Sawey: Contemporary Issues in Biology + Lab Exam 1
1/280
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
281 Terms
-if it starts with an "H"
virus
-if it doesn't start with an "H" (HIV, Hep B, Hep C, HPV, Herpes)
bacteria
-chlamydia is bacteria (t/f)
true
-herpes can be cured by antibiotics (t/f)
false
-syphillis is a virus (t/f)
false
-you can't get an sti if you've only had one partner (t/f)
false
-hpv can increase risk of cervical cancer (t/f)
true
-thalidomide was used to treat morning sickness (t/f)
true
-in us thalidomide caused seal limbs (t/f)
false
-shouldn't take vitamins with folic acid (t/f)
false
-safe to smoke 5x a week when pregnant (t/f)
false
-if you're healthy pregnant you can wait to see the doctor til the 2nd trimester (t/f)
false
-_____ are caused by
-viruses
-bacteria
-other organisms such as protozoans or body lice
STI's
-infections caused by _________
-gonorrehea
-syphilis
-chlamydia
bacteria
-how to treat a virus
treat symptoms only
-how to treat bacteria
antibiotics
-two parts of breast milk
foremilk, hindmilk
-radiation
-infection/virus
-metabolic conditions
-drugs and chemicals
teratogens
-babies receive _________ directly from the mother both during pregnancy and while breastfeeding
antibodies
-effects of one teratogen" thalidomide
seal like limbs
-never allowed in the US
-teratogen
-used to treat morning sickness and nauseau
-resulted in seal like limbs
thalidomide
-father of biology
aristotle
-observation -> hypotheses -> tests of hypotheses -> results
scientific method
-given placebo
-the variable being tested is absent
-compile results
control group
-given drug
-the variable being tested is present
-compile results
experimental group
-scientists in the field give anonymous reviews, accepting or rejecting the paper for publication
-the reviewers cannot have any personal or professional relationship with the authors
peer review and publishing process
-results become a part of the general knowledge only after they are published in this
scientific journal
-a system of ideas or misconceptions erroneously regarded as science
pseudoscience
-why is the us government still spending billions of dollars funding scientific research?
