Overview of Psychostimulants: Cocaine and Amphetamines
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Cocaine
Derived from Erythroxylon coca plant.
Amphetamines
Synthetic stimulants for various medical uses.
Pharmacokinetics
Study of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism.
Pharmacodynamics
Effects of drugs on biological systems.
Tolerance
Reduced response to a drug after repeated use.
Neuroadaptations
Brain changes due to substance use.
Cocaine History
Used for 5,000-2,000 years; Freud's studies.
Cocaine Half-life
0.5 to 1.5 hours in the body.
Cocaine + Alcohol
Forms coca ethylene during metabolism.
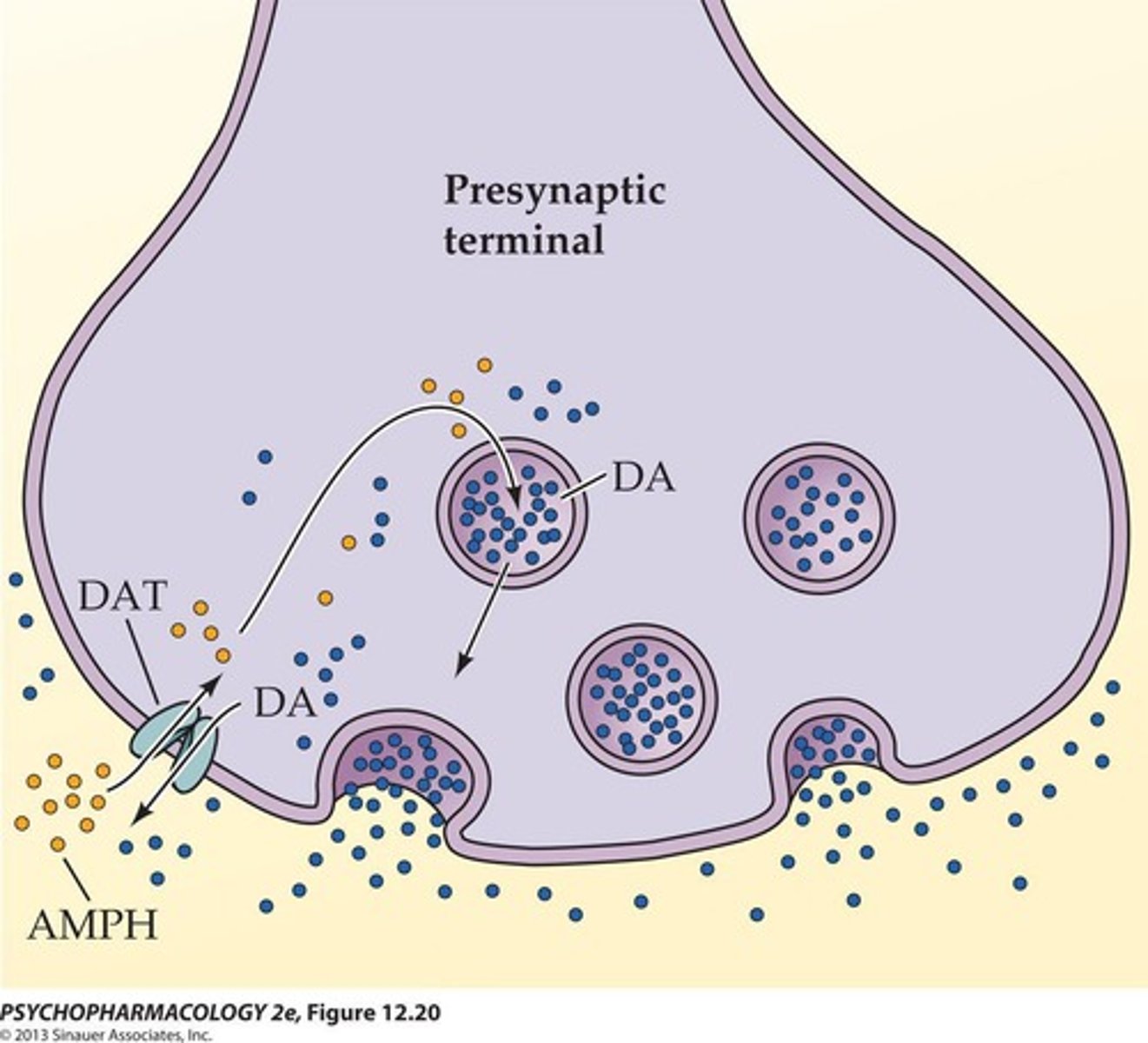
Monoamine Re-uptake Transporters
Proteins that regulate neurotransmitter levels.
Cocaine Mechanism of Action
Blocks dopamine reuptake, increasing its levels.
Crack Cocaine
Freebase form, can be smoked.
Stereotypy
Repetitive behaviors, like grooming in rodents.
Sympathomimetic Effects
Mimics sympathetic nervous system activation.
Acute Cocaine Effects
Includes heart failure, stroke, and seizures.
