Biology - Cell Membranes and Transport Across Membranes
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Explain how three features of a plasma membrane adapt it for its functions.
Phospholipid bilayer acts as a barrier to prevent polar substances from entering the cell
Membrane contains cholesterol, Increasing the strength and stability of the membrane
Gylcoproteins act as receptors
What factors increase transport across membranes?
Increase temperature = increase KE
Increase SA
Increase no. transporter proteins
Shorter diffusion distance
Smaller molecules diffuse faster
Rate of respiration/availability of ATP
What is osmosis?
Net movement of water from a high water potential to a low water potential, through a partially permeable membrane.
What is an isotonic solution?
Contains equal concentratinos of solutes on both sides.
What is a hypotonic solution?
lower solute concentration than the cell so high water potential in solution
water moves into the cell causing plant cells to swell and animal cells to swell and burst
What is a hypertonic solution?
The solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell so low water potential in solution
water moves out of the cell and into the solution causing the cell to plasmolyze
What affects osmosis?
Water potential gradient
Thickness of exchange surface
Surface area
Describe the process of co-transport in an ileum epithelial cell
1) Na+ actively transported out of ileum cells into blood by Na/K pump
2) Concentration gradient of Na+ in lumen of ileum higher than in inside epithelial cell
3) Causes sodium ions to diffuse from lumen into cell down concentration gradient using co-transporter proteins
4) sodium carries glucose/amino acid into cell via co-transporter protein.
5) Concentration of glucose/amino acid in cell higher
6) Glucose/amino acid diffuses out of cell into blood by facilitated diffusion through protein channel (down conc. gradient)
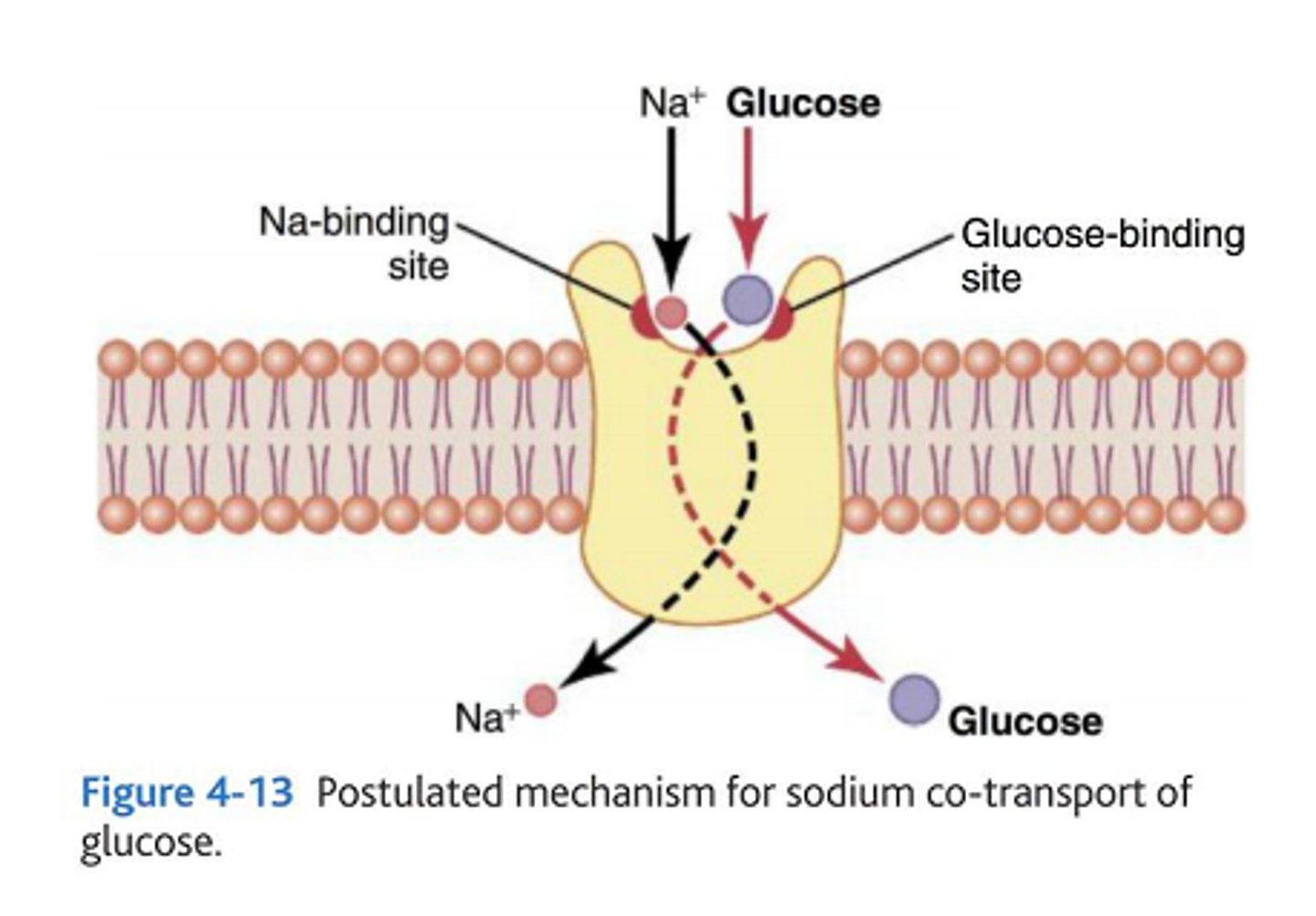
What is plasmolysis?
