KNES 2600 Lecture 10 Axial Musculature
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Axial Musculature Grouping
Organized based on their location; muscles of the:
- head & neck
- vertebral column [superficial, intermediate, & deep]
- Respiration
- Abdominal wall
Muscles groups of the head and neck
- mouth region
- eye region
- scalp region
- neck region
- muscles of mastication
- muscles of head/neck movement
Mouth region muscles
[the majority of these muscles have a right & left]
- Orbicularis oris m.
compresses and purses lips
- Zygomaticus minor m.
retracts and elevates upper lip
- Zygomaticus major m.
retracts and elevates the corner of mouth e.g., laughing
- Buccinator m.
compresses cheeks
- Risorius m.
- Mentalis m.
orbicularis oris muscle
Flat band of muscle around the upper and lower lips
action: compresses and purses lips
Risorius muscle
a slender muscle on either side of the mouth that connects to the corners of the mouth
action: draws corner of the mouth laterally
zygomaticus minor muscle
Muscles on both sides of the face that extend from the zygomatic bone to the upper lips. [superior to the the major]
action: retracts and elevates upper lip [like when smiling]
![<p>Muscles on both sides of the face that extend from the zygomatic bone to the upper lips. [superior to the the major]</p><p>action: retracts and elevates upper lip [like when smiling]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/16a11da5-0b4d-414b-bcb1-aef119aa5a50.jpg)
zygomaticus major muscle
Muscles on both sides of the face that extend from the zygomatic bone to the angle of the mouth.
action: retracts and elevates the corners of mouth [like when laughing]
![<p>Muscles on both sides of the face that extend from the zygomatic bone to the angle of the mouth.</p><p>action: retracts and elevates the corners of mouth [like when laughing]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/53061571-c265-4676-babf-bffbdc80f65e.jpg)
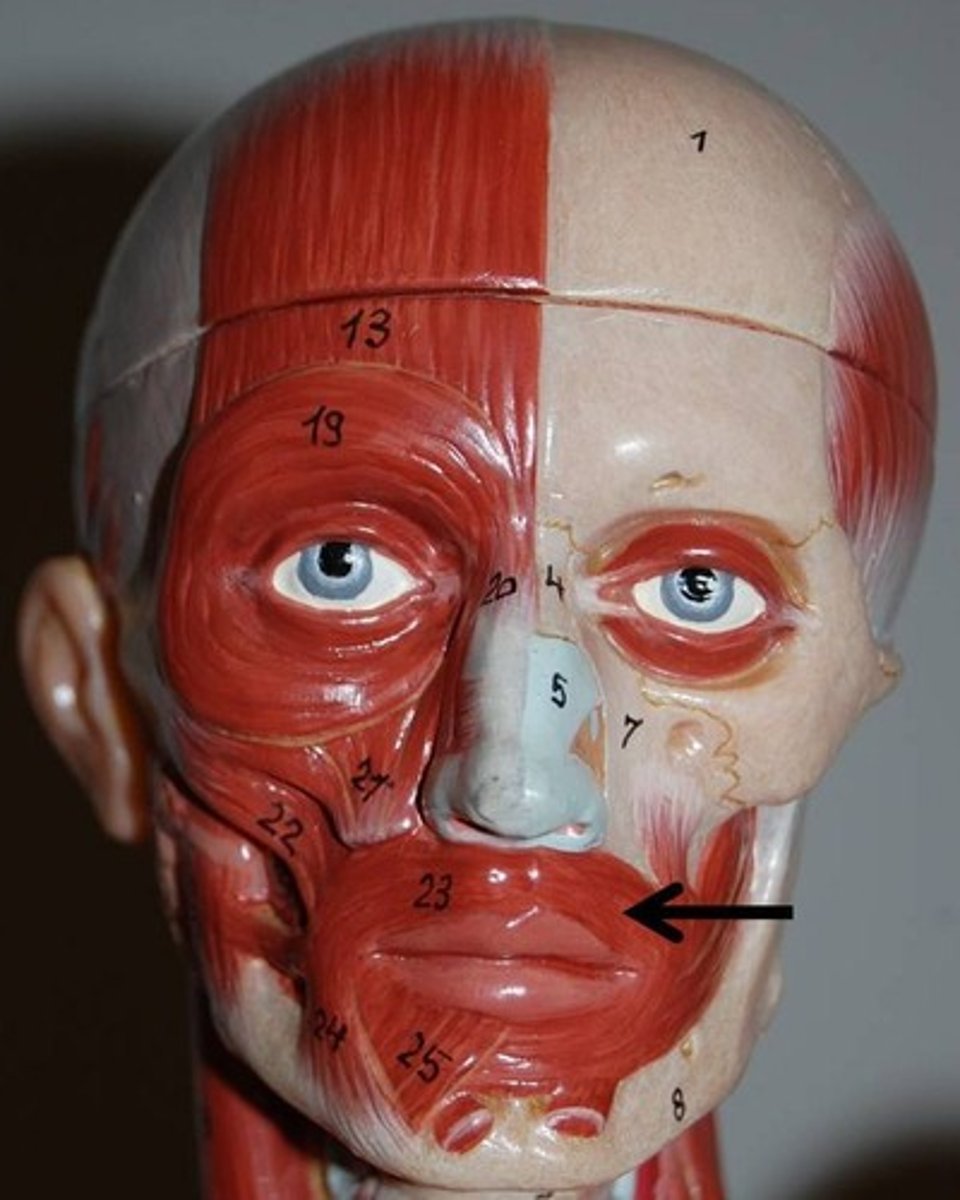
Mentalis muscle
triangular-shaped muscle located in the chin. It originates from the alveolar process of the mandible and inserts into the skin of the chin
action: protrude and evert the lower lip
buccinator muscle
Thin, flat muscle of the cheek between the upper and lower jaw
action: compresses cheeks
Muscles of the eye region
- orbicularis oculi m.
- corrugator supercilii m.
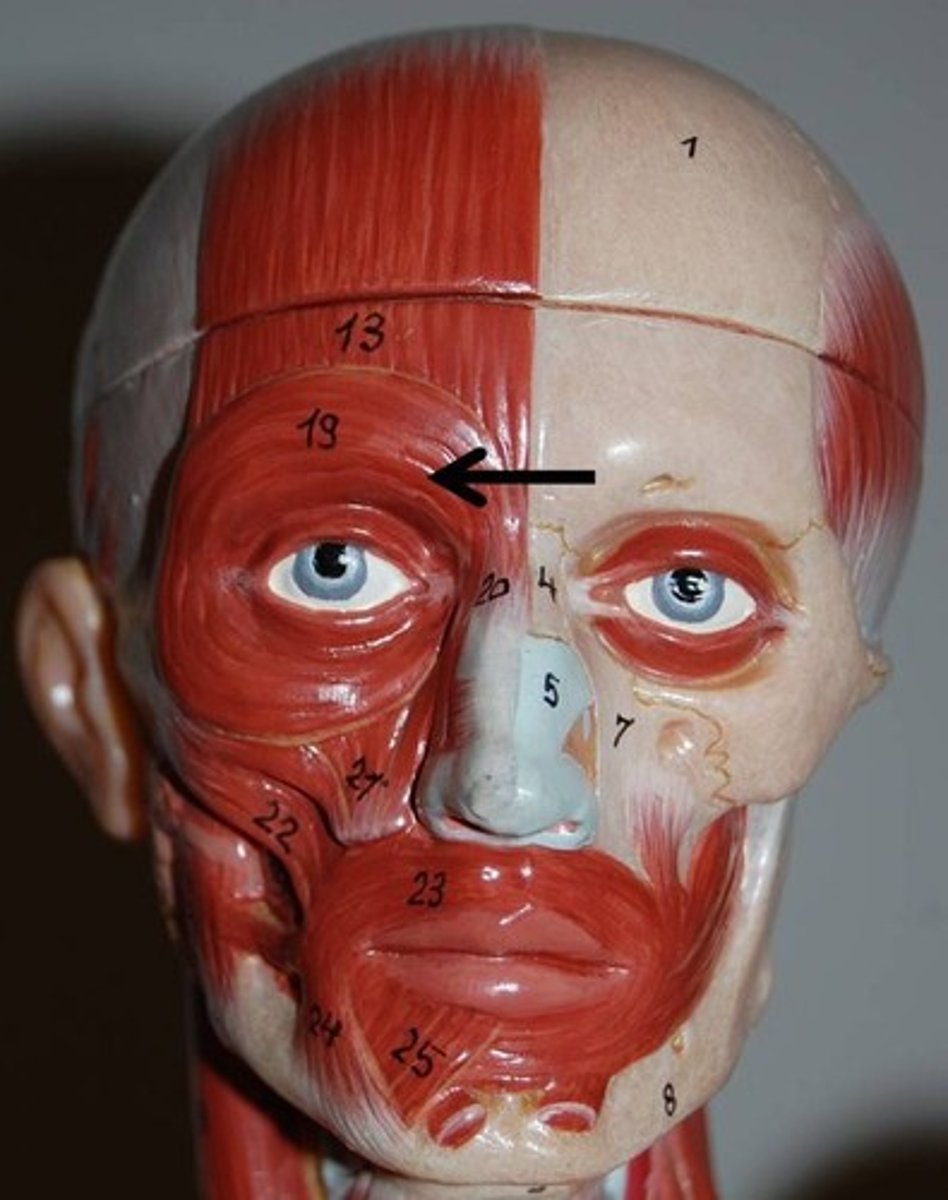
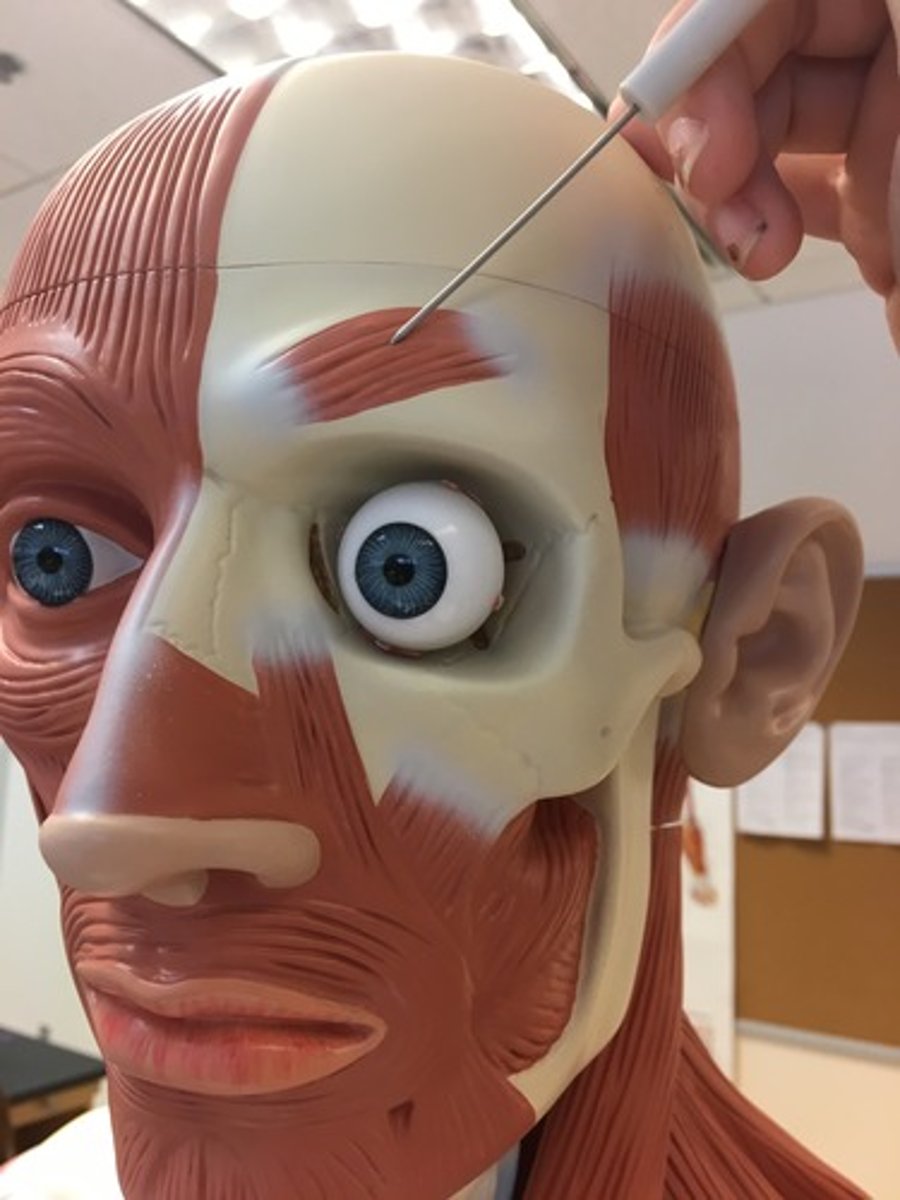
orbicularis oculi muscle
Ring muscle of the eye socket
action: closes the eyes
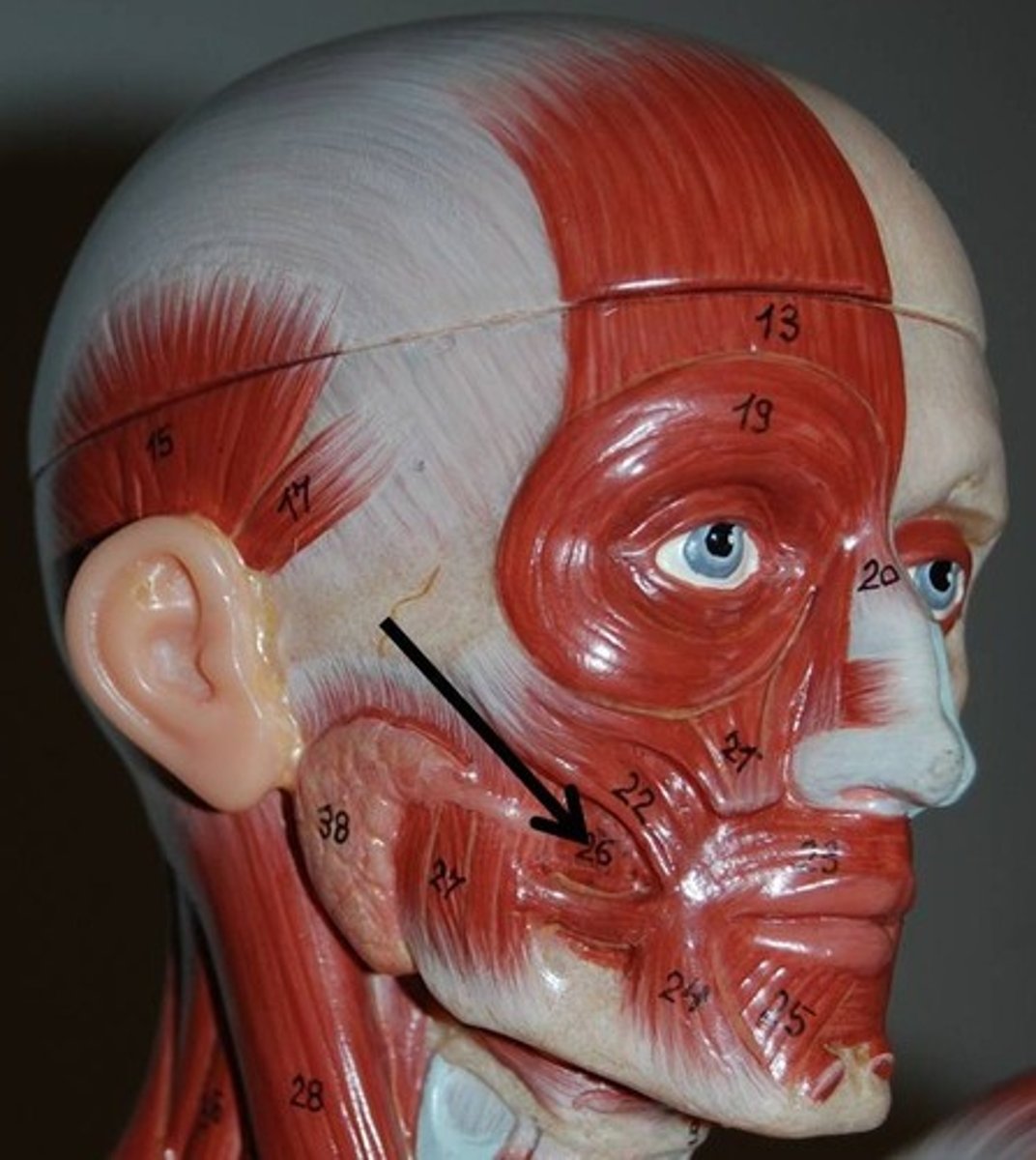
corrugator supercilii muscle
The small obliquely oriented muscle which lies between the frontal belly of the epicranius muscle and the orbicularis oculi muscle
action: pulls skin inferiorly and medially; wrinkles brow

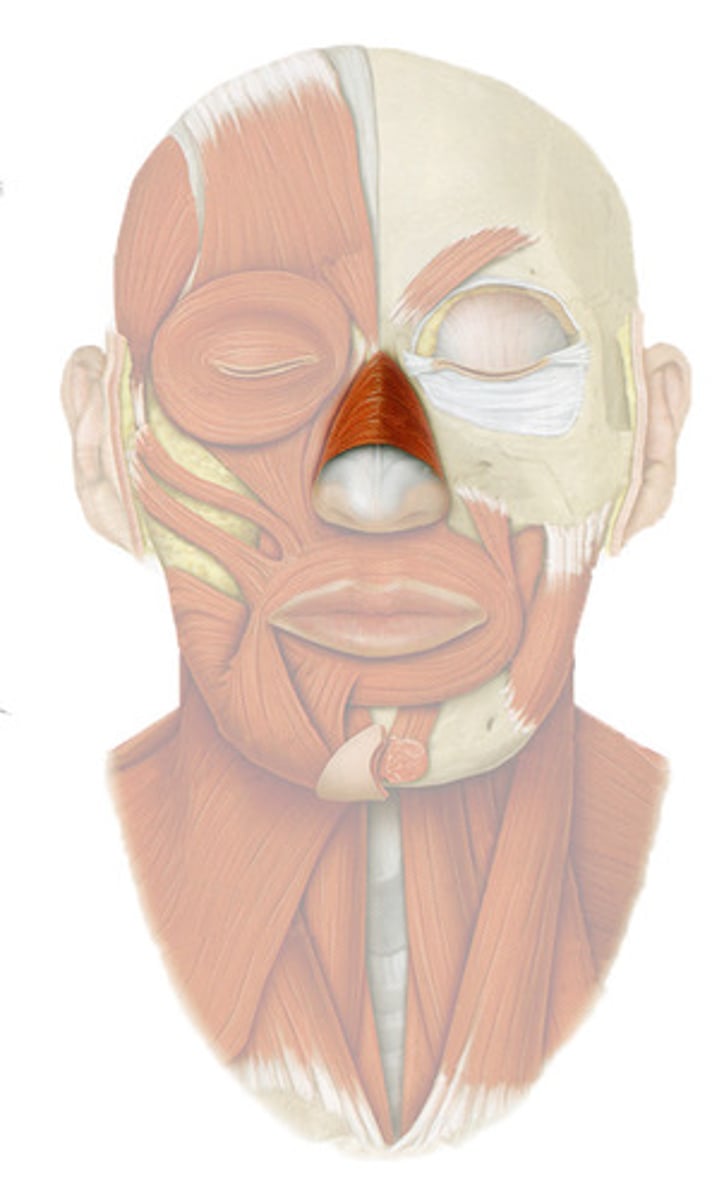
Muscles of the nose region
- Procerus m.
- Nasalis m.
