AP Exam Review
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
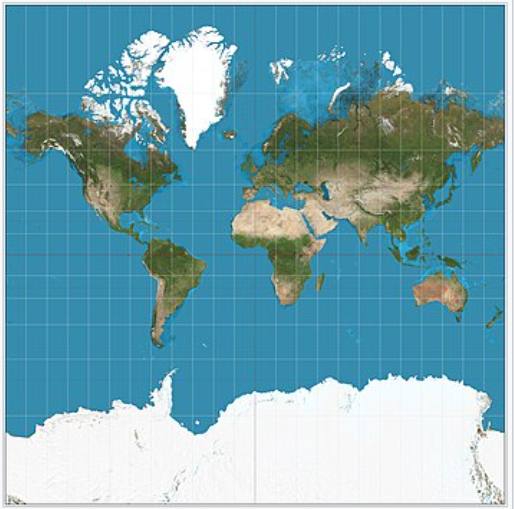
Mercator Projection
A cylindrical map projection that distorts size near the poles but maintains accurate shapes, useful for navigation.
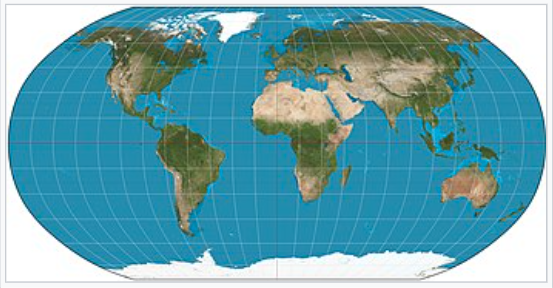
Robinson Projection
A compromise projection that shows continents with less distortion, commonly used in world maps.
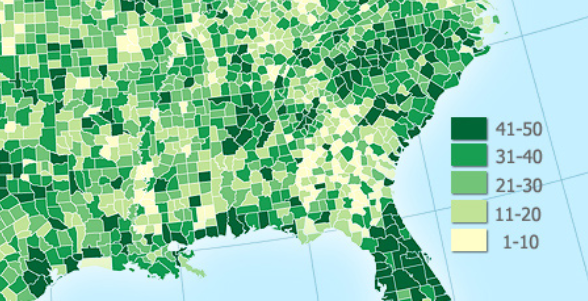
Choropleth Map
Maps that use shading to represent data, such as population density.
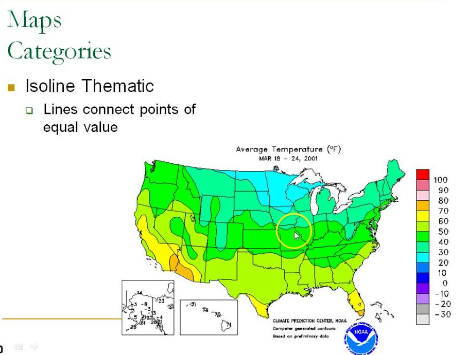
Isoline Map
Maps that connect points of equal value using lines, commonly seen in weather maps.
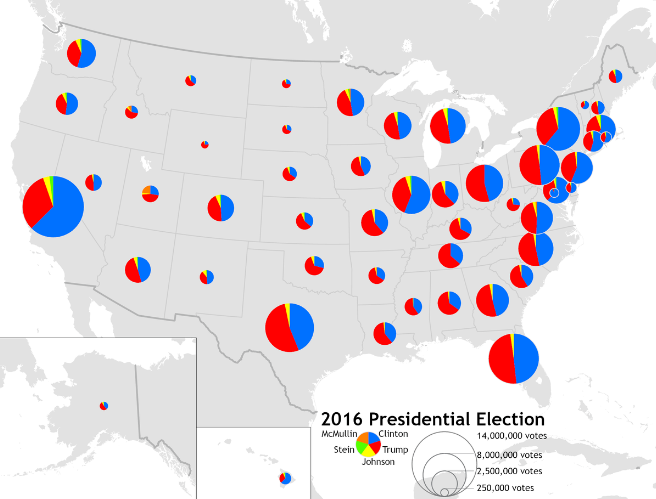
Proportional Symbol Map
Maps where symbols of different sizes represent the magnitude of a variable, like circle sizes showing population.
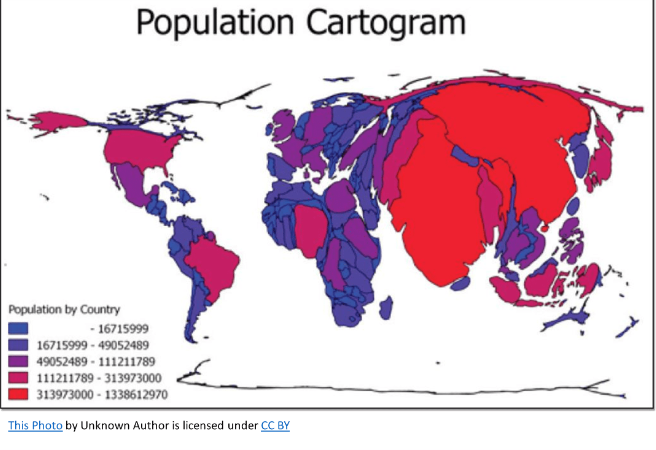
Cartogram
Maps that distort size or shape to show data, such as population information.
GPS
Global Positioning System, a satellite system for determining precise locations on Earth.
GIS
Geographic Information System, used to analyze spatial data and create detailed geographic patterns.
Remote Sensing
The collection of data about Earth's surface using satellite or aerial imagery.
Formal Region (Uniform)
Regions defined by clear boundaries and specific criteria, such as political boundaries.
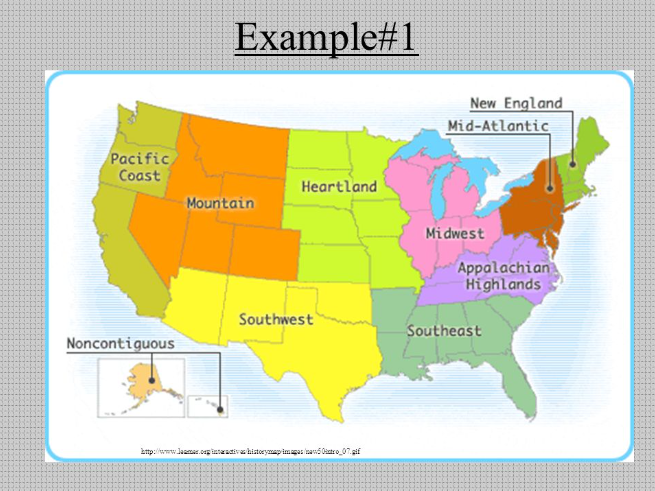
Functional Region (Nodal)
Regions defined by a central node and its influence, such as metropolitan areas.
Vernacular/perceptual Region
Regions defined by people's perceptions, like 'The South' in the U.S.
Distance Decay
The decrease in interaction as distance increases.
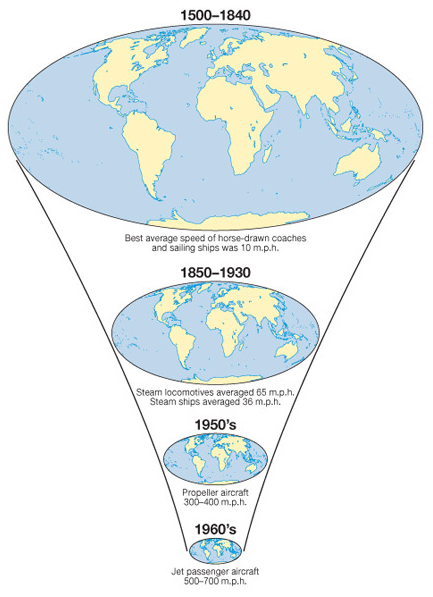
Time-Space Compression
The notion that advances in transportation and communication reduce the effective impact of distance.
Globalization
The increasing interconnectedness of the world.
Environmental Determinism
The belief that the physical environment dictates human behavior.
Possibilism
The idea that humans can adapt and make choices within environmental constraints.
Site
The physical characteristics of a place, such as landforms and climate.
Absolute Location
The exact location of a place defined by coordinates (latitude/longitude).
Relative Location/situation
The position of a place in relation to other locations.
Toponyms
The study of place names and their origins.
Sustainability
The ability to maintain processes long-term, considering environmental, social, and economic factors.
