energy resources
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
what is the magnetic energy store
the energy stored when repelling poles have been pushed closer together or when attracting poles are pulled farther apart
what is the thermal energy store
the vibrations of an object’s particles
what is the chemical energy store
the energy stored in chemical bonds, e.g food, movement (muscles), electrical cells
what is the kinetic energy store
the energy of anything moving
what is the electrostatic energy store
the energy stored when repelling charges are moved closer together or when attracting charges are pulled further apart
what is the elastic potential energy store
the energy stored when an object is stretched or squashed
what is the gravitational potential energy energy store
the energy of an object at a certain height
what is the nuclear energy store
the energy associated with nuclear interactions
what is the principle of conservation of energy
in any process energy is never created or destroyed, it is transferred from one store to another
what is the equation for efficiency
efficiency = useful energy output/total energy output * 100%
useful energy output = (efficiency * total energy output) / 100%
total energy output = (useful energy output / efficiency) / 100%
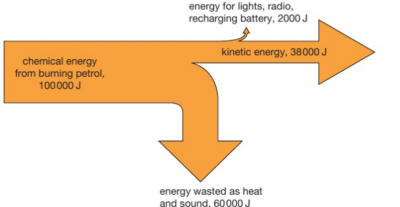
how to make a sankey diagram
the width of the arrow represents the amount of energy involved
the arrow going straight across represents the useful energy
the arrow going down represents the wasted energy
the wasted + useful energy = total energy
what is the electrostatic energy store
a force moves an object through a distance
what is the elastic potential energy store
the energy stored when an object is stretched or squashed
what is the gravitational potential energy energy store
the energy of an object at a certain height
what happens in the radiation pathway
energy transferred as a wave
what is mechanical work
a force moving an object through a distance
what is electrical work
charges moving due to a potential difference
what happens in the heating pathway
temperature difference caused electrically or by chemical reaction
what is the si unit for mass
kg
what is the si unit for energy/work done
J (joules)
what is the si unit for velocity
m/s
what is the si unit for height
m
what is the si unit for acceleration
m/s2
what is the si unit for force
N (newtons)
what is the si unit for time
s
what is the si unit for power
W (watts)
advantages and disadvantages of fossil fuels
advantages
efficient at electricity generation
reliable (doesn’t rely on weather)
readily available
disadvantages
all fossil fuels release CO2 which is a greenhouse gas
release sulphur dioxide when combusted which produces acid rain
increasing fuel costs
fossil fuels are non-renewable so they will eventually run out
advantages and disadvantages of nuclear power
advantages
reliable
lots of uranium available
efficient at energy generation
no release of CO2 or sulphur dioxide: don’t produce greenhouse gases or acid rain
disadvantages
nuclear reactors are expensive to build and maintain
hazardous radioactive waste produced
small risk of nuclear meltdown/accident
non-renewable: will run out
advantages and disadvantages of wind farms
advantages
cheap to maintain
no pollutants produced (while operating)
renewable
disadvantages
expensive to build/set up
noisy
unreliable
not pleasing to look at
advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy
advantages
renewable
reliable
efficient at electricity generation
doesn’t produce pollutants
disadvantages
can only be used in selected areas
expensive to build
advantages and disadvantages of solar energy
advantages
renewable
no pollutants produced while operating
low maintenance costs
disadvantages
dependant on sunlight
inefficient at electricity generation
take up a lot of land space
advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric power
advantages
renewable
low running costs
reliable
large amount of energy can be produced without pollution
disadvantages
can flood land upstream
affects local ecology
few locations
high upfront building costs
advantages and disadvantages of tidal power
advantages
reliable: tides are predictable
cheap to run
efficient at electricity generation
renewable
disadvantages
expensive to set up
hazardous to wildlife
advantages and disadvantages of biofuels
advantages
renewable
cheaper than fossil fuels
burned biofuels produce a lot less CO2 (combusting plants produces as much carbon as they absorb during growth)
reduces reliance on fossil fuels
disadvantages
takes up lots of land
