Pharm 2 Steroids
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
where are steroids made, what part of the adrenal gland
cortex
how do we obtain steroids?
exogenous = given through meds
AND
endogenous = our body produces it naturally
What are the functions of steroids and how ?
glucose, sodium, immune
INCREASE BLOOD GLUCOSE
INCREASE SODIUM AND WATER RETENTION
DOWN REGULATE THE IMMUNE RESPONSE
Increase blood glucose
(either endogenous or giving a steroid, the glucose will go up. ALWAYS HYPERGLYCEMIA)
Gluconeogenesis cause synthesis of glucose
Counteracting with insulin insulin decrease sugar, steroids decrease it
Increase sodium and water retention
(always POSSIBLY HYPERTENSION)
Regulate (down) the immune response
they suppress immune system. Can be good or can be bad. E.g. if someone has asthma attack, its good to rest immune system. Bad bc watch for infections.
what are the 2 major types of exogenous corticosteroids?
glucocorticoids
mineralocorticoids
how do glucocorticoids work vs mineralocorticoids
glucocorticoids = anti-inflammatory.
mineralocorticoids = sodium and water retention, increase BP
Retaining sodium and water, when the body needs to maintain blood pressure a.k.a blood volume
now lets elaborate and anti-inflammatory effects vs mineralocorticoid effects
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Steroids are anti-infl and do it in different ways. And to do this, you have to reduce immune system. The whole point of steroids.
how do they do it
•Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferations
–T cells this is suppressing immunity
–B cells
•Inhibition of interleukin production reduce interleukins, they down regulate interleukin
•Inhibition of capillary permeability to leukocytes neutrophils get trapped in blood vessel, they cant go to inflammation cite
•Inhibit prostaglandin production
•Reduce the inflammation by SUPPRESS IMMUNE SYSTEM
Mineralocorticoid Effects
Some steroids are very close to aldosterone so this is kinda a 3rd major type. GIVE TO PT WHEN EXTREMELEY HYPOTENSION ALONG W SALINE, EPINEPHRINE FOR VASCONSTRICTION
•Aldosterone like effects
–Increase serum sodium
–Increase water retention
–Increase blood pressure
–Indications
•Hypotension (severe)
– Septic shock
NBNBNBNB THE NAMES OF THE STEROIDS
CHP PTM BD
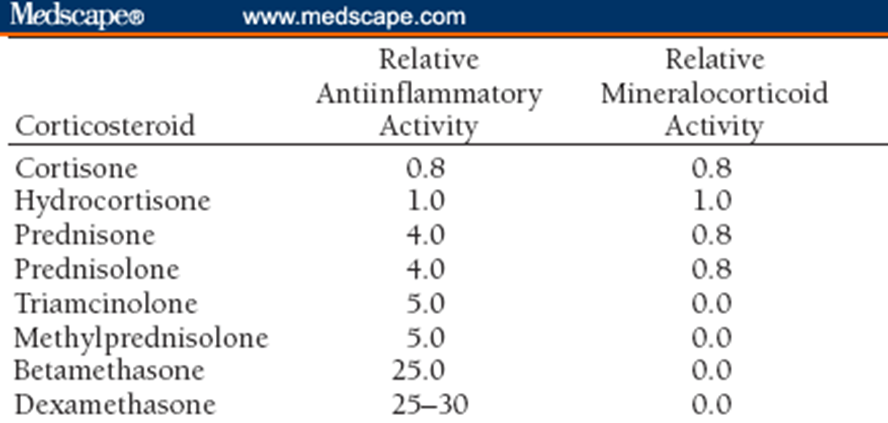
Which of the following corticosteroids has the most relative anti-inflammatory activity?
a) Cortisone
b) Hydrocortisone
c) Prednisone
d) Dexamethasone
d) Dexamethasone
Which of the following corticosteroids has the most relative anti-inflammatory activity?
a) Prednisone
b) Triamcinolone
c) Betamethasone
d) Hydrocortisone
c) Betamethasone
Which of the following corticosteroids has the most relative anti-inflammatory activity?
a) Triamcinolone
b) Prednisone
c) Hydrocortisone
d) Cortisone
a) Triamcinolone
Which of the following corticosteroids has the most relative anti-inflammatory activity?
a) Prednisolone
b) Hydrocortisone
c) Methylprednisolone
d) Cortisone
c) Methylprednisolone
Which of the following corticosteroids has the most relative anti-inflammatory activity?
a) Prednisolone
b) Cortisone
c) Prednisone
d) Hydrocortisone
c) Prednisone
Which of the following corticosteroids exhibits some relative mineralocorticoid activity?
a) Prednisone
b) Triamcinolone
c) Dexamethasone
d) Betamethasone
a) Prednisone
Among the following, which corticosteroid demonstrates a notable relative mineralocorticoid effect?
a) Prednisolone
b) Cortisone
c) Hydrocortisone
d) Prednisone
c) Hydrocortisone
(Note: Hydrocortisone has a relative mineralocorticoid activity of 1.0, which is higher than Prednisolone's 0.8, Cortisone's 0.8, and Prednisone's 0.8)
Among the following, which corticosteroid demonstrates a notable relative mineralocorticoid effect?
