Chapter 5
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary terms related to the structure and function of the skin and hypodermis, including epidermal layers, cell types, dermal structures, skin appendages, and common integumentary conditions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Skin
The body's largest organ, accounting for 7% of body weight, divided into epidermis and dermis, with varying thickness.
Epidermis
The outermost and superficial layer of the skin, composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Dermis
The second major region of the skin, lying deep to the epidermis, composed of strong, flexible connective tissue.
Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Tissue layer lying deep to the dermis, also known as superficial fascia, composed of areolar and adipose tissues, anchoring the skin and insulating the body.
Cells in the epidermis: Keratinocytes
The most abundant cell type in the epidermis, producing keratin and antibiotics and enzymes, arising from the deepest layer and dead at the skin's surface.
Keratin
A tough, fibrous protein produced by keratinocytes that gives the epidermis its protective properties.
Cells in the epidermis: Melanocytes
Cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis that manufacture and secrete melanin pigment.
Cells in the epidermis: Tactile epithelial cells (Merkel cells)
Sensory receptor cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis, attached to sensory nerve endings.
Cells in the epidermis: Dendritic cells (Langerhans cells)
Macrophage-like cells located in the stratum spinosum of the epidermis, functioning as part of the immune system.
Stratum basale (Stratum germinativum)
The deepest layer of the epidermis, attached to the underlying dermis, where cells actively divide and tactile epithelial cells and melanocytes are found.
Stratum spinosum
A layer of the epidermis containing thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin, and star-shaped dendritic cells.
Stratum granulosum
A layer of the epidermis consisting of a few layers of keratinocytes containing keratohyaline granules (to form keratin) and lamellar granules (containing waterproofing glycolipid).
Stratum lucidum
A clear layer within the epidermis present only in thick skin (palms and soles), composed of a few rows of flat, dead keratinocytes.
Stratum corneum
The thickest and most superficial layer of the epidermis, composed of dead keratinocytes and thickened plasma membranes, protecting skin against abrasion and penetration.
Dermis: Papillary dermis (superficial and thin)
The superficial layer of the dermis, containing dermal papillae that increase surface area for nutrient exchange.
Dermis: Dermal papillae
Protrusions of the papillary dermis into the epidermis that increase surface area and contribute to epidermal ridges.
Epidermal ridges (Friction ridges)
Elevations of dermal ridges that create fingerprints, increasing the gripping ability of hands and feet.
Reticular dermis
The deeper layer of the dermis, accounting for 80% of its thickness, composed of dense irregular connective tissue.
Cleavage lines
Represent separations between underlying collagen fiber bundles in the reticular dermis, important for surgical incisions.

Flexure lines
Deep creases in areas like palms, wrists, soles, and fingers where the dermis is closely attached to underlying structures.
Melanin
The most important pigment contributing to skin color, manufactured from tyrosine by melanocytes.
Carotene
A yellow-orange pigment obtained from the diet (e.g., carrots and tomatoes) that contributes to skin color.
Hemoglobin
The crimson color of oxygenated blood that shows through the epidermis, particularly in Caucasian skin where melanin content is low.
Nail
A scalelike modification of the epidermis, made of hard keratin.
Hair
A flexible strand of dead, keratinized cells made of hard keratin, consisting of a root embedded in the skin and a shaft projecting above the surface.
Medulla (deepest)
The central core of a hair.
Cortex
The layer surrounding the medulla of a hair.
Cuticle (superficial)
The outermost layer of a hair, composed of keratinized cells.
Arrector pili muscle
A bundle of smooth muscle attached to a hair follicle that contracts to make the hair stand erect, causing goosebumps.
Vellus hairs
Fine, short hairs that cover much of the body of women and children.
Terminal hairs
Coarse, longer hairs found on the scalp, in the axillary and pubic areas (after puberty), and as body hair on men.
Sebaceous glands
Glands occurring over the entire body (except palms and soles) that secrete an oily substance called sebum, usually associated with hair follicles.
