TTU STELLAR ASTRONOMY FINAL 1401
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
That the physical laws and properties of the universe are the same everywhere and in all directions is a statement of
the cosmological principle
An implication of the cosmological principle is that our location in the universe is
not special
What do astronomers mean when they say that the universe is homogeneous
galaxies are generally distributed similarly throughout the universe
What do astronomers mean when they say the universe is isotropic
the universe looks the same no matter what direction you look
in an imaginary universe, astronomer find that there are thousands of galaxies withing a few million light years in all directions, but beyond those galaxies there is nothing but empty space. Such a universe would be
isotropic but not homogenous
According to Hubbles law, as the distance of a galaxy _____ its _______ increases
increases; recessional velocity
if we lived in a galaxy 1 billion light-years from our own, what would we see?
much the same universe as we see here
As measured from earth, the spectrum of galaxy NGC 7512 reveals a receding velocity of about 7000 km/s. If an observer in that galaxy takes a spectrum of the milky way they would measure
the same 7000 km/s receding speed
all distance galaxies appear to be moving away form us. Does this mean we are in a special place, and why?
No because all observers will see the same phenomenon
galaxies move away from us in all directions because
space is expanding and there is no center to the universe
where did the big bang take place
everywhere in the universe
distant galaxy A has a larger redshift than distance but otherwise identical galaxy b. this means that galaxy A
has a larger look-back time than galaxy B
Hubbles constant H0 represents the
rate of expansion in the universe
if hubble expansion was due to an explosion throwing galaxies into space instead of space expanding everywhere, which of the following would be true?
the universe would have a measurable center
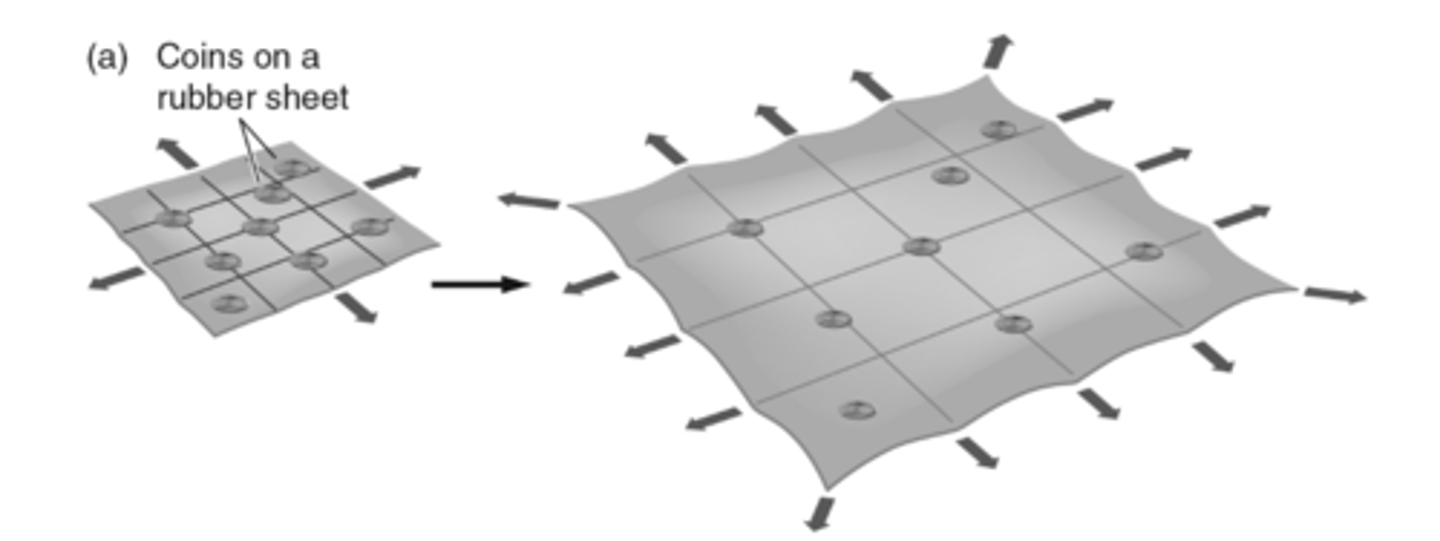
the figure below uses a rubber sheer as an analogy for hubble expansion, with coins representing galaxies. The illustration demonstrates that
galaxies may be sitting still but will move farther apart as space expands
What would you predict for the recession velocity of a galaxy whose distance is Mpc? Note that the hubble constant has a value of 70 km/s/Mpc
2940 km/s
If a galaxy has an apparent velocity of 700 km/s, what is its distance if the Hubble constant is 70 km/s/Mpc
10mpc
If the distance of a galaxy is 5 Mpc, what is its recessional velocity if the Hubble Constant is 70 km/s/Mpc
350 km/s
You observe the following 3 galaxies and measure their recession velocities: A. 2,100 km/s; B. 4,400 km/s; C. 3,050 km/s. Which of the following must be trust about these galaxies?
B is farther away from us than A
Galaxy peculiar velocities are typically about 300 km/s. How far away do you have to look in order to see recessional velocities that are 10 times this peculiar velocity?
43Mpc
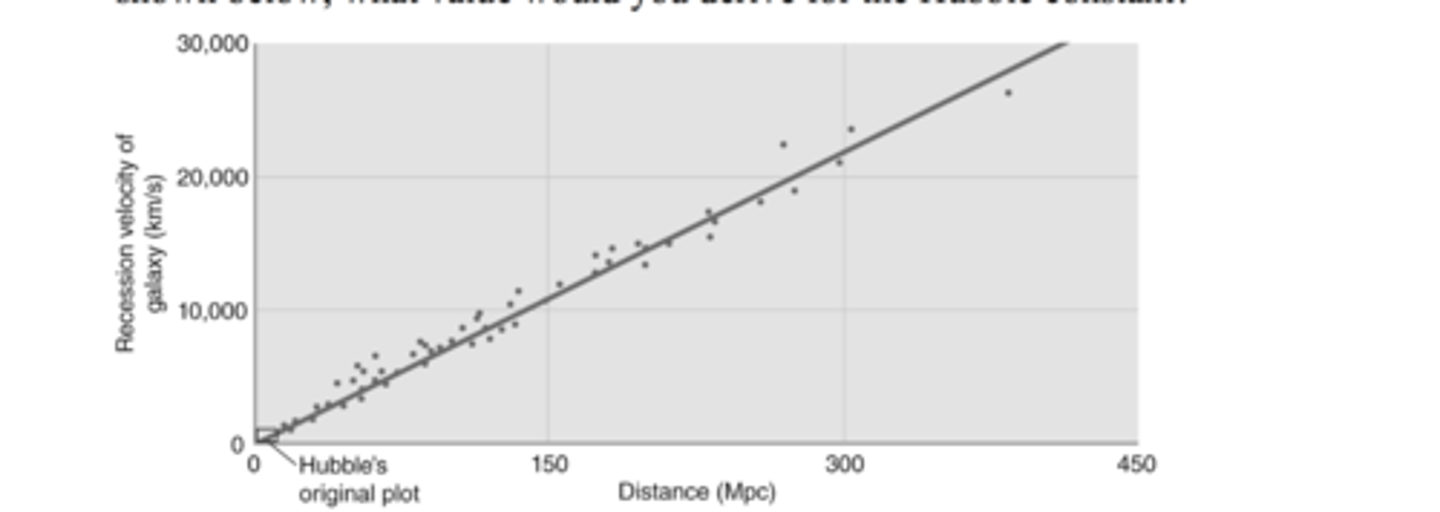
If you measured the distances and recessional velocities for a sample of galaxies and plotted the data to get the figure shown below what value would you derive for the hubble constant?
70 km/s/Mpc
If the hubble constant had a value of its current measured value of 70 km/s/Mpc, the age of the universe would be about
28 billion years
The inverse of the value of H0 gives a measurement in a unit of
time
if the scale factor of the universe changes by a factor 2 over a certain length of time, then the distance between galaxies will increase by a factor of
2
Will the increasing scale factor of the universe cause the Sun to get larger over time?
no, because the sun's self-gravity locally dominates over the expansion of the universe
the majority of the redshift that we measure form the most distance galaxies is due to
the expansion of the universe stretching the wavelengths of photons
what caused earl astronomers to believe that our galaxy is only 6000 light years across
interstellar dust blocked visible light from stars farther away
in the great debate of 1920 curtis and shapley argued over whether or not
the spiral nebulae were location outside of the milky way
the disks of spiral galaxies appear blue because
they contain active regions of star formation
the hubble classification scheme for galaxies sorts them by their
visual appearance
which of the following images shows an edge-on spiral galaxy?
D

what type of galaxy is shown in the figure below?
