CH. 9 Muscular Tissue - Dr. Jones
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
sarcoplasm
muscle cell cytoplasm
muscle fiber
long muscle cell
excitability (responsiveness)
contractility (shorten forcibly)
extensibility (stretched)
elasticity (recoil to resting length)
four main characteristics of muscles
oxygen and glucose
what do muscle fibers need to contract?
epimysium
-dense irregular connective tissue
-surrounding entire muscle; may blend with fascia
perimysium
-fibrous connective tissue
-surrounding fascicles (groups of muscle fibers)
endomysium
-fine areolar connective tissue
-surrounding each muscle fiber
-deepest of connective tissue wrapping
direct (fleshly) attachments
epimysium fused to periosteum of bone or perichondrium of cartilage
indirect attachments
connective tissue wrappings extend beyond muscle such as:
rope-like tendon (like a cord)
sheet-like aponeurosis (flatten out)
sarcolemma
muscle fiber plasma membrane
myoglobin
oxygen binding protein found only in muscle
glycosomes
specialized vesicles for glycogen storage in muscle
myofribrils
a muscle cell is a bundle of densely packed ___.
(smaller than fiber)
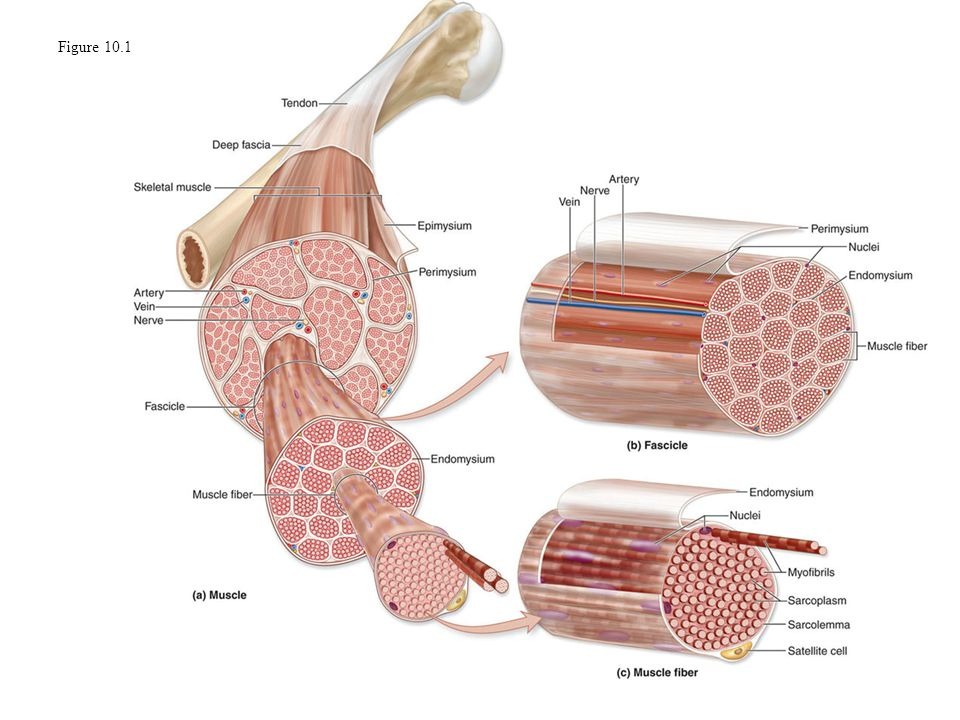
perimysium
Separate bundle of fasicles
endomysium
separate muscle fibers
myofibril
Responsible for striations in muscle fiber
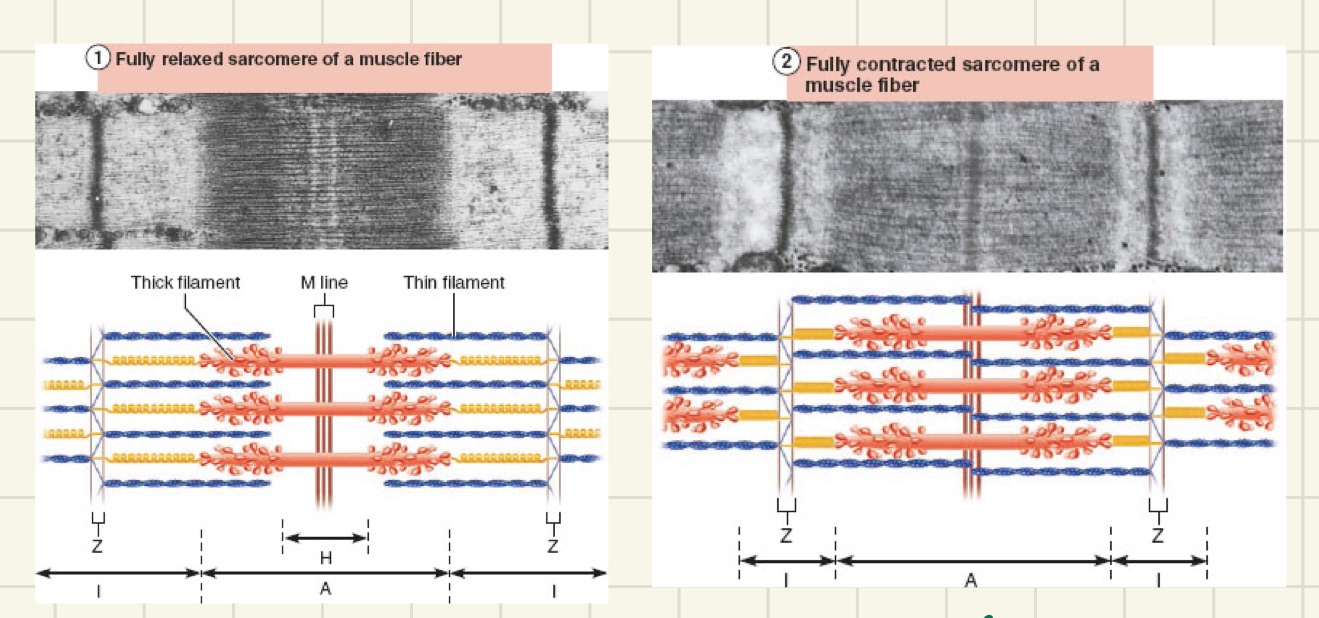
sarcomere
divides myofibril into sections
-smallest contractile unit of muscle fiber
myofilament
myofibril is a bundle of ___.
-consists of proteins that make up striations (light and dark)
actin myofilament
thin filament - I band
myosin myofilament
thick filament - A band
M line
divide sarcomere into a right and left side
H zone
zone of sarcomere that has no actin, only myosin
cross bridges
when actin and myosin touch = contraction
tropomyosin and troponin
control proteins bound to ACTIN
-act as gatekeepers if actin and myosin ever get to touch
dystrophin
holds actin in proper position for good overlap (alignment)
-responsible for dystrophy if mutated
duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
-sex-linked recessive gene (mother to son); exclusive to males
-child is clumsy and falls frequently