Sebum
Simple aveolar gland. An oily substance secreted by sebaceous glands that collects dirt, softens, and lubricates hair and skin.
Holocrine secretion
A type of secretion where the entire cell breaks up to form the secretory product, as seen in sebaceous glands.
Eccrine gland
The most numerous type of sweat gland, found mostly on palms, soles, and forehead, producing watery sweat (blood filtrate) for temperature regulation. No smell
Apocrine gland
A type of sweat gland confined to axillary, anal, and genital areas, whose ducts open to hair follicles and produce a special sweat containing fats and proteins, contributing to body odor.
Modified apocrine glands: Ceruminous glands
Modified apocrine glands that secrete earwax.
Modified apocrine glands: Mammary glands
Modified apocrine glands specialized to produce milk.
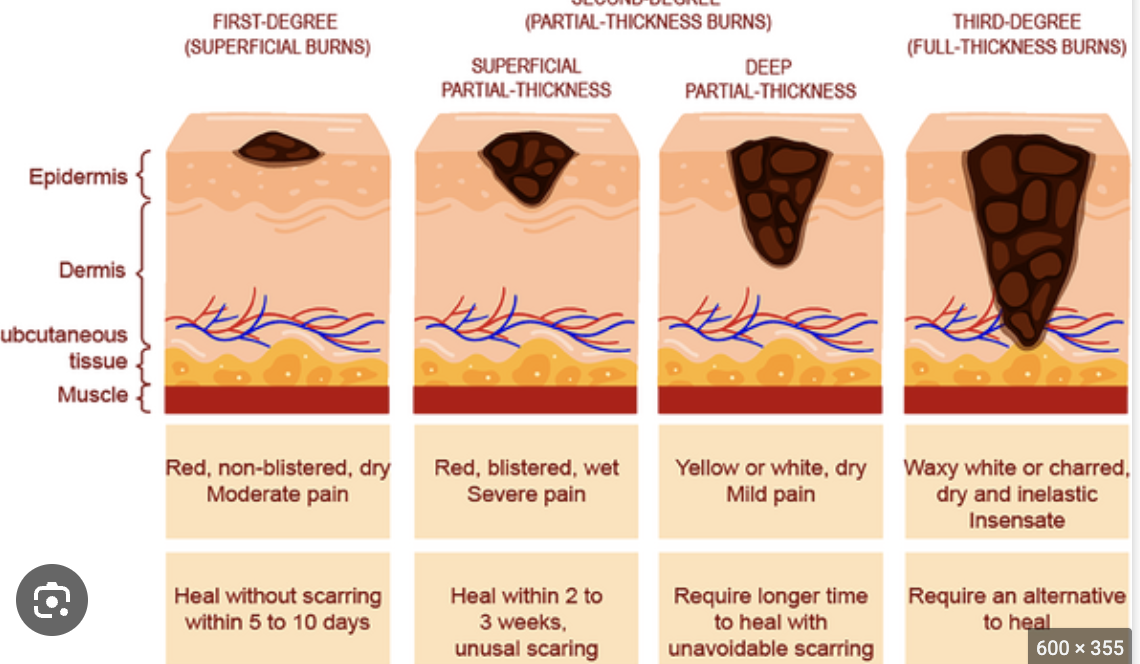
First-degree burn
A burn where only the upper epidermis is damaged, characterized by redness and pain but no blisters, healing rapidly.
Second-degree burn
A burn where the upper part of the dermis is also damaged, resulting in blisters, and typically healing with little scarring.
Third-degree burn
A severe burn that consumes the full thickness of the skin, appearing white, red, or blackened, and often requiring skin grafting.
Basal cell carcinoma
The least malignant and most common type of skin cancer, arising from cells in the stratum basale.
Squamous cell carcinoma
A type of skin cancer arising from keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum.
Melanoma
The most dangerous type of skin cancer, arising from melanocytes.
