Non specific responses
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Infection
A condition in which pathogenic microorganisms penetrate host defenses, enter the tissues, and multiply
Obligate intracellular parasites
Multiply by taking control of host cells genetic material and regulating the synthesis and assembly of new viruses
What is a fully assembled infectious virus is called?
Virion
RNA viruses are … of all viruses
70%
What is the basic structure of a virus?
Protein shell surrounding a nucleic acid core which is a capsid with a DNA/RNA
What are the types of structure of virus
Enveloped, Naked, Complex
Viruses possess the genes needed to … a host cell and … its activity
invade a host cell and redirect its activity
Gag
is a polyprotein and an acronym from group antigens
Pol
is the reverse transcriptase
Env
the envelope protein
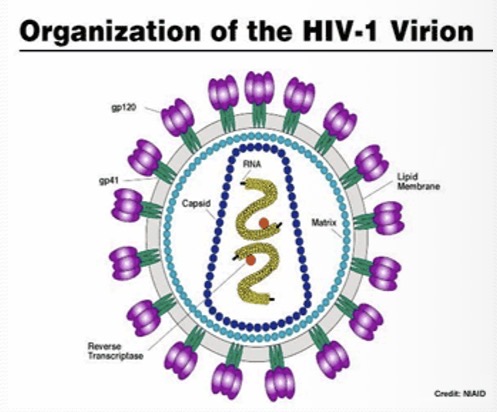
HIV
An enveloped retrovirus in the form of an mRNA genome uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome.
Provirus
DNA is then incorporated into the host cell genome by an integrase enzyme
Reverse transcriptase (RT)
An enzyme used to generate complementary DNA from an RNA template
Virions
Viruses released by infected cells that has the potential for rapid, large scale proliferation
What damage can virions do?
shut down the catabolism, genetic expression, destruction of cell membrane and organelles, release of lyosomes, cell death, latency
Synscytium
a mass of cytoplasm containing several nuclei and enclosed in a membrane but no internal cell boundaries
Inclusion
A body suspended in the cytoplasm, such as a granule
Salmonella
intracellular pathogens that are rod shaped, They only invade the GI tract usually
Gram negative bacteria can cause..
many types of infections and are spread to humans in a matter of ways obj as E. coli
Bacteria
Produce toxins that disrupt normal cell function by damaging a cell. They block the transmission of internal signals or stimulaing cells so they malfunction
Cholera toxin works by?
disrupting the ionic balance of cells’ membranes. This leads to the cells in the small intestine secreting large amounts of water into the intestine → diarrhea and dehydration
Types of Antibiotics
Penicillins, tetracyclines, and quinolones
Penicillins
Inhibit the formation of bacterial cell wall by blocking cross-linking of the cell wall structure.
Why do bacteria need cross-linking of the cell wall?
The cell wall is a protecting casing for the bacterial cell
Tertracylines
inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the subunit of the bacterial ribosome
Quinolones
Blocks DNA synthesis by inducting one of bacterial enzymes (DNA gyrase) needed in this process
What are the lines of defense in fighting an infection? (1,2,3)
Nonspecific: physical barrier, chemical, genetic
Nonspecific: Innate immune system
Specific: Adaptive/ Acquired Immune system
What occurs during the first line response to infection to the skin
Skin resists pathogen penetraction and replication
What occurs during the first line response to infection to the mucous membranes
Chemical viral inhibitors prevent attachment to cell and directly inactivate the virus
What occurs during the first line response to infection from the lysozyme
Damage bacterial cell walls, secretes an abundant amount of lysozymes like tears, saliva, human milk, and mucus
What occurs during the first line response to infection from the stain environment of the stomach?
The stomach kills many bacteria
What occurs during the first line response to infection to the specificity of viruses
They host cell receptors
What are the key players in the second line of defense in fighting an infection?