an ordinary spiral galaxy
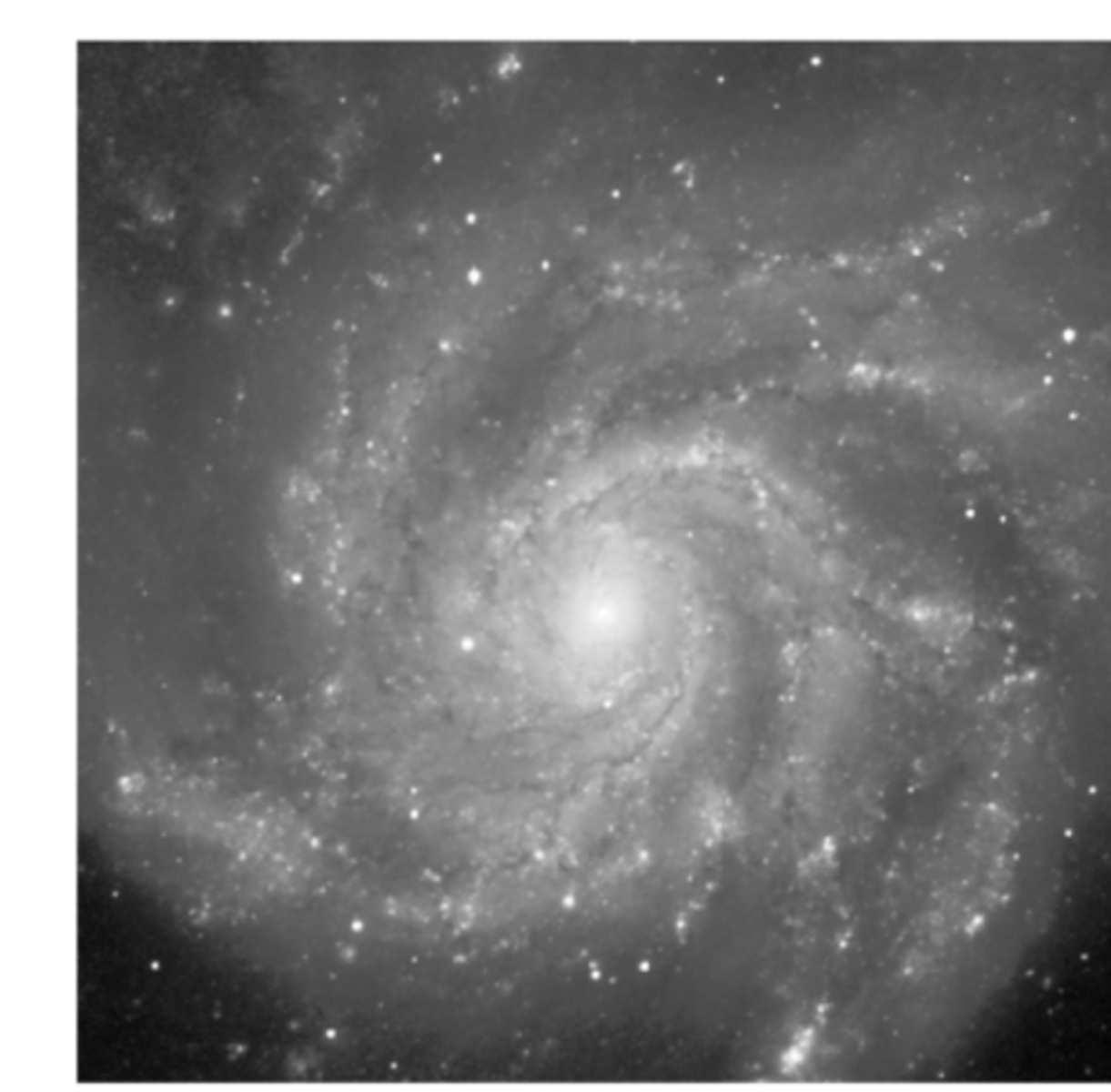

What type of galaxy is shown in the figure below?
a giant elliptical
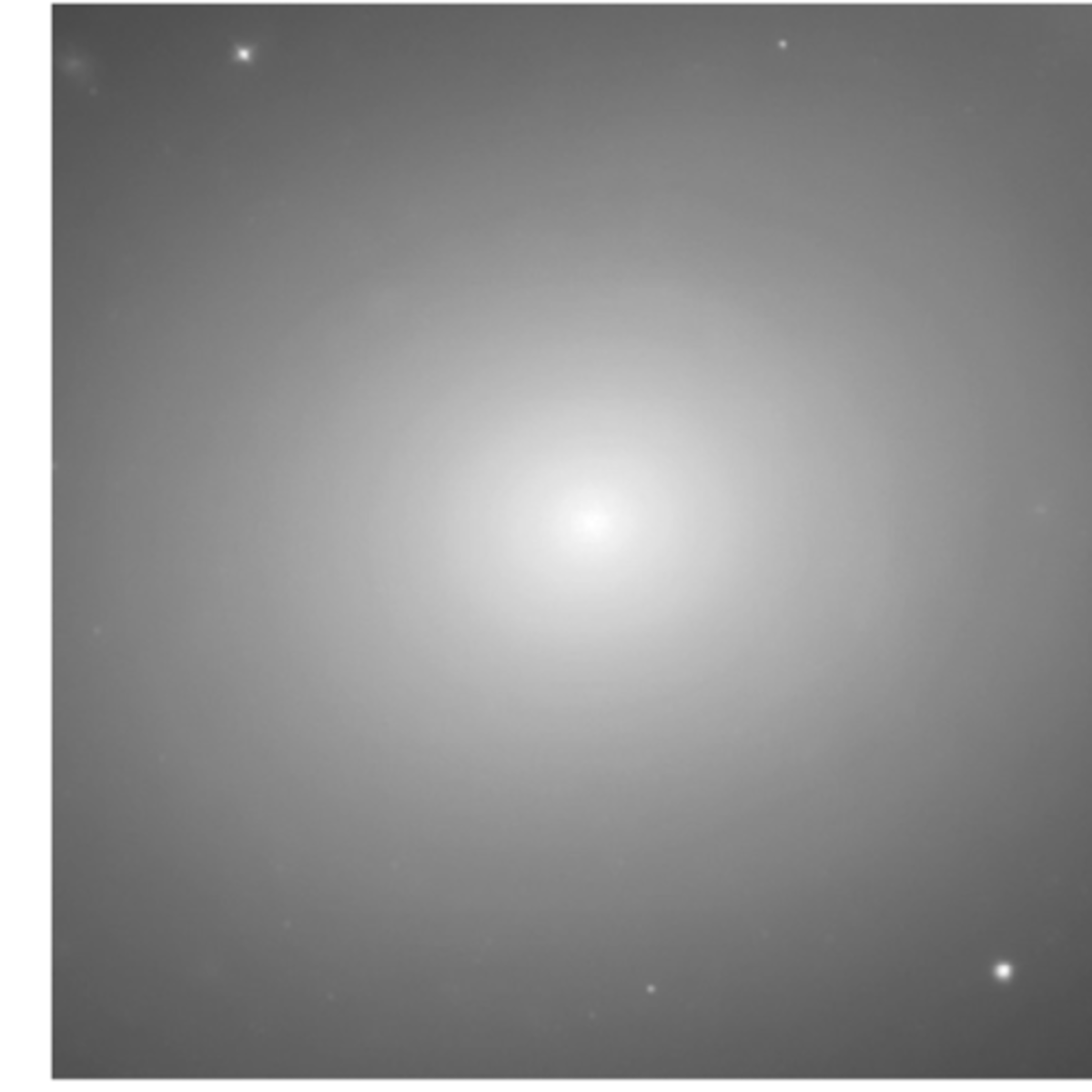

Active star formation does not typically occur in elliptical galaxies because they
contain little cold gas
Elliptical galaxies appear red because:
they contain mostly old stars
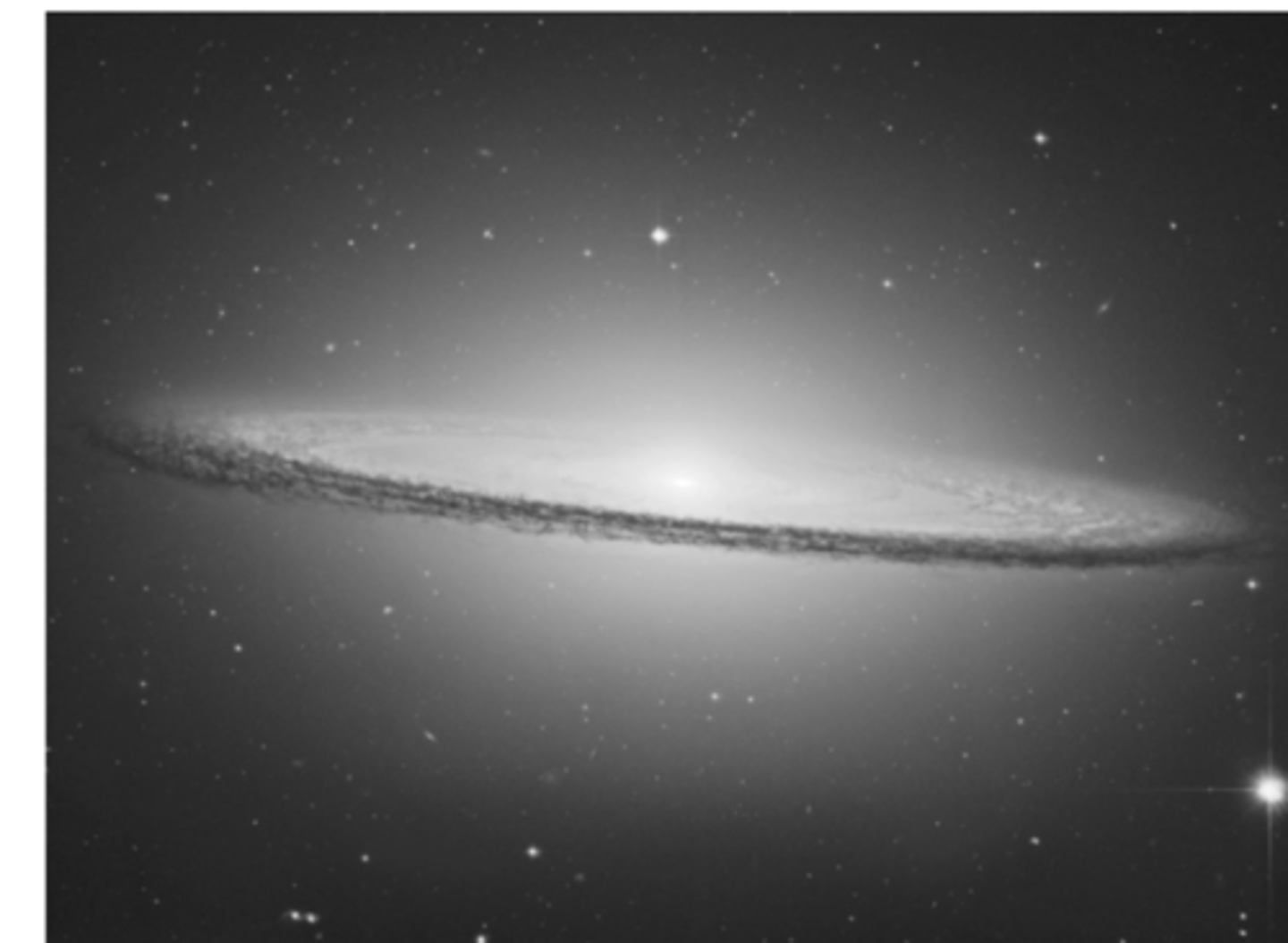
the dark features in the HST image in the figure shown below indicate
large amounts of dust

stars in the disks of spiral galaxies have orbits that are
mostly aligned in the same plane
you observe a reddish galaxy with stars that orbit in random directions. This galaxy is most likely an
elliptical galaxy
To be a standard candle an object must have a constant:
luminosity
which distance indicator can be used to measure the most distant objects
type Ia supernovae
which of the following lists distance indicators from nearest to farthest
parallax, spectroscopic parallax, Type Ia supernovae, Cepheids
the technique of using a stars spectrum to find its location on the H-R diagram which provides an estimate of its luminosity and thereby its distance is called
spectroscopic parallax
according to hubble's law as the distance of a galaxy ______ its _______ increases
