VIDEO NOTES (Classes 6 &7), Chapter 6:
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
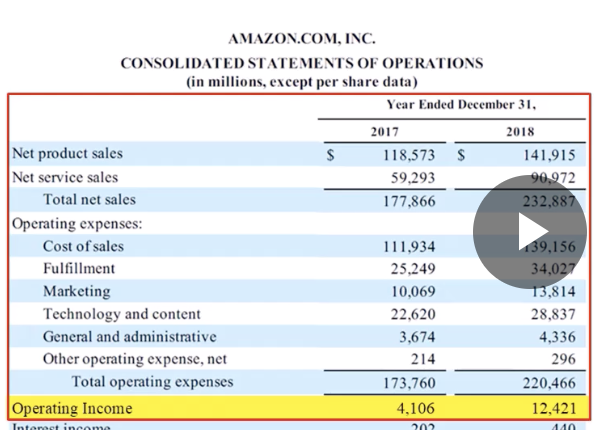
Reporting and Analyzing Revenues, Receivables and Operating Income
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What’s the income statement used for?
predict future performance
assess the creditworthiness of a company
evaluate the quality of management
How is Net Income classified?
Income from continuing operations
operating income
Revenues
Less operating expenses
cost of goods sold
selling, general & administrative expenses
research & development
depreciation & amortization
non-operating income
Interest income
Interest expense
Gains or losses on investment or financing transactions
provision for taxes
Income from discontinued operations
Operating income
The primary transactions and events of a company
Non-operating income
revenue + expenses from sources not related to income
rental income
source income
What’s revenue recognition
when and how a company records its income
often manipulated by management to meet performance targets
What’s the revenue recognition standard?
you recognize revenue when you’ve actually earned it
What are the 5 steps for the revenue recognition standard?
identify contract
identify performance obligations
Determine transaction price
allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations
Recognize revenue once you’ve earned it
What’s accrued revenue
did the work, waiting to be paid
Deferred/unearned Revenue
seller receives payment before work
What’s revenue recognition when it comes to customer purchases
Customers often purchase a product before delivery
company should pay customer back
an amount paid in advance are a current liability: unearned revenue or deferred revenue
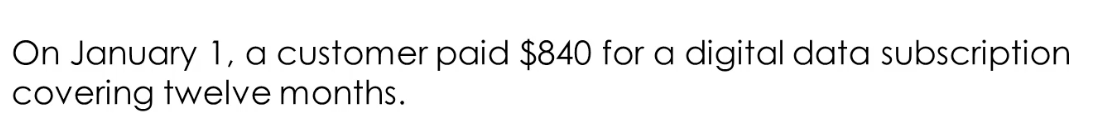
Help record amounts recieved in advance
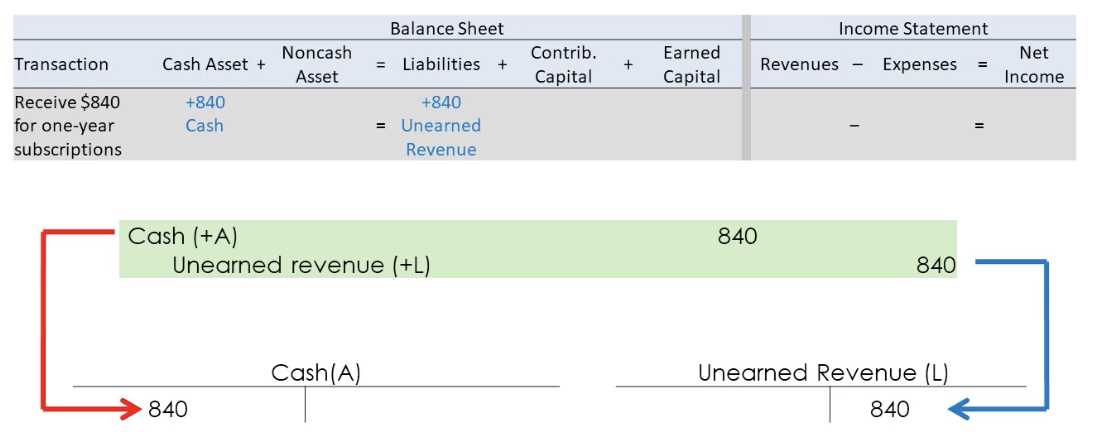

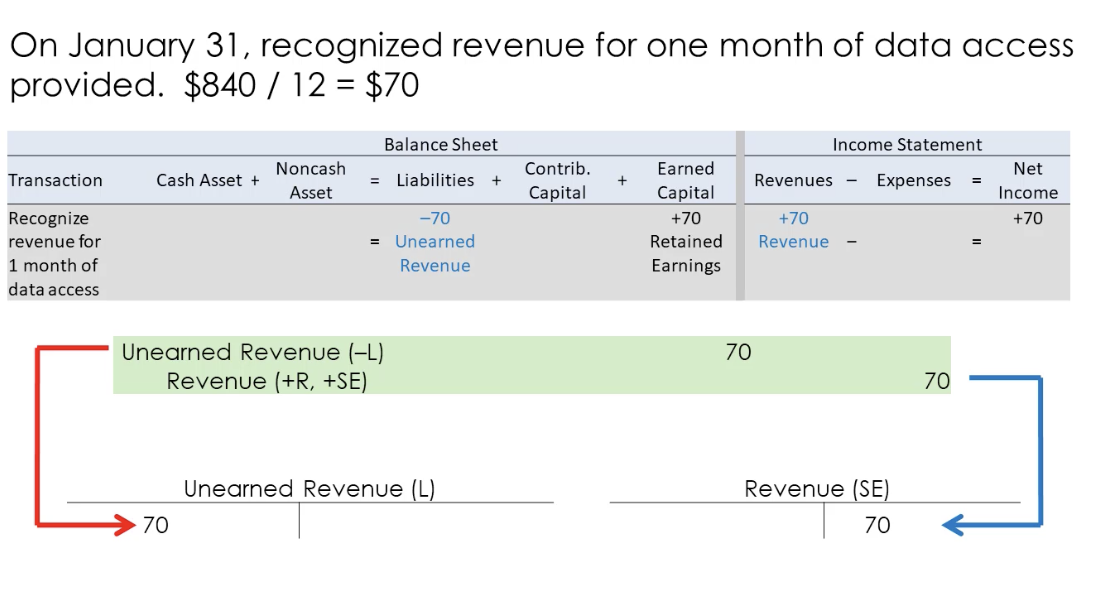
Recognize revenue for amounts previously received in advance
When G&S r delivered to the customer, the performance obligation is fulfilled
Liability is debited, revenue is credited
shown on the income statement
What are bundled sales?
2 or more goods r sold under the same price, but considered two different performance obligations
important to allocate performance obligations in proportion to their selling price
What are the complications that arise with long-term contracts?
Does this one transaction require multiple performance obligations
What’s the price
is it fufilled in a point in time or overtimeIs
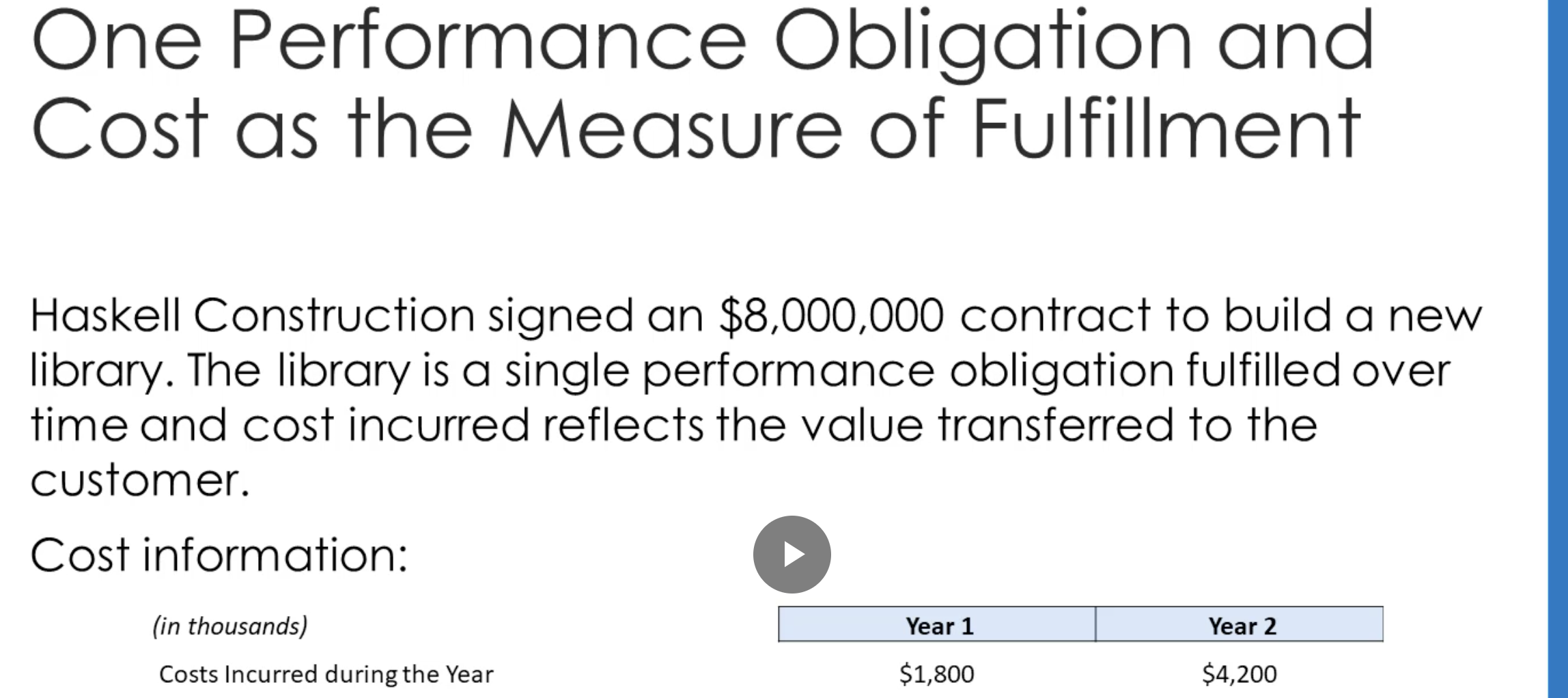
What is the performance obligation and cost as the measurement of fufillment?
