NERC System Operator Exam – Key Concepts & Formulas
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Compiled Q&A flashcards covering core formulas, frequency–voltage relationships, ACE standards, NERC time limits, operator responsibilities, and shift-factor concepts for the NERC System Operator exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is Ohm’s Law expressed for AC impedance in power systems?
Voltage equals current multiplied by impedance: V = I × Z.
What is the single-phase power formula relating voltage and current?
P = V × I.
What is the three-phase real-power formula using line-to-line voltage?
P = √3 × V(L-L) × I × power factor.
How is three-phase apparent power (S) calculated?
S = √3 × V(L-L) × I.
Which equation gives conductor power losses?
Power losses = I² × R.
How is System Load determined from Balancing Authority data?
System Load = Total Generation − Net Interchange Actual.
What simplified value of synchronous speed constant is commonly used and what does it represent?
Np = 7200 (from f = N/60 × p/2 at 60 Hz); it helps find generator poles or RPM.
Write the ACE equation used for balancing generation and frequency.
ACE = (NIa − NIs) − 10B(Fa − Fs).
In the ACE formula, what purpose does the IME term serve?
IME adjusts ACE for tie-line metering errors via operator input.
What is governor droop for a 5 % speed regulation on a 60 Hz system?
A 3 Hz band (60 × 0.05) where MW output changes proportionally to frequency change.
At what frequency deviation do governors begin proportional response in most U.S. systems?
±0.036 Hz (e.g., at 59.964 Hz or 60.036 Hz).
State the Pythagorean relationship for the power triangle.
MVA² = MW² + MVAR².
How is power factor (pf) defined?
pf = MW / MVA.
Provide the impedance formula combining resistance and reactance.
Z = √(R² + (XL − XC)²).
What are the formulas for inductive and capacitive reactance?
XL = 2πfL and XC = 1⁄(2πfC).
How does frequency affect XL and XC?
Increasing frequency raises XL (inductive) and lowers XC (capacitive). XL = 2(pi)fL and XC = 1/2(pi)fC
How is a generator’s actual MVAR capability calculated for off-nominal voltage?
MVAR output = MVARrated × (Vactual / V_rated)². This is how a capacitor’s capability is calculated as well.
Define Available Transfer Capability (ATC).
ATC = Total Transfer Capability (TTC) − reserve margins.
What term describes the angular separation between two AC waveforms?
Phase angle.
True or False: MVARs flow from higher to lower voltage magnitude.
True - but only when voltage angle is less than 20 degrees.
In which direction do MWs naturally flow with respect to voltage angle?
From higher voltage angle to lower voltage angle (downhill on the power angle).
What load change is expected for a 1 % drop in system frequency?
Approximately 2 % drop in total load (3 % in motor load).
How much load reduction typically raises island frequency by 1 Hz?
Shedding 6–10 % of the island load.
What is the Disturbance Control Standard (DCS) recovery requirement?
Return ACE to zero or the pre-contingency value within 15 minutes of a generation loss.
Within what period must contingency reserves be restored after a disturbance?
Within 90 minutes after the 15-minute recovery (total 105 minutes from event).
How long can a Balancing Authority exceed BAAL before corrective action must succeed?
Within the assigned Tv which can be no more than 30 minutes.
When must a BA notify the Reliability Coordinator if ACE cannot be calculated?
After 30 minutes of ACE calculation failure.
Who submits an interchange tag and oversees its approval?
The Sink Balancing Authority.
What is the Interconnection Reliability Operating Limit (IROL) Time to Violation (TV) rule?
Return flows within IROL in no more than 30 minutes.
How often must a TOP perform a successful real-time assessment/contingency analysis?
At least once every 30 minutes.
When must a TOP notify the RC of planned or unplanned outages?
When the outage of is or will be 30 minutes or longer.
What backup control-center requirement is specific to Reliability Coordinators?
They must have an identified Backup Control Center (BUCC).
State the 30-minute communication/monitoring failure reporting rule for operators.
Any loss of communications, monitoring, or unplanned control-center evacuation over 30 minutes must be reported to impacted entities and NERC.
How quickly must a control center transfer to its backup site and how long must tests last?
Transfer in <2 hours; test operation lasts at least 2 hours.
What is a Generator Shift Factor (GSF)?
Percentage change in line loading caused by redispatching a generator.
Define Power Transfer Distribution Factor (PTDF).
Percentage change in line loading due to an interchange transfer between two areas.
What is an Outage Transfer Distribution Factor (OTDF) used for?
Predicting loading changes during transfers while considering outages.
Explain Line Outage Distribution Factor (LODF).
Percentage of a line’s pre-contingency flow that shifts to another line when the first line trips.
During restoration, how much new load should be connected at a time?
No more than 5 % of the currently synchronized generation.
When is a manual load-shed event reportable to NERC?
If it exceeds 100 MW.
What magnitude of firm-load loss must be reported?
Loss of firm load greater than 300 MW.
What are the two key milestone requirements related to loss of a generator in DCS?
Disturbance Control Standard requires restoration of ACE to 0 after generation loss and the restoration of contingency reserve 90 minutes after the 15 min restoration period (total of 105min)
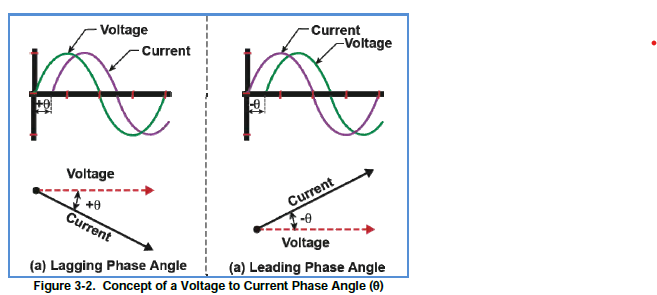
When the phase angle is lagging, which way is the power flowing?
Power is flowing into the load.
When a Balancing Authority’s ACE is Negative are they giving or receiving power?
When a Balancing Authority's ACE is negative, they are getting power
from the grid.
What are the AGC and EMS
AGC is automatic generator control and uses ACE to dispatch generation the EMS is the Energy Managment System and coordinates system operations, including monitoring and controlling generation and load.
A 5% change in voltage will typically lead to what change in the total load magnitude?
3%
What are the three Automatic Generation Control modes?
Tie Line Bias Control - standard mode using entire ACE equation and responding to frequency excursions with governor response.
Flat or Constant Frequency Control - considers only the frequency portion of the ACE equation (permission to use if islanded)
Flat or Constant Tie Line Control - Considers only the Interchange portion of the ACE equation.
During a GMD what are GICs and what risk do they pose?
During a Geomagnetic Disturbance, Geomagnetically Induces Currents exist in the earth and can enter the electric grid through grounded equipment potentially causing:
Transformer hot-spot or heating damage
Loss of Reactive Power Sources
Increased Reactive Power demand
Protective System Mis operation
Wye Grounded transformers of what rating or higher are susceptible to GIC (especially when located over igneous rock)?
200 MVA
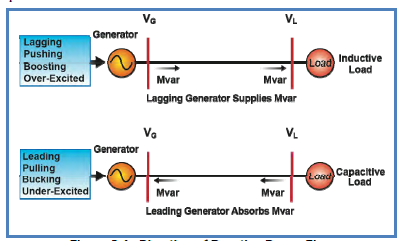
What does it mean when a Generator is Bucking?
See Picture
An RC, TOP, or BA determines during annual review of Operating Plan for control center backup functionality that a change is needed, how long do they have to get it updated and approved?
60 days
What are Energy Emergency Alert levels?
EEA 1 - All avalable gen resources in use;
EEA 2 - Load Management Procedure in effect;
EEA 3 Firm load interruption imminent or in progress… These are requested by the BA experiencing a capacity or energy deficiency.
What is CPS1 and what does it measure?
CPS1 Measures the BAs contribution to the interconnection during frequency deviations.
What is a Reliability Event
Reliability event is referred to as an event that affects or may potentially affect the reliability of the Bulk Electric System, such as loss of generation, transmission or load or violations or potential violations of operating limits.
What is the criteria for a DCS event
Loss of 80% of the BAs most severe contingency
When does a requested interchange become and implemented interchange?
Implemented Interchange - The state where the Balancing Authority enters the Confirmed Interchange into its Area Control Error equation.
Transient instability occurs when a disturbance on the system causes power angles to exceed
90 degrees
What is the rule of thumb for the amount of load decrease related to a decrease in customer voltage?
Load decreases 3% for every 5% drop in voltage.
What are the terms for a generator that is supplying reactive power to the system
Boosting, lagging, Overexcited, Pushing
How often should the Transmission Operator and Balancing Authority review and update their Loss of Control Room Functionality Operating Plan?
EOP-008, Each Reliability Coordinator, Balancing Authority, and Transmission Operator shall annually review and approve its Operating Plan for backup functionality.
A BA is expecting a capacity shortfall in the upcoming afternoon. What should they do?
A Balancing Authority anticipating an operating capacity or energy emergency shall perform actions in their Operating Plan which should include, bringing on all available generation, postponing equipment maintenance, scheduling interchange purchases in advance, and being prepared to reduce firm load.
What is defined as a scheme designed to detect abnormal or predetermined system conditions and automatically take corrective actions (such as adjusting/tripping generation or tripping load) to maintain system reliability.
Remedial Action Scheme - The Glossary of Terms Used in Reliability Standards, Remedial Action Scheme is a scheme designed to detect predetermined System conditions and automatically take corrective actions that may include, but not limited to, adjusting or tripping generation, tripping load, or re-configurattion. to maintain ystem stability, acceptable voltage, or power flows.
Some Interconnection previously referred to a Remedial Action Scheme as a Special Potection System. Remedial Action Scheme is the updated term.
What are the two rules about relationship of frequency to customer load?
Restoration: shed 6-10% of load to gain 1Hz; other circumstances 1% change in Freq. results in 2% change in load.
If a high voltage current (HVDC) ties is on the Scheduling Path for a transaction, the ____________ shall coordinate the Interchange Schedule with the Transmission Operator of the HVDC tie.
R3 - Each Balancing Authority in whose area the high-voltage direct current tie is controlled shall coordinate the Confirmed Interchange prior to its implementation with the Transmission Operator of the high-voltage direct current tie.
NERC Standard INT-009, Requirement 3
- NERC Standard INT-003
With regards to Voltage Control Theory, as long as power angles are less than ______ degrees, reactive power will flow from the higher to the lower voltage magnitude.
The power angle is the Voltage phase angle difference between two locations in the power system. The reactive power transferred between two points is determined by the voltage magnitudes at the two points and the cosine of the power angle between the points. Reactive power does normally flow from the high to the low voltage bus. This is a rule of thumb every system operator should know. However, ... we assumed the power angle was small and so ignored the cosine term. If δ had been large (> 20°), we could not have ignored the cosine term. When power angles exceed approximately 20°, the rule of thumb that reactive power flows from high to low voltage no longer applies. EPRI 3.3.3