Procerus muscle
Covers the bridge of the nose
action: wrinkles the nose
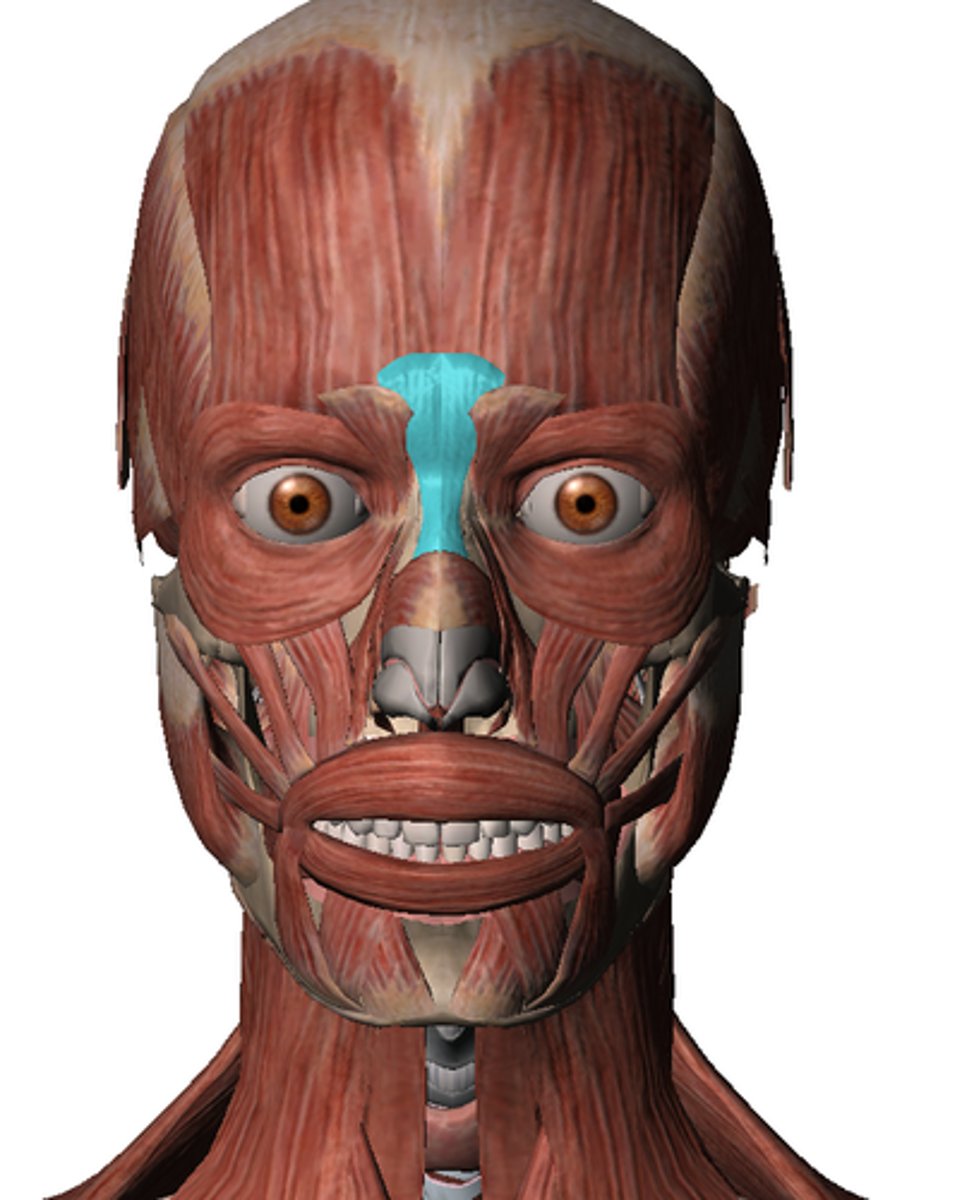

Nasalis muscle
Two-part muscle which covers the sides of the nose
action: compresses bridge, depresses tip of nose, elevates corner of nostrils
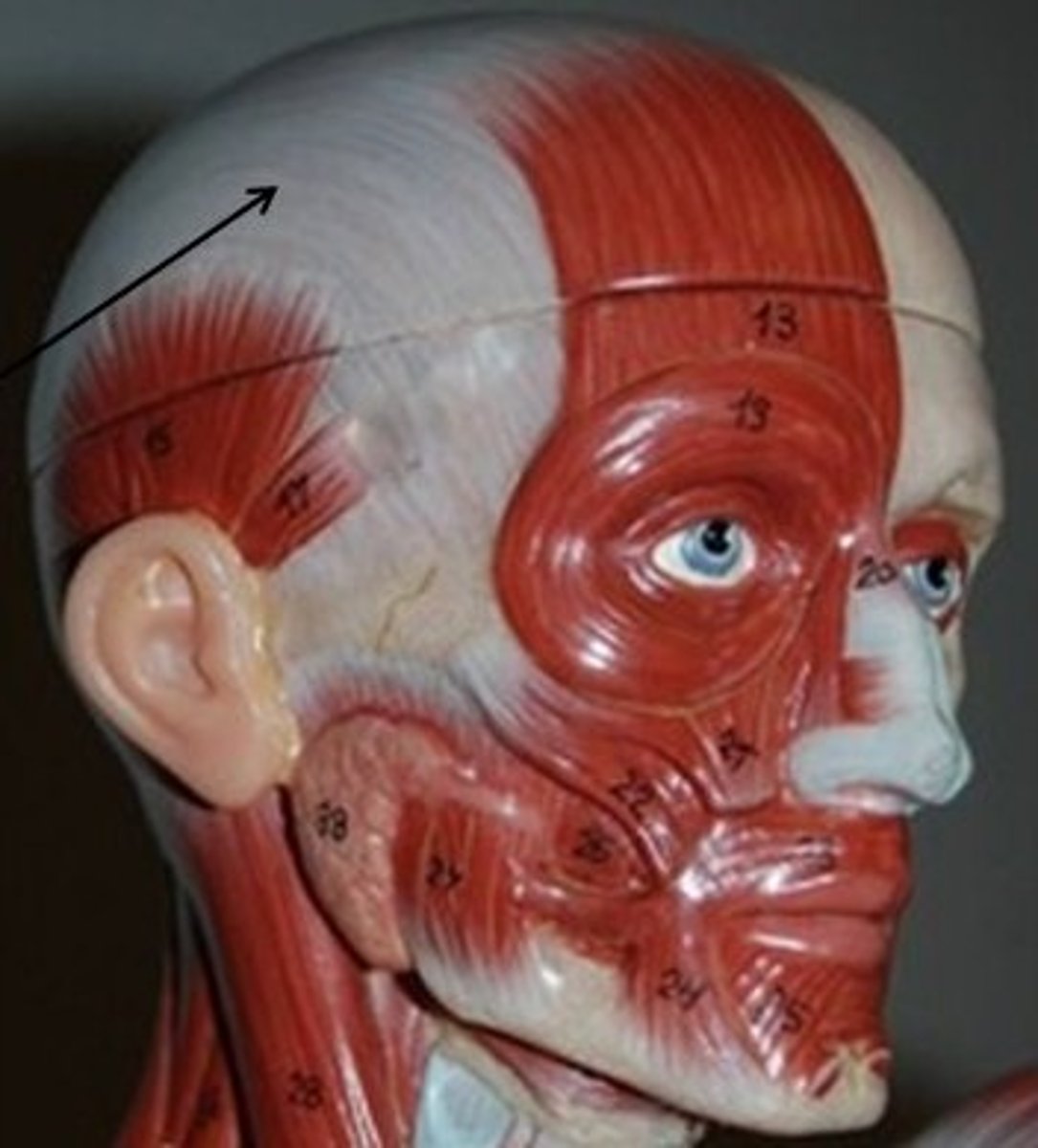
Muscles of the scalp region
- occipito frontalis m.
+ frontal belly of occipitofrontalis m.
+ occipital belly of occipitofrontalis m.
+ epicranial aponeurosis
- Superior Auricularis m.
- Anterior Auricularis m.
- Posterior Auricularis m.
frontal belly of occipitofrontalis muscle
muscle on the forehead
action: raises eyebrows, wrinkles skin of forehead
occipital belly of occipitofrontalis muscle
back of the head
action: tenses and retracts scalp
epicranial aponeurosis
the long flat tendon that connects the frontal & occipital bellies of the occipitofrontalis m.
Superior Auricularis muscle
highest muscle connected to the ear
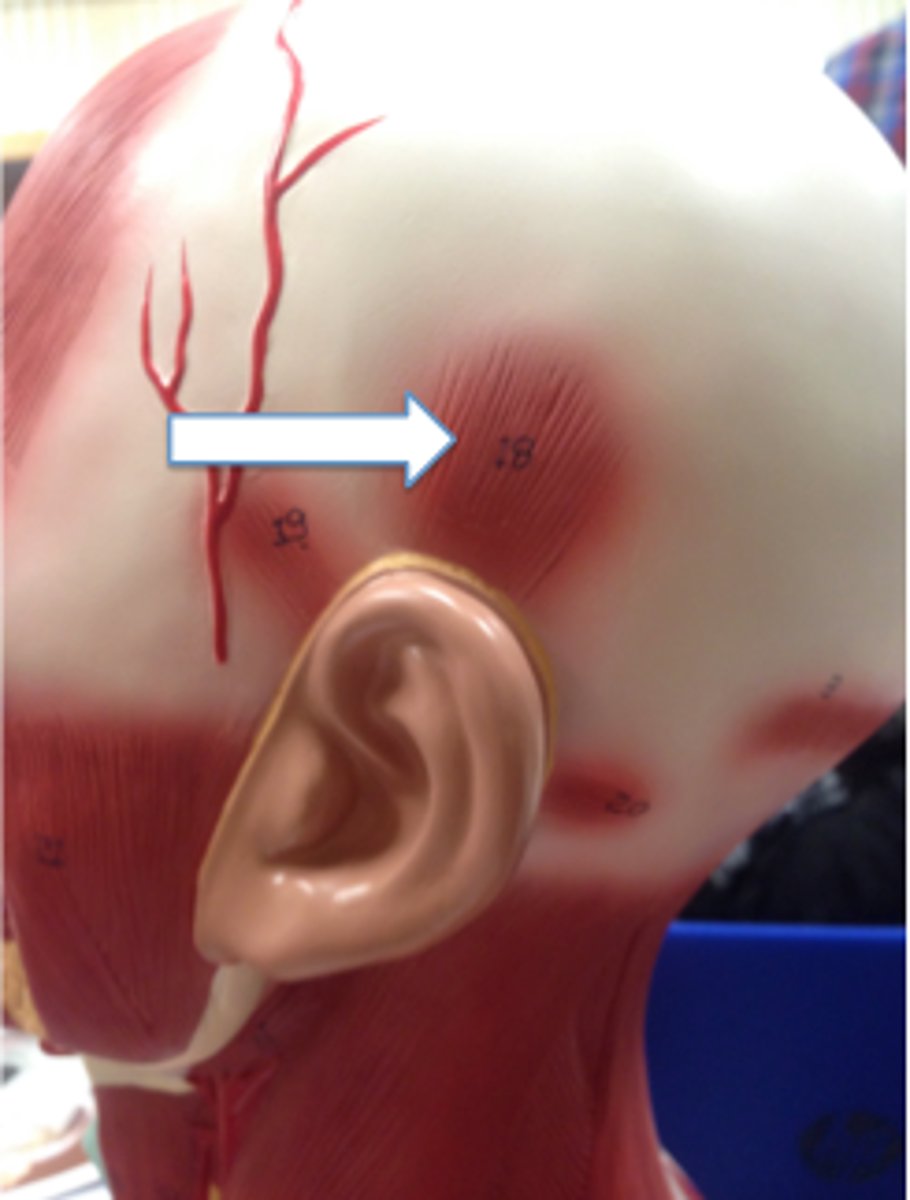
Anterior Auricularis muscle
furthest forward muscle connected to the ear
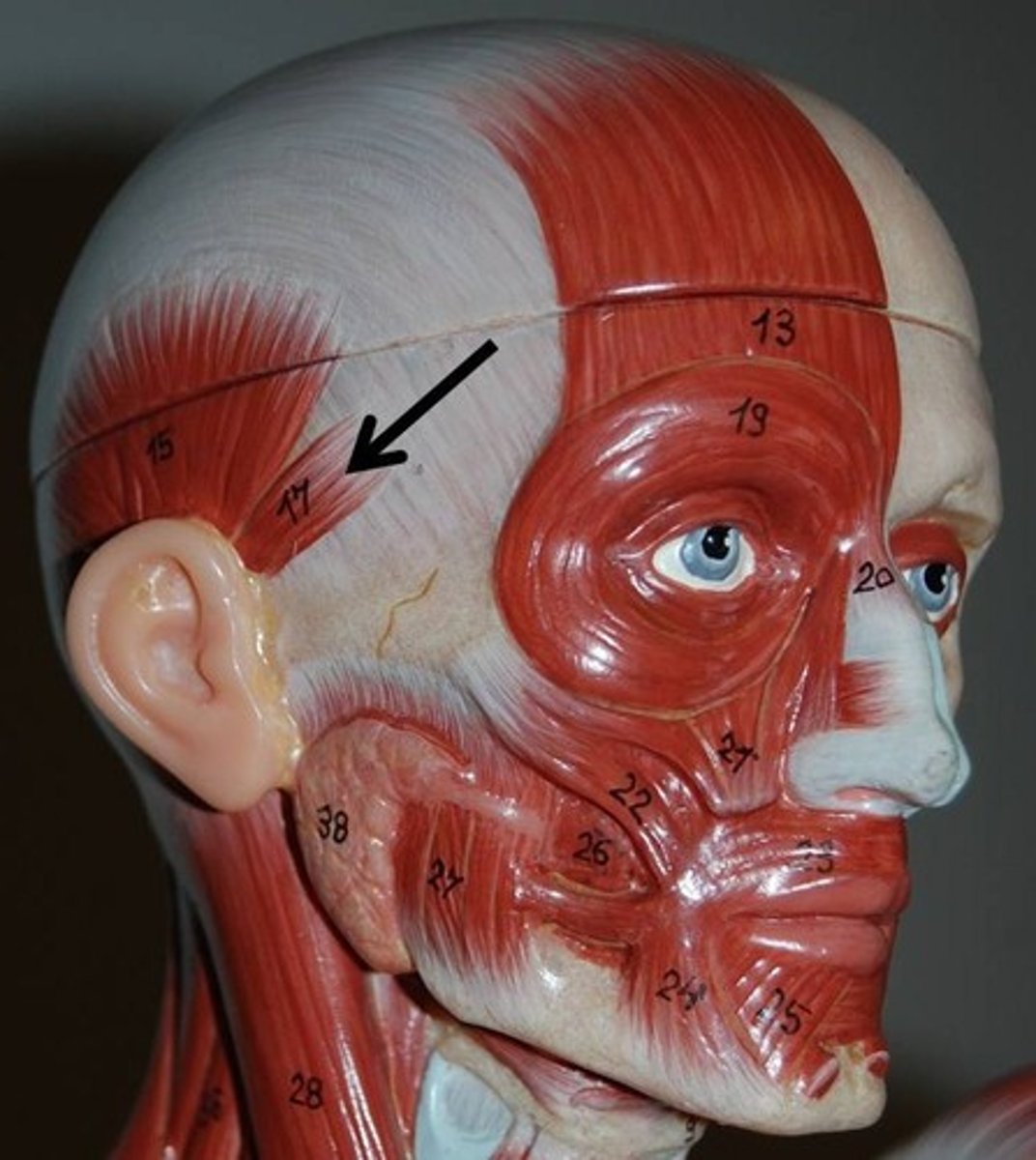
Posterior Auricularis muscle
furthest back muscle connected to the ear
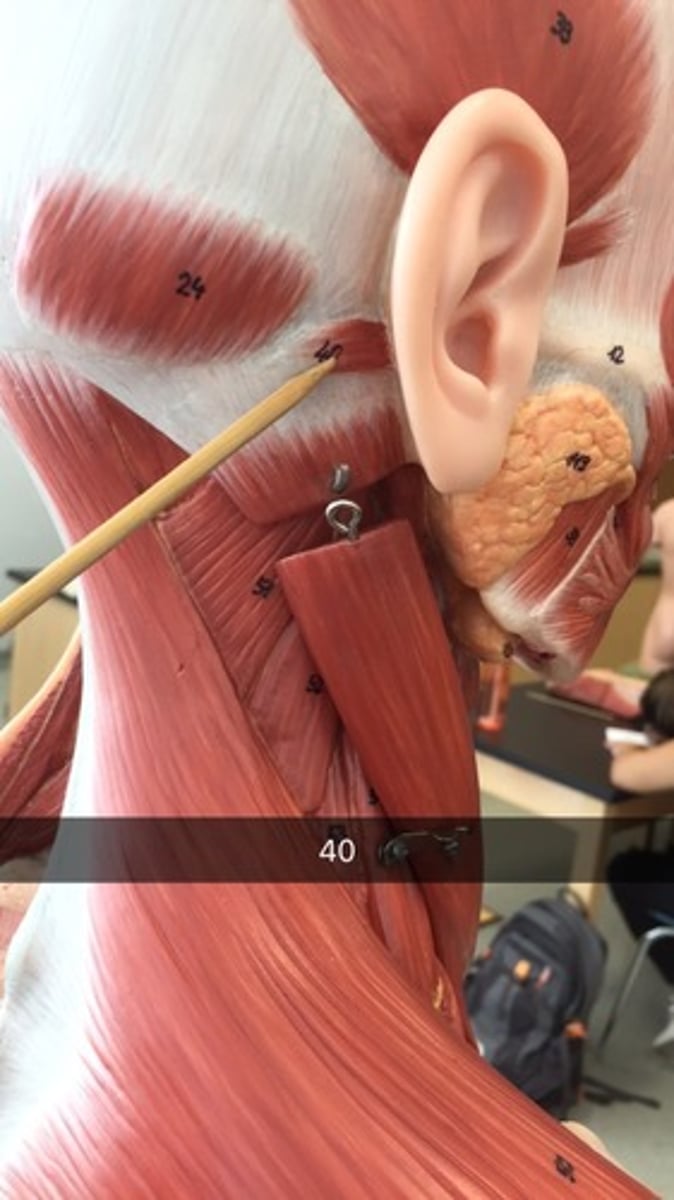
Muscles of the Neck region
- platysma m.
- sternocleidomastoid m.
