordination, learning
Pons
sleep and arousal
Medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing, survival function
temporal lobe
hearing, smell, memory
occipital lobe
vision
parietal lobe
receives sensory input for touch, spatial relations.
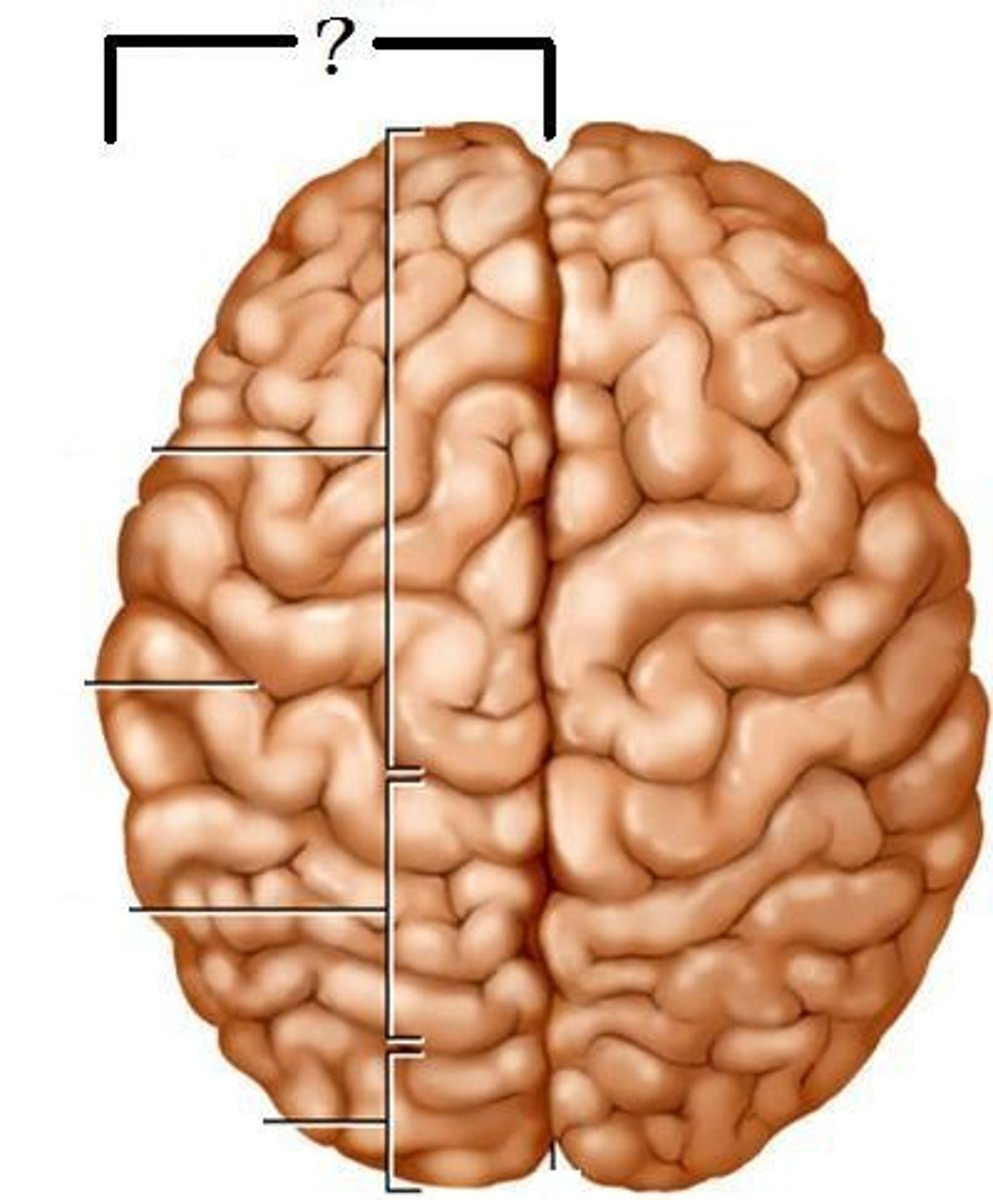
