Biology Final Exam
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Binary Fission
form of asexual reproduction in which batcteria divide
DNA replication
first step of bacterial replication
DNA is copied
Interphase
Nucleoli are present during this phase of the cell cycle, where the cell prepares for division by growing and replicating its DNA.
Telophase
Often accompanies cytokinesis, the final stage of mitosis, where the chromosomes decondense and the nuclear envelope re-forms around each set of chromosomes.
Prophase
Chromatin fibers become discrete chromosomes which become visible
Anaphase
Centromeres divide and sister chromatids become full-fledged chromosomes and migrate to opposite poles
Preometaphase
Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores during this phase
Miotic Phase
In what phase do both the contents of the nucleus and the cytoplasm divide that encompasses mitosis and cytokinesis
Prophase
First stage of mitosis, when centrosomes begin moving toward opposite poles and the nuclear envelope breaks up
Metaphase
occurs in the middle of mitosis, when the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and start their migration toward opposite poles during this phase of mitosis
Telophase
final stage of mitosis, when the chromosomes have arrived at the poles and the nuclear envelopes of the two new cells form
Cyokinesis
the division of the cytoplasm that occurs in conjunction with telophase, the last phase of mitosis
Three
How many major checkpoints are there in mitosis that regulate the process of the cell cycle
G1 phase
A
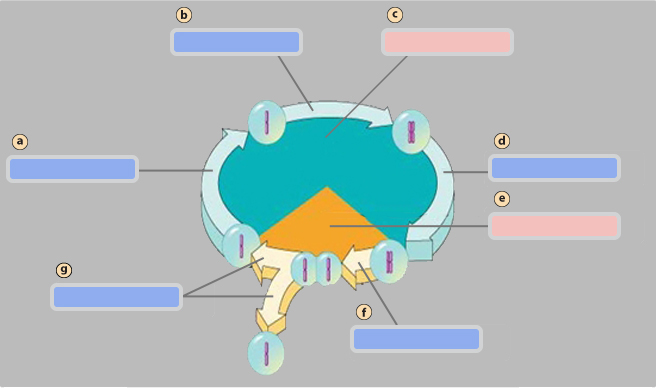
S phase
B
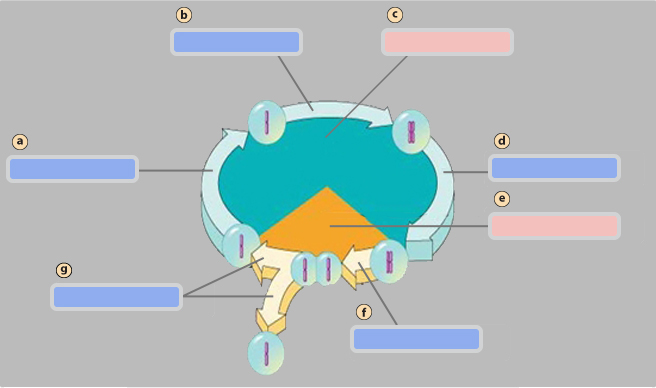
Interphase
C
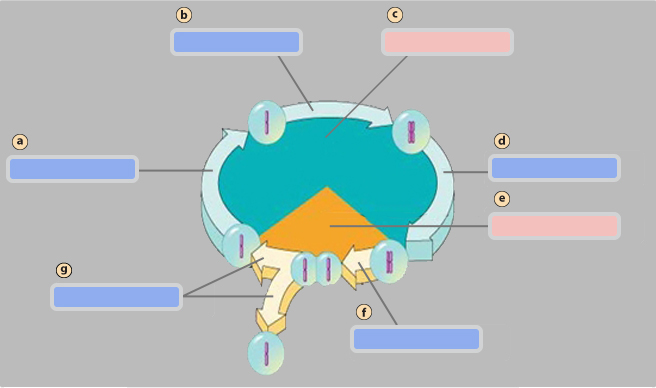
G2 phase
D
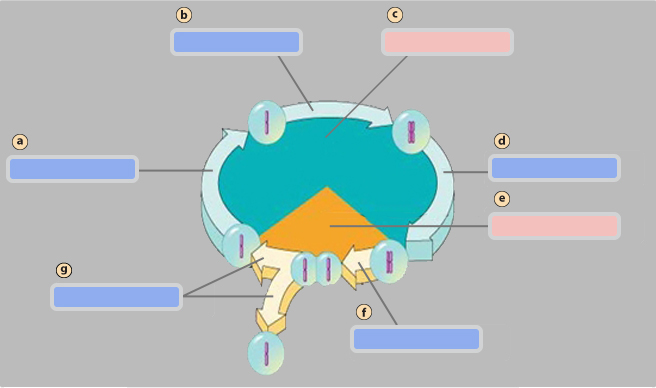
Mitotic (M) phase
E
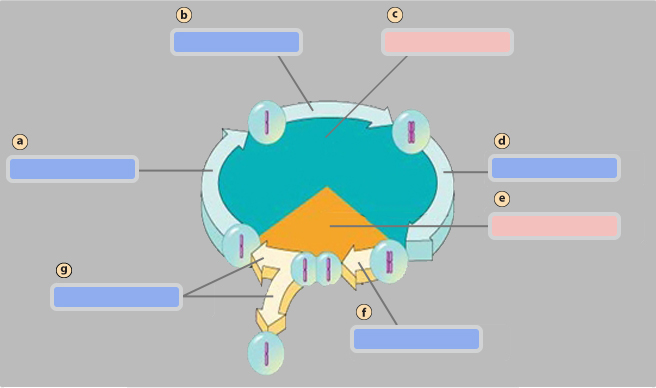
Mitosis
F
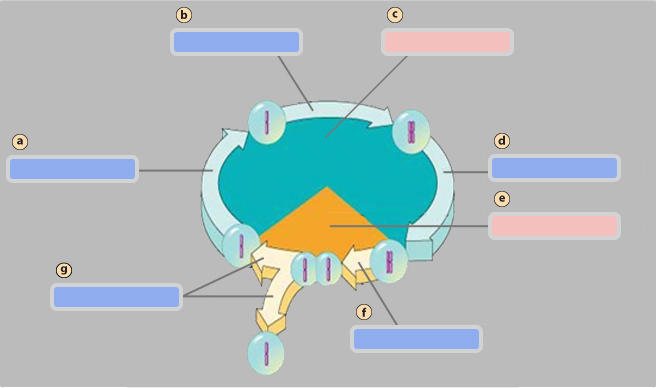
Cytokinesis
G
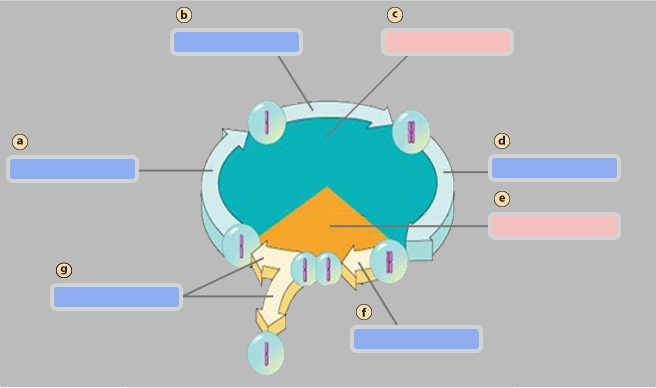
Pair of homologous chromosomes
A
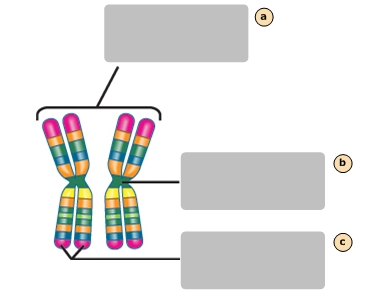
Centromete
B
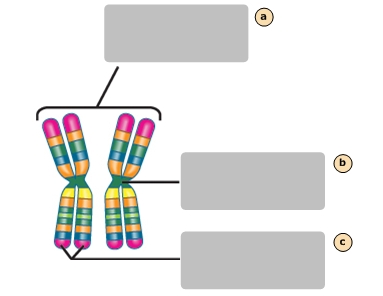
Sister chromatids
C
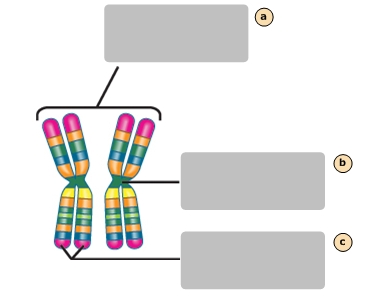
Fat
Carcinogen that promotes colon cancer
Four
How many haploid cells does Meiosis produce
One
How many diploid cells does Meiosis start with
Prophase I
Phase of meiosis in which homologous chromosomes stick together in pairs Segments of nonsister chromatids trade places resulting in recombination.
