Chem - Nuclear Energy
1/65
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
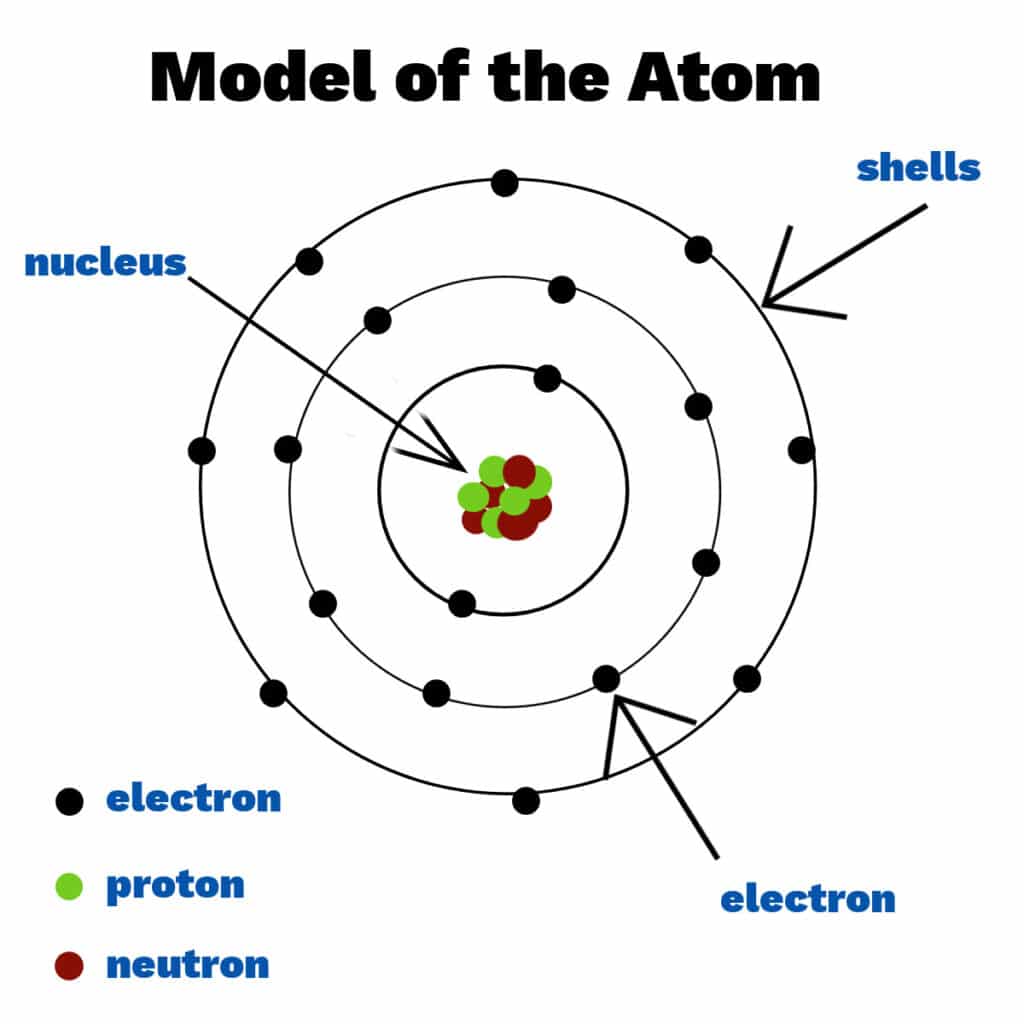
What is an Atom?
The smallest particle of an element that keeps the properties of an element. Made of 3 subatomic particles
What are the 3 subatomic particles?
Proton (p+), Neutron (n o), Electron (e-)
What subatomic particles are located in the Nucleus?
Proton (p+) and Neutron (n o)
What subatomic particle is found outside the Nucleus?
Electron (e-)
What subatomic particle has no charge?
Neutron (n o)
What 2 subatomic particles have charges?
Proton (+1) and Electron (-1)
What 2 subatomic particles contribute to the mass?
Proton (+1) and Neutron (+1)
What is the mass of an Electron?
Very small
What is the atomic number?
The amount of protons
What do protons do?
They identify the element
What is a mass number?
The total amount of Protons and Neutrons
What is a charge?
An atom has a charge if there are an unequal number of protons and electrons in an element
What are Ions?
