3- cell specialisation
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
The order of levels
The cell is he basic unit of life
Organisms are made from millions of cells
Different cells within the organism are specialised for different roles
Specialised cell-tissue-organ-organ system- organism
Specialisation of cells
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells
These cells undergo mitosis and then differentiate Into a specialised cell for a specific function
Erythrocyte- red blood cell
Biconcave shape which increases the surface area
No nucleus or organelles
Increases space for haemoglobin
Small ands flexible to squeeze through capillaries
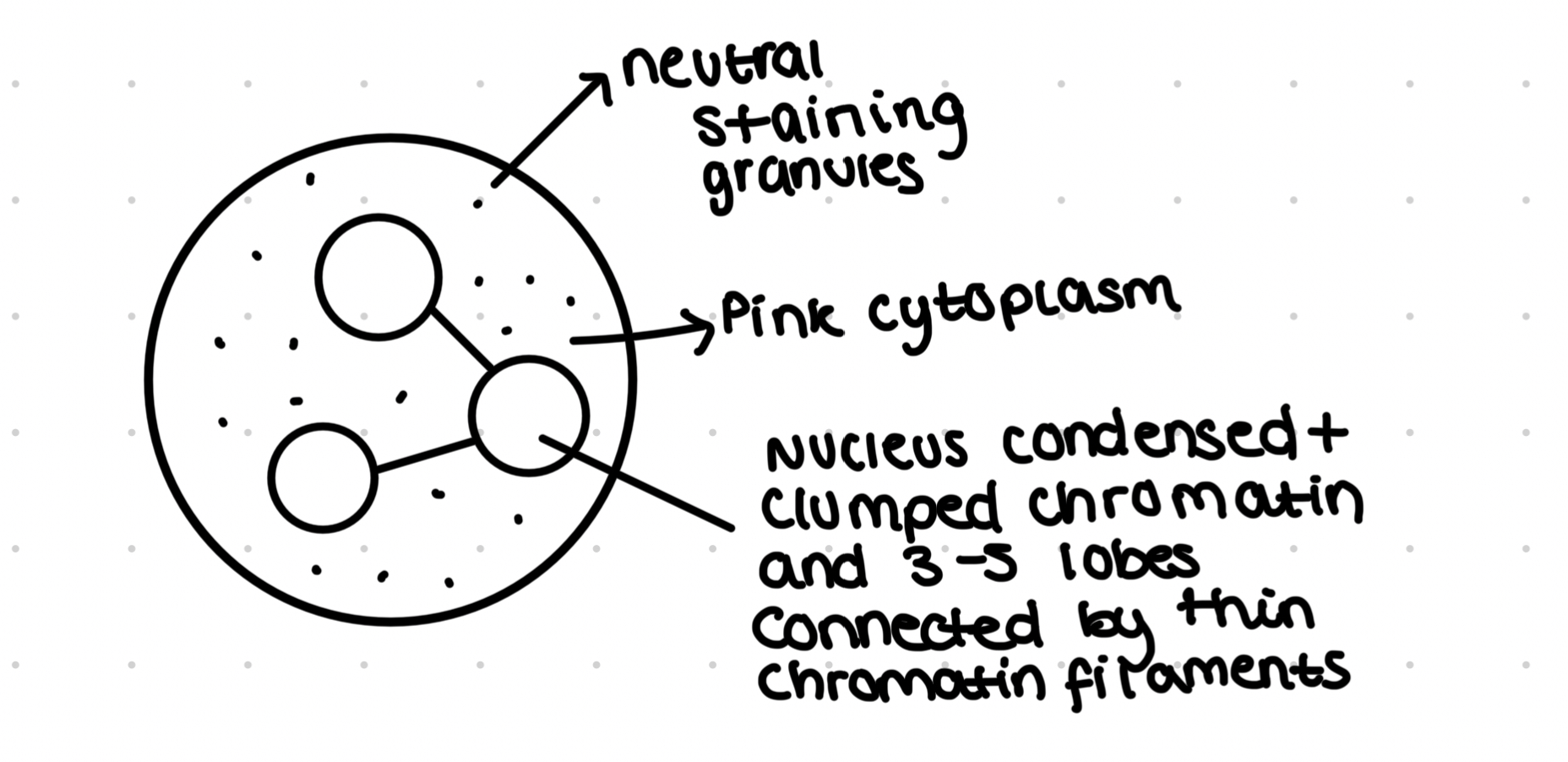
Neutrophils- cells
White blood cell with an essential role in the immune system
Multilobed nucelus to allow it to squeeze through small gaps to get to infection sites
Granular cytoplasm containers many lysosomes that contain enzymes
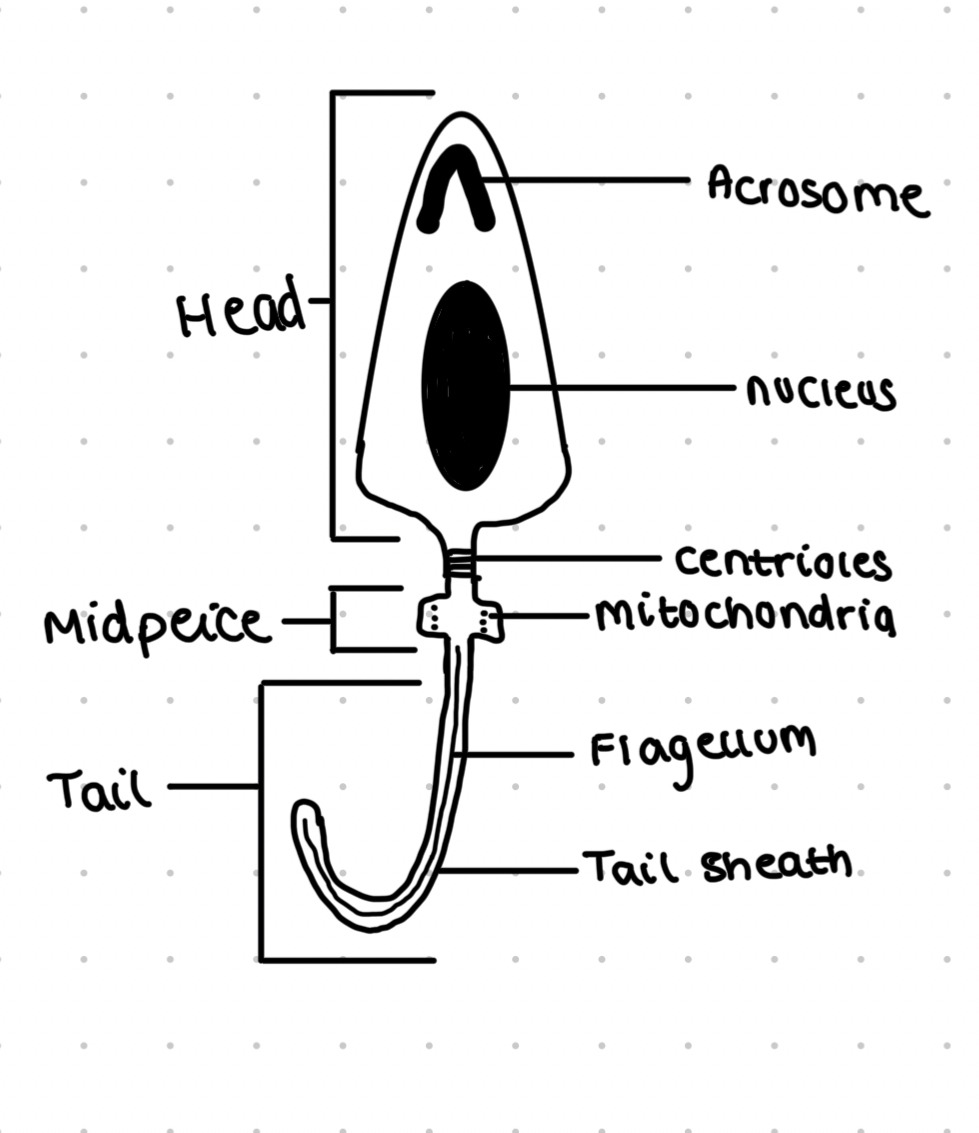
Sperm cell
Male gametes
Have a tail for movement
