Bio 102 Exam 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
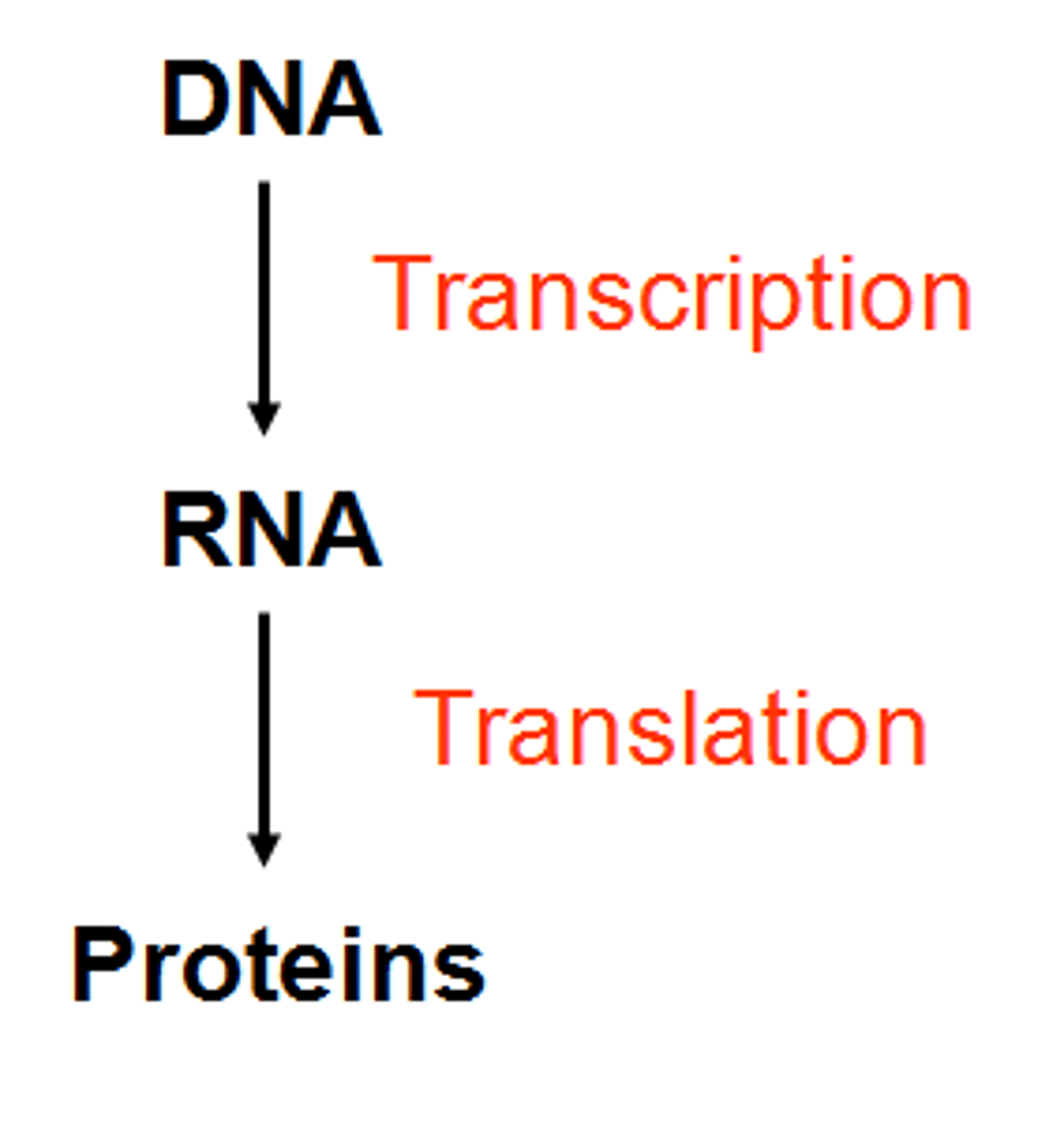
Central Dogma
information only flows from
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
mRNA Processing
location: nucleus
the transcript must be modified to become mature mRNA
capping, Poly-A tail, and splicing occur
Capping
5 inch guanine nucleotide at the end of the pre-mRNA shortly after the start of transcription.
