5.parasitology- arthropods
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
evolved
arthropods are the most ________ parasite
all macroscopic
are arthropods microscopic or macroscopic or both?
jointed
arthropods have _____ limbs
exoskeleton
what is the hard shell that covers the external part of the arthropod called?
chitin, protein, calcium salts
what is the exoskeleton of the arthropod make up of?
respiratory, nervous, circulatory, excretory, digestive, reproductive
what body systems do arthropods have?
we can physically distinguish the 2 sexes
what does it mean that arthropods are dioecious?
it is divided into segments
arthropods have a metameric body. what does this mean?
yes, it is called a coelem
do arthropods have an internal body cavity?
yes
are arthropods bilaterally symmetric?
dioecious
because we can distinguish the different sexes, we say that arthropods are ________

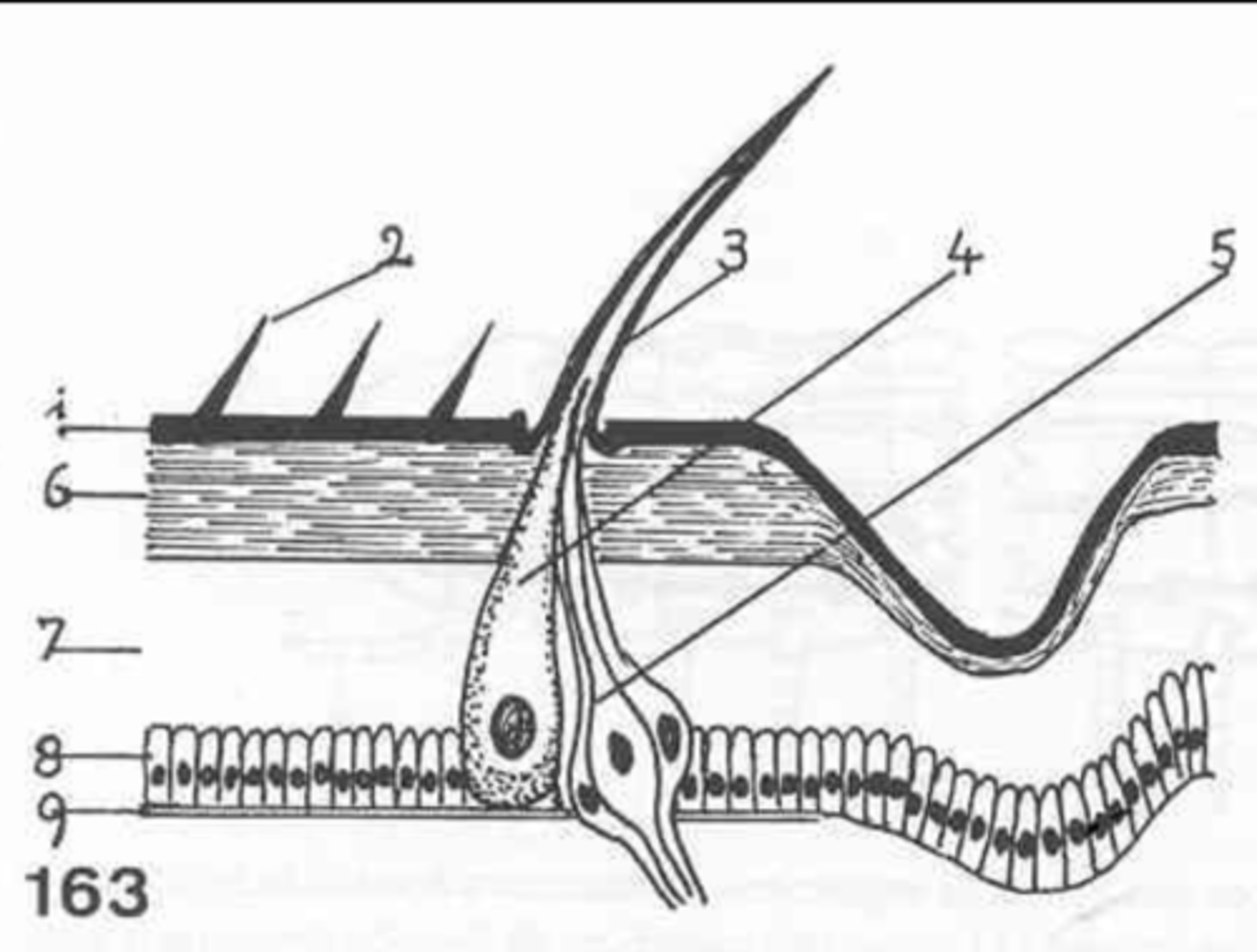
epicuticle
exocuticle
endocuticle
what are the 3 layers of the cuticle?
NO CELLS
what type of cells are in the cuticle?
hypodermis
what is the first layer of cells under the cuticle called?
epicuticle
what at layer 1 called?
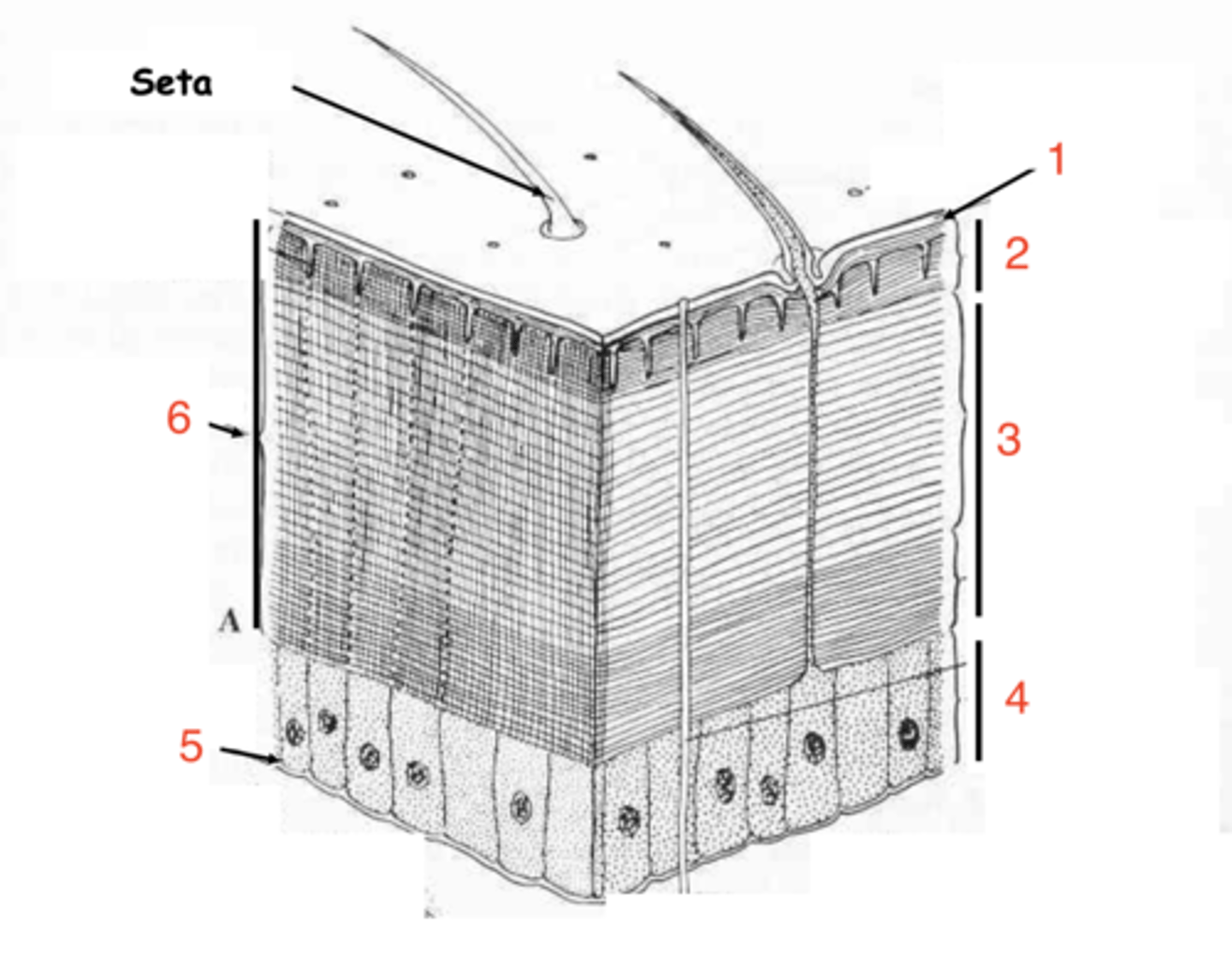
exocuticle
what is layer 2?