Charged atoms, due to losing or gaining electrons
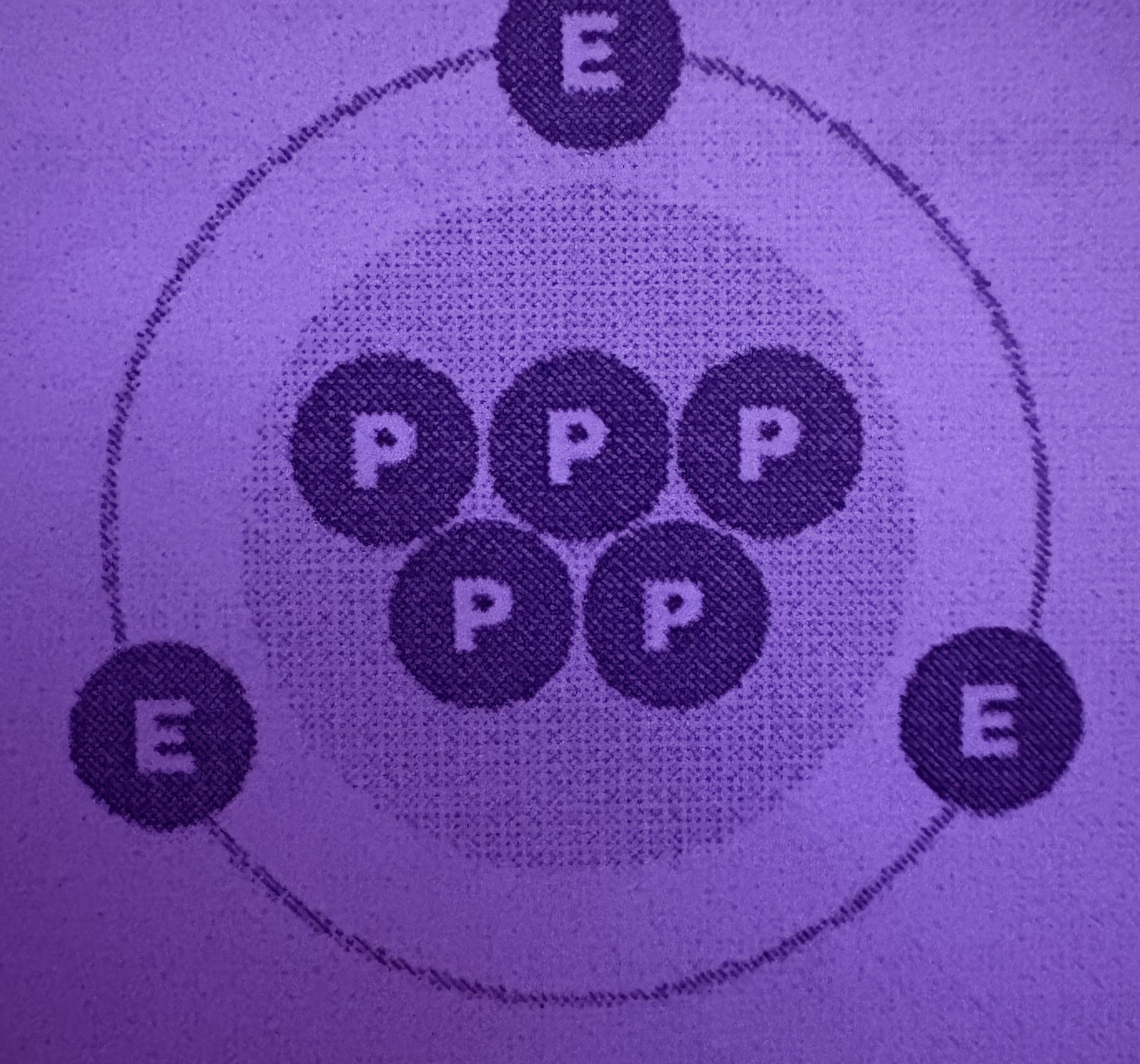
What is a Cation?