-why can nonscientists have confidence in the information published in the reputable (time magazine, new york times, smithsonian)?
-if you had to design a study to investigate the effects of a new drug on human health, what type of design would you use and how does it work?
-site of gamete formation (sperm or spermatozoa) and testosterone production
-contains many coiled tubes called seminferous tubules
-located in the scrotum which suspends the ______ outside of the body cavity where they are kept cooler than normal body temperature
testis (testes)
-site of sperm cell during maturation
-a chamber sitting on top of each testis
-sperm are stored and mature inside it
epididymis
-during sexual activity, sperm cells travel from the epididymis up the right and left ____ _________ into the body cavity
-loops over the unreters of the urinary system and arrive at the prostate gland
-the sperm then travel into a "tunnel" through prostate gland called the ejaculatory duct
vas deferens
-produced in seminiferous tubules in testes -> stored in epididymis -> vas deferens -> urethra
pathway of sperm
-accessory glands
-mucus and fructose
-nourishment for sperm
seminal vesicles
-accessory glands
-thin milky white fluid that contains nutrients for sperm
prostate gland
-accessory glands
-clear lubricating fluid that is alkaline and neutralizes the acid environment of the penile urethra
bulbourethral glands (cowper's gland)
-sperm from testicles
-fluid from seminal vesicles
-fluid from prostate gland
-fluid from bulbourethral glands (cowper's gland)
composition of semen
-the pituitary gland produces these
follicle stimulating hormone (fsh) and luteinizing hormone (lh)
-follicle stimulating hormone (fsh) -luteinizing hormone (lh)
-hormones that travel through the bloodstream to the testes where they cause the cells of the seminiferous tubules to begin producing the male gametes (sperm)
-stimulate the testes to begin production of testosterone
-travels from the testes through the bloodstream where it targets many tissues throughout the body
-responsible for male secondary sex characteristics
-stimulates growth of many body tissues including muscle, bone, and cartilage, as well as influencing male sex behavior and aggression