A mid piece which contains many mitochondria to supply ATP for movement
Acrosome on the head of the sperm contains digestive enzymes to penetrate the egg
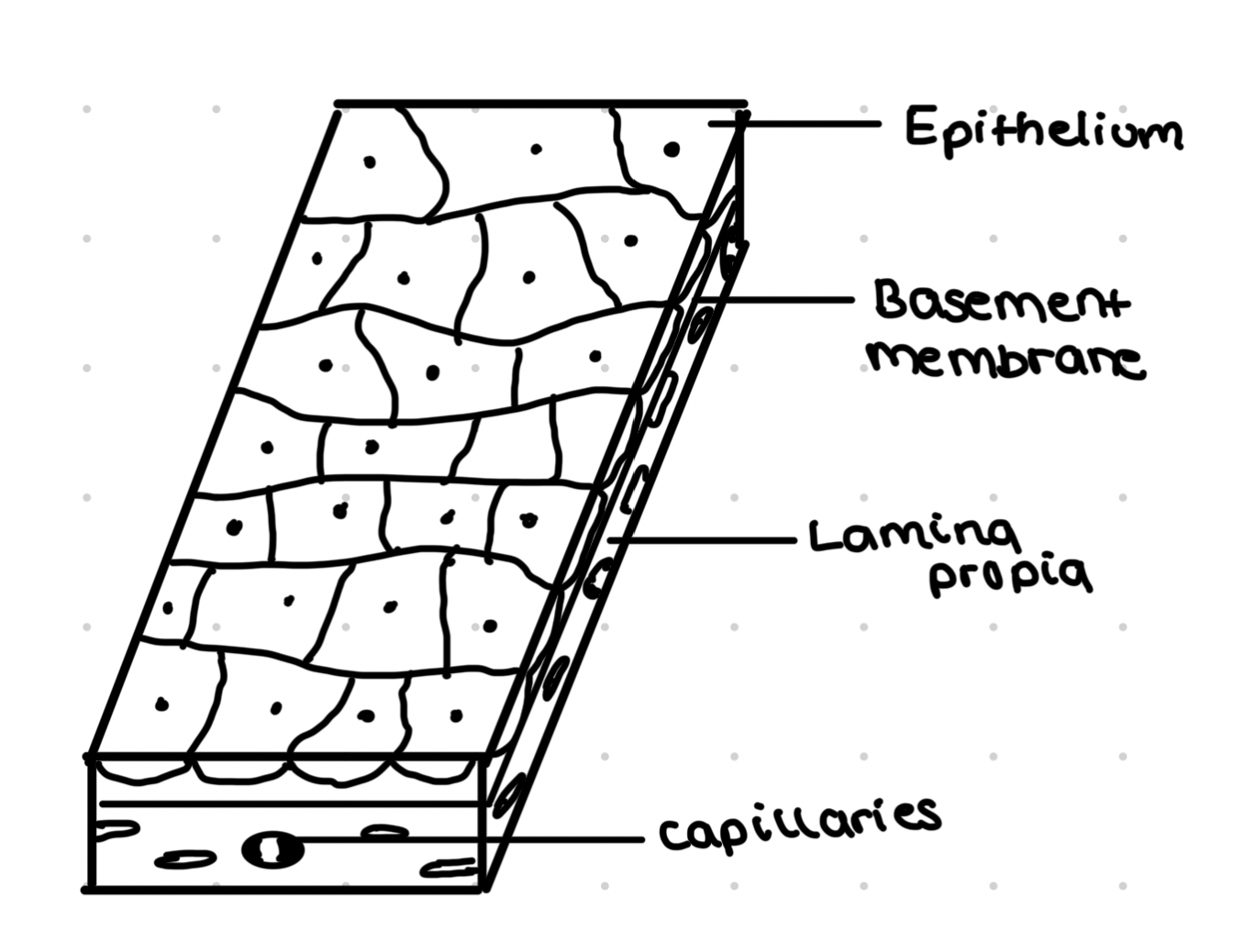
Squamous epithelial cell
Sometimes known as pavement epithelial cell
Flattened cells
Layer of single flattened cells sit on basement membrane
Forms lining of blood vessels and alveoli
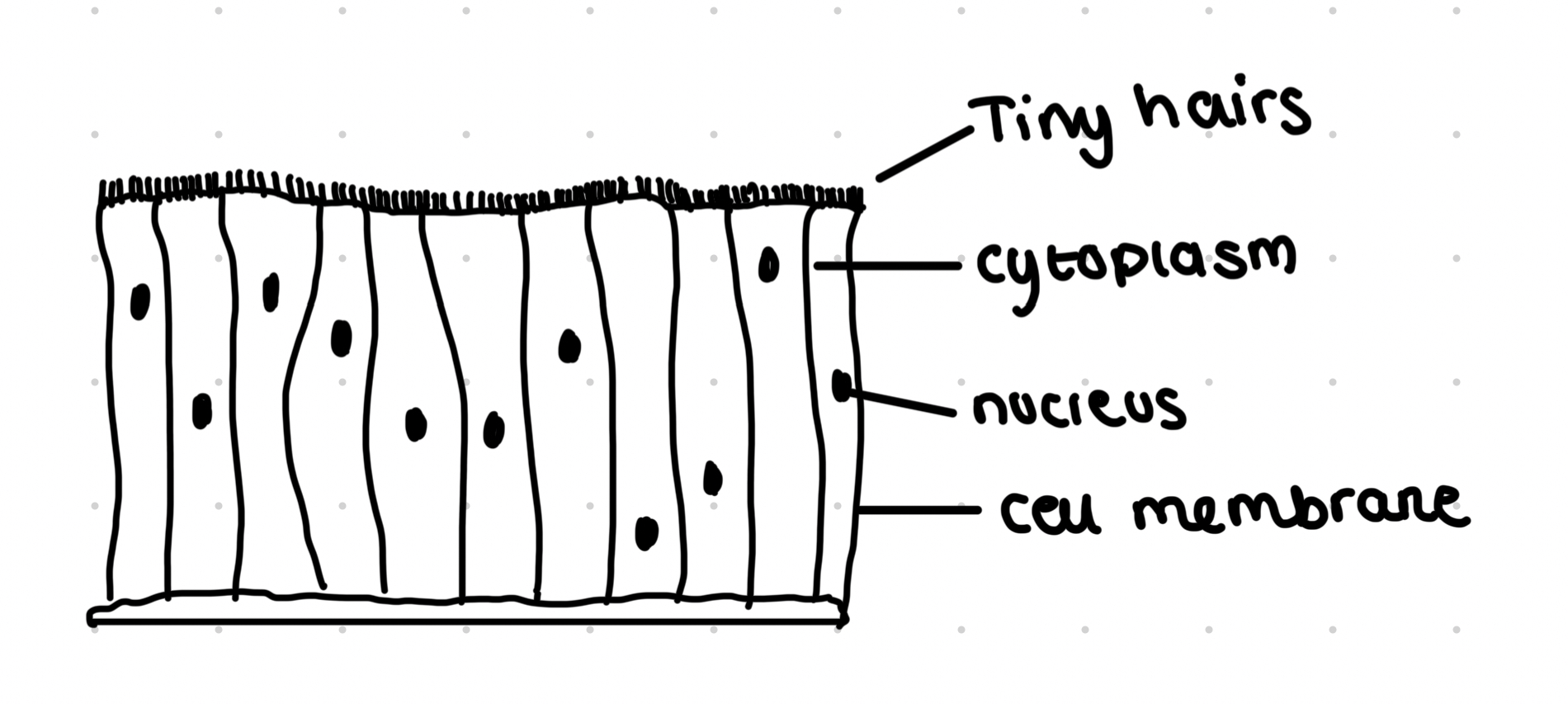
Ciliated epithelium cell
Hair like cilia on cells
Move in rhythmic manner
Lines the trachea
Moves mucus out of lungs
Many mitochondria to supply ATP for movement of the cilia
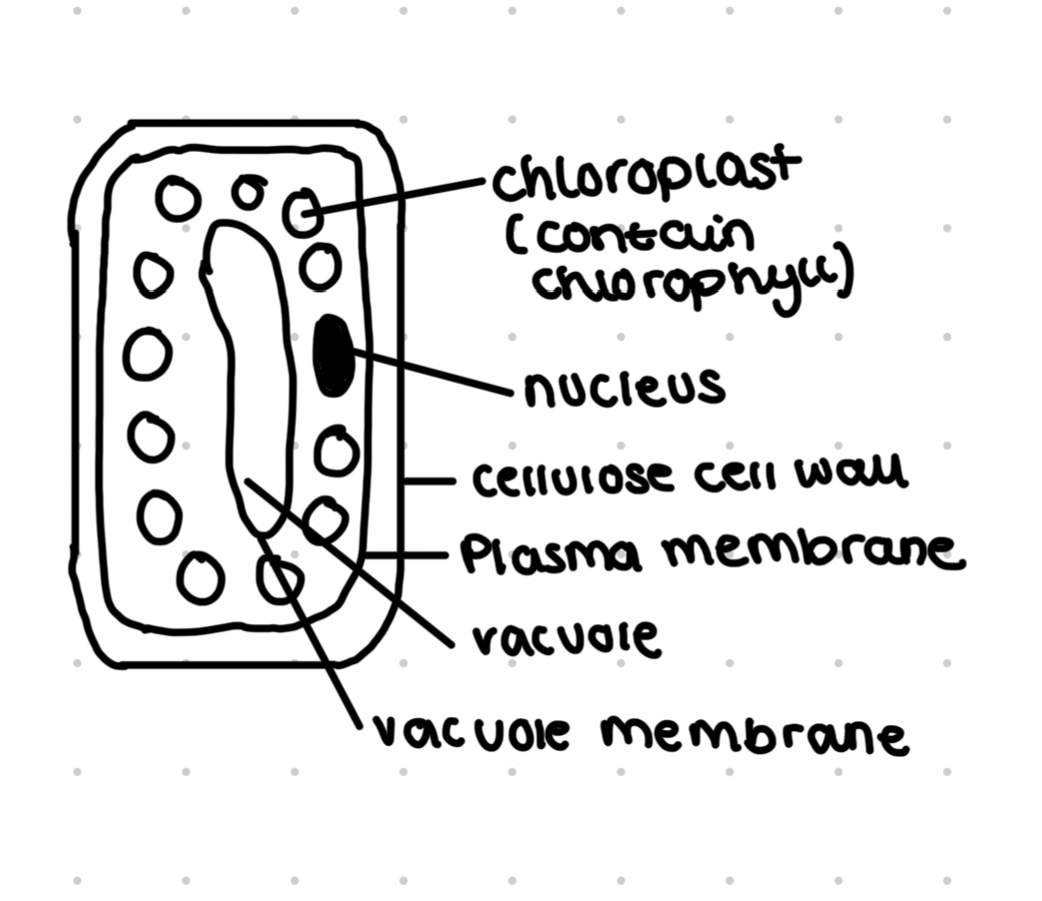
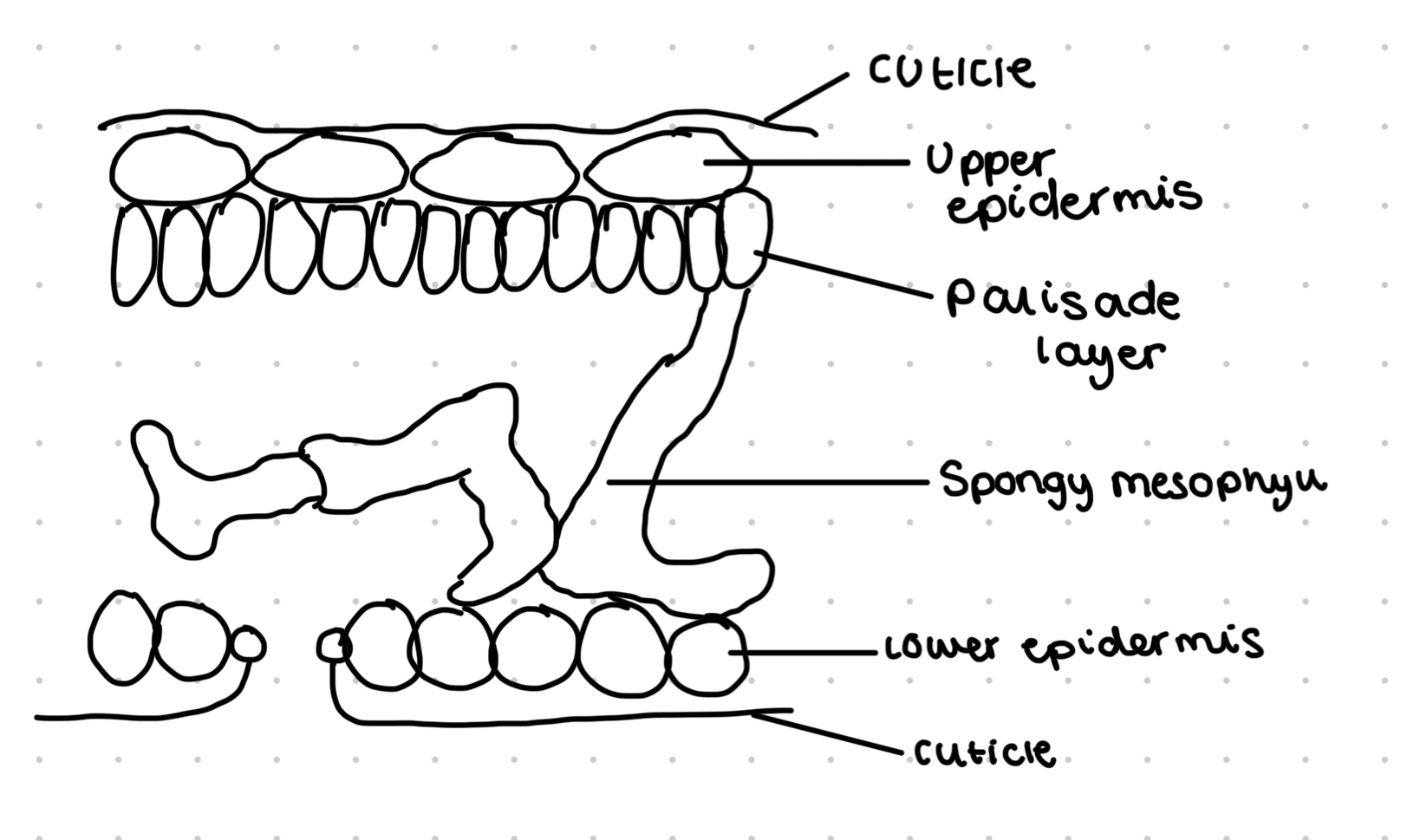
Palisade cell
Present in the mesophyll
Large numbers of chloroplasts containing chlorophyll for photosynthesis
Thin cell walls to increase rate of diffusion
Large vacuole maintains turgidity
Chloroplasts can move to light source
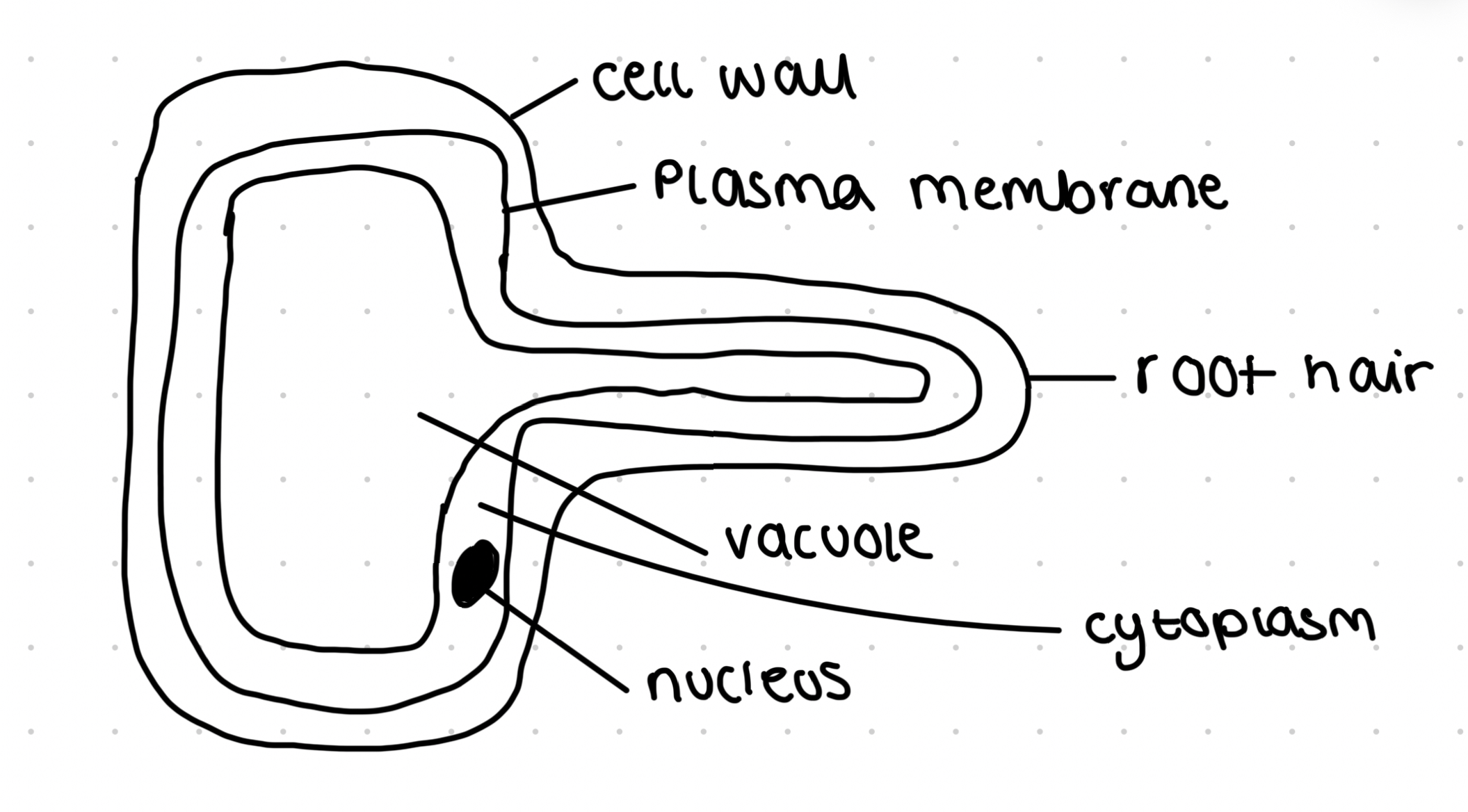
Root hair cell
Water enters by osmosis
Present at surface of roots near growing tips
Long extensions increase surface area for uptake of water and internal ions