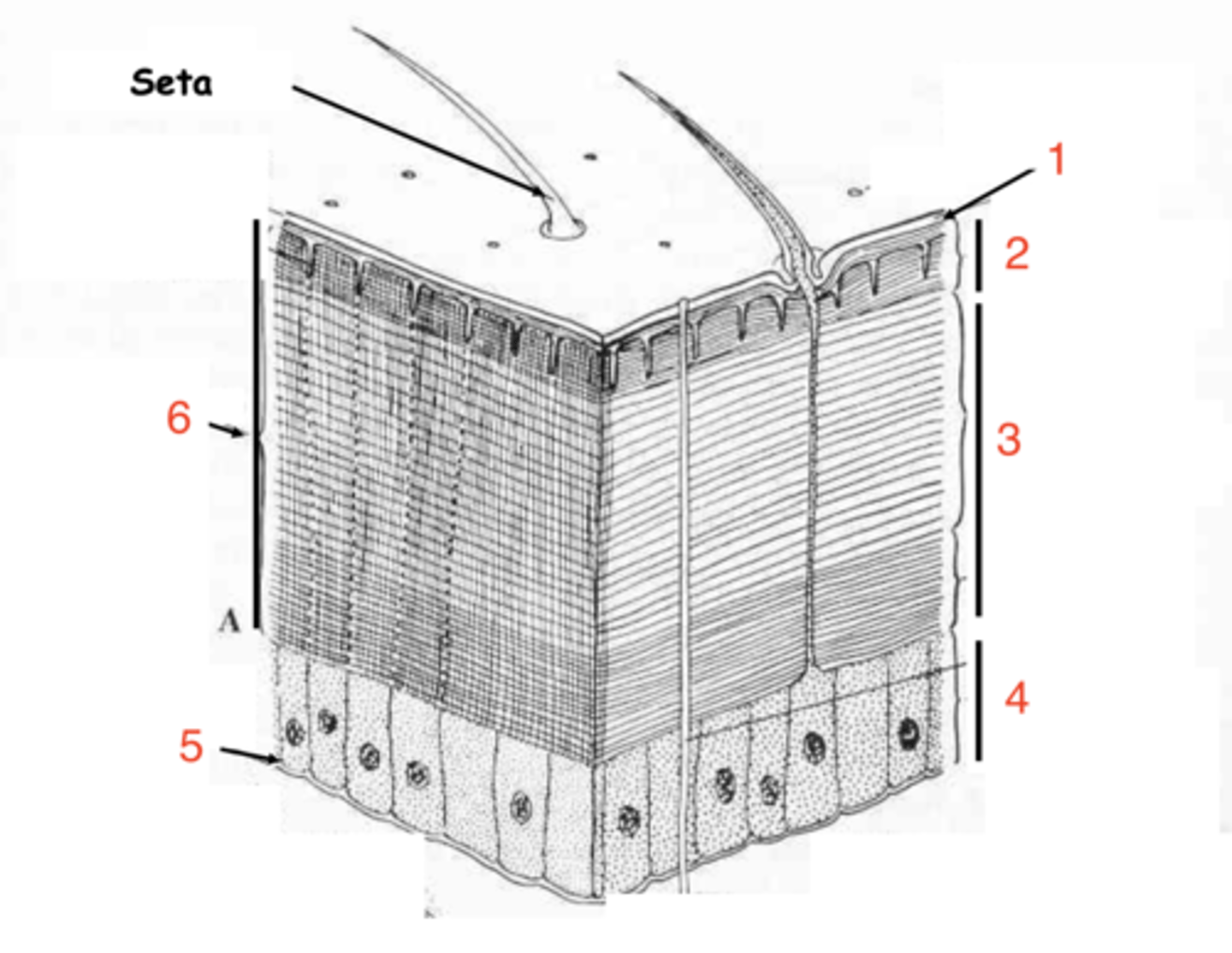
layer 3
where is the endocuticle?
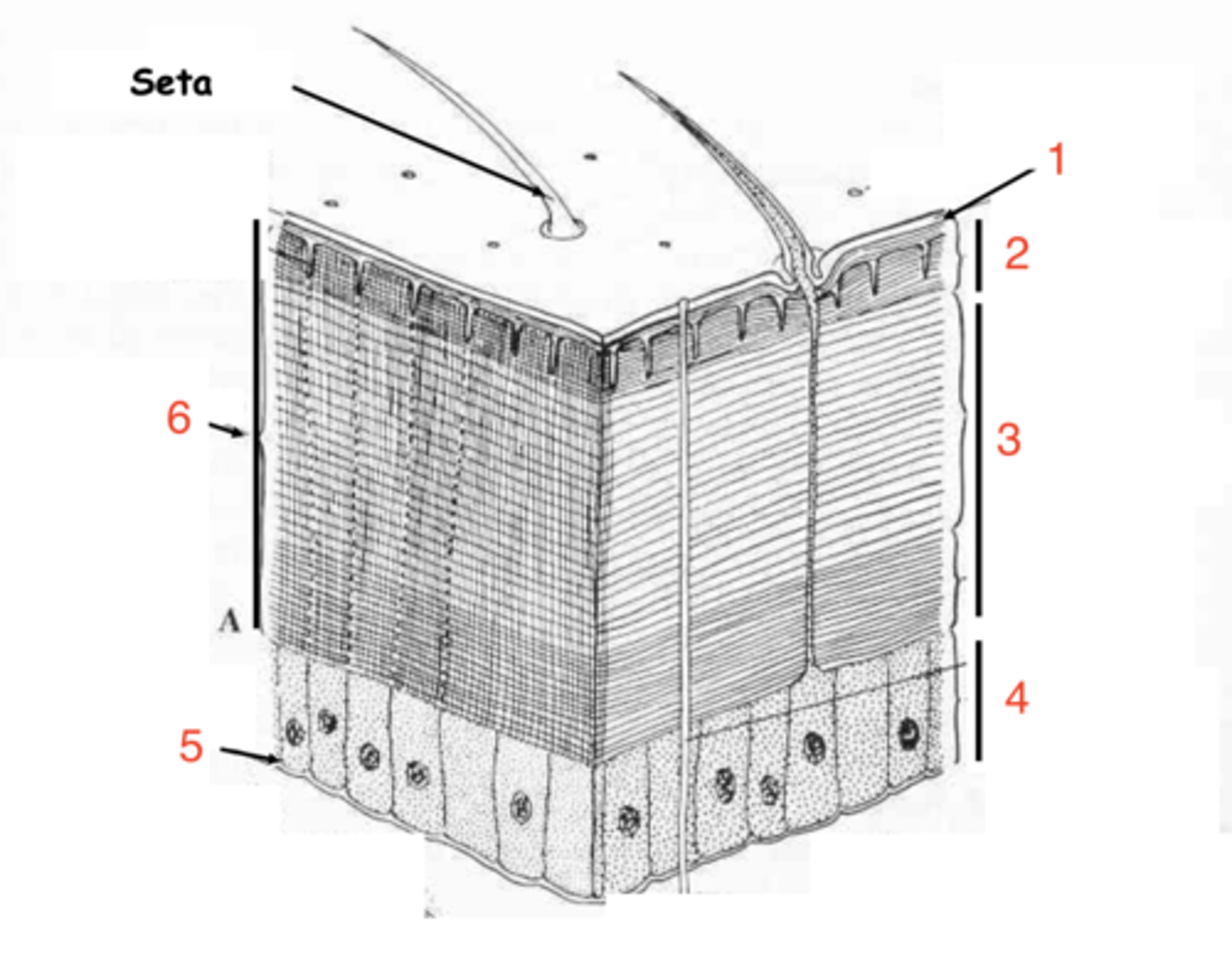
layer 4
where is the hypodermis?
