Market Failure
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Market Failure
When the price mechanism fails to allocate resources efficiently
Complete Market Failure
There is a ‘missing market’ - no market exists. Governments need to intervene and provide it.
An example is national defence.
Partial Market Failure
When the market functions, but either the price or quantity supplied of the good/service is wrong.
An example is healthcare. If left to market forces some people wouldn’t be able to afford the treatment they need.
Externalities
The effects that producing or consuming a good/service has on third parties. They can either by positive or negative.
Why market failure occurs
In a free market the price mechanism will only take into account the private costs and benefits, but not the external costs and benefits.
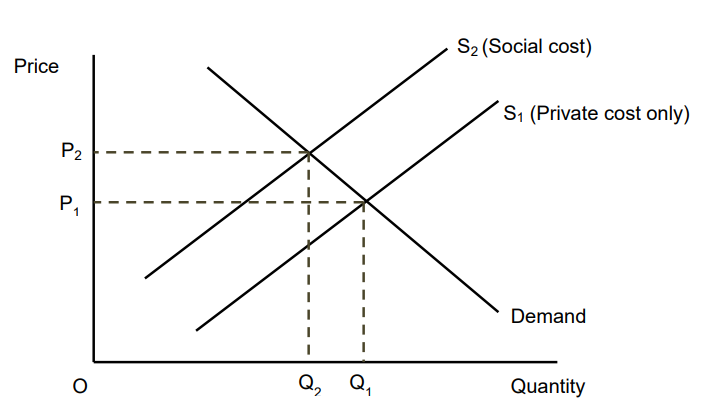
Ignoring Negative Production Externalities
Social cost of production is higher than private cost
If the external cost of production was taken into account the supply curve would shift left
In the free market there is overproduction and underpricing of this good
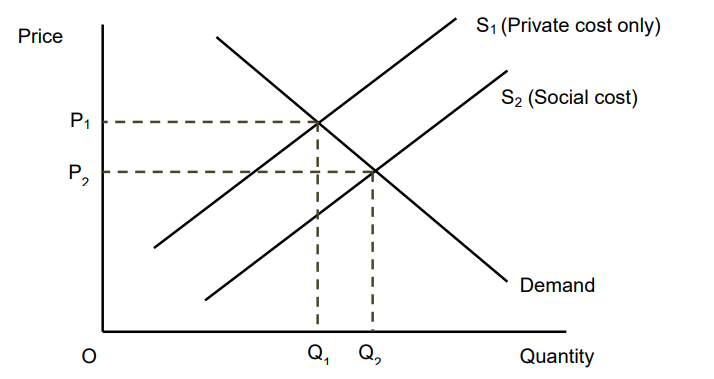
Ignoring Positive Production Externalities
The private cost of production is higher than the social cost - production of the good reduces costs for third parties
If the reduction in external cost was taken into account the supply curve would shift right
In the free market there is underproduction and overpricing of the good
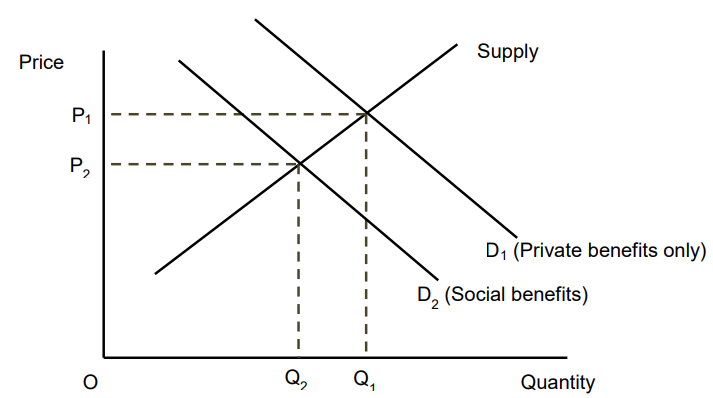
Ignoring Negative Consumption Externalities
The private benefit of consumption is higher than the social benefit
If the reduction in external benefit was taken into account the demand curve would shift left
In the free market there is overconsumption and overpricing of the good
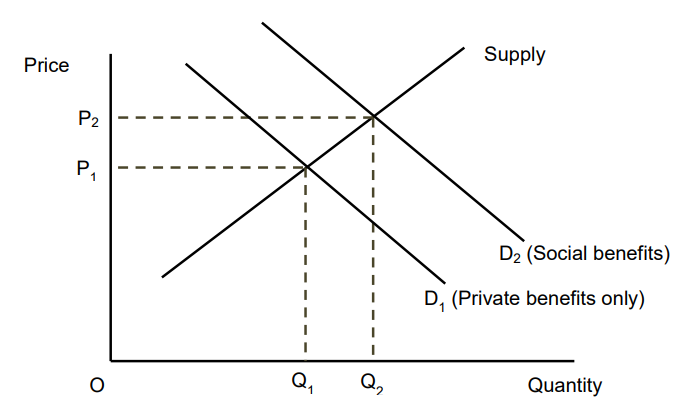
Ignoring Positive Consumption Externalities
The private benefit of consumption is lower than the social benefit
If the external benefit was taken into account the demand curve would shift right
In the free market there is underconsumption and underpricing of this good
Merit goods
Goods which benefit both individuals and society as a whole due to the positive externalities that result from their consumption.
Social benefits > private benefits
Why merit goods tend to be underconsumed
In the free market its positive externalities are ignored so production and consumption will be below the socially optimal level
Consumers don’t always realise the full benefits that merit goods provide due to imperfect information
Demerit goods
Goods whose consumption is regarded as being harmful to the people who consume them and society due to the negative externalities that result from their consumption.
Social costs > private costs
Why demerit goods tend to be overconsumed
Negative externalities are ignored so production and consumption will be above social optimum
Due to imperfect information consumers don’t always realise the harm that demerit goods cause
Characteristics of a public good
Non-excludable and non-rival
Exampes of public goods include firework displays and lighthouses.
Quasi public goods
Goods which exhibit some characteristics of a public good but not fully.
Free rider problem
Once a public good is provided it is impossible to stop people from benefitting from it, even if they haven’t paid towards it.
Asymmetric information
When buyers have more information than sellers (or vice versa) in a market
Immobile factors of production
This results in an inefficient allocation of resources - market failure.
Monopoly Market Failure
Monopolies cause market failure and the misallocation of resources.