Cocaine Withdrawal Symptoms
Last 1-10 weeks; includes anhedonia.
Amphetamine History
First synthesized in 1887 for asthma treatment.
Amphetamine Half-life
7-30 hours, longer than cocaine.
Amphetamine Psychosis
Psychotic symptoms resembling schizophrenia.
DA Exocytosis
Dopamine release from neurons.
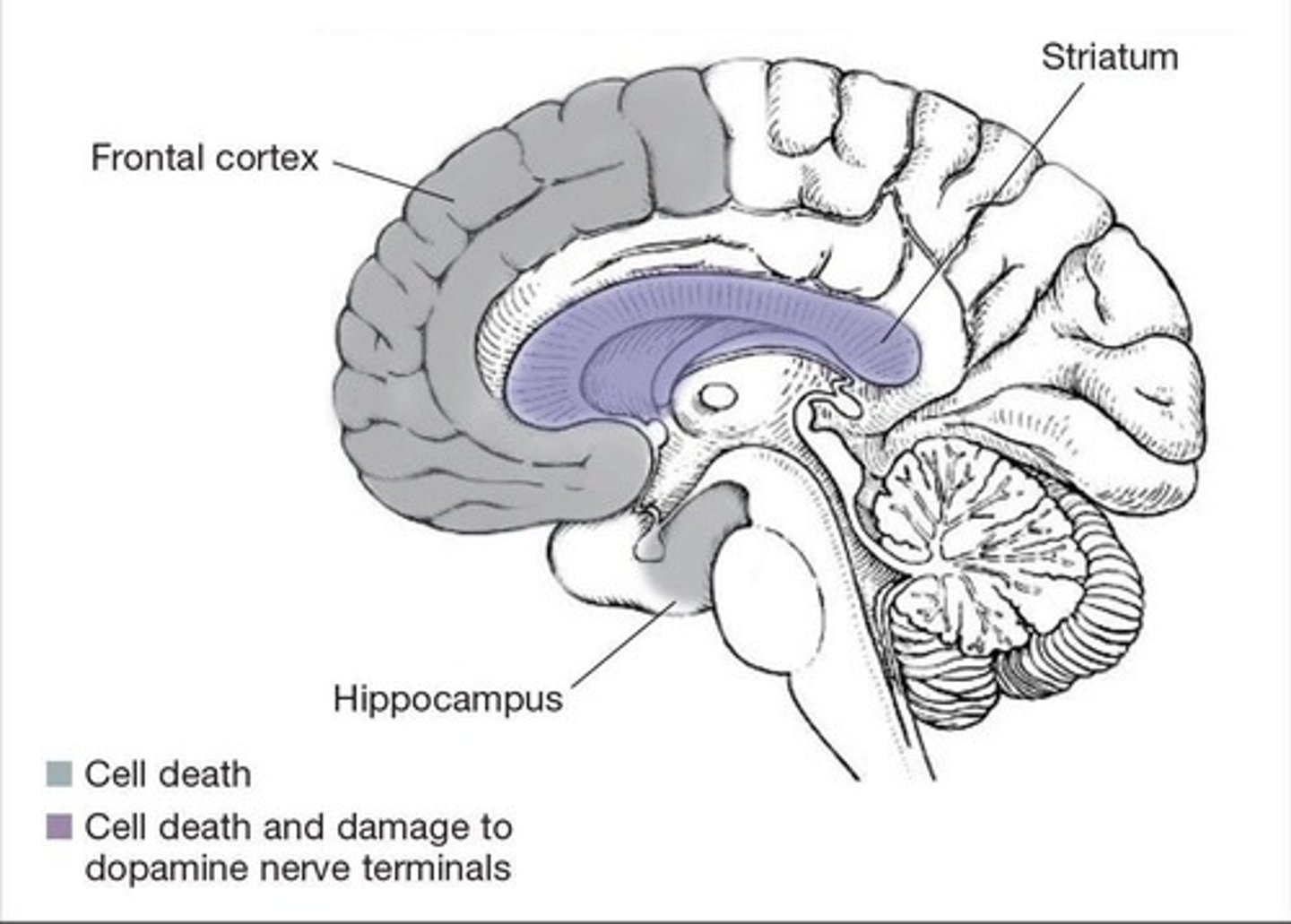
Methamphetamine Neuroadaptations
Damages dopamine and serotonin axons.
Methylphenidate
Ritalin; used for ADHD treatment.
Ecstasy (MDMA)
Releases dopamine and serotonin, mild hallucinations.
ADHD Symptoms
Inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity in children.
PFC Functions
Maintains attention, vigilance, and cognitive processes.
Dexedrine
D-amphetamine used for ADHD treatment.
Strattera
Atomoxetine; non-stimulant ADHD medication.
Behavioral Therapies
Non-drug approaches to treat substance abuse.
Hyperactivity
General increase in motor output
Epigenetic Studies
Dysregulated/malfunctioning of the following in PFC
Cathinone
Khat Plant