Kepler's Laws Diagram | Quizlet
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
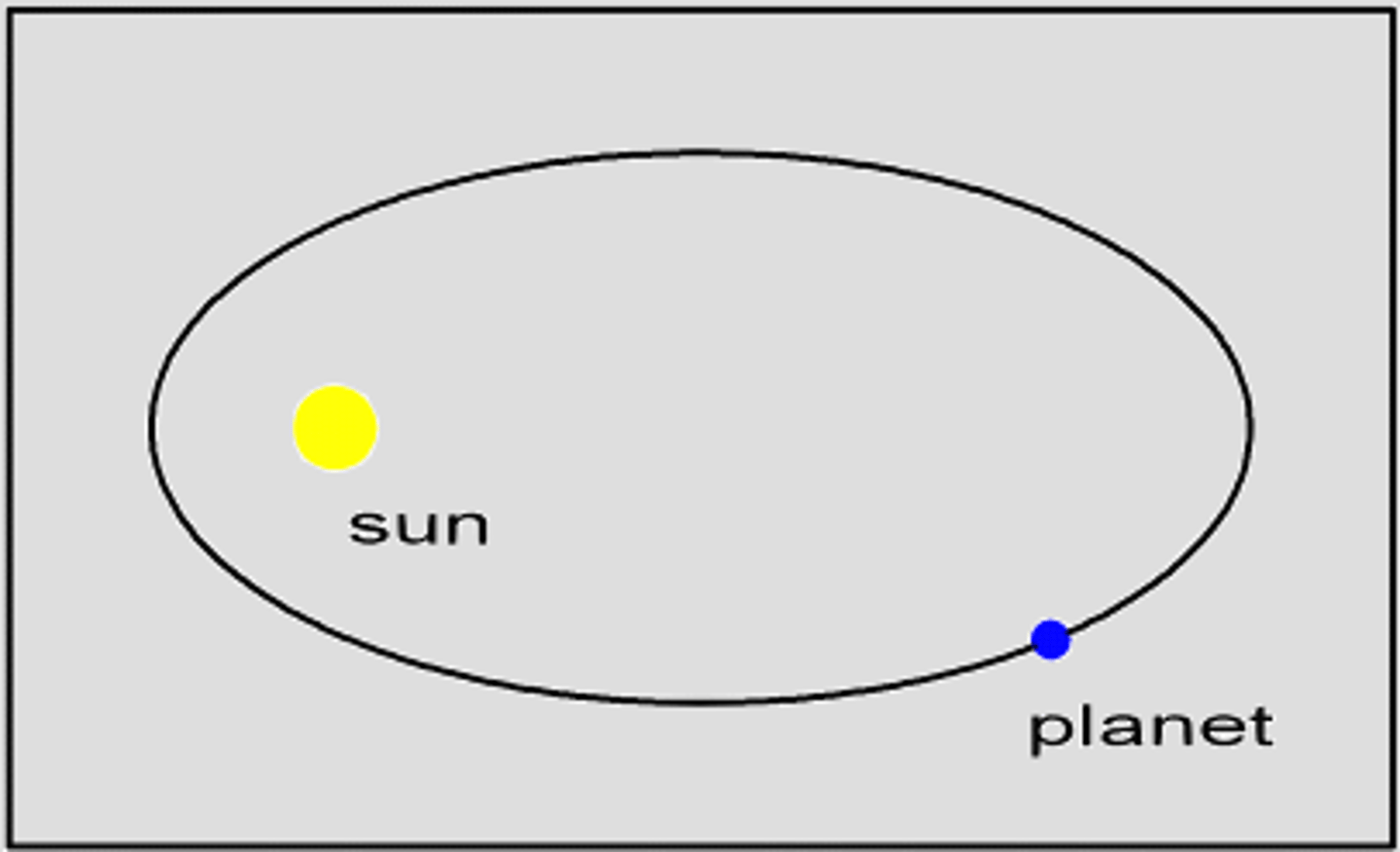
Kepler's First Law
The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci.
