Genetics Mid-Lab Exam Dr. Siegfried SBU
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
variable automatic micropipette
This is an instrument used in lab that can measure different volumes of samples that are accurate
fixed volume micropipette
These instruments are pre-set to a specific volume for obtaining accurate samples
0.001 liter
1 ml = _______ liter
1,000 ml
1 liter = ______ ml
1000 microliters
1ml=__ microliter
0.001 ml
1 microliter= __ml
0.01 ml
10 microliters= __ ml
0.02 ml
20 microliters=__ ml
0.05 ml
50 microliters=__ml
0.1
100 microliters=__ml
1,000 times greater
How many times greater is a ml than a microliter?
1,000 times greater
How many times greater is a liter than a ml?
1 million times bigger
How many times greater is a liter than a microliter?
International System of Units and the worlds most widely used measurement system
The metric system is the SI. What does this mean?
Viscosity
A liquid's resistance to flow due to its thickness
Scientific notation
A method of writing or displaying numbers in terms of a decimal number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of 10.
ACcurate is Correct (or Close to real value) PRecise is Repeating (or Repeatable)
What is the difference between accuracy and precision?
embryonic
In animals, cell division is occurring at its fasted rate during _______ development in the blastula.
primary meristems
For plants, cell division occurs in the ___________ in the root tips and branch tips.
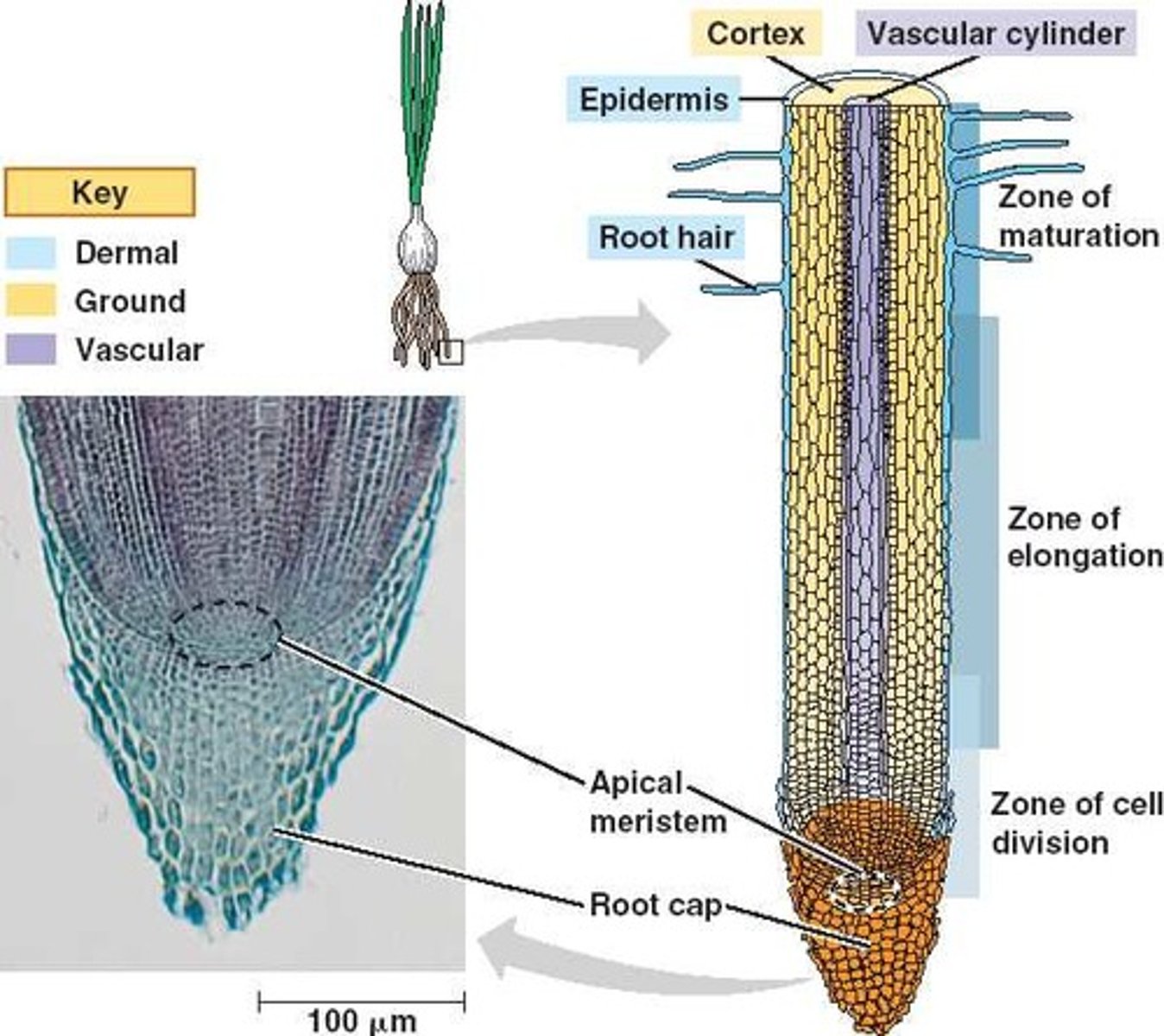
length of each stage.
By knowing how long a cell cycle can last and then comparing the number of cells in each stage as a percentage of time it should be possible to infer the __________.