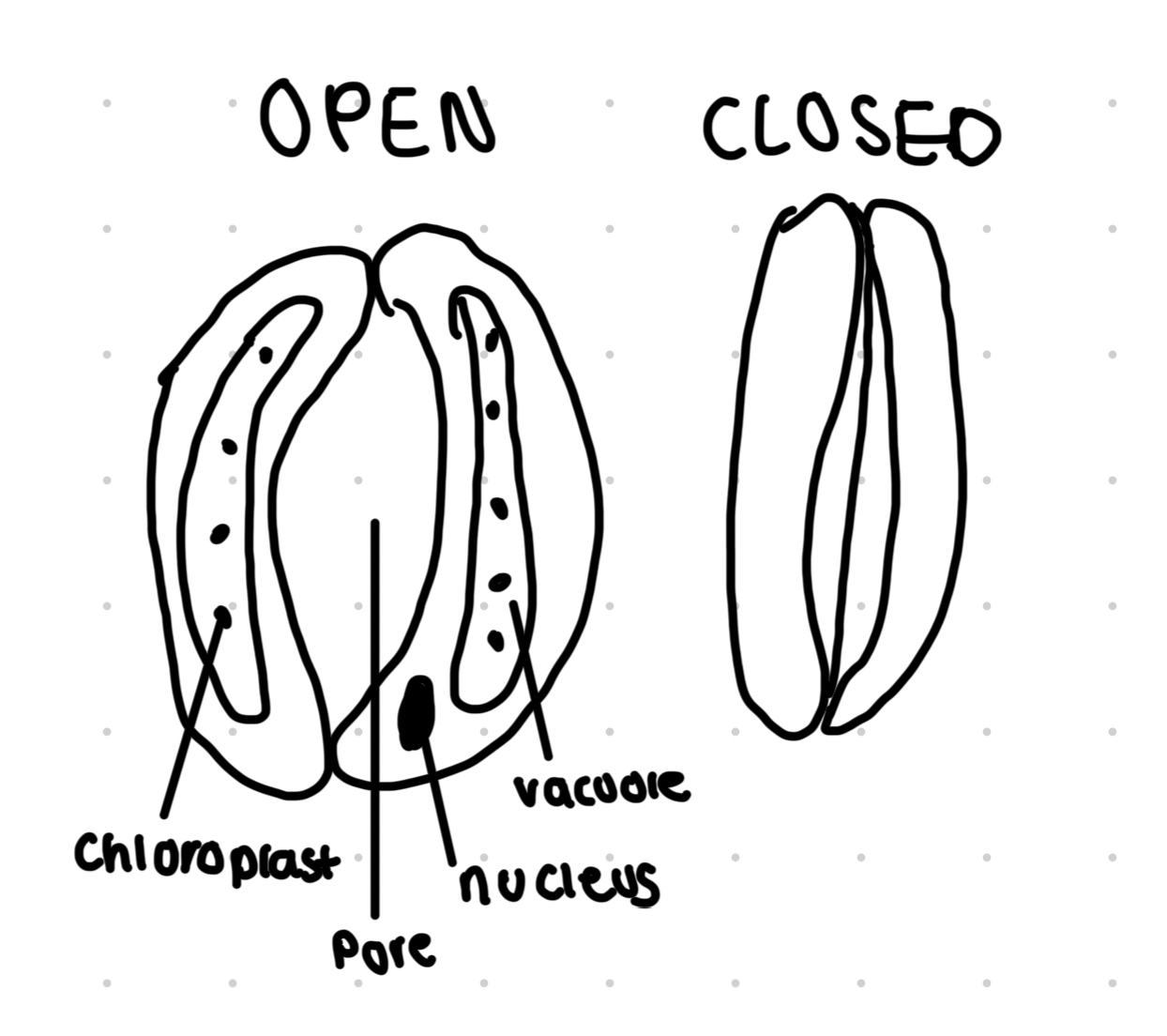
Guard cell
Pairs of guard cells form openings called stomata
When guard cells lose water they change shape and the stomata close, this conserves water
The cell wall of a guard cells is thicker one side which gives rise to the opening
Tissues
Collection of differentiated cells that have specialised functions
4 main tissue types:
Epithelial- forms linings
Connective- holds structures together
Muscle
Nervous
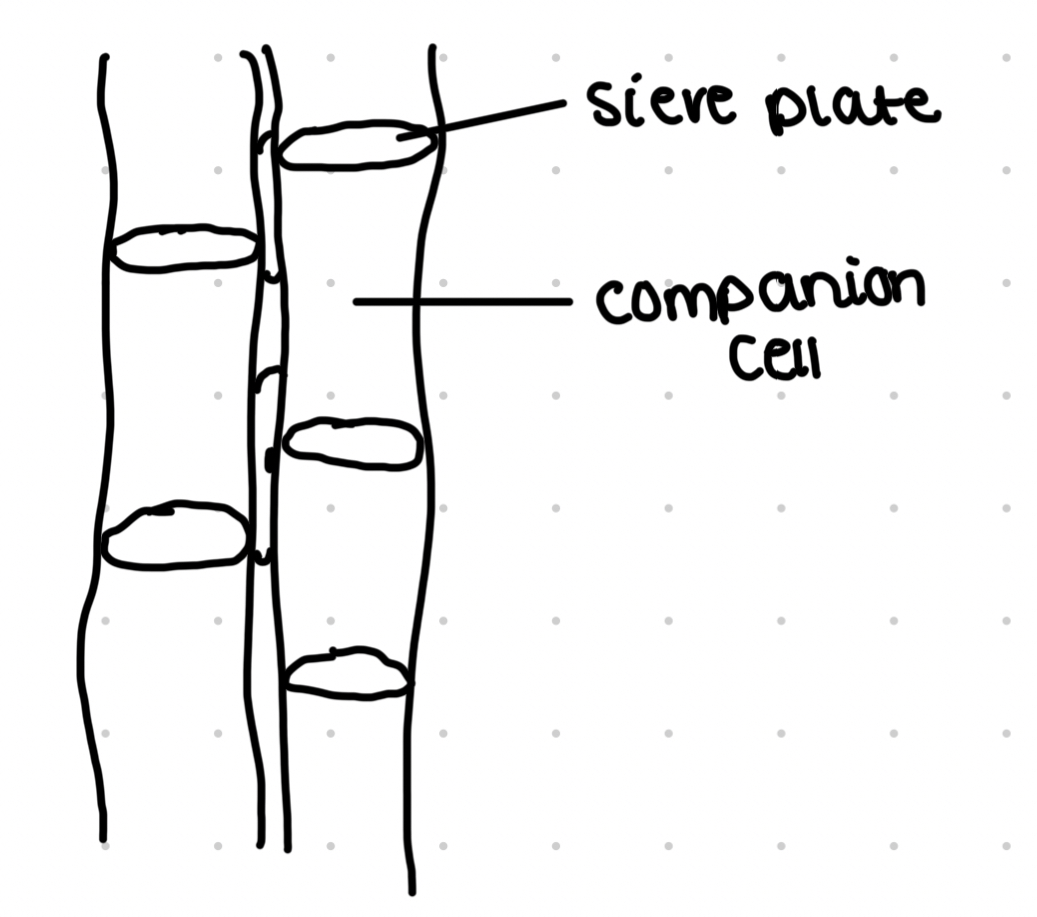
Phloem tissue
