mitochondria quick flashcards
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what do mitochondria do
convert energy in food into energy (ATP) through a process that uses oxygen (cellular respiration)
what makes mitochondrial membrane proteins
free ribosomes
structure of mitochondria
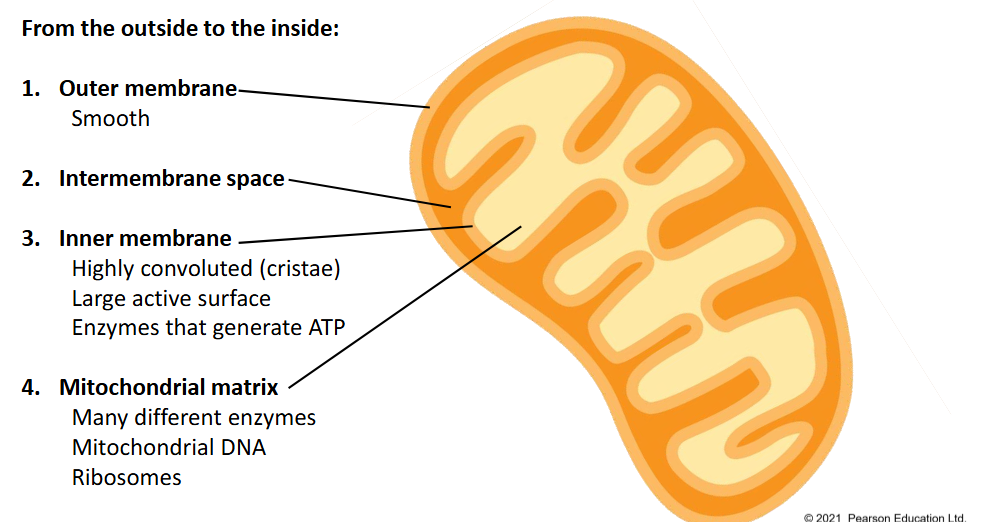
how is the inner membrane specialized to its function
has cristae for more surface area
large active surface
have enzymes that generate ATP
what is the mitochondrial matrix
has many different enzymes
has mitochondrial DNA
has ribosomes
how is mitochondrial DNA inherited
maternally
what are the waste products of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide
water
heat
what is glycolysis
breaks down glucose (C6) into two pyruvates (C3) using 2 ATP
net output: 2 ATP, 2 NADH
is glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic
can be aerobic (respiration)
can be anaerobic (fermentation)
aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria for eukaryotes and cytoplasm for prokaryotes
what is the citric acid cycle
pyruvate is converted into acetyl coA which enters the Krebs Cycle
acetly coA is oxidized and generates 1 ATP, 3 NADH and 1 FADH2 per cycle
2 pyruvate molecules = cycle repeats twice
2 CO2 as waste product
what does pyruvate dehydrogenase catalyze
oxidation of pyruvate, releasing the first CO2 of cellular respiration
reduction of NAD+ to NADH
combines the remaining two-carbon fragment with coA to form acetly CoA
what is oxidative phosphorylation
NADH and FADH2 donate electrons to electron transport chain
electrons move down series of electron acceptors (incl cytochromes) creating a proton gradient
electron carries alternate between reduced and oxidized states as they accept (reduced) & donate (oxidized) electrons
final electron acceptor is oxygen, making water
how is ATP made in oxidative phosphorylation
the energy released from the electrons going down the ETC is used to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space
this generates a proton motive force, creating high concentration of H+ in intermembrane space
ATP synthases uses the proton gradient to make ATP through chemiosmosis