blastula
an animal embryo at the early stage of development when it is a hollow ball of cells
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
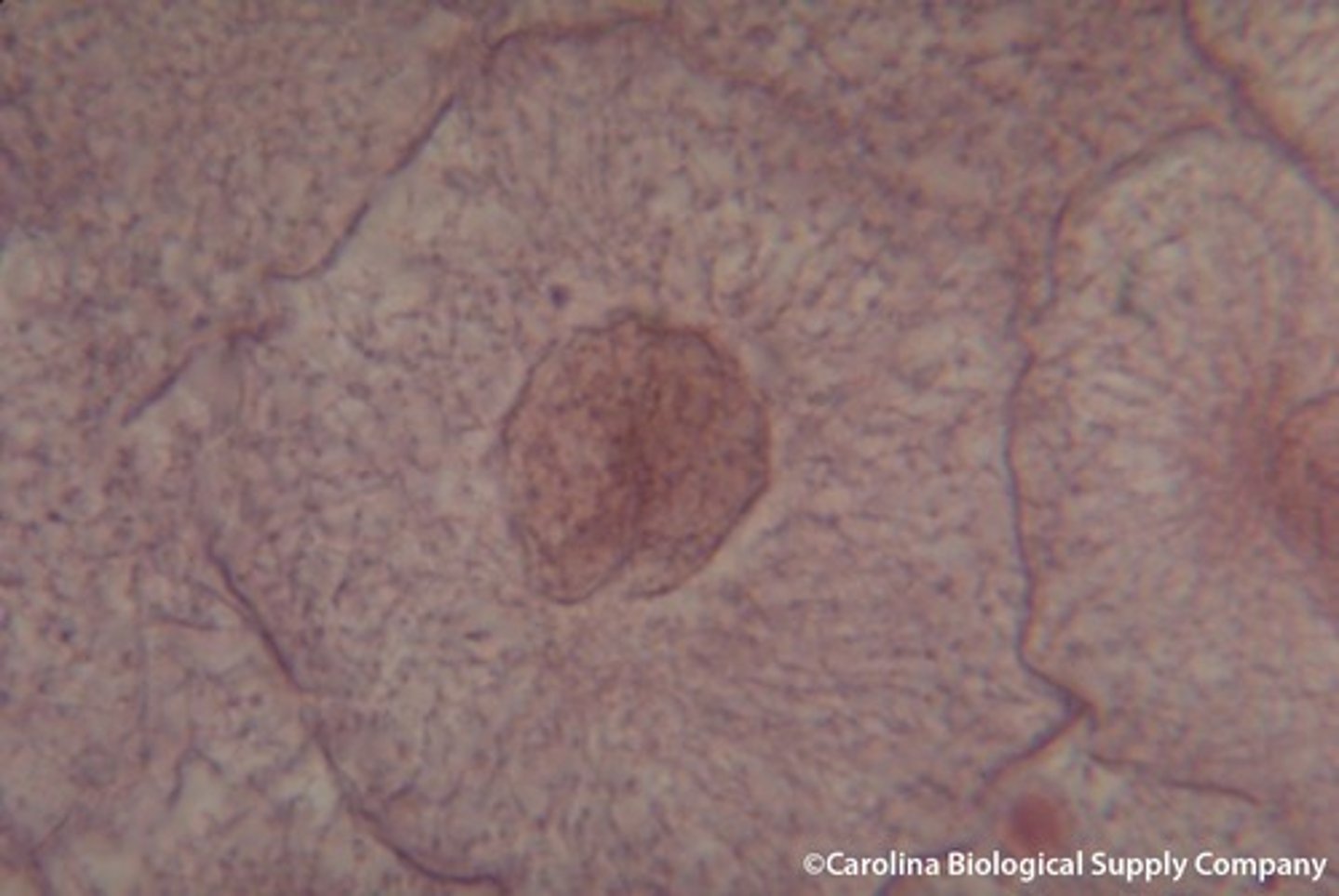
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