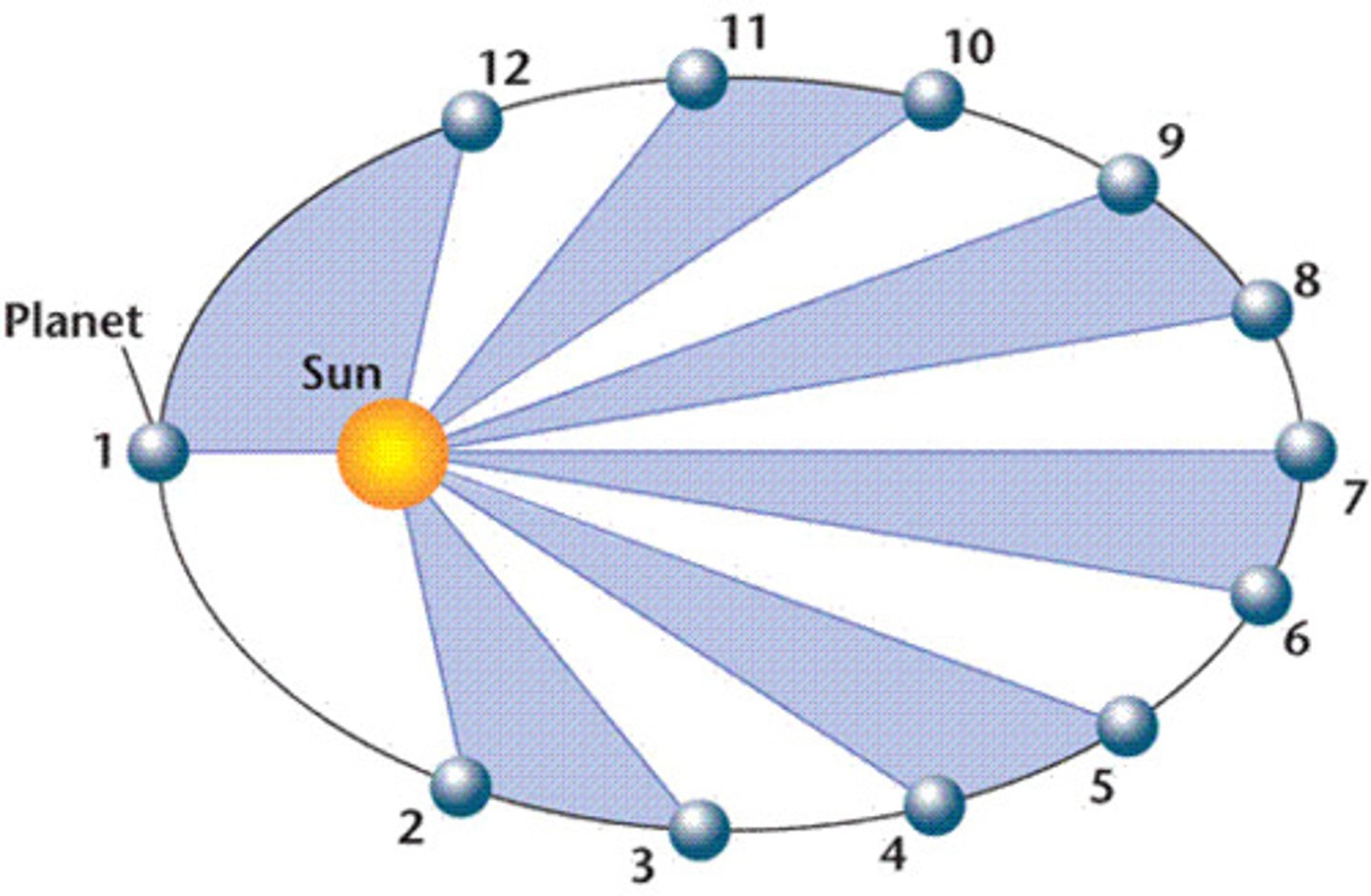
Kepler's Second Law
A line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time.