-caused by defective gene for dystriophin (links thin filaments to matrix which helps stabilize sarcolemma)
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Network of smooth endoplasmic reticulum tubules surrounding each MYOFIBRIL
-runs length of muscle fiber
-only responds to electrical stimulation
-stores calcium
sarcoplasmic reticulum
stores Ca2+ when the fiber is at rest
T tubules
allow electrical nerve transmissions to reach deep into the interior of each muscle fiber
-”transverse”
-portions of plasma membrane weave in and around each myofibril so they can receive electrical stimulation
contraction
the activation of cross bridges to generate force
tension
shortening occurs when __ is generated by cross bridges
ends
contraction __ when cross bridges become inactive
sliding filament model of contraction
thin filaments slide past thick filaments, causing actin and myosin to overlap
-neither thick nor thin filaments change length, just overlap
cross bridge shortening of muscle fiber
-I bands shorten
-Z discs become closer
-H zones disappear
-A bands move closer to each other
action potentials
big electrical signals
-stimulate skeletal muscle
acetylcholine (ACh)
what neurotransmitter action potential uses (chemical)
chemically-gated ion channels
ion channel opened by chemical messengers such as neurotransmitters
Ex. ACh receptors on muscle cells
voltage-gated ion channels
ion channel receptor open or close in response to electrical changes in membrane potential
axons
long, threadlike extensions of motor neurons > travel from central nervous system to skeletal muscle
(long tail of neuron-which is in brain)
neuromuscular junction
where neuron and muscle meet
-also called motor end plate
-equal to amt muscle fibers
axon terminal
end of axon
synaptic cleft
gel-filled space between axon terminal and muscle
synatic vesicles
contain acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter
acetylcholine (ACh)
can diffuse over synaptic cleft which bind to muscle via receptors
Action potential arrives at axon terminal
1st event at neuromuscular junction
voltage-gated CALCIUM channels open, calcium enters motor neuron
2nd event at neuromuscular junction
after action potential arrives at axon terminal, what happens next?