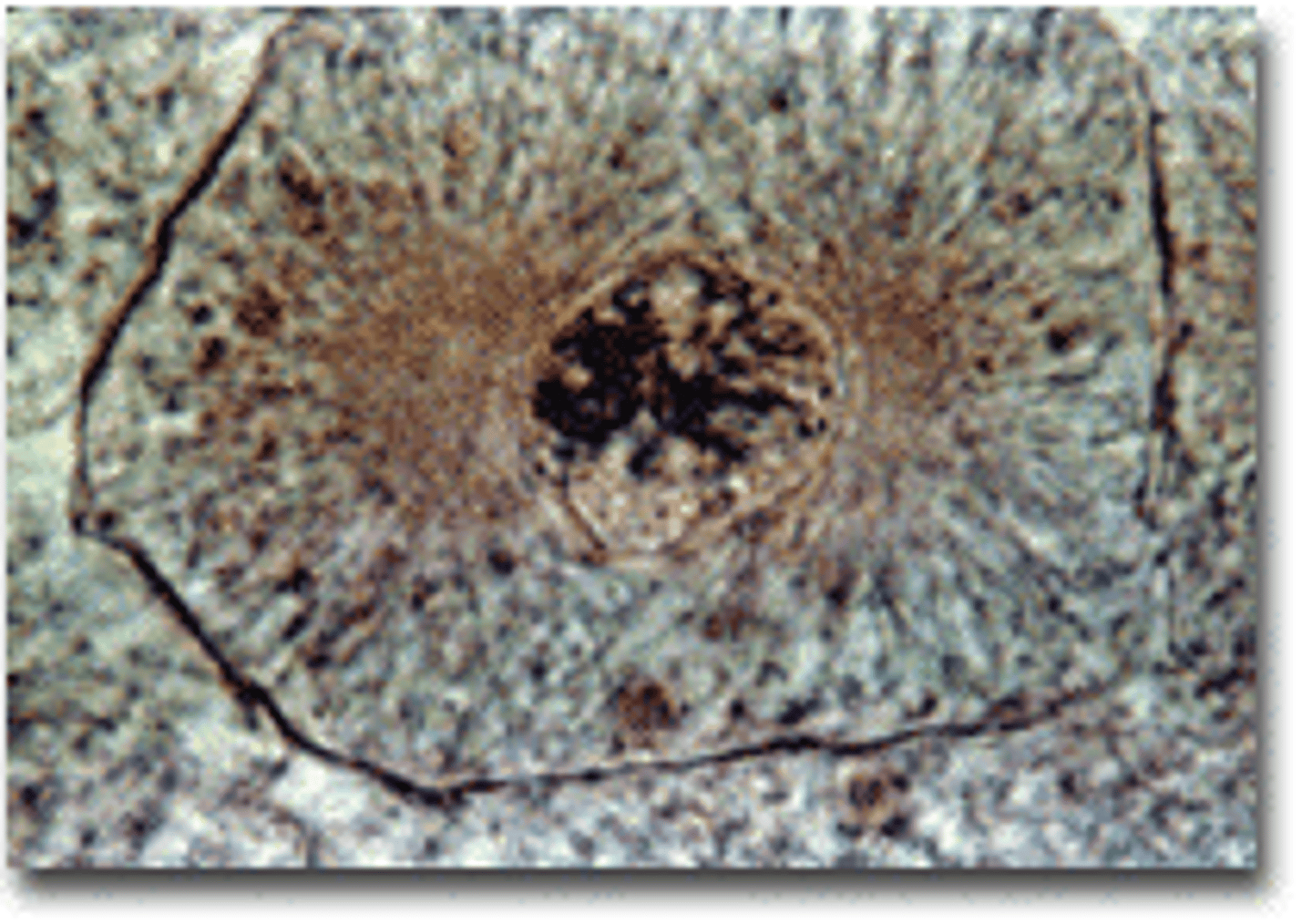
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
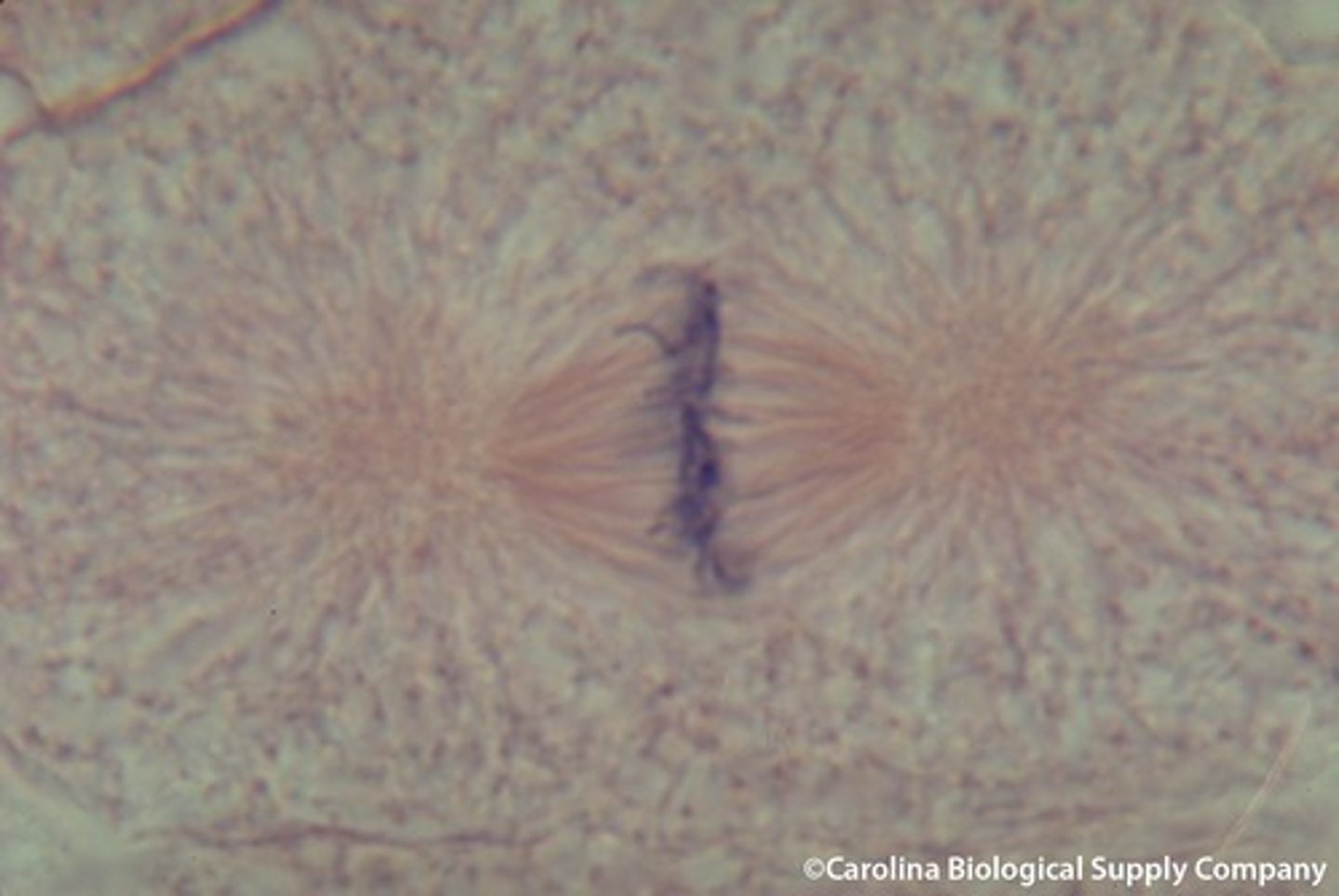
Anaphase
the stage of meiotic or mitotic cell division in which the chromosomes move away from one another to opposite poles of the spindle.