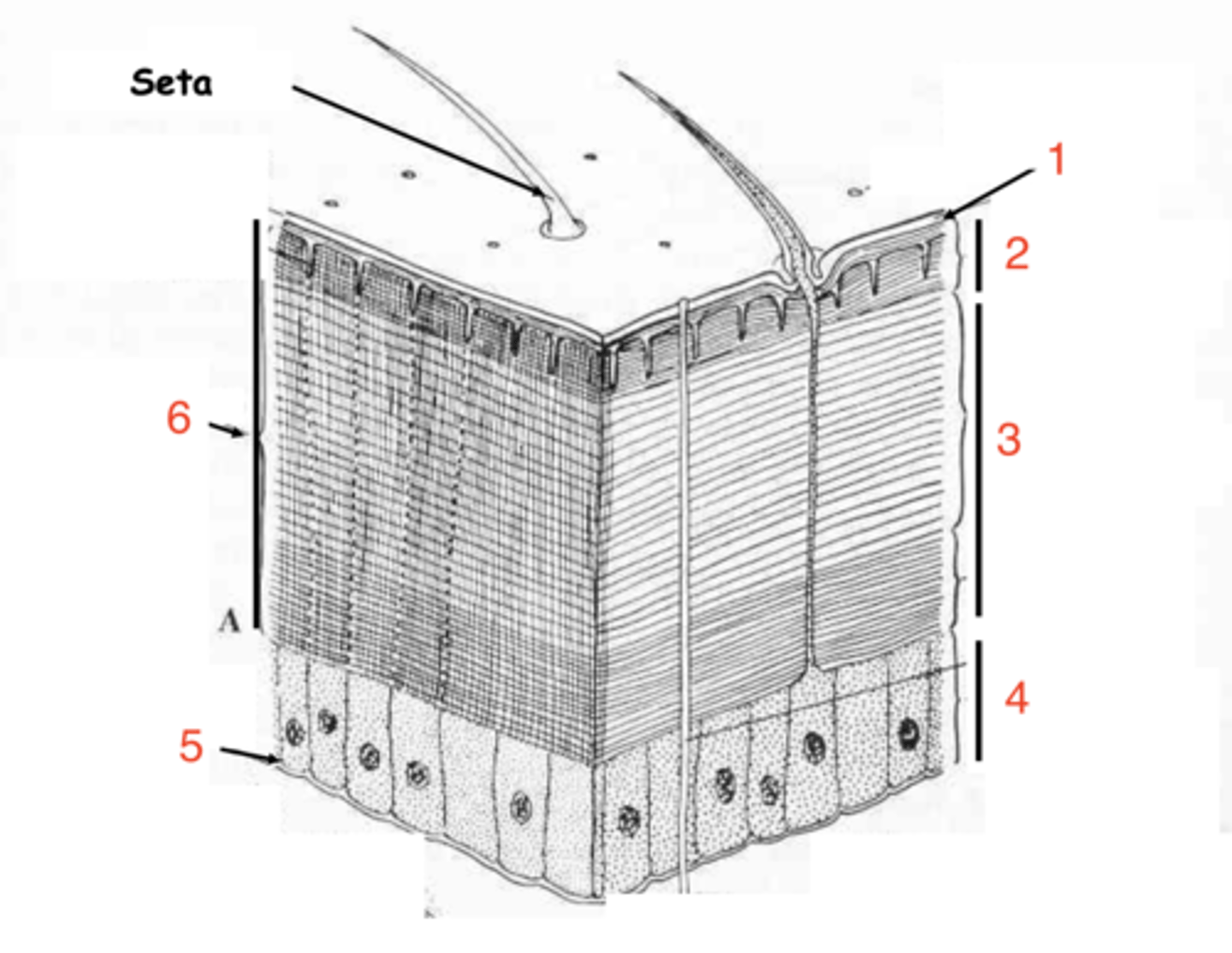
basal membrane
what is 5?
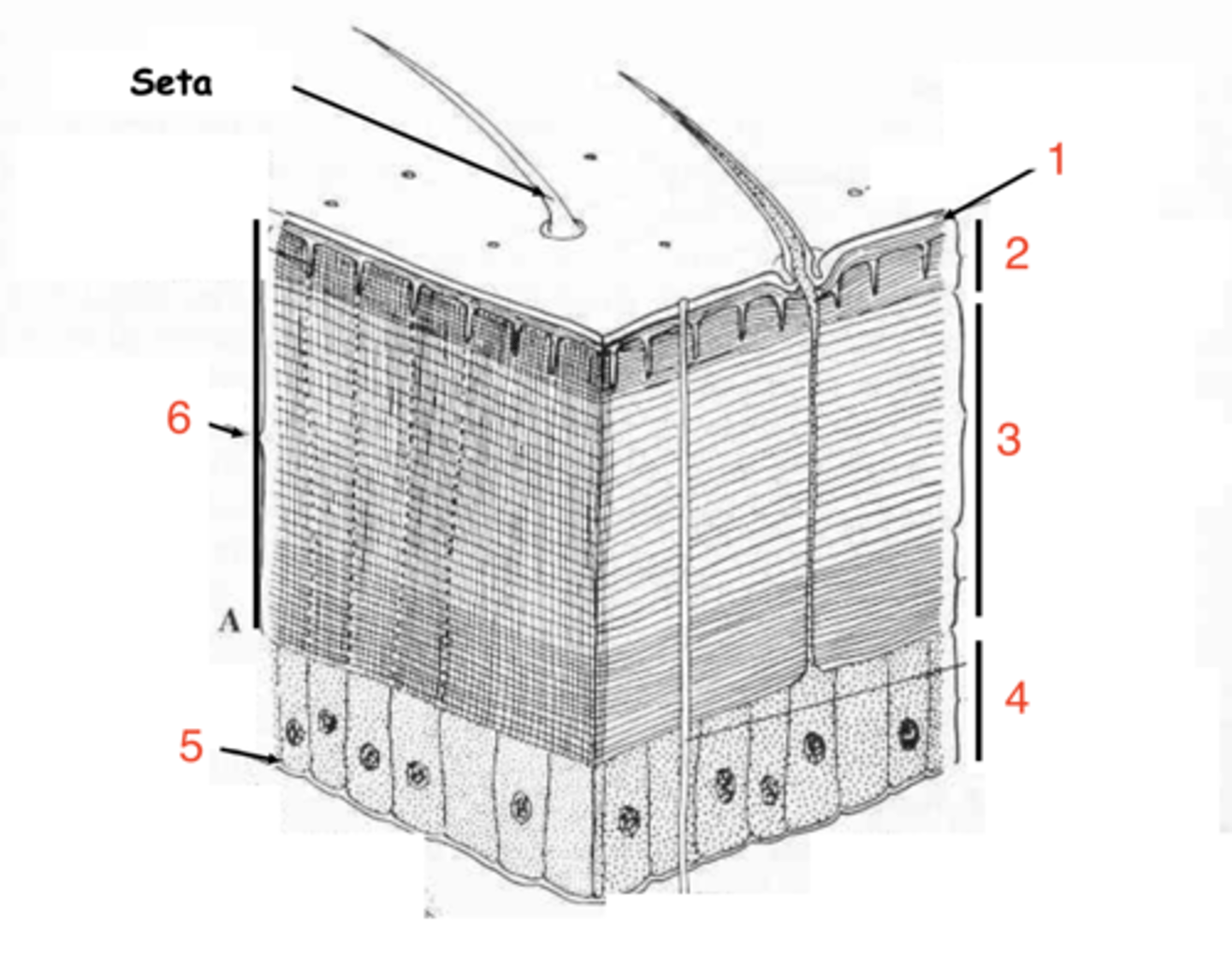
protection
muscle insertion
gives rigitidy/shape
what are the 3 functions of the cuticle (exoskeleton)?