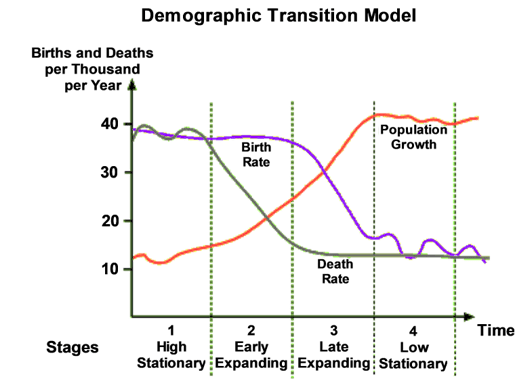
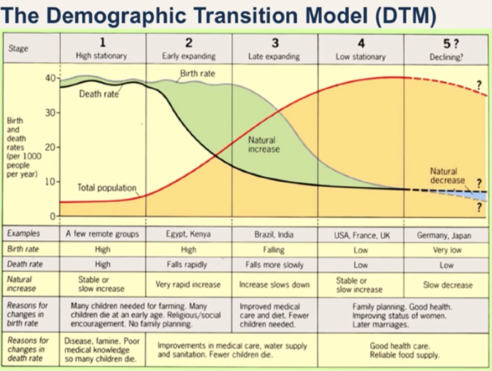
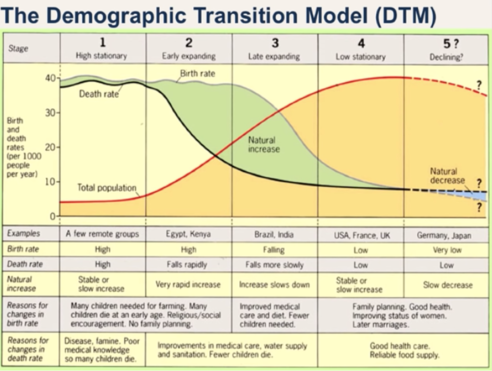
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
A model explaining the shift from high birth/death rates to low rates as a country develops.
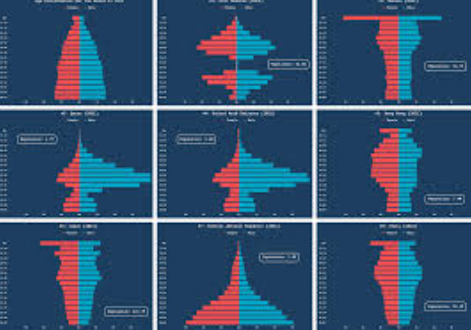
Population Pyramid
Visual representations showing the distribution of age groups in a population, typically by gender.
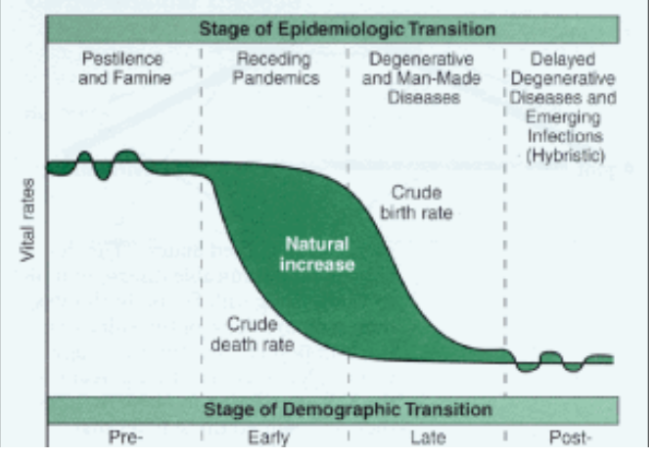
Epidemiologic Transition Model
Describes changes in causes of death across different stages of the DTM.
Thomas Malthus
Theory that population growth will outstrip resources, leading to famine and poverty.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman is expected to have during her lifetime.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum population that an environment can support.
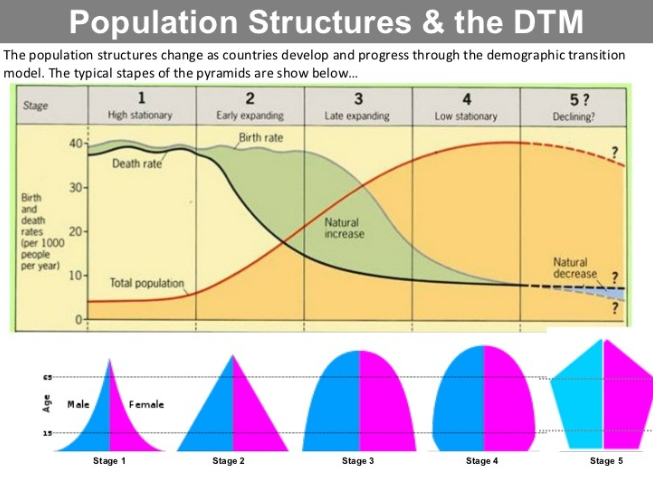
Dependency Ratios (DTM)
The ratio of the dependent population (children and elderly) to the working-age population.
