FINAL EXAM A&P 2- BROWN ETSU
1/266
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
267 Terms
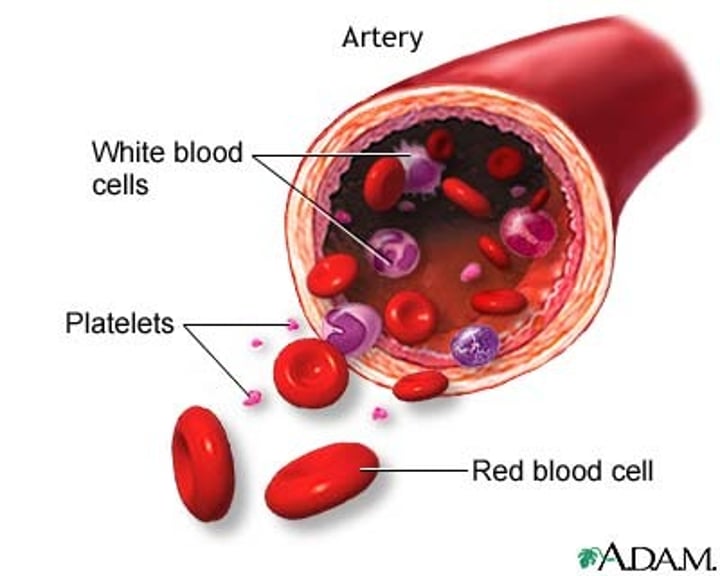
Formed Elements
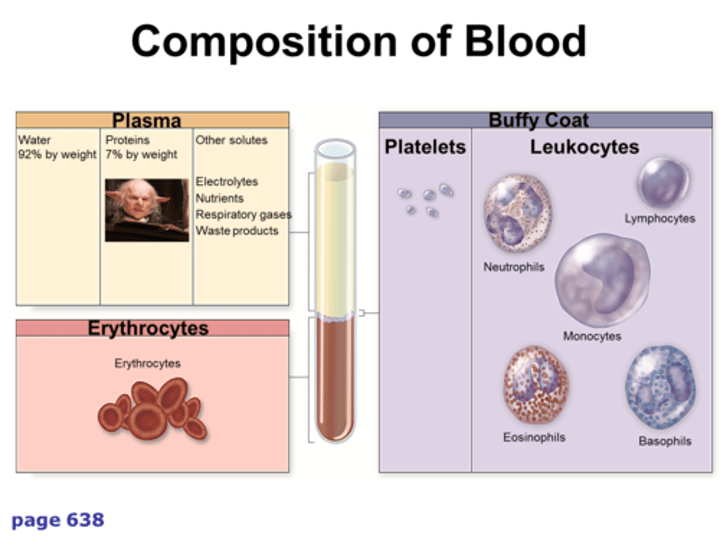
cellular components of blood; that is, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
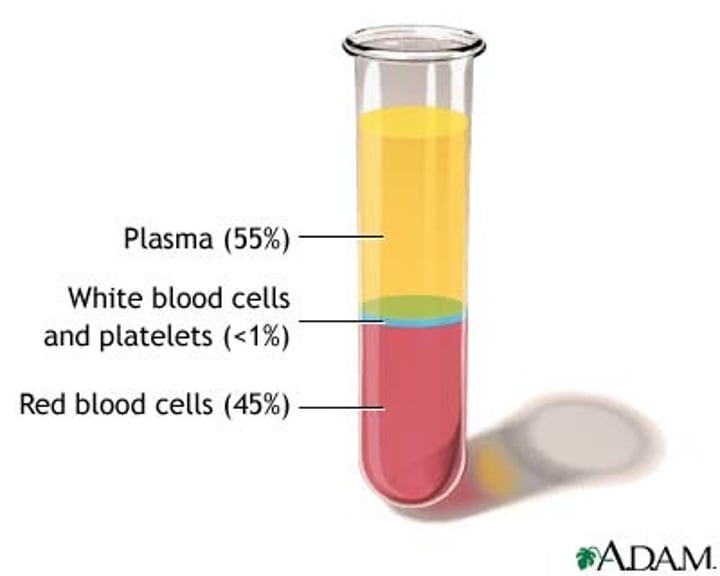
Plasma
in blood, the liquid extracellular matrix composed of water that circulates the formed elements and dissolved materials throughout the cardiovascular system
Average Blood Volume
5 liters
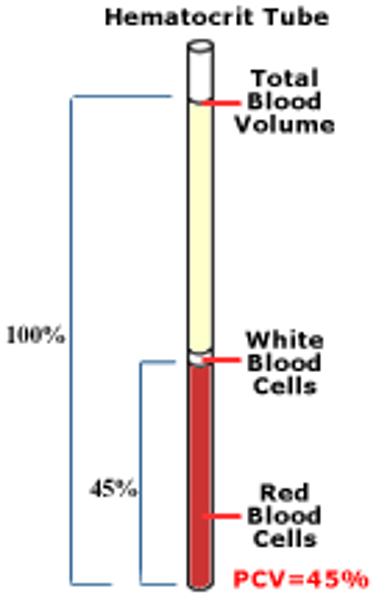
Hematocrit
(also, packed cell volume) the volume percentage of erythrocytes in a centrifuged blood
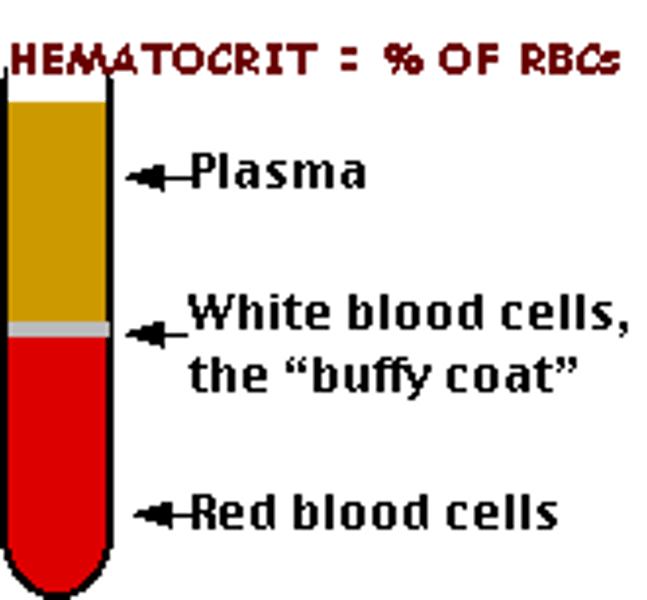
Normal Hematocrit Value
about 45%
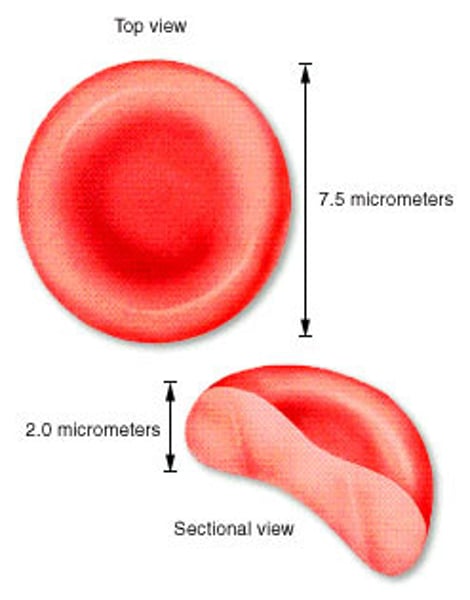
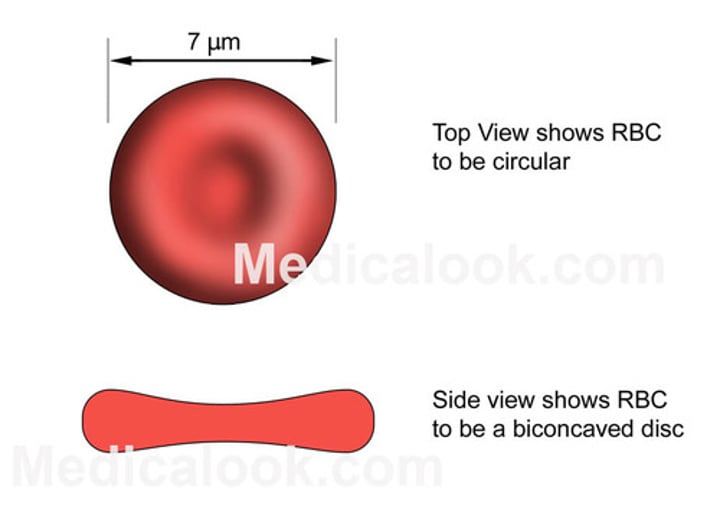
Erythrocyte
(also, red blood cell) mature myeloid blood cell that is composed mostly of hemoglobin and functions primarily in the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Biconcave Disk
shape of red blood cell
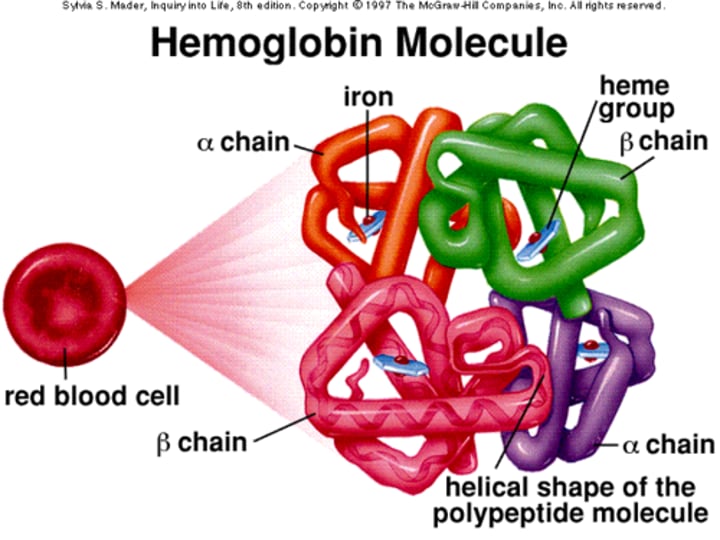
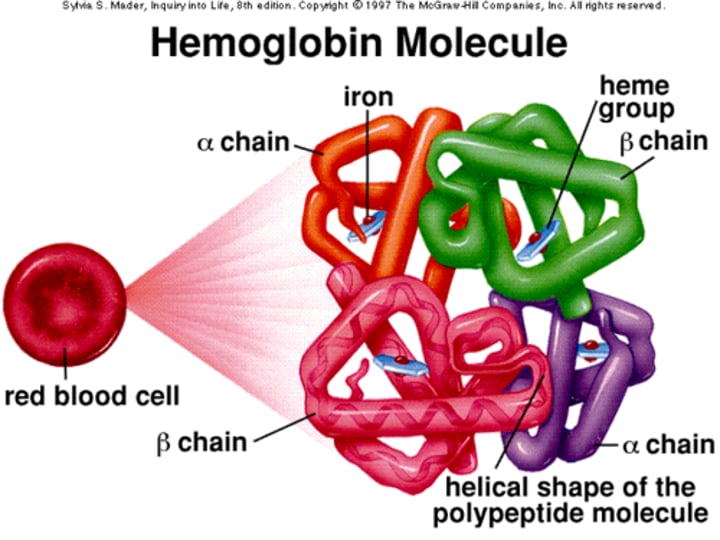
Hemoglobin
oxygen-carrying compound in erythrocytes
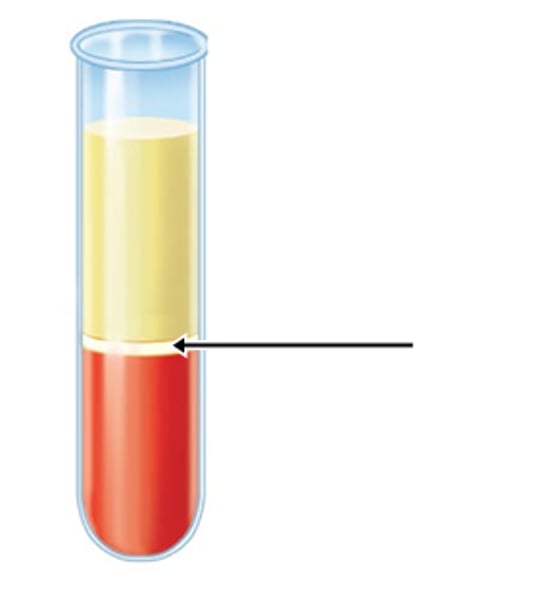
Buffy Coat
thin, pale layer of leukocytes and platelets that separates the erythrocytes from the plasma in a sample of centrifuged blood
Size of Erythrocytes
7.5 um
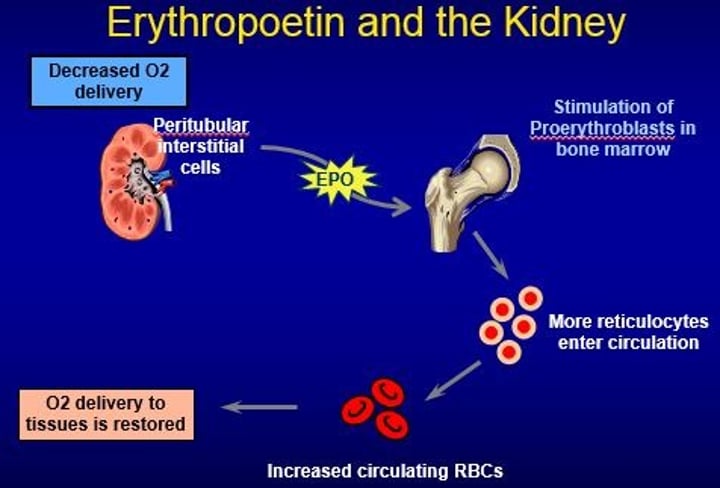
Erythropoietin
a glycoprotein that triggers the bone marrow to produce RBCs; secreted by the kidney in response to low oxygen levels
Heme
red, iron-containing pigment to which oxygen binds in hemoglobin
Biliverdin
green bile pigment produced when the non-iron portion of heme is degraded into a waste product; converted to bilirubin in the liver
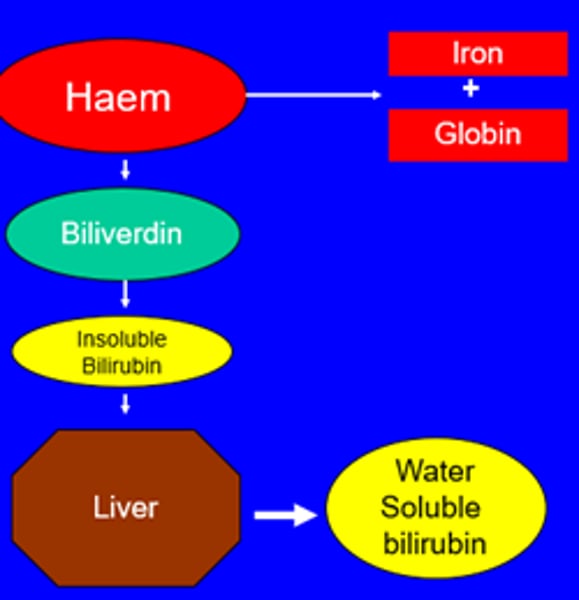
Bilirubin
yellow bile pigment produced when the iron is removed from heme and is further broken down into waste products
Anemia
deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin
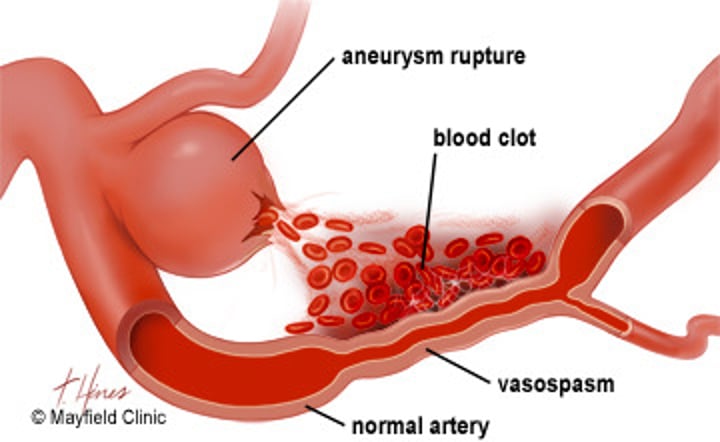
Vasospasm
the initial step in hemostasis, in which the smooth muscle in the walls of the ruptured or damaged blood vessels contracts
Platelets
(also, thrombocytes) one of the formed elements of the blood that consists of cell fragments broken off from megakaryocytes
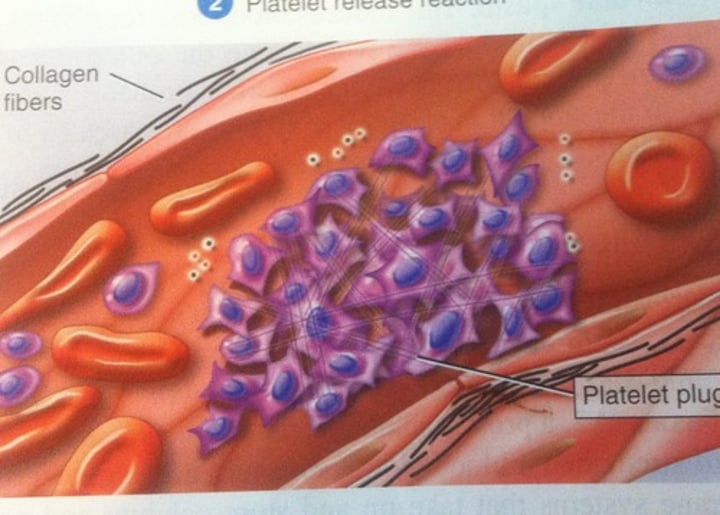
Platelet Plug Formation
accumulation and adhesion of platelets at the site of blood vessel injury
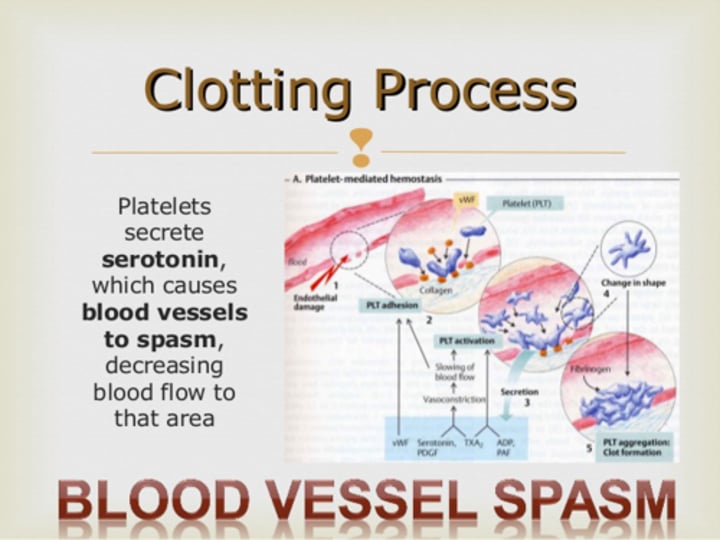
Serotonin
a compound present in blood platelets and serum that constricts the blood vessels and acts as a neurotransmitter.
Prothrombin Activator
converts prothrombin to thrombin
Prothrombin
a protein present in blood plasma that is converted into active thrombin during coagulation. (inactive thrombin)
Thrombin
the enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin during coagulation
Fibrinogen
soluble, a plasma protein that is converted to fibrin in the clotting process
Fibrin
insoluble, filamentous protein that forms the structure of a blood clot
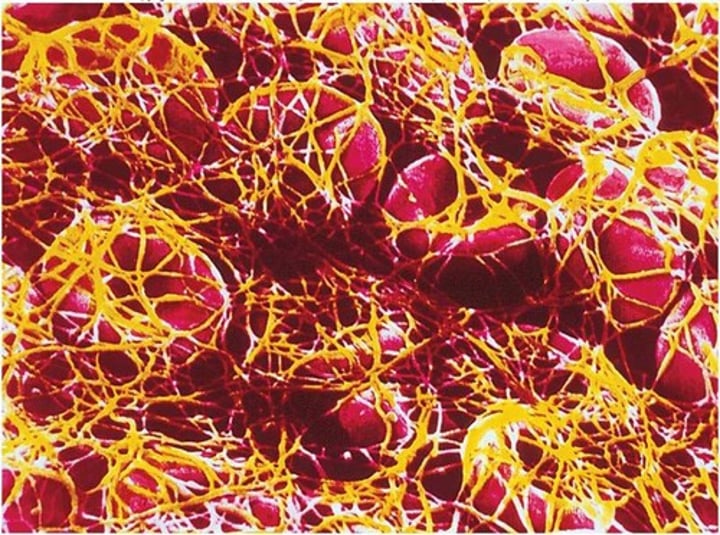
Thrombus
aggregation of fibrin, platelets, and erythrocytes in an intact artery or vein
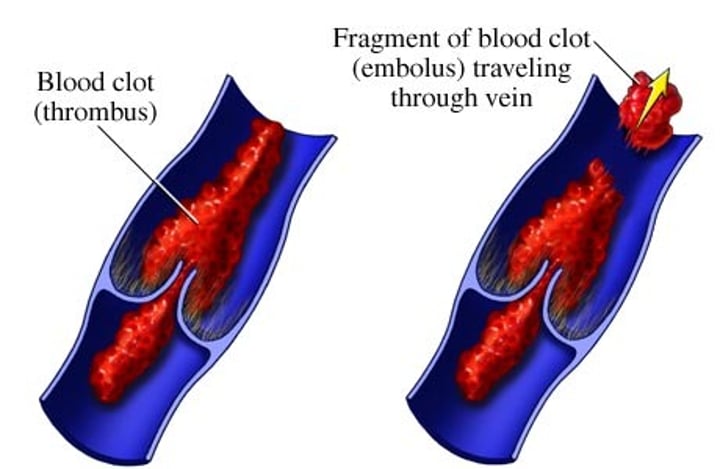
Embolus
thrombus that has broken free from the blood vessel wall and entered the circulation
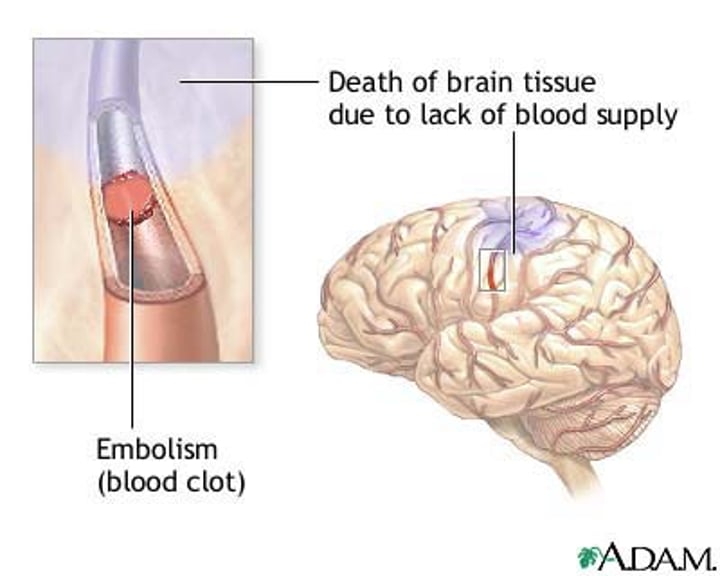
Embolism
the sudden blockage of a blood vessel by an embolus
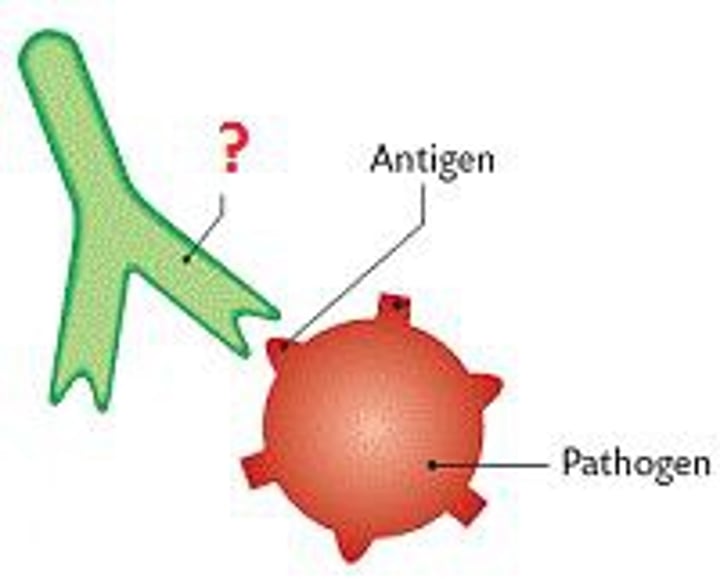
Antigen
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
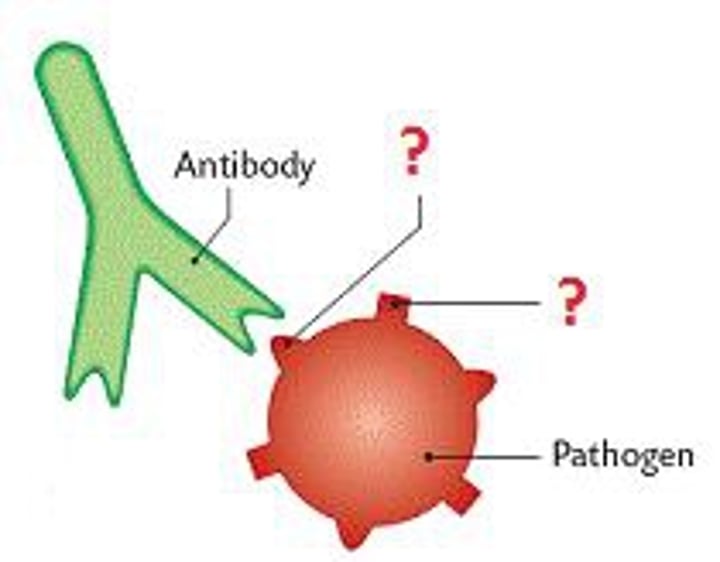
Antibody
(also, immunoglobins or gamma globulins) antigen-specific proteins produced by specialized B lymphocytes that protect the body by binding to foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses
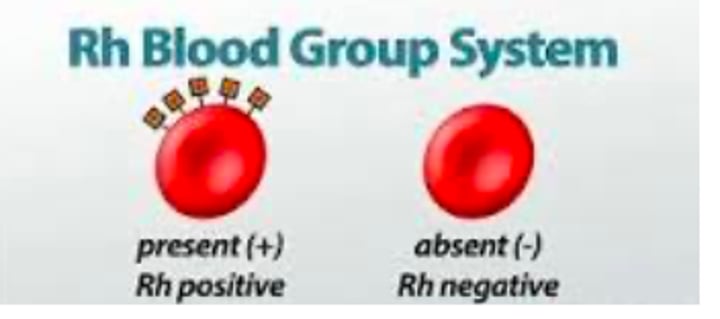
Rh factor
blood type classification based on the presence or absences of the antigen Rh on the erythrocyte membrane surface
Universal Donor
individual with type O- blood
Universal Recipient
AB+
Leukocyte
(also, white blood cell) colorless, nucleated blood cell, the chief function of which is to protect the body from disease
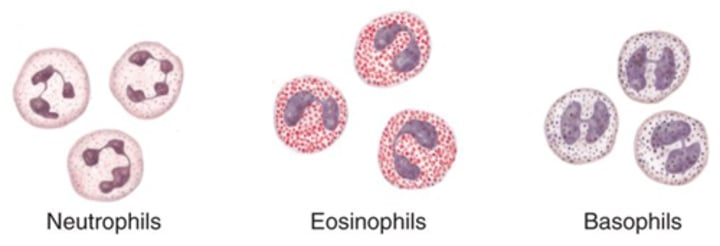
Neutrophil
54-62% of WBC; granulocytes that stain with a neutral dye and are the most numerous of the leukocytes; especially active against bacteria
Eosinophil
1-3% of WBC; granulocytes that stain with eosin; they release antihistamines and are especially active against parasitic worms
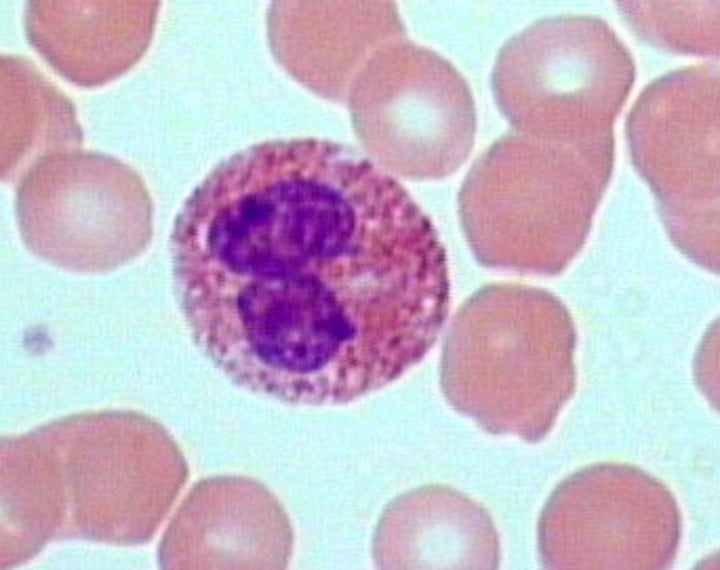
Basophil
<1% of WBC; granulocytes that stain with basic (alkaline) stain and histamine and heparin; mediates the inflammatory response
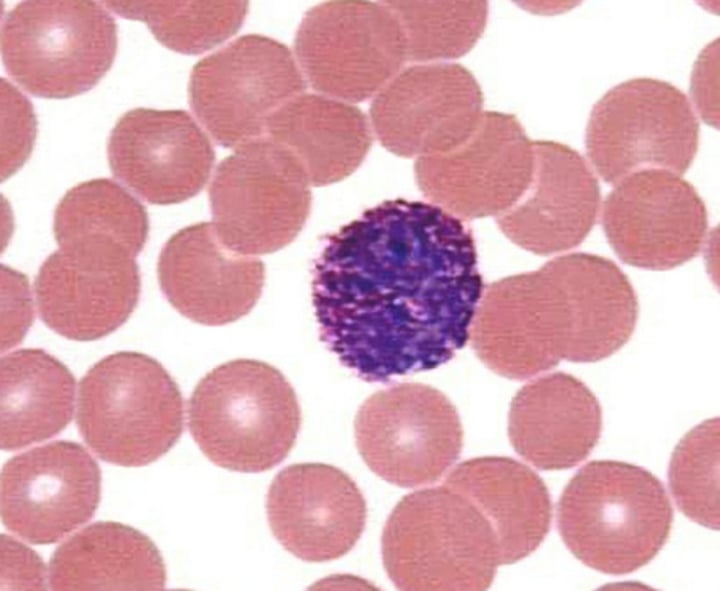
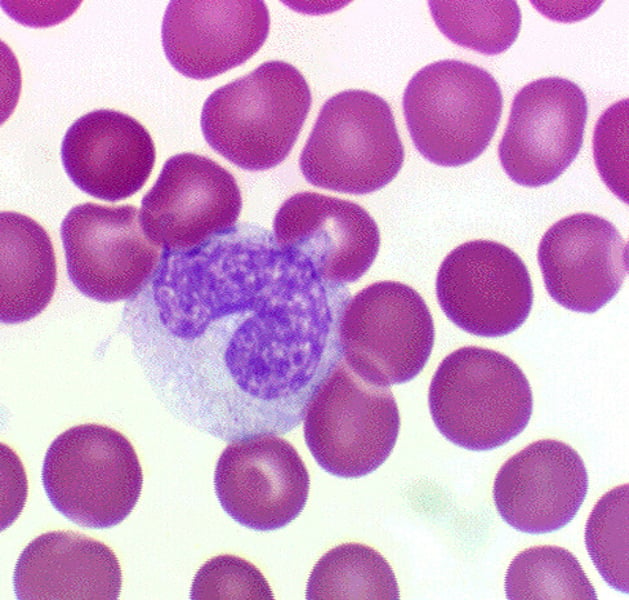
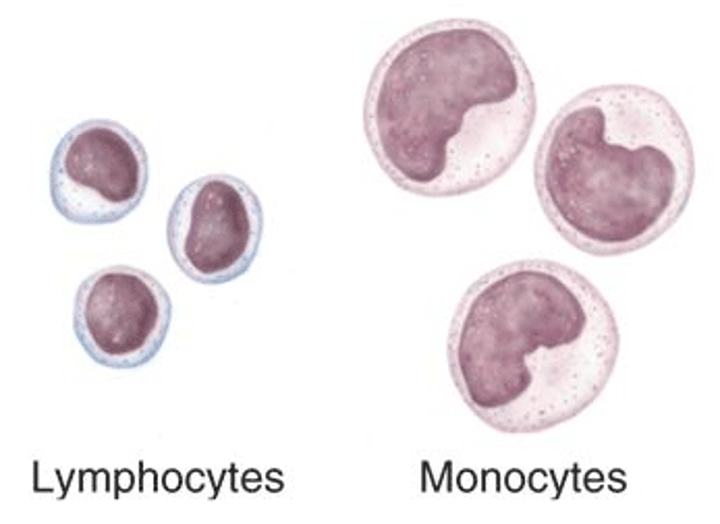
Monocyte
3-9% of WBC; agranular leukocytes of the myeloid stem cell line that circulate in the bloodstream; tissue monocytes are macrophages
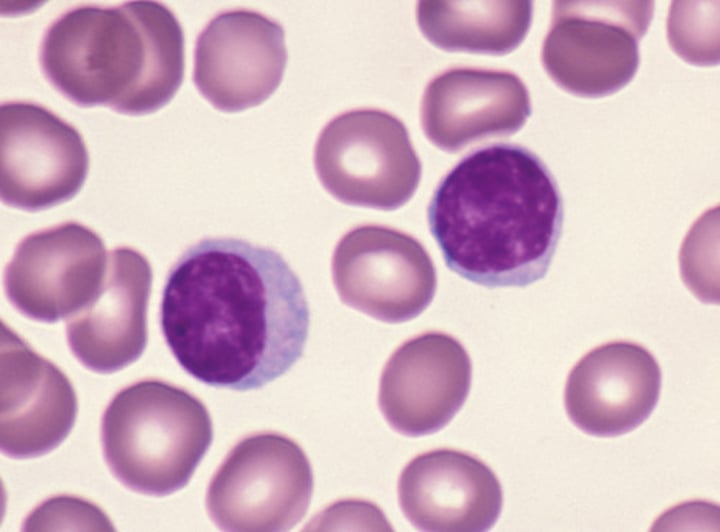
Lymphocyte
25-33% of WBC; 2 types are T and B lymphocytes; agranular leukocyte of the lymphoid stem cell line, many of which function in specific immunity
Granulocyte
leukocytes with abundant granules in their cytoplasm; specifically, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
Agranulocyte
leukocyte with few granules in their cytoplasm; specifically, monocytes, lymphocytes, and NK cells
DIFF
differential white blood cell count indicates the % of each type of WBC in the blood

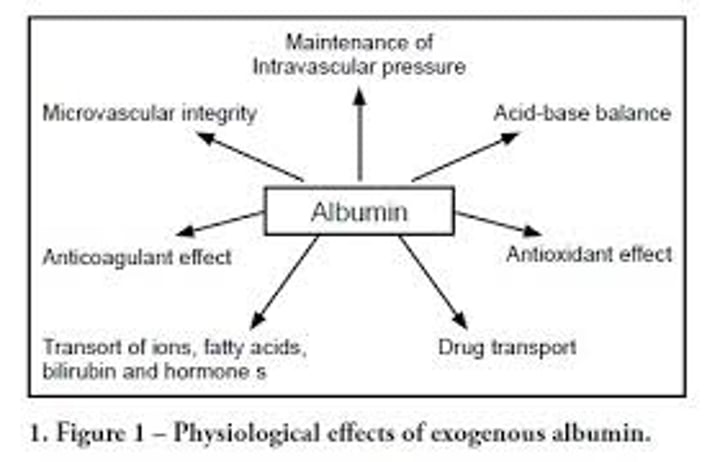
Albumins
most abundant plasma protein, accounting for most of the osmotic pressure of plasma
Globulins
heterogeneous group of plasma proteins that includes transport proteins, clotting factors, immune proteins, and others
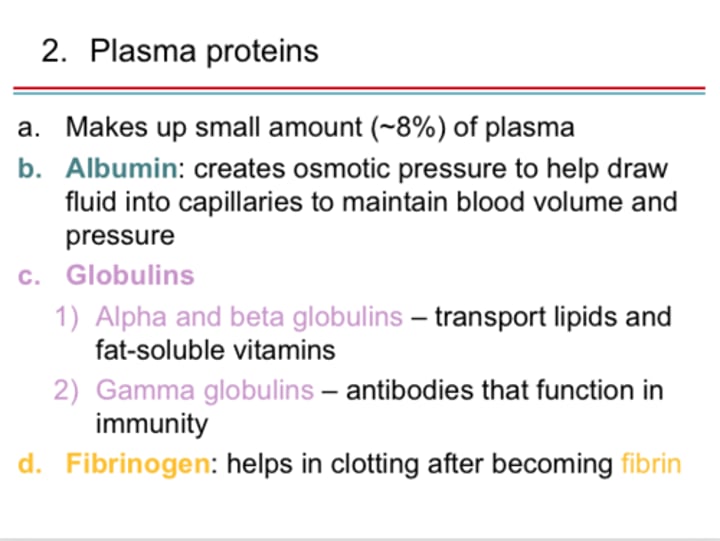
Plasma Protiens
Makes up about 7% and the 3 types are albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen
Plasma Gases
oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen
Non-Protein N Substances (NPNS)
plasma wastes
What are the major NPNS?
urea, uric acid, creatinine, creatine, bilirubin
Electrolytes
Substances that release ions in water; maintains osmotic pressure, resting membrane potential, pH

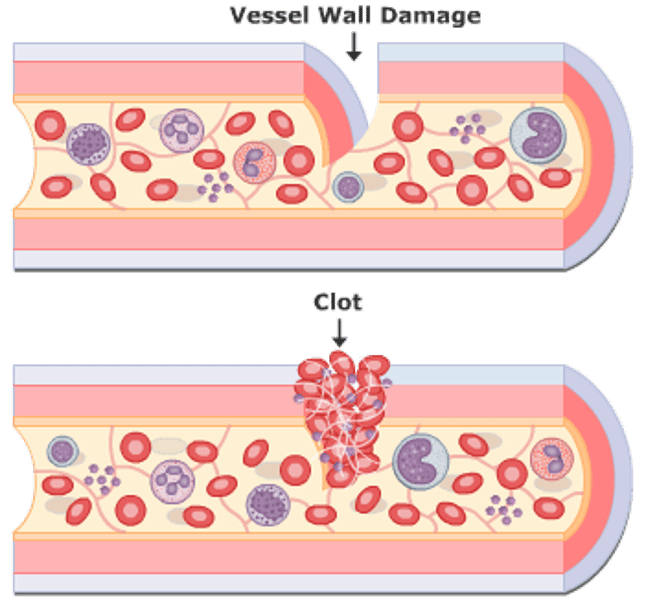
Hemostasis
physiological process by which bleeding ceases
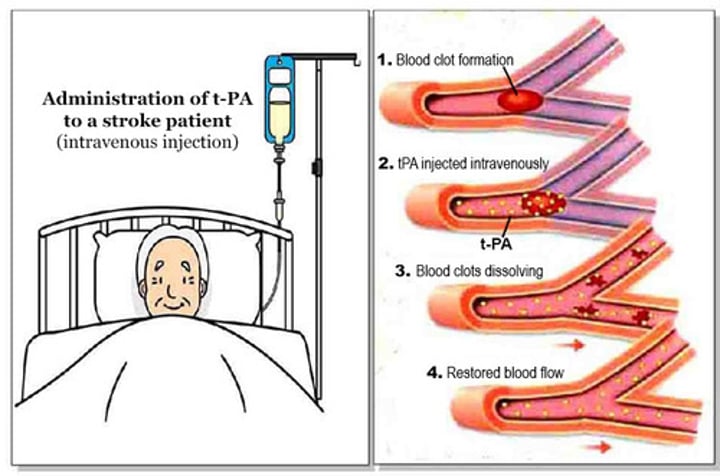
TPA
tissue plasminogen activator; a fibrinolytic substance; a clot-dissolving drug
Warfarin
a fibrinolytic substance; a clot-dissolving drug

Heparin
a fibrinolytic substance; a clot-dissolving drug; short acting anticoagulant stored in mass cells and released when tissues are injured, opposes prothrombin
What are all the formed elements blood?
RBC, WBC, and Platelets
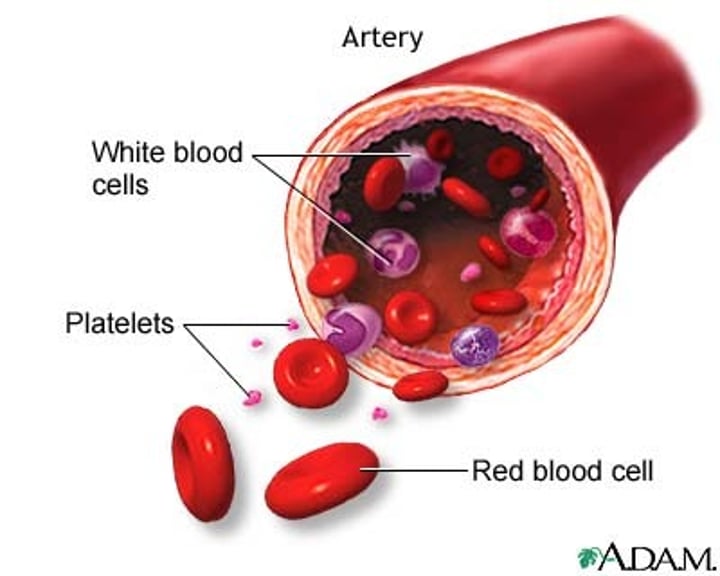
What do red blood cells do?
transport oxygen
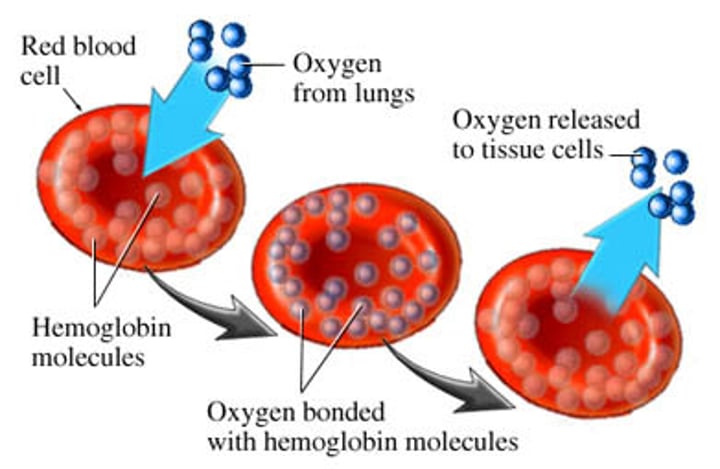
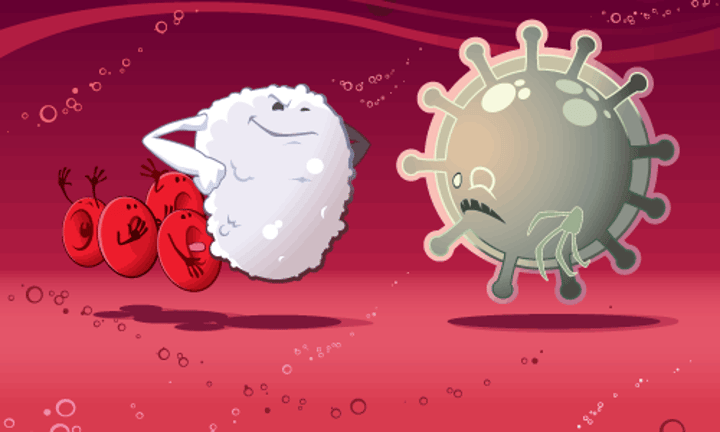
What do white blood cells do?
-They can change shape to ingest microbes - this process is phagocytosis
-Others produce antibodies to fight microbes
-Some produce antitoxins to neutralize any toxins produced by the microbes
-They have a nucleus
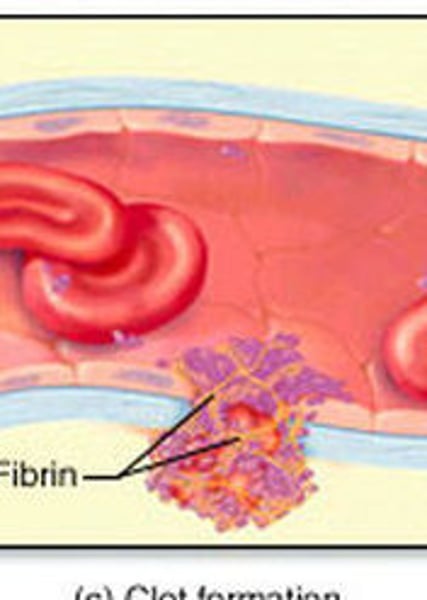
What does platelets do?
clot blood
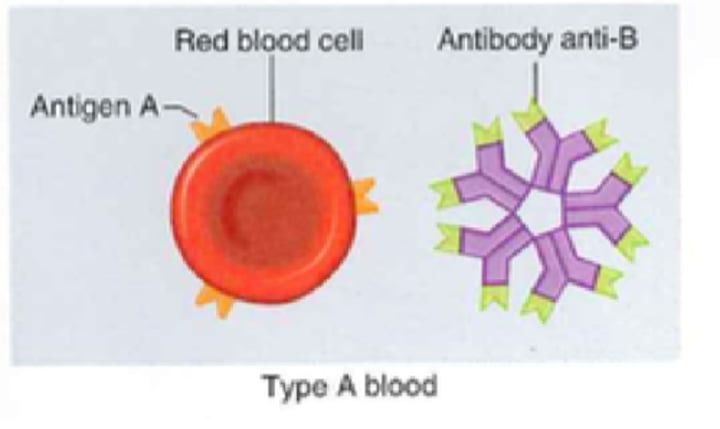
Type A- Blood
- A antigens
- Anti-B antibodies
- No Rh antigens
-Can receive from A- and O-
Type A+ Blood
- A antigen
- Anti-B antibodies
- Rh antigens
- Can receive from A+, A-, O+, and O-
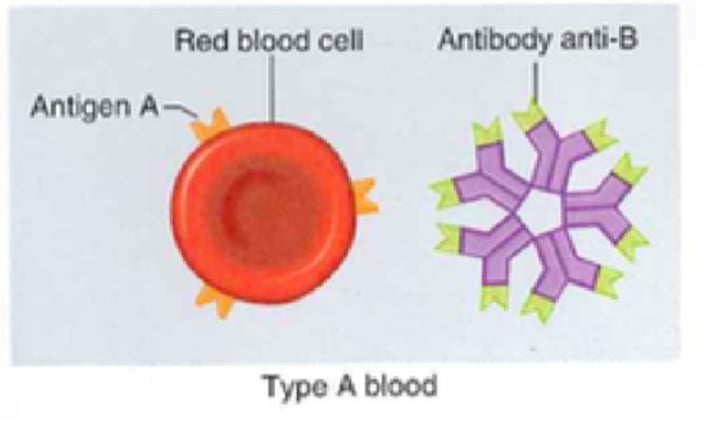
Type B- Blood
- B antigen
- Anti-A antibodies
- No Rh antigens
- Can receive from B- and O-
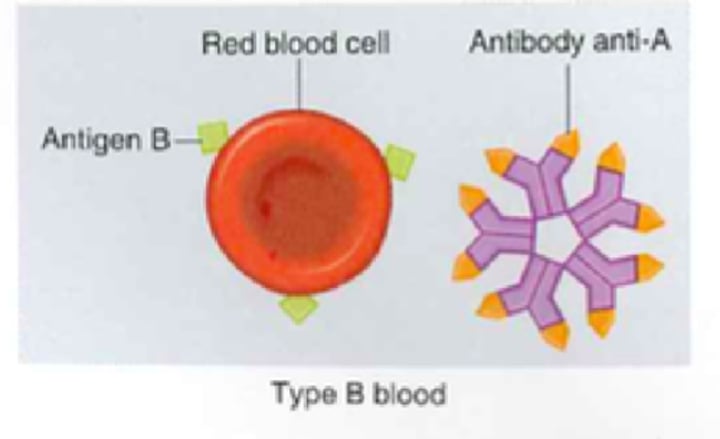
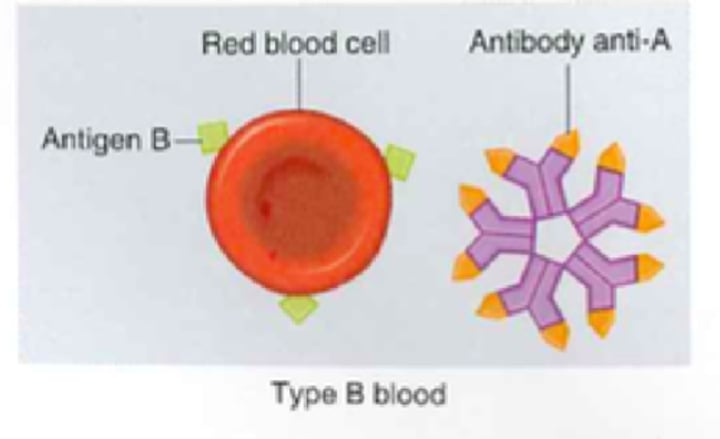
Type B+ Blood
- B antigen
- Anti-A antibodies
- Rh antigens
- Can receive from B+, B-, O+, O-
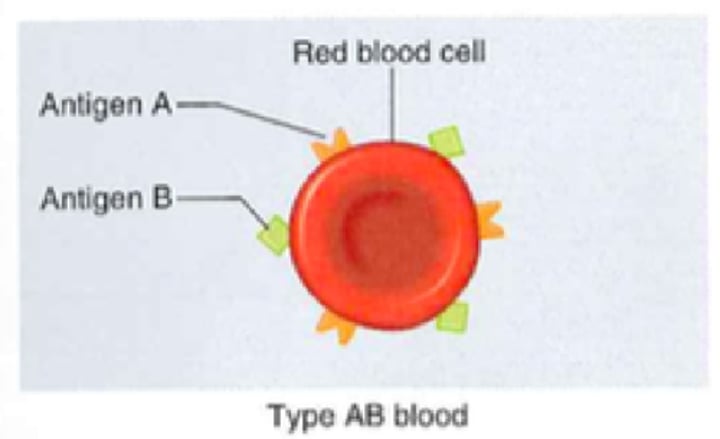
Type AB- Blood
- A and B antigen
- No antibodies
- No Rh antigens
- Can receive from AB-, A-, B-, and O-
Type AB+ Blood
- A and B antigen
- No antibodies
- Rh antigens
- Can receive from all blood types
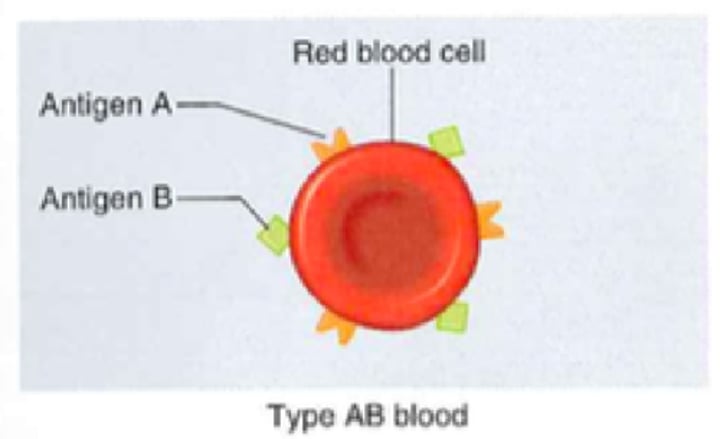
Type O- Blood
- No antigens
- Anti-A and B antibodies
- No Rh antigens
- Can receive from O-
- Can donate to all blood types
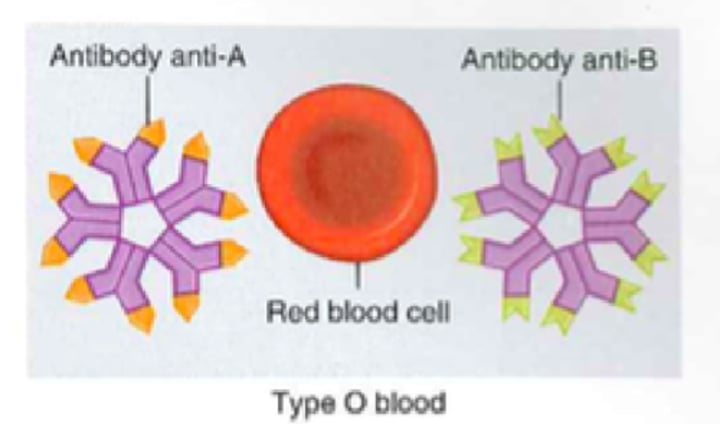
Type O+ Blood
- No antigens
- Anti-A and B antibodies
- Rh antigens
- Can receive from O- and O+
- Can donate to all Rh+ blood types
When are anti-ABO antibodies produced?
shortly after birth
When are anti-Rh antibodies produced?
ONLY after sensitization
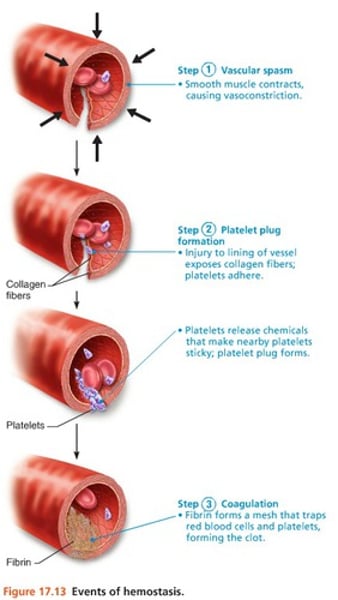
Steps of Clotting Mechanism (hemostasis)
1. Break in the vessel wall
2. As blood escapes, platelets contact collagen fibers
3. Platelets stick to collagen and each other, forming a platelet plug
-platelet releases serotonin(vasoconstrictor) and prothrombin activator
-the prothrombin activator with calcium turns prothrombin(inactive) into thrombin(active)
-Thrombin(active) turns fibrinogen(soluble) into fibrin(insoluble)
4. This creates a blood clot
What is the difference between a thrombus, embolus, and embolism?
-Thrombus- aggregation of fibrin, platelets, and erythrocytes in an intact artery or vein
-Embolus- thrombus that has broken free from the blood vessel wall and entered the circulation
-Embolism- the sudden blockage of a blood vessel by an embolus
Endocardium
the innermost layer of the heart lining the heart chambers and heart valves; composed of endothelium reinforced with a thin layer of connective tissue that binds to the myocardium
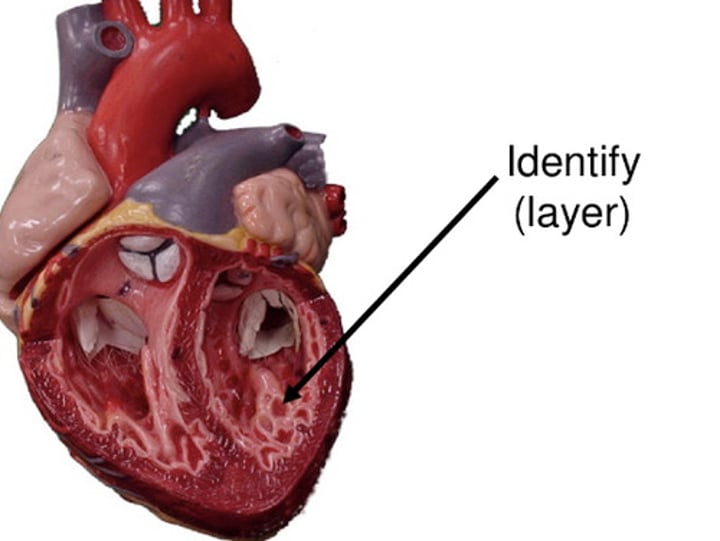
Myocardium
thickest layer of the heart composed of cardiac muscle cells built upon a framework of primarily collagenous fibers and blood vessels that supply it and the nervous fibers that help to regulate it
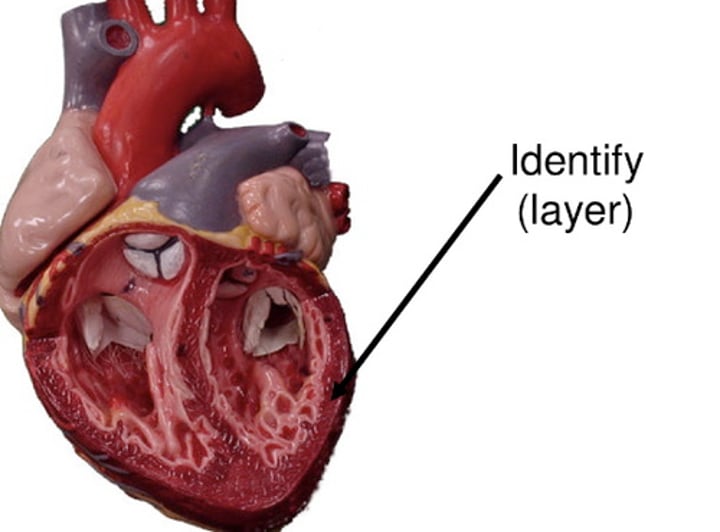
Epicardium
the innermost layer of the serous pericardium and the outermost layer of the heart wall; used when talking about the outer layer of layer of heart
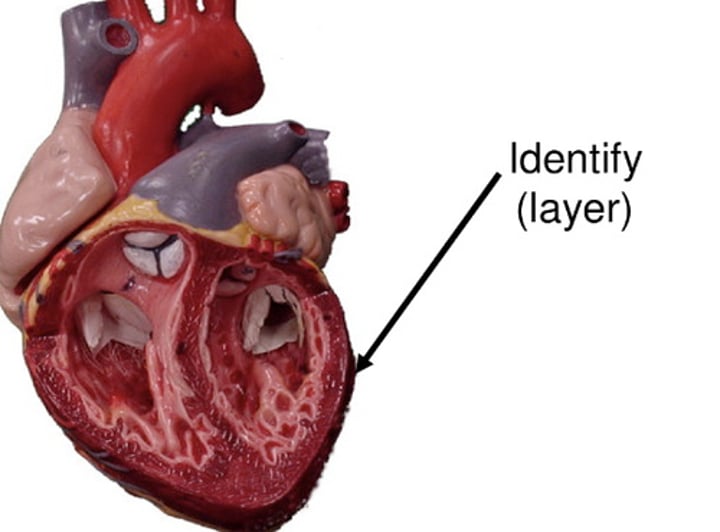
Visceral Pericardium
the innermost layer of the serous pericardium and the outermost layer of the heart wall; used when talking about the innermost layer of the serous pericardium
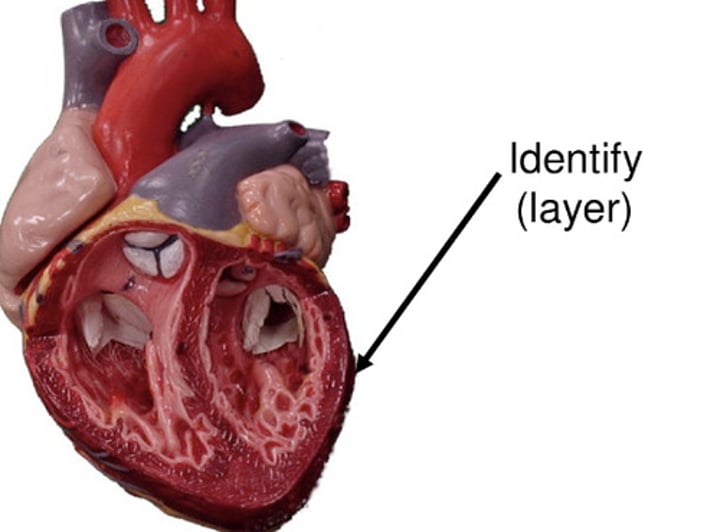
Parietal Pericardium
part of the membrane that separates the heart from other mediastinal structures; the outermost layer of serous pericardium
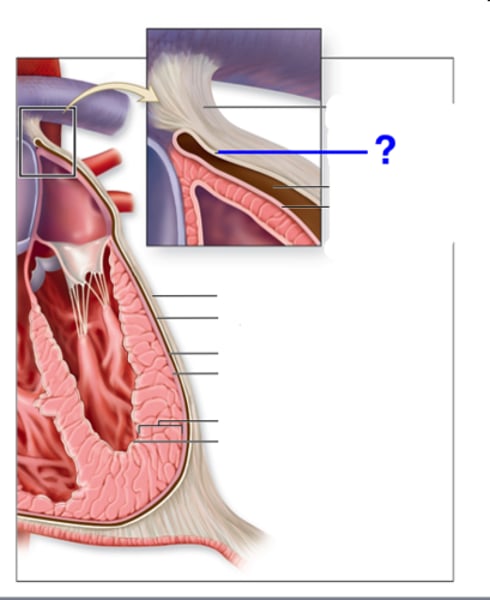
Fibrous Pericardium
the tough, white fibrous connective tissue that is the outer layer of the pericardium
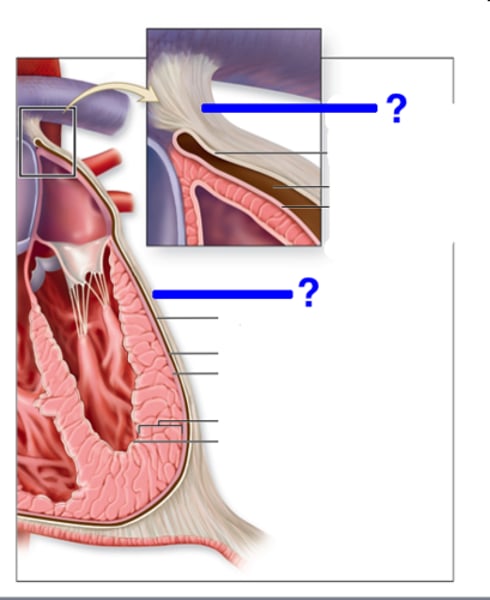
Serous Pericardium
the thinner, more delicate membrane that forms a double layer around the heart; made of the Visceral and Parietal Pericardium
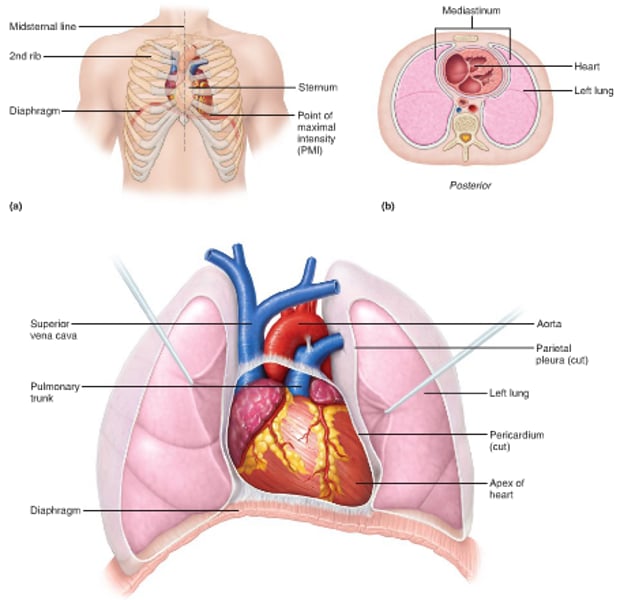
Location of the Heart
Thorax between the lungs in the inferior mediastinum
Atrium
(plural=atria) upper or receiving chamber of the heart that pumps blood into the lower chambers prior to their contraction; the right atrium receives blood systemic circuit that flows into the right ventricle; the left receives blood from the pulmonary circuit that flows into the left ventricle
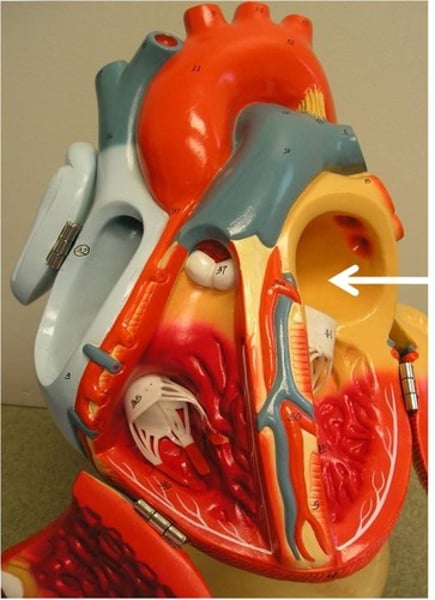
Ventricle
one of the primary pumping chambers of the heart located in the lower portion of the heart; the left ventricle is the major pumping chamber on the lower left side of the heart that ejects blood into the systemic circuit via the aorta and receives blood from the left atrium; the right ventricle is the major pumping chamber on the lower side of the heart the ejects blood into the pulmonary circuit via the pulmonary trunk and receives blood from the right atrium
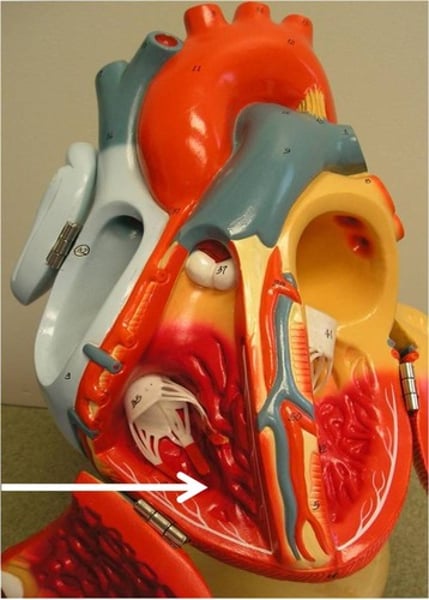
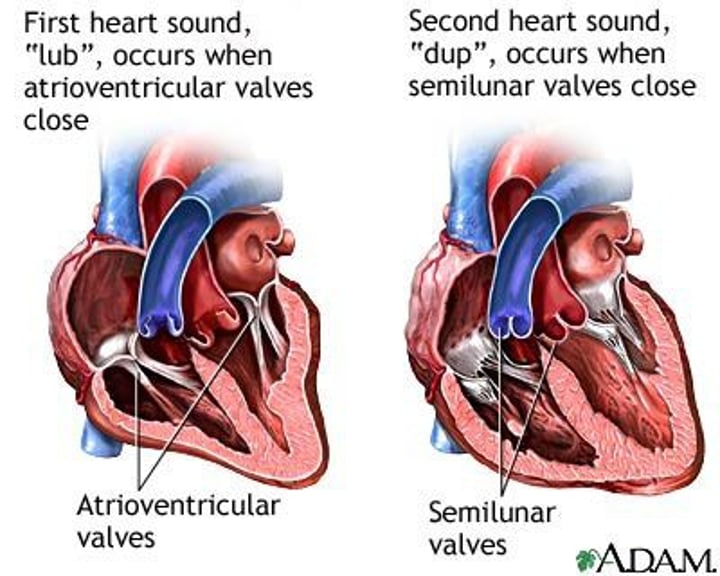
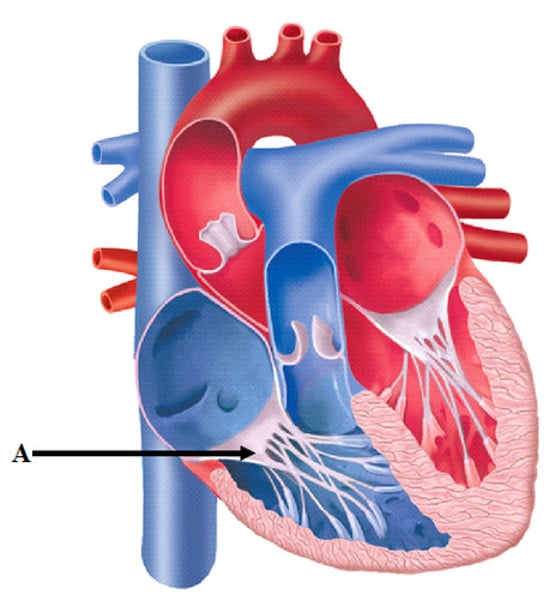
AV valves
one-way valves located between the atria and the ventricles; the valve on the right is called the tricuspid valve, and the one on the left is the mitral or bicuspid valve
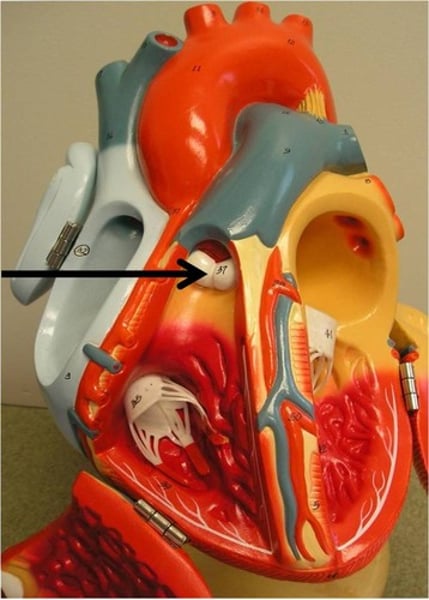
SL valves
valves located at the base of the pulmonary trunk(pulmonary valve) and the base of the aorta(aortic valve)
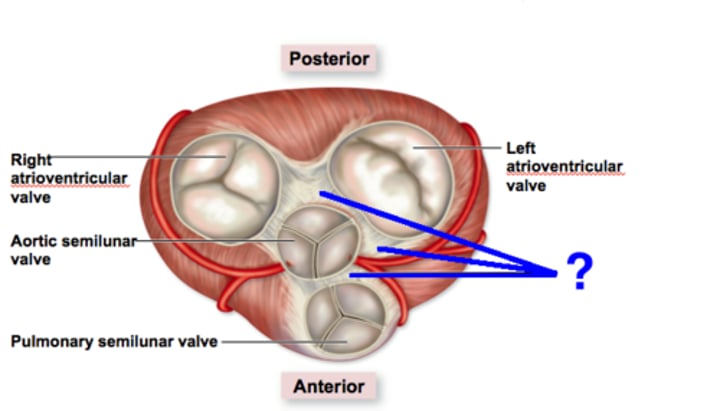
Skeleton of the Heart
rings of dense connective tissue surrounding the pulmonary trunk and aorta
Artery
A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart; may be carrying or distributing vessel
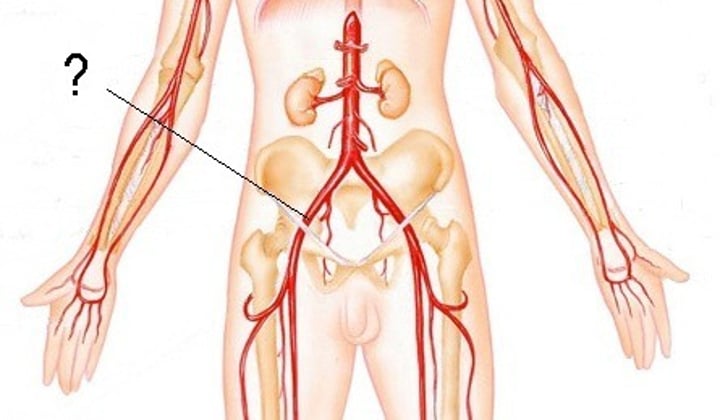
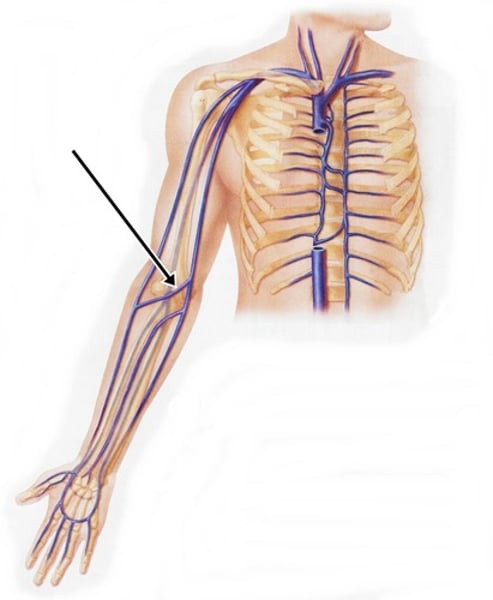
Vein
blood vessels that carry blood to the heart
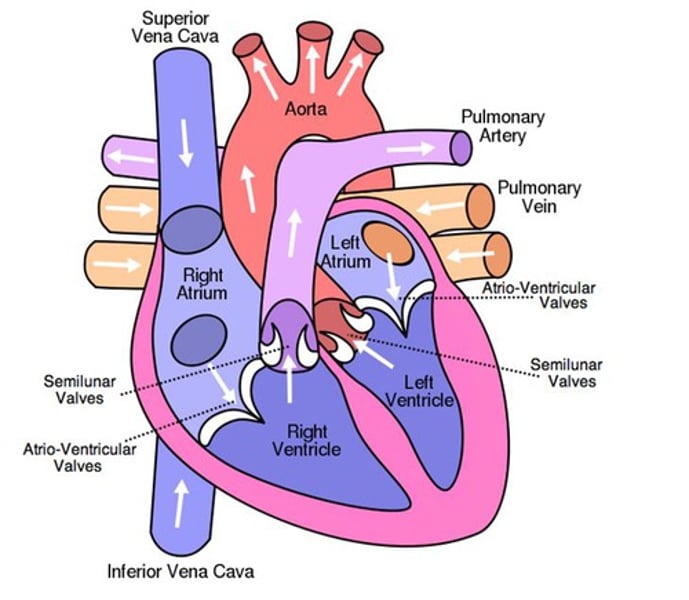
Chambers and Valves of the heart
-Right and left atria
-Right and left ventricles
-Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral/bicuspid)
-Semilunar valves (pulmonary and aortic)
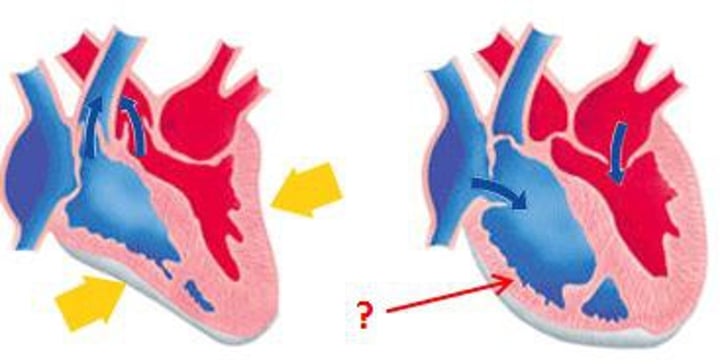
Systole
period of time when the heart muscle is contracting
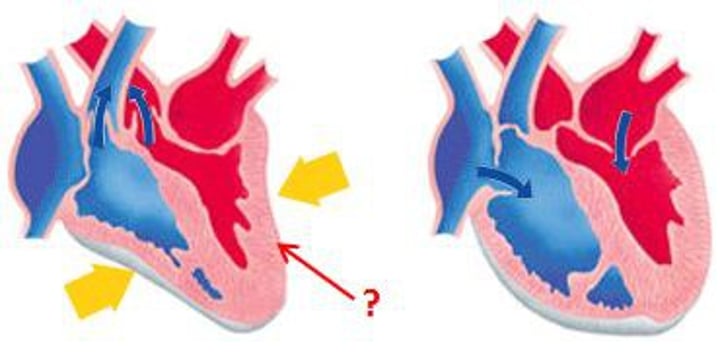
Diastole
period of time when the heart muscle is relaxed and the chambers fill with blood
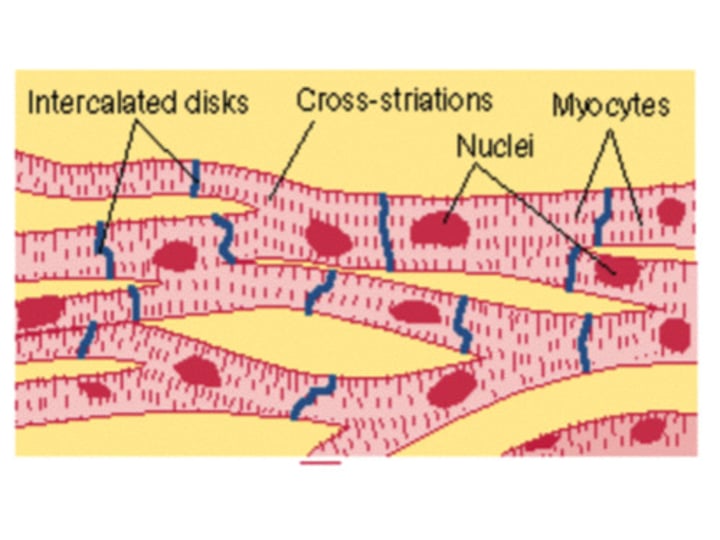
Cardiac Myocytes
heart muscle cells
Functional Syncytium
merging cells performing as a unit; those of the heart are joined electrically