8 million revenue, 6 million cost over 2 years. first year, spend 30% of costs, second year, spend 70% of costs. What’s the expense recognized and gross profit?


What happens when a performance obligation is fulfilled at a point in time?

Whats the difference between performance obligations fulfilled overtime and performance obligations fulfilled at a point in time?
Difference: when the revenue and gross profit are recognized
they both show a gross profit and expense of 2mil, 6mil
its just for overtime, the expenses and profits are recognized over multiple years
What are account receivables and the risks that come with them
when companies offer credit
Companies are afraid of users not paying, so GAAP requires companies to estimate and deduct expected credit losses
What’s Net Realizable Value?
GAAP requires companies to estimate and deduct expected credit losses

What’s a contra-asset?
the amount a company expects that its customers will not pay
How can contra-asset accounts be estimated?
through an aging analysis
receivables owed by customers
percentage of sales
uncollectible accounts among current-period sales
Aging of Accounts Receivable Example
Longer the account has been standing, less likely to be paid back


Percentage of Sales example
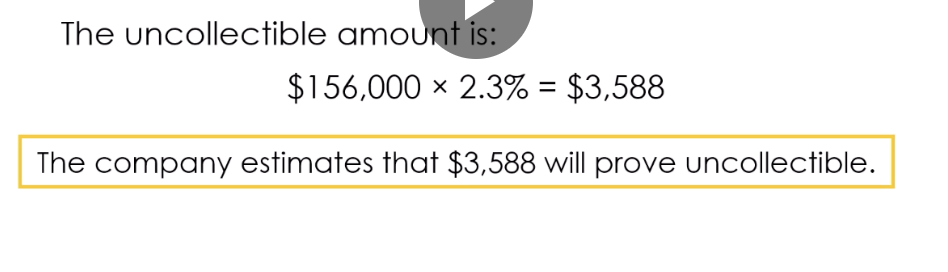
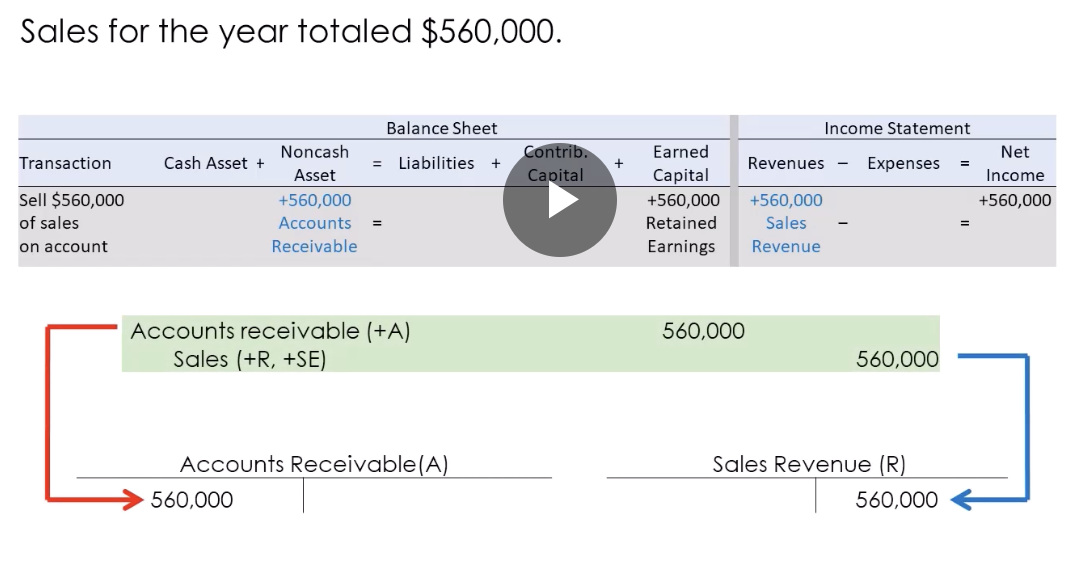
Record sales on account
