4.3 Formation of a new species
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
variation in population examples
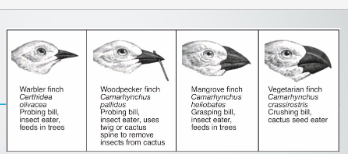
Different beak forms of Galapagos finches
anti-biotics resistant bacteria
Inbreeding definition
mating of genetically closely related individuals
Inbreeding consequences
loss of genetic diversity, prevents evolution
results in homozygosity which can increase the chances of offspring having recessive/harmful traits
Inbreeding depression
lower birth weight
less resistance to disease, predators and environment
less successful reproduction
Outbreeding definition
production of offspring from the mating or breeding of genetically unrelated individuals
outbreeding outcomes
increases genetic variation
promotes heterozygosity
a way to introduce new desirable traits
example of inbreeding
royal families, hemophilia
outbreeding in plants
most plants cross pollinate and are therefore natural out breeders
Founder effect definition
loss of genetic variation when a very small number of individuals from a larger population establish a new colony
how does the Founder Effect occur?
due to migration or geographic isolation
what does the founder effect do for a population?
the gene pool may be quite different from that of the original population
eventually, the founder population can become a new species
potential for rapid changes in a colony’s gene frequency suggests the founder effect is an important driving force in the evolution of new species
Example of the founder effect
The cheetah
It is hypothesise that about 10,000 years ago due to climatic change a major extinction of large vertebrates occurred. All but the small group of cheater died out forcing close family relatives to mate with each other
Recent genetic analysis with mtDNA shows an extremely low genetic diversity
Cheetah show signs of inbreeding depression
About 5% of cheetah survived to adulthood
convergent evolution
process during which species that are not closely related to each other independently evolve similar kinds of traits to adapt to similar environments
analogous structures
Divergent evolution
process in which a trait held by a common ancestor evolves into different variations over time
homologous structures
Main types of speciation
Geographic (allopatric): due to part of the population becoming isolated
Sympatric: population occupies same geographical area
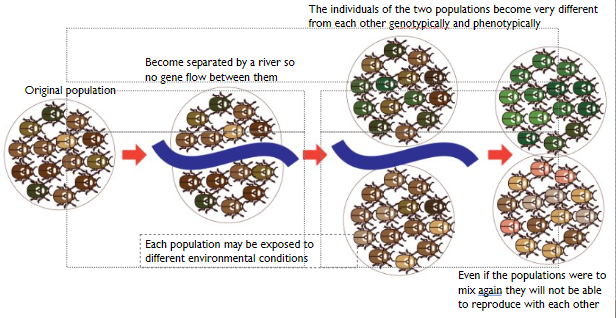
Geographic speciation

geographical speciation flow chart
Example of Geographical speciation
Galapagos finches. The Galapagos islands are volcanic islands that emerged from the sea relatively recently 3-4 million years ago
A group of finches is hypothesised to have landed on the island from the mainland driven by strong winds
on the island they remained permanently isolated from their point of origin and we're free to evolve because there was
an absence of pre-existing predators
no competition from other land birds
a variety of empty ecological nations
Stages in the speciation process: division of habitat
division of food resources by trophic (feeding) specialization
periods of food scarcity and growing population increased competition
large number of open ecological niches promoted the development of feeding specialisations.
beak types
grasping beaks- fruits and insects
crushing beaks - eats seeds, ticks
probing beaks - small to search in crevices
Reproductive isolation definition
A mechanism that prevents two or more species from exchanging genes (interbreeding) and producing fertile hybrids even though they are not geographically separated
Reproductive isolation consequences
breeding at different times of the year
species-specific courtship behaviour
adaptation of plants to different pollinators
infertile offspring
Breeding at different times of the year
Different species often have different mating seasons and plants flower at different times of the year which prevents mating opportunities
Examples
Grey headed parrot: April to August and Cape parrot: August to February
Species specific courtship behaviour
Activity to signal sexual readiness
Prevents different species from interbreeding even though they territories overlap
Species specific courtship behaviour examples
Breeding display
Stridulating songs e.g. male cicadas
Secretion of pheromones
Breeding plumage
Adaptation by plants to different pollinators
Flowers designed so that only one specific pollinator can get to the pollen
Foul smelling flowers to attract flies
Dull coloured flowers (open at night) with a strong fruity or musty scent to attract mice and bats.