increases; recessional velocity
the spectra of most galaxies tells us that
galaxies appear to be moving away from us
the rotation curve of a galaxy is a plot of the rotation speed as a function of the
radius from the center
what makes up the majority of the mass of an individual spiral galaxy
dark matter
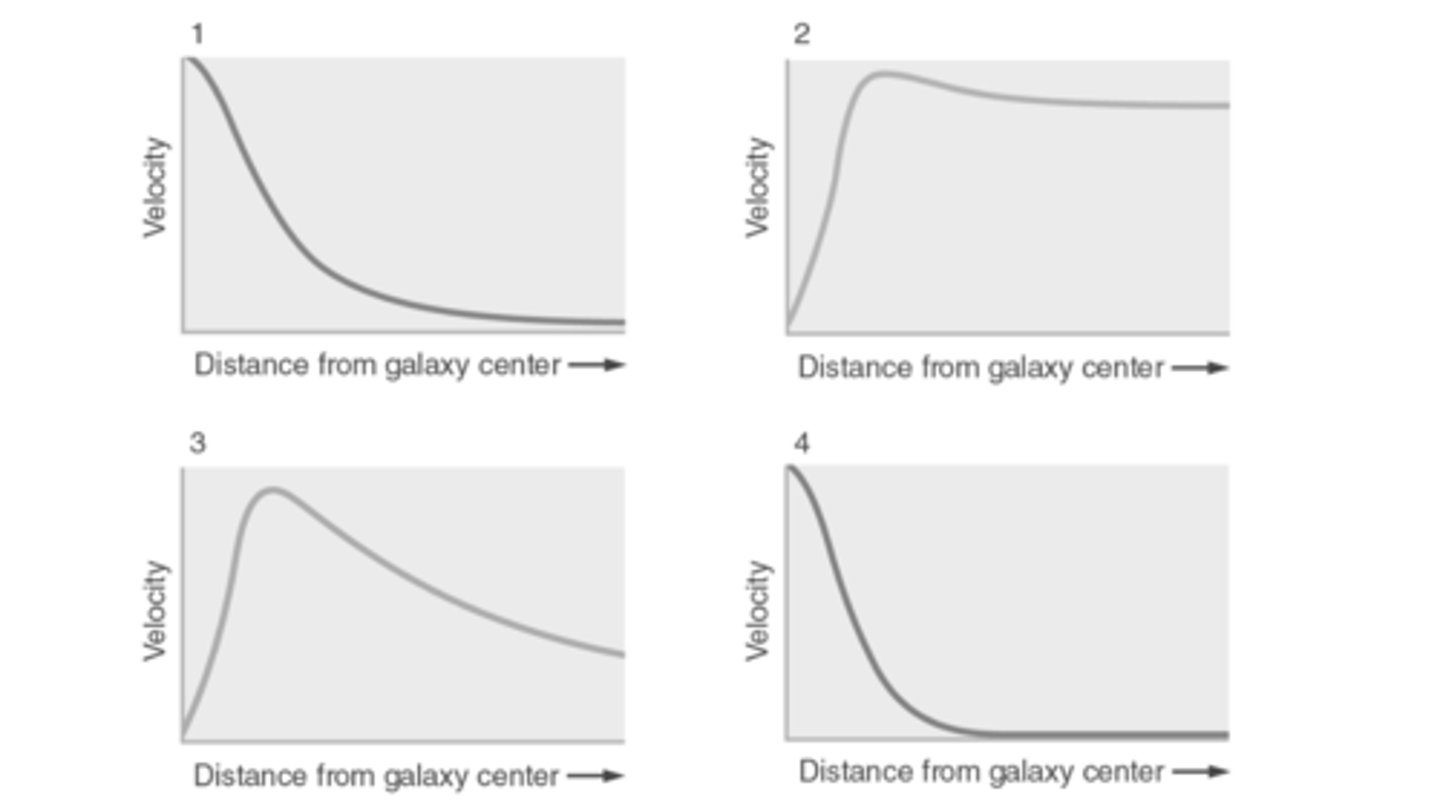
Which of the galactic rotation curves in the figure below is closest to what is actually measured for galaxies?
B (2)
roughly what percentage of the total mass of a galaxy is made up of luminous or normal matter?
5-10%
How did astronomers determine that elliptical galaxies are composed mostly of dark matter?
they measured the X-ray emission from hot gas gravitationally bound to the galaxies
the term dark in dark matter refers to the fact that
it does not absorb or emit light
dark matter is most likely made up of
elementary particles that have mass but do not interact much with normal matter
in most cases, it is impossible to observe the host galaxies of quasars because
quasars outshine the host galaxies by a few orders of magnitude
quasars are most likely to be found
at extreme distances
More luminous giant galaxies tend to have __________ supermassive black holes at their centers.