Sales for the year totaled 560,000
Recording estimated bad debt expense
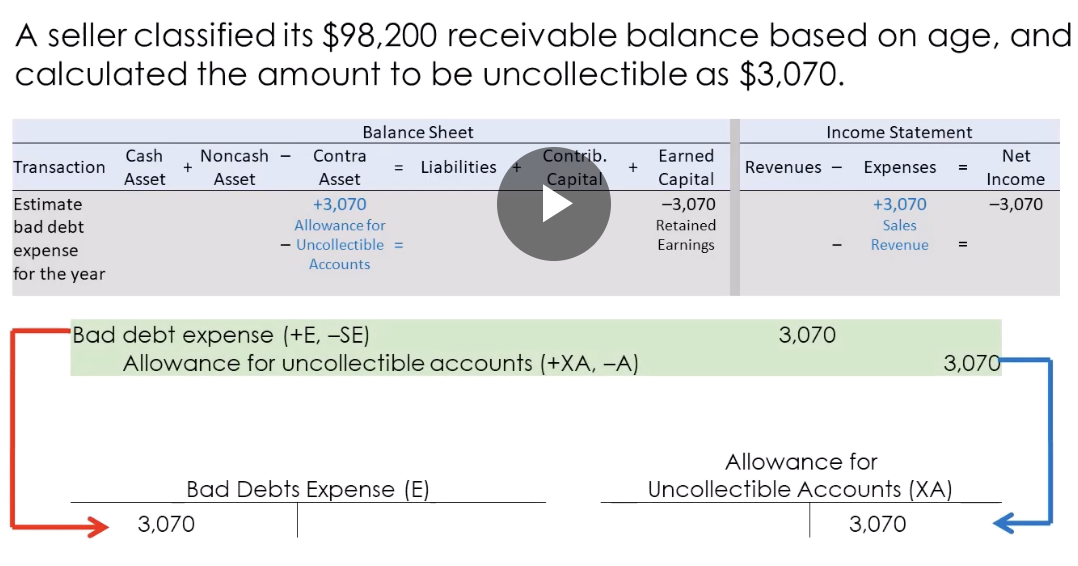
A seller classified its $98,200 receivable balance based on age, and calculated the amount to be uncollectible as $3,070
Recording Write-Offs of Uncollectible Accounts
During the next accounting period, the seller determined that customers owing $2,100 were not going to pay. The accounts were written off
write offs dont affect net income

Why are there no changes that occur to the net realizable value of receivables?
the write-off causes assets to increase and decrease by the same amount
What are two ways account receivables can raise operating revenue
Pledging
uses receivables as make up for the loan
Factoring
receivables are sold to a bank or finance company
How do account receivables appear to improve the appearene of the financial statements
companies shift income to make it appear better whenever they want
2019: overestimate the amount of bad debt, make it appear as if they have lower profits
accounted all the debt in 2019
it makes 2020’s profit looks higher than they actually are
How do you compare allowance accounts? aka uncollectible
comparing gross receivables in percentages reflect differences
What’s, NOPAT, Net Operating Profit After Taxes
Net income that can evaluate a company’s overall performance
What’s NOPAT’s formula?