calcium entry causes RELEASE of acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft
3rd event at neuromuscular junction
after voltage-gated calcium channels open due to action potential and calcium enters motor neuron, what happens next with calcium?
ACh diffuses across to ACh RECEPTORS (chemical gates) on the sarcolemma
4th event at neuromuscular junction
after calcium causes the release of ACh into the synaptic cleft, what happens to the ACh?
ACh binds to ACh receptors on the muscle, which OPENS the gates, allowing Na+ (sodium) to enter muscle; results in end plate potential
5th event at neuromuscular junction
after ACh diffuses across ACh receptors what happens next?
acetylcholinesterase
an enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), terminating any nerve signals responsible for muscle contraction
myasthenia gravis
autoimmune disease which immune system destroys ACh receptors
-weakened contraction of muscle.. need to get channels on muscle to open via ACh first!)
negative
the inside of a muscle fiber is more ___ than the outside
end plate potential
local depolarization (becomes more positive)
-ACh released from motor neuron bind to ACh receptors on sarcolemma
-chemically gated ion channels (ligands) on sarcolemma to open
-ACh diffuse into muscle fiber; causing interior of sarcolemma to become less negative (MORE POSITIVE)
Na+
outside of muscle cell there is lots of ___ compared to inside
K+
inside of muscle cell there is more __ compared to outside
-70mV
voltage when muscle is at rest
-55-50mV
point of no return - voltage threshold ; muscle contraction
repolarization
restoration of resting conditions (back to negative)
-K+ go out of cell rapidly bringing cell back to initial resting membrane voltage
refractory period
muscle fiber cannot be stimulated for a specific amount of time, until repolarization is complete
depolarization
Na+ entry to a cell causes…?
repolarization
K+ exiting a cell causes..?
contraction
Ca+ release leads to ___.
Ca+
what do you need to remove troponin and tropomyosin in order for actin and myosin to overlap (cross bridge) - create contraction?
ATP
what enable the actin-myosin cross-bridge to detach?
rigor mortis
3-4 hours after death muscles begin to stiffen
-actin myosin connected, nothing to release it due to no ATP
load
opposing force to muscle contraction; what the muscle is working against
nerve
groups of axons of neuron
muscle twitch
single action potential in muscle
latent period
delay of action potential of neuron; no muscle tension seen
period of contraction
cross bridge formation; tension increase
period of relaxation
reentry into sarcoplasmic reticulum; tension declines to zero slowly
muscle tone
constant, slightly contracted state of all muscles
-keeps muscle steady, healthy, ready to respond
isometric contraction
no shortening; not enough to overcome load
-muscle tension increases but does not exceed load
-load is greater than max tension muscle can generate ex. when you stand up
isotonic contraction
muscle shortens because muscle tension exceeds load
-muscle changes length and moves load
-concentric or eccentric
concentric contraction
isotonic contraction
-muscle shorten and does work
ex. biceps contract to pick up a book
eccentric contraction
muscle lengthens and generates force
ex. laying a book down causes biceps to lengthen while generating a force
disuse atrophy
degeneration and loss of mass
-due to immobilization or loss of neural stimulation (nervous system not able to convey signal)
ex. cast over leg allow bone to heal but muscle weakens over time
top-down
muscular development occurs head to toe or ___.
-a baby can lift its head before it can walk
myoblast-like skeletal muscle satellite cells
limited regenerative abiity
cardiomyocytes
can divide at a modest rate, but if injured is mostly replacced by connective tissue
smooth muscle
regenerates throughout life
sarcopenia
loss of muscle mass
-age 30
intermittent claudication
limping