Unit 1 - Introduction to Environmental Management
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What’s an LIC?
Gross Nat’l Income per capita < $1086
e.g.) Chad, Uganda, & Ethiopia
Africa has the most
What’s an HIC?
GNI per capita > $13,205
e.g) Canada, Sweden, U.S.A.
Biggest impact on global climate
What is sustainability?
the ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Must take into account environmental, social, and economic factors
Why are we living unsustainably?
population growth and a finite # of resources
What is interception?
precipitation is stopped from reaching the ground by the presence of trees and other plants
What is surface run-off?
precipitation that runs over the ground into streams/rivers
What is through flow?
infiltrated water flows through the soil
What is groundwater flow?
infiltrated water flows through rocks
What are the main components of Earth’s atmosphere?
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide
Argon
Water vapor
What is the troposphere?
Where we live
Temp. decreases w/height; wind speeds increase w/height
Where global warming occurs
Tropopause = top layer
What is the stratosphere?
Contains the ozone layer
Temp. increases w/height
Stratopause = top layer
What is the ozone?
Absorbs harmful UV radiation
10-50km above the surface
Protects from skin cancer, a weakened immune system, & damage to vision/cataracts
What is the mesosphere?
no dust, ozone, or water vapor
Coldest layer → temp. decreases with height
Mesopause = top layer
What is the thermosphere?
Temp. rises rapidly with height → absorbs UV rays
Thermopause = top layer
Outline the greenhouse effect:
UV radiation passes through the Earth’s atmosphere and is absorbed the Earth’s surface
Some energy is re-emitted back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation
GHGs absorb some of this infrared radiation, preventing it from leaving the atmosphere
What is a biome?
a form of ecosystems that are smaller than the biosphere; a geographical region w/specific climate, vegetation, and animal life
What is an ecosystem?
all living things (biotic) together with all non-living things (abiotic) in an area
What are some biotic factors?
producers, consumers, and decomposers
What are some abiotic factors?
temperature, humidity, water, oxygen, light, pH
What is a population?
a group of individuals belonging to the same species living in a defined area
What is a community?
a group of populations of different species that live together in an area and interact with each other
What is a habitat?
the place within an ecosystem where an organism lives
What is a niche?
the role of a species/organism within the ecosystem
What is competition?
when both organisms require the same resource
Intraspecific: 2 members of the same species
Interspecific: 2 different species
What is grazing?
when species move from one victim to another w/o fully killing its victim
What is predation?
one organism consumes another in a dominant relationship
What is photosynthesis?
the process by which plants synthesise glucose using carbon dioxide, water, and energy from the sun
What’s the chemical formula for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
What are limiting factors of photosynthesis?
availability of water, concentration of carbon dioxide & the availability of light
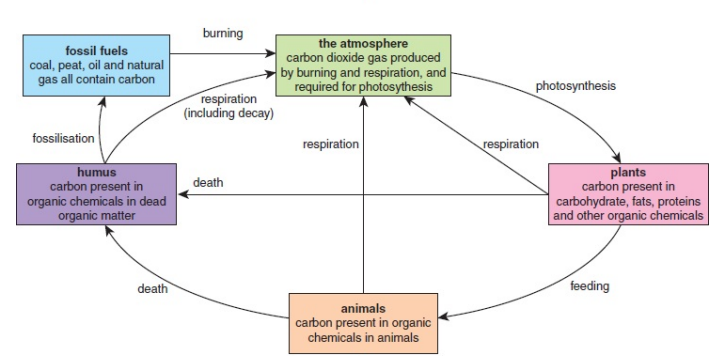
How does photosynthesis contribute to the carbon cycle?
Carbon reservoir in the atmosphere → fixation by photosynthesis → in living things
Forms carbon stores
What are producers?
organisms within an ecosystem that can carry out photosynthesis
What are primary consumers?
organisms within an ecosystem that derive their food from producers
What are secondary consumers?
organisms within an ecosystem that derive their food from primary consumers
What are tertiary consumers?
organisms within an ecosystem that derive their food from secondary consumers
What are decomposers?
organisms within an ecosystem that derive their food from the bodies of dead organisms
What are trophic levels?
feeding levels within food chains
Energy is ___ in a food chain
transferred between organisms
starts with a producer
How is energy lost in food chains?
as respiration and waste products
What is aerobic respiration?
the chemical reactions in cells that break down glucose molecules and release energy, carbon dioxide and water
What is the chemical formula for aerobic respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
The carbon cycle: