AP Government Chapter 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
Unalienable
A human right based on nature or God

2
New cards
Articles of Confederation
A weak constitution that governed America during the Revolutionary War

3
New cards
Constitutional Convention
A meeting in Philadelphia in 1787 that produced a new constitution

4
New cards
Shay's Rebellion
A 1787 rebellion in which ex-Revolutionary War soldiers attempted to prevent foreclosures of farms as a result of high interest rates and taxes

5
New cards
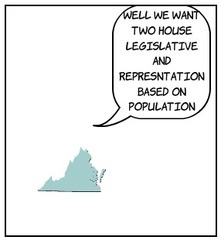
Virginia Plan
Proposal to create a strong national government
6
New cards
New Jersey Plan
Proposal to create a weak national government

7
New cards
Great Compromise
Plan to have a popularly elected House based on state population and a state-selected Senate, with two members for each state

8
New cards
republic
A government in which elected representatives make the decisions

9
New cards
judicial review
The power of the courts to declare laws unconstitutional

10
New cards
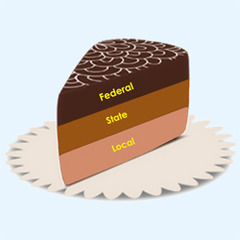
federalism
government authority shared by national and local governments
11
New cards
enumerated powers
powers given to the national government alone

12
New cards
reserved powers
powers given to the state government alone

13
New cards
concurrent powers
powers shared by the national and state governments

14
New cards
checks and balances
authority shared by three branches of government

15
New cards
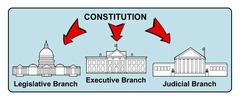
separation of powers
constitutional authority is shared by three different branches of government
16
New cards
faction
a group with a distinct political interest

17
New cards
federalists
those who favor a stronger national government

18
New cards
antifederalists
those who favor a weaker national government

19
New cards
coalition
an alliance of groups

20
New cards
Bill of Rights
first ten amendments to the constitution

21
New cards
habeas corpus
an order to produce an arrested person before a judge

22
New cards
bill of attainder
a law that declares a person, without a trail, to be guilty of a crime

23
New cards
ex post facto law
a law that makes an act criminal although the act was legal when it was committed

24
New cards
amendments
a new provision in the Constitution that has been ratified by the states

25
New cards
line-item veto
An executive's ability to block a particular provision in a bill passed by the legislature