weather, dehydration, trauma
what does the cuticle protect the arthropod from?
cuticle/exoskeleton
what part of the arthropod gives it shape?
cuticle/exoskeleton
what part of the arthropod is for protection?
cuticle/exoskeleton
what part of the arthropod is indigestible by predators?
the plates of the exoskeleton, joined by joints- allowing movement
what are sclerites?
into the exoskeleton/cuticle
where do they muscles of an arthropoda insert?
sclerites
what are the plates of the exoskeleton called?
microtriguia and setae
what are the 2 important sensorial structures that arthropods have?
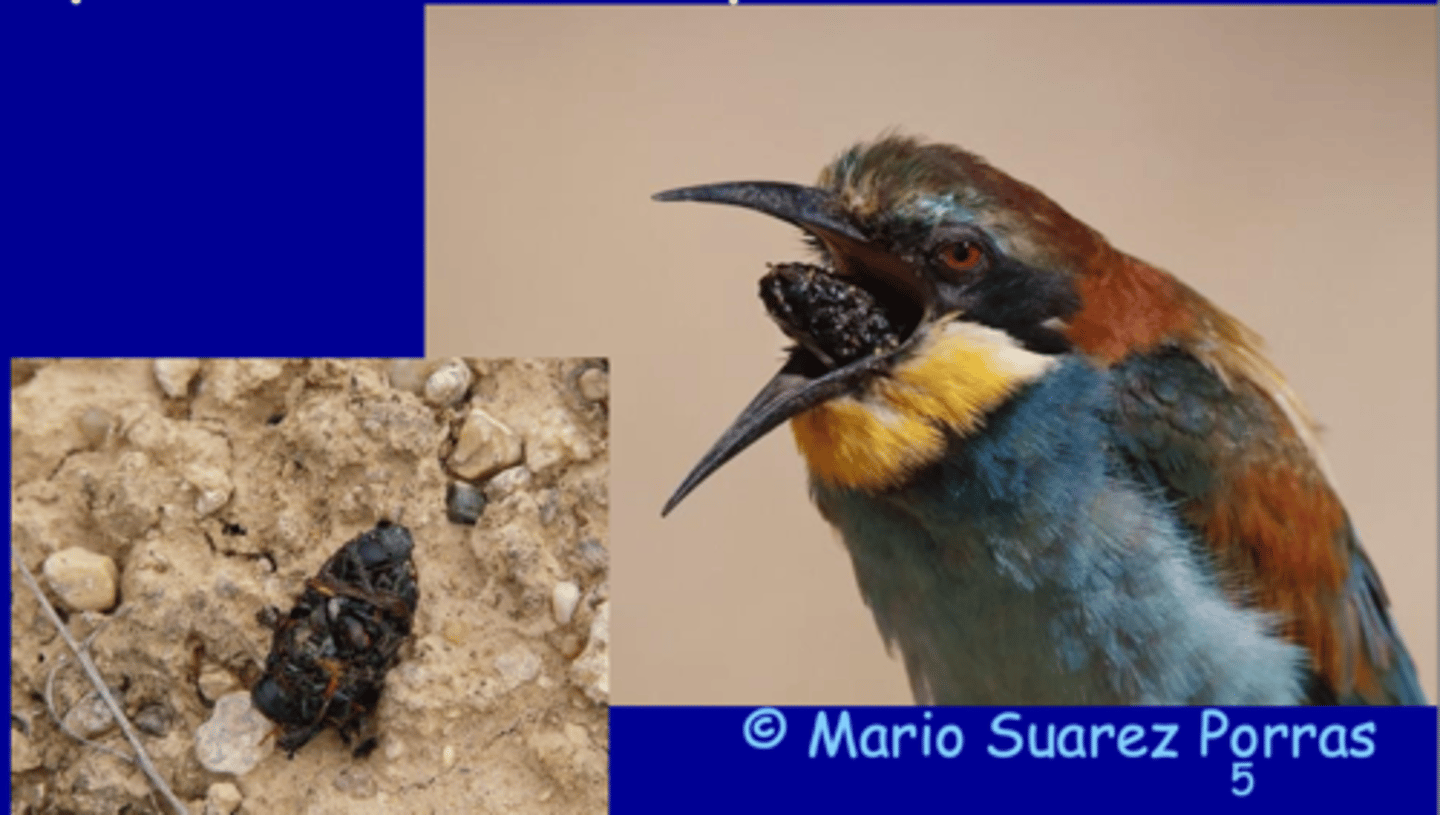
because their cuticle/exoskeleton is indigestible
why does a bird cough up this pellet when eating an arthropod?

fine hairs on the surface of the exoskeleton
what are microtriguia?
microtriguia
what are the fine hairs on the surface of the exoskeleton called?
long hairs, connected to neurons
what are setae?
setae
are setae or microtriguia connected to neurons?
microtriguia, setae
_____ are the short hairs on the exoskeleton, while _____ are the long hairs
microtriguia
what is 2?