Kepler's Third Law
The square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit. (a squared = p cubed)
Aphelion
farthest distance away from the foci of a body rotating around the foci. Earth to sun = ~152 million km.
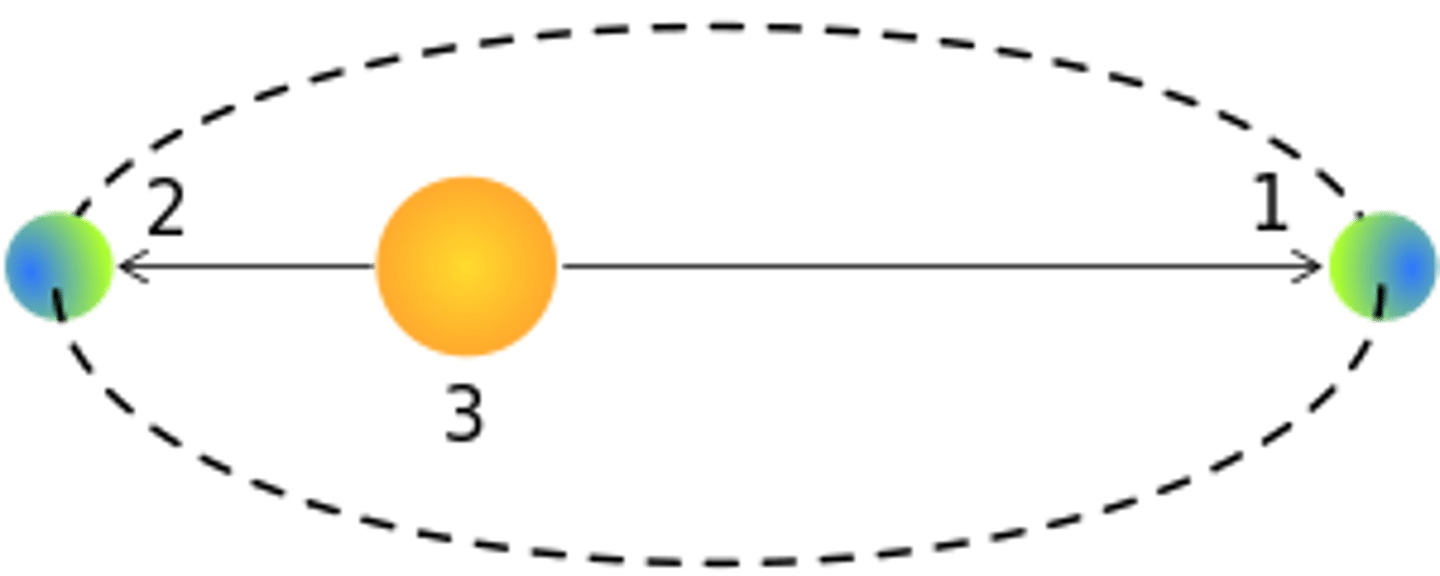
Perihelion
closest distance away from the foci of a body rotating around the foci. Earth to sun = ~147 million km.