testosterone
-when testosterone levels rise due to the action of FSH and LH
-the testosterone has an inhibiting effect on the pituitary which causes FSH and LH to decline
-eventually leading to a decline in testosterone production
-if testosterone becomes too low, the negative feedback stops and the pituitary responds by producing more FSH and LH which causes testosterone production to increase
-this process keeps testosterone and sperm production under control and at a relatively constant level
-basically in works somewhat like a thermostat and the temperature in your house
negative feedback
-size of walnut until about 50 years old
-urethra open
normal prostate
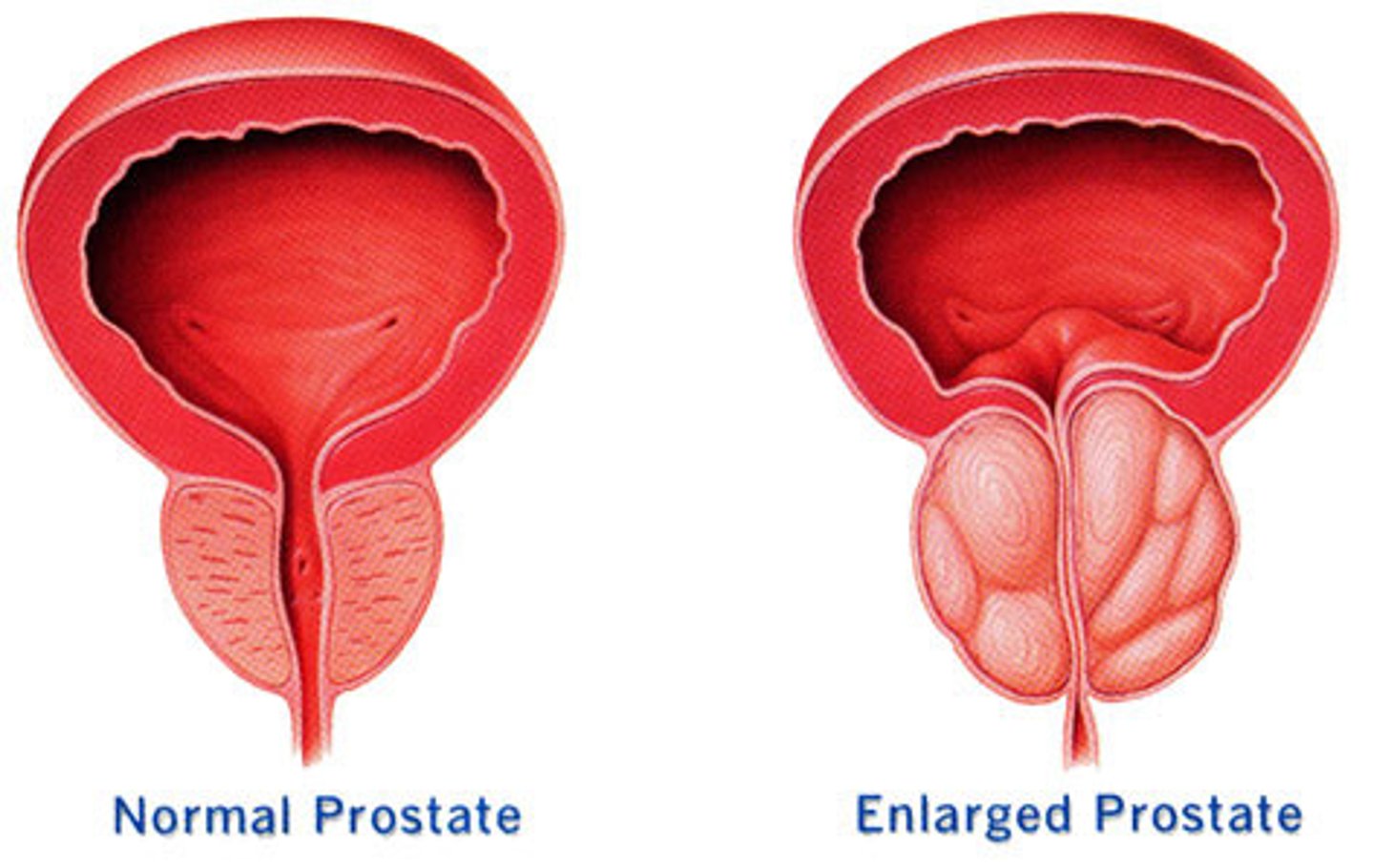
-after 50 years of age, can enlarge to size of lemon/peach
-urethra squeezed
-restricts the urethra which can cause difficulty when urinating
-dilates bladder
-dilates ureters
-causes discomfort
enlarged prostate
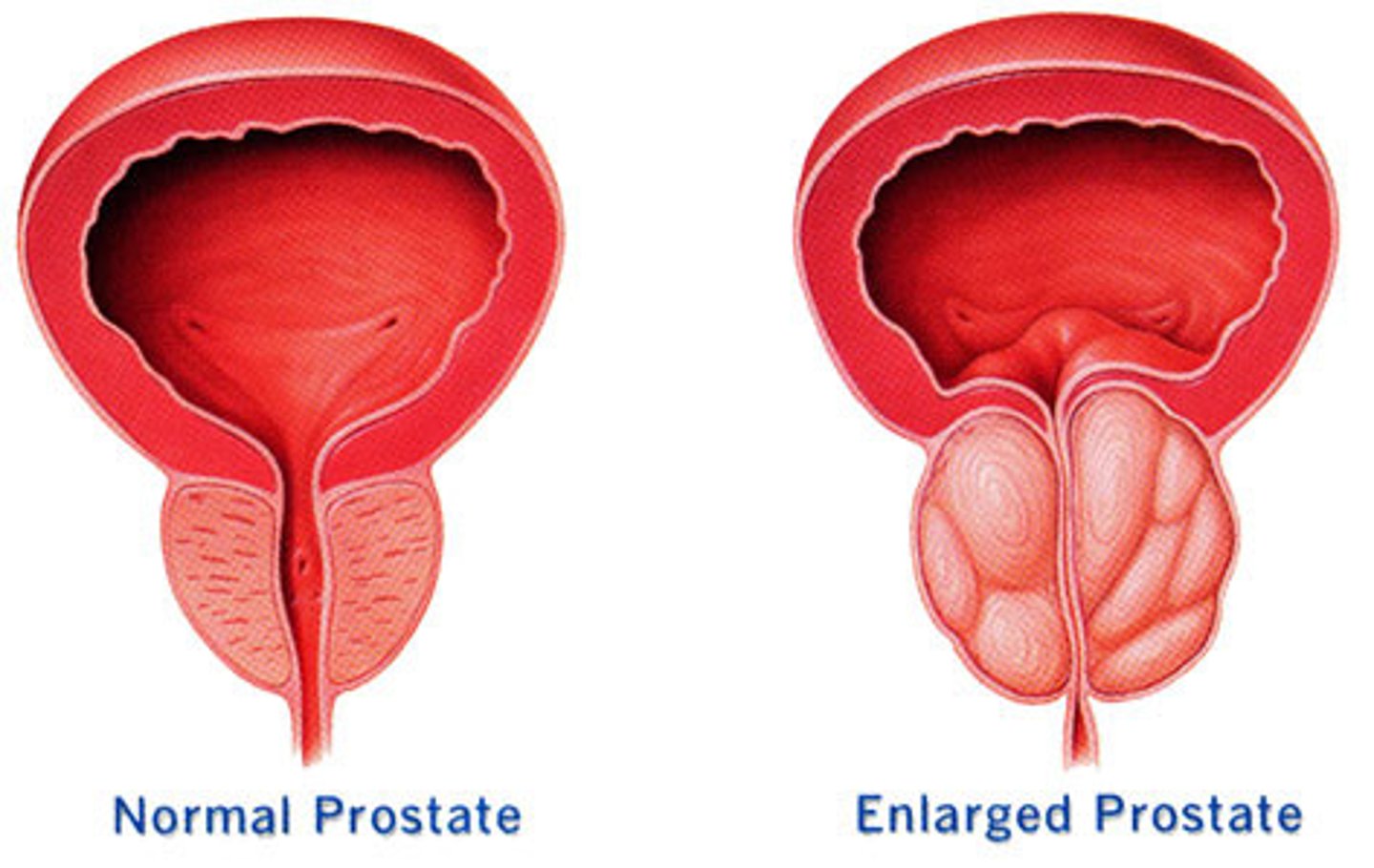
-located below the urinary bladder and the urethra passes through
prostate gland
-treatment for an enlarged prostate
-in this process, a resectoscope is inserted into the penile urethra up to the enlarged prostate
-electrical loop is extended which removes excessive prostate tissue, opening up the urethral orifice
transurethral resection of the prostate
-17% of men will be diagnosed with this during their lifetime
-3% of men will die from this disease
-second most common form of cancer in men (after skin cancer)
-second most common cause of cancer death (after lung cancer)
-slow growing
-kills if the cells leave the area and spread throughout the body through the lymph and circulatory system (metastatic)
prostate cancer
-age
-ancestry
-family history
-farmers
prostate cancer risk factors
-the risk of prostate cancer increases as a man _______
ages
-this group has the highest incidence and mortality from prostate cancer
african americans
-vasectomies
-bicycling
-sexual frequency
factors not causing prostate cancer
-goal is to detect prostate cancer in the __________ stage of the disease
earliest
-refers to the fingers of the hand
digital (rectal exam)
-what age do you start annual digital rectal exams?