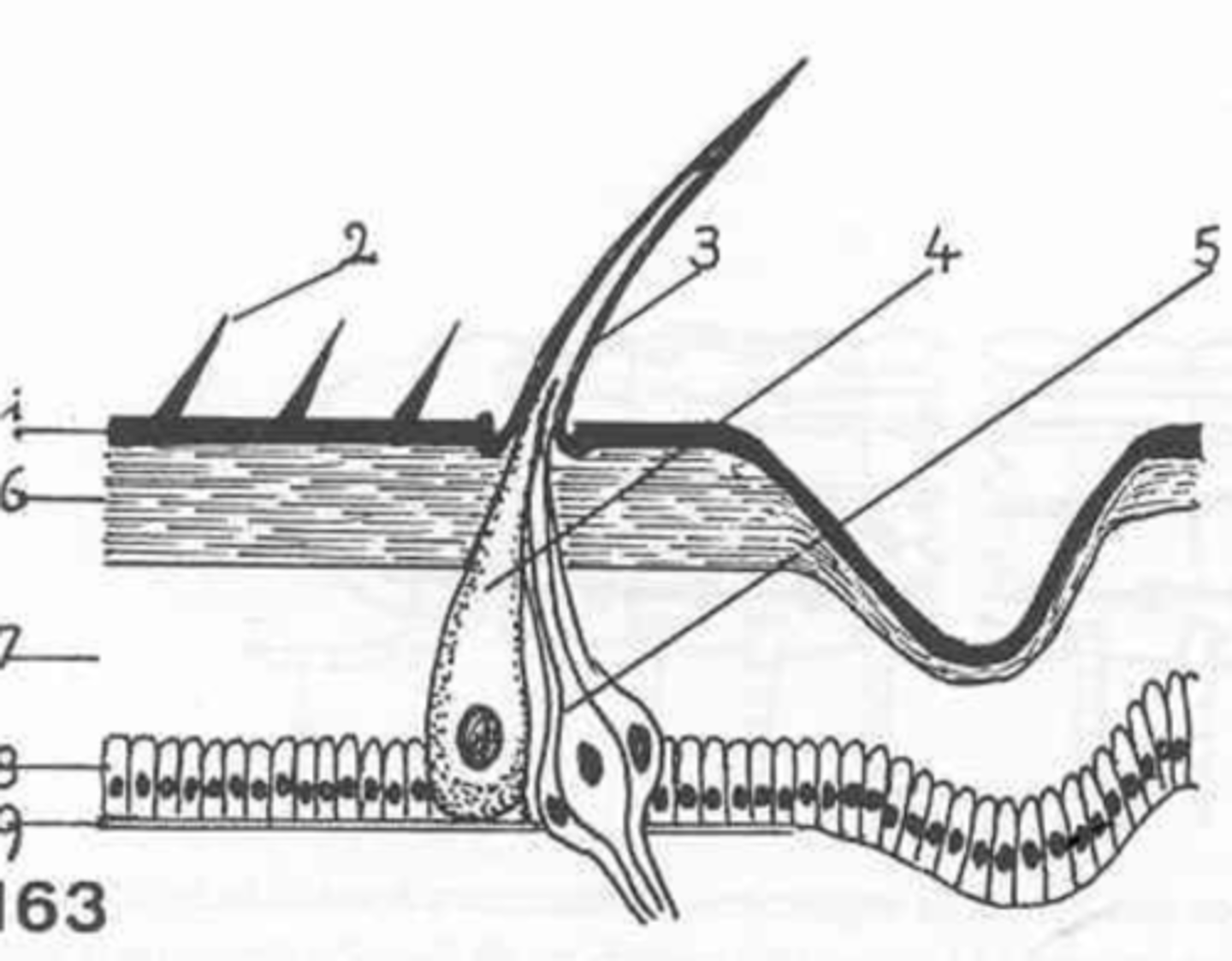
setae
what is this?
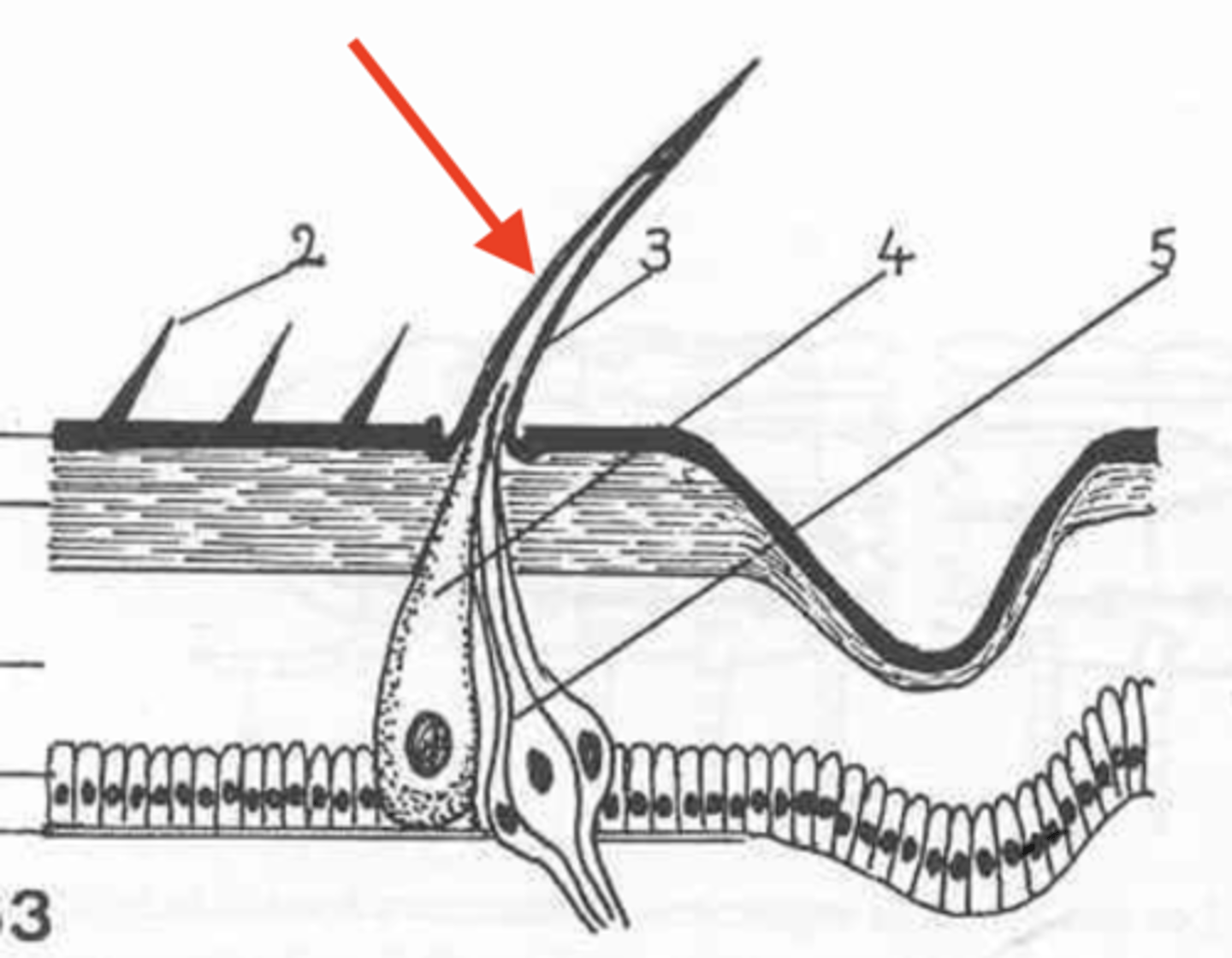
no
are microtriguia connected to neurons?
1
which is the epicuticle?