more-massive
AGNs are most likely powered by
accreting supermassive black holes
the unified model of AGN suggests that quasars, seyfert galaxies and radio galaxies are
similar phenomena but viewed from different angles
what happens to active galaxies when their AGNs run out of fuel
they simply become normal galaxies
if the sun were to be instantly replaces by a 1 Msun black hole, the gravitational pull of the black hole would be
the same as it is now
The event horizon of a black hole is
the radius at which the escape speed from the black hole equals the speed of light
what is the significance of the Schwarzschild radius around a black hole?
it is the radius at which the escape velocity equals the speed of light
if the sun turned into a black hole what would be the radius of its event horizon?
3km
if you were to fall to within the event horizon of a black hole, you would
never be able to escape
A person would experience ____________ as he or she approached the event horizon of a black hole.
extremely strong tidal forces
Even if a black hole emitted no light, we can still detect it
through gravitational effects on surrounding gas or stars
a red giant star found to be orbiting an unseen object with a short orbital period. by measuring the speed at which it orbits, astronmers deduce that the unseen object has a mass of 10 Msun. this object is probably a _______ because ______
black hole; its mass is too large to be a neutron star or a white dwarf
black holes that are stellar remnants can be found by searching for
variable x-ray sources
the detection of gravitational waves is important evidence for
general relativity
general relativity predicts that coalescing massive objects would trigger
gravitational waves
The dominant mechanism by which high-mass stars generate energy on the main sequence is called
the CNO cycle
in the CNO cycle, carbon is used as a catalyst for the fusion of hydrogen into helium. this means that
carbon facilitates the reaction but is not consumed in it
the fundamental stellar property that determines the major evolutionary differences in the life history of stars is
MASS
As a high-mass main-sequence star evolves off the main sequence, it follows a __________ on the H-R diagram.
nearly horizontal path
Massive stars synthesize chemical elements going from helium up to iron:
only in the core of the star
If a 25 M¤ main-sequence star loses mass at a rate of 10-6 M¤/yr then how much mass will it lose in its 7-million-year lifetime?