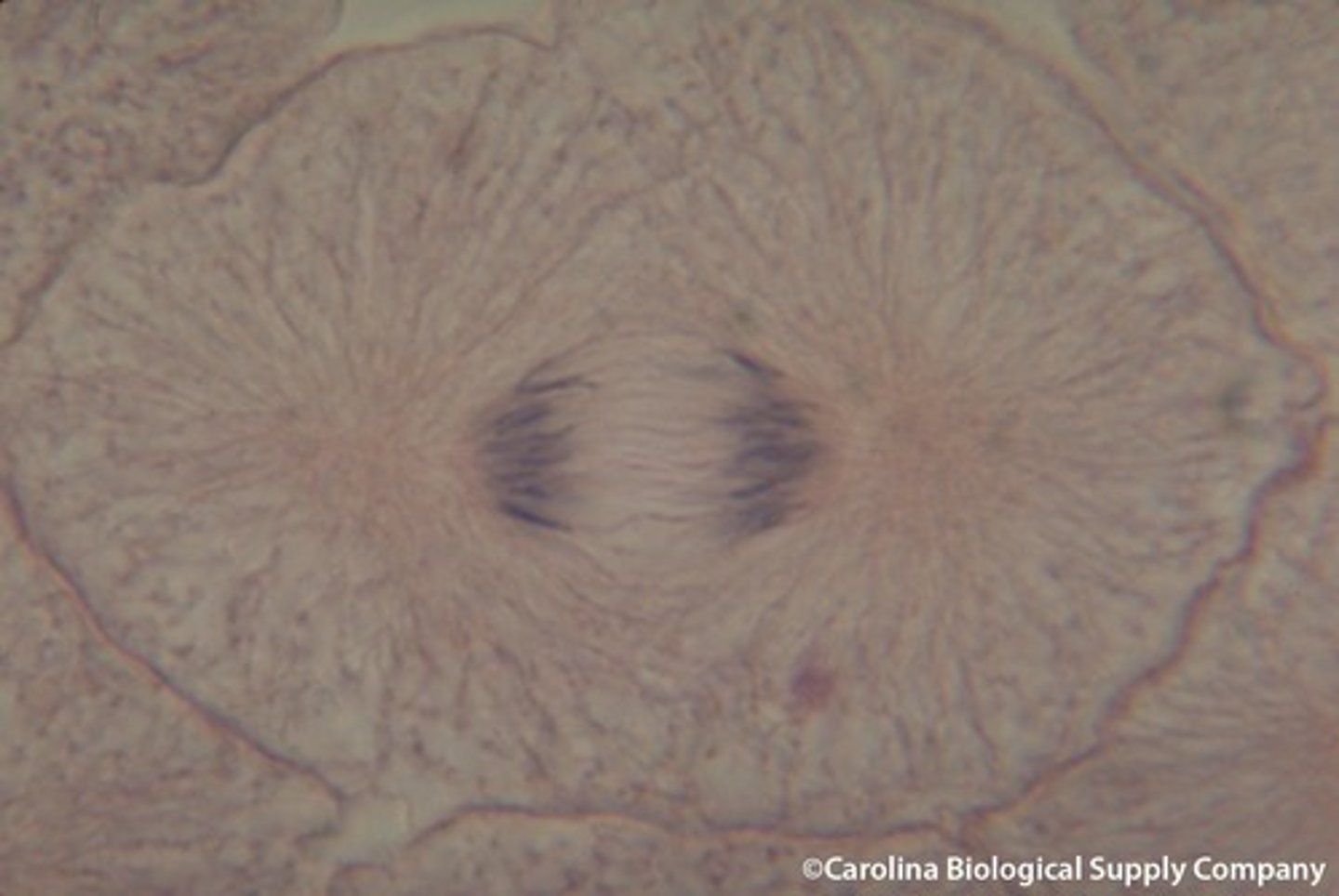
Telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.
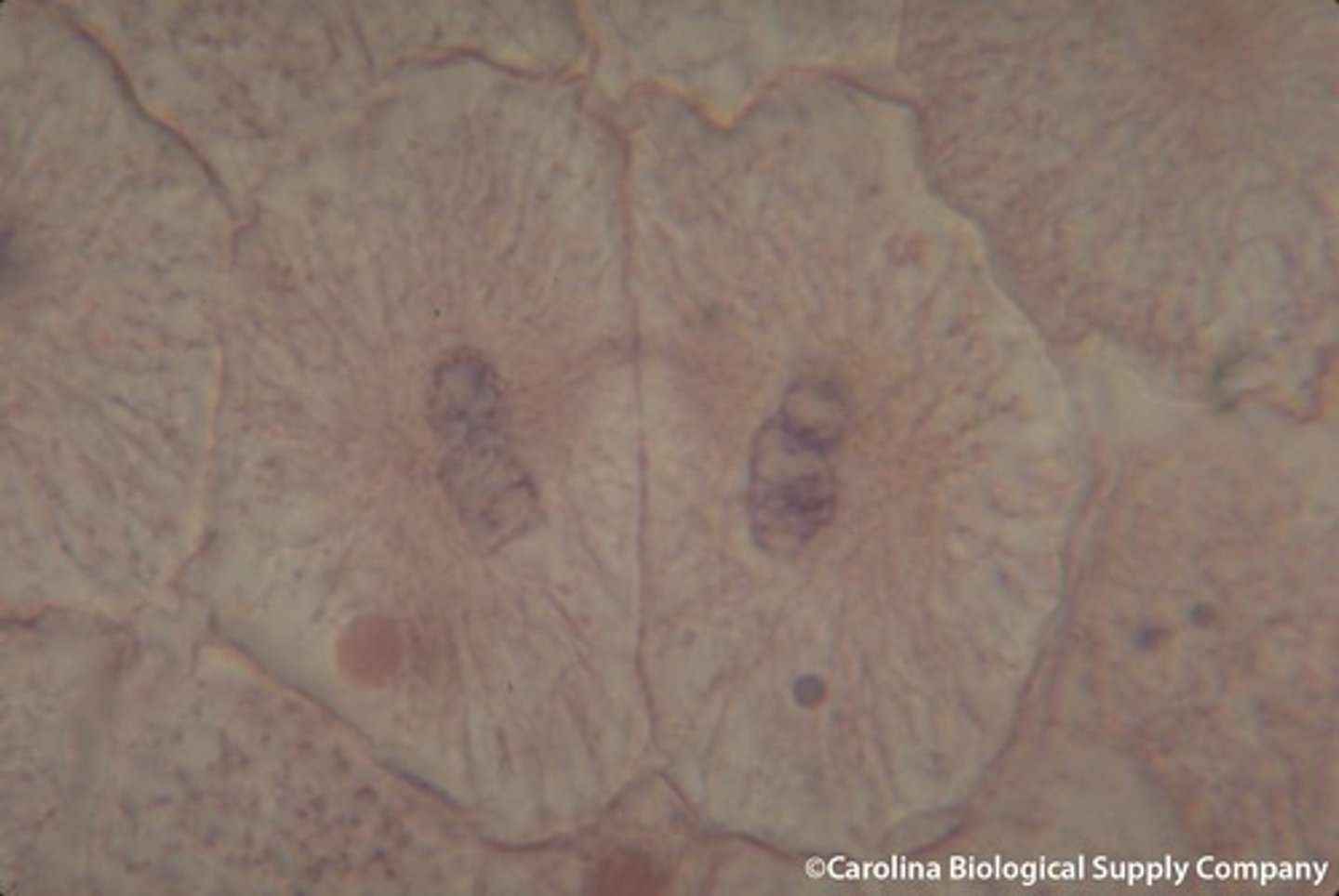
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
Prometaphase
The second stage of mitosis, in which the nuclear envelope fragments and the spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes.