Lanugo
Fine, downy hairs that cover a fetus at 5-6 months of development.
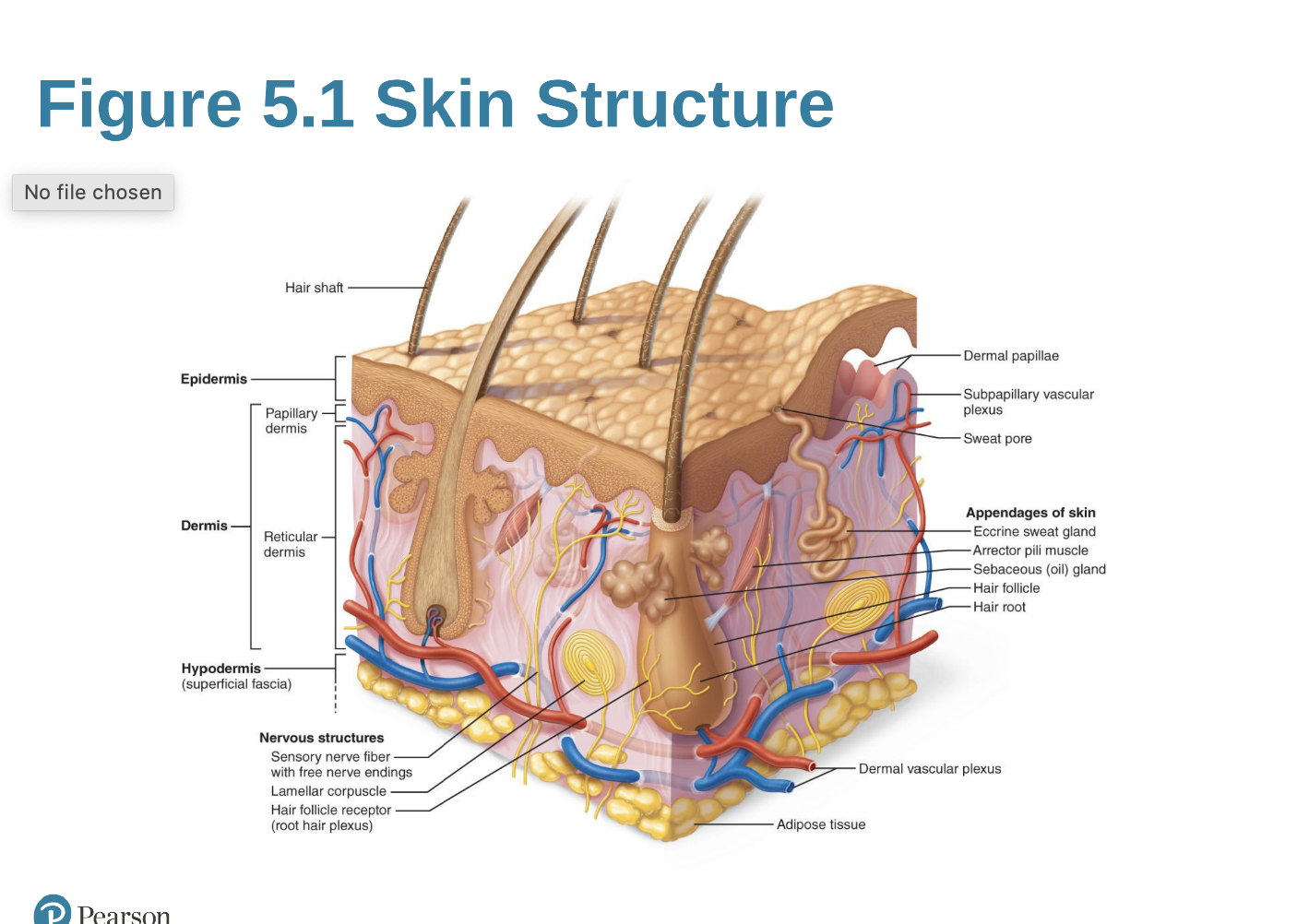
ID Structure
deep fascia
A connective tissue layer that surrounds muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, providing support and compartmentalization. Is between muscles and the hypodermis.