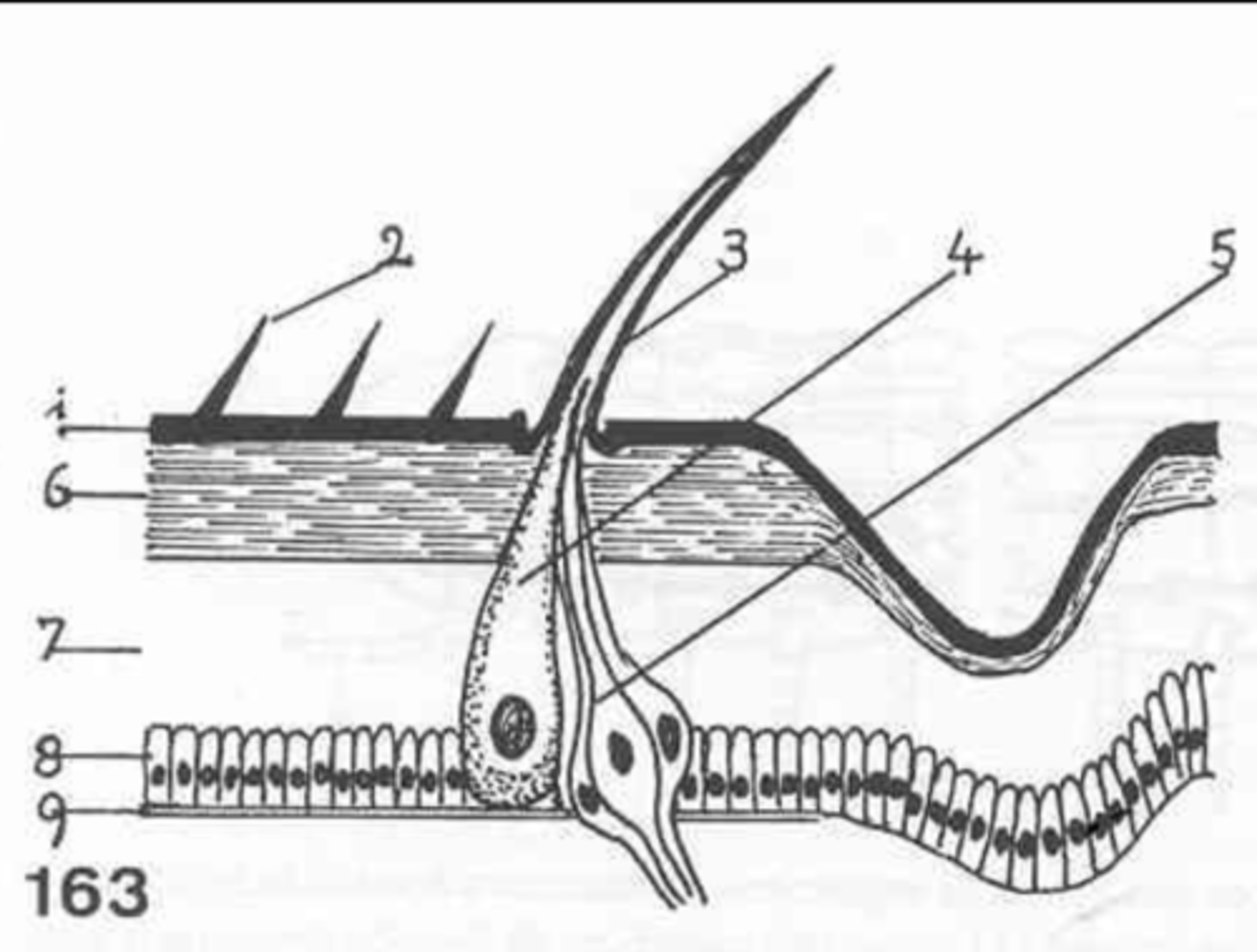
neurons attached to the setae
what is 5?
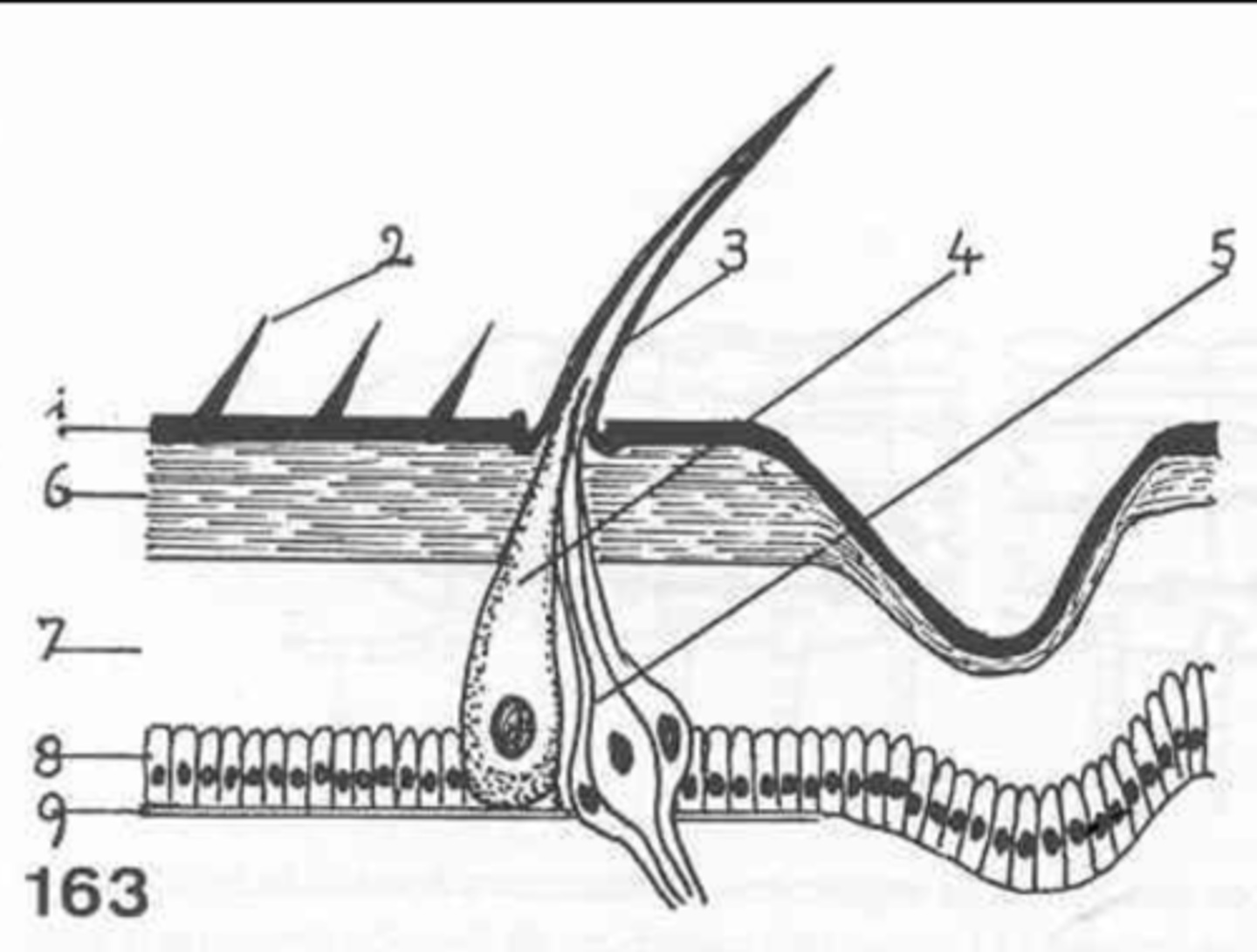
6
where is the exocuticle?