No, it merely provides a rough estimate of confidence of your hypothesis
Does a Chi-square analysis prove that your hypothesis is correct?
the probability that categorical data that you collected supports your hypothesis
What is the Chi-Square statistical test used to determine?
when there is a need to examine the similarities between two or more populations or variables on some characteristics of interest
When is a Chi-Square analysis used?
Chi-square analysis
The _______ can handle more than one variable or population at the same time
deviations of observed frequencies from expected frequencies
What does a Chi-square allow us to test for?
test of independence
A method of assessing whether two categorical variables are associated or dependent.
goodness of fit test
a test for comparing observed frequencies with theoretically predicted frequencies
Test of Homogeneity
A test whether different populations are similar (or homogeneous) to some common characteristics
(1) Test whether two or more distributions are identical.
(2) Compare a distribution with a reference distribution such as the normal distribution.
(3) Goodness-of-Fit test
(4) Test of Independence
(5) Test of Homogeneity
(6) Use to make inference about the population variance
A Chi-square analysis is appropriate when ______ is needed (list off as many as you can)
False. You can never accept a null hypothesis because it is a theoretical sample size that cannot be proven. A null hypothesis acts as a starting point because the statement is accepted as true in the absence of additional information. A null hypothesis can either be rejected or failed to reject
True or False: A null hypothesis can be rejected or accepted
null hypothesis, frequency distribution, sample
Fill in the blanks: tests a _______ stating that the ________ of certain events observed in a _____ is consistent with a particular theoretical distribution. A common case for this is where the events each cover an outcome of a categorical variable.
catagorical variable
A variable used to assign an object or person to a group; defined by specific characteristics. Also called qualitative or nominal variable.
Chi-Square
What is this equation? MEMOREIZE IT
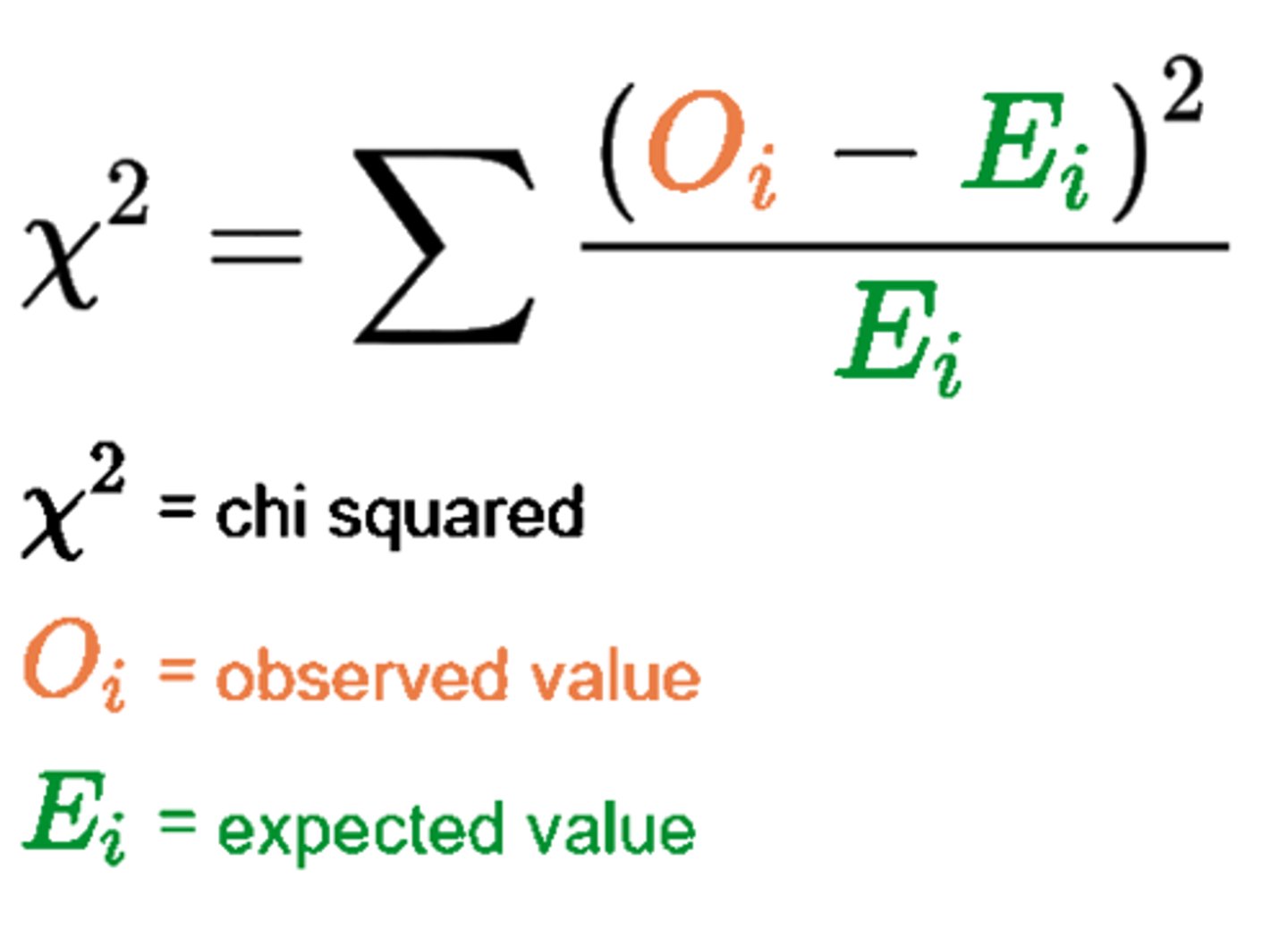
degrees of freedom (df)
The maximum number of logically independent values, which are values that have the freedom to vary in the data sample. "N-1"
Degrees of Freedom (DF)
Parameter used to look up chi-square values from the chi-square distribution table. It is related to the sample size or number of classification of data within a category.
1. Random sample - A random sampling of the data from a fixed distribution or population
2. Sample size (whole table) - A sample with a sufficiently large size is assumed
◦ If a chi square test is conducted on a sample with a smaller size, then the chi square test will yield an inaccurate inference. The researcher, by using chi square test on small samples, might end up committing a Type 2 Error
3. Expected Cell Count - Adequate expected cell counts
◦A common rule is 5 or more in all cells of a 2-by-2 table, and 5 or more in 80% of cells in larger tables, but no cells with zero expected count
4. Independence - The observations are always assumed to be independent of each other
◦ This means chi-square cannot be used to test correlated data (matched pairs, panel data)
Name some Chi-Square analysis assumptions
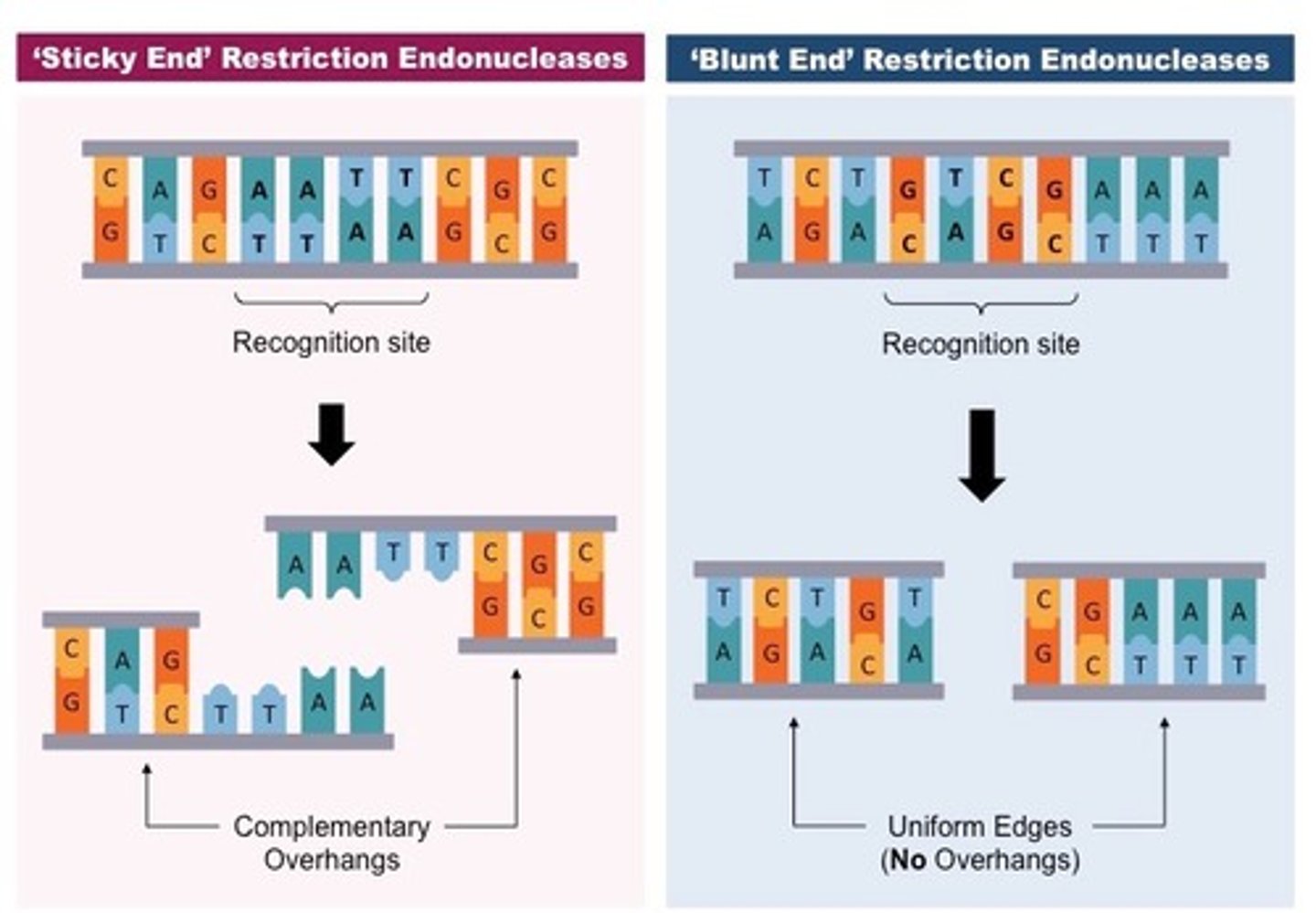
Restriction Enzymes
________ are endonucleases which catalyze the cleavage of the phosphate bonds within both strands of DNA. They require Mg+2 for activity and generate a 5 prime (5') phosphate and a 3 prime (3') hydroxyl group at the point of cleavage.
They only cut at very specific palindromic sequences of bases
What is the distinguishing factor of restriction enzymes?
The first letter of the genus followed by the first two letters of the species. The type of strain or substrain sometimes follows the species designation in the name. Finally, a Roman numeral is always used to designate one out of possibly several different restriction enzymes produced by the same organism or by different substrains of the same strain.
How are restriction enzymes names?
Palindromic sequence
A highly specific base pair sequence that have the same base pair when read from 5'-3'. A specific restriction enzyme will recognize this and cleave.
Yes, usually both DNA strands have the same base sequence when read 5'-3'
Are recognition sites usually symmetrical?
"sticky" or "cohesive" because the single-stranded regions are complementary
EcoR1 cleaves will leave a staggered cleavage site. The resulting DNA fragments are called _____ or ______.
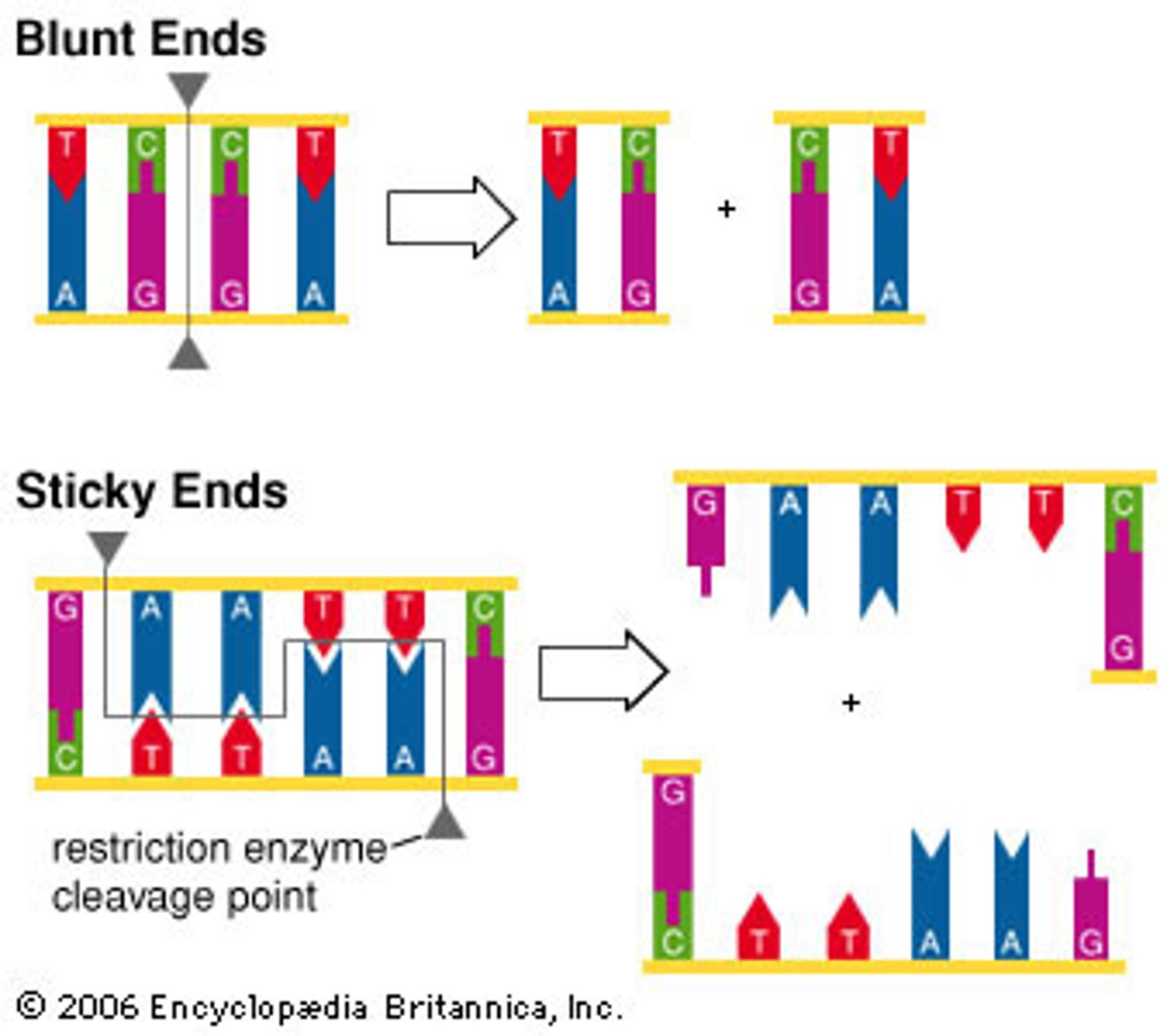
"blunt" ends
Some restriction enzymes, such as Hae III, introduce cuts that are opposite of each other. This type of cleavage generates _____ ends.
variable base positions
Some restriction enzymes, like Ava I, recognize _______ like pyrimidines or purines
degenerate recognition sites (Py=C or T & Pu=G or A)
Some enzymes have ________, meaning that they contain one or more base pairs that are not specifically defined
The only bases the enzyme truly "recognizes" base pairs at the ends, which form a palindrome. Hyphenated sites
There are some restriction enzymes, like Bgl I, that recognize sites that are divided by a certain number of totally variable bases (N=A,G,C or T). What is the enzyme recognizing and what are these restriction sites called?
4^n, where n is the length of the recognition site in base pairs.
Statistically an enzyme will cut one for every _______.
True
T or F: In general, the longer the DNA molecule, the greater the probability that a given recognition site will occur
Partials. Partials can arise if low amounts of enzyme are used or the reaction is stopped after a short time. In reality, reactions containing partials also contain some molecules that have been completely cleaved.
If a DNA molecule contains several recognition sites for a restriction enzyme, then under certain experimental conditions, it is possible that certain sites are cleaved and not others. These incompletely cleaved fragments of DNA are called _______
negative (DNA), positive (electrode)
DNA has a strong _____ charge at neutral pH and migrates through the gel towards the _____ electrode
Agarose gel electrophoresis
_________ is a powerful separation method frequently used to analyze DNA fragments generated by restriction enzymes. The gel consists of microscopic pores that act as a molecular sieve. Samples of DNA are loaded into wells made in the gel during casting. Direct current is then applied.
False. Some may not be visible after agarose gel electrophoresis. Since there is less mass in the bands containing smaller fragments, they stain with less intensity and may be undetectable
True or False: Smaller fragments generated by a restriction enzyme, such as those generated by Hind III, will always be visible
To prevent the "sticky" ends from reannealing
Why would a person heat Lambda DNA fragments prior to electrophoresis?
13. (48,502/4,096)+1. The 1 is added because the fragment is linear. So for every one cut 2 fragments are produced.
A linear DNA fragment 48,502 bp and EcoRI cleaves once for every 4,096 bp. How many cleaves will EcoRI make?
True
True or False: The probability that a specific enzyme will cut, or "digest", a piece of DNA is directly proportional to the length of its recognition site
1. insufficient amount of enzyme
2. reaction time is stopped short
Give some reasons why a DNA strand may not be fully digested
dominant
Familial cancers constitute a very small fraction of the total reported cancers and occur in ________ inherited patterns.
Germline mutations. They can be detected in familial pedigrees.
Mutation that are directly inherited are referred to as _________.
Somatic
This type of mutation does not have direct genetic links. Instead, it is acquired during an individual's life
Hypothesis that most tumor suppressor genes require both alleles to be inactivated, either through mutations or through inheritance
Explain the "two-hit" hypothesis
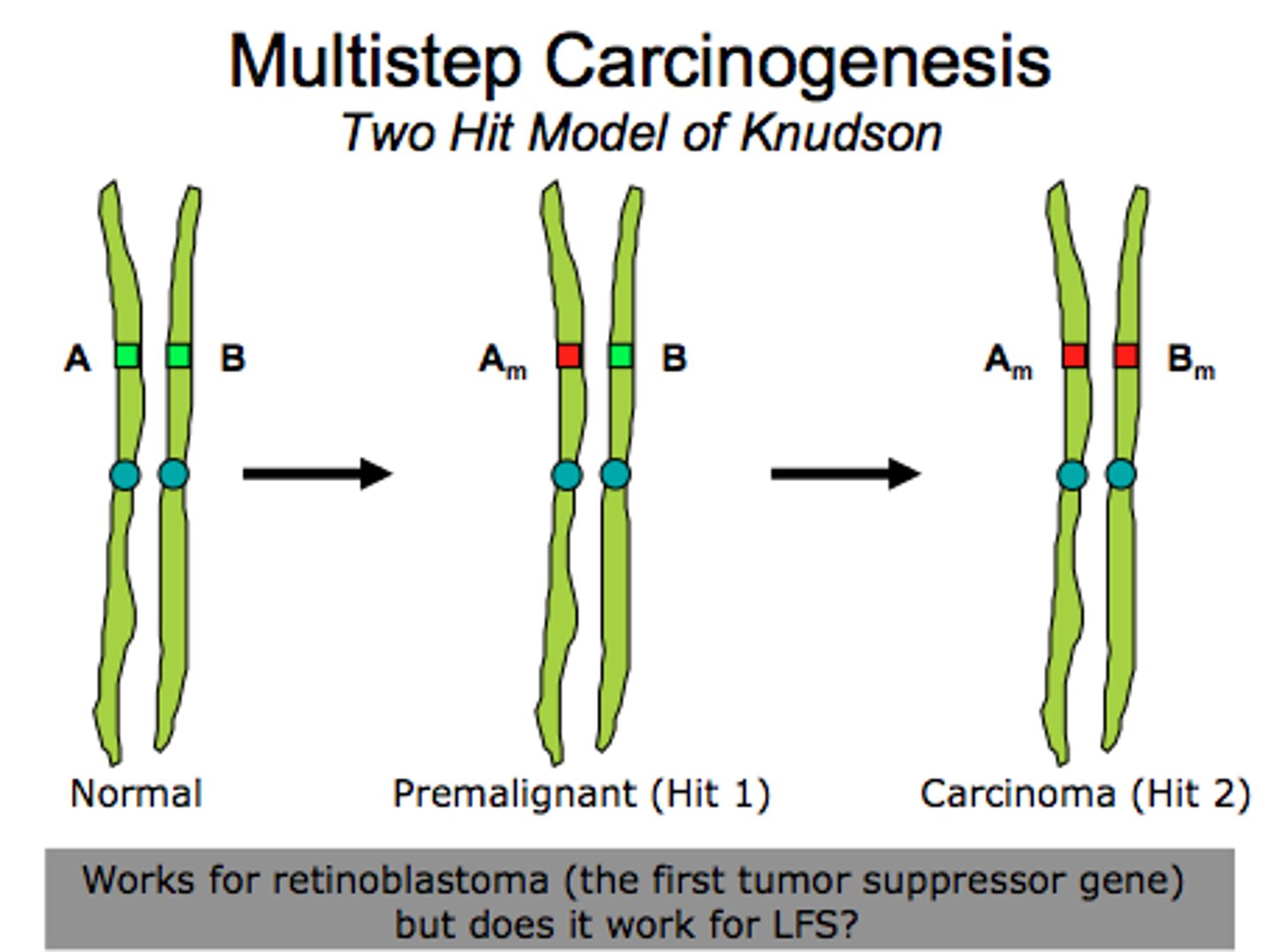
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
ln ____________, a notable feature in family pedigrees, include a sarcoma patient and at least two immediate relatives with other cancers before the age of 45, as well as multiple cancers in other family members
Endonuclease
This is an enzyme that cleaves the phosphate bonds within DNA and require Mg^2+ for activity
5' phosphate, 3' OH group
Endonuclease cut a specific base sequence and generate a __________ and a _________ at cleavage point
Endonuclease
An enzyme which cleaves a polynucleotide chain by separating nucleotides other than the two end ones
bacteria
Restriction enzymes are produced by a ________ (ex. blue-green algae
Escherichia coli RY13. Restriction Enzymes are named from organism they are isolated from. 1st 2 letters of genus, 2 letters of species, Roman numeral designated substrain (EcoRI)
What does Eco RI sand for.
A double stranded sequence of bases where a restriction enzyme cleaves
What is a recognition site?
4-8 bps
How long are restriction enzyme sites (how many bp)?
Palindromes
These restriction enzyme sequences are the same 5'-3' and 3'-5'.
False. Plasmid DNA will become linear DNA when cleaved for the 1st time
True or False: when plasmid DNA is cleaved on its 1st restriction site there will be two DNA fragments
2 DNA fragments
Linear DNA will yield ____ fragments when cleaved for the first time
Chromosomal DNA
What is another name for linear DNA
Many restriction enzymes are sensitive to the DNA methylation states. Cleavage may be blocked, or impaired, when a particular base in the enzyme's recognition site is modified.
Endogenous DNA must be protected from cleavage or the cell will be destroyed. What chemical group can provide protection?
seaweed
Agarose is extracted from _____.
1. Attraction to the electrical field
2. Weight of the fragments
Molecules are seperated in electrophoresis based on what 2 theories
phosphates
What part of DNA has a negative charge?
1. So you can see the DNA as you load it
2. It contains glycerol or sucrose to create weight and allow the DNA to sink to the bottom of the wells
Why are DNA samples usually mixed with loading dye?
1. DNA moves through gel pores (acts as sieve)
2. DNA contains various sizes of fragments
3. Larger the DNA fragments, slower the movement because of migration difficulties
4.Separation between large and small fragments continues to give you bands
5. With appropraite tools, like a marker of known band fragments, you can then assign weights and sizes to the unknown DNA fragments
Explain electrophoresis and the movement of DNA fragments