consumes resources that are needed for food production
wind power description, energy store input, and energy pathway
wind turns turbine directly to generate electricity
kinetic store of wind→ kinetic store of turbine → kinetic store of generator
mechanical
hydroelectric power description, energy store input, and energy pathway
water is stored at a height and when it’s released, rushing water turns turbines directly to generate electricity
gpe → kinetic via mechanical
kinetic → electrostatic via mechanical
geothermal power description, energy store input, and energy pathway
hot rocks underground are used to heat water to produce steam to turn turbines which produce electricity
thermal
heating
solar cells power description, energy store input, and energy pathway
solar cells use light to generate electricity
nuclear → electrosatic
radiation
fossil fuels power description, energy store input, and energy pathway
fossil fuels are combusted to evaporate water into steam which turns turbines, generating electricity
chemical
heating
nuclear power description, energy store input, and energy pathway
nuclear fuels are reacted to boil water into steam which turns turbines to generate electricity
Nuclear store of fuel → thermal store of water → kinetic store of turbine → kinetic store of generator
heating
tidal power description, energy store input, and energy pathway
the movement of water due to tides turns turbines directly to generate electricity
kinetic energy of tides → kinetic store of turbine → kinetic store of generator
mechanical pathway
solar panels power description, energy store input, and energy pathway
solar panels use thermal radiation to heat water, producing warm water for household use
nuclear → thermal
radiation
????
biofuel description, energy store input, and energy pathway
plant matter, ethanol or methane can be produced and used in place of fossil fuels
(i.e they are combusted to evaporate water into steam which turns turbines, generating electricity)
chemical → kinetic via heating
kinetic → electrostatic via mechanical
what is the equation for the stopping distance of a vehicle
stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
factors affecting vehicle thinking distance
speed
speed of car
reaction time
being tired
alcohol
drugs
distraction
what is the thinking distance
the distance the car travels during the driver’s reaction time
what is the braking distance
the distance the car travels from the point where the brakes are applied to when the car stops
factors affecting vehicle braking distance
speed of car
mass of car
condition/quality of brakes
condition of road (i.e if it is wet or icy)
condition of tyres (bald tyres can’t grip road properly)
what is the relationship between velocity and braking distance
braking distance is proportional to velocity2
if velocity increases by 3, braking distance increases by 32
how to work out the stopping distance without knowing the thinking or braking distance
substitute stopping distance into the equation work done = force * distance moved
to find the stopping distance, rearrange the equation to get distance moved (stopping distance) = work done / force
what is the equation for work done(/energy transferred)
work done (J) = force (N) * distance moved (m)
force = work done / distance moved
distance moved = work done / force
what is the relationship between work done and energy transferred
work done is equal to energy transferred
what is the equation for gravitational potential energy
GPE = mass (kg) * gravitational field strength (N/kg) * height (m)
what is the equation for kinetic energy + how can you rearrange it
KE = ½ * mass (kg) * velocity2 (m/s)
KE = ½mv2
m = 2KE/v2
v = √(2KE/m)
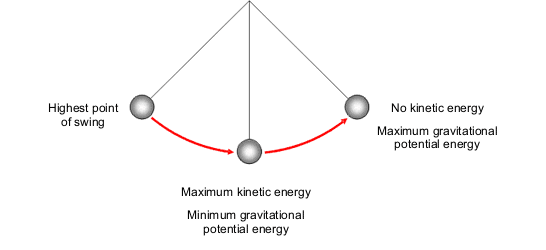
how does conservation of energy make a link between gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy and work
energy transferred = work done
energy is transferred between gpe and kinetic energy in examples such as pendulums and rollercoasters
this makes a link between all three because work done converts gpe into kinetic energy or vice versa
how can power be defined as the rate of energy transfer
power = work done/time
work done = energy transferred
if work done/time is the rate of work being done, energy transferred/time is the rate of energy being transferred
what is the equation for power
power (W) = work done (J) / time (s)
p = w/t
power can also be measured in J/s.
work done = energy transferred so it could also be energy transferred/time
function of the turbine
usefully converts heat energy to kinetic energy
function of the generator
usefully converts kinetic energy to electrical energy