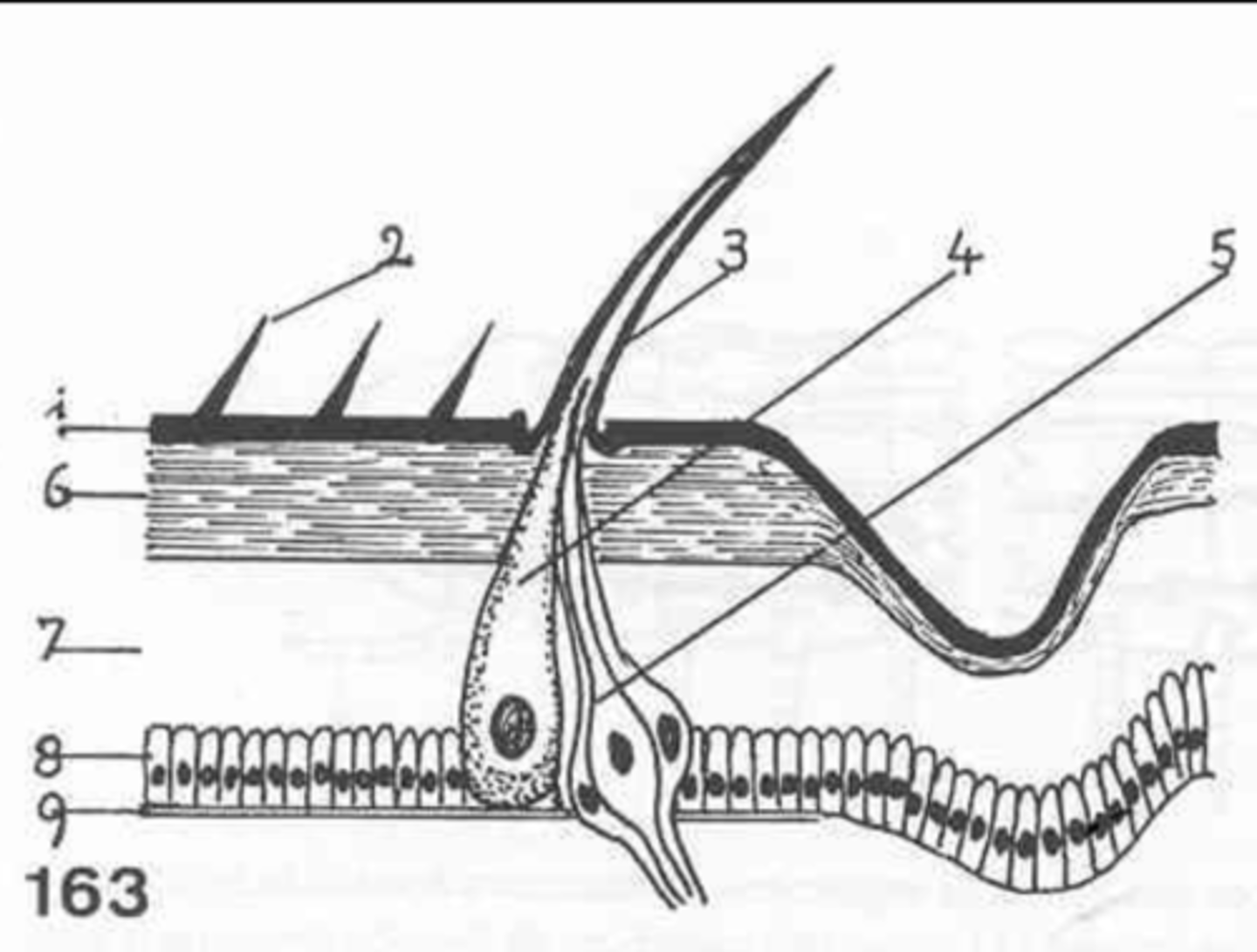
endocuticle
what is layer 7?
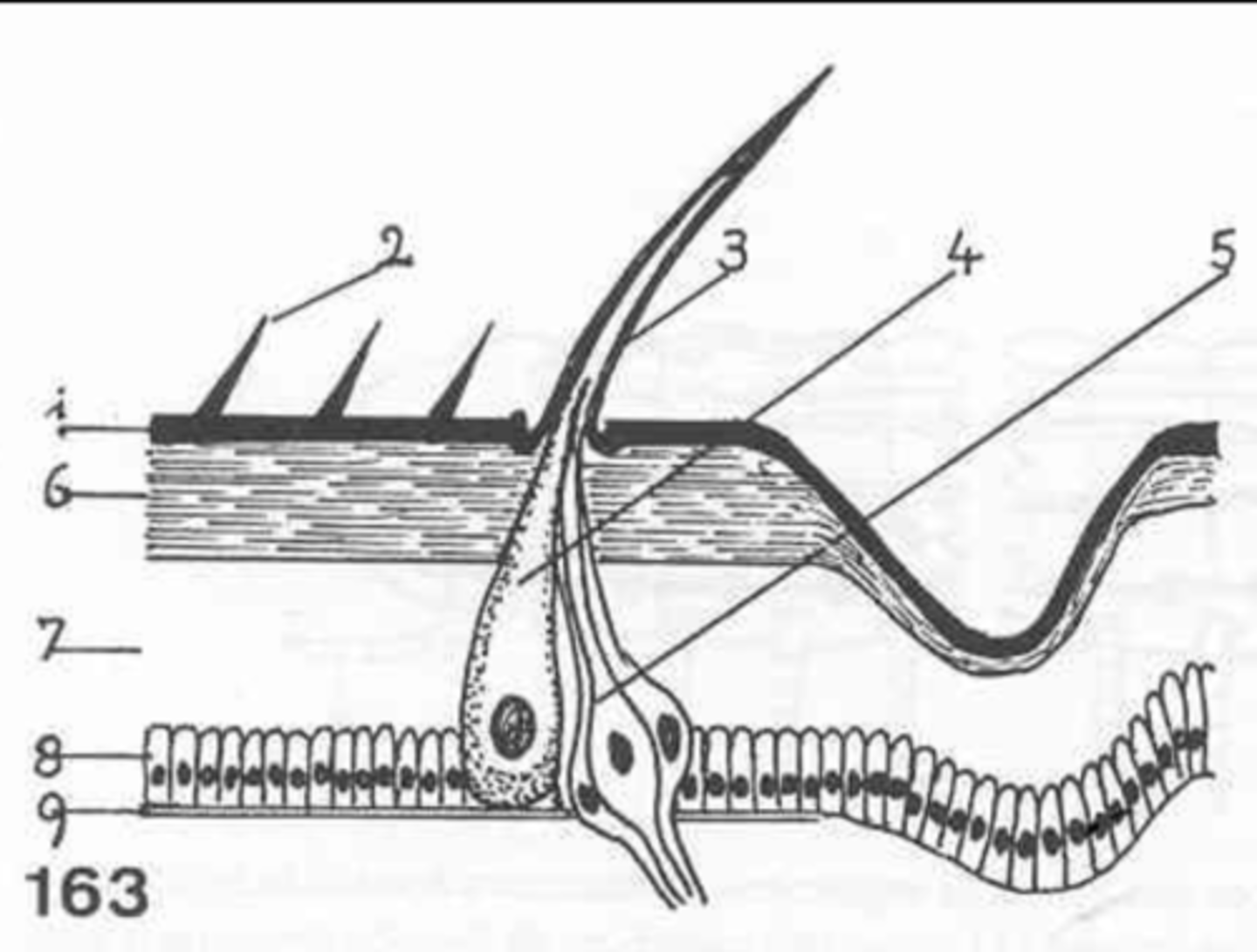
hypodermis
the cells at 8 make up the _________
the change of exoskeleton for growth or evolution between stages
what is moult?
hormones
the moulting process is controlled by ______
the arthropod goes through a complete metamorphosis- egg, larva, pupa, adult
what does holometabolous mean?
the arthopod has an incomplete metamorphosis and skips usually the larval stage: egg, nymph, adult
what does hemimetabolous mean?
holo-
an arthopod that goes through these cycles: egg, larva, pupa, adult- is called ______metabolous
hemi-
an arthopod that goes through these cycles: egg, nymph, adult- is called ______metabolous
moult
what is this process of changing the exoskeleton called?

head, thorax, abdomen
what are the 3 sections of the arthropod's body called?
head
which- head, thorax, abdomen- is sensorial?
thorax
which- head, thorax, abdomen- is locomotive?
abdomen
which- head, thorax, abdomen- is for reproduction and organs?
sometimes
do arthropods have eyes?
sometimes eyes
antennae/chelicerae
mouthparts
what parts are included in the head?
prothorax
mesothorax
metathorax
what are the 3 divisions of the thorax of an arthropod?
gills
what special feature do aquatic arthropods have?
no- only aquatic arthropods
do all arthropods have gills?
no- only terrestrial arthropods
do all arthropods have a trachea?
yes
do all arthropods have mouthparts?
no- gas exchange made by several trachea
do arthropods have lungs?
moults
_____ are necessary to grow and evolve to the next stage
antennae/chelicerae
what is 2+3?