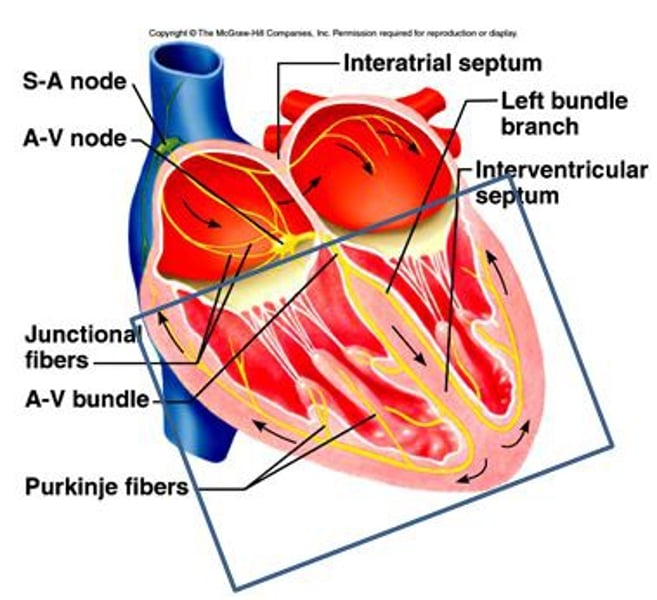
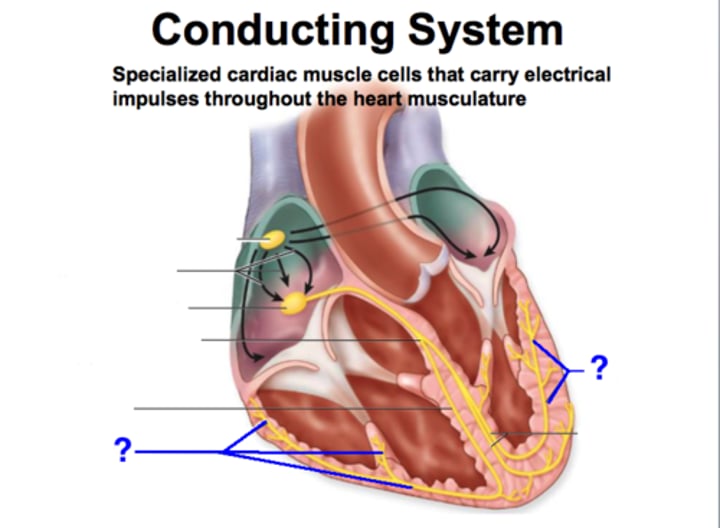
CCS
cardiac conduction system
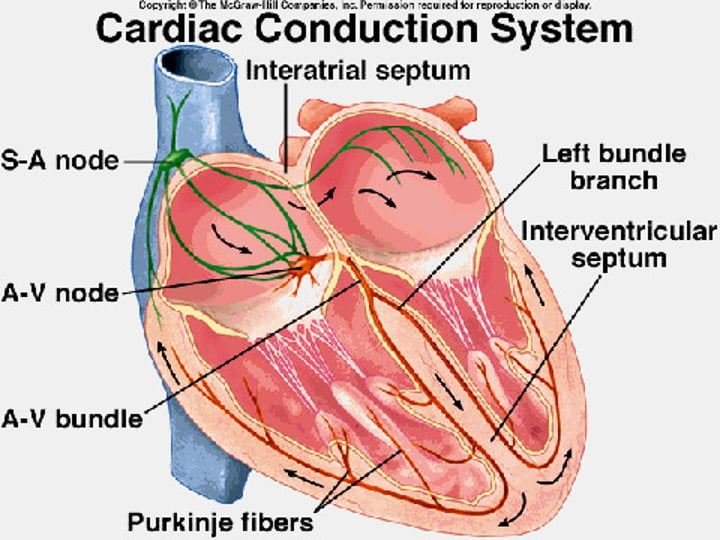
SA Node
known as the pacemaker, a specialized clump of myocardial conducting cells located in the superior portion of the right atrium that has the highest inherent rate of depolarization that then spreads throughout the heart (Sinoatrial Node)
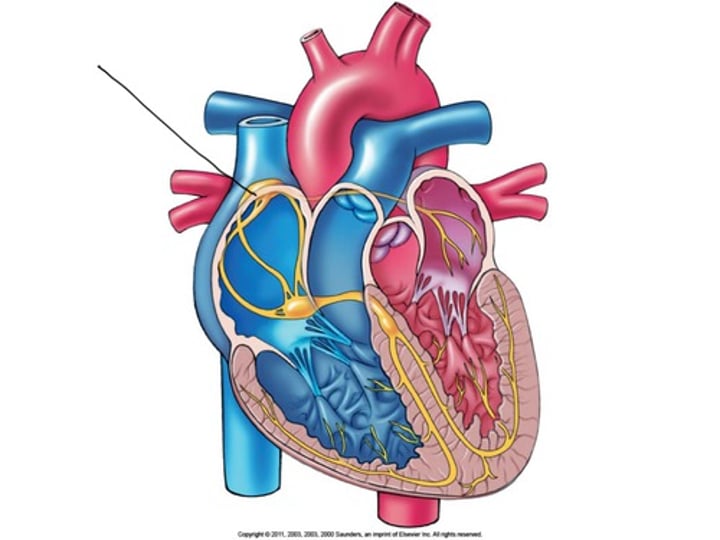
AV Node
a clump of myocardial cells located in the inferior portion of the right atrium within the atrioventricular septum; receives the impulse from the SA node, pauses, and then transmits it into specialized conducting cells within the interventricular septum (atrioventricular node)
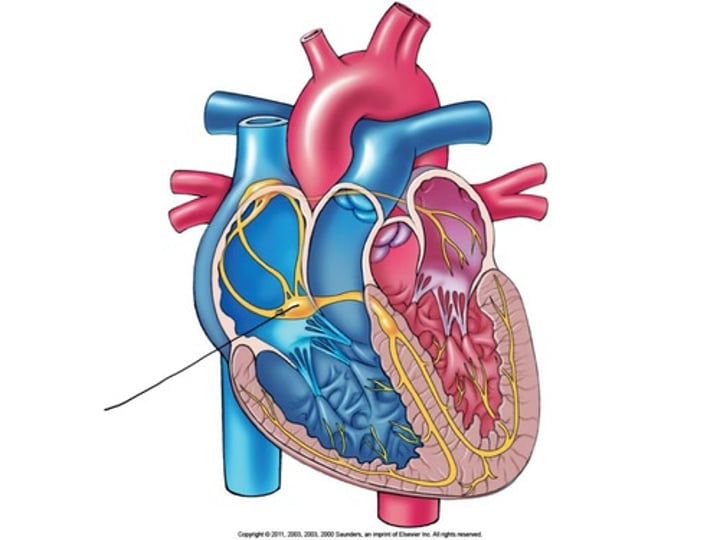
Bundle Branch Block
impulse is delayed or blocked within the bundle branches of the normal conduction pathway
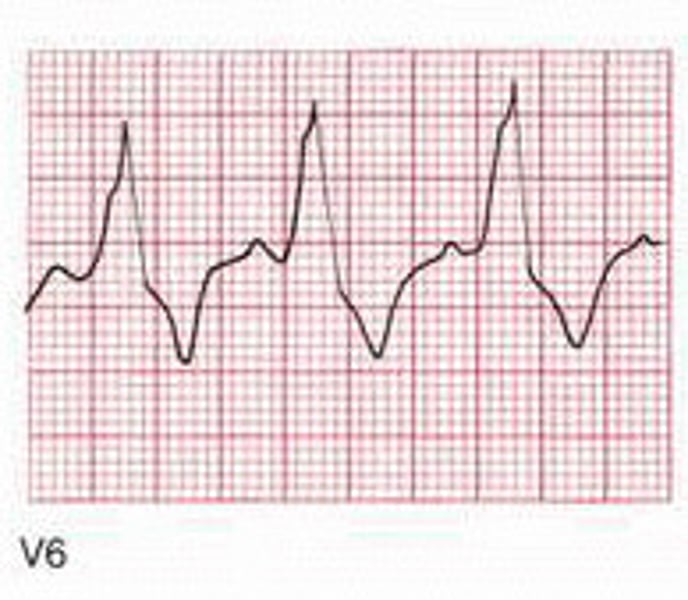
Bundle Branches
Branches off the Bundle of His that conduct impulses to the left and right ventricles
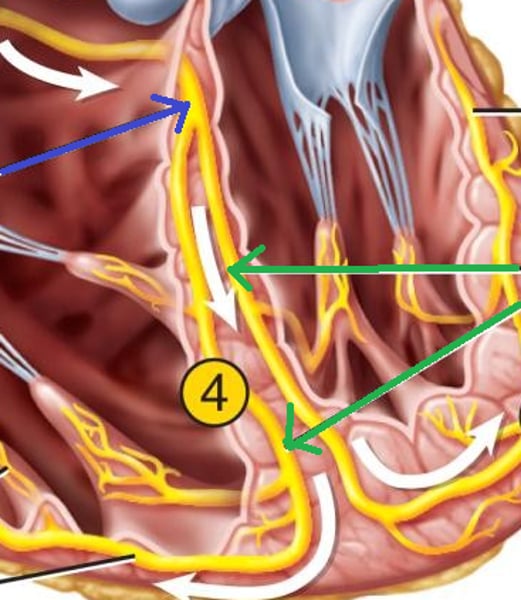
Purkinje Fibers
specialized myocardial conduction fibers that arise from the bundle branches and spread the impulse to the myocardial contraction fibers of the ventricles
Components of an ECG
P wave, QRS complex, T wave
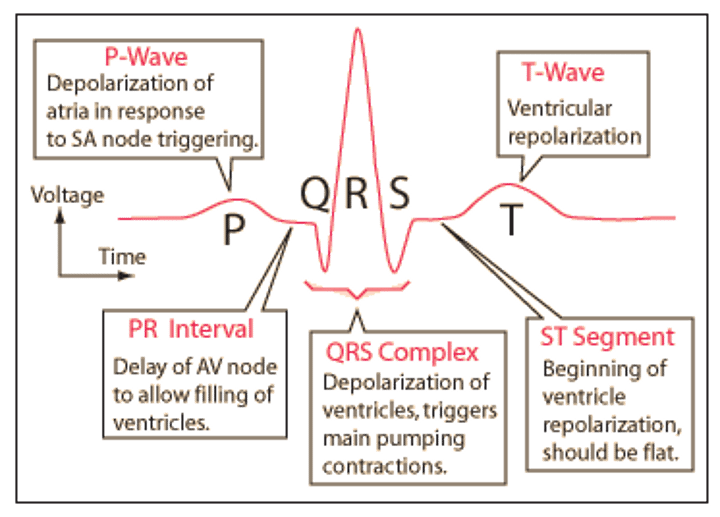
Depolarization
Systole; contraction; when myocytes trigger other myocytes to contract a certain part of the heart
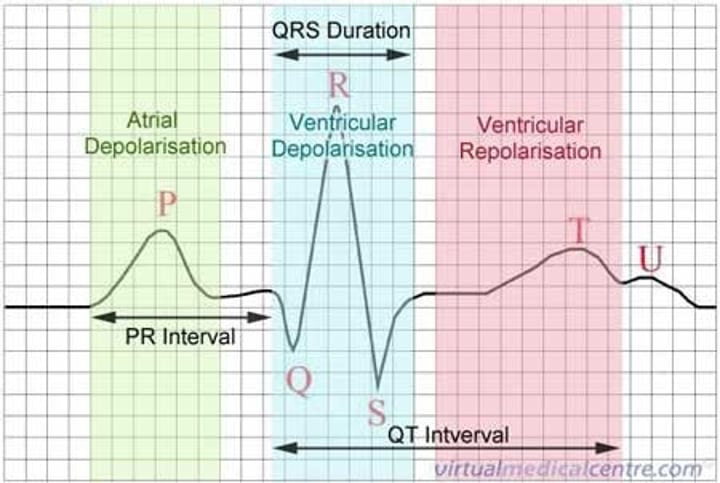
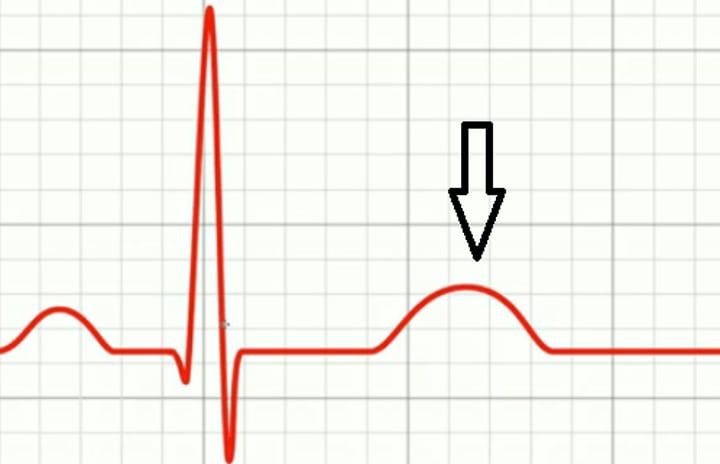
Repolarization
Diastole; relaxing; when myocytes calm down and relax that part of the heart
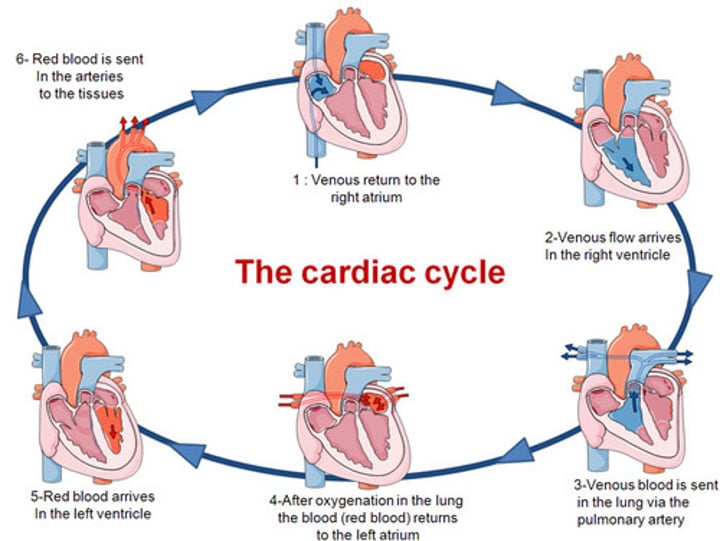
Cardiac Cycle
period of time between the onset of atrial contraction (atrial systole) and ventricular relaxation (ventricular diastole)
Lubb
closure of the tricuspid and mitral valves at the beginning of systole
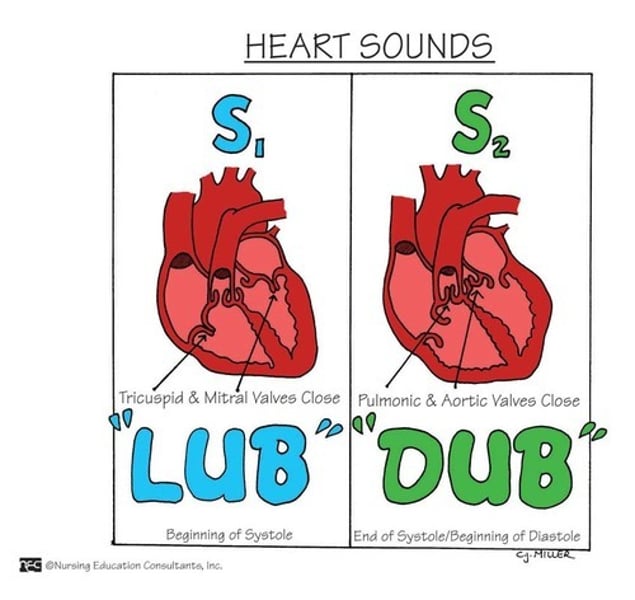
Dupp
closing of semilunar valves