Positively charged, more protons than electrons
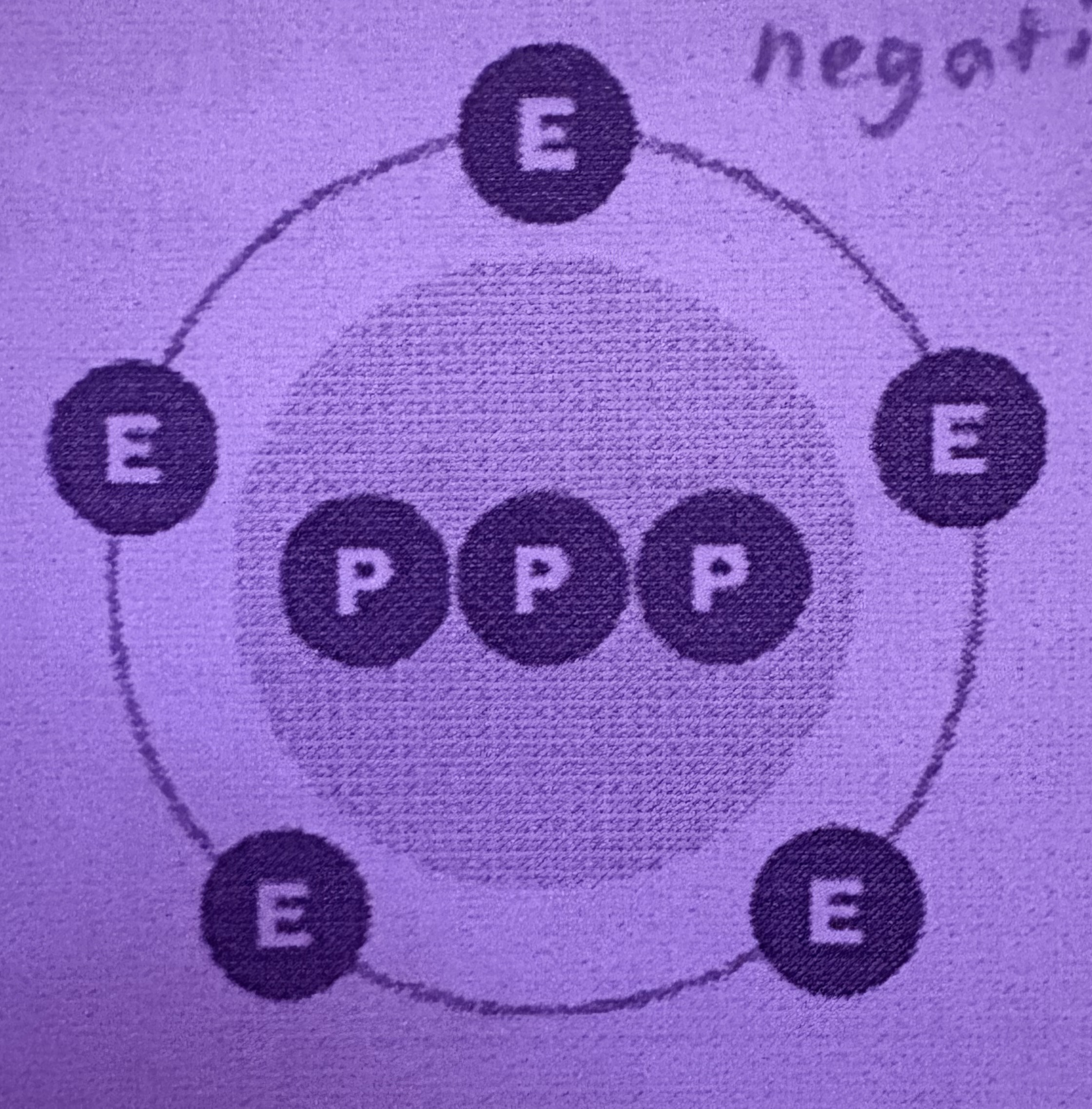
What is an Anion?
Negatively charged, more electrons than neutrons
Why are Ions different?
Differ by number of electrons (charge) + same element
What are Isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with different masses due to different numbers of neutrons
What is Percent abundance?
% of the isotope in the total amount of atoms
What is the equation for amu?
A.M x % abundance + A.M x % abundance
What is the equation for percent abundance?
amu (molar mass) = m1 (x) + m2 (1-x)
Why is there a 0% chance that a single atom will have the exact atomic mass listed on the periodic table?
The atomic mass on the periodic table is the average of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element. Since each atom is a specific isotope, no single atom can have the exact average value
How can you tell which isotope of an element is most abundant?
It’s the one closest to the element’s amu on the periodic table
What is a Nuclide?
A distinct atom characterized by a specific number of protons and neutrons, it’s the way scientists talk about a specific type of atom
What is Radioactivity?
An unstable atom changes into another atom by undergoing decay (breaking down the nucleus) from the nucleus of an atom
Why do some atoms undergo nuclear decay?
They’re unstable and trying to become more stable
What are the different types of Nuclear Reactions?