40
-in what exam do physicians feel for marble-sized tumors
digital rectal exam
-an antigen is a type of protein
-tests for protein in blood that reflects abnormal increases in the prostate
prostate specific antigen (PSA) test
-PSA levels increase with ____ and temporarily after ___________
age, ejaculation
-ultrasound probe inserted through anus
-biopsy needles injected into prostate from rectum
-attempting to detect cancer in stage A
-analysis of cancer spread and cell type (Gleason Scale)
needle biopsy for prostate cancer if PSA is abnormally high
-a system of grading prostate cancer tissue based on how it looks under a microscope
-range from 2-10 and indicate how likely it is that a tumor will spread
-low score means the cancer tissue is similar to normal prostate tissue and the tumor is less likely to spread
-high score means the cancer tissue is very different from normal and the tumor is more likely to spread
gleason score
-blood in your urine (almost all patients)
-blood in your semen which can last for up to six weeks posing no problem for sex partner (almost all)
-blood in your stools from bowel (almost all)
-discomfort in your prostate from bruising due to biopsies (1 in 2 & 1 in 10 patients)
-infection in your urine requiring antibiotics (1 in 10 patients 10%)
-temporary problems with erections caused by bruising from the biopsies (1 in 20 patients 5%)
after effects of prostate biopsy
-what is more prevalent? prostate or lung cancer?
prostate
-what cancer has a higher death rate? prostate or lung cancer?
lung
-is prostate or lung cancer more deadly?
lung
-a prostate surgery
-complete removal of prostate gland
-most effective way to cure prostate cancer
radical prostatectomy
-a prostate surgery
-leaves prostate tissue near nerves
nerve-spring prostatectomy
-incontinence (most men eventually regain control of bladder function)
-impotence (some men never regain normal sexual function)
side effects of surgeries (because of nerve damage)
-alternative treatments to prostatectomies
-high doses of radiation are aimed at the prostate cancer in order to kill the cancerous tissue
-good for those who cannot withstand the physical demands of surgery or those who want to reduce the risk of side effects such as incontinence and impotence
beam radiation treatments
-small pellets of radioactive material (size of rice grains)
-inserted into the prostate gland where they deliver their radiation treatment from inside the body
-these pellets deliver twice the dose of radiation as external beam radiation are left in place when they are done delivering the radiation
radioactive seed implants
-less recovery time
-can impair sexual function
-may not eliminate all tumor cells
-surgery is not possible after radiation
side effects of radiation
-type of therapy
-drugs eliminate or block testosterone production by testes
-used when cancer has spread beyond the prostate
hormone therapy
-can impair sexual function and cause hot sweats, irritability
-does not eliminate tumor cells but halts the cell growth
side effects of hormone therapy
-percent of surviving prostate cancer after 5 years
98.6%
-a vasectomy involves cutting pieces out of both vas derens. why does a vasectomy result in sterility?
-what are some of the problems in using PSA tests to screen for prostate cancer
only detects 80% of prostate cancer (psa test= blood test)
-what would you expect to happen to a man's PSA as he develops prostate cancer and then has a prostatectomy the removes all of his prostate
-why is late stage prostate cancer so deadly?
this is the stage where the cancer will usually have metastasized (spreading of cancer cells)
-follicle of ovary produces egg -> egg passes down oviduct -> egg passes thru uterus -> egg passes thru vagina
pathway of egg is unfertilized
-part in the female system
-site of gamete formation (egg or ovum) and hormone production
ovary
-part in the female system
-tube which travels from the ovary to the uterus
-site of egg fertilization by sperm cell
oviduct (fallopian tube)
-part in the female system
-muscular organ where implantation of the blastocyst (pre-embryo) and development of the fetus occurs
uterus
-part in the female system
-"neck" of the uterus which extends into the vaginal canal
cervix
-part in the female system
-muscular tube that receives the penis during intercourse
-site of sperm deposition
-also serves as the birth canal
vagina
-the cyclic buildup and breakdown of the endometrium as the uterus prepares monthly for an embryo (fertilized egg)
menstrual cycle
-layer of the uterus which becomes highly vascular in preparation for implantation of embryo
-this layer is shed each month when pregnancy does not occur
endometrium
-the age of the first menstrual cycle has _________ with time
declined
-age of first menstrual cycle has gotten _________ throughout the years
earlier
-reasons why the age has gotten earlier throughout the years for the first menstruation
-nutrition
-obesity (possibly)
(bigger the girl=earlier first menstruation)
-at puberty the hypothalamus in the brain begins producing "releasing hormones" (GnRH) which controls the activity of the pituitary gland
-the pituitary responds to the releasing hormones by producing it's own hormones; LH and FSH.