a) Betamethasone
b) Dexamethasone
c) Prednisolone
d) Methylprednisolone
c) Prednisolone
Among the following, which corticosteroid demonstrates a notable relative mineralocorticoid effect?
a) Prednisolone
b) Triamcinolone
c) Betamethasone
d) Cortisone
d) Cortisone
(Note: Both Cortisone and Hydrocortisone have mineralocorticoid activity, but Hydrocortisone has a higher value of 1.0 compared to Cortisone's 0.8)
Among the following, which corticosteroid demonstrates a notable relative mineralocorticoid effect?
a) Betamethasone
b) Cortisone
c) Triamcinolone
d) Hydrocortisone
b) Hydrocortisone
Dosage forms

what should you NB about steroids and wanting to be off of them and also the time of day you take them
They taper you off
Don’t take steroids at night bc they cause insomnia, they mess w endogenous cortisol
INDICATIONS (2) what are the indications for steroids?
autoimmune diseases
Post Traumatic/ Surgical Treatment
give some examples of autoimmune diseases
–Rheumatoid arthritis
–Sjogren’s disease
–Post- transplantation
this avoids rejection bc they supress immune system
Solid organ
–Anaphylactic reactions
–Asthma
–Allergic rhinitis
–Traumatic injuries and inflammation
–Shock and critically ill patients
give an example of a post traumatic/surgical treatment in dentistry
Removal of impacted mandibular molar tooth
why would you give a steroid to someone who gets their wisdom tooth removes?
To reduce the inflammation following traumatic procedures
Sometimes opioids are not enough, or acetaminophen is not anti inflammatory. So sometimes you only have NSAIDS or steroids
true or false, i should give steroids to someone who has asthma, why or why not
True
BC OF INFLAMMATION corticosteroids help reduce inflammation and control asthma symptoms.
true or false, i should give steroids to someone who has a sore throat
False
true or false, i should give steroids to someone who has allergic rhinitis or any kind of anaphylactic shock
True
because corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and help manage severe allergic reactions.
Remember, steroids are given when its exacerbated
Steroid ADRs (6) just list them rn
cardiovascular
Infections
GI
Osteoporosis
Ophthalmic
Dermatological
CARDIOVASCULAR what does it cause and how
Hypertension
due to sodium retention and increased blood volume
>also Increase renal excretion of potassium increase volume in blood, therefore increase BP
>also Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis so they maintain BP
CAN WE OR CAN WE NOT REVERSE THE HYPERTENSION CAUSED BY STEROIDS
yes, its reversable
INFECTIONS what does it cause and how
Increase susceptibility to infections
•Due to impaired cell mediated immunity
•Both T & B cells are affected
You can give them anti-viral or anti-fungal meds at the same time to prevent infection
GI. what does it cause and how
causes gastrointestinal perforations like ulcers or fistulas
OR EVEN
Oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis
AND
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)
bc they work similar to NSAIDS, bleeding (due to ulcer) in the GI.
NBNBNB is it bad to use a steroid and NSAID at the same time? why or why not?
ITS SOOOO BAD
avoid NSAID AND STEROID AT THE SAME TIME
If you have to, use them for the shortest period possible bc they both increase the risk of GI bleeding
remember that a fistula is an opening of GI all the way to the skin
A non-sterile environment like the GI, crossing into sterile environments like the blood
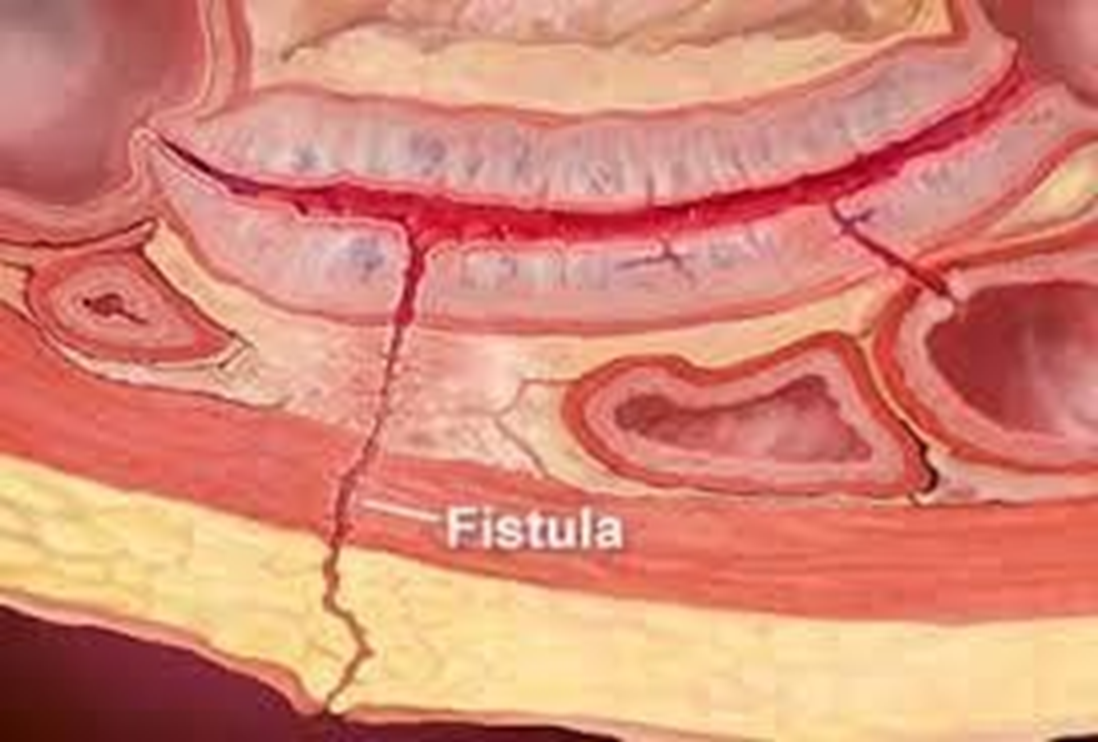
how is PUD caused
–Due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis prostaglandins protect GI from ulcer. Steroids and NSAIDS inhibit them
Cumulative dose
–Risk factors
Concurrent NSAID use
which effect is common in post- transplant patent if no appropriate prophylactic regimen
Oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis
Osteoporosis. how.
