Corneal Ectasias & Degenerations
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
corneal ectasia
a thinning & bulging of the cornea
keratoconus
genetic link & associated with several systemic conditions, environmental factors
progressive, noninflammatory, bilateral ectatic corneal disease
characterized by focal thinning & weakening that leads to corneal distortion
onset: 2nd-6th decade
earlier onset correlated w/ more severe disease
signs/sx:
irregular astigmatism
myopia
corneal scarring
gradually decreasing visual clarity accompanied by ghosting/doubling of images
glare, halos, photophobia
itching, irritation
eye strain
eye pain
scissoring ret reflex
Fleischer rings
striae
focal thinning of cornea
Fleischer ring
iron deposition at base of cone in keratoconus due to sharp change in curvature of the cornea
striae
micro-creases in posterior cornea due to stretching of the corneal tissue seen in keratoconus
hydrops
rupture of endothelium due to severe thinning seen in keratoconus, corneal edema, AC rxn common, takes months to resolve
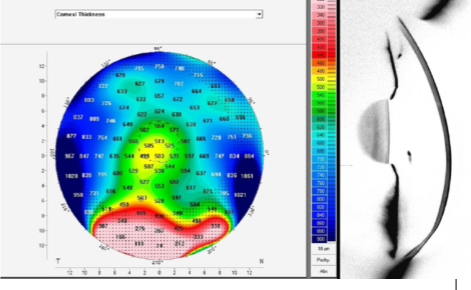
steep central Ks, superior to inferior asymmetry, astigmatism >1.5D, skewed radial axes >21deg
describe the classic keratoconic corneal topography
corneal tomography, provides true elevation of anterior & posterior cornea, corneal thickness, & corneal curvature
what is the best tool for detecting keratoconus early on and what information does it tell us?
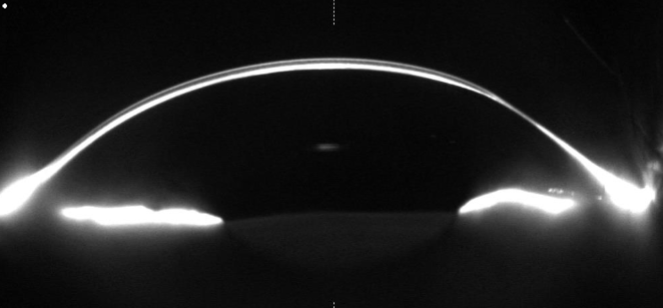
keratoglobus
rare, bilateral, globular configuration of the cornea which can resemble keratoconus w/ the exception that the cornea is diffusely, uniformly thinned, particularly in the periphery