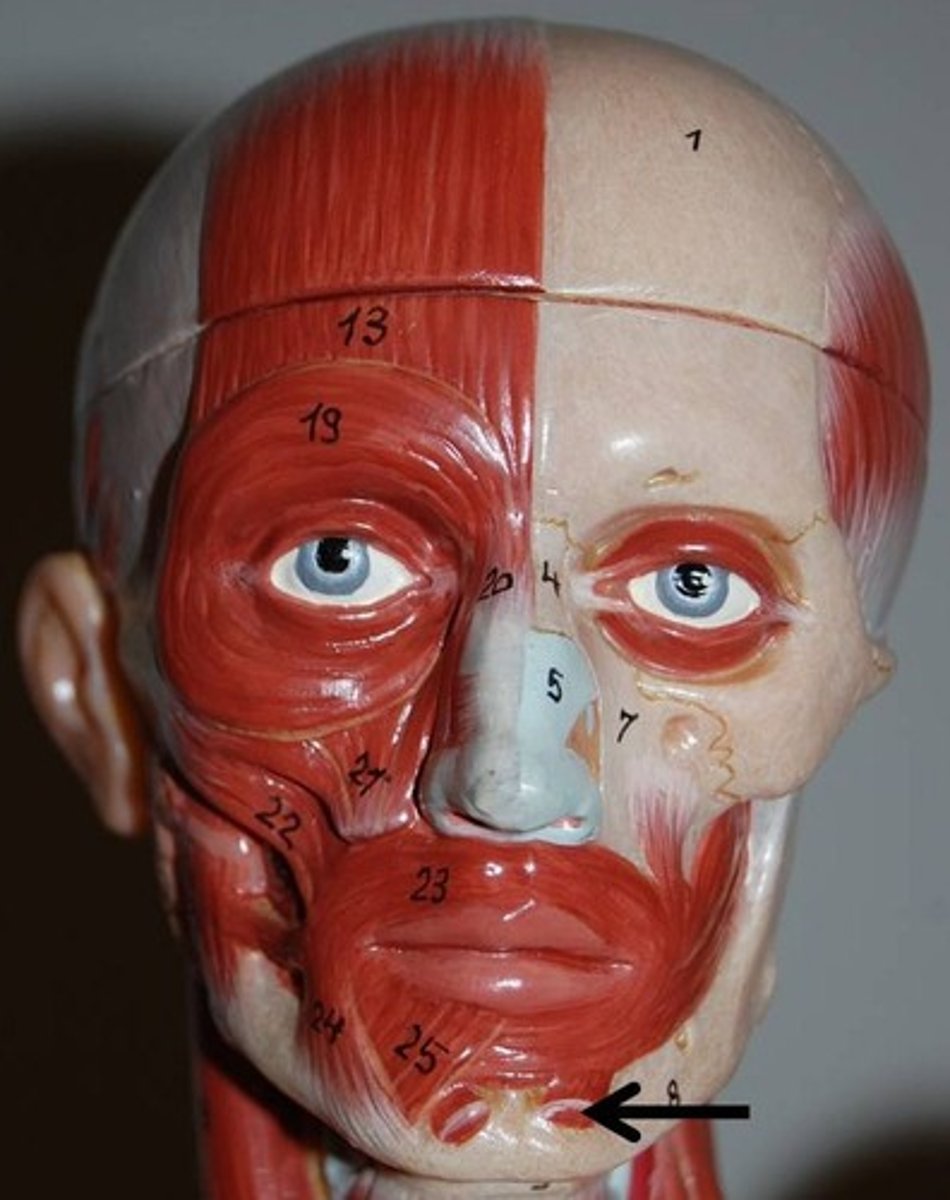
platysma muscle
Broad muscle extending from the chest and shoulder muscles to the side of the chin
action: tenses the skin of neck; pulls lower lip inferiorly
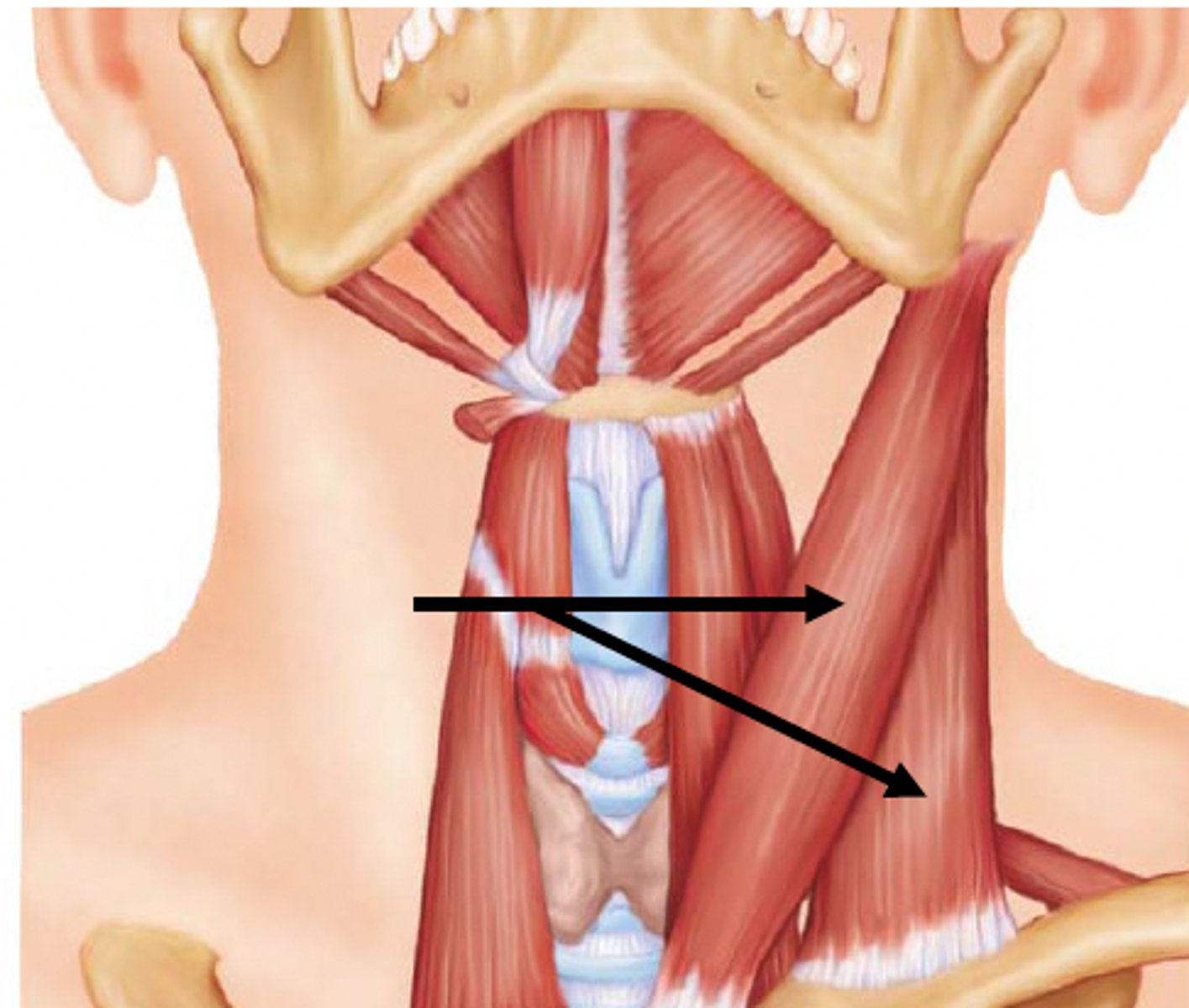
sternocleidomastoid muscle origin [2], insertion [1], & action
Origin:
manubrium; sternal end of clavicle
Insertion:
Mastoid process of temporal bone
action:
- unilateral: laterally flexes head to same side; rotates head opposite side
- bilateral: flexes neck; protracts head; aids in inhalation
Muscles of mastication
- masseter m.
- temporalis m.
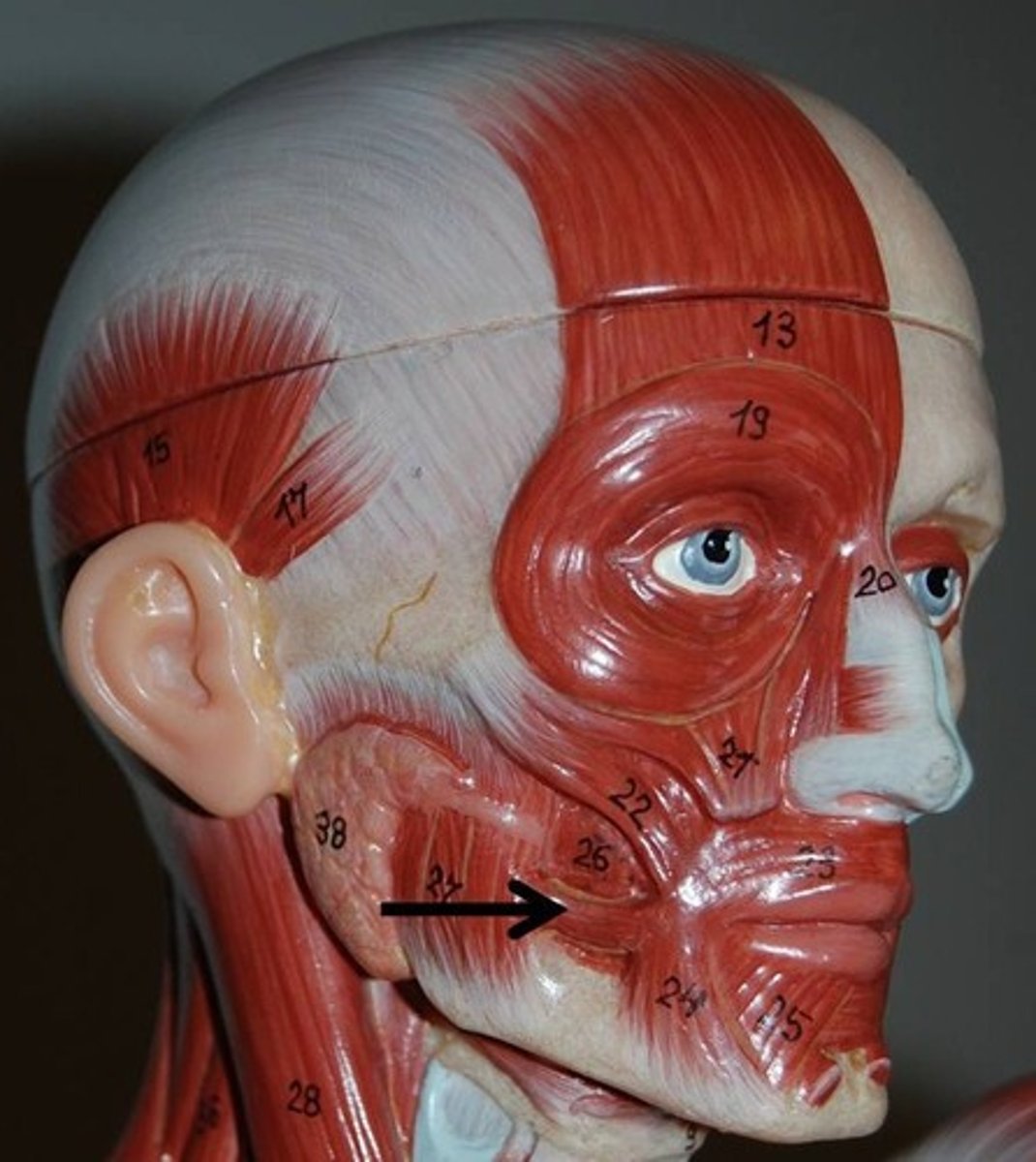
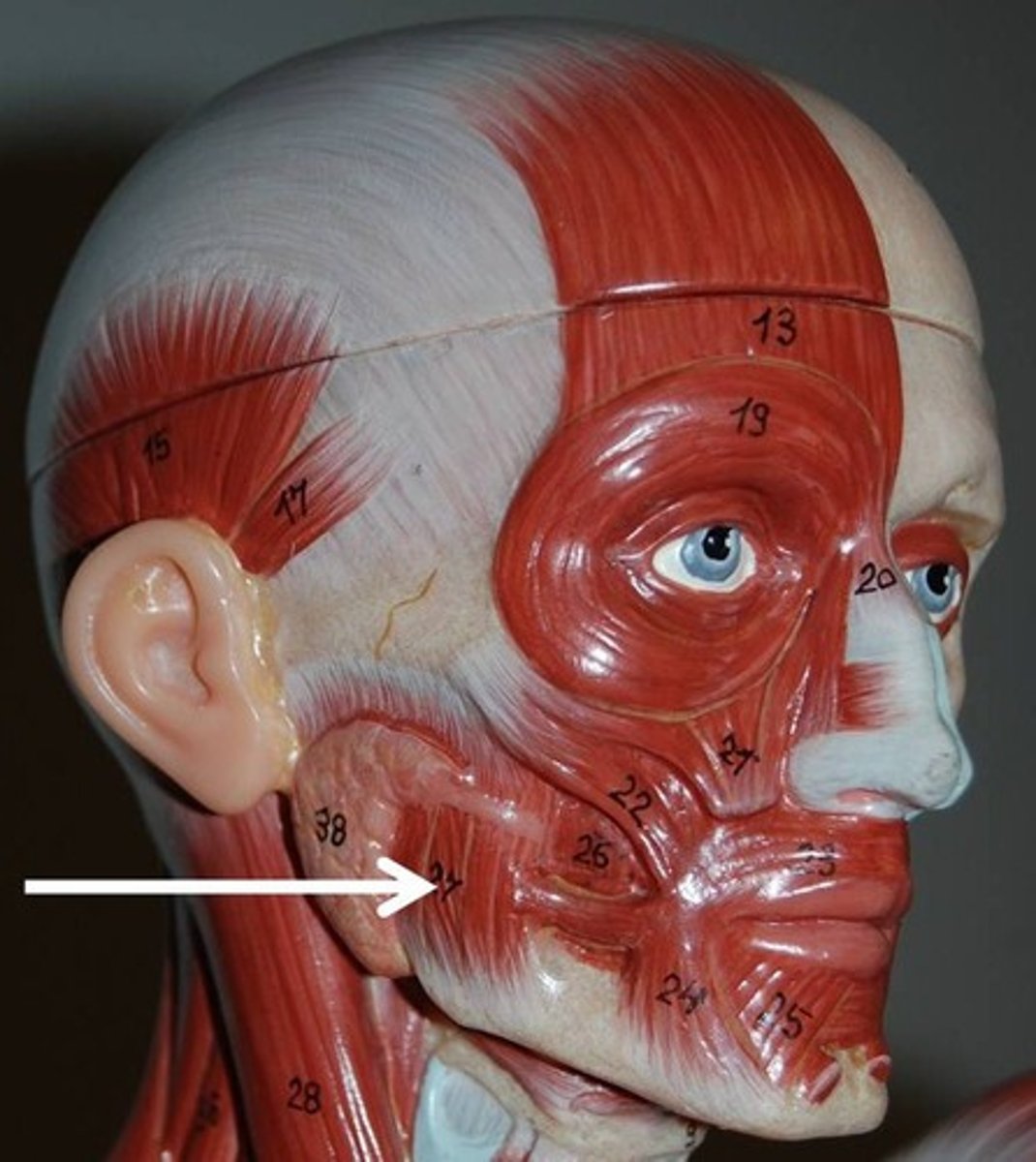
masseter muscle
Insertion: Mandible
Origin: Zygomatic arch
action: closes jaw; assists in protraction, retraction, and side to side movement of the mandible
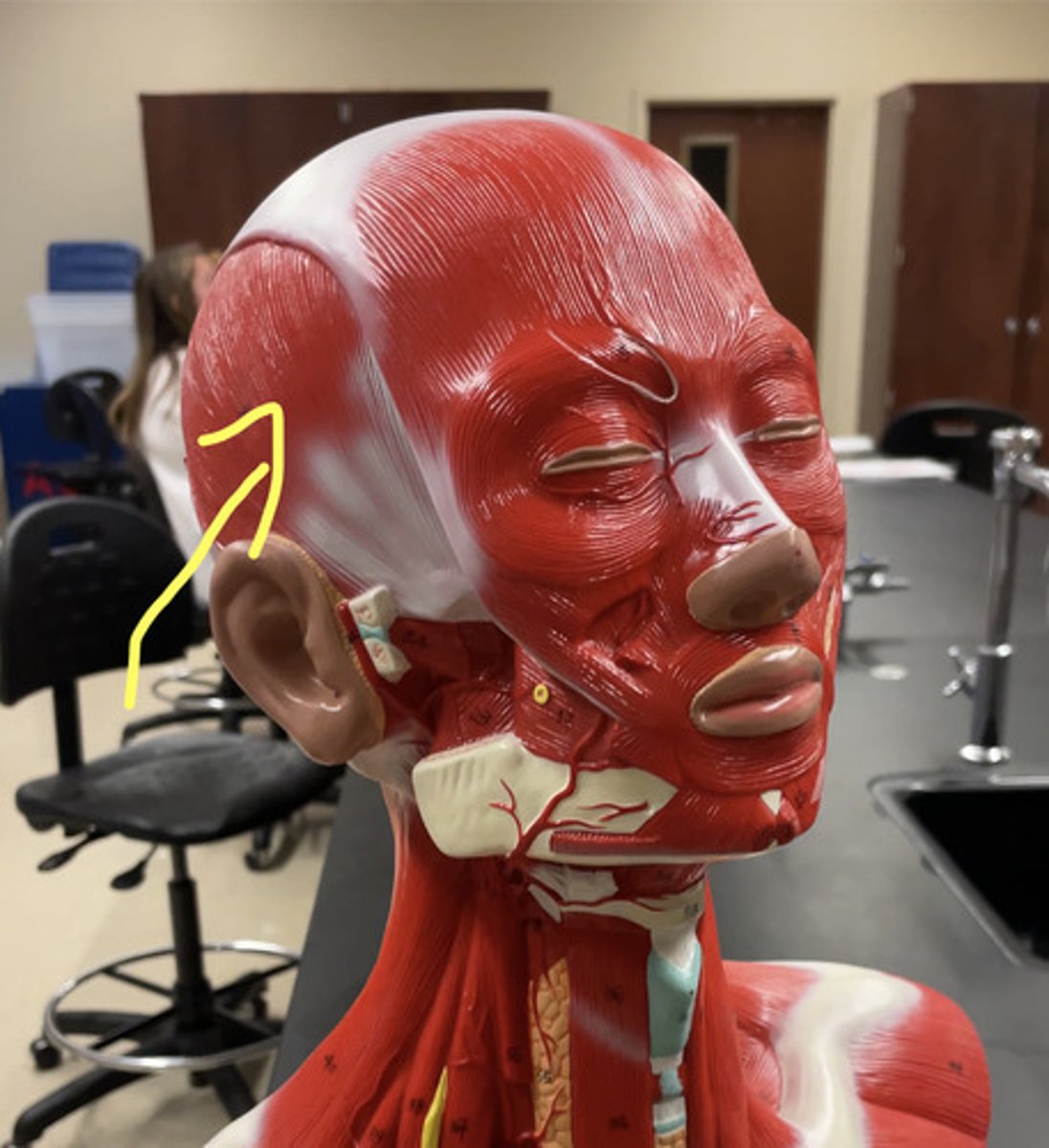
Temporalis muscle
muscles connecting to the sides of the head
action: close the jaw; assists in retracting and moving the mandible from side to side
Muscles that move the head and neck
- sternocleidomastoid m.
- scalenes mm.
+ anterior scalene m.
+ middle scalene m.
+ posterior scalene m.
scalene muscles: origin, insertion, and action
Origin:
transverse processes C2-C7
Insertion:
- anterior and middle - 1st rib
- posterior - 2nd rib
Action:
flexes and side bends the neck; elevates ribs 1 & 2 [aids in inhalation]
![<p>Origin:</p><p>transverse processes C2-C7</p><p>Insertion:</p><p>- anterior and middle - 1st rib</p><p>- posterior - 2nd rib</p><p>Action:</p><p>flexes and side bends the neck; elevates ribs 1 & 2 [aids in inhalation]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/255b6697-75cb-41e1-9f0c-f49e609eda6c.png)
anterior scalene m.
middle scalene m.
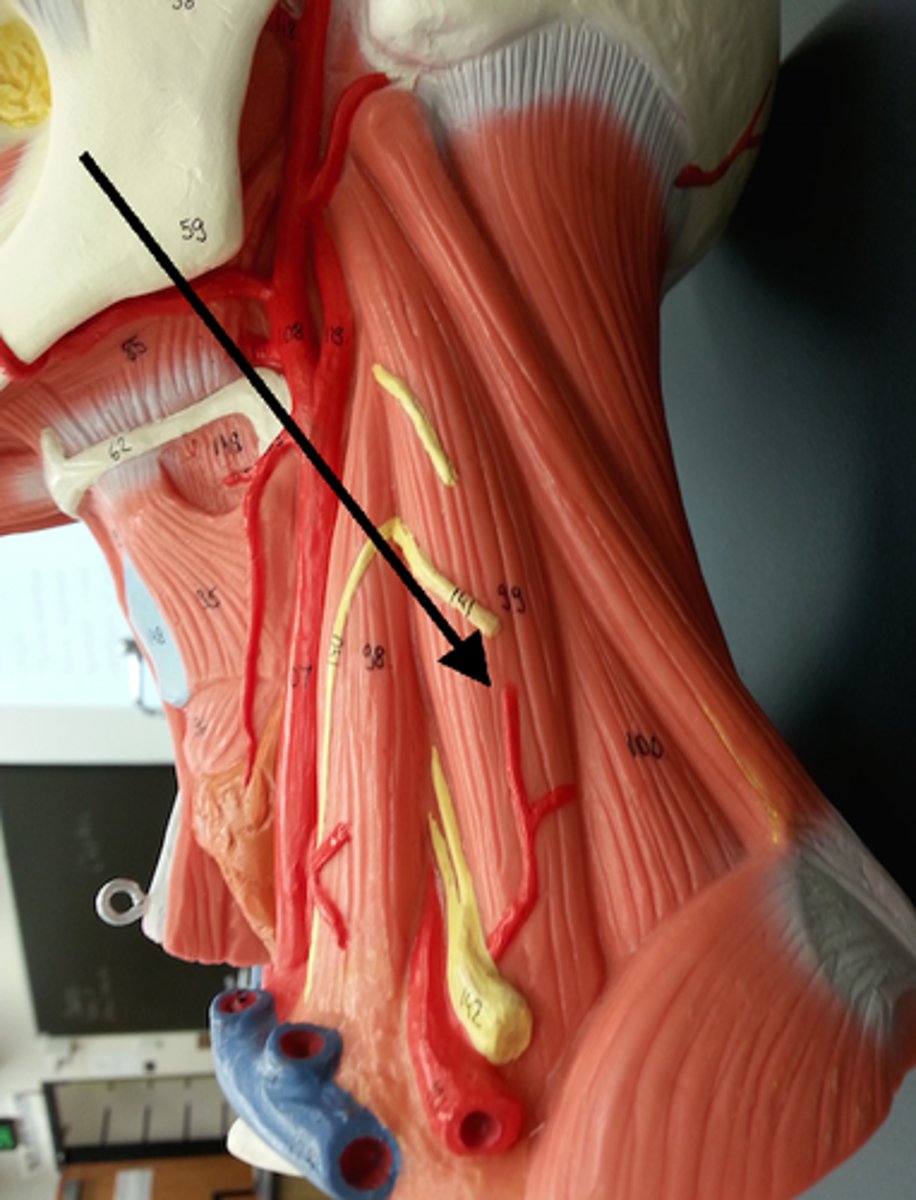
posterior scalene m.