- This protects the mRNA from degrading
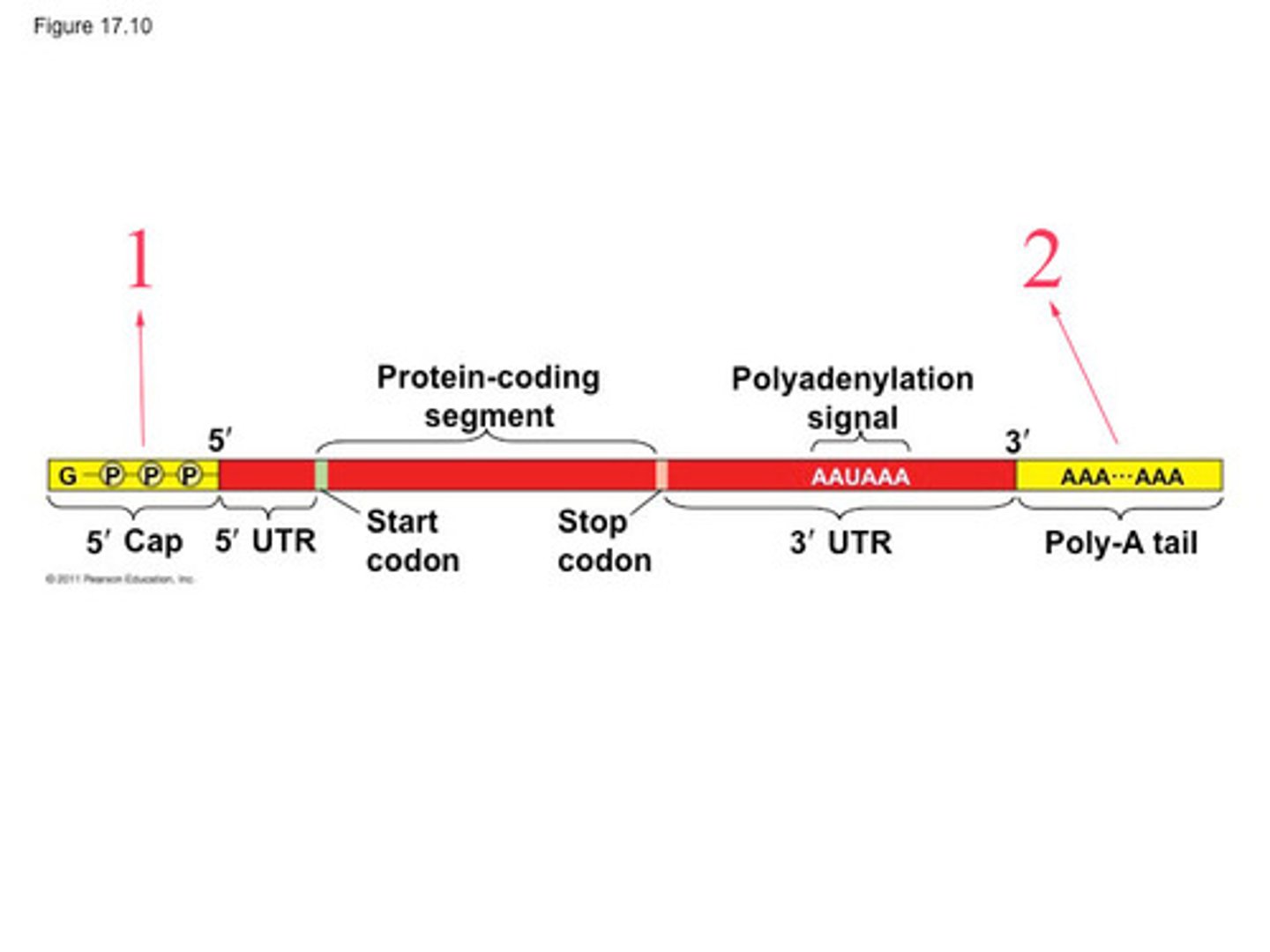
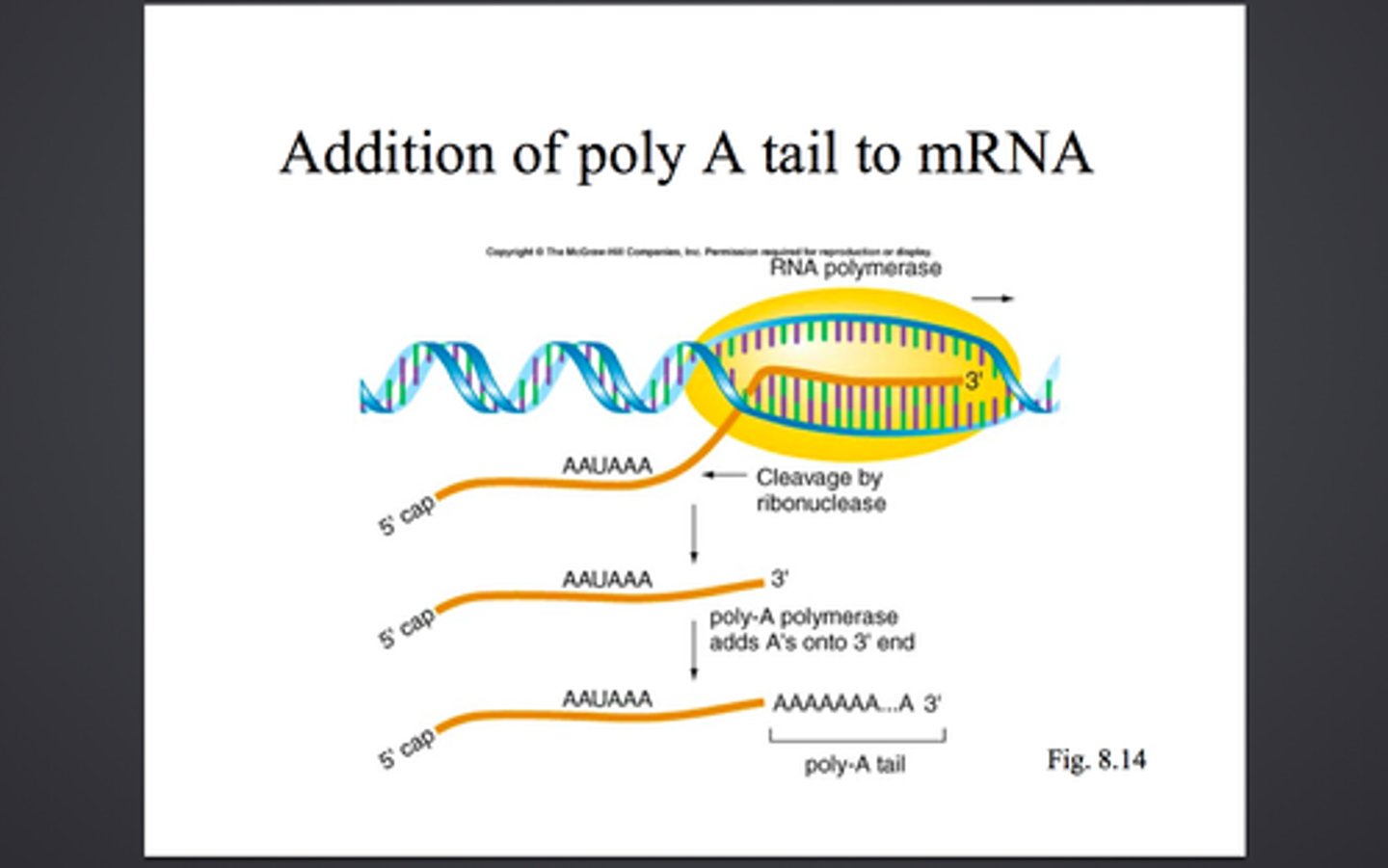
Polyadenylation
The poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of the mRNA. the tail protects the mRNA from degrading and assists in the export of MRNA
- determines how much protein should be made
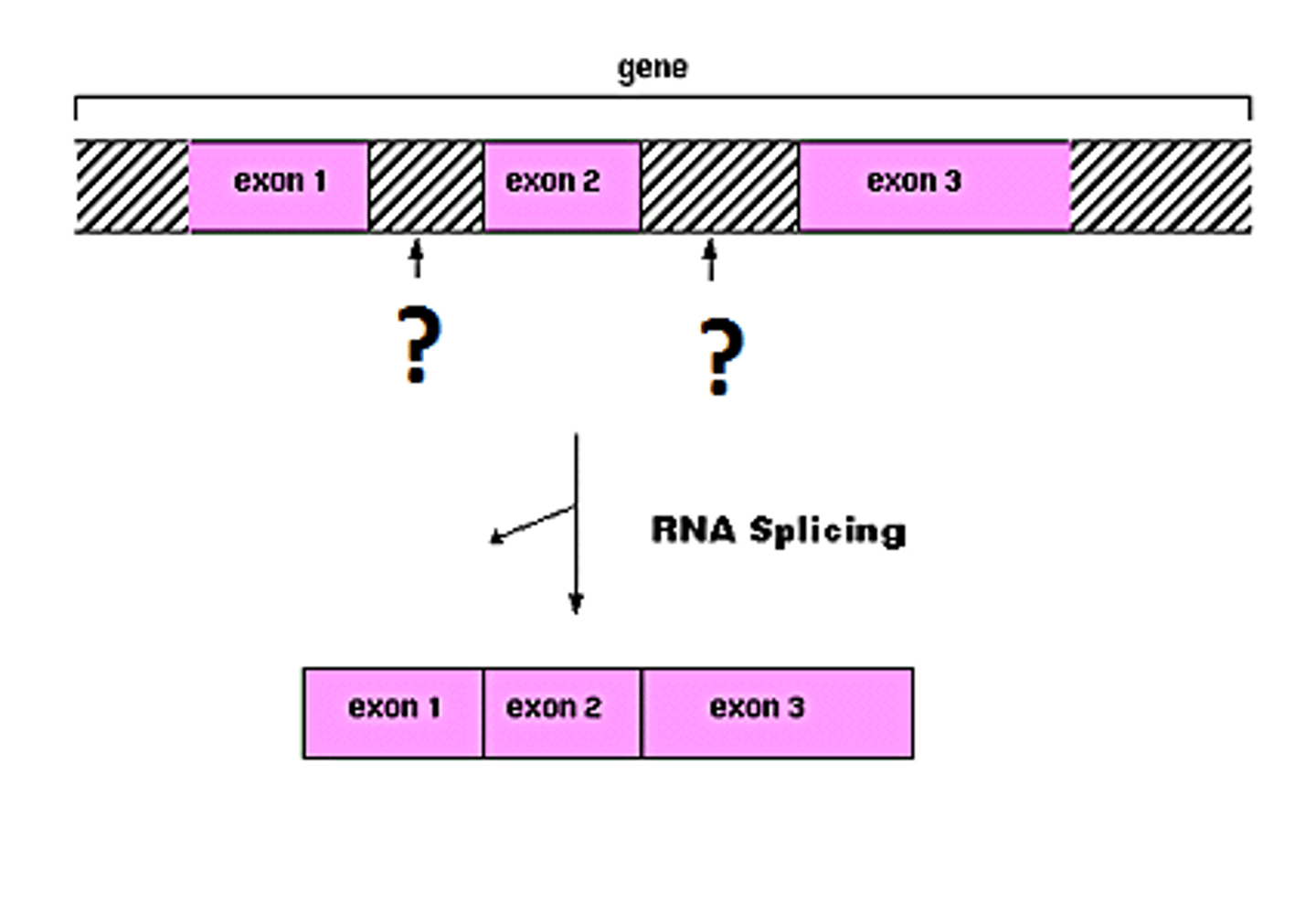
Splicing
the removal of introns which is junk DNA
this is done by the spliceosome
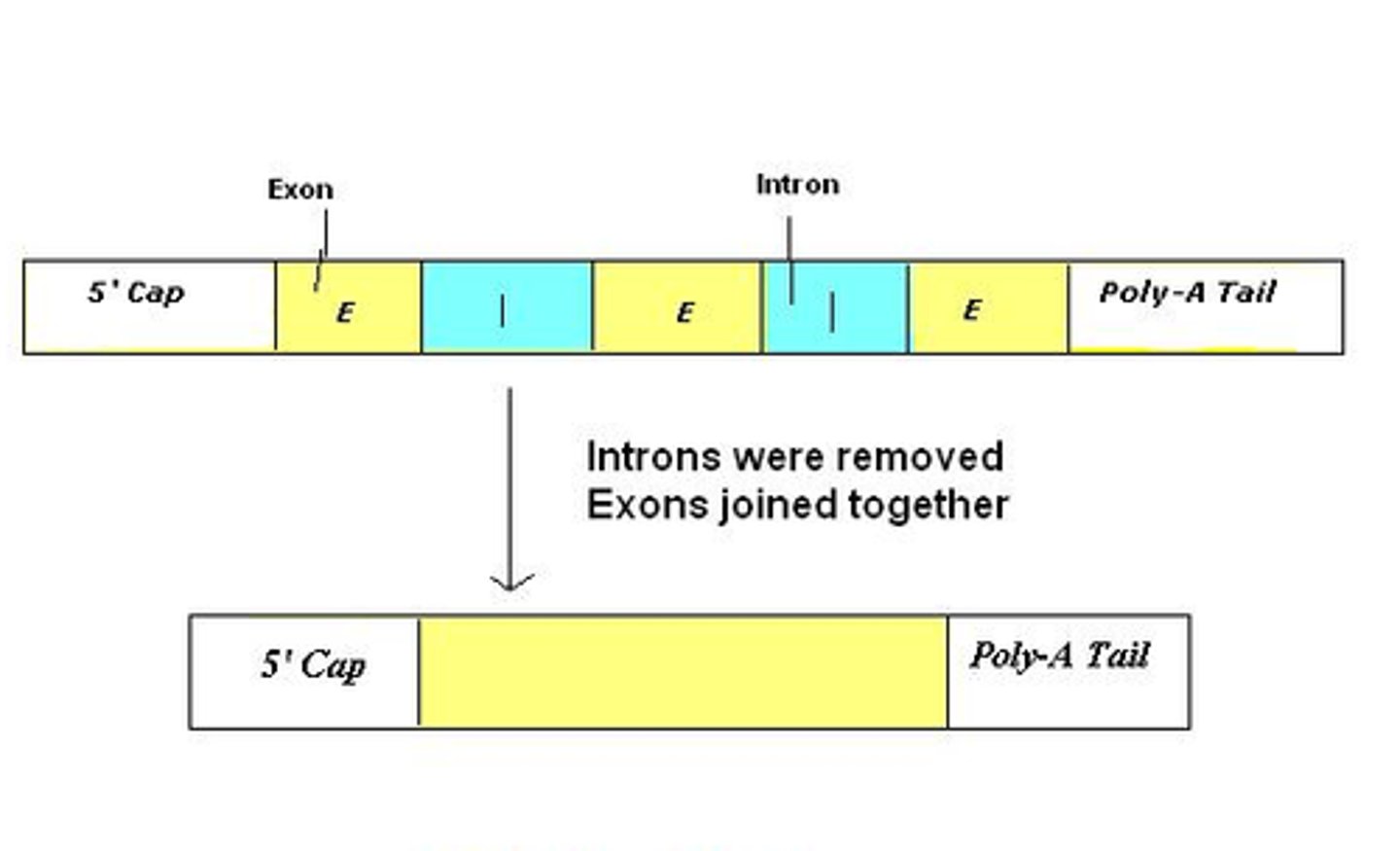
Exons
Sequences that will be translated aka coding
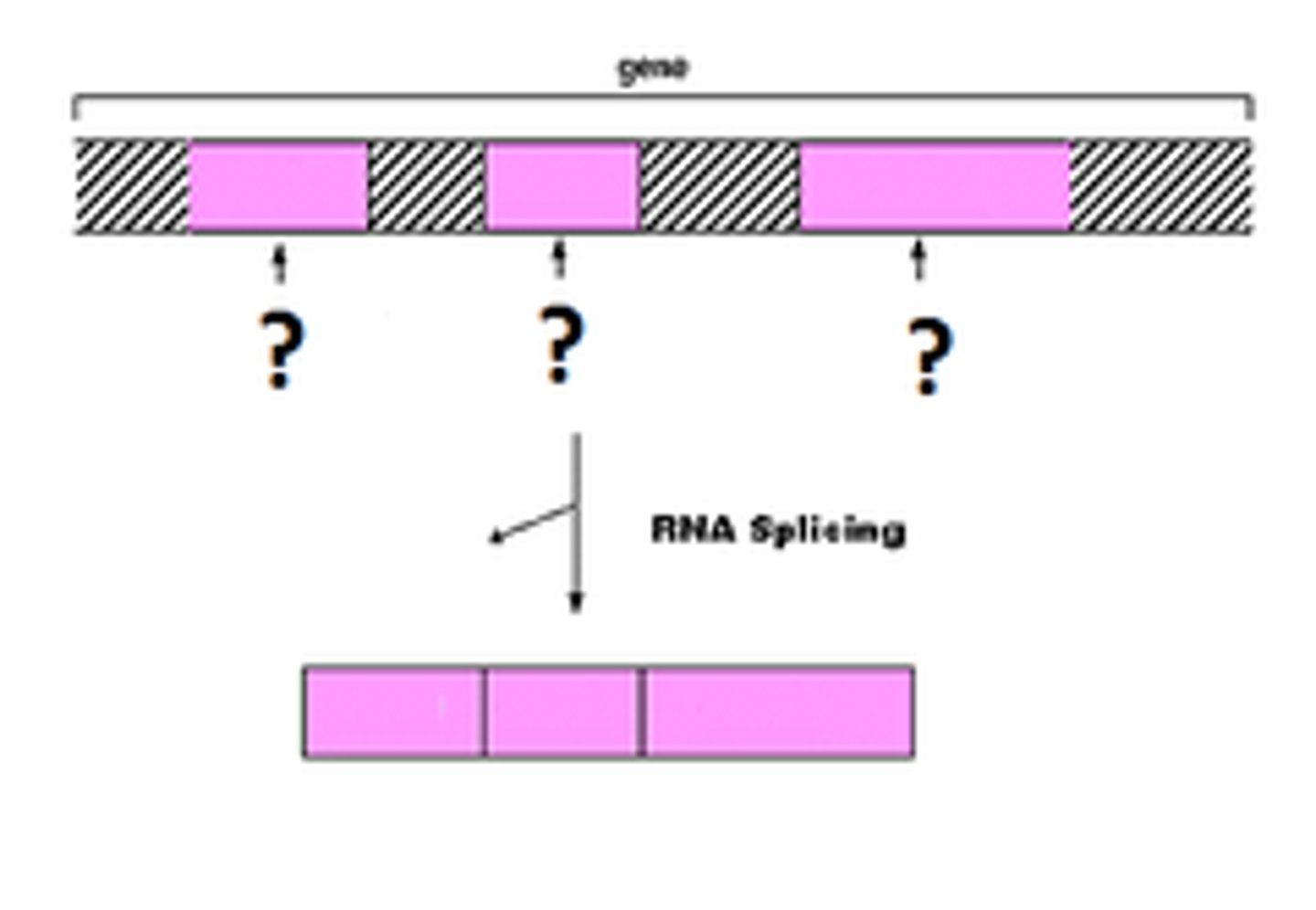
Introns
non coding sequences
Transcription
Location: Nucleus