onset: at birth
signs/sx:
myopia
astigmatism
rupture of globe can easily occur and patients must be cautioned to avoid trauma
associated with systemic collagen disorders
pellucid marginal degeneration
rare
characterized by inferior corneal thinning & corneal ectasia above the area of thinning
thinned area is usually confined to circumferential band-shaped area inside inferior limbus (4:00-8:00)
protrusion above the area of thinning
painless, bilateral, asymmetric
signs/sx:
significant ATR & irregular astigmatism
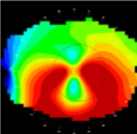
“crab claw” corneal maps
“beer belly” cornea
tx:
CL, surgery
corneal arcus senilis
involutional, common, age related
etiology: deposition of cholesterol, triglycerides, & phospholipids in peripheral stromal cornea
may be associated with abnormalities in blood lipids
unilateral suggestions vascular occlusion on side w/o arcus
most often age related (universal by 8th decade)
appearance:
complete/incomplete (inferior first, then superior, then circumferential)
yellow-white, perilimbal hazy opacity
clear perilimbal zone
lipid first noted in Descemet’s membrane, then Bowman’s layer
corneal farinata
involutional, common, age related
etiology:
AD
manifestation of senile changes
appearance:
gray-white, small, dustlike dots & flecks deep in the stroma or pre-Descemet’s zone
no vascularization
axially diffuse or annular distribution
flour like appearance
visually insignificant
furrow degeneration
involutional, common, age related
etiology:
age
appearance:
painless, thinning of cornea
in area b/t arcus senilus & limbus
no tendency to perforate
no vascularization