7 Msun
If you measure the average brightness and pulsation period of a Cepheid variable star, you can also determine its:
distance
During the main-sequence evolution of a massive star, increasingly heavier elements are fused in the core until the core is filled with
Iron
massive stars explode soon after fusion to iron begins because
fusion of elements heavier than iron requires energy so the star runs out of fuel and cannot hold itself up against gravity
where did the iron in your blood come from?
nuclear reactions in the cores of massive stars
Massive stars explode when they
run out of nuclear fuel in their core, and the cores collapse
which of the following is in the correct order for elements fused (as fuel) in the core of late stage high mass stars?
hydrogen, helium, carbon, neon, oxygen, silicone
When the core of a massive star collapses, a neutron star forms because:
protons and electrons combine to make neutrons
supernovae are very energetic events. of the following events which is the brightest that a supernova can outshine at their maximum?
our entire milky way galaxy
the luminosity of type II supernova ________ with time
first increases, then decreases
if the core of a high mass star remains at the center of a type II supernova remnant, that core will be classified as a
neutron star
Neutron stars have masses that range from:
1.4 M¤ to 2 M¤
a neutron star contains a mass of up to 2 Msun in a sphere with a diameter approximately the size of
a small city
which of the following characteristics is common for a neutron star
enormous magnetic field
a neutron star in a mass transfer binary system is called
an x-ray binary
short gamma ray bursts (GRBs) are most likely caused by
merging neutron stars
what is the characteristic observational signal produced by a pulsar
regularly timed pulses of light
what characteristic of a star cluster is used to determine its age
the color of the main sequence turnoff in the cluster
what should be true about the oldest stars in the milky way
they would have a few heavy elements because there was not much chance for the earlier generations of stars to explode as supernovae before these stars formed
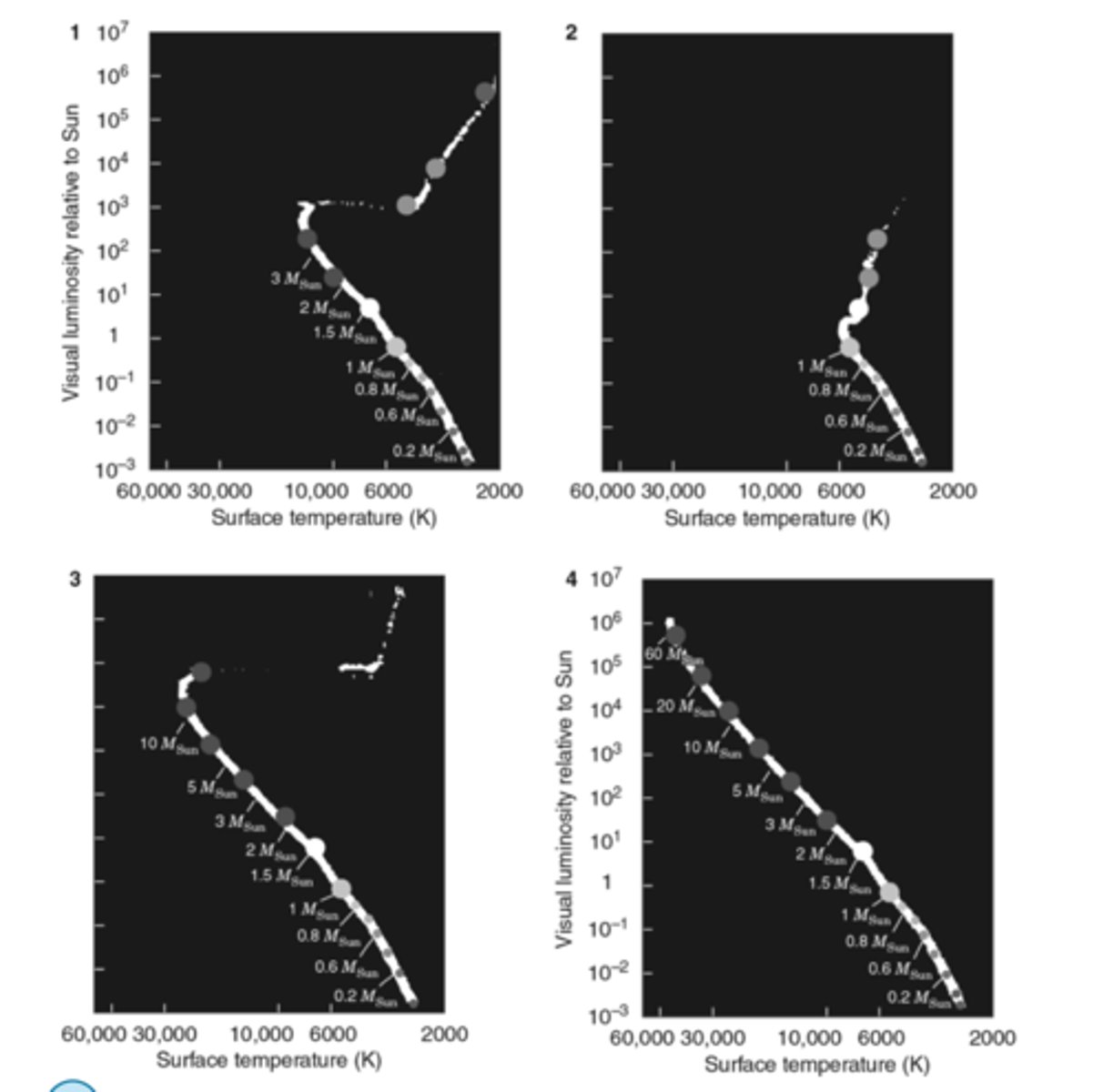
list the H-R diagrams in the figure shown below from oldest to youngest
2,1,3,4
which of these clusters in the figure shown are open clusters?