Inflammatory response, phagocytosis, complement, interferons, and cytokines
What are the key players in the third line of defense
Antibodies, T cells, B cells, accessory cells, cytokines
The innate immune system will… than specific response
Act sooner
The innate immune system responses are … spectrum
broad
The innate immune system will have … of lasting protective immunity
No memory
Pathogen associated molecular patterns PAMPs
found on pathogens such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that are found on the outer membrane of bacteria
Damage associated molecular patterns DAMPs
cell components that are released during cell damage or death such as the presence of DNA anywhere other than the nucleus or mitochondria → triggers responses mediated by TLR9
pattern recognition receptors PPRs
These will identify PAMPs and DAMPs and are found on particular immune cells like phagocytic cells such as Toll like receptors TLRs
Will like receptors TLRs
A PPR. A class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single, membrane spanning, non catalytic receptors that usually are expressed on sentinel cells. They mainly recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes
Cytokine
Any of a number of substances that are secreted by certain cells of the immune system and have an effect on other cellsW
What are examples of cytokines?
Interferons (IFN), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin (IL), and growth factors
Pyrogen
A polypeptide that produces fever by causing metabolic changes in the hypothalamus. It raises the set point of the hypothalamic thermostat
What are types of Pyrogens
exogenous and endogenous
What produces exogenous peptides
infectious agents
What produces endogenous peptides
Cells in the body like macrophages
Why are fevers important
they inhibit the multiplication of temperature sensitive viruses and stimulate immune reactions of phagocytosis
What are temperature sensitive viruses
poliovirus, cold viruses, herpes zoster virus
What can stem cells in the bone marrow become?
granulocytes, monocytes, and T/B lymphocytes
Granulocytes
A class of white blood cell that has granules in the cytoplasm
Monocytes
A type of white blood cells clear cytoplasm that are larger and migrate to site of infection and divide into macrophages and dendritic cells
Lymphocytes
A broader term for three types, NK cells, T cells, and B cell. These are found in the lymph and have no granules in their cytoplasm
Where are B cells located?
bone marrow
Where are T cells located
thymus
Where do natural killer cells function?
In innate immunity or adaptive immunity
What conditions are T cells used?
Cell mediates, cytotoxic adaptive immunity
What conditions are B cells used?
humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity
Monocytes differentiate into…
macrophages and dendritic cells
Inflammation
The response is activated by cell and tissue damage that is induced by pathogens. This response interferes with further pathogen replication/multiplication
What are the three stags of inflammation?
Vacular changes, swelling, production of chemical mediators
What occurs during vascular changes in inflammation
increased circulation, vasodilation, redness and warmth
What occurs during swelling
This occurs due to the leakage of macular fluid such as pus which is formed at the site of inflammation
What occurs as the production of chemical mediators rise?
Fever is inducted and stimulates the white blood cells to prevent the spread of the pathogen
What are examples of chemical medicators?