Net Income - [(Non-operating revenues - Non-operating expenses) x (1 - statutory tax rate)]
![<p>Net Income - [(Non-operating revenues - Non-operating expenses) x (1 - statutory tax rate)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6cab045b-bff9-4bf5-8259-cfa14ef6533c.png)
What’s RNOA, Return Net Operating Assets?
how well the company is performing relative to its core objective
What’s RNOA’s formula?
Net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT) / Average net operating assets
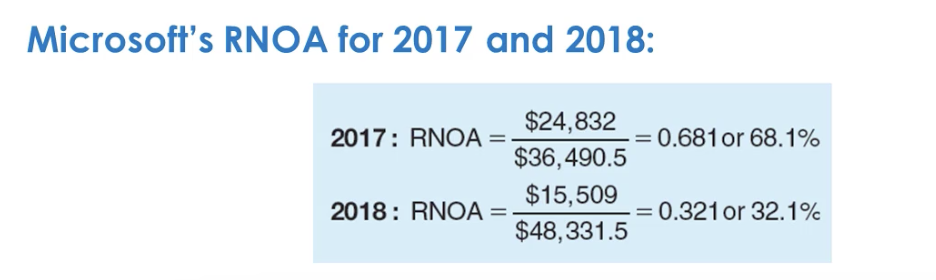
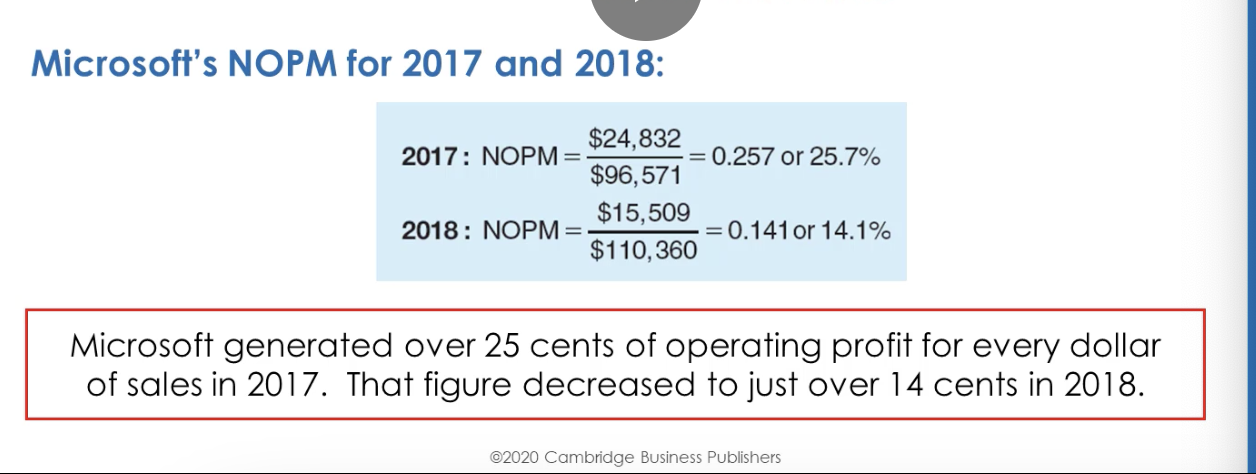
What’s NOPM, Net Operating Profit Margin?
overall operating profitability of a company relative to its sales revenue
What’s NOPM formula?
NOPM = NOPAT / Sales Revenue
What’s ART, Assets Receivable Turnover?
The investment in receivables required to generate one dollar of sales
What’s ART formula?
Sales Revenue / Average Accounts Receivable
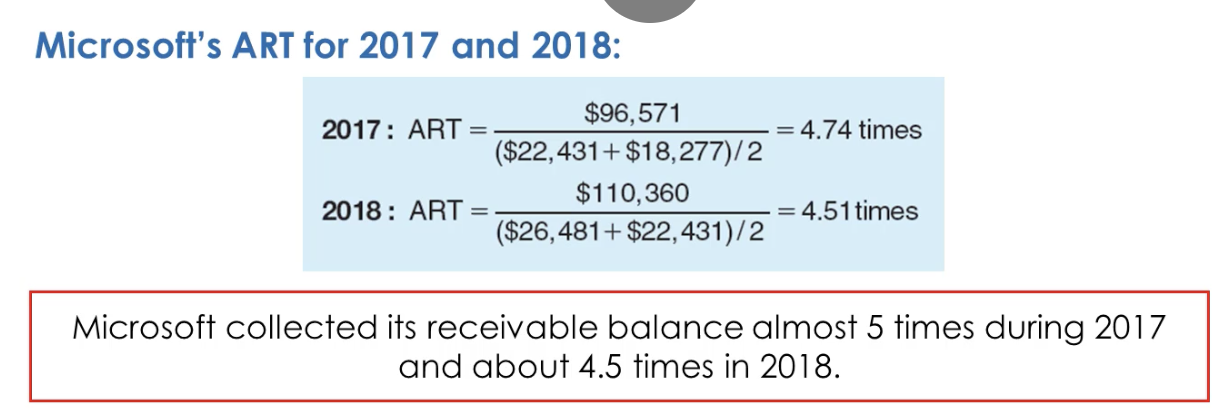
What does a higher receivable turnover imply?