-FSH and LH travel through the bloodstream to the ovary where they cause changes to occur in the ovary
-in response to FSH, the cells around one early stage ovum (called a follicle) begin to grow and produce estrogen which causes female sex characteristics and causes the endometrium of the uterus to prepare for a pregnancy
-in response to LH, the follicle (with the developing egg inside) ruptures and the egg is released.
-after ovulation, the "old" follicle produces progesterone which causes the endometrium of the uterus to be maintained in case of pregnancy
how hormones regulate the female reproductive system
-principle way the body maintains homeostasis
-when estrogen and progesterone levels rise
-have a negative effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary which slows their production of GnRH, FSH, and LH
-once estrogen and progesterone levels drop low enough
-cause the hypothalamus and pituitary to begin production again
-keeps sex hormones in balance from puberty until menopause
negative feedback
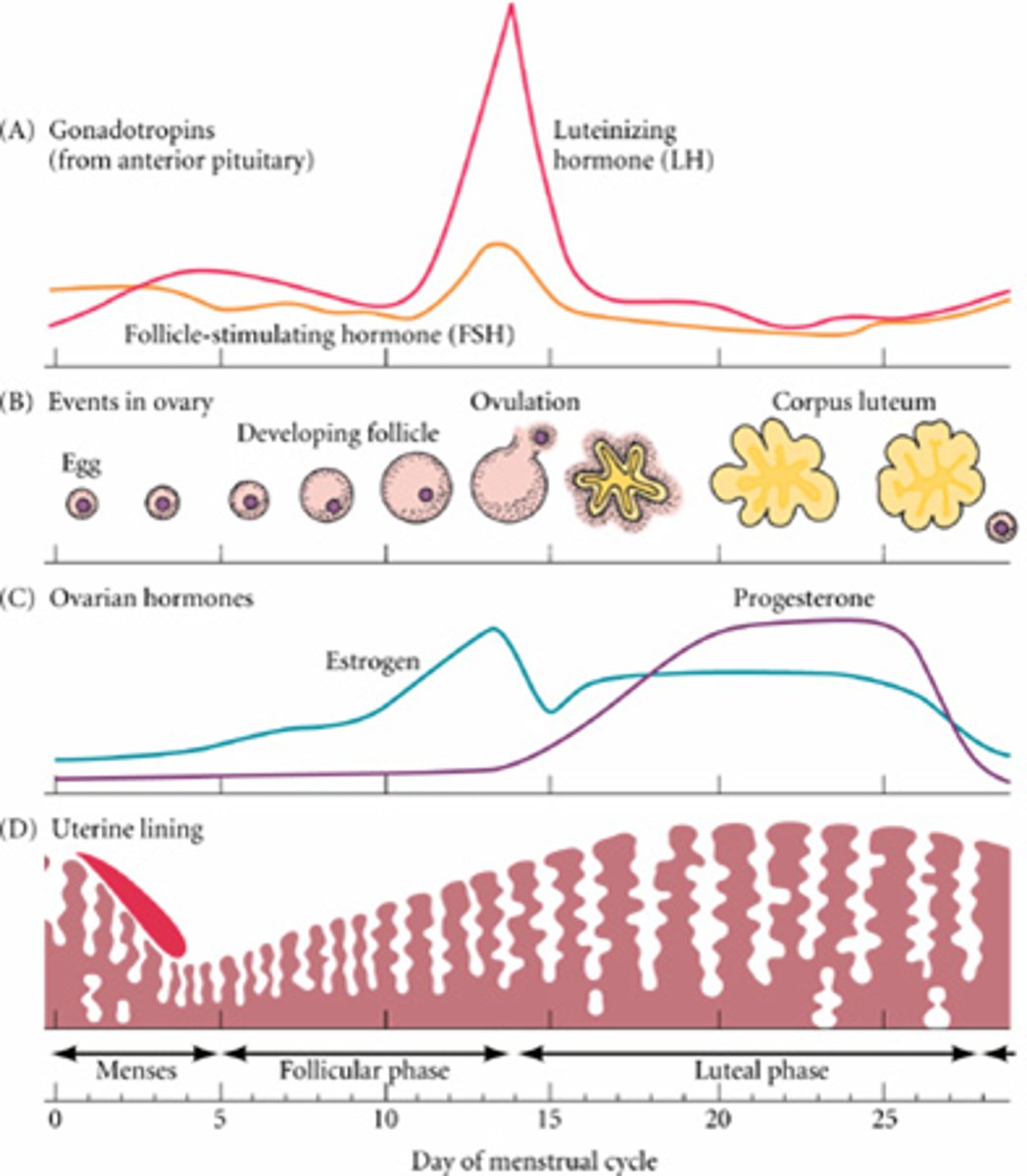
-this graph depicts the levels of FSH and LH that are being produced by the pituitary in response to the releasing hormones from the hypothalamus -around day 12 or 13, the levels of these hormones "surge"
-this surge in hormones will cause the developing follicle in the ovary to release an egg into the oviduct where it may be fertilized
top panel
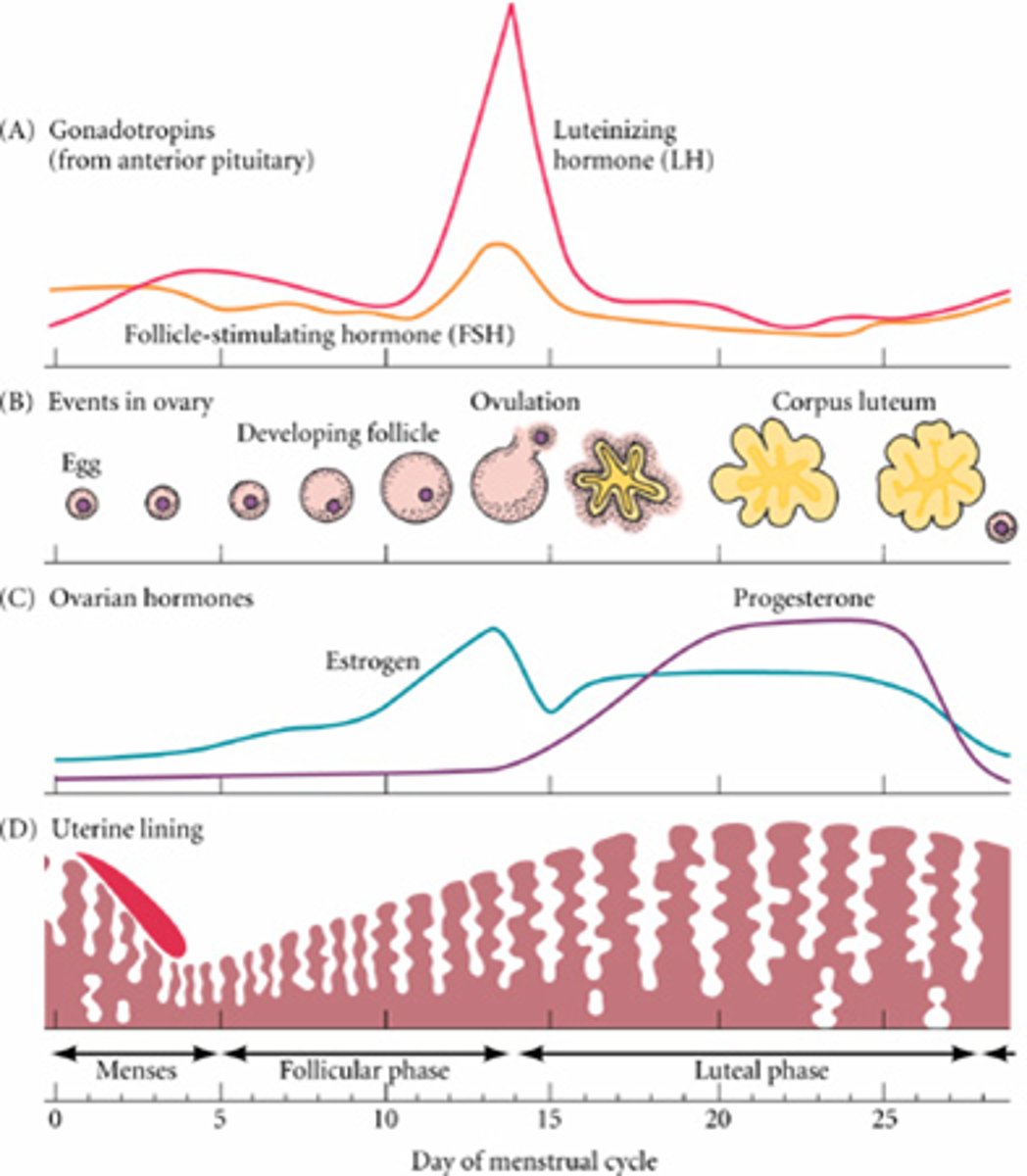
-what happens in the ovary in response to FSH and LH from the pituitary
-FSH causes cells around the developing ovum (the follicle) begin to grow