may see a scalloped arcus margin
Hassall-Henle bodies
involutional, common, age related
etiology:
age
appearance:
peripheral, localized, nodular thickening of Descemet’s membrane
looks the same as corneal guttata but peripheral
small, circular, dark areas w/in normal endothelial mosaic on specular reflection
anterior crocodile shagreen
involutional, common, age related
bilateral, polygonal, grayish-white opacities separated by clear tissue in deep areas of epithelium & Bowman’s
typically located axially
vision not usually affected
looks like scales
most prominent centrally
posterior crocodile shagreen
involutional, common, age related
bilateral
grayish-white opacities in deep stroma & Descemet’s
appear as small, polygonal patches of various sizes separated by dark regions
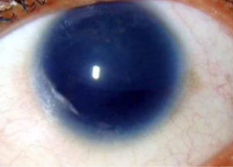
white limbal girdle of vogt
involutional, common, age related
etiology:
age, found commonly in patients over 45yo
appearance:
white, narrow, crescentic, irregular, chalky opacity
in temporal & medial limbal areas of Bowman’s
nasal greater than temporal in interpalpebral zone
no vascularization
vision unaffected
arc shape
may/may not have a clear interval
may resemble early band keratopathy
early calcific band keratopathy (type 1)
lucid interval
fine crystals
swiss cheese holes
sightly more superficial
rather smooth central edge
calcium
calcium-adjacent conjunctiva
true Vogt’s girdle (type 2)
no lucid interval
chalklike flecks
no “holes”
slightly deeper
thornlike extensions from central edge
elastosis
pinguecula-adjacent conjunctiva
amyloid degeneration
non-involutional, uncommon
bilateral, innocuous degenerative condition usually seen after age 50 if going to appear