Fission, Fusion
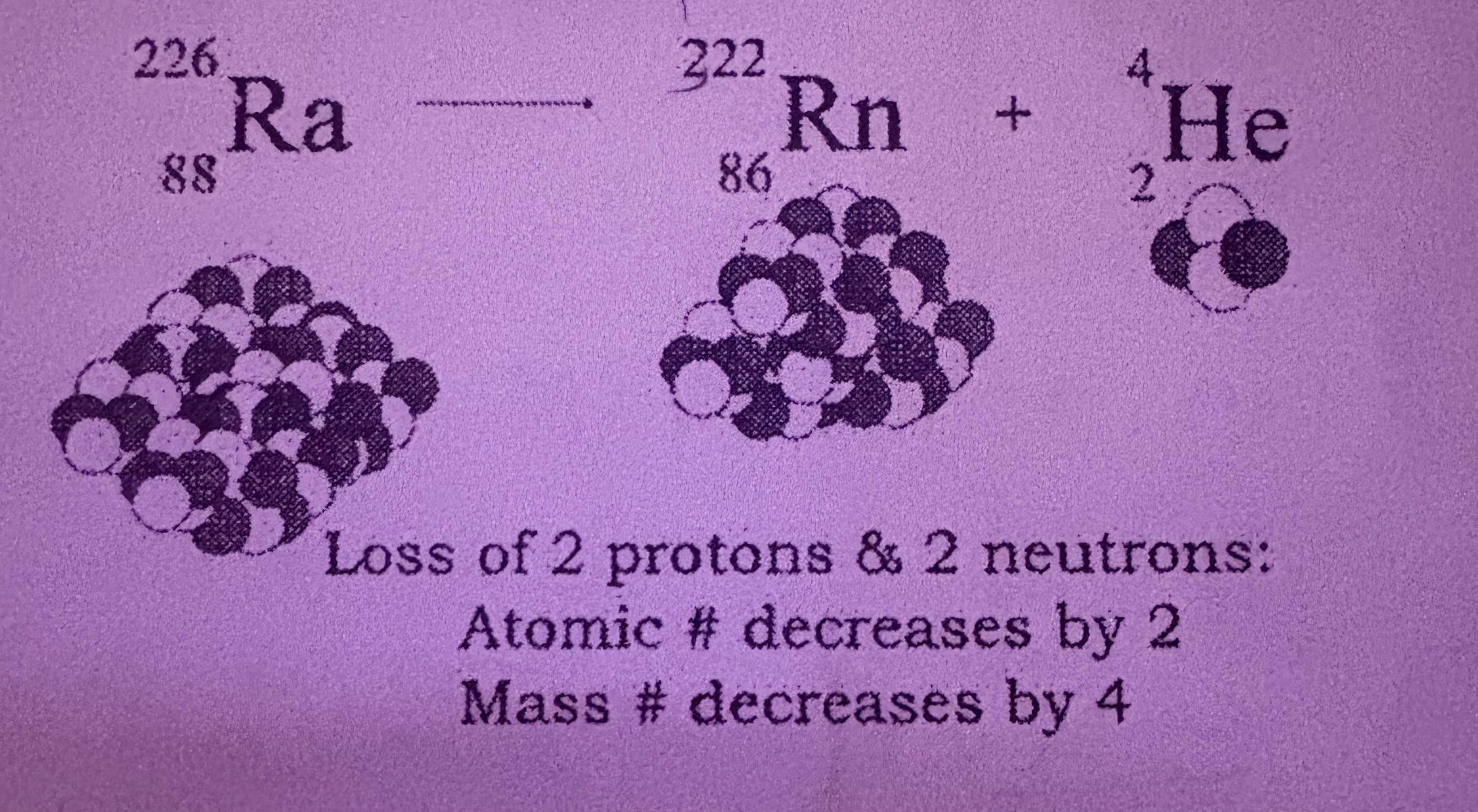
What is Alpha Decay?