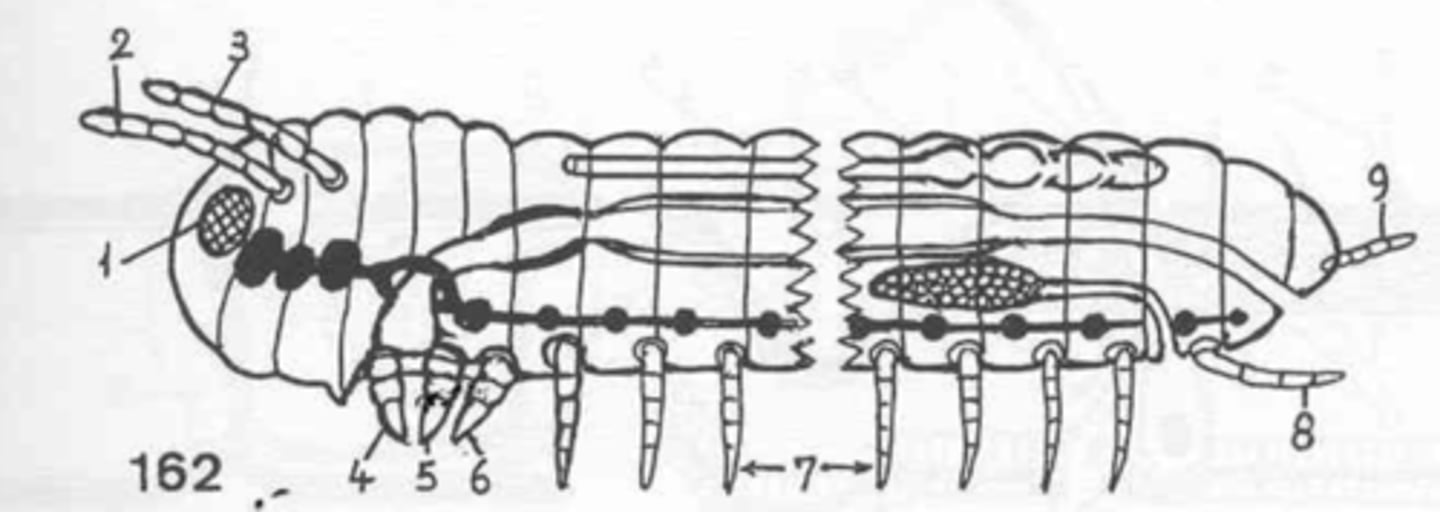
mouthparts
what is 4+5+6?
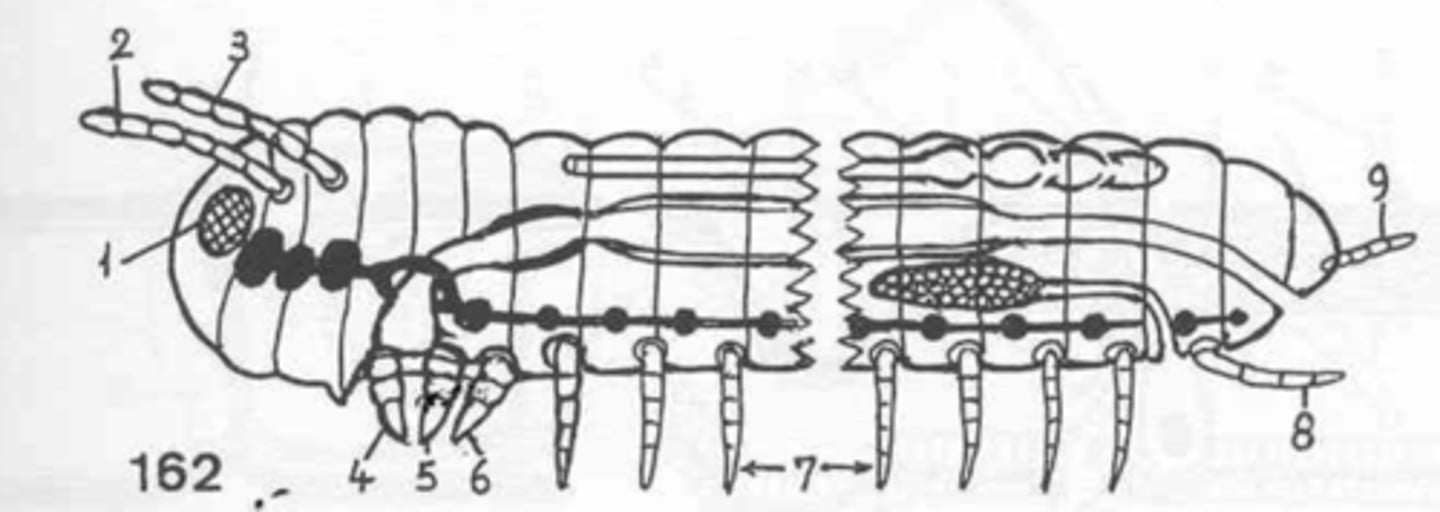
male copulatory organ/female ovipositor
what is 8?
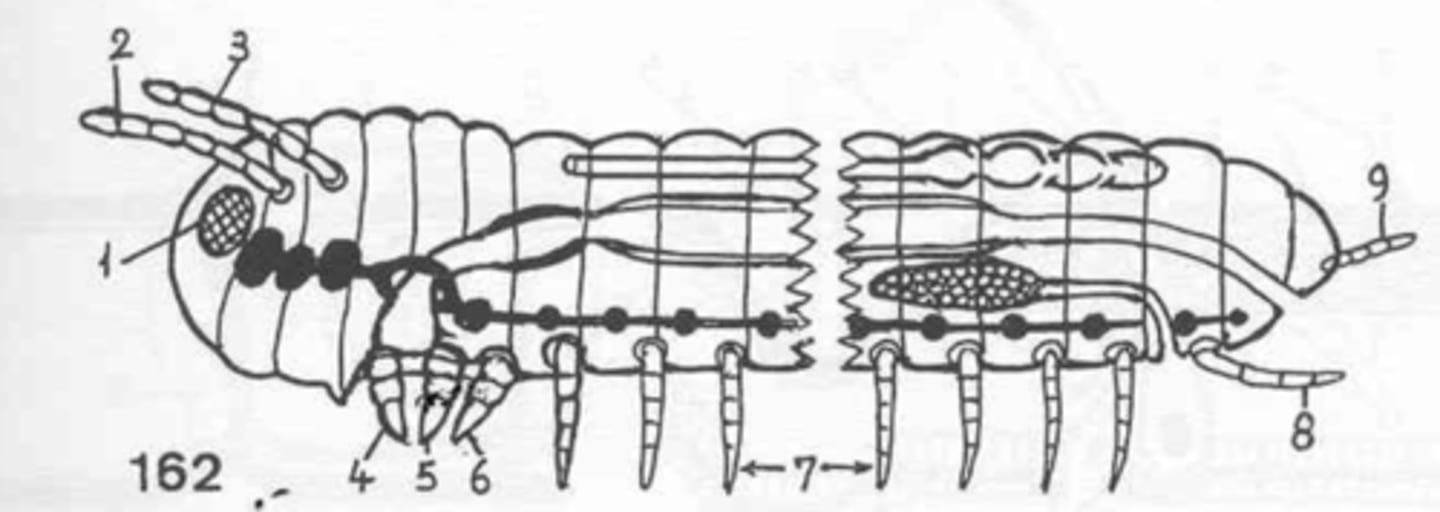
they are individual rather than fused
what is unique about the coxa of an arthopod?
a patella
what do arthropods have between the femur and tibia?
the way that arthropods can breathe through their own skin
what is tegument respiration?
yes
do all arthropods have an anus?
1.buccal capsule
2. mouth
3. pharynx
4. crop
5. esophagus
6. stomach
7. anus
name the parts of the arthropod digestive system