NGC 290 and NGC 6530
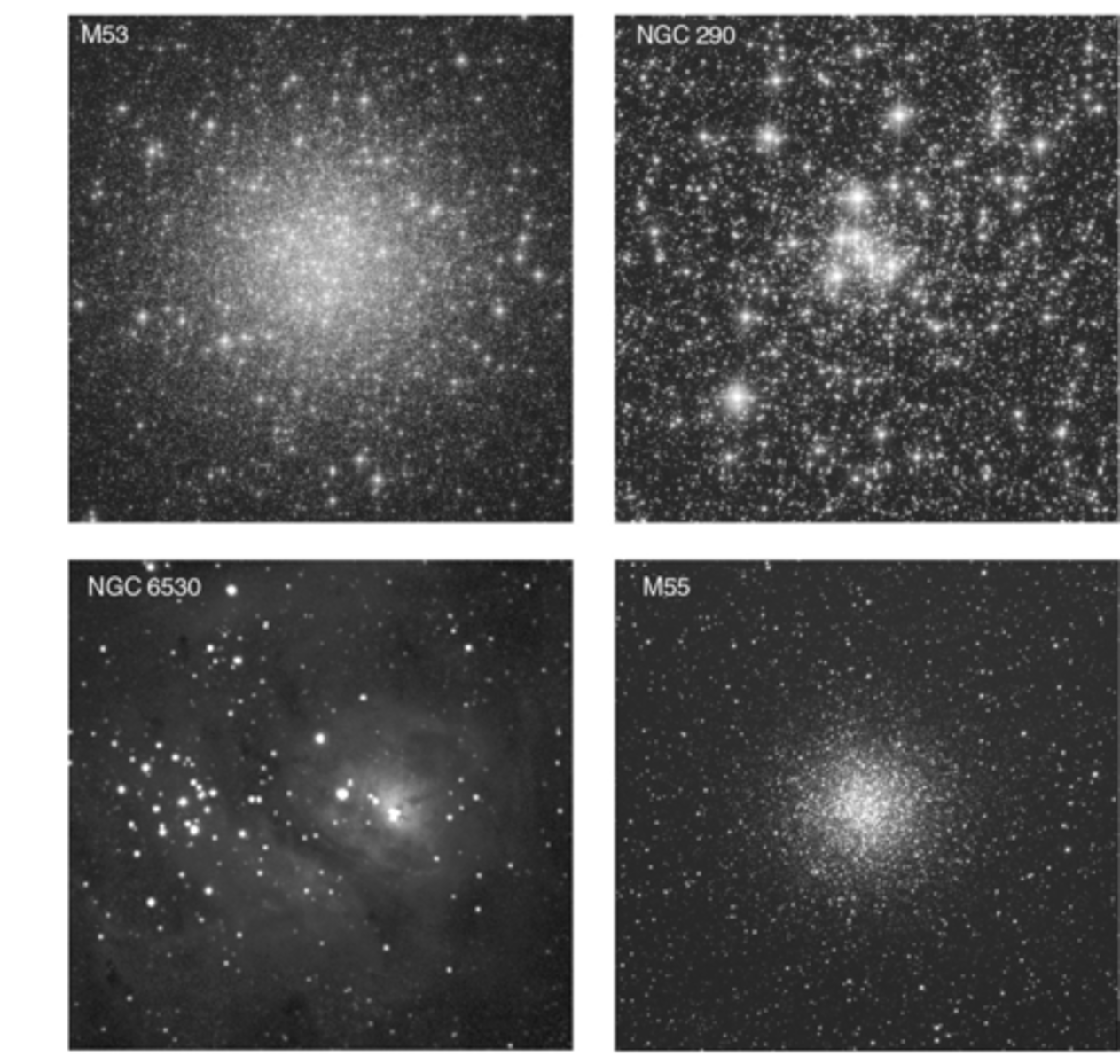

in young clusters the light is dominated by
luminous hot, blue, and some red supergiants
what provides us the best blues as to the age of a galaxy like ours
the H-R diagram of globular clusters of stars
how do astronomers know that the sun and our solar system formed from the remnants of other stars
elements heavier than hydrogen and helium formed within other stars and then were ejected into space by supernovae
the area of a circle is related to is diameter by the A=1/4 pieD^2 formula. Using algebra to solve for D we find that
D=(4A/pie)^1/2
The volume of a sphere is related to its radius by the formular V=4/3 pie R^3, using algebra to solve for R we get
R=(3V/4pie)^1/3
declination is a measure of a stars location relative to the
celestial equator