two
Meiosis I produces _____ cells, each of which is haploid
haploid
Meiosis I produces two cells, each of which is _____.
haploid
Meiosis II typically produces four cells, each of which is _____.
four
Meiosis II typically produces _____ cells, each of which is haploid.
Anaphase II
Phase in meiosis in which sister chromatids separate
Telophase I
At the end of ______ and cytokinesis, haploid cells contain chromosomes that each consist of two sister chromatids
Prophase I
Phase in meiosis in which synapsis occurs
Synapsis
the pairing of homologous chromosomes
Anaphase I
Phase in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes migrate to opposite poles
Metaphase II
Phase in meiosis in which chromosomes align single file along the equator of a haploid cell
Telophase II
Phase in meiosis in which at the end there are four haploid cells
Prophase II
Phase in meiosis in which a spindle forms in a haploid cell
Homozygous
When both of the alleles of a given gene pair are the same
Gene pool
All the genes in a population are that population’s _____.
Genetic drift
a process based on the role of chance
Mutation
Occurs when there is a change in the DNA sequence of a gene
Gene flow
Due to the fact that when people travel or migrate they take their alleles with them, the ease of travel across the globe increases _____.
Metaphase I
Homologous pairs of chromosomes are lined up independently of other such pairs during _____.
Thymine
Specific base pair of adenine
Cytosine
Specific base pair of guanine
Nuclotides
DNA is composed of building blocks called
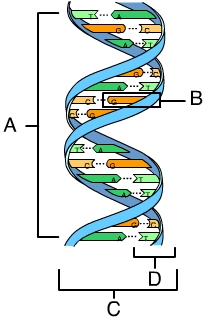
Double helix
Eukaryotic DNA organization appearance
Helicase
first step in the replication of DNA is catalyzed by
template
An old DNA strand is used as a _____ for the assembly of a new DNA strand.
ligase
Short segments of newly synthesized DNA are joined into a continuous strand by
D
Which of these is responsible for the catalyzing the formation of an RNA primer
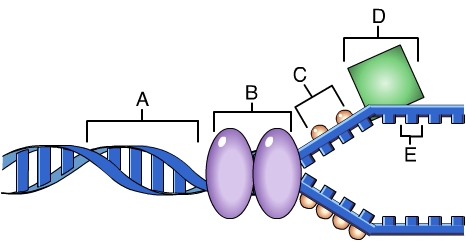
DNA polymerases
build new strands of DNA by adding DNA nucleotides onw at a time
ligase
The molecule that seals the gaps between the pieces of DNA in the lagging strand
B
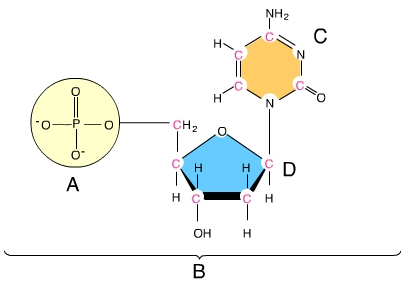
nucleotide
nucleotide
This us an image of a(n) ________
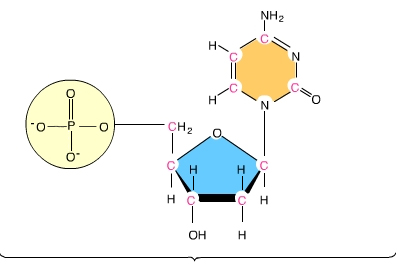
phosphate group
A
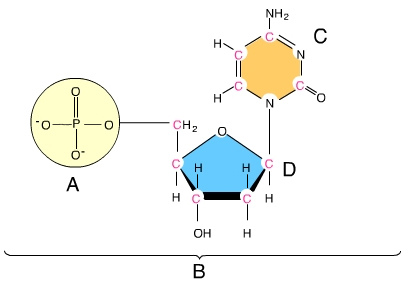
nitrogenous base
C
transcription
What name is given to the process in which a strand of DNA is used as a template for the manufacture of a strand of pre-mRNA
translation
the process by whuch information encoded in RNA is used to manufacture a polypeptide
RNA processing
the name given to the process in which pre-mRNA is edited into mRNA
amino acids
Polypeptides are assembled from
mRNA
RNA processing converts the RNA transcript into
RNA polymerase
Grey unit represents

the promoter
green unit represents

DNA
the blue strand represents the

tRNA
B
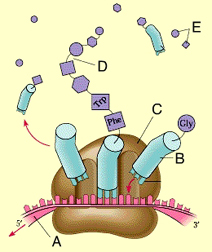
true
The site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm is the ribosome. True or False?
RNA polymerase
protein made up of amino acids