TNF via chemotaxis and phagocytosis, INF via inhibiting virus replication, and IL via activation of wbc
Exudate
A mass of cells and blood that has seeped out of blood vessels or an organ. Occurs during inflammation
Transudate
An extravascular fluid with a low protein content because of the increase fluid pressures or diminished colloid oncotic forces in the plasma
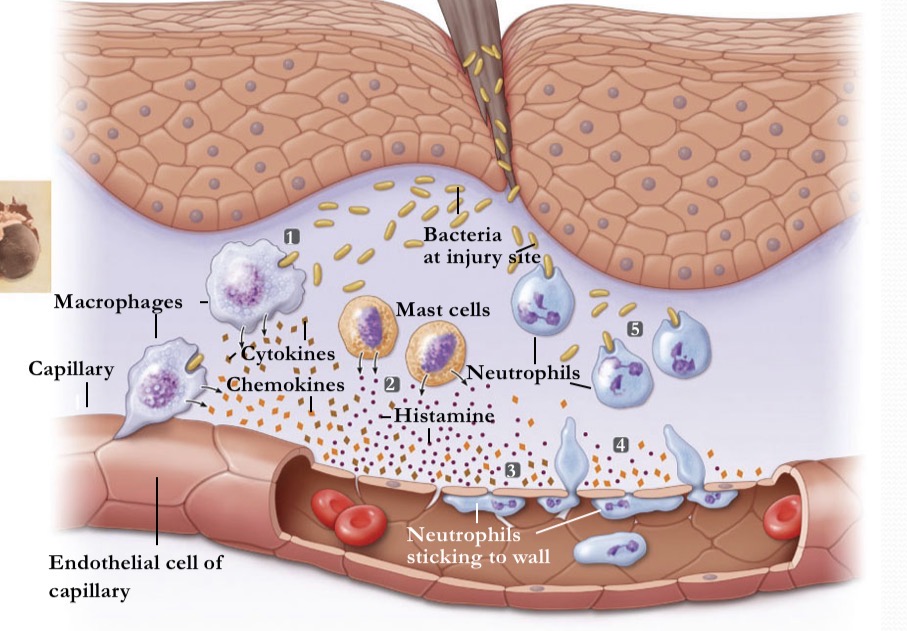
What occurs during inflammation at stage 1?
A break in the skin induces bacteria
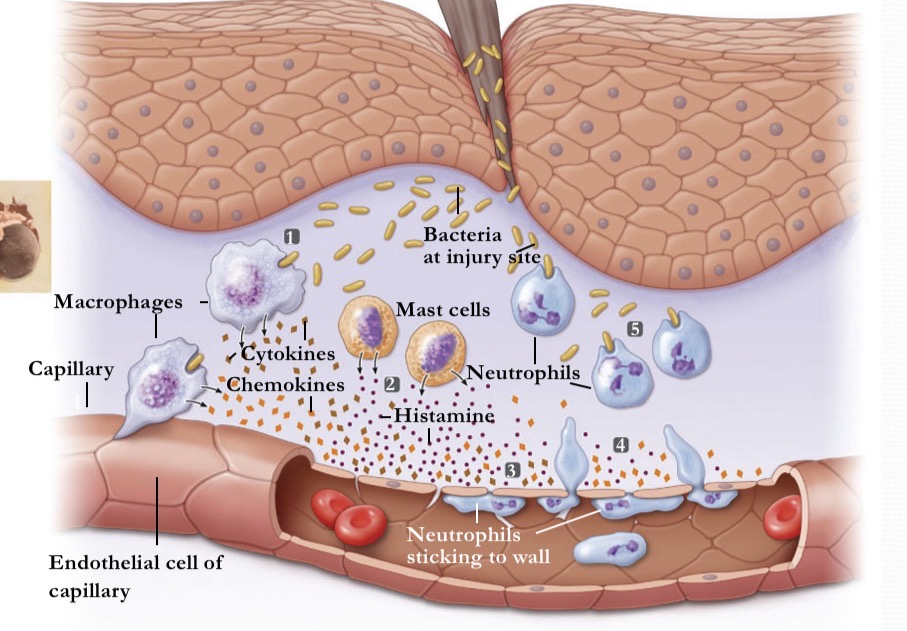
What occurs during inflammation at stage 2
activated mast cells release histamine
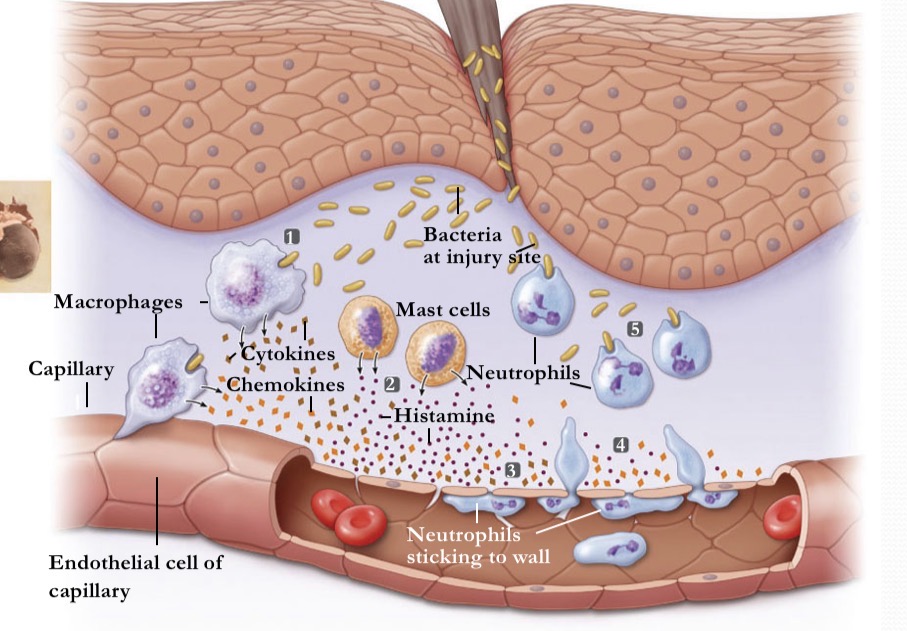
What occurs during inflammation at stage 3
histamine and cytokines dilate local blood vessels
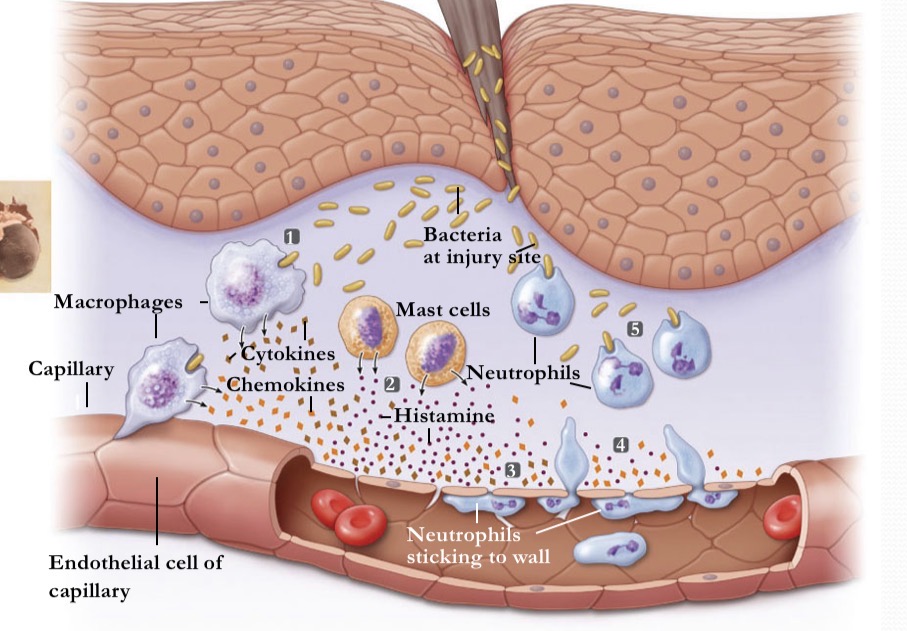
What occurs during inflammation at stage 4
chemokines attract neutrophils, which pass between cells of the blood vessel wall
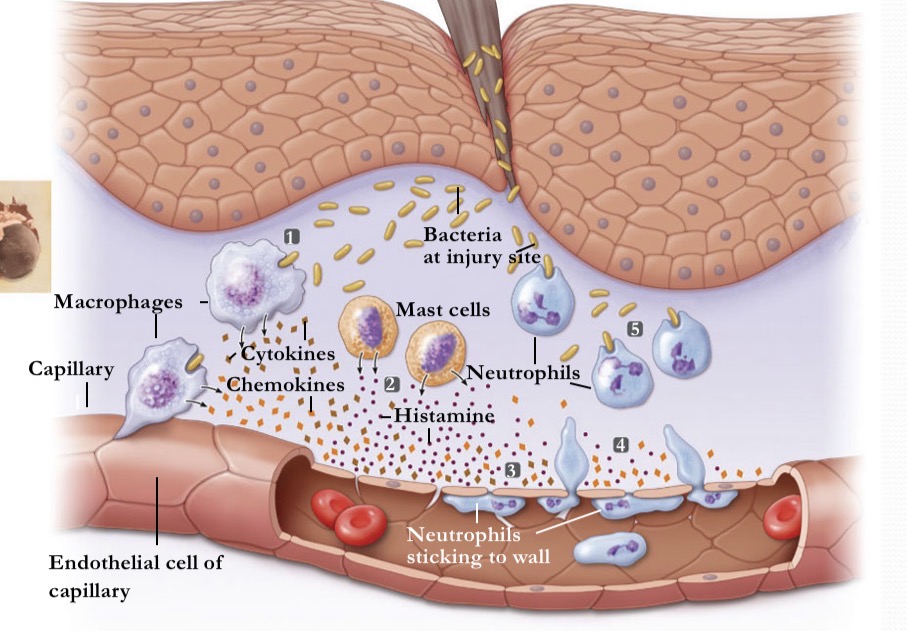
What occurs during inflammation at stage 5
Neutrophils engulf the pathogens and destroy theCm
Chemokine
Type of cytokine that induces directed chemotaxis in nearby responsive cells
Histamine
A part of an immune response to freedom pathogens, this is produced via basophils and mast cells in the near by connective tissue.