Pro-Natal Policies (DTM)
Policies encouraging higher birth rates, such as tax breaks and maternity leave.
Anti-Natal Policies (DTM)
Policies aimed at limiting population growth, like China's one-child policy.
Arithmetic Density
Total population divided by total land area.
Physiologic Density
Population per unit of arable land.
Agricultural Density
Number of farmers per unit of arable land.
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration
Basic principles outlining why and how people migrate, often for economic reasons.

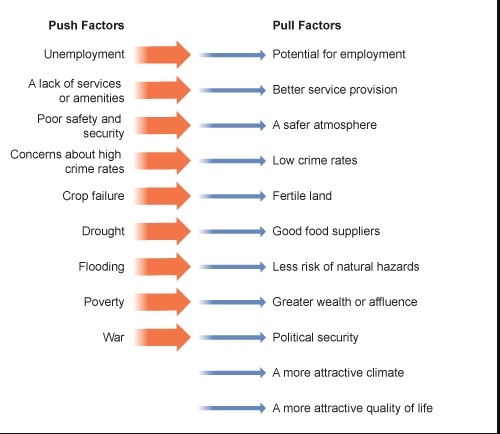
Push Factors (Categories and EX)
Circumstances that drive people away from their current location, like war or famine.

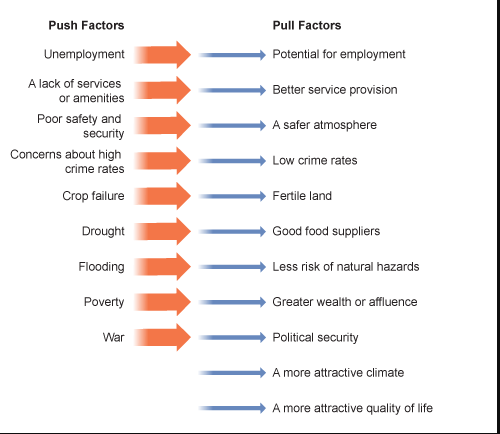
Pull Factors (Categories and EX)
Attractions that draw people to a new location, such as job opportunities.
Refugees
People who flee their home country due to fear of persecution.
Asylum Seekers
Individuals seeking protection in another country.
Rural to Urban Migration
Movement from rural areas to cities(urban), usually for industrial jobs and urbanization.
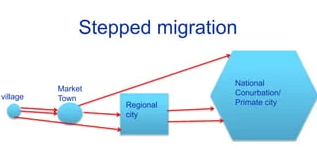
Step Migration
Migration occurring in stages, often from small towns to larger cities (think about stairs).
Brain Drain
The emigration of skilled workers from a country.
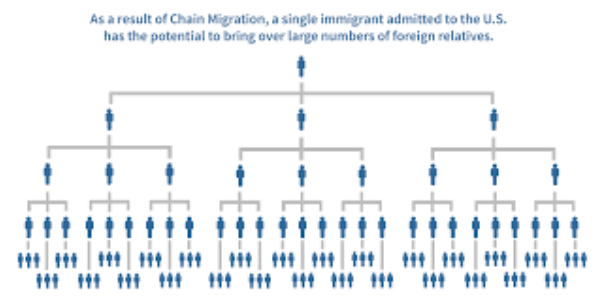
Chain Migration
Migration where individuals follow others to the same destination.
Cultural Traits
Elements that compose a culture, including language, religion, and customs.

Cultural Landscape
The visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape.

Sequent Occupance
Successive societies leaving their mark on the landscape over time.
Centripetal Forces
Forces that unite a country or society.
Centrifugal Forces
Forces that divide a country or society.

Relocation Diffusion
Spread of culture through the physical movement of people.

Contagious Diffusion
Spread of ideas through people, such as social media.

Hierarchical Diffusion
Spread starting from larger cities to smaller areas.
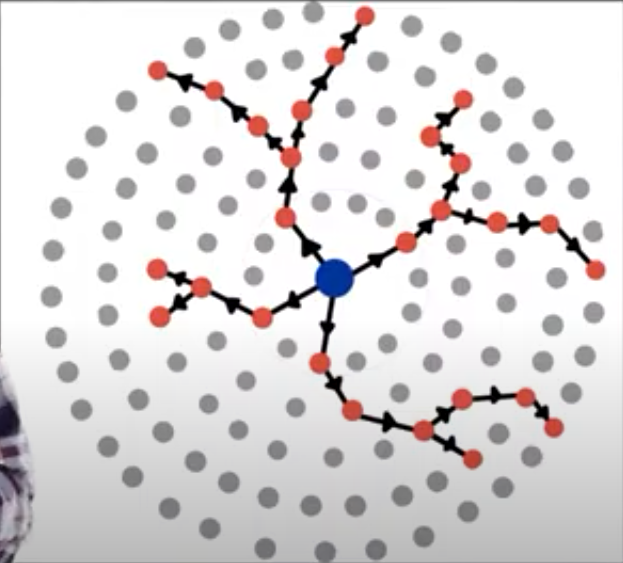

Stimulus Diffusion
Spread of an idea that is adapted to fit a new environment.
Acculturation
Cultural change due to contact with another culture.
Assimilation
Process where individuals adopt another culture's traits.
Ethnocentrism
Judging another culture based on the standards of one's own.
Cultural Relativism
The belief that no culture is superior to another.
Syncretism
The blending of different cultural or religious beliefs.
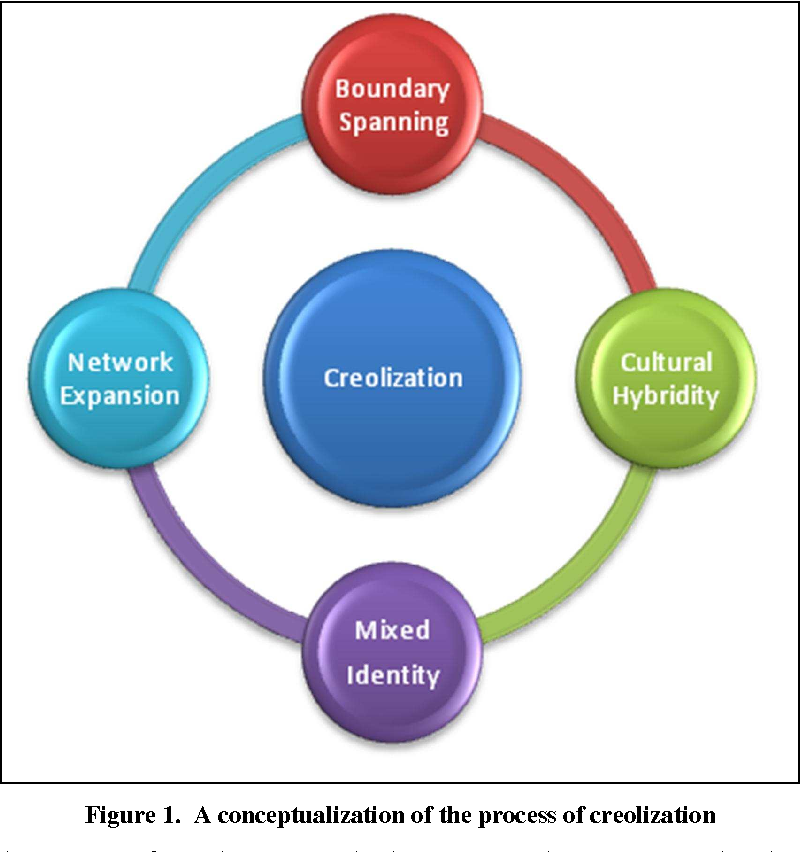
Creolization
Mixing of two or more languages to create a new one.
Taboo
Cultural prohibitions against certain actions or behaviors.
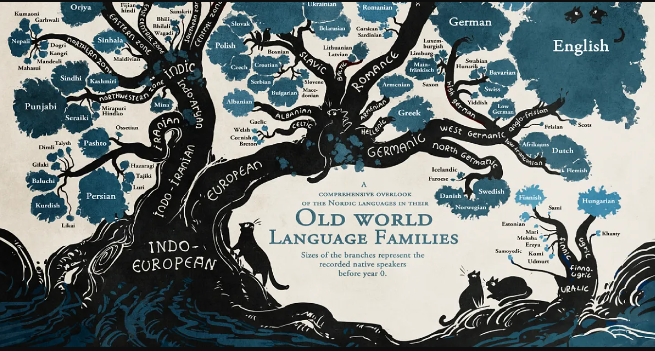
Language Family
A large group of related languages, such as Indo-European.