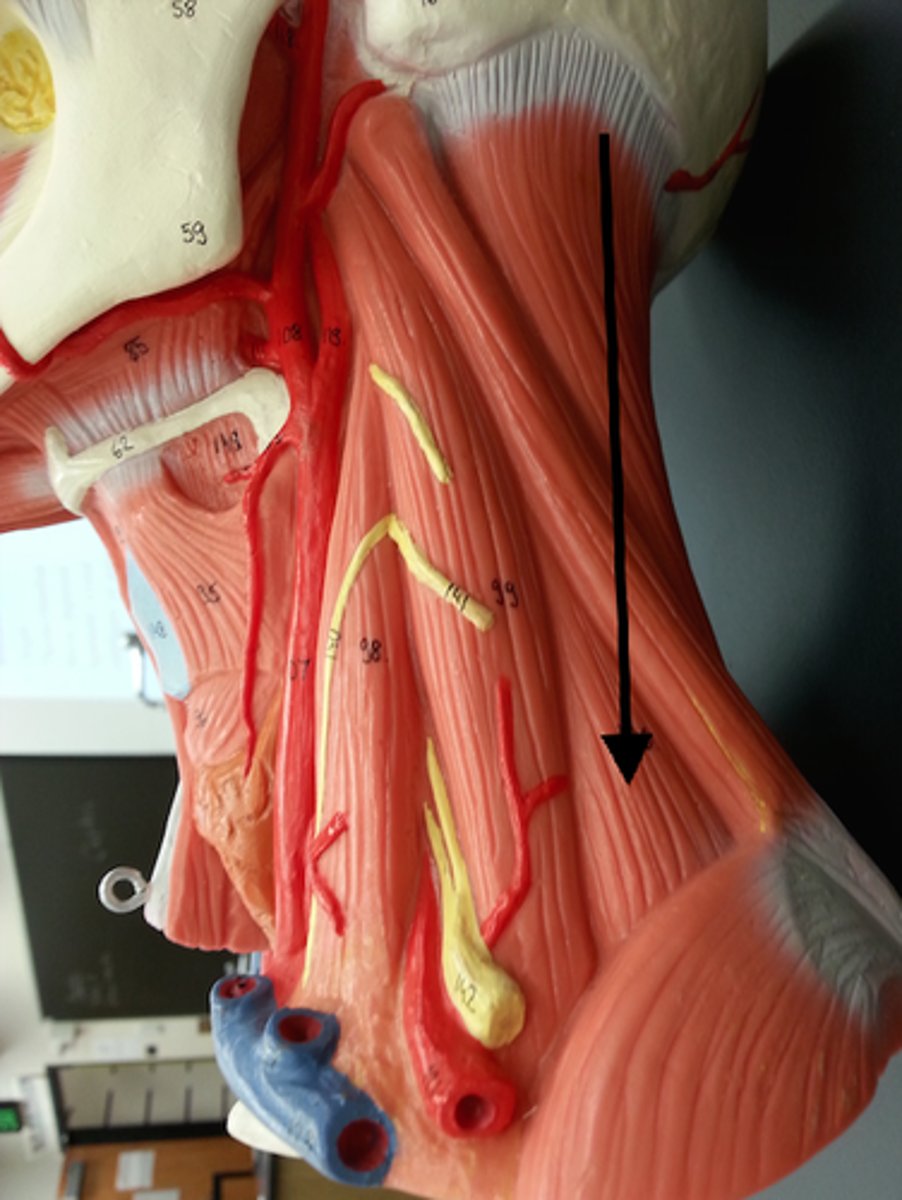
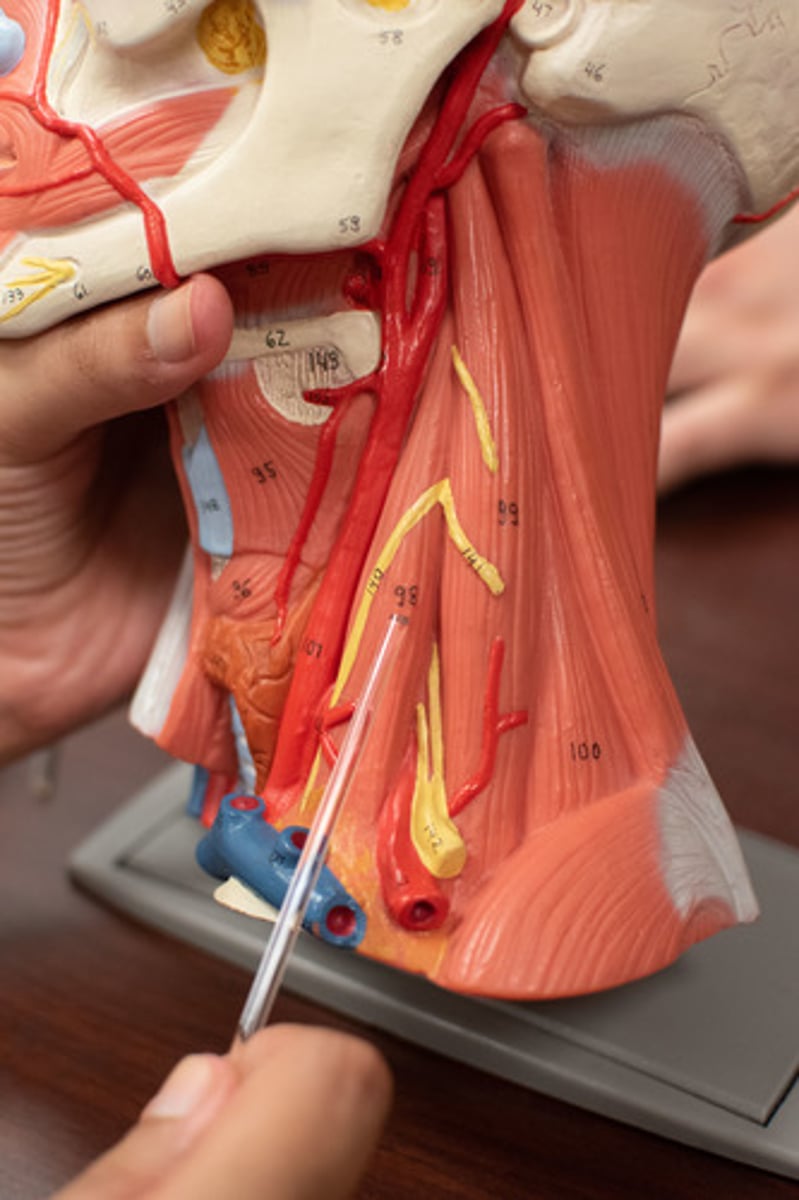
Scalene hiatus
opening formed by the anterior and middle scalene muscles
it allows for the passage of the subclavian artery & nerve bundles.
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Compression syndrome of upper limb neurovascular bundle at the level of scalene muscles and first rib. [the scalene hiatus is too small & compressed]
can be tested using the Adson Maneuver
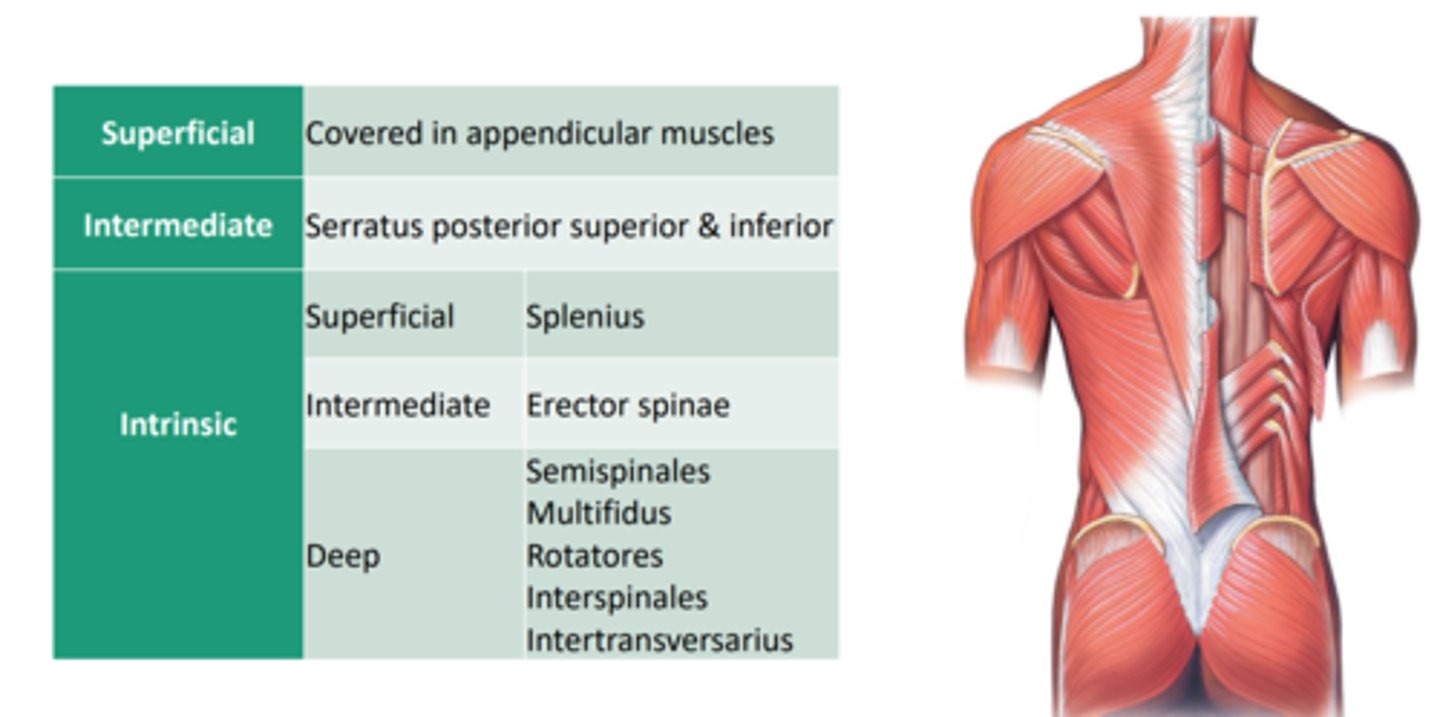
Layers of the Muscles of the vertebral column
- Superficial layer [extrinsic back muscles]
- Intermediate layer [extrinsic back muscles]
- Deep layer [intrinsic or true back muscles]
All muscles of the vertebral column divided into layers
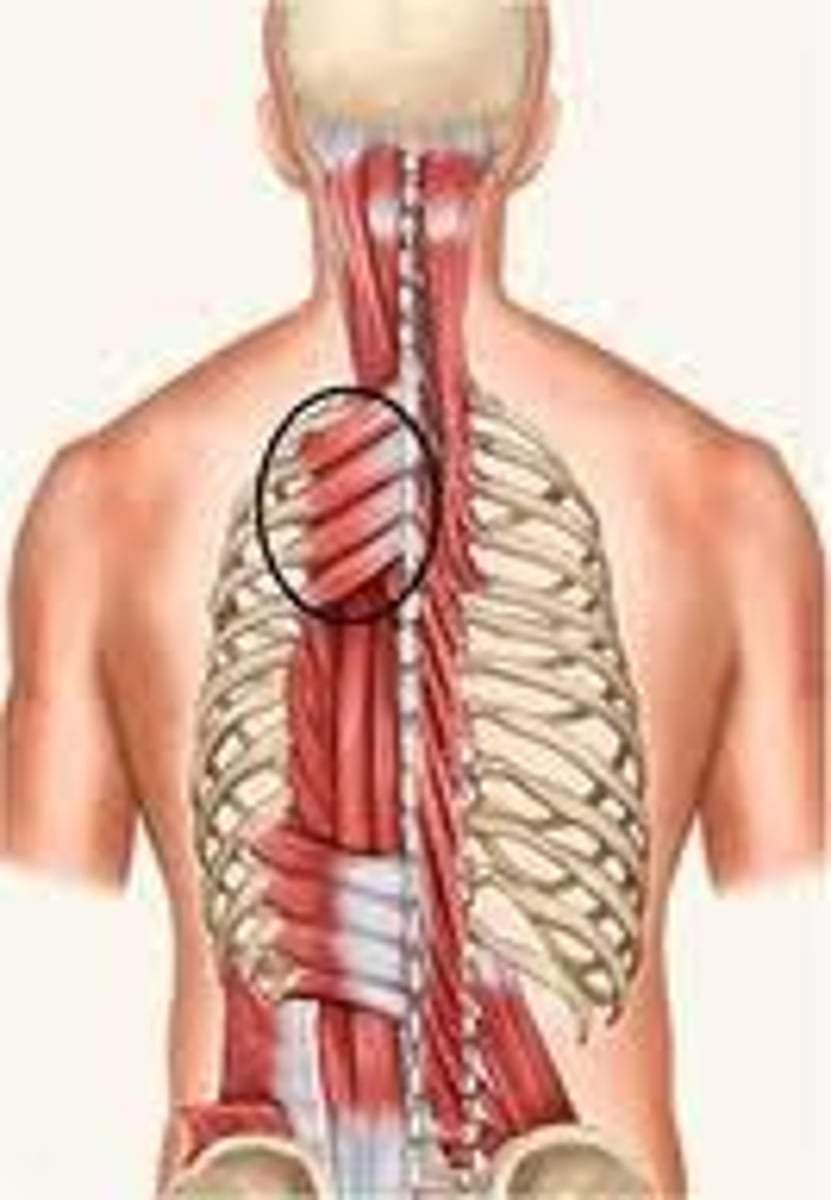
Muscles of respiration
- serratus posterior superior m.
- serratus posterior inferior m.