•Decrease calcium GI absorption
•Increase calcium renal excretion
•Decrease androgen and estrogen production
•Inhibition of osteoblasts proliferation
•Inhibition of osteocytes proliferation and induction their apoptosis
•Stimulation of osteoclasts bone resorption activities
whats the solution to Prevent Corticosteroid Induced Osteoporosis
SO GIVE THEM CALCIUM AND VITAMIN D SUPPLIMENT if they’re on steroids for months.
Ophthalmic (THERES TWO THAT HAPPEN IN OPHTHALMIC)
first what are they
Glaucoma
and
Cataracts
Glaucoma. how?
Increase intraocular pressure (IOP)
•Reduction aqueous humor outflow
Dose and duration dependent
NBNBNB True or false, if a steroid is more anti-inflammatory it causes more glaucoma
TRUEEEEE bc they increase intraocular pressure (IOP)
for example, dexamethasone is really anti-inflammatory and can lead to higher IOP/glaucoma
NBNBNB state which steroids are the most common, moderate incidence, and least common for glaucoma
–Most common with: betamethasone, dexamethasone
–Moderate incidence with: prednisone
–Least happened with: hydrocortisone
is a glaucoma reversable when you stop the steroid?
YES except if theres optic nerve damage
Cataracts. caused how?
–Opacification of the lens
–Dose and duration dependent
•Long term use
is a cataract reversable when you stop the steroid?
irreversible, BUT corrected by surgery
Dermatological. what happens and what about healing?
acne
happens after long term use, like weeks or months of using
•Cutaneous and subcutaneous atrophy
•Delayed wound healing
imagine combines w diabetes
so Yes they worsen the acne, but if the pt has SUPER INFLAMMED BAD acne, then you acc want to use a steroid
does the acne go away after discontinuing steroids?
–In most cases disappear when steroids is discontinued
just know that steroids affect growth
Cushing and Adrenal Suppression and preventing them
does steroids cause Cushing Syndrome and how?
whats all involved in Cushings?
•Caused by high doses of steroids over long period of time
–Redistribution of body fat
•Dorsocervical & supraclavicular
•Moon facing
•Central obesity
•Poor wound healing
•Easily bruising
•Hypertension
HYPERGLYCEMIA
how do we Prevent Cushing Syndrome
•Follow up
•Monitor
•Evaluate indication and consider discontinuation if possible
NBNBNB some things to remember about how to discontinue steroids, when to and when not to taper and why we taper instead of just cutting to off.
•We discontinue by tapering.
If you don’t taper the steroid PRECISSLY and just keep taking it or don’t do it all the way, the disease gets worse and you have to start again, so do it ASAP bc it takes a long time, either weeks or months.
•If pt is on steriods less than 2wks there’s no need to taper
•The reason we taper is bc the body gets confused since we produce it endogenous. The body stops producing it bc it thinks we have enough.
Adrenal Suppression. What causes it and what can it exist with.
HPA is a condition where the adrenal glands do not produce adequate steroid hormones, often due to prolonged steroid use. Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and low blood pressure.
•HPA axis suppression (a decrease in the body's ability to produce cortisols)
•High dose steroids more than a week
–Studies show as early as 5 days and as late as 3 weeks of HPA suppression post- steroid use
•In many cases, patients develop both Cushing’s and adrenal suppression concomitantly
Prevent Adrenal Suppression
•Tapering off the medication over days or weeks
–Depends on dose and duration of use
–Monitor symptoms
•Hypotension
•Hyponatremia
•Inflammatory disease exacerbation