Histamine increases the … of the capillaries to… and some proteins. This allows the to.. in the infected tissues
permeability of the capillaries to the exc and some proteins to allow them to engage pathogens in the infected tissues
Phagocytosis
Type of endocytosis where the cell membrane actively insults large particles or cells into vesiclesC
Antihistamines
Drugs that treat allergic rhinitis and other allergiesw
What symptoms and antihistamines help with?
Nasal congestion, sneezing, hives
Rhinitis
Inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane of the nose that is characterized by a runny nose and stuffiness. This occurs typically because of a common cold or a seasonal allergy
Chemotaxis
Tendency of cells to migrate in response to a chemical stimulus
What are the main types of phagocyte
Neurtrophils, monocytes, macrophagesN
Neutrophils are
a type of granulocyte and are short livedm
Monocytes
Large and agranulated
Macrophages differentiate from
monocytes
Monocytes
Are attracted to a damaged site by chemical substances through chemotaxis and are triggered by. Range of stimuli including damaged cells, pathogens, and cytokines that help release by macrophages already at the site
Interferon (IFN)
A glycoprotein produced primarily by fibroblasts, NK lymphocytes, macrophages, epithelial cells, t-cells. It’s not virus specific
What initiates IFN synthesis
the binding of a virus to a host cell initiates
Where will IFN be secreted>
Into the extracellular space
When IFN binds to another host cell, what occurs?
It induces the production of proteins and degrades the viral RNA or prevents translation of viral proteins.
What is a benefit of the IFN not being antiviral specific?
IFN can be used a general treatment in combination with another to treat a viral infection before they find a better alternative
Complement
A Nonspecific group of proteins found in the blood plasma that form a membrane attack complex that kills cells via creating holes in the membrane. This is nonspecific and specific immunity
Cascade
sequential series of events in which the first substance activates the next
what are the three types of complement cascades?
classical, alternative, lectin
RNA interference (RNAi)
Cellular mechanism, destroys viral dsRNA, inhibits virus life cycle
How do Natural killer cells help in nonspecific defense
They can be activated by interferons and they can secrete orthotic and enzymes in response to infection
What does perforin do
creates pore in target cells and ruptures infected cells
What does secreted enzymes do
to degrade DNA, trigger apoptosis (programmed cell death)