Attention and Control Essay
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is choking (and reference)?
The occurrence of inferior performance despite striving and incentives for superior performance" (Baumeister 1986)
What is an example of choking in a high pressure sporting situation (and reference)?
Having a lower free throw accuracy later on in a game when the score is close (Toma 2017)
What is hot-hand perception (and reference)?
The belief that someone who has been successful is more likely to succeed again (Gilovich 1985)
How does hot-hand perception link to choking, and what evidence is there for this?
Raises expectations and importance on the ‘hot athlete‘, increasing pressure on them
Scoring a 3rd consecutive shot in basketball is only 46% probable
Explain the Theory of Challenge and Threat States in Athletes (TCTSA)?
Jones 2009
Goal relevant evaluative situation = the stressful situation the athlete is in
Demands = the demands required of the athlete in the situation
Resources = the resources the athlete believes they have avalable (such as physical skill, self-efficacy, perceived control)
Coping potential = The athletes overall idea if they can cope with the situation or not, YES or NO
Challenge state = occurs when coping potential is YES, causes facilitative psycho and somatic changes
Threat state = occurs when coping potential is NO, causing debilitative psycho and somatic changes
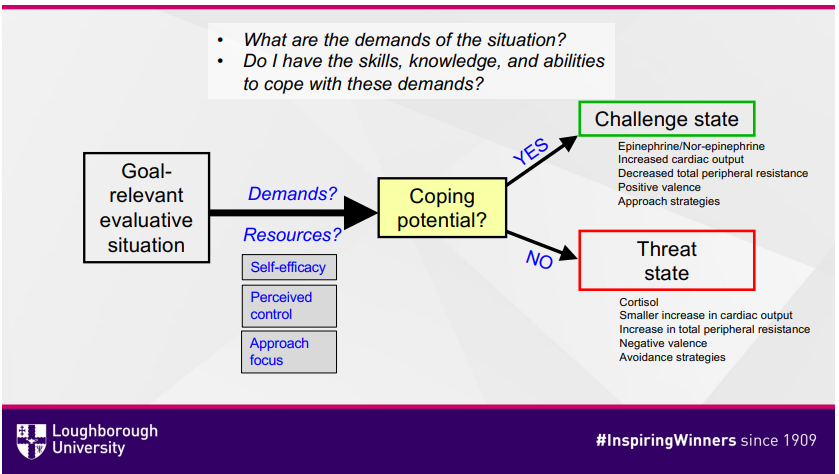
What are the types of demands of a situation?
Task difficulty
Individual responsibility
Expectations
Self-paced skill
Match situation
Distractors (internal and external)
What is the Contingency-Competence-Control (CCC) model?
Jordet 2006
CCC model focuses on the perceived control of an athlete in a situation
It states that an athletes perception of control influences their resource appraisal
THREAT STATE = athlete fixates on uncontrollable factors
CHALLENGE STATE = athlete fixates on controllable factors
What 2 factors determine perceived control in the CCC model?
Perceived outcome contingency = how much the athlete believes the outcome is determined by skill or luck
Perceived competence = how skilled and capable the athlete believes they are
What is Jordet’s 2006 research for CCC on Penalty shootouts
Interviewed 10 penalty takers from a euros
When player’s perceived contingency and competence, their cognitive and somatic anxiety reduced
What is stress inoculation training (and reference)?
Meichenbaum 1985
Strategy to emphasise the development of coping strategies and self-control
What are the stages of stress inoculation training?
Educated on how self-talk influences emotions and behaviour
Trained to self-monitor and recognise anxiety increasing thoughts
Practice positive self-talk, imagery, mental rehearsal. focus on the cognitive strategies
Practice relaxation, behavioural rehearsal. focus on the somatic strategies
Introduced to graded exposure of stressful situations, where they implement their new techniques
What evidence supports the effectiveness of stress inoculation theory?
Study on exposing athletes to high-pressure situation found that there was a large positive effect on performance under pressure (g = 0.85)
What are pre-performance routines (and reference)?
(Moran 1996)
"a sequence of task-relevant thoughts and actions which an athlete engages in systematically prior to the athletes performance of a specific sports skill"
How are pre-performance routines useful for a elite athlete during a simple skill?
Simple skills are autonomous meaning low cognitive demands. This increases the potential of internal and external distractors
Therefore a pre-performance routine can help distract away from anxiety and stressors
What is Singer’s 5 step strategy to create a pre-performance routine?