Loss of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, atomic number decreases by 2 and mass number by 4, mass and atomic number are conserved, is Helium (4 2 He)
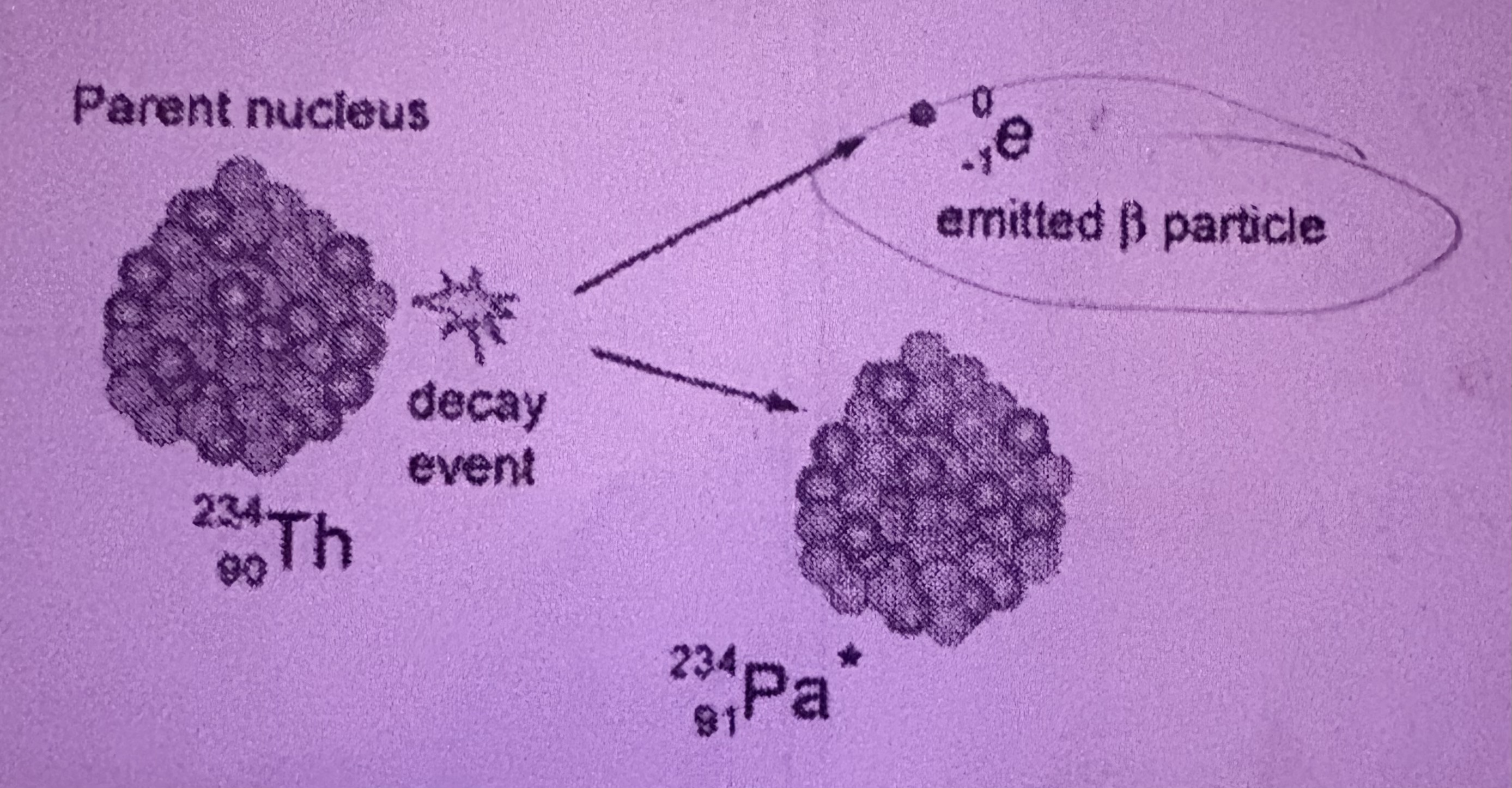
What is Beta Decay?
An electron, neutron is turned into a proton, atomic number increases by 1 and mass number stays the same, 0 -1 e
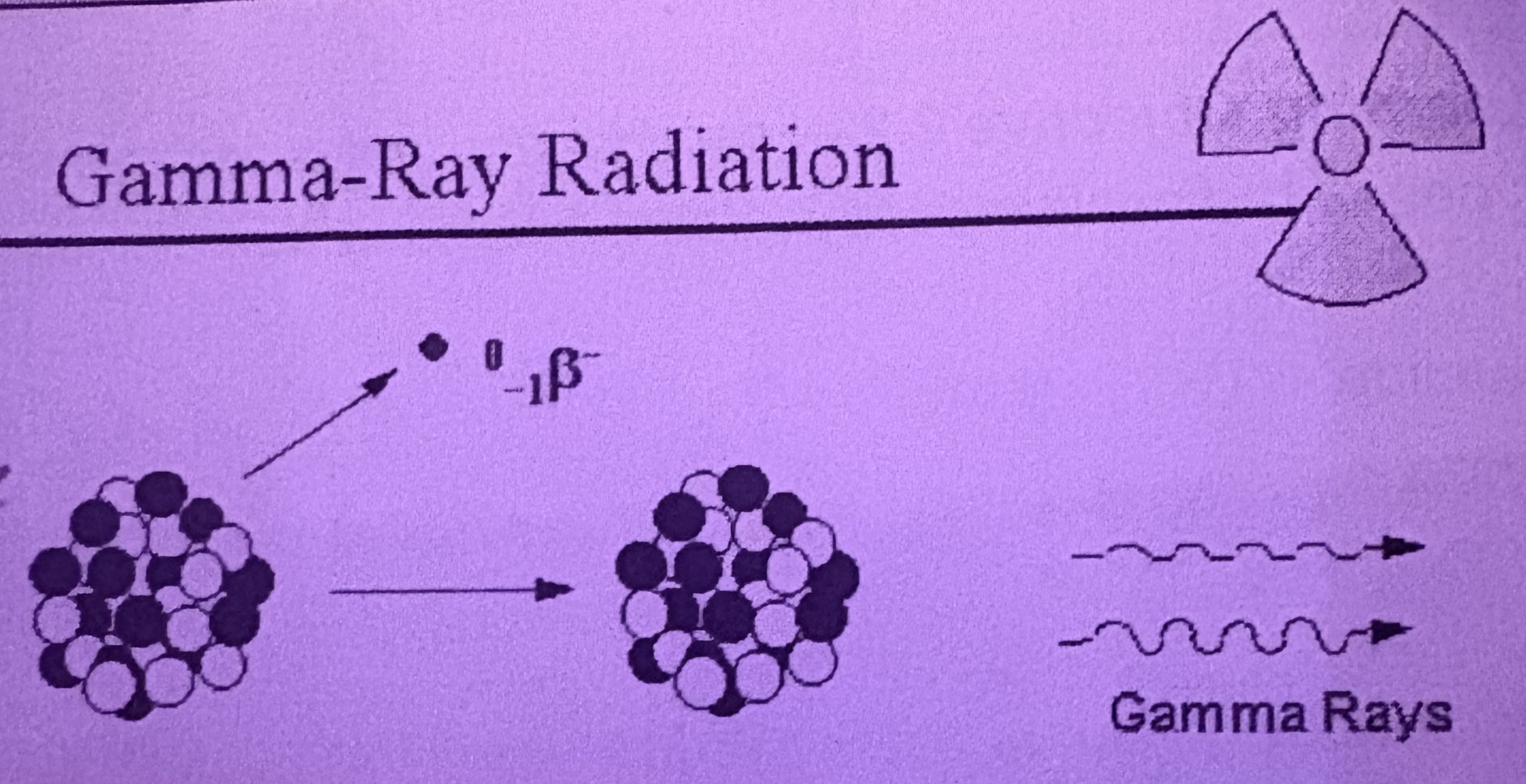
What is Gamma Decay?
Is a very high energy radiation released from the nucleus, is electromagnetic= not a particle an energy wave, doesn’t affect the element measurably
What are the properties of Alpha Decay?
Biggest (heaviest), slowest, least able to penetrate skin
What are the properties of Beta Decay?
Carries a negative charge, can penetrate the skin, can be blocked by wood and metals
What are the properties of Gamma Decay?
High energy waves (not a particle), can go through the skin and impact the body on a cellular level
How does Alpha Decay occur?
When an unstable atom’s nucleus releases 2 protons and 2 neutrons (alpha particle)
How does Beta Decay occur?
When a neutron changes into a proton releasing a beta particle (an electron)