-as the follicle grows, the cells of the follicle begin producing estrogen which is responsible for female sex characteristics
-surge of LH around day 13 causes the mature follicle to rupture and release the ovum into the oviduct where it may be fertilized
second panel
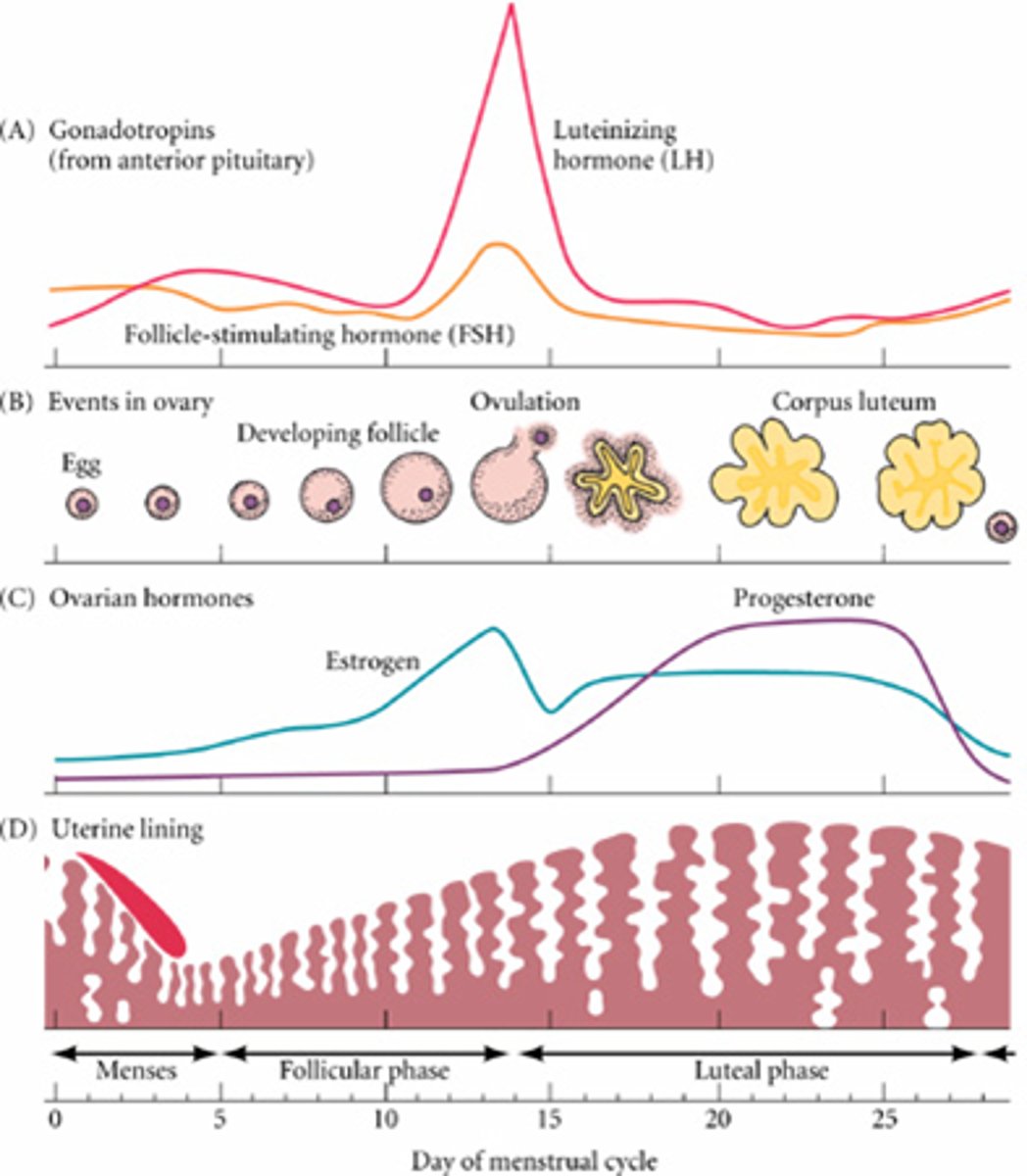
-shows the levels of estrogen and progesterone during the 28-day cycle
-estrogen= responsible for female sex characteristics and the thickening of the uterine lining is produced by the developing follicle in the ovary
-as the follicle is growing during the first 14 days of the cycle, estrogen begins to climb
-progesterone= produced in large quantities until after day 14 (ovulation)
-progesterone=maintains the uterine lining in case of pregnancy
third panel
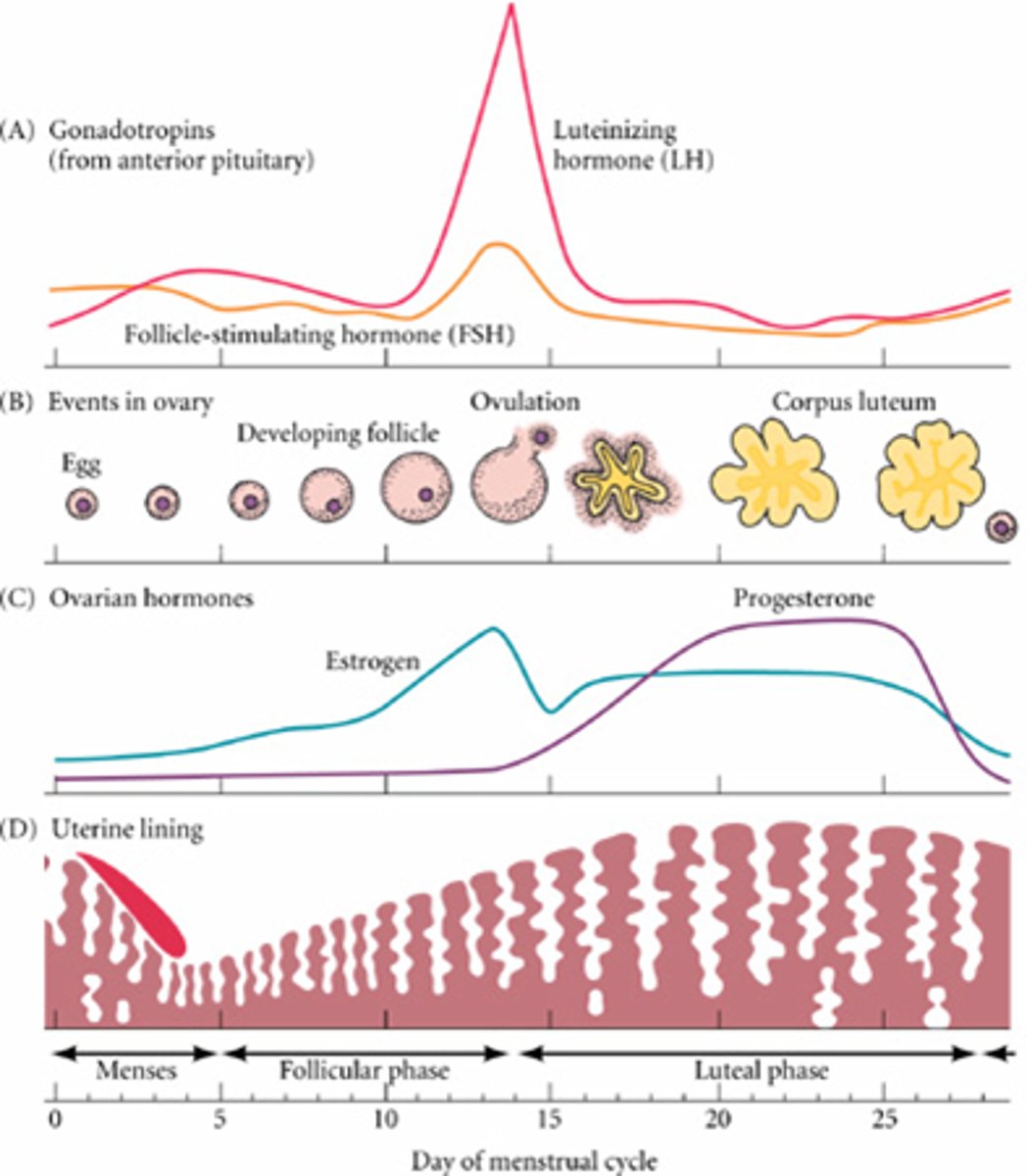
-shows the breakdown and development of the endometrium of the uterus in response to estrogen and progesterone
-when the levels of estrogen and progesterone are low, the endometrium breaks down and is sloughed off
-when levels of estrogen and progesterone rise, the endometrium thickens
-in order for pregnancy to occur, the endometrium must be thick and filled with blood vessels
-after ovulation (when fertilization can occur) the endometrium is the thickest
bottom panel
-pregnancy hormone
-study thickness of endometrium
progesterone
-women are born with ____ of their eggs (100s of thousands-million)
all
-men produce much ______ everyday
sperm
-inside lining of the uterus
endometrium
-after 14 days there is a surge in LH
-you would have sex during this time if you want a baby
ovulation
-day 1 of the 28 day cycle is the first day of __________
menstruation