Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Honors Unit 1 Part 1
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study terms for Unit 1 Basic Terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is the definition of the term Anatomy?
Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism
What is the definition of the term Physiology?
Physiology is the study of how that organism’s body functions
What is developmental anatomy?
Changes in the human body during growth from child to adult
What is Embryology?
Study of anatomy during first 8 weeks after conception.
What is Surface Anatomy?
Using touch on the outside of the body
What is Regional Anatomy?
Specialized focus on one portion of the body
What is Gross Anatomy?
A general overview of large portions of the body at one time
What is Microscopic anatomy?
Specialized focus on cells and tissues only seen with a microscope
What is Systematic anatomy?
Studying one body system at a time
Add on question: What is the difference between Regional Anatomy, Gross anatomy, and Systemic anatomy?
Gross Anatomy → Study of structures visible to the naked eye (umbrella term).
Regional Anatomy → Study of all structures in one body region (e.g., head, neck).
Systemic Anatomy → Study of the body by systems (e.g., skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular).
(Answer from chatGPT)
Add on question: How do anatomy and physiology differ?
Anatomy is the structure, Physiology is how the whole organism functions (Personal answer)
What are the levels of organization in the human body?
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ System/System → Organism
Define the term, Cell
Smallest unit of all living things
Define the term, Tissue
Similar cells with a common function or goal
Define the term, Organ
Made of 2 or more types of tissue types
Define the term, Organ System/System
Group of organs working toward a common goal
Define the term, Organism
Highest level of structural organization for an individual
What are the 11 body systems?
Skeletal System, Nervous System, Circulatory System, Respiratory System, Digestive System, Muscular System, Integumentary System, Lymphatic System, Excretory System, Endocrine System, Reproductive System
What is the function and major organs associated with the Skeletal System?
Function: Provides support and protection, gives body shape
Major Organs: Bones, Ligaments, Cartilage, Joints
What is the function and major organs associated with the Nervous System?
Function: Detects impulses from the senses, often referred to as the control center
Major Organs: Brain, Spinal cord, Senses, Nerves
What is the function and major organs associated with the Circulatory System?
Function: Transports nutrients and gases around the body
Major Organs: Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood
What is the function and major organs associated with the Respiratory System?
Function: Exchanges gases with environment (Oxygen and CO2)
Major Organs: Lungs, Sinuses, Diaphragm
What is the function and major organs associated with the Digestive System?
Function: Breaks down and absorbs food
Major Organs: Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Intestines, Liver, Gallbladder
What is the function and major organs associated with the Muscular System?
Function: Provides movement for all parts of the body
Major Organs: Skeletal and Smooth muscles
What is the function and major organs associated with the Integumentary System?
Function: Protect the body, regulate temperature, and prevent water loss
Major Organs: Skin, Hair, Nails
What is the function and major organs associated with the Lymphatic System?
Function: Fights infection and provides fluid for cells
Major Organ: Spleen, Thymus gland, Lymphatic vessels, Lymph nodes
What is the function and major organs associated with the Excretory/Urinary system?
Function: Removes waste from the blood
Major Organs: Kidneys, Bladder, Ureters, Urethra
What is the function and major organs associated with the Endocrine System?
Function: Secretes hormones
Major Organs: Glands (Hypothalamus, pineal, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries or testes)
What is the function and major organs associated with the Reproductive System?
Function: Produces cells used in sexual reproduction
Female Major Organs: Ovaries, Vagina, Uterus, Mammary glands
Male Major Organs: Testes, Penis, Prostate gland
What functions are necessary for life?
Maintaining Boundaries, Movement, Responsiveness, Digestion
Define the term, Maintaining Boundaries
Acts as a filter letting some substances in and keeps others out (Example: Skin absorbs and keeps in water, this prevents entry of unwanted pathogens)
Define the term, Movement
Ability to change position or state in the environment, this includes movements internally (Example: Digestive contractions)
Define the term, Responsiveness
Sensing and reacting to changes in the environment (Example: Pain felt when finger is cut with a knife)
Define the term, Digestion
Breaking down and absorbing nutrients (Example: Chewing in the mouth and the churning of food in the stomach)
What are the basic 5 survival needs?