amounts receivables are being collected more quickly
What’s Average Collection Period?
Says how long, on average, a company takes to collect its outstanding receivables (aka DSO Days Sales outstanding)
What’s the formula for Average Collection Period?
Average Collection period = Average Accounts Receivable / Average Daily Sales (sales /365 days) = ART
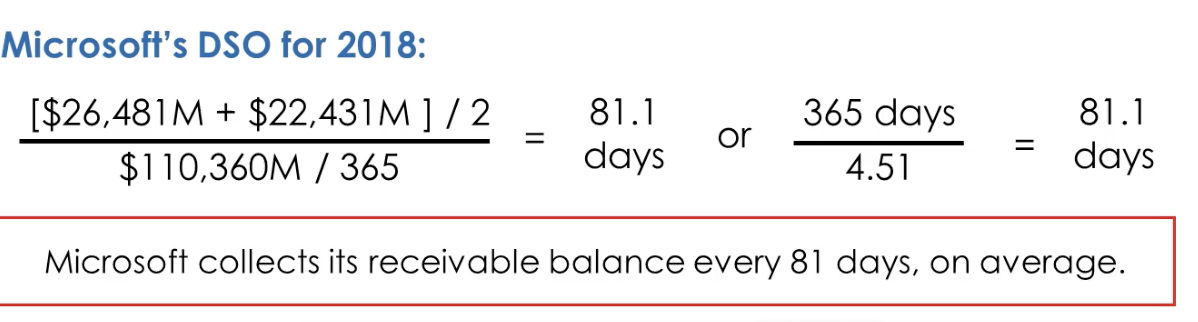
What are the possible reasons for turnover rates to decline/look worse
deterioration
sellers have extended its credit terms
sellers take a longer time paying customers
What’s Asset turnover?
it indicates efficiency and productivity
What’s earning management?
management hides true economic performance of a company
What are 2 motives for earnings management?
Mislead investors and creditors
influence legal contracts, loan agreements
What are some tactics for Earning Management?
Transaction timing
Overly optimistic or pessimistic
estimating in accrual accounting
revenue recognition with certain timing
depreciation expense estimates
bad debt expense
What’s Channel Stuffing?
another earning management tactic
when a company uses its market power over customers to make them purchase more goods then necessary
it can be recorded as revenue
Strategic timing
its another earning management tactic
management can control what time certain things are reported, to change financial statements. To smooth income
Income smoothing
Big bath
Whats income smoothing
mgmt tries to make income look steady and consistent overtime
Whats Big Bath?
Occurs when MGMT makes one year look bad, and the subsequent ones look better
What’s Mischaracterizing transactions?
a company pretends a deal was fairly made, when in reality, they are both secretly connected or when a buyer is apart of the company
What’s Quality of Earnings
how honest a company reports income, it shows the real underlying business performance
Why do we seperate recurring and non-reccuring things on the income statement?
To evaluate and compare performance
Compare normal business results year to year
One-time events shouldn’t confuse
separating helps make a good judgment of the company
to estimate future company values
Predict how much money the company will make with recurring income
forecast based on steady, repeatable earnings
What’s restructuring charges?
expenses and losses due to reorganization of company’s operations
What’s discontinued operations?
income from the business’ discontinued parts
What’s Discontinued operations?
when a company sells off or shuts down a seperate part of its business
it must be a seperately identifiable part of the business
How is Discontinued operations reported?
separately from continuing operations on the income statement
“Income from discontinued operations, net of income taxes”

What’s restructing costs?
expenses a company has when it reorganizes itself, but without selling an entire business unit
the company keeps the business, just changes how it operates
How are restructuring costs reported?
reported as part of the company’s normal, ongoing business results
What are the two components of restructuring costs?
employee severance costs
estimated cost of firing employee
Asset Write-downs
write down of longterm asset, such as building, as a result of closing or relocating business