Process: DNA sequence of a gene is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA) which then carries the genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
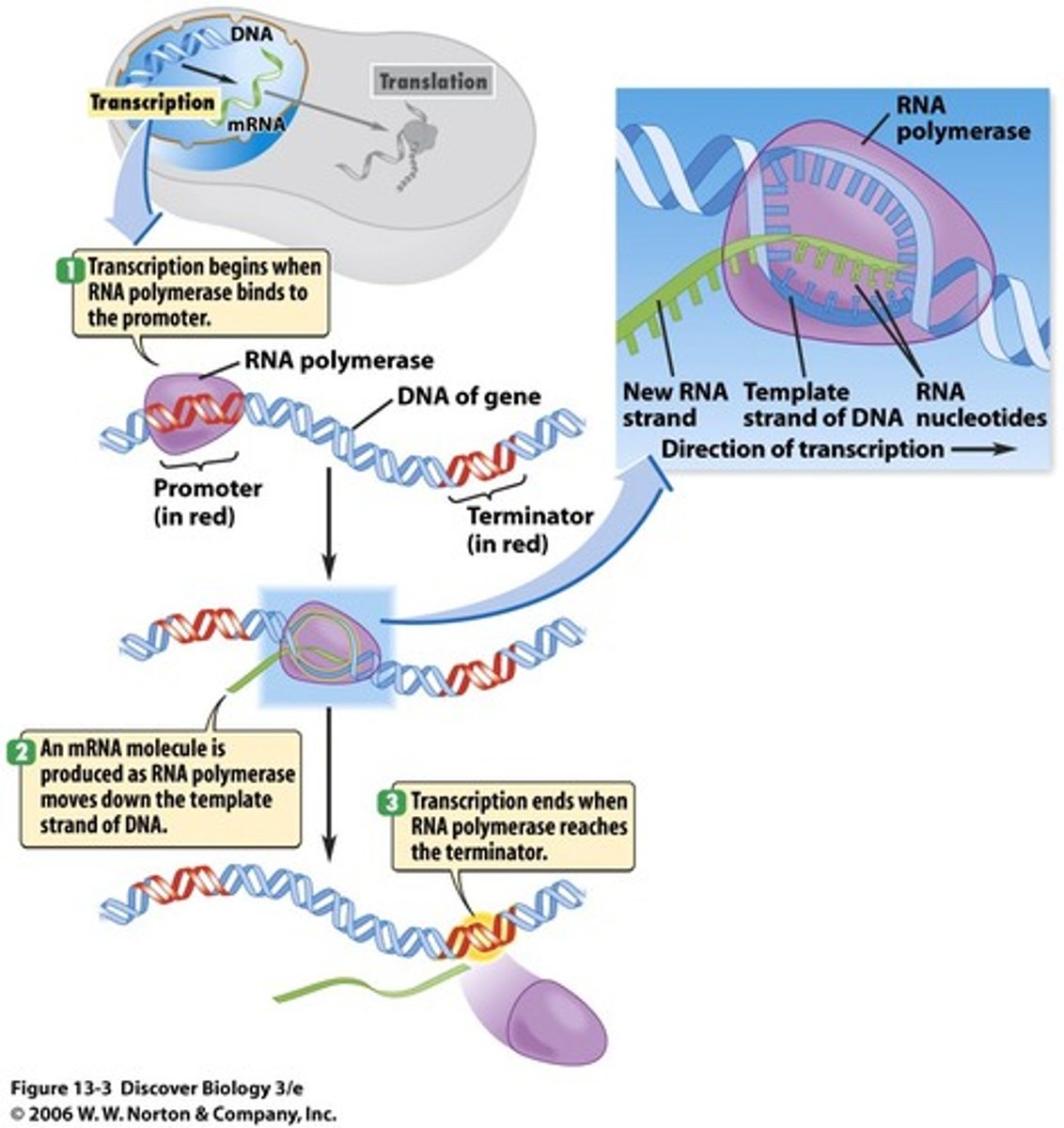
Transcription Unit
promoter
start site
terminator
3 types of RNA
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
mRNA