appearance:
polymorphic, refractile, punctate, comma-shaped & filamentous amyloid deposits throughout stroma
most prominent centrally & posteriorly
best seen in retroillumination
small, salmon pink to yellow-white central, raised, fleshy, waxy masses w/ a nodular surfac eon the cornea & conjunctiva
may be vascularized
patients are asymptomatic
band keratopathy
non-involutional, uncommon
etiology:
calcium salts depositing in anterior stroma & Bowman’s layer
occur from localized ocular inflammatory disease (chronic uveitis, silicone oil in AC, or systemic diseases causing hypercalcemia)
most are idiopathic
appearance:
deposits in interpalpebral fissure of BM/Bowman’s membrane
lucid interval
Swiss cheese appearance (holes represent areas where small nerves penetrate)
tx:
topical lubricants
bandage CL
EDTA & anesthetic plus scraping (chelation)
phototherapeutic keratectomy
lamellar keratoplasty
can reoccur
lipid degeneration
non-involutional, uncommon
etiology:
primary or secondary problem as a result of local or systemic disease, trauma, & after severe corneal disease
appearance:
dense, yellow-white opacity that may fan out with feathery edges from blood vessels in the affected corneal area
tx:
control underlying disease
argon laser or needle point cautery to feeder vessels
penetrating keratoplasty
Salzmann’s nodular degeneration
non-involutional, uncommon
etiology:
chronic inflammation
most common comorbidities: MGD, CL wear, peripheral corneal vascularization, pterygium, keratoconjunctivitis, exposure keratitis
appearance:
discrete, elevated, bluish-white superficial stromal opacities
raised nodules