serratus posterior superior muscle origin, insertion & action
Origin:
Spinous processes of C7-T3
Insertion:
superior border of ribs 2-5
Action:
elevates ribs, aids in inhalation
serratus posterior inferior muscle origin, insertion & action
Origin:
spinous processes T10-L3
Insertion:
inferior border of ribs 9-12
Action:
depresses ribs, aids in inhalation
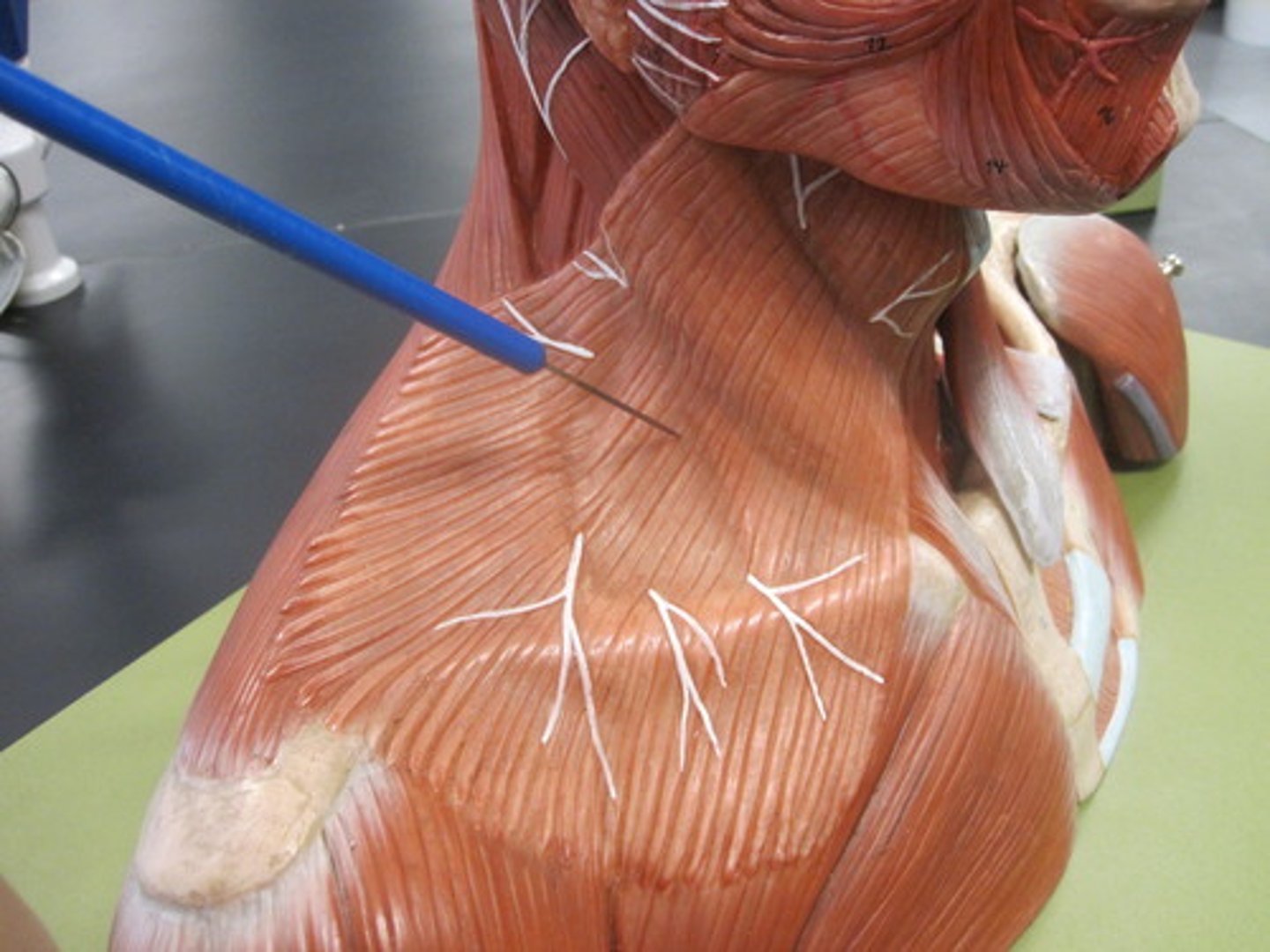
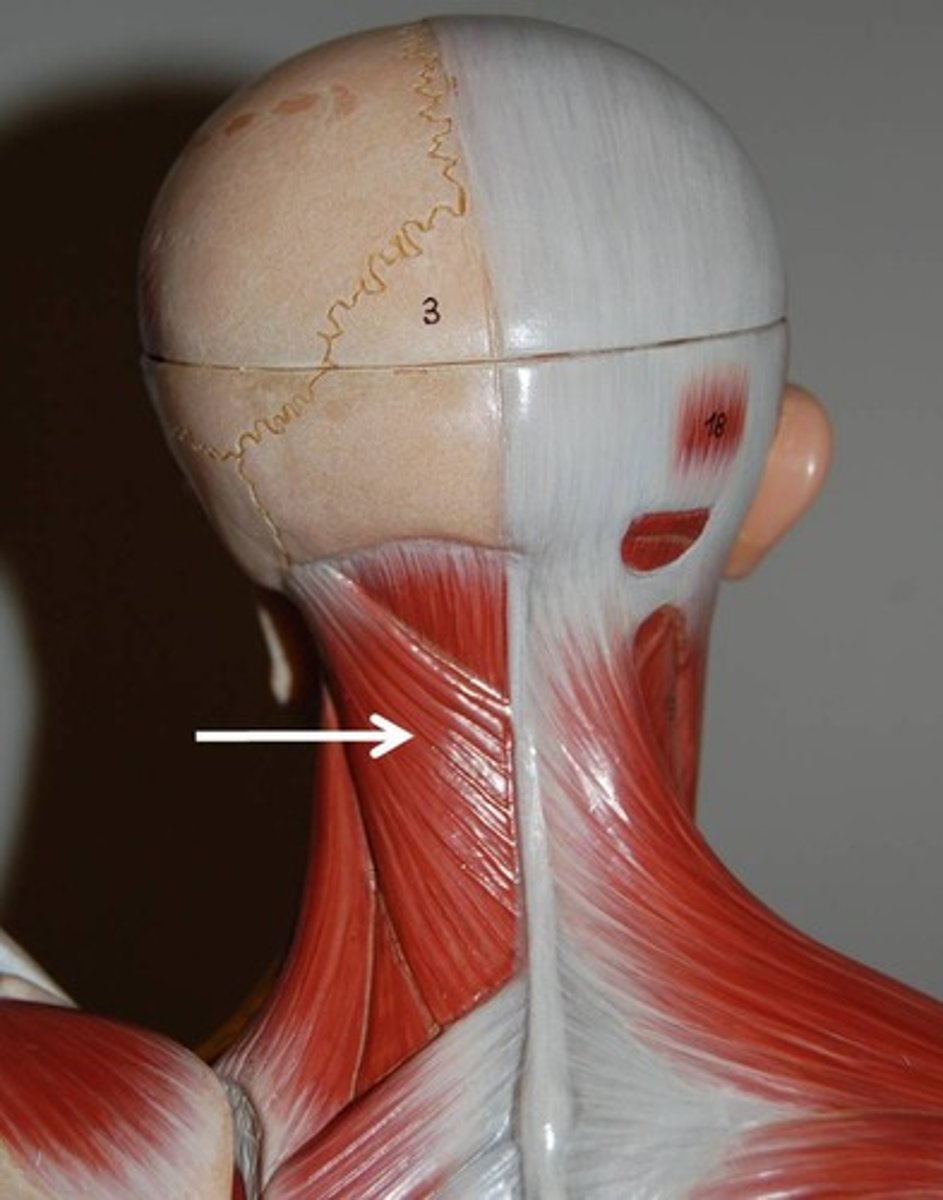
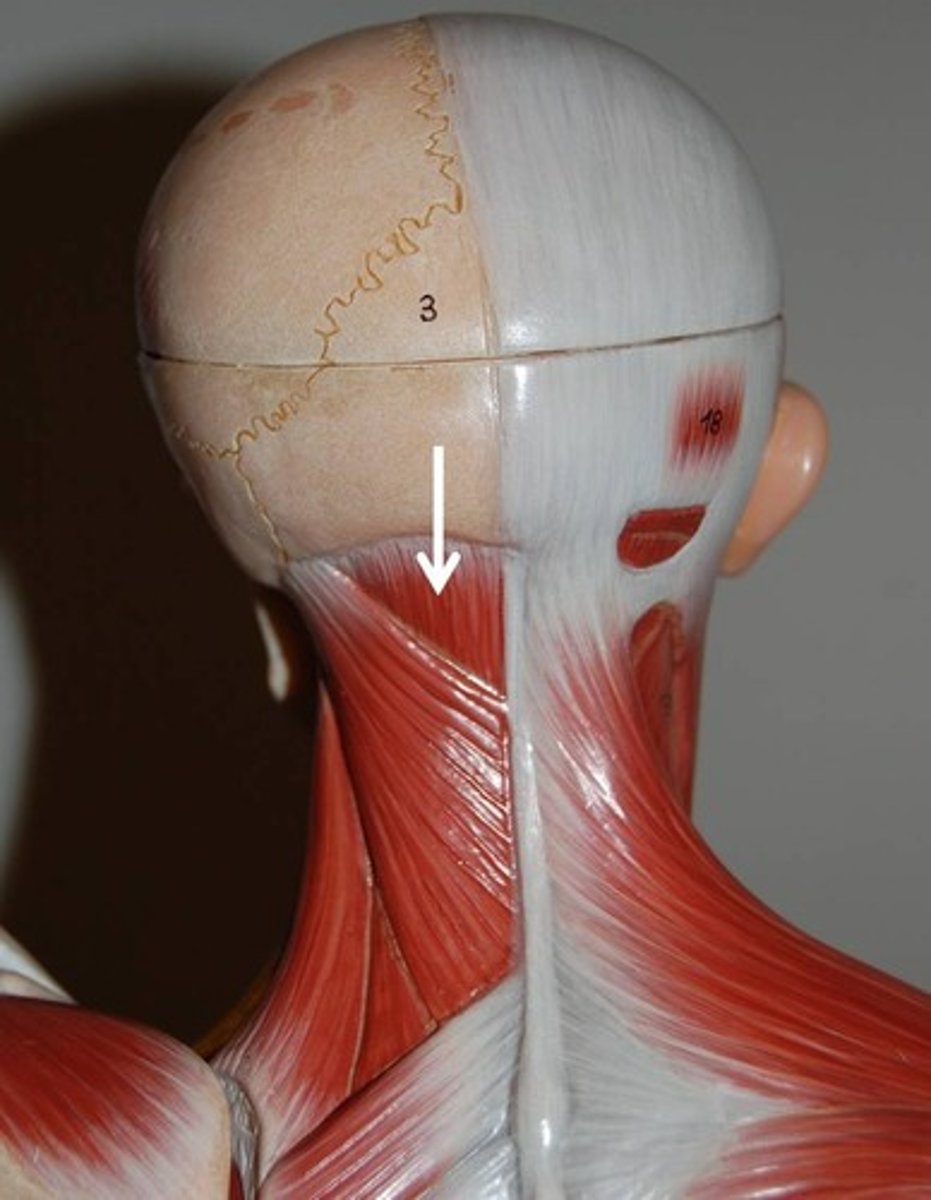
Superficial intrinsic back muscles
- Splenius muscle:
splenius cervicis & splenius capitis m.
splenius cervicis muscle origin [2] & insertion[1]
Origin:
ligamentum nuchae; spinous processes T3-6
Insertion:
Transverse process C1-3
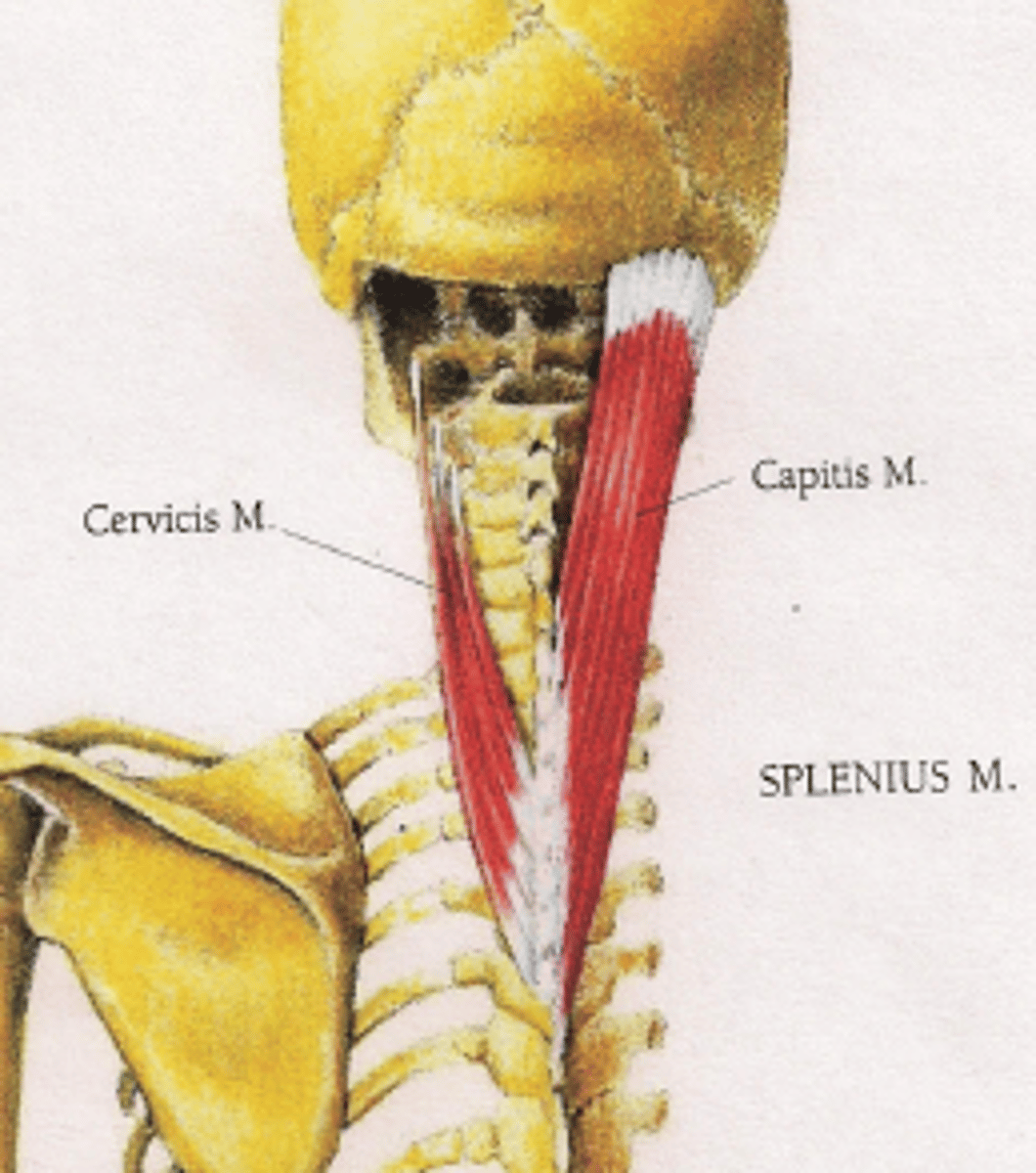
Splenius capitis m. origin[2] & insertion
Origin:
ligamentum nuchae; spinous processes C7-T4
Insertion:
mastoid process & occipital bone
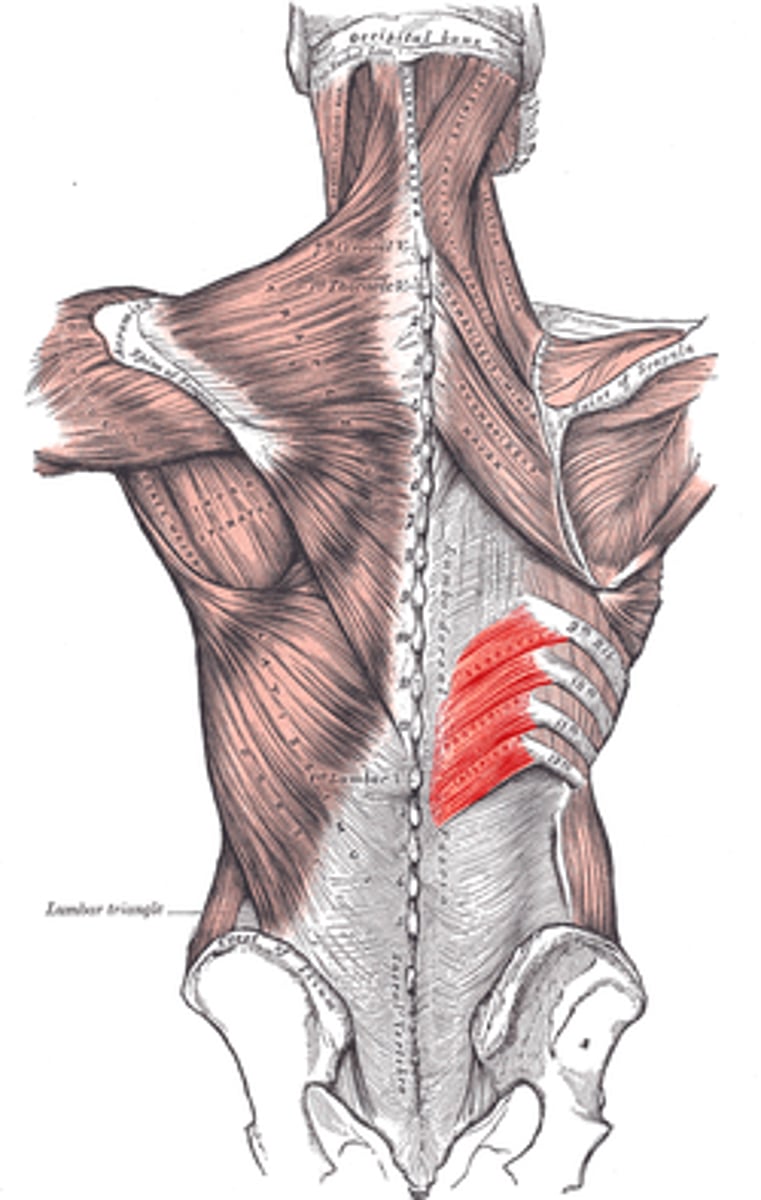
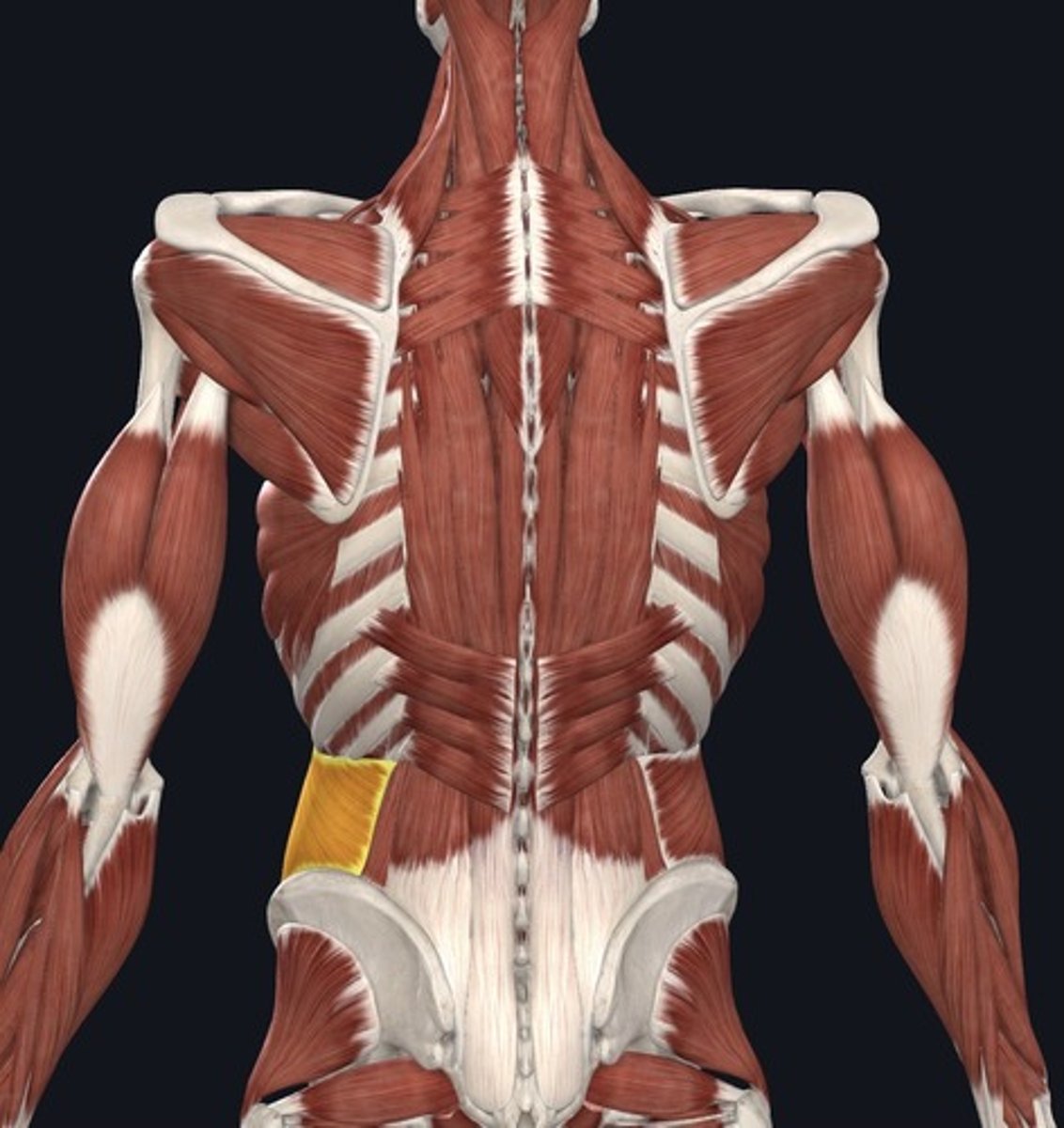
Intermediate intrinsic back muscles
- Erector Spinae muscles
consists of 3 columns [lateral to medial]
+ iliocostalis thoracis m.
+ longissimus thoracis m.
