Systems Path section 5 - The heart (pg 1-25)
what happens when heart can't meet demands (MC) or increased tissue command occurs results in cognition "backing up" in pulmonary and systemic circulation
heart failure (CHF)
heart failure symptoms
dyspnea, fatigue, orthopnea, tachycardia
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what happens when heart can't meet demands (MC) or increased tissue command occurs results in cognition "backing up" in pulmonary and systemic circulation
heart failure (CHF)
heart failure symptoms
dyspnea, fatigue, orthopnea, tachycardia
how does CHF occur?
increased tissue congestion and complications due to compensations
who gets CHF?
older individuals or those that have had MI (and other risks)
causes of CHF
history of MI, HTN, CAD
Systolic dysfunction (CHF) results in
weak contraction
diastolic dysfunction (CHF) results in
failed relaxation
valvular dysfunction (CHF) results in
failure to effectively seal
forward failure (CHF) results in
insufficient output
backward failure (CHF) results in
congestion
forward failure is almost always accompanied by what?
backward failure (impacts virtually every organ)
The greater the stretch, the stronger is the heart's contraction.
Result is increased output
Cost is increased O2 and tension
frank-starling law
which neurohumoral mechanism increases HR and contractility?
NE
which neurohumoral mechanism causes diuresis and vasodilation?
ANP
structural changes associated with compensated heart failure
cardiac hypertrophy
