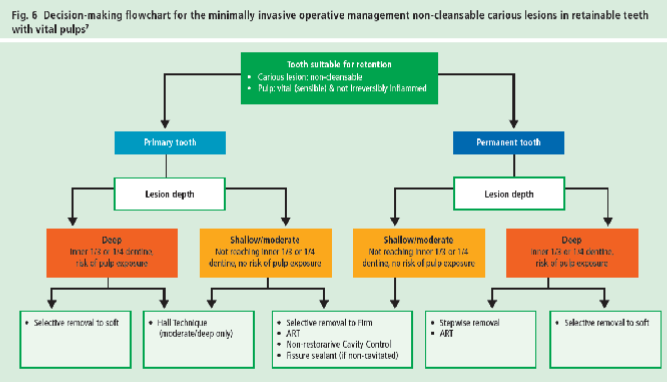
minimal intervention dentistry - stabilisation of caries and ART
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what did G.V.Black show that can arrest carious process
plaque control alone can arrest carious process
describe arrested caries
dark
hard
non-progressive
how can root caries in dentine be arrested
plaque control and the use of fluoride can arrest the process
++ve cavitated lesion = open to the oral environment so can use fluoride on it
how was caries historically removed
remove all infected dentine
often remove all stained dentine too
if necessary = expose pulp and carry out RCT
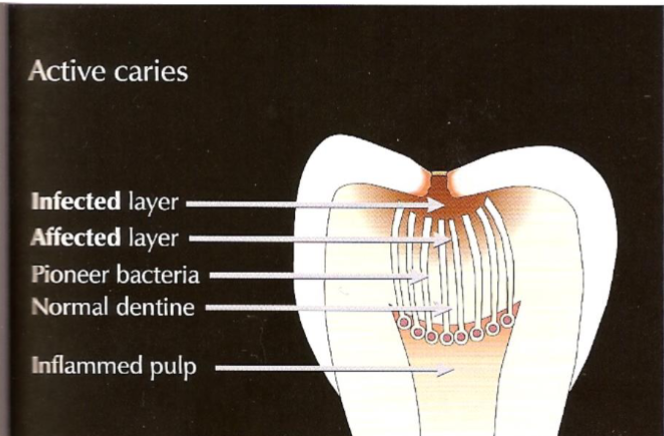
what is the pulpal response to caries
micro-organisms in plaque affect dentine and pulp (dentine has a physiological defence mechanism)
minerals plug tubules as they sclerose
this creates a translucent zone
where does secondary dentine formation occur
at pulpal side
where does tertiary dentine occur
where rapid caries activity occurs
when does pulpal inflammation occur
occurs early on in the caries process
pulp response can be detected by the white spot lesion in enamel
deep caries relates to chronic inflammation of the pulp
what does deep caries associate with
creation of tertiary dentine wh
what is tertiary dentine
contains irregular tubules which do not connect to those of original dentine
hence its less permeable
when does pulp death occur
when the bacteria invades the pulp itself
what is the pulp response during cavity preparations
new dentinal tubules are opened up by the cutting instruments (removal of smear layer)
they dont have sclerotic areas to protect them
pulp may then may be affected by heat and chemical
pulpal damage leads to signifcant damage and bacterial invasions = the pulp may be able to withstand
what does the stepwise caries removal technique show
shows that sealing carious dentine without any cavity preparations at all results in non-progression of the lesions
restorations can last 10 years in this state
how does the stepwise caries removal technique work
takes advantage of the reparative capabilities of the pulp
leave some soft demineralised dentine over pulp (soft dentine left over pulp = prevents exposing it)
peripheral caries still removed (this allows tight seal between tooth and restoration)
place GIC over pulp and restore cavity with GIC
definitive restoration placed at either time or 2/3 years later (GIC can chip or break hence definitive restoration needed ++ dont place GIC on molars)
why is GIC used as a seal in the stepwise caries removal technique
GIC is adhesive so forms a good seal to cavity
define soft dentine
deforms when a sharp probe is pressed into it