usually arranged in circular fashion around pupil area
often appear w/in or adjacent to an area of previous scarring, occur over old scars
can lead to poor TF wetting, dellen, irregular astigmatism, discomfort, & poor vision if on visual axis
tx:
none
scraping
superficial keratectomy
lamellar keratoplasty or excimer
CLs
spheroidal degeneration
non-involutional, uncommon
etiology:
related to geographic or climactic conditions or previous inflammation
males who have worked outdoors
appearance:
bilateral, spherical, translucent, golden-brown oily droplets under epithelium or conjunctiva at 3 & 9:00
may also be noted central, superficial stroma in a band shape, often in interpalpebral zones
proteinaceous deposits
fluoresce brightly in UV
tx:
usually none unless progressive & causing visual impairment, then superficial/lamellar keratectomy or corneal transplant
protection from UV
Terrien’s marginal degeneration
non-involutional, uncommon
etiology:
unknown
usually in younger males, often after 4th decade
appearance:
slowly progressive, marginal thinning, bilateral
non-inflammatory
gradual development over years
can cause significant irregular/ATR astigmatism
marginal opacification
superficial vascularization
thinning of corneal stroma margin, beginning superonasally, spread circumferentially
early punctate stromal opacities
advancing edge exhibits lipid deposition
epithelium intact
corneal perforation possible
may look like early arcus
may develop pseudopterygia
tx:
if perforation is threatened or if astigmatism is severe, then reconstructive full thickness or lamellar corneal graft
scleral GPCL
Mooren’s ulcer
rare
etiology:
unknown