type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
tRNA
type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
rRNA
type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
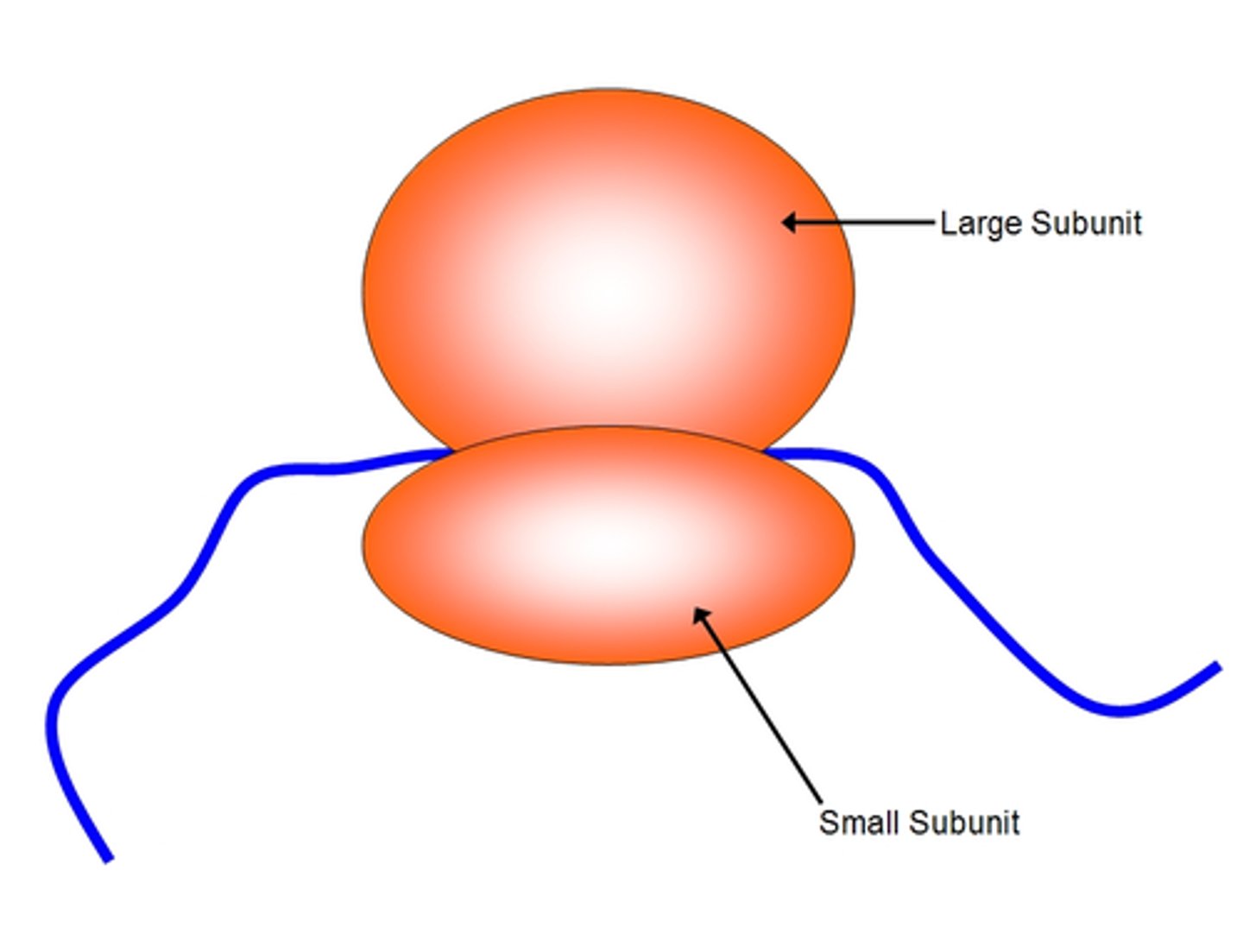
Translation
location: cytoplasm
Mature mRNA is used as a template to synthesize a protein. this process takes place on ribosomes, which are either free floating or on the rough ER.
