Biology Lab: Metric Units, Conversions, and SI System Basics
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the primary advantage of using the metric system in scientific measurements?
It is based on a decimal (base 10) number system, making measurements and conversions easier.
What is the relationship between milliliters, grams, and cubic centimeters of water?
1 ml of water = 1 gram of water = 1 cm³ of water.
What is the metric prefix for 1000?
Kilo (k).
What is the metric prefix for 100?
Hecto (h).
What is the metric prefix for 10?
Deka (da).
What is the base unit in the metric system?
1 (the base unit itself).
What is the metric prefix for 1/10?
Deci (d).
What is the metric prefix for 1/100?
Centi (c).
What is the metric prefix for 1/1000?
Milli (m).
What mnemonic can help remember metric prefixes?
King Henry Died Unexpectedly Drinking Chocolate Milk.
How do you convert units when moving up the metric chart?
You divide by 10 or move the decimal one place to the left.
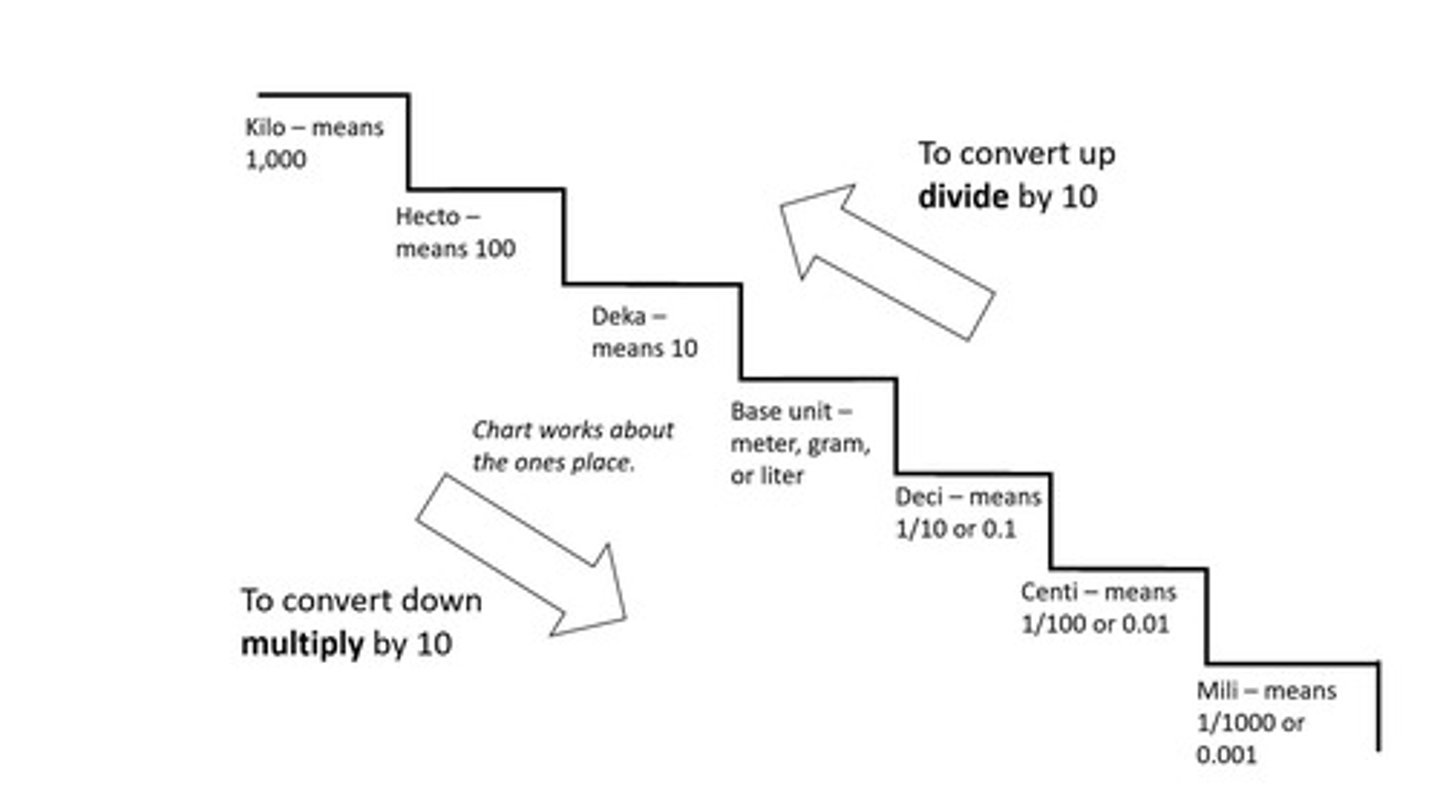
How do you convert units when moving down the metric chart?
You multiply by 10 or move the decimal one place to the right.
Convert 2 kilometers to meters.
2 kilometers = 2000 meters.
Convert 345 milligrams to grams.
345 mg = 0.345 g.
What is the purpose of the Factor Label Method?
To convert between different units of measurement systematically.
What are the base metric units for length, volume, and weight?
Meter (m) for length, liter (L) for volume, and gram (g) for weight.
Why is it important for scientists to use the same standards of measurement?
It allows research conducted around the world to be compared and understood more easily.
What are the three main metric units discussed in the lab?
Length (meter), volume (liter), and weight (gram).
What is the significance of the International System of Units (SI)?
It provides a standardized system for scientific measurements globally.
What is the metric prefix for 10^2?
Hecto (h).
What is the metric prefix for 10^-3?
Milli (m).