Shrinkage of a cell due to water being removed due to a hypertonic solution.
Why is it called the fluid mosaic model?
The phospholipid bilayer fluid as molecules move laterally in membrane and proteins scattered in mosaic pattern.
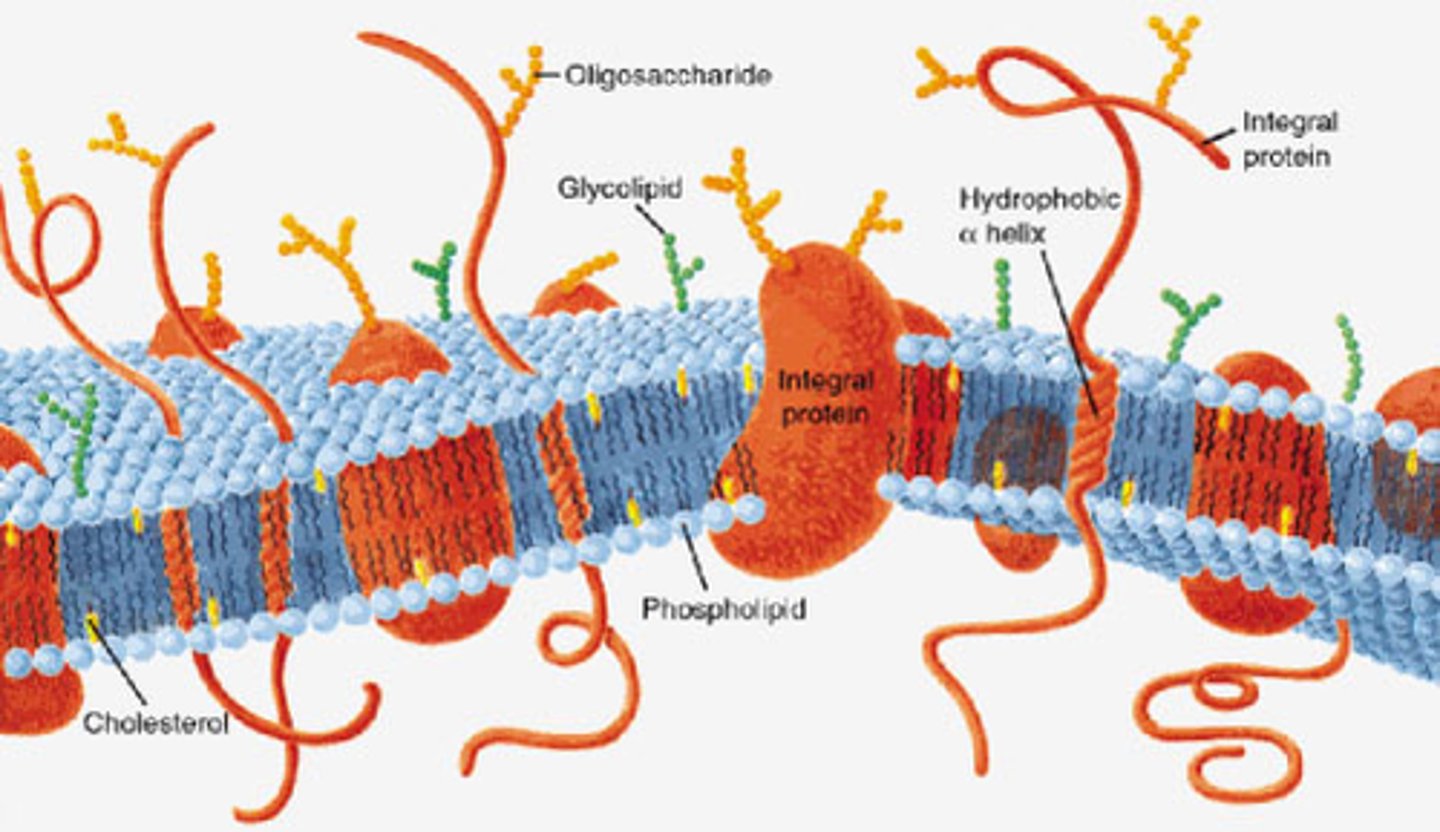
Many different substances enter and leave a cell by crossing the cell surface membrane. Describe how substances can cross a cell surface membrane.
By diffusion - substances move DOWN a concentration gradient
Simple diffusion - through bilayer, molecules are small and/non-polar
Facilitated diffusion - substances diffuse though transport proteins (carrier/channel proteins)
By osmosis - movement of water only down a concentration gradient
By active transport - ATP used in transporting substances against concentration gradient
Co-transport of glucose and amino acids using Na+ ions
Endocytosis and exocytosis - bulk transport of substances into/out of a cell
What are the roles of proteins?
