Protein Synthesis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
The Central Dogma
the flow of genetic info from DNA (via replication) → RNA (via transcription) → proteins (via translation)
Protein synthesis is
the process of translating genetic information into functional proteins through transcription and translation
begins in the nucleus & completes in the cytoplasam
Transcription
DNA Splicing/DNA Processing
Translation
Transcription
first step of protein synthesis: process of copying a segment of DNA into COMPLEMENTARY (opposite) mRNA, which occurs in the nucleus
initiation
1st of transcription: RNA polymerase attaches to the prompter of a gene unwinding the double helix
a transcription bubble: is formed
prompter: mRNA start codon, AUG. methionine
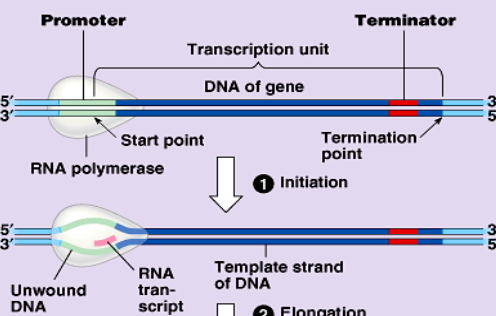
elongation
step 2 of transcription: RNA polymerase reads the DNA to synthesize a complementary RNA copy from 5’→3’
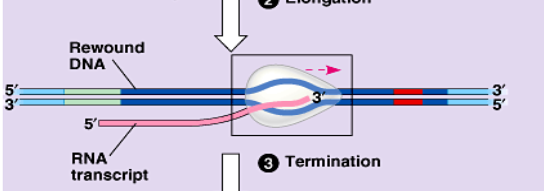
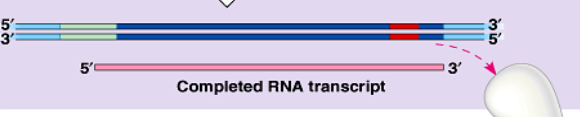
termination
when RNA polymerase/prompter reach the termination site the mRNA is complete
DNA splicing/DNA processing
2nd step of protein synthesis: the mRNA copy from transcription is processed so its ready to leave the nucleus
mRNA has exons & introns that are not needed for protein synthesis → spliceosomes remove introns
5’ Guanine cap added to allow mRNA to exit nucleus
3’ Poly(A) tail added to allow mRNA to exit nucleus
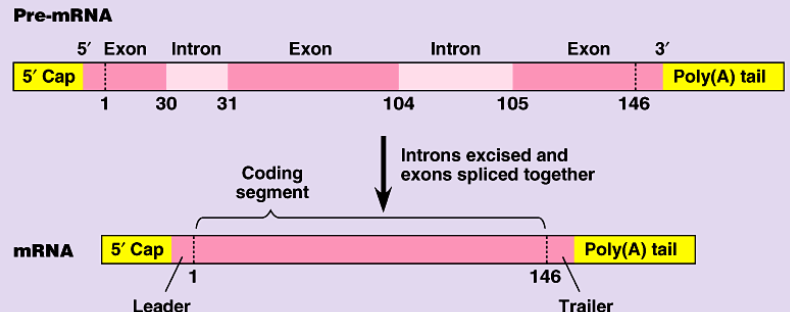
exons & introns
segments of mRNA → exons are needed codes, introns are not needed
spliceosomes
remove the introns in loops (excised introns) to splice the exons together
spliceosome component: snRNPs + other proteins
snRNP: small nuclear ribonucleoprotein
snRNA: small nuclear ribonucleic acid
protein
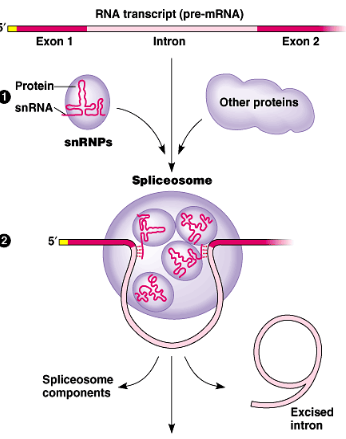
5’ end of mRNA
receives a Guanine cap to protect it and facilitate export from the nucleus.