can be removed by hand excavator with little force
(infected dentine )
define leathery dentine
doesnt deform when a sharp probe is pressed into it
can still be removed with little force
has a latent ‘tackiness’
(affected dentine)
define firm dentine
physically resistant to hand excavation
needs pressure with excavator to remove it
define hard dentine
only sharp cutting edge or a bur can lift it
scratchy sound when probe is run over it
(sound dentine)
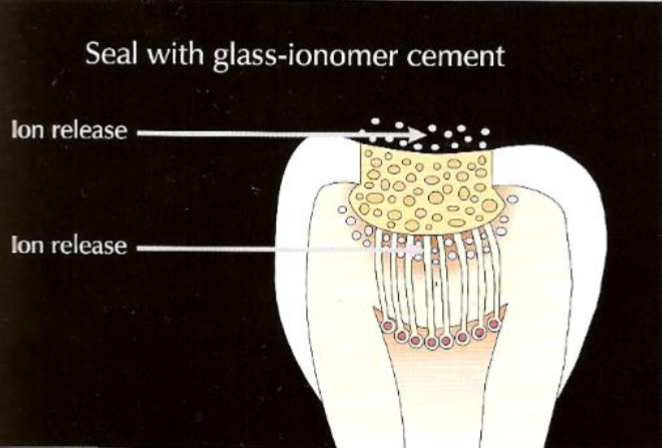
how does GIC help stop the progression of caries into the pulp
GIC eliminates air and carbohydrates leaking into the cavity
bacteria are therefore inactive
lactobacilli die and the number of streptococcus bacteria reduce (the rest of the organisms do not cause caries)
GIC also leaches fluoride and calcium ions to help with mineralisation
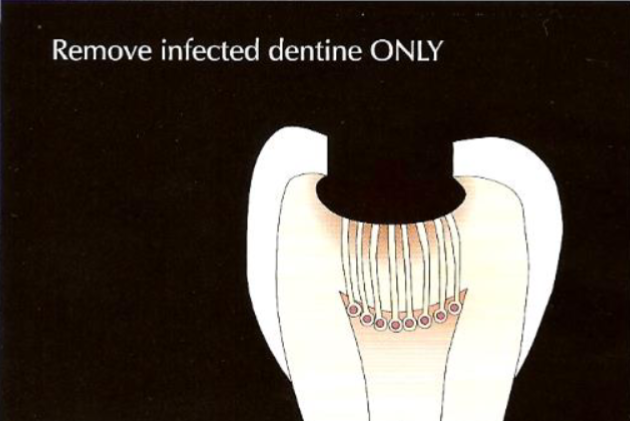
remove infected dentine
leave affected dentine
what was the previous stepwise technique (no longer done)
soft dentine over pulp is left (prevent exposing pulp)
CaOH placed over pulp to kill bacteria
dress tooth with GIC
dressing left for 6 weeks to 6 months
lesion reassessed (cavity preparation completed)
restored with permanent material
not all stained dentine is removed as it can still remineralise under final restoration
what was the role of CaOH
stimulates secondary and tertiary dentine
is bacteriocidal
in simple words explain how the stepwise cavity preparation is done
exposure avoided
pulp is left to remain itself
cariogenic bacteria render inactive
tooth encouraged to remineralise
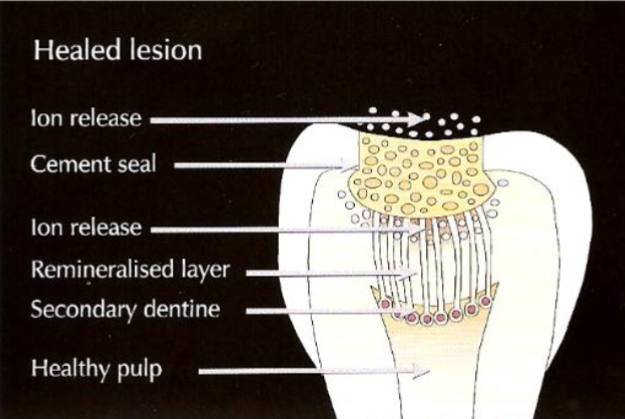
what is ART
atraumatic restorative technique
when is ART used
used in underdeveloped countries
use din children or very nervous adults to stabilise caries
used to ‘buy time’ to prevent the progression of caries and symptoms
what does ART do
hand instruments remove superficial infected dentine
affected dentine left over pulp
GIC placed
doesnt replace tooth form, aesthetics and function
what does ART aim to do
preventative measures are introduced sot he patient is acclimatised to dental treatment (e.g. prophy)
intention is to stabilise things in short term while co-operation of the patient is achieved through acclimatisation
dressing the tooth moves biofilm to the surface and hopefully arrests the caries
teeth can then be reassessed later
what 2 components does ART consist of
a preventative ART sealant
a restorative ART restoration
what is ART sealant
high viscosity GIC (HVGIC) is placed over pits and fissures prone to caries using finger technique
excess removed by hand with excavator
what is ART restoration
removal of soft dentine with hand instruments and placement of high viscosity GIC