How does Gamma Decay occur?
When the nucleus of an atom releases extra energy after alpha or beta decay
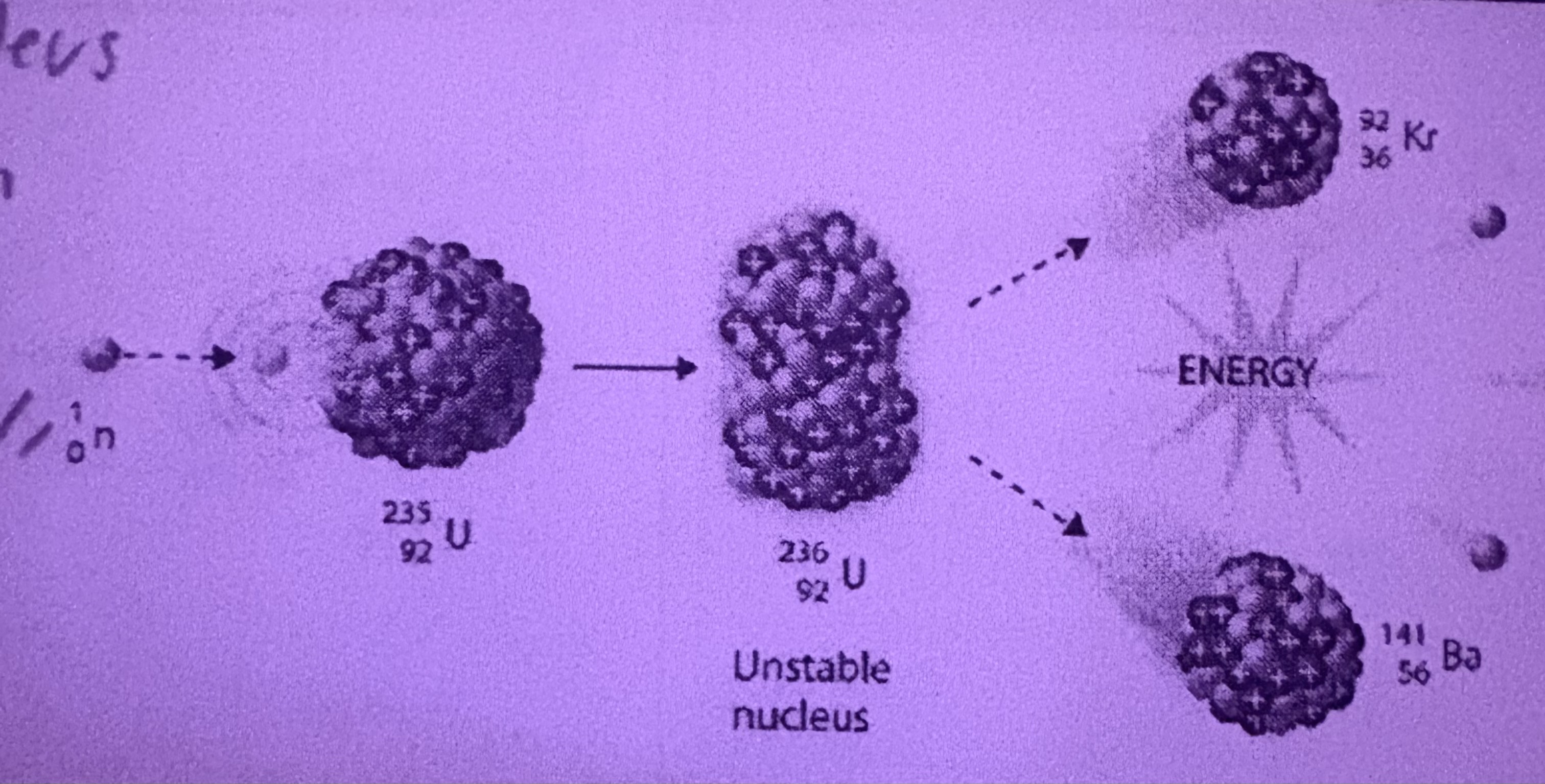
What is Fission?
The splitting of a large nucleus into smaller nuclei when hit by a neutron
What is Fission used for?
Nuclear Energy and Nuclear Weapons
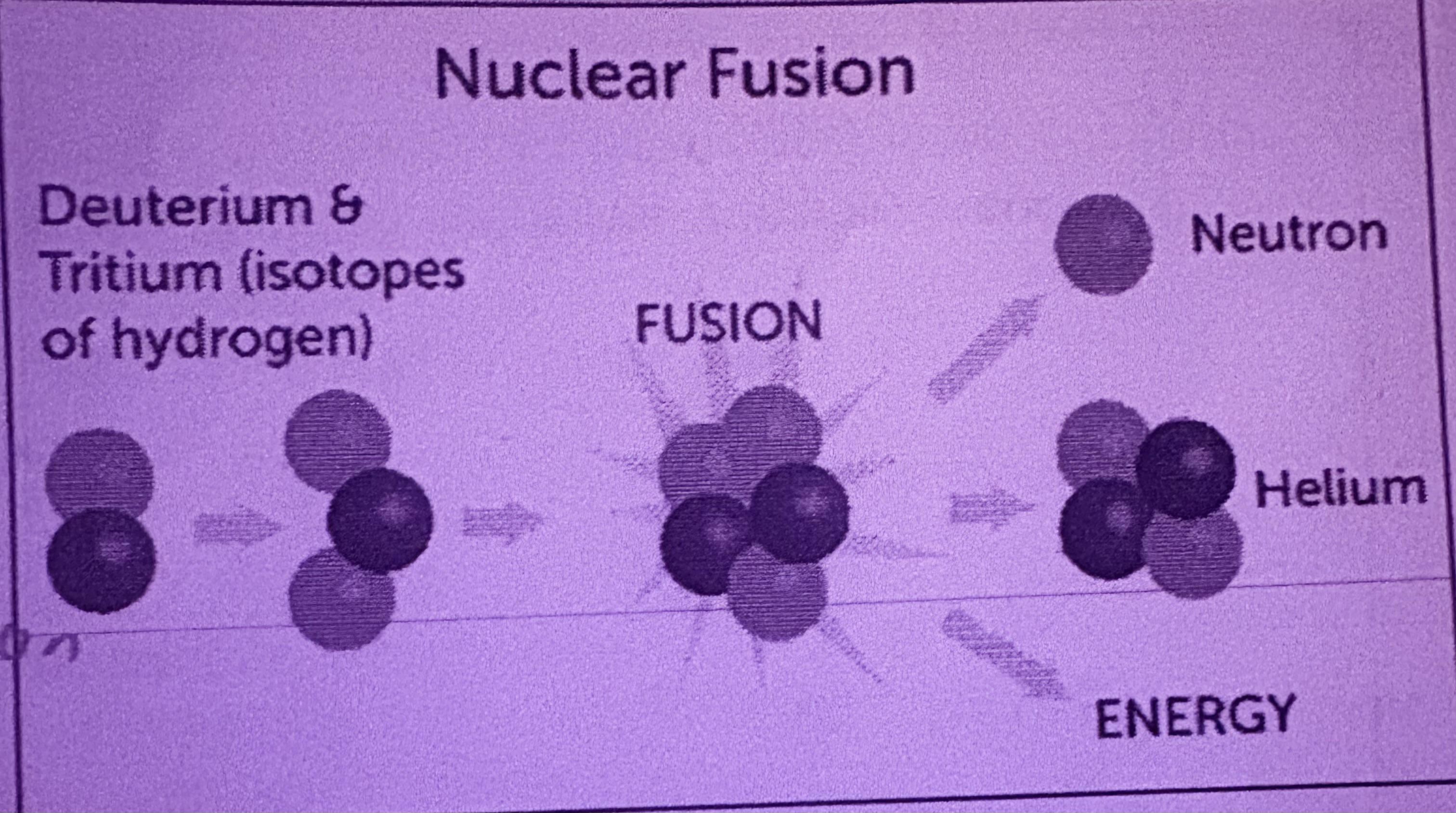
What is Fusion?
Separate elements combine to make a larger element, occurs on the sun, releases way more energy than Fission
Does fission occur naturally?
No, it must be started with rare isotopes, free neutrons, and the right conditions that never happen on their own
Does fusion occur naturally?
Yes, like with the sun and stars
What does fission produce?
Large amounts of energy and radioactive waste
What does fusion produce?
More energy and less waste than fission
What element is commonly used in fission?
Uranium-235
What elements are involved in fusion?
Hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium
Where does fusion occur?
In the sun and under extreme temperature and pressure
What do both fission and fusion involve?
The nucleus and release of lots of energy
How is fission used today?