3’ end of mRNA
receives a Poly(A) cap to protect it and facilitate export from the nucleus.
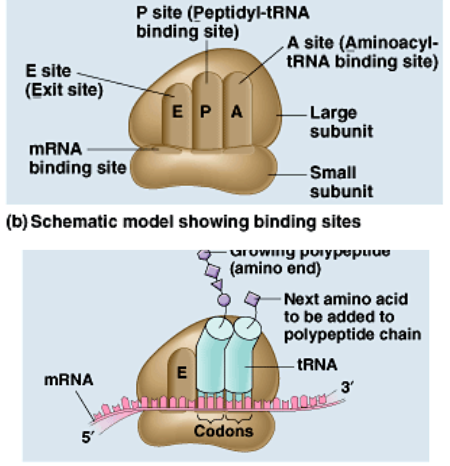
Translation
3rd step of protein synthesis: uses mRNA copy as blueprint for amino acid string/polypeptide (tRNA is attracted bc OPPOSITE& hydrogen bonds)→ protein
step 1 of translation
ribosomes attach to the AUG/start codon of the mRNA
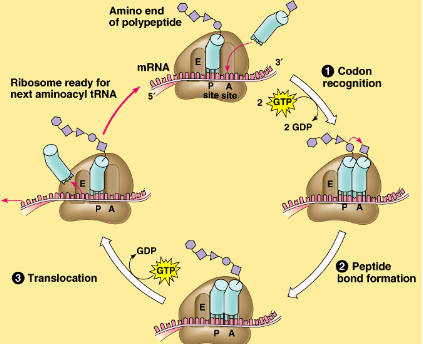
step 2 of translation
Codon Recognition: A site (Aminoacyl-tRNA binding site)
ribosomes reads mRNA in groups of 3 bases (codons) & binds complementary anti-codon/tRNA to mRNA
uses energy: 2GTP → 2GDP
step 3 of translation
Peptide bond formation: P site (Peptidyl-tRNA binding site)
ribosome forms peptide bonds between amino acids at end of tRNA to growing polypeptide chain
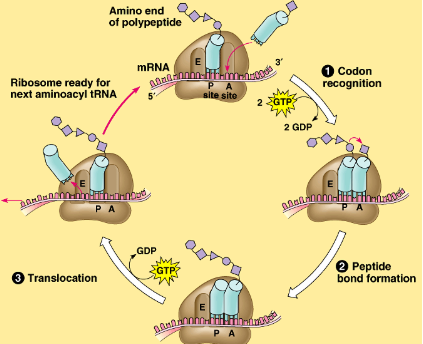
step 4 of translation
Translocation: E site (Exit site)
ribosome moves down the mRNA, shifting the tRNA to the E site (exits), so the ribosome is ready for the next tRNA/codon
uses energy: 1 GTP → GDP
end of translation
when ribosome reads stop codon it detaches from the mRNA
polypeptide chain folds into final protein form!
translation stop codons
UGA, UAG, UAA
codon
series of 3 bases which code for 1 amino acid
Transcription & Translation start @ 3’ so it synthesizes 5’→3’
messenger RNA
mRNA: carries/contains genetic code from DNA from nucleus → cytoplasm
synthesized in nucleus via transcription
unstable
ribosomal RNA
rRNA: part of ribosome that ensures proper placement of mRNA & tRNA
synthesized in nucleus, exists in ribosome, assist in translation
stable
transfer RNA
tRNA: brings amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis, matching its anticodon end to complementary mRNA codons
synthesized in nucleus, exists in cytoplasm
stable: hydrogen bonding RNA (sometimes double helix)
folds in on self
mRNA strand → corresponding DNA template
complementary