Vascular tissue used for transport of organic nutrients
Columns of sieve tube cells separated by sieve plates
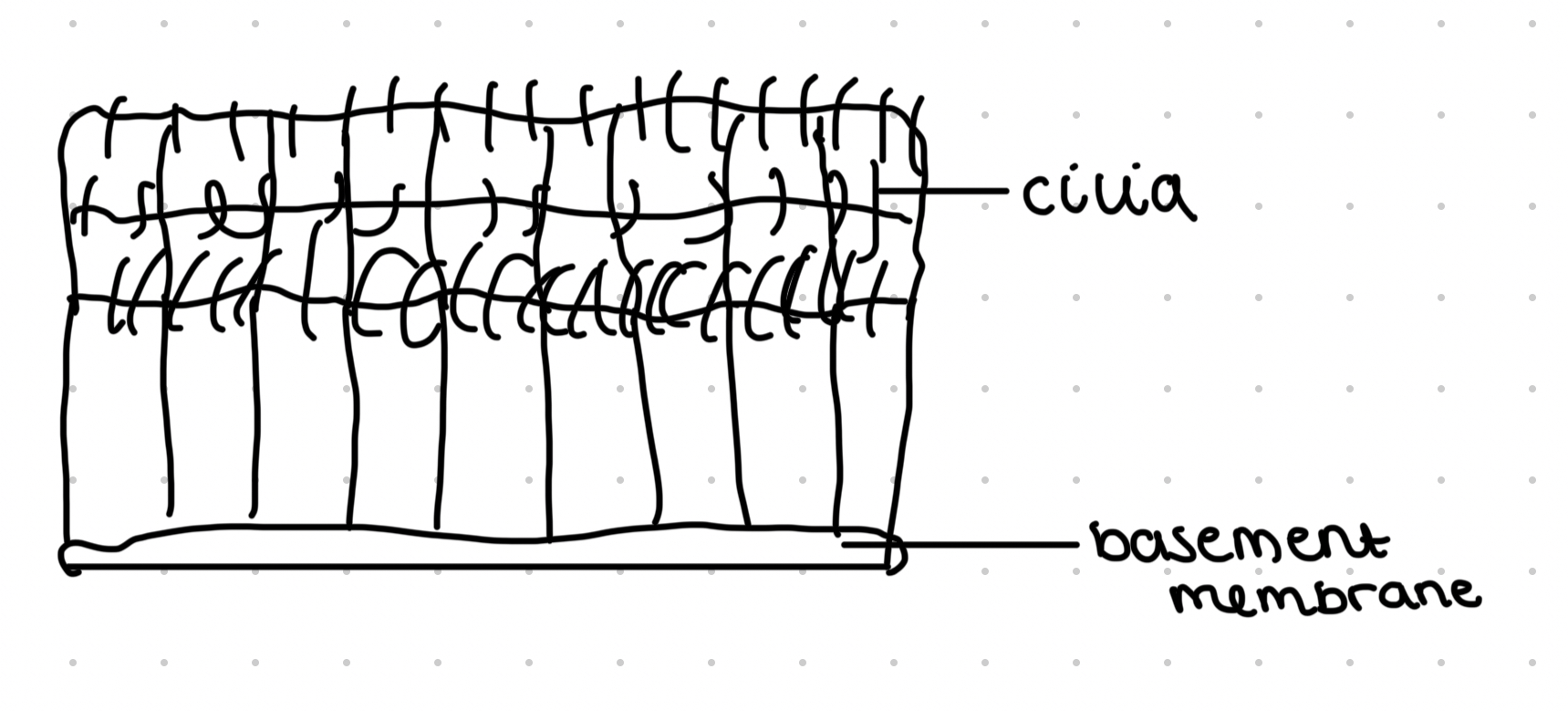
Ciliated epithelial tissue
Ciliated epithelial cells and goblet cells
Lines trachea
Goblet cells produce mucus which traps dirt and pathogens
Ciliated cells move mucus out of lungs
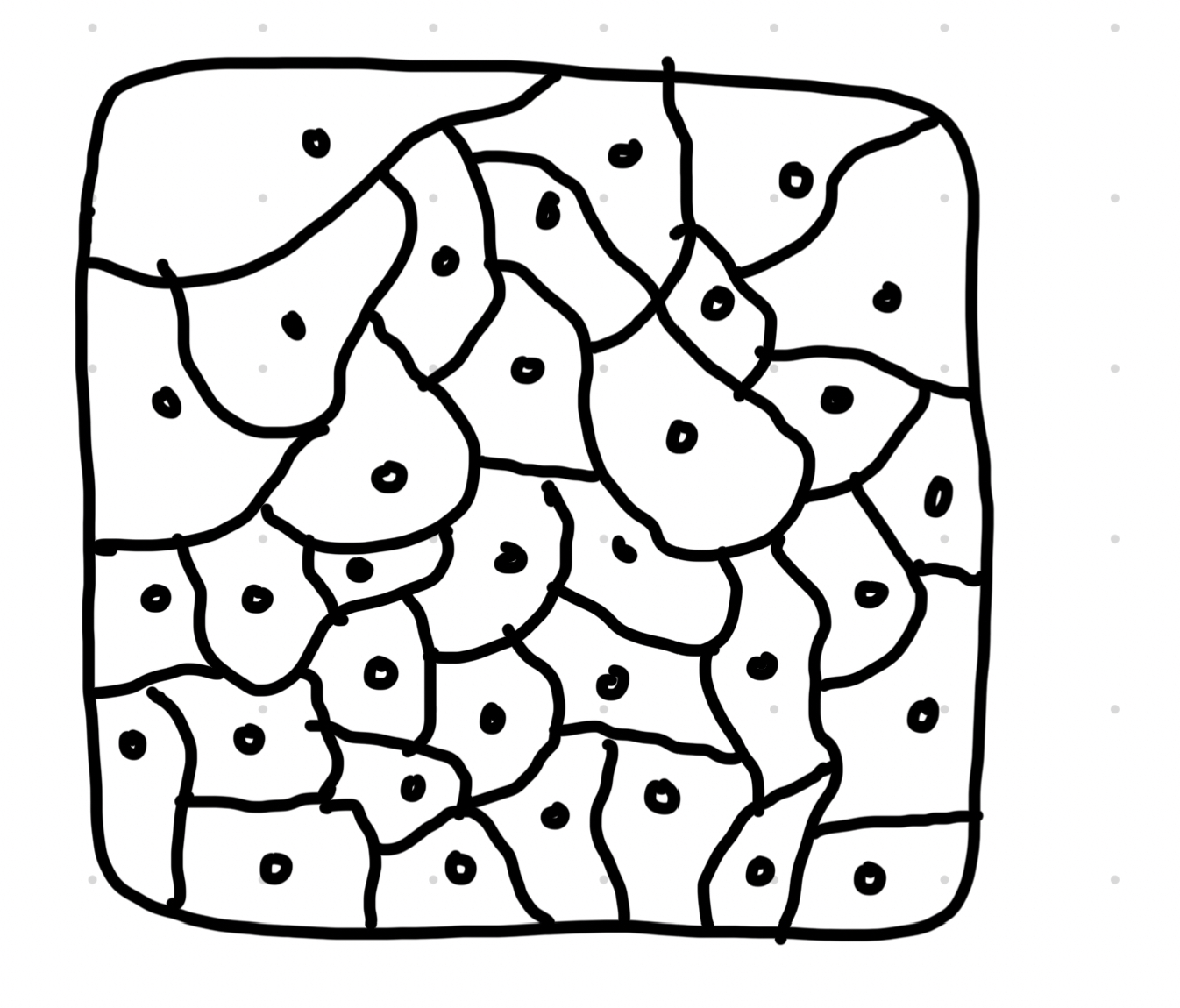
Cartilage tissue
Connective tissue found in outer ear, nose and end of bones
Contains collagen and elastin
Firm, flexible connective tissue