cost is increased O2 consumption
what type of cardiac hypertrophy is pathologic resulting in increased pressure (HTN/valve stenosis)
concentric hypertrophy
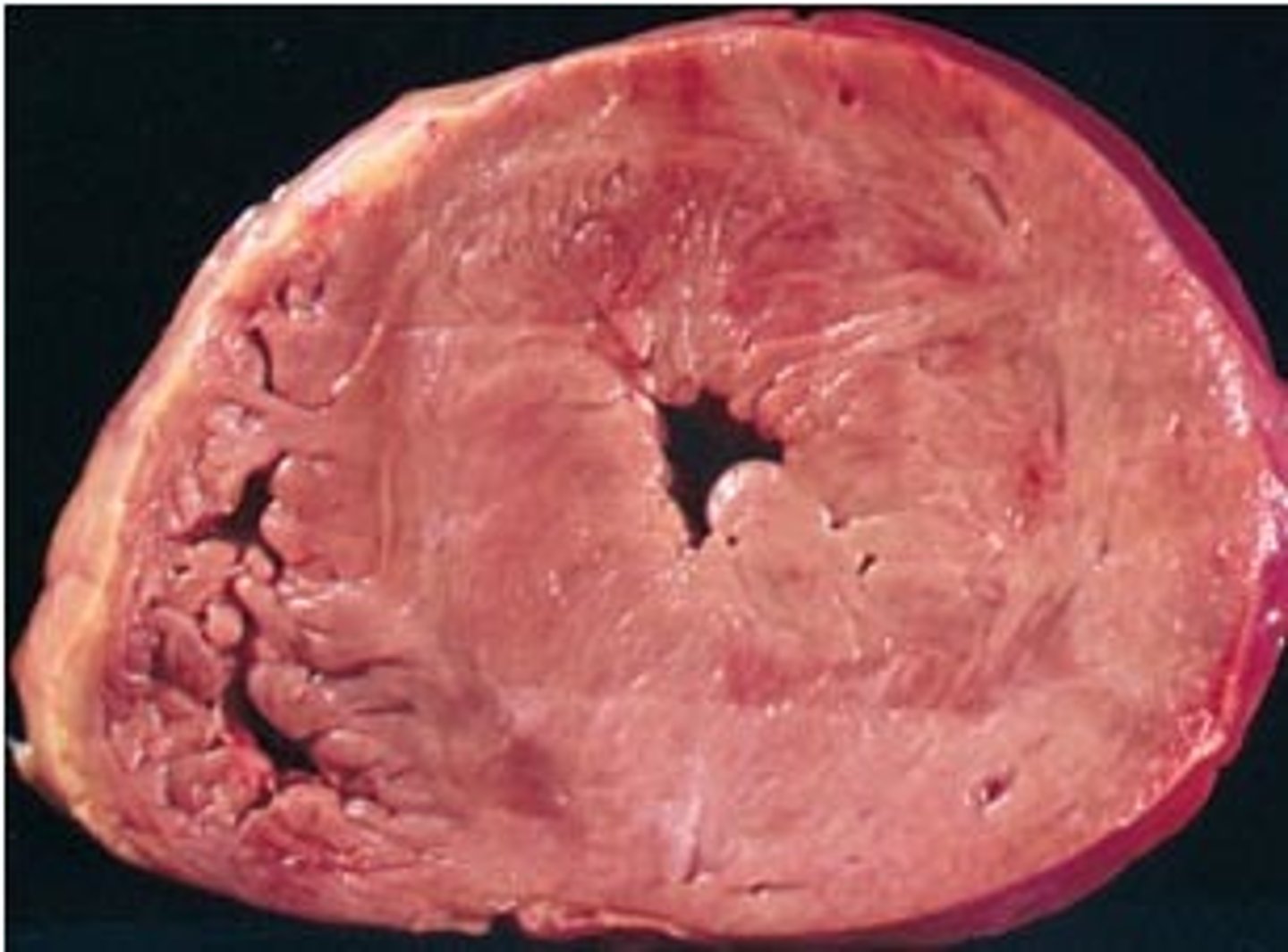
what type of cardiac hypertrophy is physiologic and causes increased volume, bradycardia, and increased capillary density
eccentric hypertrophy
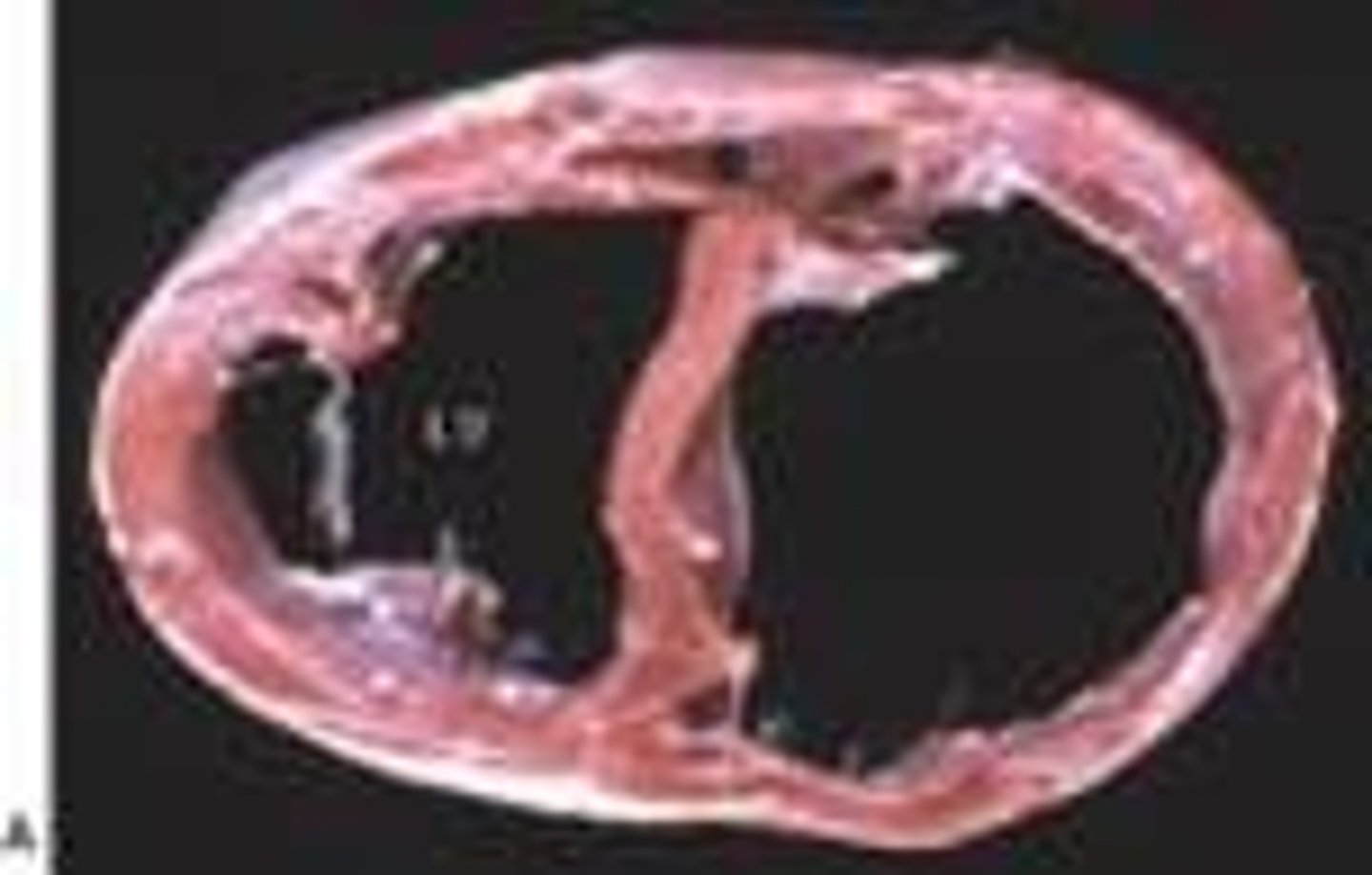
causes of left sided heart failure
HTN, CAD, valve disorders, cardiomyopathies
effects of left-sided heart failure
left ventricle hypertrophies, gradual decreased cardiac output (causing pulmonary edema), cough, dyspnea, rales, orthopnea, tachycardia
left ventricle decreased output and hypertrophy, increased pulmonary HTN
left-sided heart failure
how does left-sided heart failure occur?
prior damage to left side of heart from MI/cardiomyopathies
who gets left-sided heart failure?
those with previous complications
causes of left-sided heart failure
history of CAD, HTN, cardiomyopathies and MI
what is the MC cause of right-sided heart failure?
left sided heart failure
what is right ventricle pump failure, MC from left heart failure but also from lung pathologies?
right-sided heart failure
how does someone get right-sided heart failure?
increase pressure in pulmonary circulation -> hypertrophy
who gets right-sided heart failure?
those with hx of left heart failure or lung pathologies
when heart is overloaded by increased pressure
hypertensive heart disease
types of hypertensive heart diseases
systemic and pulmonary