Information
what does mRNA carry away from the nucleus
Ribsosome
the site of protein synthesis in the cell
gametes
For a mutation to affect the evolution of an animal species, it must occur eithin
Gene expression
a term that relates to the flow of genetic information from DNA to proteins
Codominance
a pattern of inheritance in which heterozygotes express phenotypes of both of the homozygotes
homozygous
an organism that has two identical alleles of a gene for a given character
polygenic inheritance
a form of inheritance in which the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between either of the homozygous phenotypes
heterozygous
an organism that has two different alleles of a gene for a given character
phenotype
an organism’s traits- including its outward appearance, behavior, and other observable or measurable characteristics
genotype
an organism’s genetic makeup — its actual combination of alleles
multiple alleles
when three or more alleles of the same gene exist in a population
bbgg
What is the genotype of the parent with orange eyes and white skin (both are recessive traits)
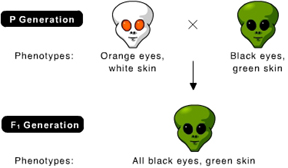
locus
Changing the physical position of a gene changes the gene’s
phenotype
the physical manifestation of an organism’s genes
dominant
if in a heterozygous individual, only one allele is expressed in the phenotype, that allele is
recessive
an allele whose effect is masked when paired with a dominant allele is
Heterozygotes
two different alleles
homozygous recessive
in pea plants, purple flower color is dominant to white flower color. Describe the genotype of a white flower
Pp
A purple flowered pea plant self-fertilizes and produces both purple and white offspring. What is its genotype?
Pp x pp
A pea plant with purple flowers (and unknown genotype is crossed with a pea plant with white flowers. One-half of the offspring have purple flowers and one half have white flowers. What are the genotypes of the parent plants?
dihybrid
A cross between two individuals with black eyes and green skin which results in an individual with orange eyes and white skin is an example of what kinf id cross
Anaphase I
During which phase of the cell cycle does the law of independent assortment occur?
Incomplete dominance
A pure breeding plant with red flowers is crossed with a pure breeding plant with white flowers. The offspring all have pink flowers. What pattern of inheritance does this involve?
heterozygous
When the two gametes that fuse to form a zygote contain different alleles of a given gene, the offspring is
nucleotides
What are the basic building blocks that are used to construct a gene?
recessive
what type of allele produces its effects in only homozygous individuals
segregation
What alleles on a pair of homologous chromosomes move into different gametes during meiosis
AB
Blood typing is often used as evidence in paternity cases in court. In one case, the mother had type B and the child has blood type O. What blood type could the father not have
Codominance
Occurs when both of the alleles in a heterozygote are equally expressed phenotypically in an individual