Nuclear weapons
What are advantages of fission?
Produces a lot of energy from a small amount of fuel, doesn’t release air pollution like burning fossil fuels
What are the disadvantages of fission?
Creates radioactive that’s hard to get rid of, can cause dangerous accidents like meltdowns, used for nuclear bombs
How is fusion used in real life today?
It powers the sun and stars, but humans don’t yet use it for energy on Earth
What are the advantages of fusion?
Produces way more energy than fission, makes almost no radioactive waste, uses hydrogen, which is easy to find
What are the disadvantages of fusion?
Needs extremely high temperatures and pressure, we don’t have the technology to make it work safely and cheaply on Earth yet
What is Half-life (t 1/2)?
The time it takes for a substance to decay half its mass/ concentration
What is the half-life of flourine-17?
70 sec
What is the half-life of uranium-238?
4.5 billion years
What is the half-life of carbon-14?
5,730 years
What are radioactive isotopes?
A version of an element that has an unstable nucleus and naturally breaks down over time, releasing energy in the form of radiation
What are radioactive isotopes used for?
In medicine by being used to diagnose diseases with scans by injecting patients with it for that the PT scanner or Pet scan can better spot it, and treat conditions like cancer
What is the half-life formula?
A= Ao x (1/2) t/h
What does the half-life formula stand for?
Time (t), half-life (h), the initial amount of the radioisotope (Ao), the final amount of the radioisotope (A)
What is conserved during nuclear reactions?
Mass number and charge
What makes an Element stable?
It has the right number of neutrons for its protons, so it doesn’t break apart. Ex. Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons that’s balanced
What makes an element unstable?
It has too many or too few neutrons. Ex. Carbon-14 has 6 protons but 8 neutrons, so the extra neutrons makes it unstable, so it gives off radiation
What are observations?
A factual statement based upon what you can gather with your senses
What are inferences?
A conclusion based upon observations and prior experience
What are the different types of nuclear decay?
Alpha Decay, Beta Decay, Gamma Decay