Ready = think positively of the performances expectations
Image = mentally picture performing the skill and feeling the movement
Focus = focus on a meaningful cue and concentrate on one relevant cue (e.g. a target to hit during a conversion)
Execute = perform the skill whilst not thinking about anything but the movement
Evaluate = use feedback to assess the performance and effectiveness, and make adjustments if necessary
What evidence did Cotterill 2010 find on Singers 5 step pre-performance routines?
Emphasis on FOCUS + EXECUTE replicate identical results as the full 5 step strategy
What is quiet eye?
“The final fixation on the target before the initiation of the movement“
For example, the ball in golf
What evidence did Vine 2011 find about quiet eye?
When going from a pre-test to a pressure test for basketball free throws:
Quiet eye group rose from 50 to 60% accurate
Control group went from 50 to 36% accurate
Therefore we can train athletes quiet eye to focus for longer during a task
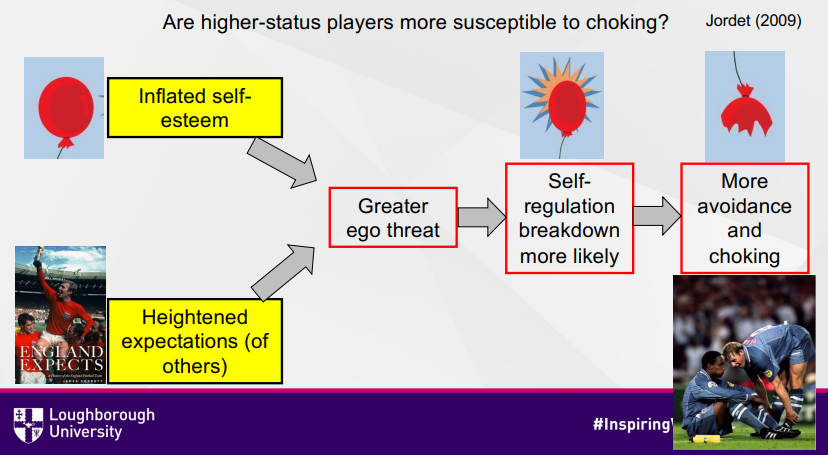
Why are higher status players more likely to choke?
High status players have an inflated self-esteem and heightened expectations on them
This causes a greater ego threat on them if they fail, causing more anxiety
This increases the risk of self-regulation to breakdown, leading to choking
What did Jordet’s 2009 study on high status players show?
41 players who took 67 penalties
Current high status = 65% accurate
Future high status = 89% accurate
This shows the skill was there, but the high status wasn’t affecting them at the time
What did Jordet 2006 study on avoidance behaviour in penalty shootouts show?
Involved 359 kicks (25+ and 34-)
Kickers engaged in 3x more avoidance looking for negative valence shots than positive valence shots
Positive valence kicks had a 30% higher success rate
Positive valence shots took double the time of other shots
What are different valenced shots in a penalty shootout (Jordet 2006)?
Positive valence = a kick to win the game
Negative valence = a kick to not lose the game
Neutral valence = any other kick
What are the 2 components of attentional control theory?
Top-down = conscious and deliberate attention guided by the athletes goals and strategies
Bottom-down = automatic and reactive attention which is based on threatening stimuli
What did Wilson et al 2009 study show about attentional control theory?
Study on anxiety increasing during a penalty which would be analysed:
26% more fixations on the keeper
Increase of 56% fixation time on the keeper
Kicks being 14cm closer to the keeper
How can TCTSA be used for an intervention?
Focus on the athletes appraisal of demands and resources, which will positively favour the performers resources
Therefore use language (positive self-talk and teammates support) and behaviour that emphasises self-efficacy, perceived control, and approach behaviour (e.g. "back yourself, be confident")
What did Turners’ 2014 study on TCTSA show?
46 novice climbers watched a video, half with a challenge statement and half with threat statement
Challenge video saw higher self efficacy and control, and lower cardiac output and muscle tension
Threat video saw lower cardiac output and higher muscle tension
Therefore changing the demands and resources can directly affect their state towards a task
What did Jordet 2012 study on penalties show?
8 players interviewed about a euros penalty shootout
35 stressors were identified around the end of extra time
17/35 were easily manageable (e.g. told the order of penalty takers)
What are challenge approaches to a penalty shootout?
P = plan the kick order and accept players may miss, acknowledging its a group task
R = relish the task, not fearing failure
E = educating players, e.g. which way a keeper dives
P = practice individual strategy, practice different techniques of penalties
A = anxcited, remind the player the anxiety is a positive effect
R = rehearse, practice the penalties especially under pressure situations
E = embrace sport science expertise