+ spinalis group
![<p>- Erector Spinae muscles</p><p>consists of 3 columns [lateral to medial]</p><p>+ iliocostalis thoracis m. </p><p>+ longissimus thoracis m.</p><p>+ spinalis group</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f8858989-2839-4e8b-afe3-deb44e6bc1b6.png)
Erector Spinae muscles collective origin [4], insertion [3], and action
aka. iliocostalis, longissimus & spinalis groups [columns] of the Spinae muscles
Origin:
iliac crest, sacral crest, lumbar spinous processes, and thoracodorsal fascia
Insertion:
vertebral transverse processes, ribs, & mastoid process
iliocostalis thoracis m.
most lateral erector spinae muscle
goes from the ilium of the pelvis all the way to the 1st rib
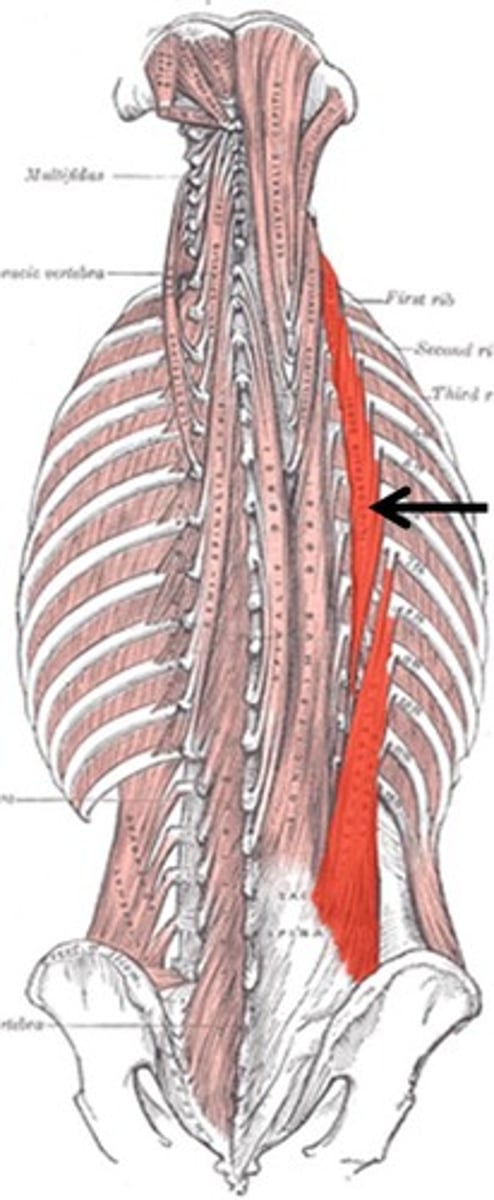
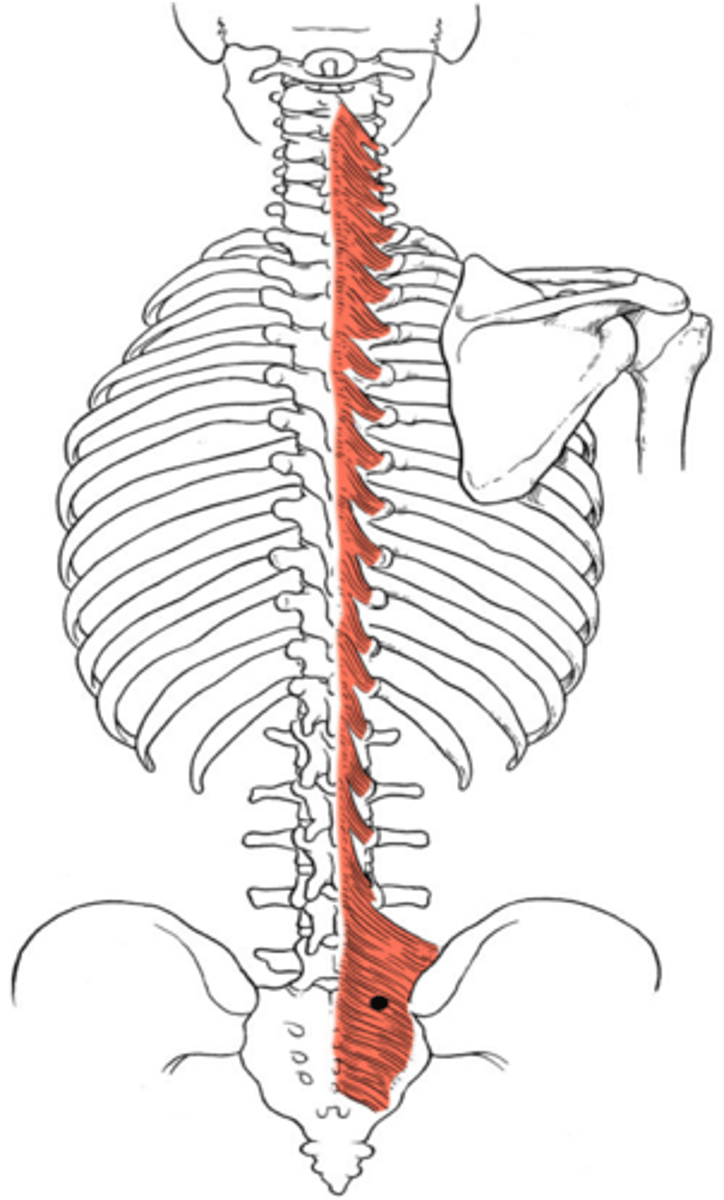
longissimus thoracis m.
longest erector spinae muscle sitting in-between the others.
goes from the lumbar region to the back of the head.
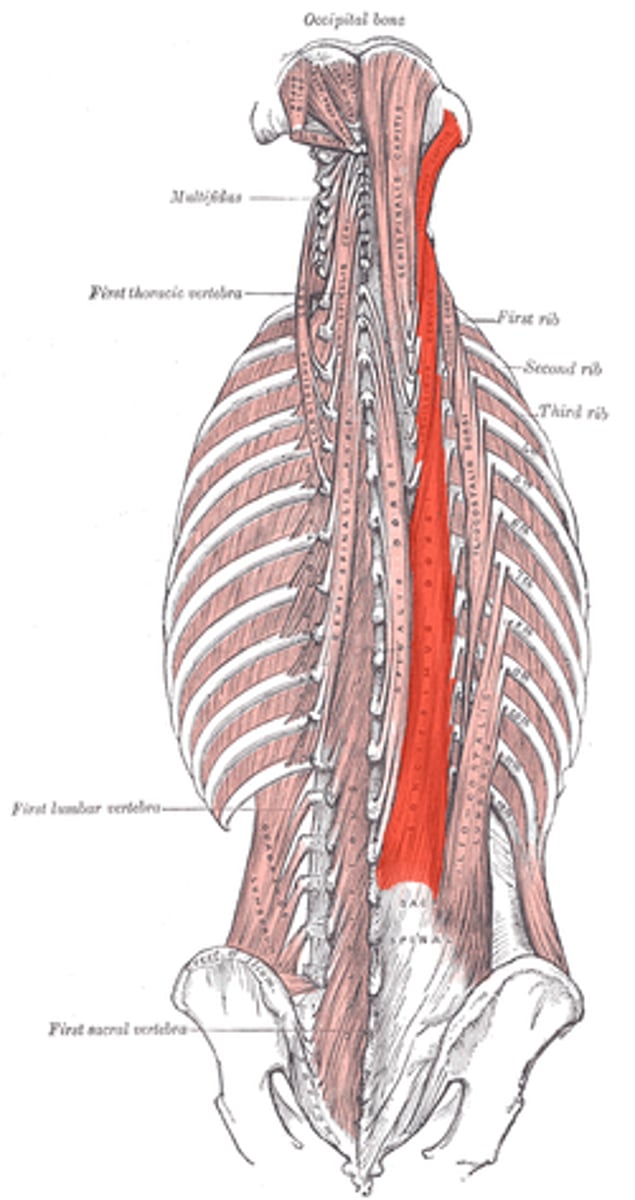
Deep intrinsic back muscles
- Semispinalis capitis m.
- Multifidus m.
- Rotatores m. [brevis & longus]
- interspinales
- intertransversarii m.
collective actions of all deep intrinsic back muscles
- stabilizes and provides delicate adjustment of vertebrae; slightly extends and rotates vertebrae
(- Semispinalis m.
- Multifidus m.
- Rotatores [brevis & longus]
- interspinales
- intertransversarii )
semispinalis capitis muscle origin [1] & insertion [2]
Origin:
Transverse processes T1-10
Insertion:
Occipital bone and spinous processes C2-T5
multifidus muscle origin [2] & insertion [1]
Origin:
sacrum and transverse processes of each vertebra
Insertion:
spinous process of the 3rd or 4th more superior vertebra
rotatores muscle [brevis & longus] origin [1] & insertion [1]
origin:
T.P. of vertebra
Insertion:
S.P. of superior vertebra
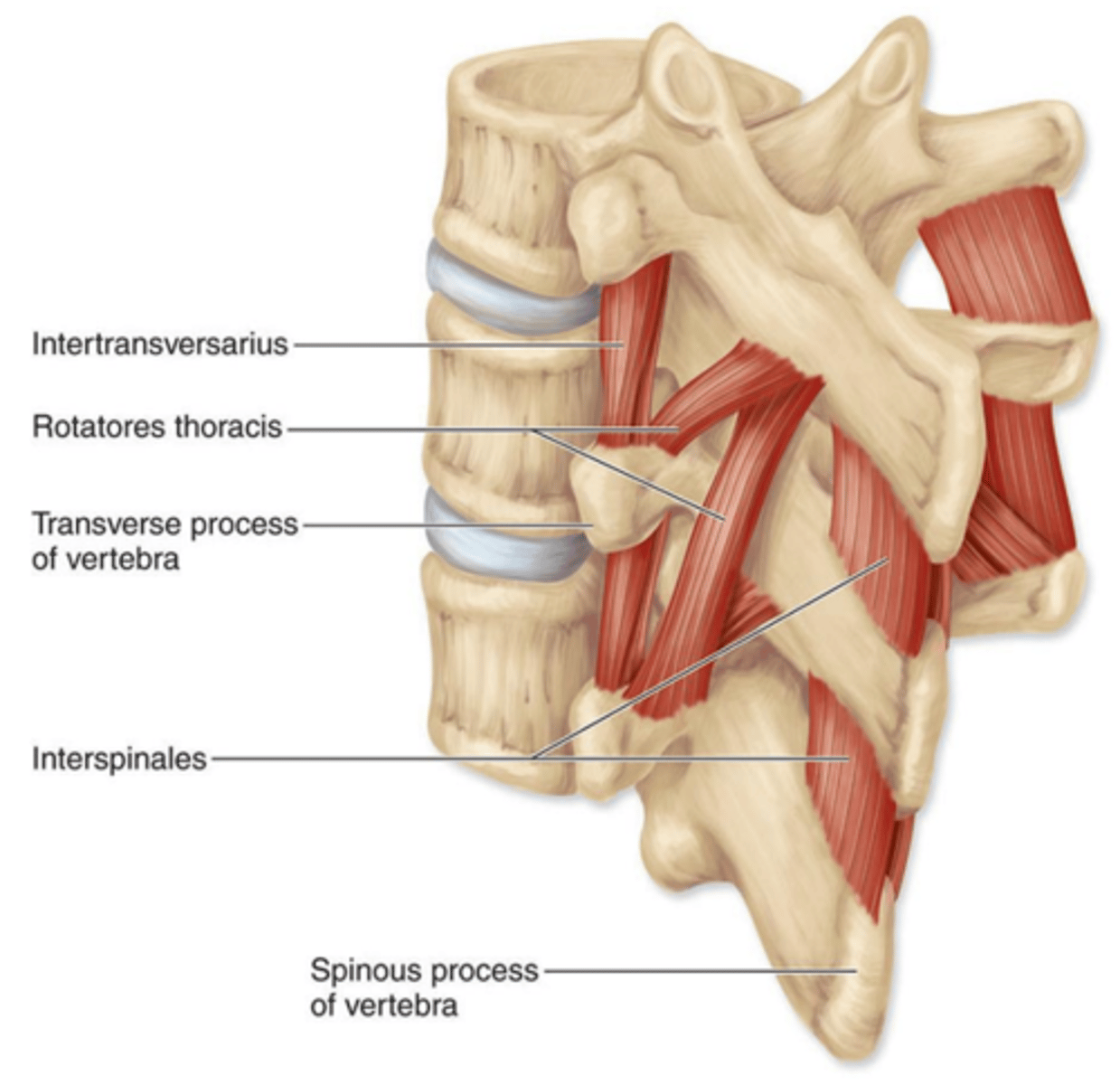
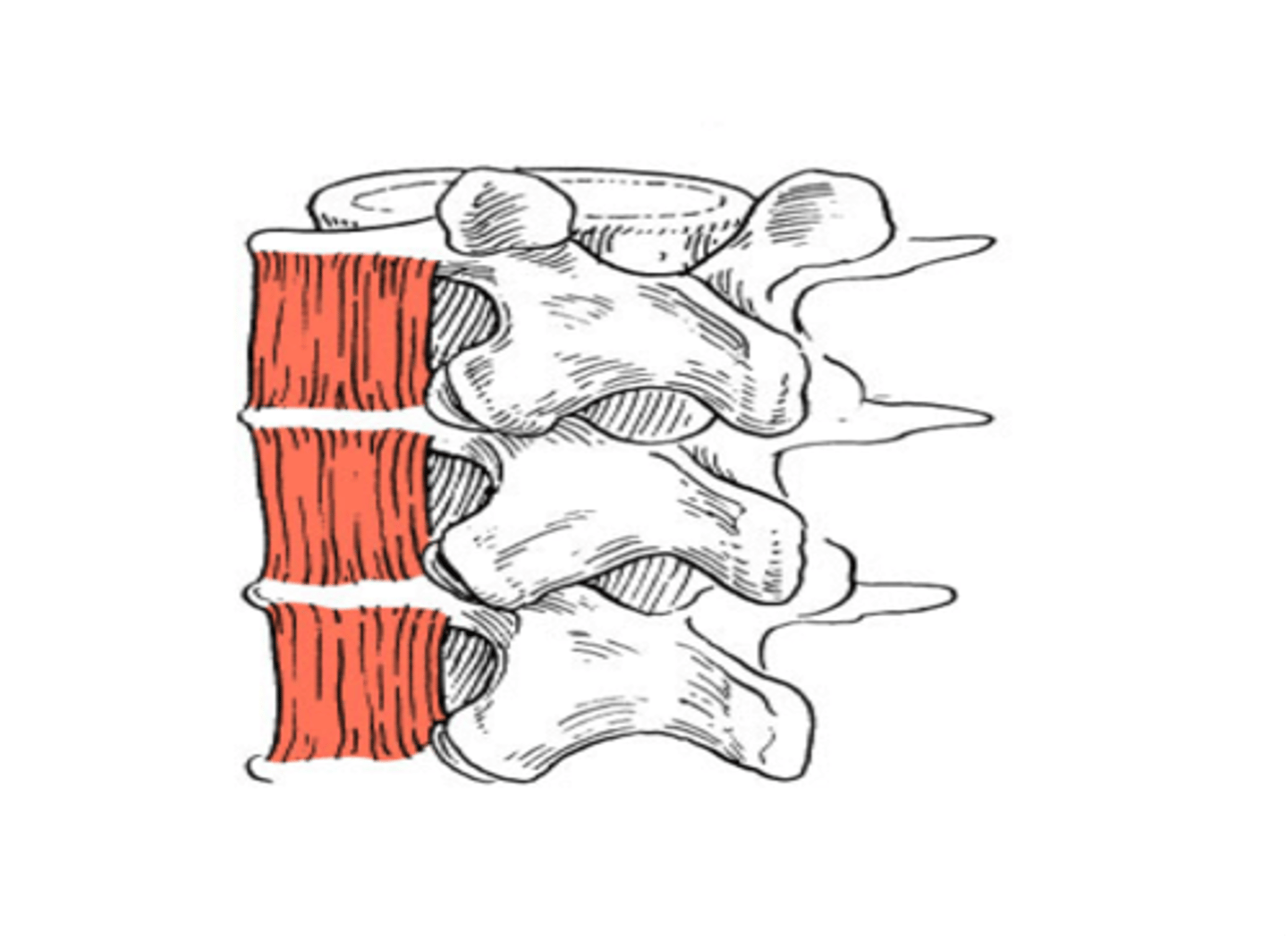
interspinales origin & insertion
origin:
S.P. of vertebra
Insertion:
S.P. of superior vertabra
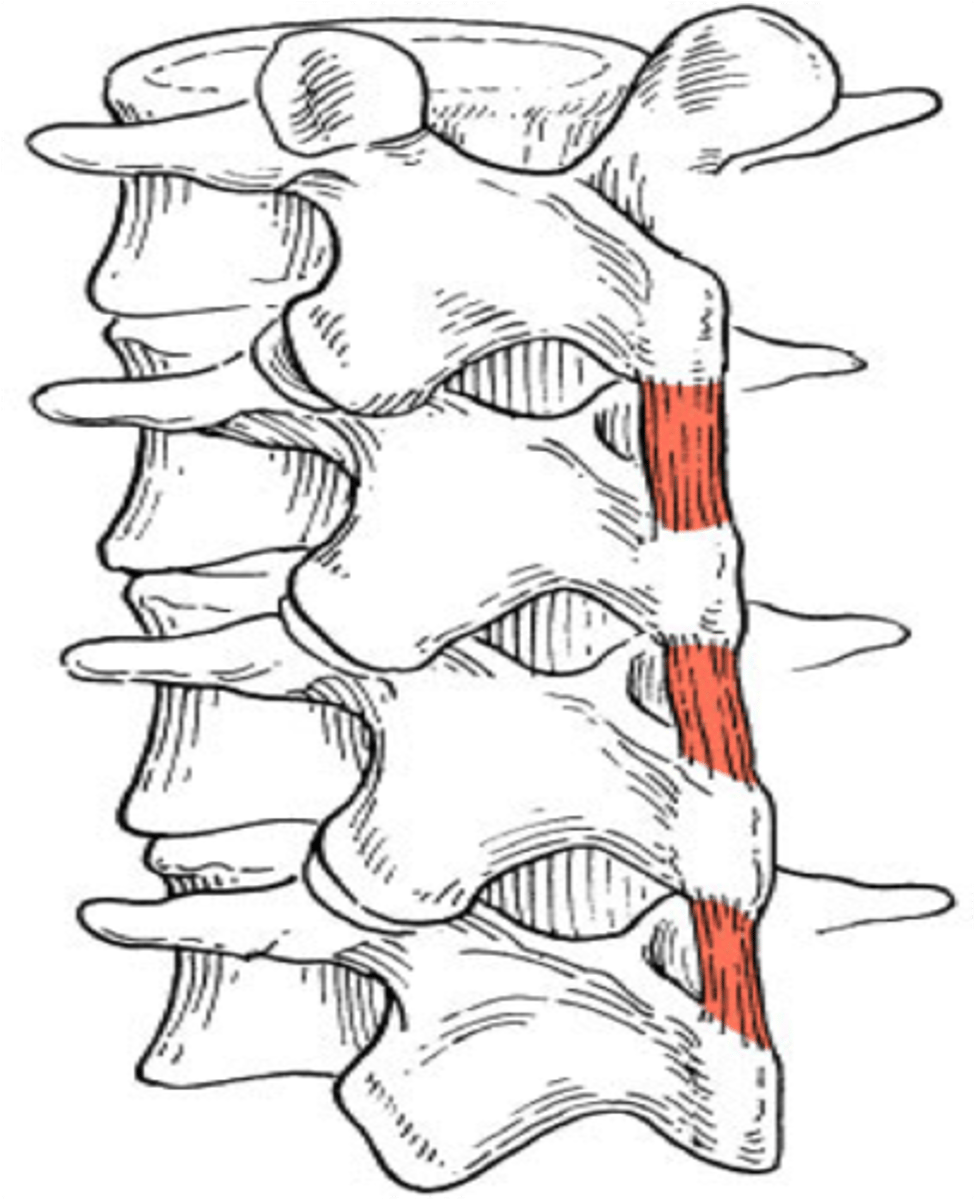
intertransversarii muscle origin and insertion
Origin:
TP of vertebra
Insertion
TP of superior vertebra
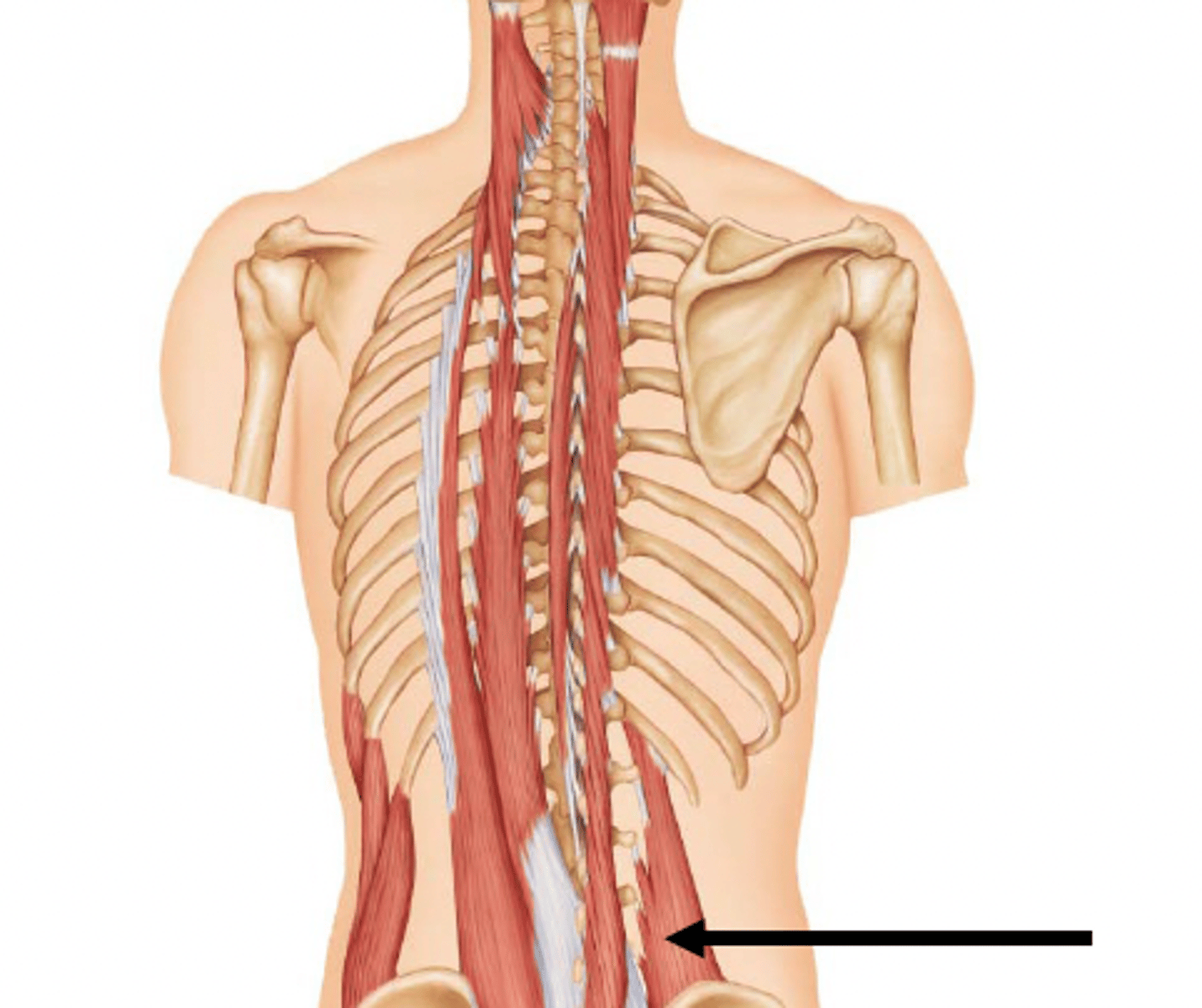
Spinal flexors
- Quadratus lumborum muscle
Quadratus lumborum muscle origin [1], insertion [2] & action
Origin:
iliac crest
Insertion:
12th rib and T.P. of lumbar vertebrae
action:
- unilateral: laterally flexes vertebral column
- bilateral: depresses ribs during forced exhalation; stabilizes diaphragm during inhalation
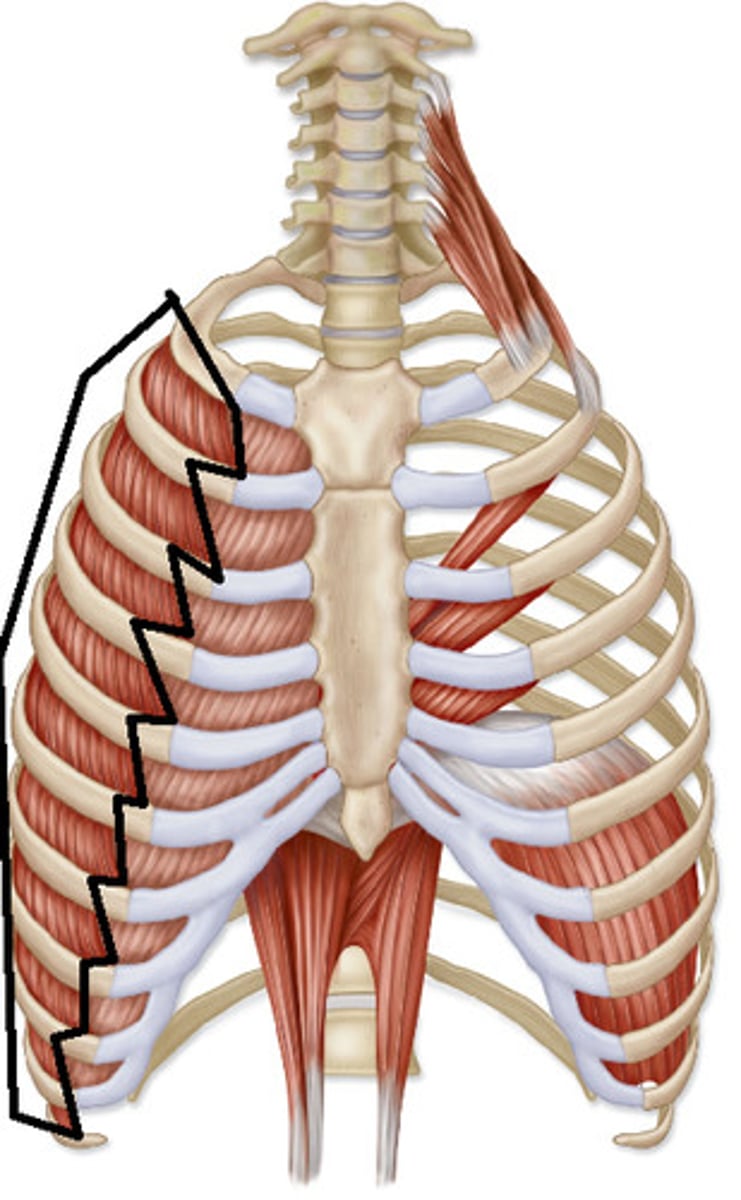
Muscles of respiration
- external intercostals m.