The Skin and Hypodermis (Five important functions): Protection
Cushions organs and protects from bumps,
chemicals, water loss, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation
The Skin and Hypodermis (Five important functions): body temperature regulation
Capillary network and sweat glands regulate heat loss
The Skin and Hypodermis (Five important functions): Excretion
Urea, salts, and water lost through sweat
The Skin and Hypodermis (Five important functions): production of vitamin D
Epidermal cells use UV radiation to synthesize vitamin D
The Skin and Hypodermis (Five important functions): Sensory reception
Contains sense organs associated with nerve endings
layers of the epidermis ( deep to superficial)
• Stratum basale
• Stratum spinosum
• Stratum granulosum
• Stratum lucidum (only in thick skin)
• Stratum corneum
Vascular plexuses
Network of blood vessels in the dermis that regulates temperature and supplies nutrients.
Dermal plexus
Network of blood vessels located between the reticular dermis and hypodermis, playing a crucial role in thermoregulation and nutrient supply.
Subpapillary plexus
plexus: Network of blood vessels located just beneath the papillary dermis, involved in thermoregulation and nutrient delivery to the epidermis.
hair thinning and baldness
Hair loss conditions characterized by reduced hair density and bald patches, often due to genetic, hormonal, or environmental factors.
Biggest concern beside infection of patient in hospital with burn
dehydration
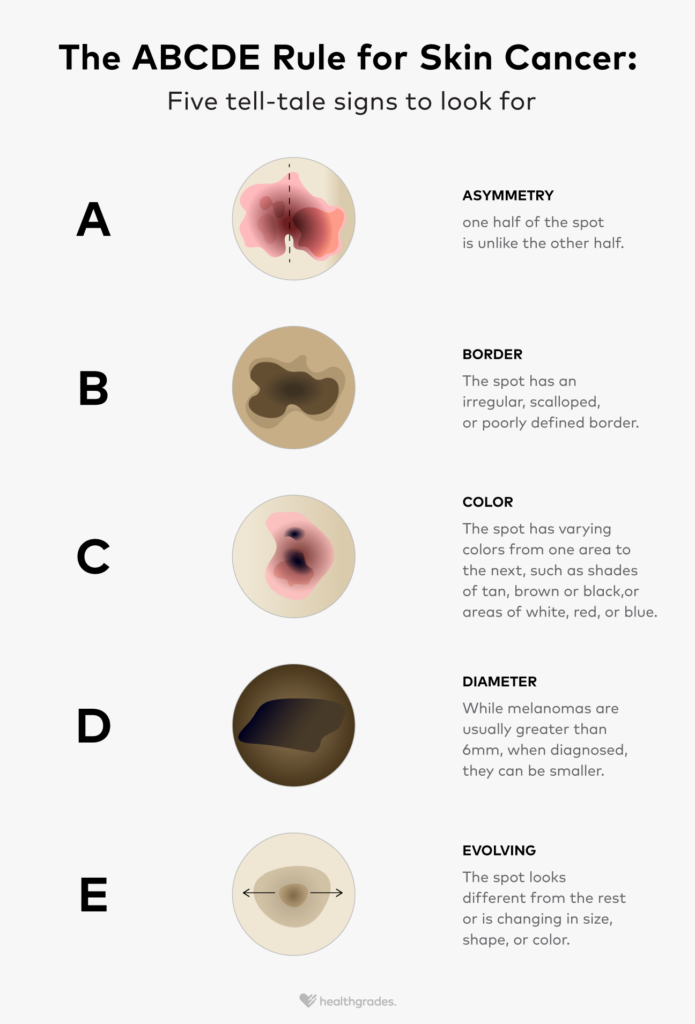
ABCDE Rules
A guide for melanoma detection that stands for Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, and Evolving.