left hemisphere
controls the right side of the body; analytical, language, math
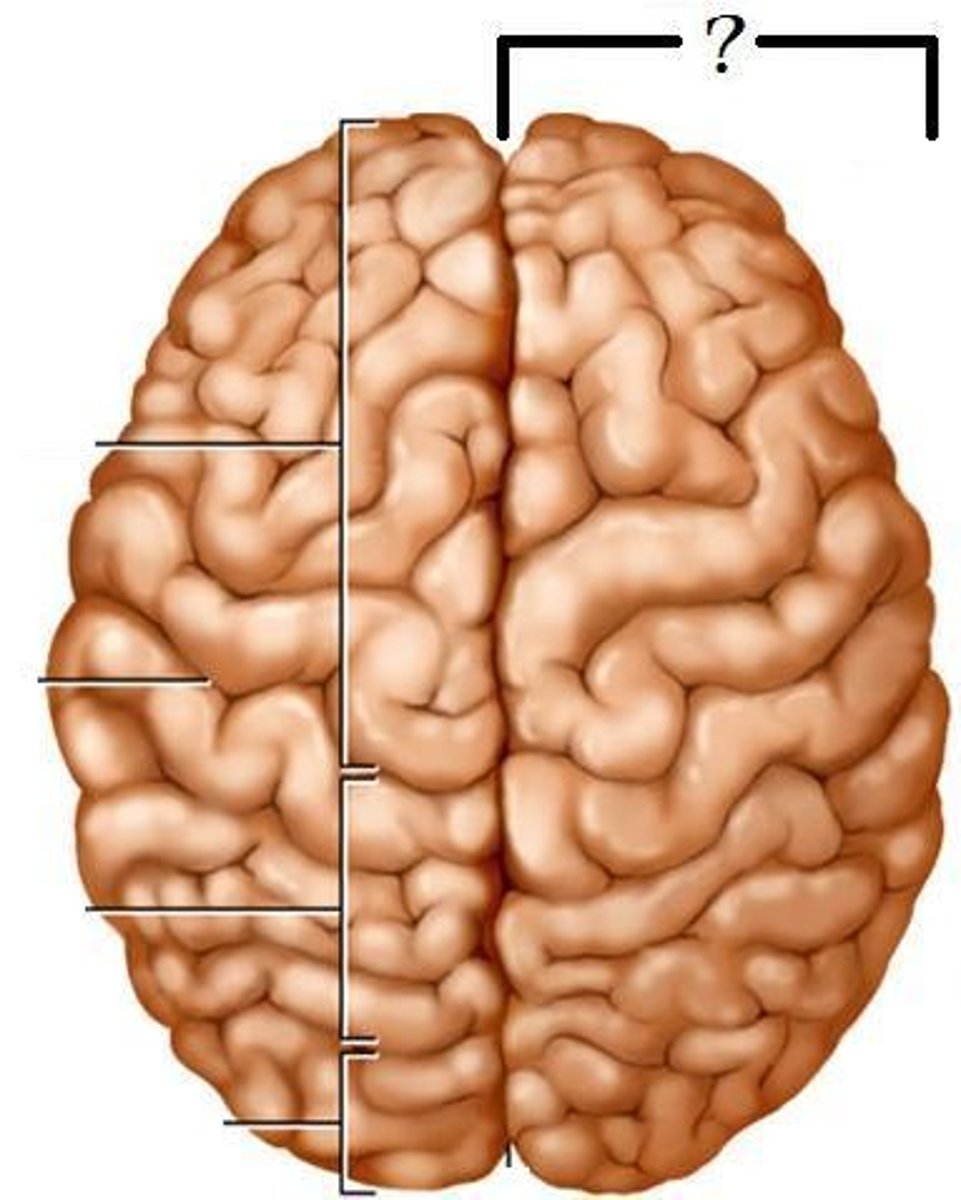
right hemisphere
controls the left side of the body; creative, intuitive, spacial, emotional thought
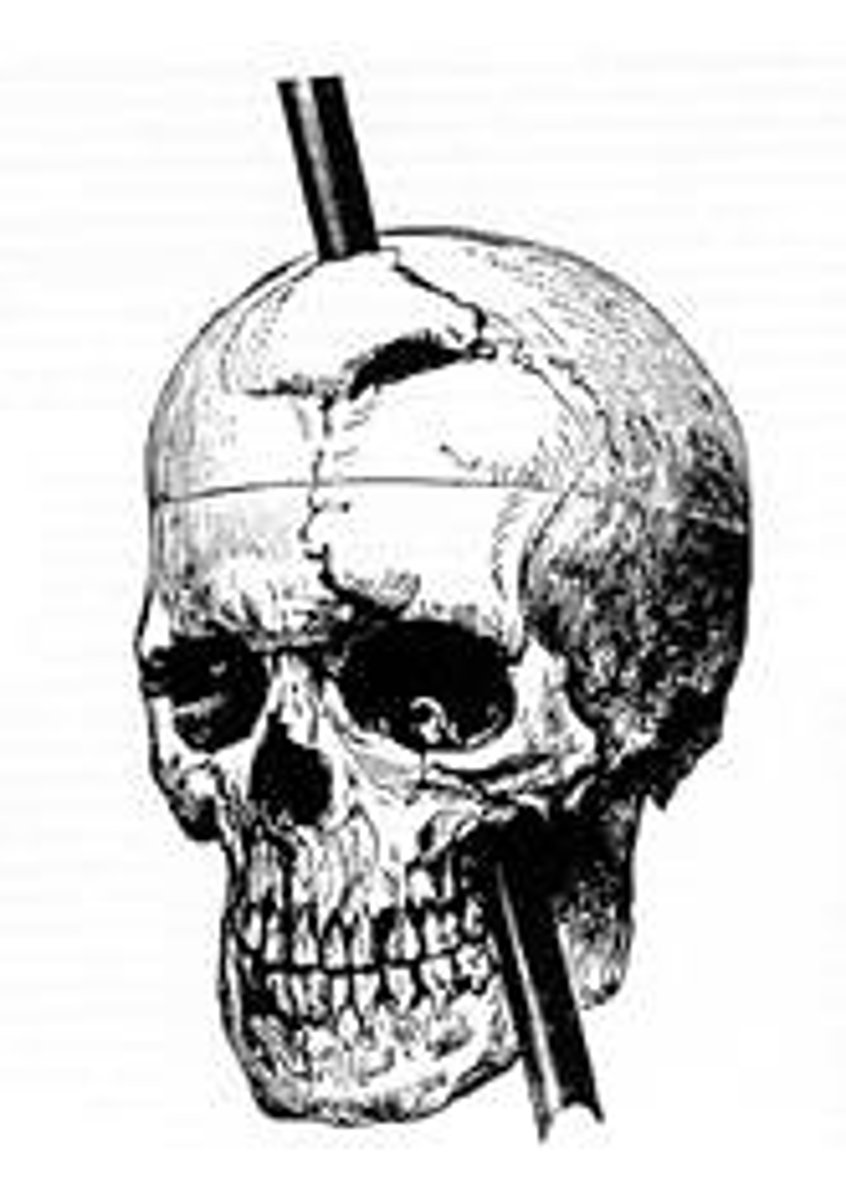
Phineas Gage
railroad worker who survived a severe brain injury that dramatically changed his personality and behavior; case played a role in the development of the understanding of the localization of brain function
Corupus Callosum
connects the two hemispheres of the brain