- internal intercostals m.
- transversus thoracis m.
- diaphragm m.
external intercostals m. origin, insertion & action
origin:
inferior border of rib
insertion:
superior border of rib
action:
elevates ribs
internal intercostals m. origin, insertion & action
origin:
superior border of rib
insertion:
inferior border of superior rib
action: depresses ribs
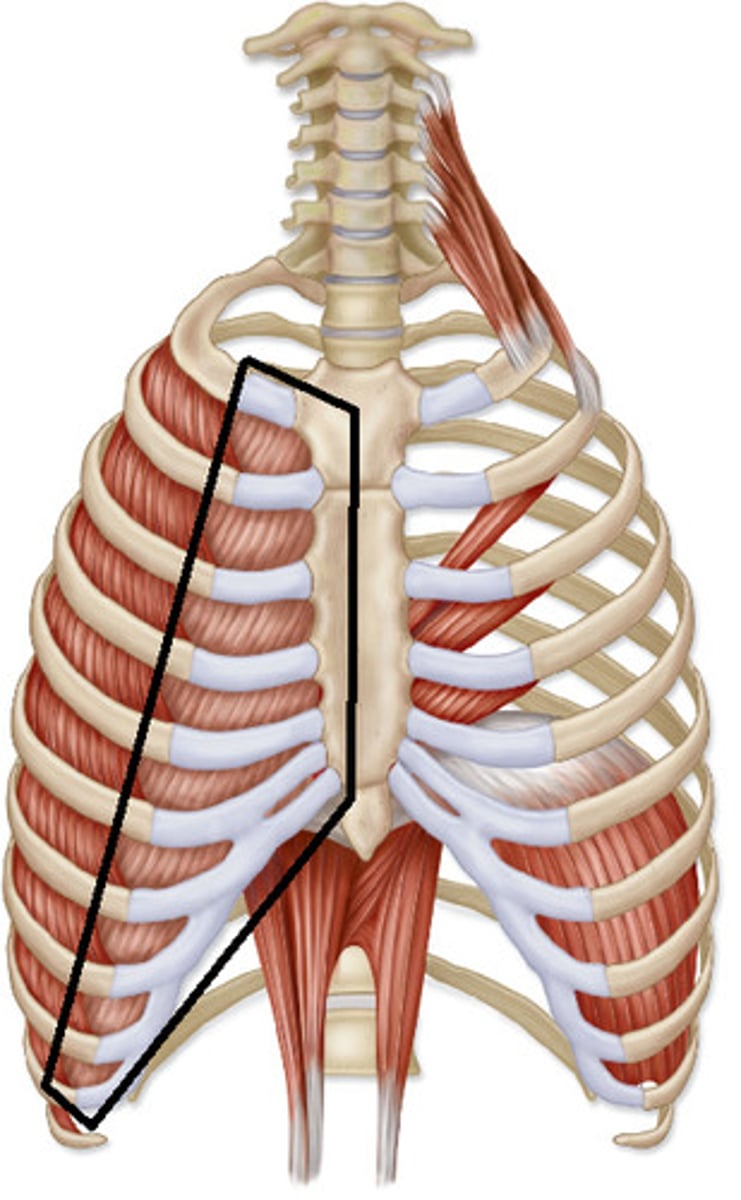
external incrcostals vs. internal intercostals
They have different fiber directions
internal intercostals domino fall towards the midline.
external intercostals domino laterally.
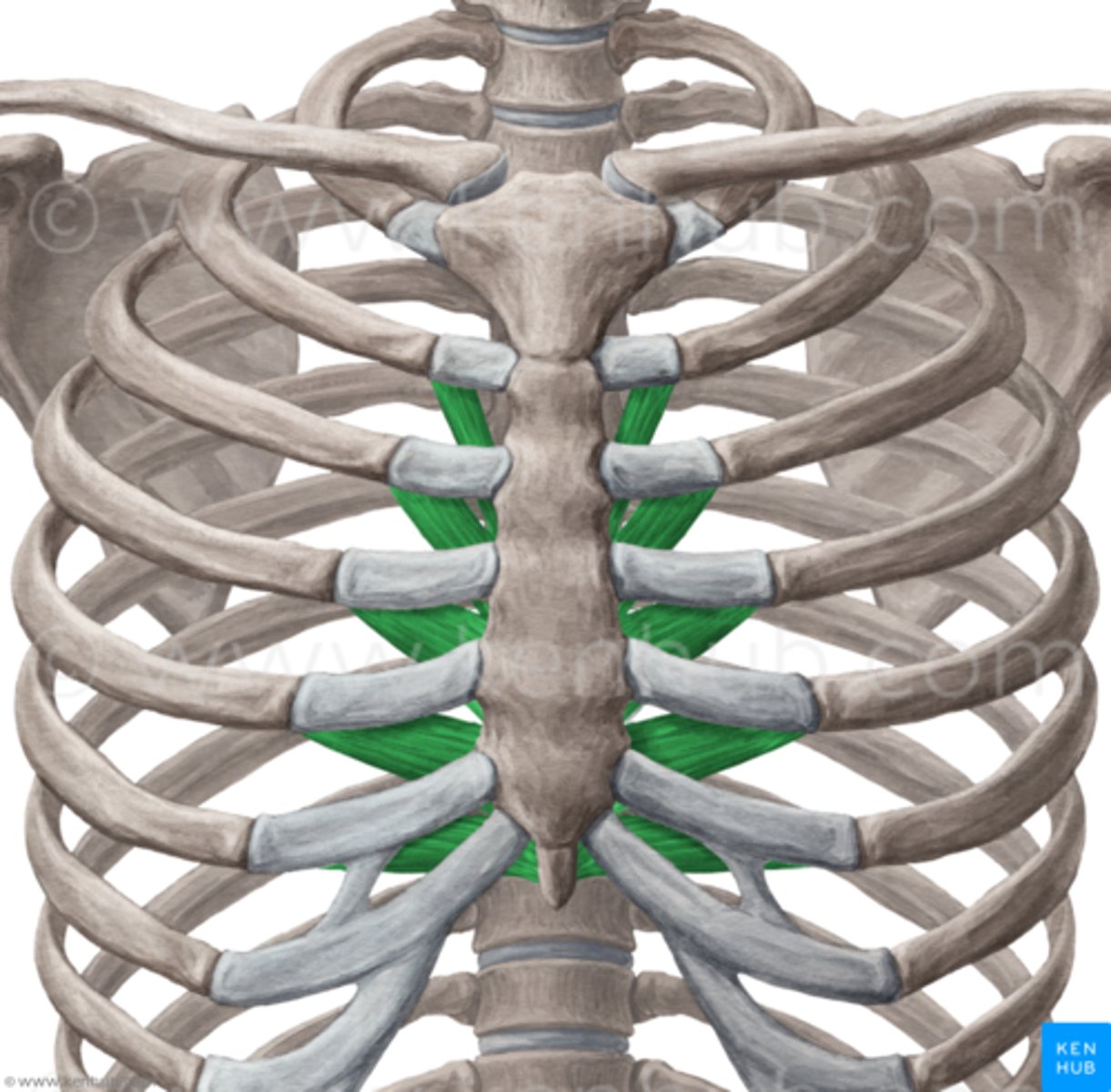
Transversus thoracis m. origin, insertion & action
origin:
posterior surface of sternum
insertion:
cartilage of ribs 2-6
action:
minimal significance, depresses ribs
diaphragm m. origin [3], insertion [1] & action
origin:
xiphoid process, ribs 7-12 [associated costal cartilage], & anterior surface of lumbar vertebrae
insertion:
central tendinous sheet
action:
contraction expands thoracic cavity & compresses abdominopelvic cavity
![<p>origin:</p><p>xiphoid process, ribs 7-12 [associated costal cartilage], & anterior surface of lumbar vertebrae</p><p>insertion:</p><p>central tendinous sheet</p><p>action:</p><p>contraction expands thoracic cavity & compresses abdominopelvic cavity</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/aaf77a4b-c1c5-4757-b896-144455564cec.jpg)
All muscles of respiration
Key abdominal structures
- Rectus sheath
- Inguinal ligament
- Linea Alba ["white line"]
- Thoracolumbar fascia
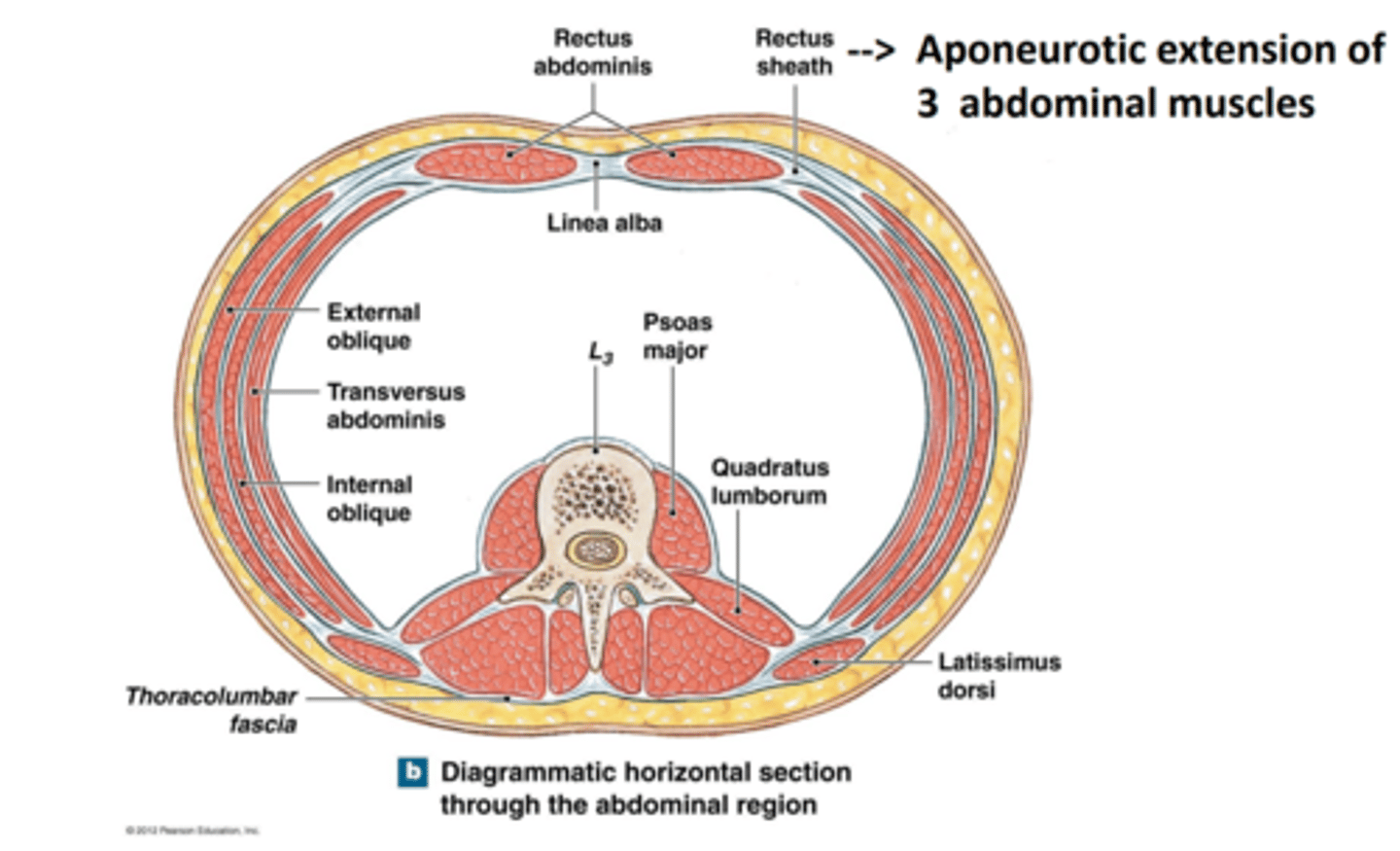
Rectus sheath
aponeurotic extensions of 3 flat abdominal muscles
aponeurosis = flattened tendon
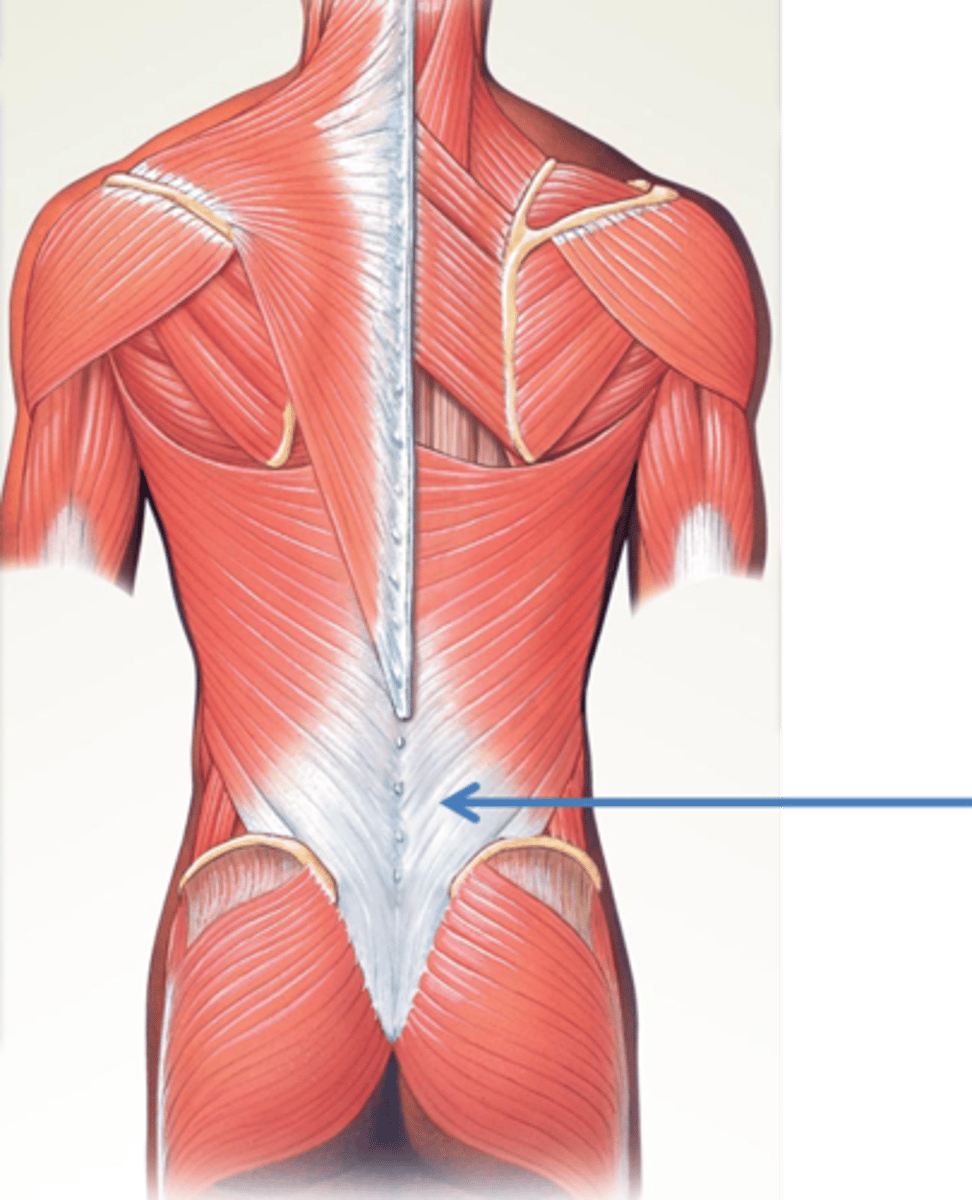
Thoracolumbar fascia
the deep membrane throughout the posterior thorax
Linea Alba ["white line"]
Fibrous structure that runs down the midline of the abdomen
Xiphoid process to pubic bone
Inguinal ligament
a ligament [fibrous band] extending from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine
- forming lower border of abdomen
![<p>a ligament [fibrous band] extending from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine</p><p>- forming lower border of abdomen</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/59270e40-e7d1-445f-b907-b30b6e91fd05.jpg)
Muscles of the abdominal wall
- rectus abdominis m.