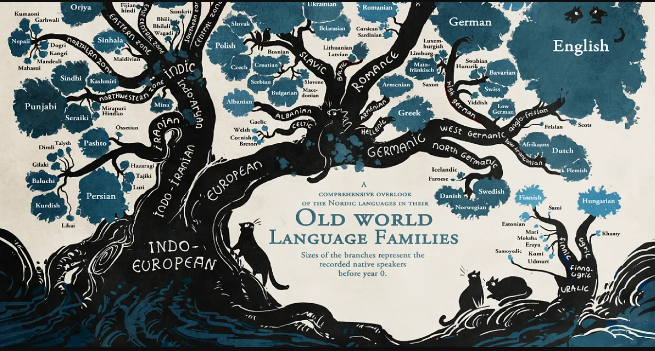
Language Branch
A smaller group within a language family, like Germanic within Indo-European.
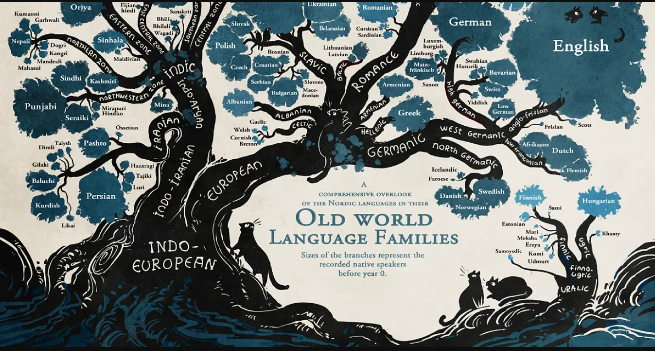
Language Group
Set of related languages within a branch, such as Spanish and Italian.
Lingua Franca
A common language used for communication between speakers of different languages.
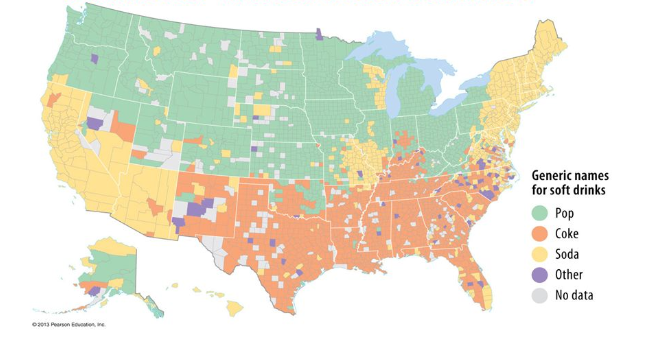
Isogloss
A geographical boundary marking the limits of a linguistic feature.
Ethnic Religions
Religions linked to a particular ethnic group, like Judaism.
Universalizing Religions
Religions that aim to convert people worldwide, such as Christianity.
Monotheistic Religions
Religions that believe in one deity, including Christianity and Islam.
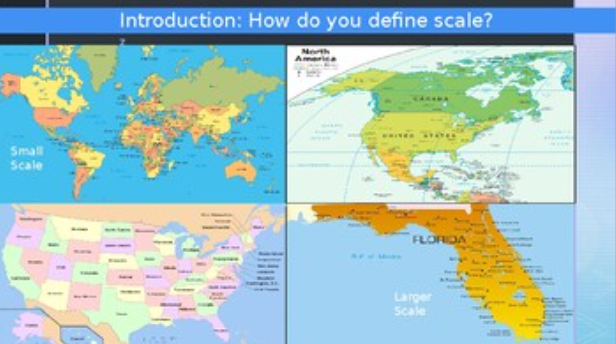
Scale
Scale is about the size or extent of the study area (local, regional, national, global, etc.)
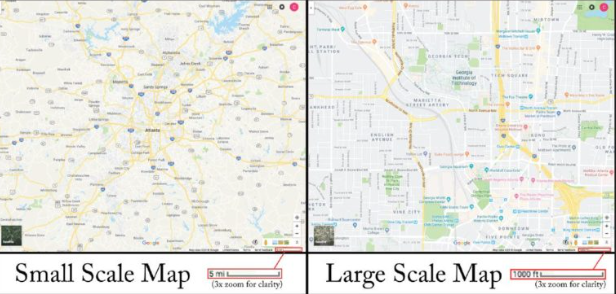
Scale of analysis
Is about the level of detail and unit of analysis (individual, neighborhood, country, etc.)
Census
an official count of a population that collects key information about people and households.
Intervening Obstacles
________________ are barriers that make it harder for people to move or migrate from one place to another, such as physical, economic, political, or social challenges.
Intervening Opportunities
_____________ are better options that appear during migration and cause people to settle in a place before reaching their original destination.