immune component to stromal antigens, possibly triggered by injury
benign form often seen unilaterally in older, white, female patients, better response to tx
more severe form often seen in young males, bilateral, & poor response to tx, more common in blacks & Indian origin
appearance:
marginal ulcer
severe, painful
central & circumferentially progressing
inflammation, corneal infiltration
epithelial breakdown
perforation can occur
tx:
no well established tx
topical & systemic steroids
immunosuppressants
lamellar graft if perforation occurs (often unsuccessful)
Mooren’s ulcer
unilateral or bilateral
pain & inflammation
epithelial breakdown at central edge of active ulcers, stains w/ NaFl
spreads centrally & circumferentially
slow or rapid progression
overhanging central edge
can become vascularized w/ healing
no lipid
can cause corneal melting & destruction
perforation occurs in severe cases
Terrien’s marginal degeneration
usually symmetric & bilateral
usually painless & not inflamed
epithelium intact, no NaFl staining
spreads circumferentially
slow progression
gradual central edge
vascularized base
lipid deposits
usually main problem is astigmatism caused by ectasia
perforation occurs in 15% of cases as a result of minor trauma
keratoconus
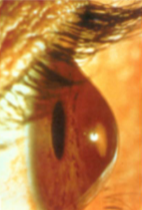
scissoring (keratoconus)
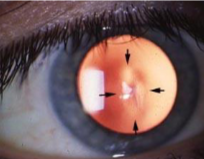
striae (keratoconus)
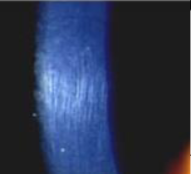
Fleischer rings (keratoconus)
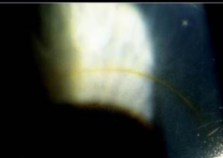
corneal scarring (keratoconus)
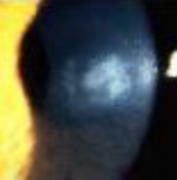
focal thinning (keratoconus)

Fleischer ring (keratoconus)
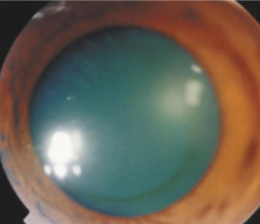
Fleischer ring (keratoconus)