Nutrients, Oxygen, Normal Body Temperature, Water, Normal atmospheric pressure
How do the life functions aid in survival?
Nutrients, Digestion and metabolism allows us the properly absorb food
Oxygen, Heart and lungs exchange gases with the environment
Normal Body Temperature, Skin/Blood/Muscles help us maintain our temperature
Water, Allows molecules to move through the body
Normal atmospheric pressure, Provides appropriate gas exchanges between lungs and environment
What is the anatomical position?
Anatomical terminology helps anatomists discuss parts of the body easily and efficiently. In the position, Body is straight with feet slight apart and thumbs pointed away from the body.
What are key directional terms?
Directional terms help anatomists compare the location of one body structure to another
What is the difference between the terms Lateral and Medial?
Lateral, Outward of the body
Medial, Near the center of the body
What is the difference between the terms Proximal and Distal?
Proximal, Near the reference point or center
Distal, Further away from the reference point or center
What is the difference between the terms Superior(Cranial) and Inferior(Caudal)?
Superior(Cranial), The highest point (The top of the head)
Inferior(Caudal), The lowest point (The soles of your feet)
What is the difference between the terms Anterior(Ventral) and Posterior(Dorsal)?
Anterior(Ventral), Near the front or on the front of
Posterior(Dorsal), Near the back or on the back of
What is the difference between the terms Deep and Superficial?
Deep, Away from the body surface, more internal
Superficial, Towards the body surface
Add on question: What is the difference between anatomical position and directional terms?
Anatomical position is used to describe the locations in the body while the directional terms are used to show the relation of one structure to another.
What are the 3 body planes?
Median (Midsagittal) Plane
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Transverse Plane
Where is the median (midsagittal) plane located?
The plane cuts vertically through the body in anatomical position (Side View)
Where is the frontal (coronal) plane located?
The plane cuts through the body in the anatomical position horizontally (Front View)
Where is the transverse plane located?
A flat plane that cuts through half the body (Top View)
What are the 2 cavities associated with the Dorsal Body Cavity and where are they located?
Cranial Cavity, Located in the skull
Vertebral Cavity, Located along the spinal cord
What are the 2 cavities associated with the Ventral Body Cavity and where are they located?
Thoracic Cavity, Located near the heart and lungs
Abdominopelvic Cavity, Located in Abdominal and lower pelvis area
What are the 2 cavities associated with the Abdominopelvic Cavity and where are they located?
Abdominal Cavity, Located in the Abdominal
Pelvic Cavity, Located in the Pelvic
What is the name of the membrane the major body cavities are surrounded by?
Meninges
The ventral body cavity protects which organ?
The visceral organs
What is the double layered membrane the ventral body cavity is lined by?
The serosa, inner layer is called the visceral serosa and the outer layer is called the parietal serosa. Between these two layers is fluid called serous fluid.
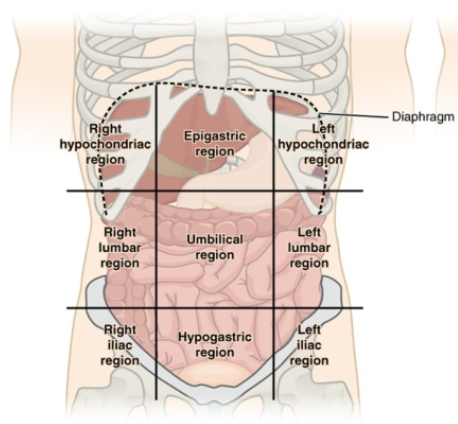
Name all the regions in the abdominal region
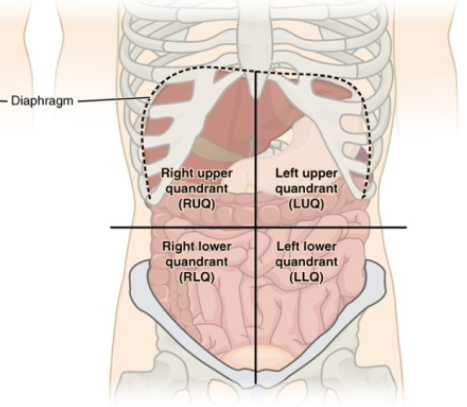
Name all the quadrants in the abdominal area