Unit 1.1 - Nervous System & Drugs
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
Nature-Nurture
The long-standing debate over whether heredity (nature) or experience (nurture) most influences behavior and mental processes
Evolutionary Psychology
The study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, based on the principle of natural selection
Natural Selection
The principle that inherited traits enabling an organism to survive and reproduce in a specific environment are most likely to be passed to the next generation
Key steps in Natural Selection
Variation in offspring, 2. Competition for survival, 3. Adaptation of traits, 4. Selection of the fittest traits over time
Mutation
A random error in gene replication that leads to a change
Behavior Genetics
The study of the relative power and limits of genetic (nature) and environmental (nurture) influences on behavior
Heredity
The genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring
Environment (in psychology)
All non-genetic influences, from external factors like people around us to pre-natal conditions like a mother's diet
Adaptive Flexibility
The human capacity to learn and adapt to varied environments, which gives us high fitness (ability to survive and reproduce)
The Human Genome
The complete set of genetic material in an organism; humans share around 95% of their genetics with each other
Monozygotic Twins
Identical twins resulting from one fertilized egg splitting; they are genetically identical and always the same sex
Dizygotic Twins
Fraternal twins resulting from two separate eggs fertilized by two different sperm; they are no more genetically alike than regular siblings
Findings from Twin Studies (Identical apart)
Identical twins raised separately show striking similarities in tastes, physical attributes, personality, abilities, interests, and fears
Adoption Studies Findings
Adopted children's personalities generally do not resemble their adoptive parents or adopted siblings; personality is more linked to biological parents
Epigenetics
The study of environmental influences on gene expression (phenotype) that occur without a change to the DNA sequence
Gene Expression
Whether a gene is active (expressed) or inactive (turned off)
Epigenetic Marks
Molecules attached to parts of DNA that signal whether a gene should be turned on or ignored (turned off), often created by environmental experiences
Genetic Determinism (Correction)
The belief that genes determine who you are (inaccurate); genes are probabilistic—they only give the probability of expressing a trait
Intergenerational Trauma
The concept that environmental influences (like trauma) can create epigenetic marks that are potentially passed down to the next generation
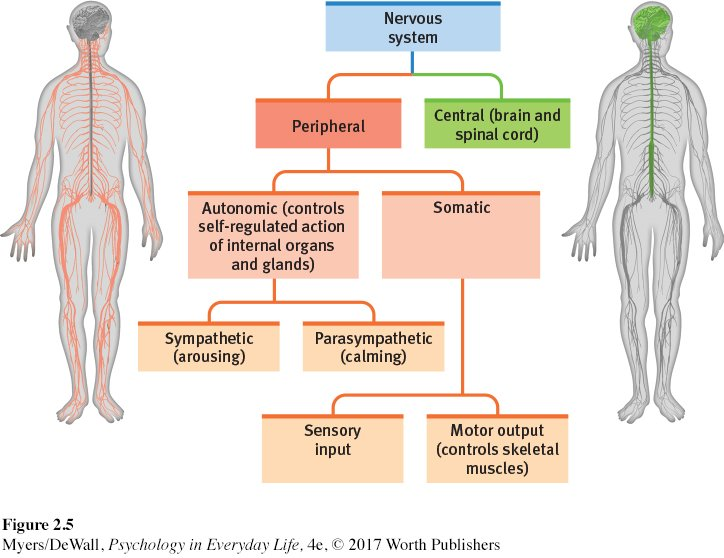
Nervous System
The body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, made up of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The division of the nervous system consisting of the Brain and Spinal Cord; coordinates incoming sensory and outgoing motor messages
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body; includes all the nerve endings not in the brain or spinal cord
Nerves
Bundled axons of many neurons that form neural cables connecting the CNS with muscles, glands, and sense organs
Sensory Neurons (Afferent)
Carry information from the peripheral (sense organs) to the CNS
Motor Neurons (Efferent)
Carry messages out of the CNS to the peripheral (muscles and glands)
Interneurons
Neurons within the CNS (brain and spinal cord) that internally communicate and intervene between sensory inputs and motor outputs
Somatic Nervous System
DIVISION OF PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM that controls the body's voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
DIVISION OF PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: that controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs, managing functions you are not consciously thinking of
Broken into Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Sympathetic Nervous System
The division of the Autonomic System that arouses the body, mobilizing energy for action (e.g., fight, flight, or freeze)
SIMP GETS AROUSED
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The division of the Autonomic System that calms the body, conserving its energy (e.g., rest and digest)
PARACHUTE SLOW DOWN
Homeostasis
The process by which the body's systems are kept in a state of balance (the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work to maintain this)
Reflex Arc
A simple, fast pathway in the spinal cord that allows the body to respond very quickly to extreme situations without the information first reaching the brain
REFLEX HAPPEN ONLY INVOLVE SPINAL CORD