Astronomical Unit (AU)
the distance from the earth to the sun. ~150 million km
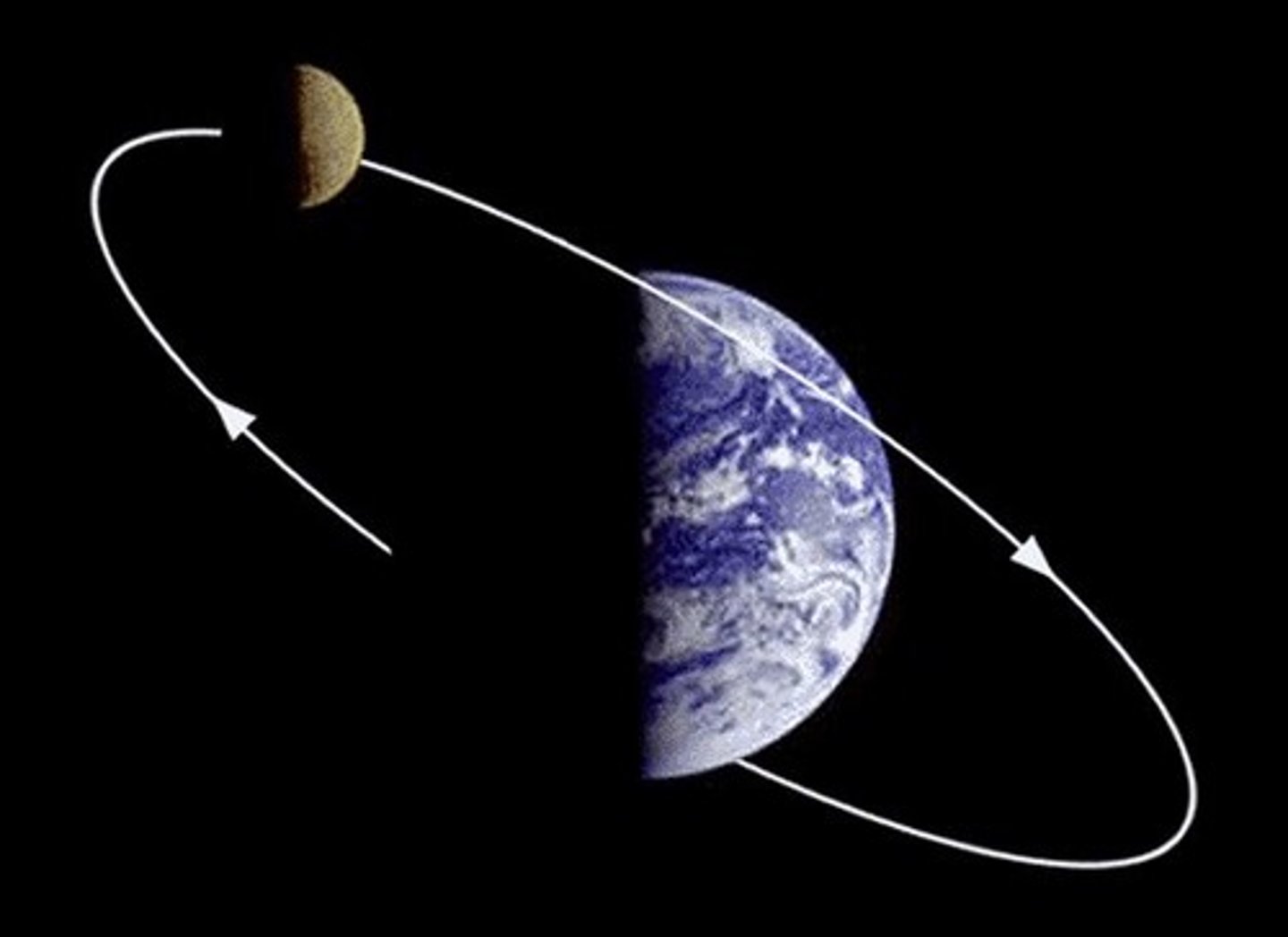
Orbit
The curved path of a celestial object about a point in space
Period
The time that it takes a complete cycle
Major Axis
Longest Line (top to bottom in vertical, left to right in horizontal, in this example V1 to V2)
Minor Axis
Shortest Line (left to right in vertical, top to bottom in horizontal, in this example P1 to P2)
Semi Major Axis
Half of the Major Axis (C to one of the Vs)
Semi Minor Axis
Half of the Minor Axis (C to one of the Ps)
Vertex
Both end points of the Major Axis (V1, V2)
TERM
Co vertex
DEFINITION
Both endpoints of the Minor Axis (P1, P2)
Focus
Points near the vertex (F1, F2)
eccentricity of an ellipse
the ratio of the distance between the foci to the major axis (the ration of F1 to F2 and V1 to V2)
TERM
Foci
DEFINITION
two points inside the ellipse that characterize its shape and curvature
TERM
vertices
DEFINITION
endpoints of the major axis
TERM
center
DEFINITION
the intersection of the major and minor axes