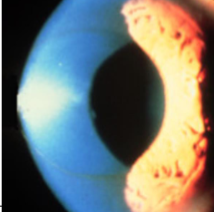
striae (keratoconus)
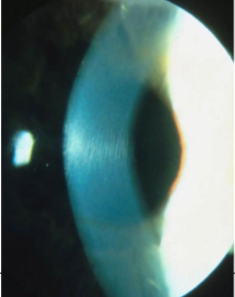
striae (keratoconus)
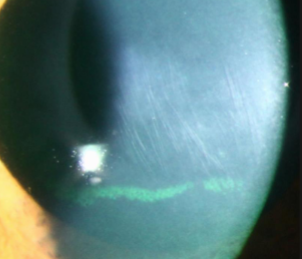
striae (keratoconus)

corneal scarring (keratoconus)
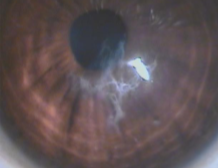
corneal scarring (keratoconus)
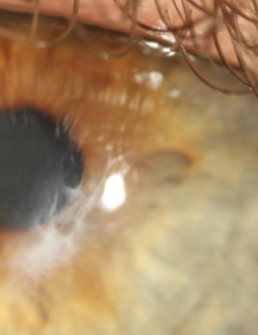
corneal scarring (keratoconus)
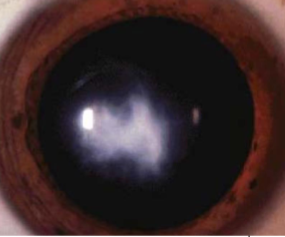
hydrops (keratoconus)
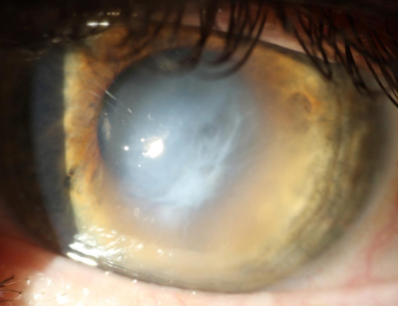
keratoconus
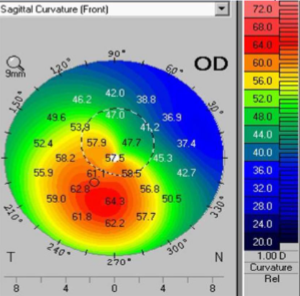
keratoconus
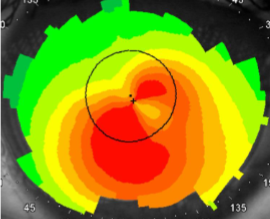
keratoconus
keratoglobus
pellucid marginal degeneration
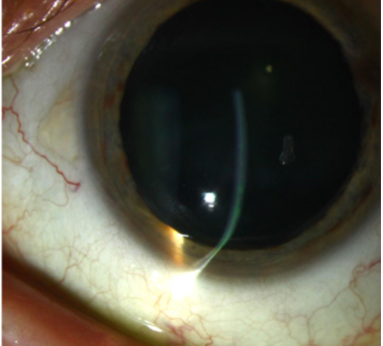
pellucid marginal degeneration
pellucid marginal degeneration
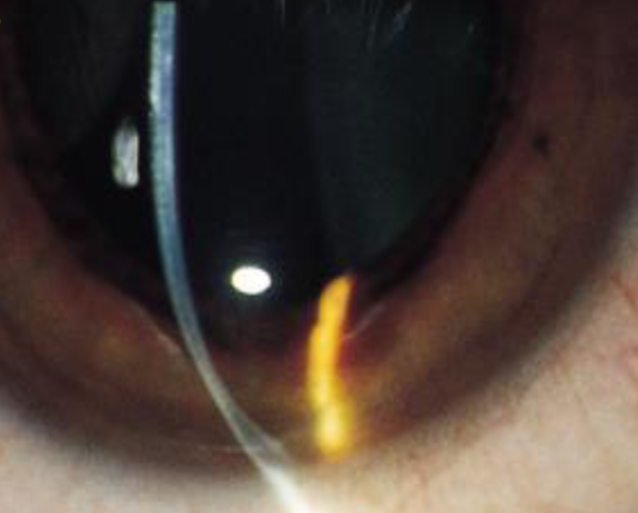
pellucid marginal degeneration
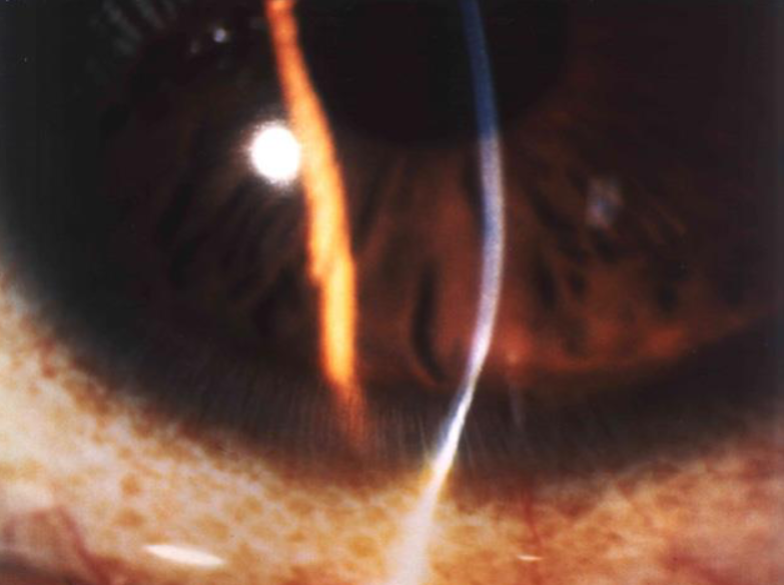
corneal arcus senilis
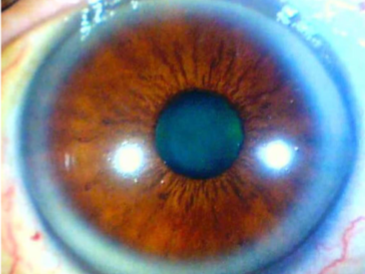
corneal arcus senilis
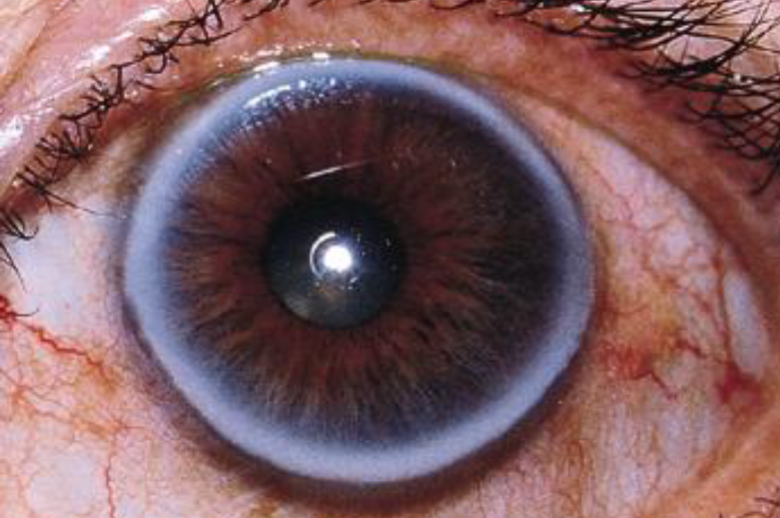
corneal arcus senilis
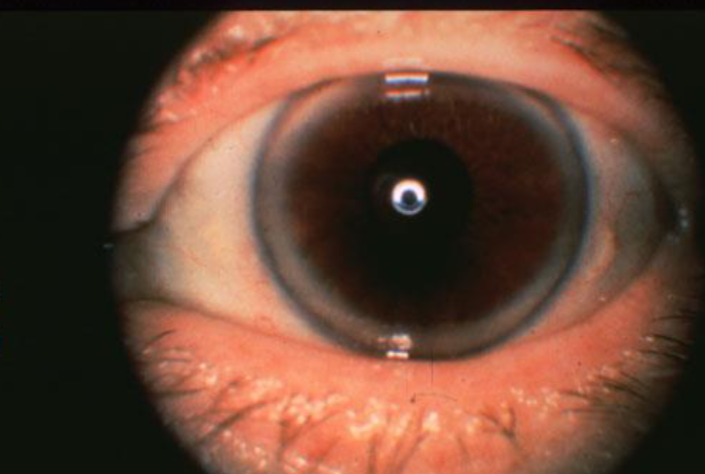
corneal farinata
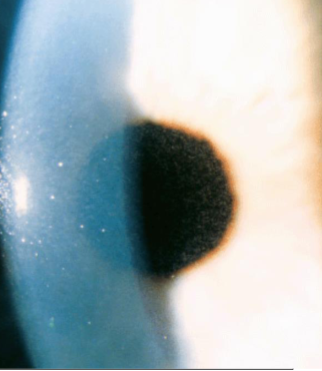
furrow degeneration
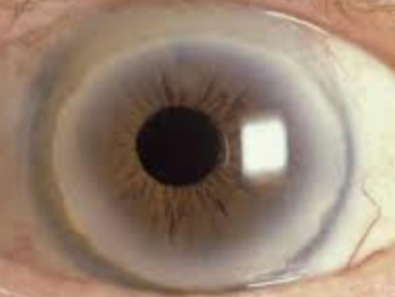
Hassall-Henle bodies

anterior crocodile shagreen
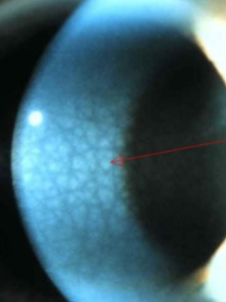
anterior crocodile shagreen
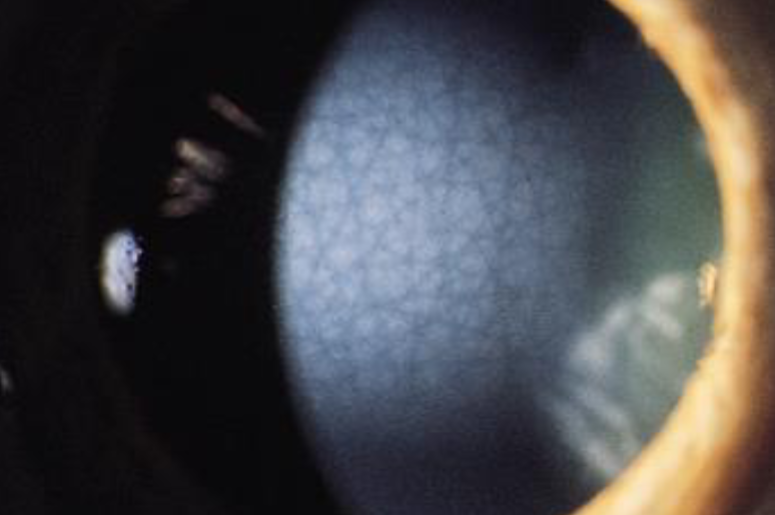
posterior crocodile shagreen
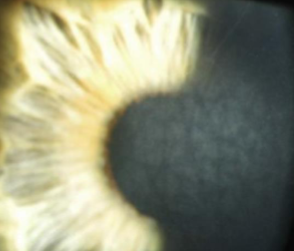
white limbal girdle of vogt
white limbal girdle of vogt

white limbal girdle of vogt
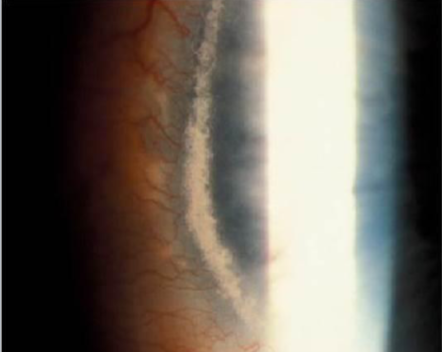
white limbal girdle of vogt
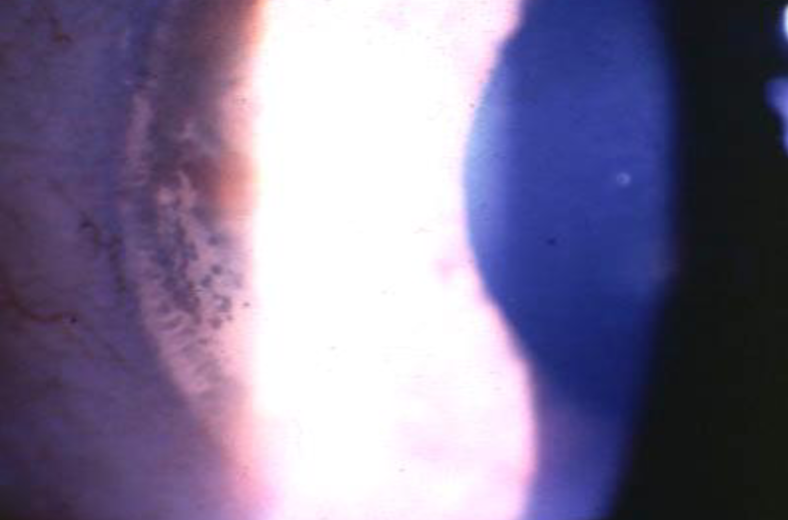
amyloid degeneration
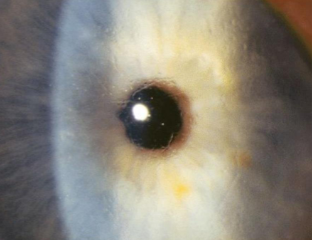
amyloid degeneration
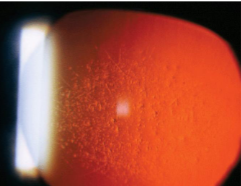
band keratopathy
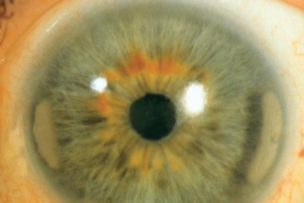
band keratopathy
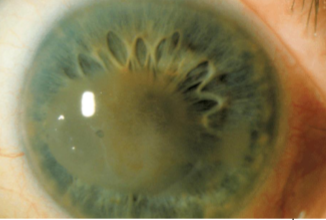
band keratopathy
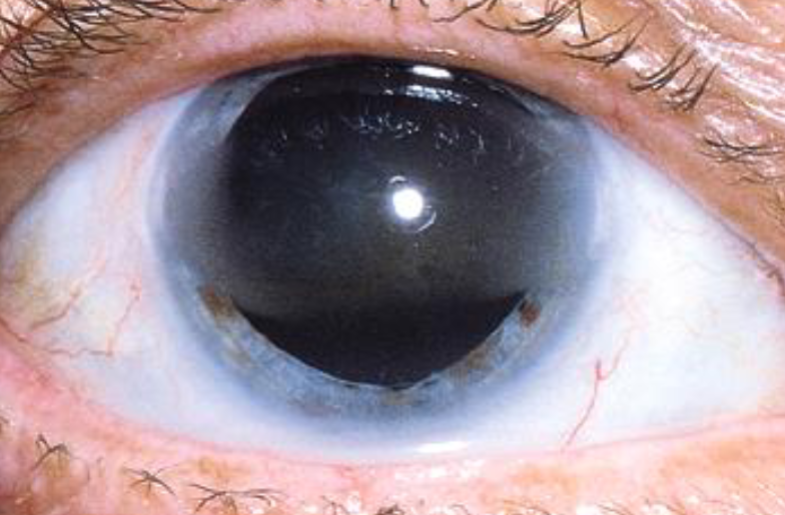
band keratopathy
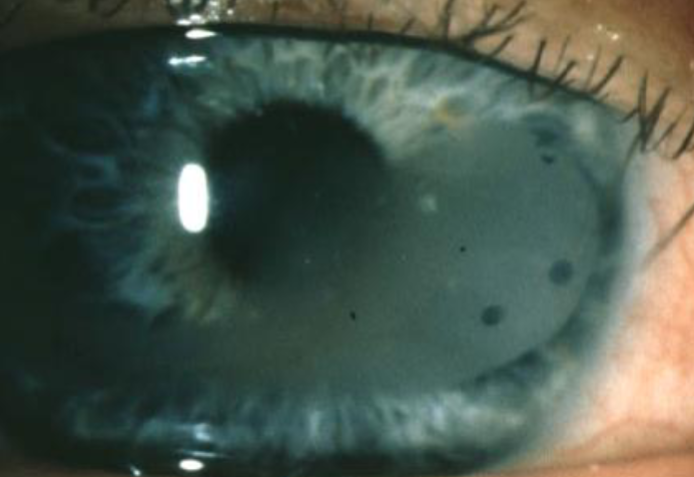
band keratopathy
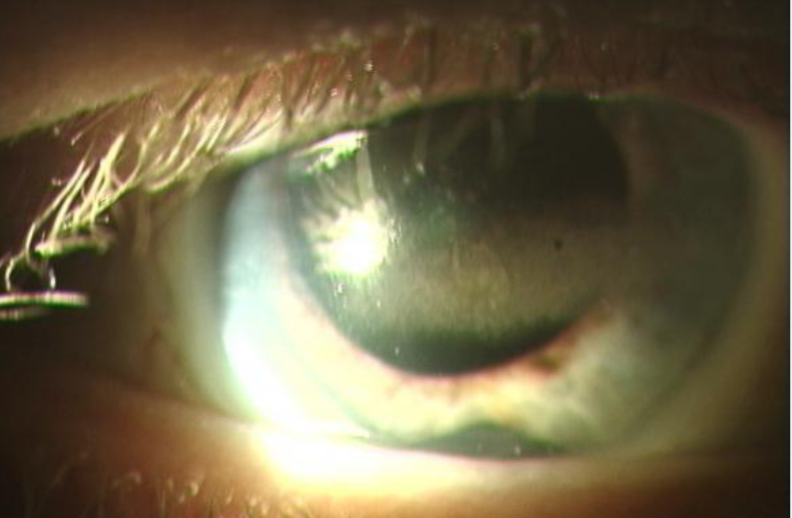
band keratopathy
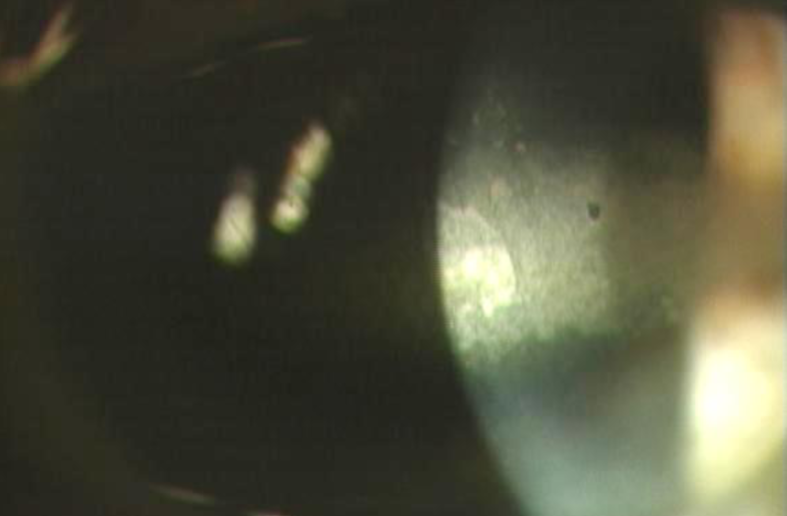

band keratopathy
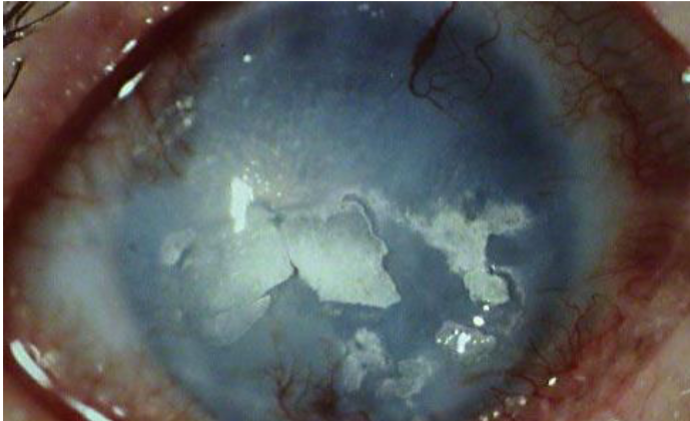
lipid degeneration
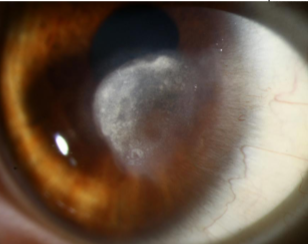
lipid degeneration
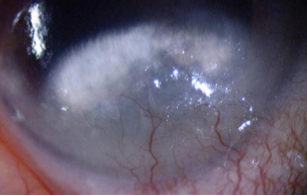
lipid degeneration
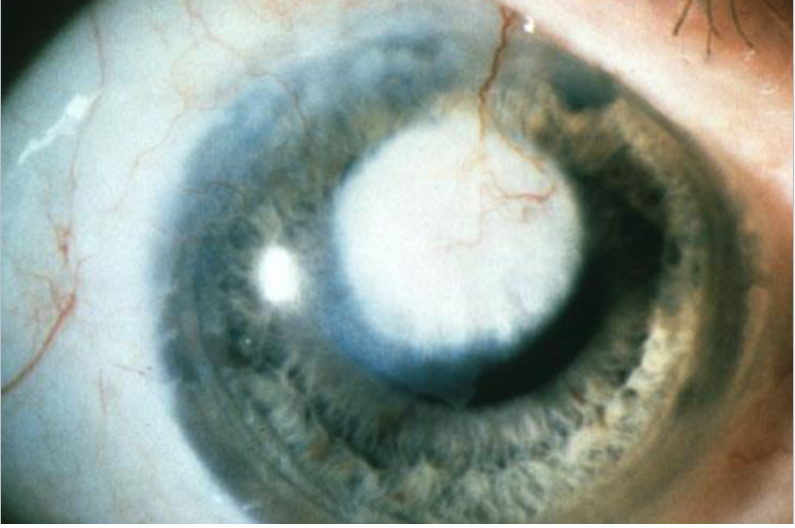
Salzmann’s nodular degeneration
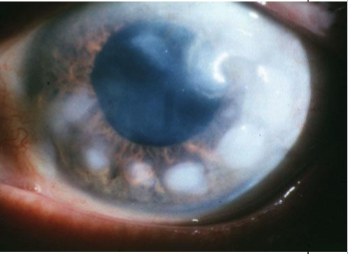
Salzmann’s nodular degeneration
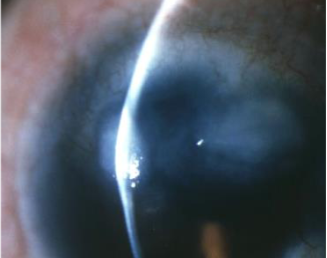
Salzmann’s nodular degeneration
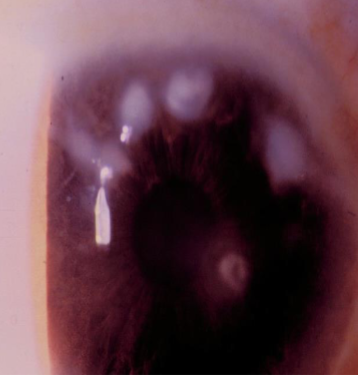
Salzmann’s nodular degeneration
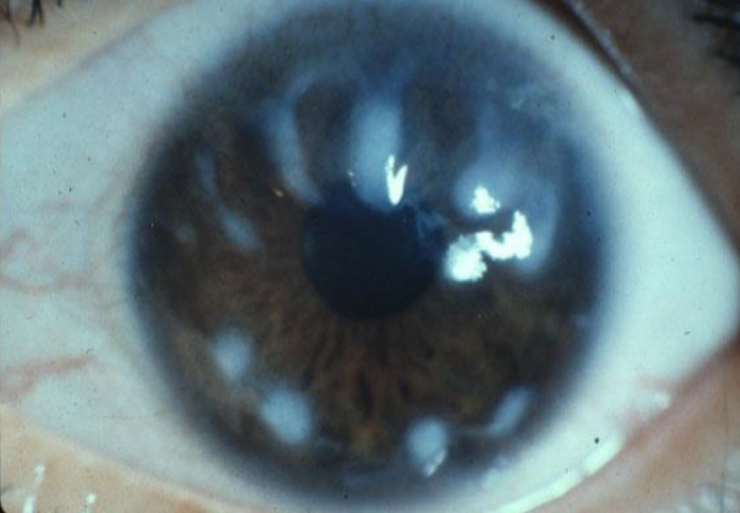
spheroidal degeneration
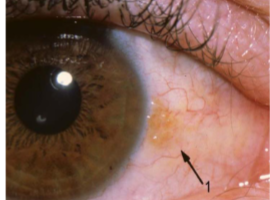
spheroidal degeneration
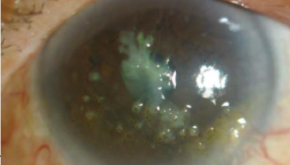
spheroidal degeneration
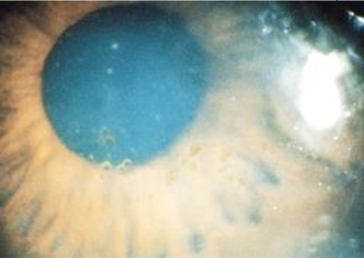
spheroidal degeneration
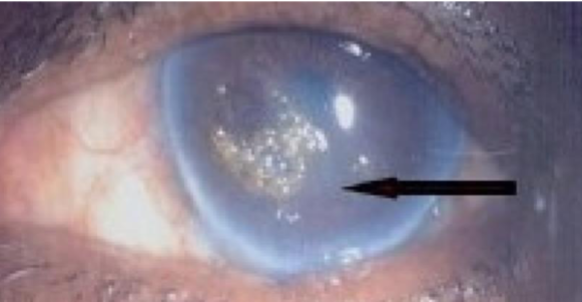
Terrien’s marginal degeneration
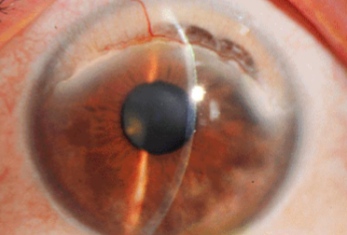
Terrien’s marginal degeneration
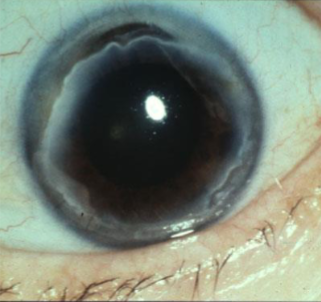
Terrien’s marginal degeneration
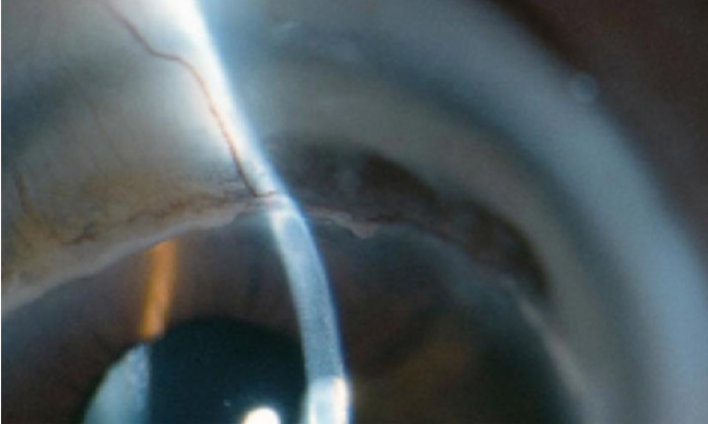
Terrien’s marginal degeneration
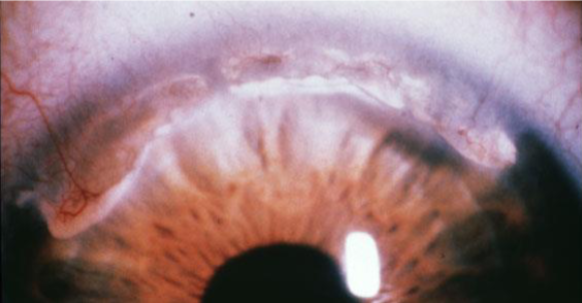
Mooren’s ulcer
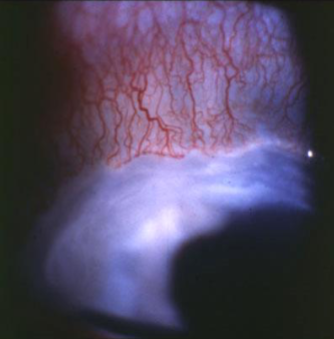
Mooren’s ulcer
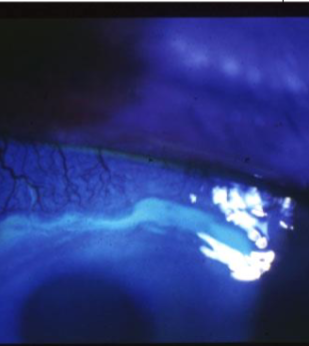
Mooren’s ulcer
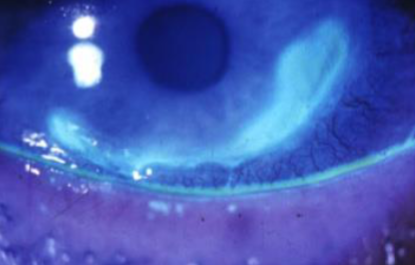
Mooren’s ulcer