Neuron
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Cell Body (Soma)
The core of the neuron containing the nucleus; it produces genetic information and directs protein synthesis (the cell's life-support center)
Dendrites
Bushy, branching extensions of the neuron that receive and integrate messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
Axon
The neuron extension that passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
Myelin Sheath
A fatty tissue layer encasing the axons; it insulates the axon and increases the speed of neural impulse transmission
Terminal Branches (of the axon)
The end of the axon that contains synaptic vesicles (containers) that store and release neurotransmitters to enable communication across the synapse
Glial Cells
The "worker bees" of the nervous system; they support, nourish, and protect neurons and play a role in learning, thinking, memory, and creating the myelin sheath
Myelination Development
The process of creating the Myelin Sheath, which is not complete until about age 25; it's crucial for behavior, movement, and thought
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
A condition caused by the deterioration of the myelin sheath, leading to motor impairments
Action Potential
A brief electrical charge that travels down the axon; transmit information
ALL OR NONE RESPONSE: More stimulation does NOT mean more intense transmission
Resting Potential
The state of a neuron when it is not firing; the interior of the axon is negatively charged (polarized)
Negative in, positive out
Refractory Period
A brief pause after a neuron has fired, during which it cannot fire again until it restores the resting state
Waiting for equilibrium with the environment → All Axon need to Repolarize
Reuptake
The process by which the sending neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters from the synapse
The sending neurons takes back the UNBOUND (non-absorbed) neurotransmitters
DRUGS: Some drugs prevent reabsorption by blocking reuptake in the dendrite of the sending
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Enables role in Muscle action, learning, memory→ MAJOR role in communication between motor neurons and skeletal muscles
Major part in voluntary movement
Deterioration linked to Alzheimer's disease.
Norepinephrine
Helps control alertness and arousal. Undersupply can lead to a depressed mood.
Hormone and neurotransmitter
The Firing of a Neuron (Steps)
Action Potential Begins: First Section Axon OPENS GATES where Na+ ions flood in
Depolarization: The flood of Na ions leads to depolarization, and signals to the next axon section to open
Repolarization: Once the Na+ ions move to the second part, K+ ions on the OUTSIDE (not in the axon) repolarize
Depolarization and Repolarization repeat
Entering Refectory Period
Divisions of the Nervous System
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic
Sympathetic | Parasympathetic |
|
|
2 Types of Neural Signals
Excitatory Signal: Gas Pedal on Car → Trigger Action
Inhibitory Signal: Brake on car → Depress action
More excitatory than inhibitory impulses → Reach THRESHOLD → ACTION POTENTIAL
Use Toilets to Explain Action Potential & Refectory Period
Action Potential: Pressing the toilet harder (after exceeding the minimum) does not make it flush faster
For a more intense response, fire MORE neurons
Refectory Period: Neurons need Breaks → After FLUSH TOILET, need wait a bit before flush
Endorphins
Morphine Within → Natural substance, opiate-like neurotransmitter and suppress pain and pleasure
Help runners to push past a wall and keep going
END PAI\n
Problem With Pain Suppression: Might not realize how badly injured they are → Lessen impact of pain
Adrenaline/ Epinephrine
Increases heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar → Boosts energy in flight/ flight responses
Secreted through adrenal glands
When the fight or flight response, the adrenal glands release epinephrine and norepinephrine to energize the body
Endocrine System
Body’s SLOW chemical communication system → Glands and fat tissue that secrete hormones into blood stream
If nervous system is sending a text, endocrine system is writing a letter
Hormones
Chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, and travel through the blood stream to affect other tissues
Pituitary Gland
Endocrine system’s most influential gland → Regulate growth and control other endocrine glands
regulates hormone release for SOME glands
Part of both the Central Nervous and Endocrine System → Near the Brain
Endocrine System vs Nervous System (BIG TABLE)
Endocrine System | Nervous System |
|
|
Ghrelin & Leptin
Ghrelin: Stimulates Hunger
Leptin: Decreases hunger, regulate food intake and fat storage