Chondocyte cells embedded in an extracellular matrix
Prevents bones rubbing together
Some fish have whole skeletons made of cartilage
Muscle tissue
Shortens in length to move bones
Skeletal muscle fibres contain microfibrils
Muscle fibres are separated by connective tissue
Plant epidermal tissue
Single layer of closely packed cells
Waxy waterproof cuticle to reduce water loss
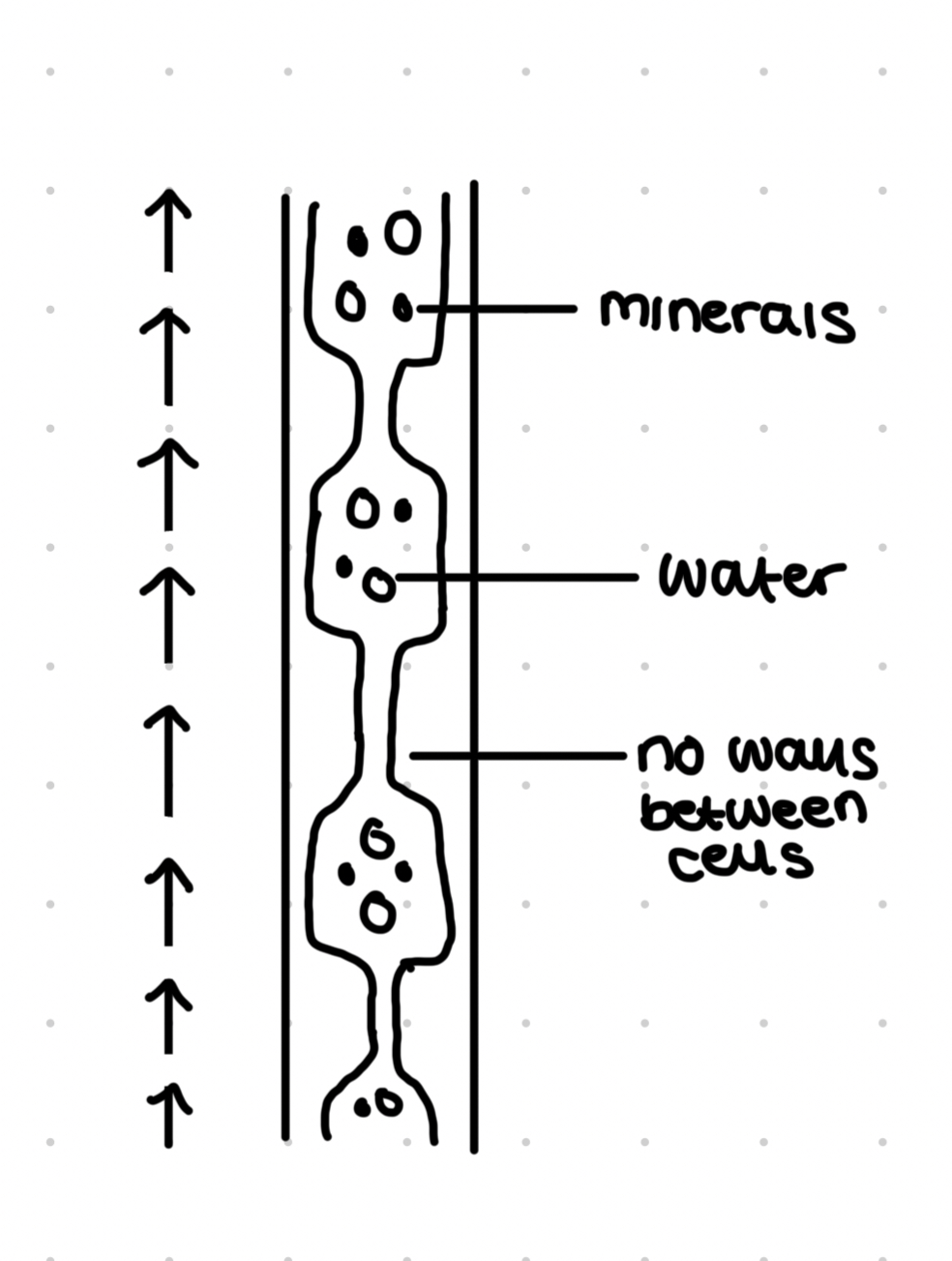
Xylem tissue
Transport water and minerals
Vessel elements as re elonged dead cells
Strengthened with lignin which gives structural support
Organs
Collection of tissue that are adapted to perform a particular function in an organism
E.g
Heart- made up of muscle tissue and connective tissue, adapted for pumping blood around the body
Organ systems
Number of organs working together to perform a function
Skeletal system: provides structure to body, protects internal organs
Muscular systems: supports body and allows it to move
Digestive system: breaks down food and absorbs its nutrients
Respiratory system: takes in oxygen and releases water gases