Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the ICF?
fluid inside cells
What is ECF?
fluid outside cells
What is determined by a fluid intake?
ingested food, drinking and food
What is metabolic water?
the product of a chemical reaction in the body
What is determined by fluid output?
expired air, sweat, cutaneous transpiration, feces, urinary obligatory/ facultative
What is urine obligatory?
urine produced in a day
What is urine faculative?
extra urine when you're hydrated
After drinking water what happens?
Cells swell(hypertonic) as they take in water, water moves into cell
After sweating what happens?
Water moves out of the cell, cells shrink(hypotonic)
Renin-Angiotensin System steps
1. JG apparatus detects low BP
JG apparatus releases renin.
Renin converts to angiotensinogen to angiotensin 1
ACE converts angiotensin 1 to 2
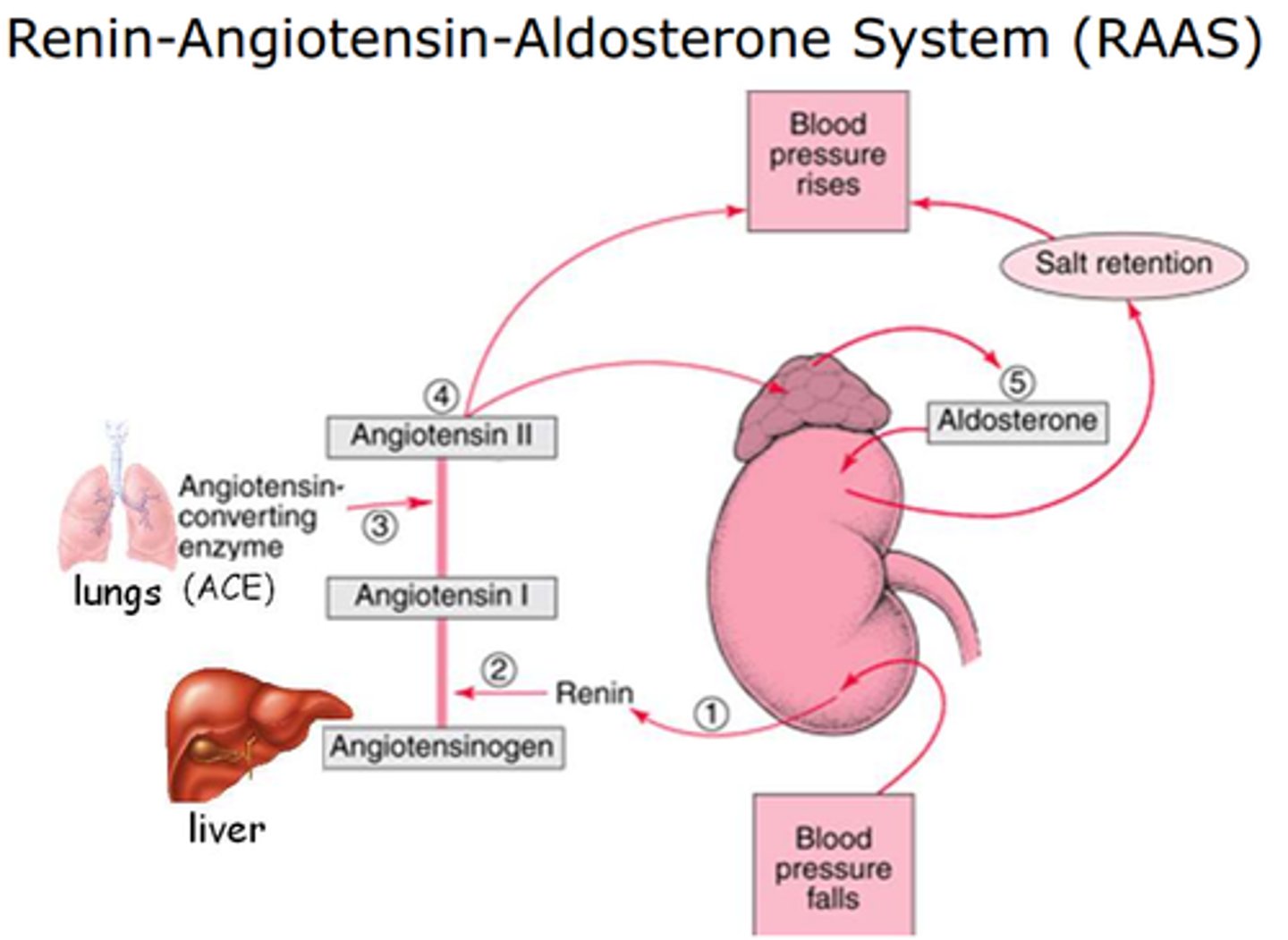
Angiotensin 2 binds to?
Vasoconstriction, decreased GFR rate, drinking water, release aldosterone
Aldosterone steps
Angiotensin 2
Adrenal cortex releases aldosterone and binds to kidneys
ADH steps
Hypothalamus increases nerve signals to post pituitary to release ADH in blood
ADH does what?
vasoconstriction, thirst center activation, increase water reabsorption
ANP steps
High BP detected
1. Atria responds to stimuli and releases ANP
ANP does what?
vasodilation and decrease GFR rate
What is water intoxication?
when excess water in body cells swell
Infant dehydration
immature kidneys cant concentrate urine
greater fluid lost due to body size
Eldery dehydration
kidneys less effective with diluting urine
What is nonelectrolytes?
molecules that don't disassociate in a solution
What are electrolytes?
disassociate in a solution to form cations and anions
What cations are in the intracellular fluid?
K+ a lot inside cell, less on outside
What anions are in the ICF?
PO3-4 and proteins inside the cell
What is outside of the cell in Interstitual fluid?
NA+, Cl-, HCO3-
What is on the outside of blood plasma?
mostly Na+, Cl-, proteins(outside too)
What are ways we can balance sodium?
aldosterone, ANP, ADH
Aldosterone balances sodium by?
retains Na + and water
ADH balances sodium how?
retains water
What does ANP do with sodium balance?
increases extortion of Na+ and H20
How do we increase and decrease Na?
decrease: blood is watery
> water moves in
What are K+ ions required for?
neuromuscular activities and control heart rhythm
Potassium balance
heart can stop=too much K+, cardiac arrest respiratory distress
Diagram of Na
1. Sodium flows into cell.
2. calcium flows in cell(depolarization)
K+ flows out (repolarization)
Redistribution of K+
H+ in blood plasma, specific hormones in the blood, change blood plasma
Hyperkalemia/hypokalemia
high/low potassium
Increased H+ in ECF
H comes in, K+ leaves out
Hypernatremia/Hyponatremia
high/ low sodium levels
Hypercalcemia/ hypocalcemia
high/ low calcium
Hyperchloremia/hypochloremia
high/low calcium
What is a good pH balance
7(neutral)
What is an acid?
pH below 7,
what is determines a base?
high #s
What is HCI?
acid found in stomach lining
What is basic?
proton remover
What is alkaline?
ph of 8 and up
What is the pH formula?
-log[H+]
What's the normal range for pH?
7.35-7.45
What pH range is alkalosis?
below 7.35
What pH range is acidosis?
above 7.45
What can acidosis lead to?
coma and death
What can alkalosis lead to?
seizures and then death
Kidney buffer system
lasts for days, works within hours
Lung buffer system
Fastest, kicks within minutes
plasma buffer system
works within seconds