Cell growth, Replace dead cells
Acts as enzymes and hormones
Provides structural support
Receptors
Allows transport (carrier/channel proteins)
What are the roles of cholesterol?
Reduces lateral movement of membrane and makes less fluid
What are the roles of glycolipids?
Recognition sites/receptors (T helper cells)
Maintain stability
Help cells to attach to one another forming tissues
Describe and explain the functions of the cell surface membrane
Transport via simple/facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, co-transport
Cell signalling as hormones bind to receptor proteins
Membrane-bound organelles in Eukaryotic cytoplasm allows metabolic reactions to take place
Isolates enzymes that may digest/damage the cell
Provides internal transport system - RER
Surface for reactions on RER (ribosomes embedded in plasma membrane)
Immune response as contains glycoprotein receptors/antibodies (T helper cells and B cells)
What happens to the phospholipid bilayer as temperature increases?
Phospholipids move around more as they gain more KE, increasing the permeability of the membrane
Eventually denatures and even more permeable
What is diffusion?
Net movement of particles from a high concentration to lower concentration - passive as no energy required
What is facilitated diffusion?
Movement of charged ions across a membrane through transport proteins (channel/carrier proteins)
What is active transport?
the movement of molecules through membrane using carrier proteins against concentration gradient
ATP hydrolysed to provide energy for active transport
Co-transporters type of carrier protein that simultaneously bind to two molecules
Give two differences between facilitated diffusion and osmosis.
Omosis is the movement of water molecules (only) down a water potential gradient
Facilitated diffusion requires protein carriers or channel proteins whereas osmosis doesn't
Give three properties of an unknown substance that would allow it to diffuse through the membrane.
non-polar substance
lipid soluble
small substance
Explain the link between active transport and the presence of large number of mitochondria in a cell.
Mitochondria are the site of aerobic respiration which produces ATP
ATP is needed for active transport, to move substances against their concentration gradient
Explain why the rate of diffusion is more rapid at higher temperatures.
Particles have more kinetic energy so particles move faster
The water potential of a plant cell is -400kPa.
The cell is put into a solution with a water potential of -650kPa.
Describe and explain what will happen to the cell.
The water potential of the solution is more negative/lower than the water potential of the plant cell
Water will move outside the plant cell, by osmosis.
This will cause the plant cell to become plasmolysed (water loss from osmosis, resulting in gaps between the cell wall and cell membrane)
Carrot cylinders were left for 18 hours in the sucrose solution. Explain why they were left for a long time.
So the water potential of the carrot cylinders and solution reach osmotic equilibrium.
Explain how you would use a graph to predict the concentration of sucrose that would show no change in length of the carrot cylinders.
Plot results on a graph and draw a line or curve of best fit. Find the x-intercept (or where the line crosses the x-axis)
How many molecules are produced when a triglyceride molecule is completely hydrolysed?
4 molecules - 1 glycogen and 3 fatty acid tails
Many biological molecules are polymers. Explain why triglycerides are not polymers.
Triglycerides are not made up of monomers
Explain the meaning of a saturated molecule.
No double bonds between the CARBON ATOMS
A drop of phospholipid with a volume of 1mm^3 was put onto A drop of phospholipid spread out to form a film on the surgace of the water which covered an area of 400 000 mm^2. Calculate the length (x) of a single phospholipid molecule. Show your working. (2)
Volume of a Cylinder = CSA X Length(X)
X = V/CSA
X = 1/ 400 000
X = 2.5 X10^-6
Explain what causes the phospholipid molecule to be arranged in a particular way when put in water.
Hydrophilic heads face towards the water and Hydrophobic heads face away from the water.
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide. Name one chemical element present in a phospholipid which would not be present in chitin.
Phosphorus
The absorption of glucose into a cell leads to the movement of water into a cell. Explain how.
The absorption of glucose makes the water potential of the cell lower
Water moves into the cell down a water potential gradient by osmosis
The students gave the results as a ratio. What is the advantage of giving the reults as a ratio? (2)
Allows for comparison, because discs have different inital masses
Explain how taking repeated readings can improve the reliability of results.
Allows one to calculate a mean and therefore reduces the effect of anomalies or allows one to identify anomalies
The students used a graph of their results to find the sodium chloride solution with the same water potential as the apple discs. Describe how they did this.
- Plot NaCl concentration against ratio
- Draw a line of best fit
- Find where the ratio is 1 (x-intercept is 1)
The students were advised that they could improve their graph by taking additional readings. Explain how.
- More readings = more reliable line of best fit
- So the point where the ratio is 1 is more reliable
Cyanide is a substance which affects respiration. Explain the effect of cyanide on the uptake of sodium ions by the tissue.
Cyanide stops respiration (ETC)
So no ATP
ATP required for active transport so uptake of Na+ ions decreases