- pyramidalis m.
- external oblique m.
- internal oblique m.
- transversus abdominus m.
Muscles of the abdominal wall collective function
- supports & protect abdominal organs
- contract to increase abdominal pressure
Muscles of the abdominal wall superior view
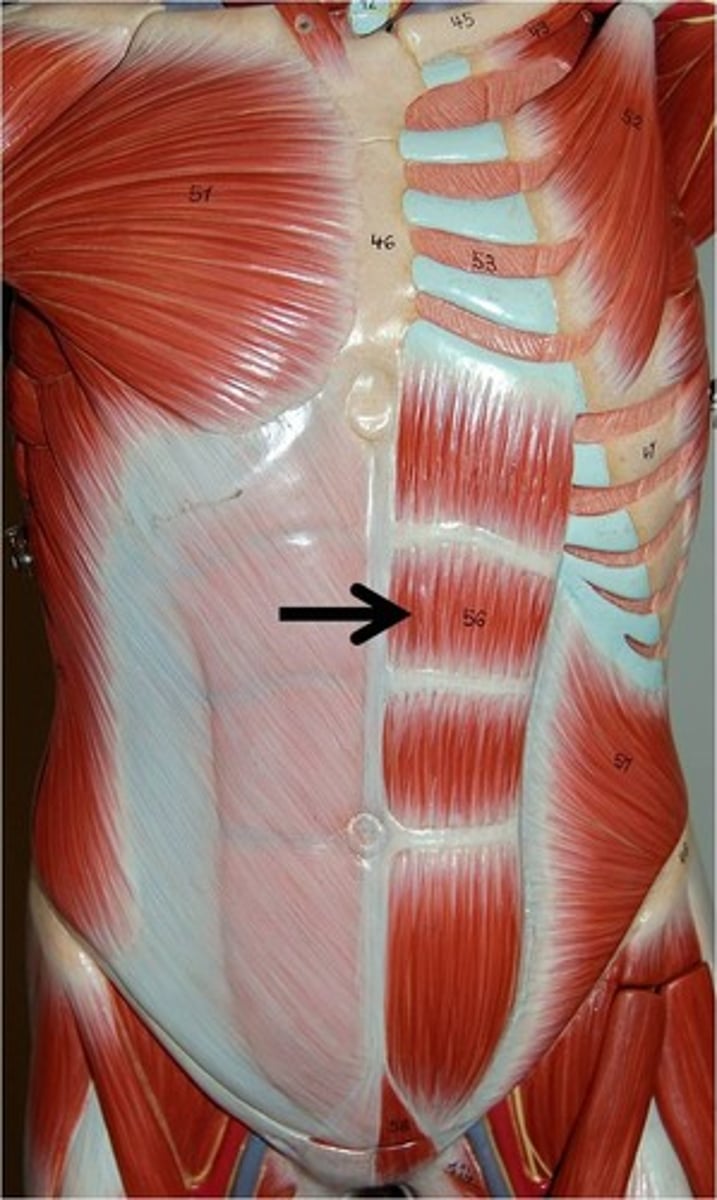
Rectus Abdominus m. origin [1], insertion [2], & action
origin:
pubis
insertion:
cartilage of ribs 5-7 & xiphoid process
action:
flexes vertebral column; acts to resist vertebral motion; forced exhalation
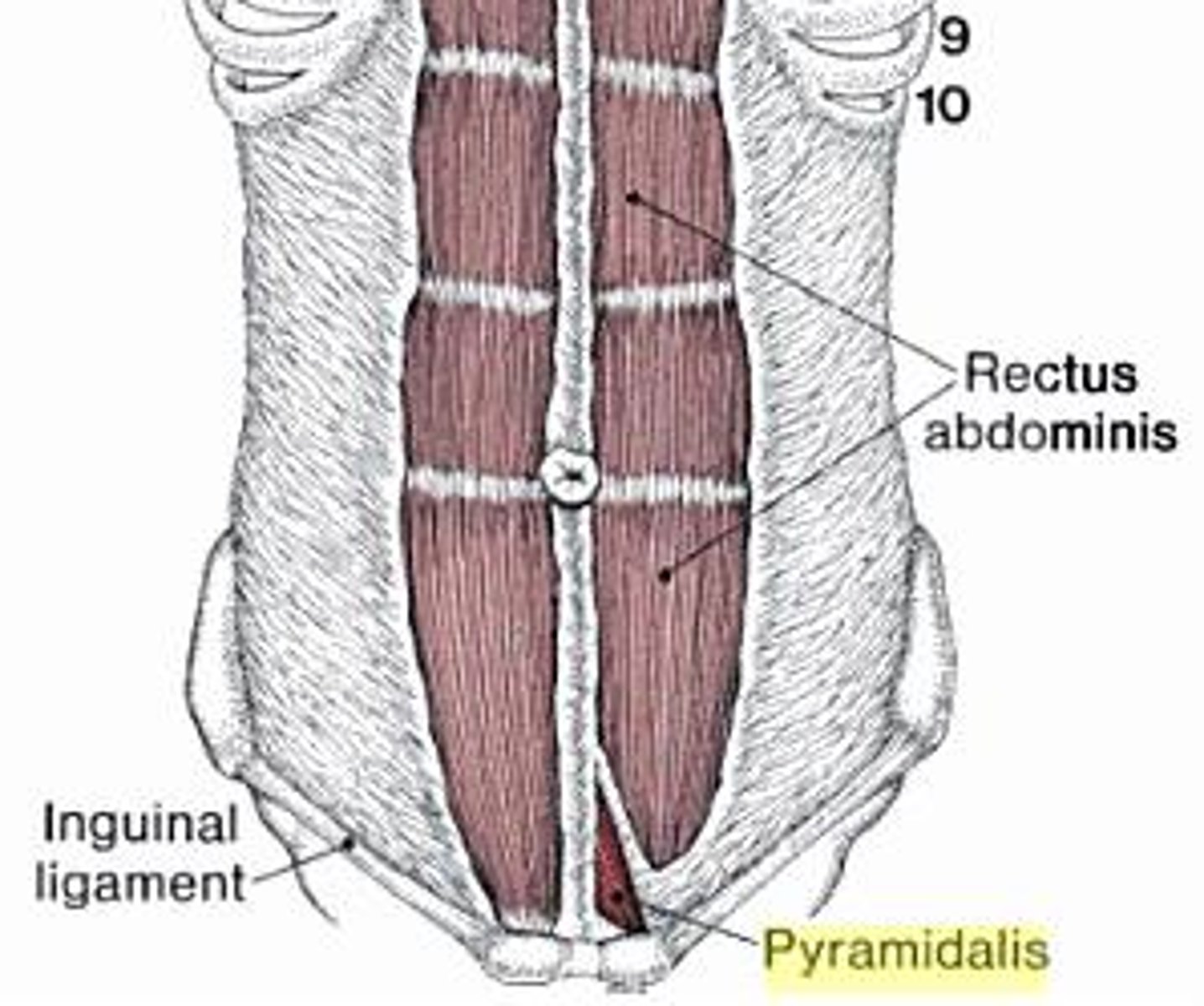
Pyramidalis m. origin , insertion, & action
- small triangular muscle anterior to the rectus and contained within the rectus sheath
- absent in ~20% of the population
origin:
pubic crest and symphysis
insertion linea alba
action: tenses linea alba
External oblique m. origin [1], insertion [2], & action
Origin:
ribs 5-12
Insertion:
linea alba and iliac crest
action:
depresses ribs; flexes and laterally rotates vertebral column to the opposite side
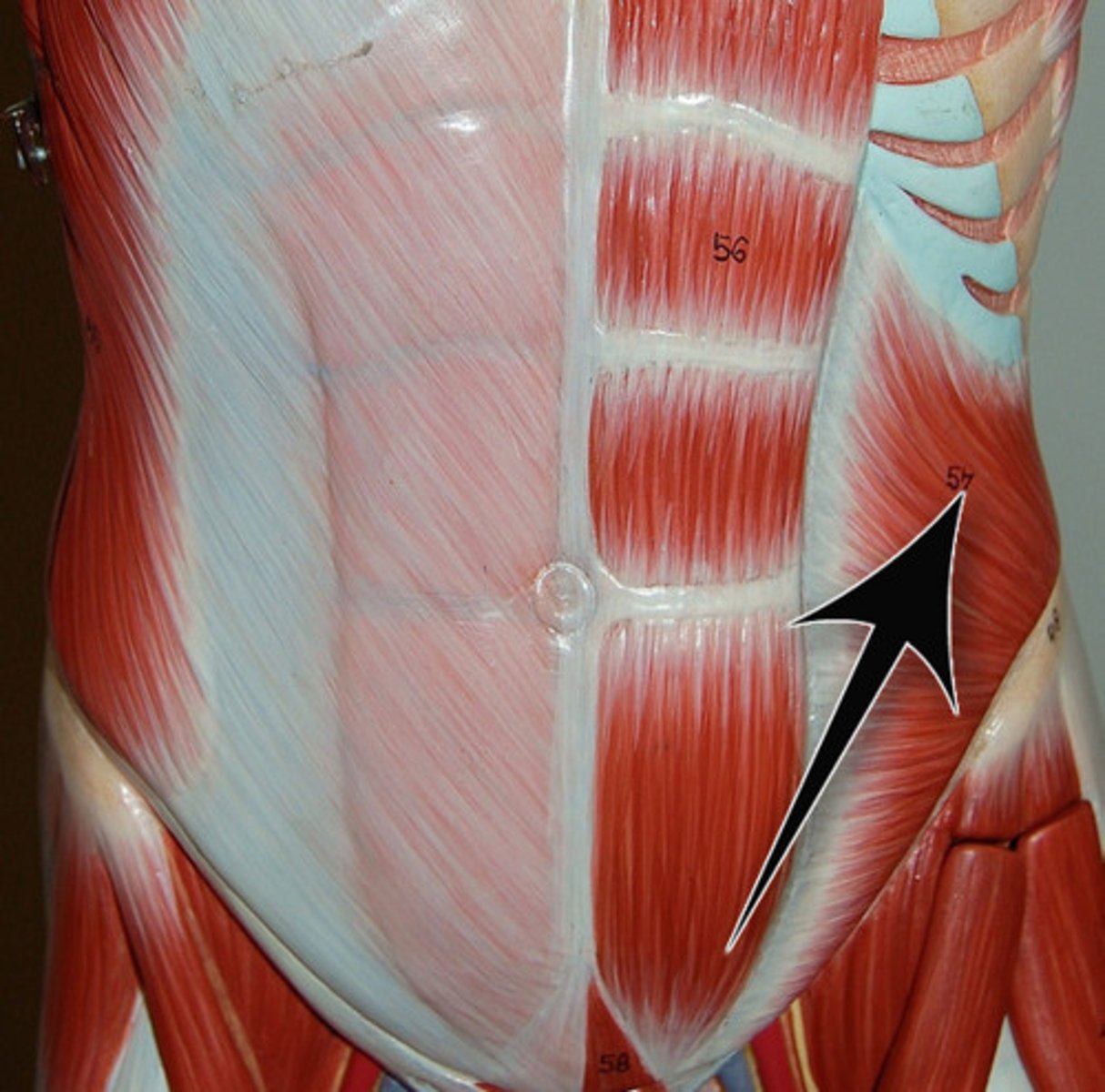
External oblique m. lateral view
clearly shows its extension from ribs 5-12 to insert into the linea alba and iliac crest
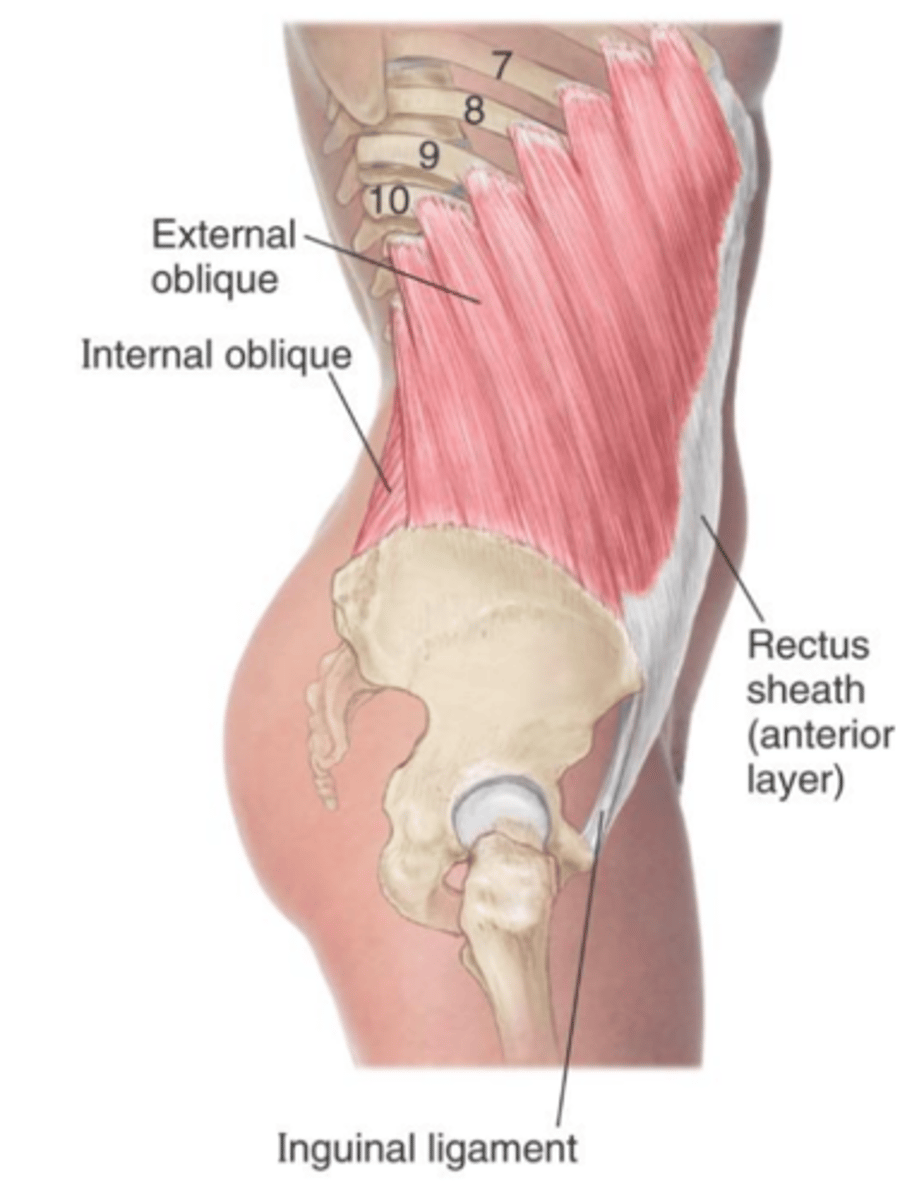
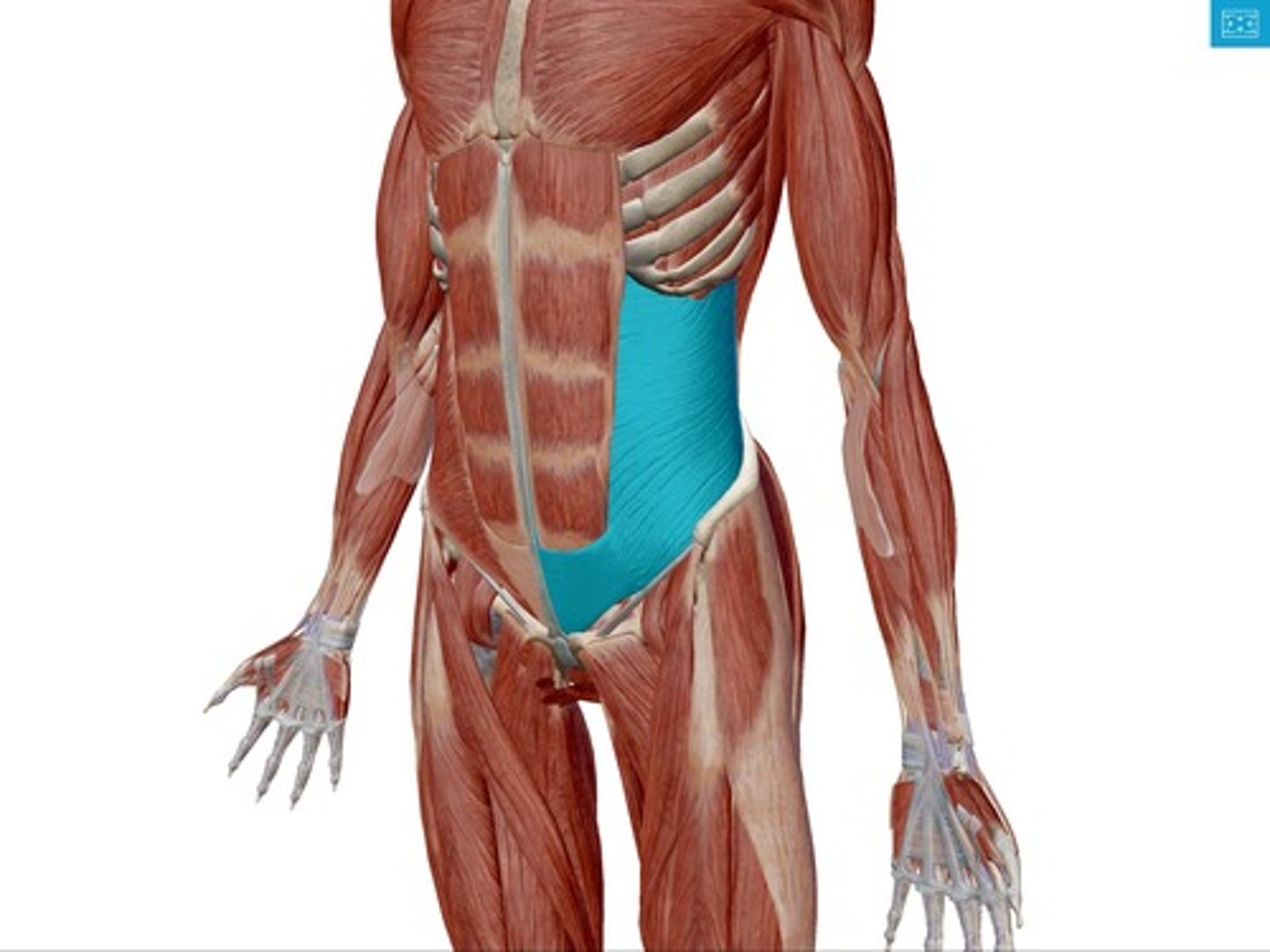
Internal oblique muscle origin[3], insertion [3], & action [2]
Origin:
thoracolumbar fascia; inguinal ligament; iliac crest
Insertion:
inferior surfaces of ribs 7-12 ; linea alba; pubis
Action:
depresses ribs; flexes and laterally rotates vertebral column to the same side
Transversus abdominis muscle origin [3], insertion [2], & action
Origin:
thoracolumbar fascia; iliac crest; ribs 7-12
Insertion:
Pubis & linea alba
action:
compresses abdomen; forced exhalation