Ribosome
site of protein synthesis (makes proteins)
decode mRNA
form peptide bonds
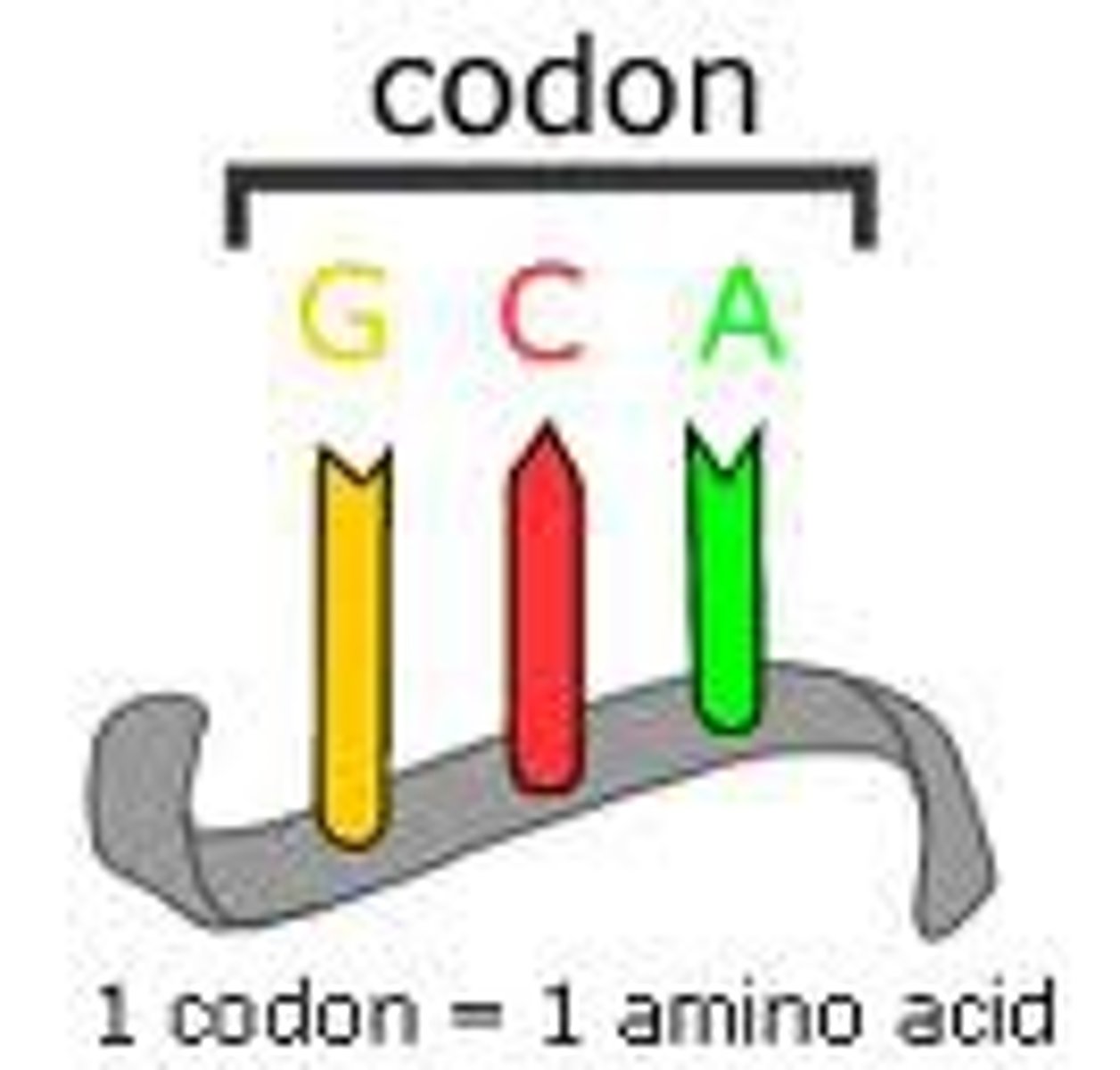
Codon
A block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid
3:1 ratio
Ex) UUA, UGA, UAG
anti-codon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon

Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
Proportions of genotypes do no change in a population if...
- No mutation takes place
- No genes are transferred to or from other sources
- Random mating is occurring
- The population size is very large
- No selection occurs
Used to calculate allele frequencies.
Natural Selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
ex) tall neck giraffes are more likely to live with food at higher elevation than small neck giraffes.
gene flow
movements of alleles from one population to another
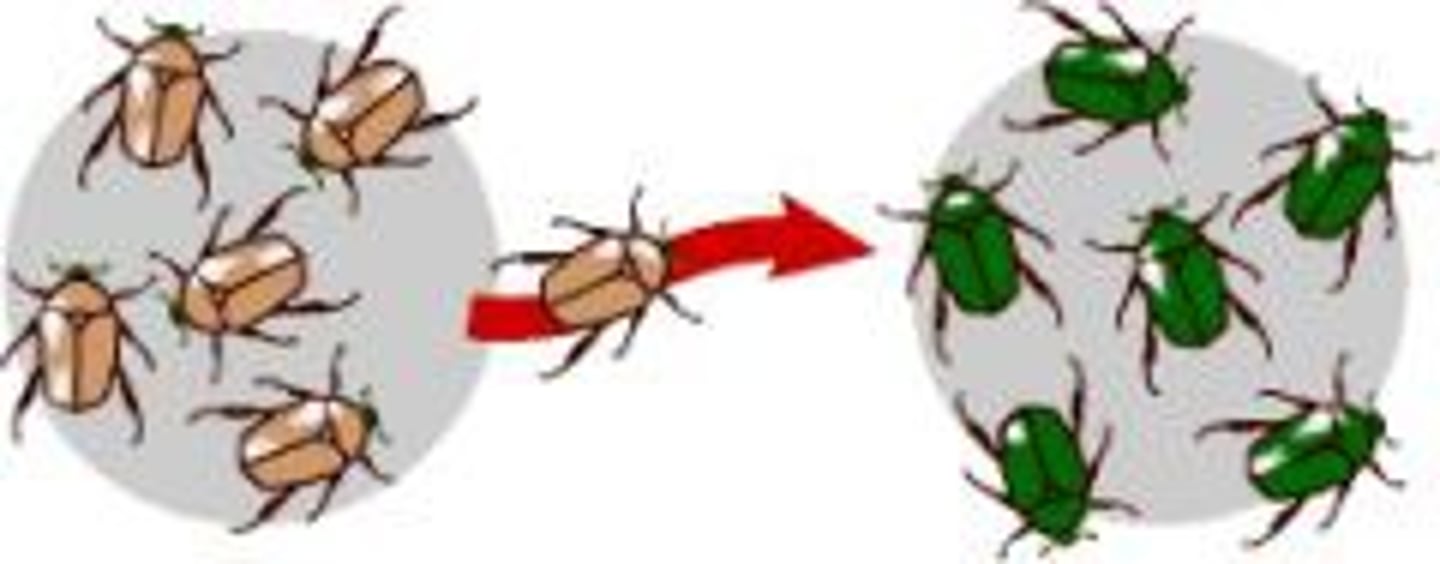
genetic drift
in small populations, allele frequency may change by chance alone.
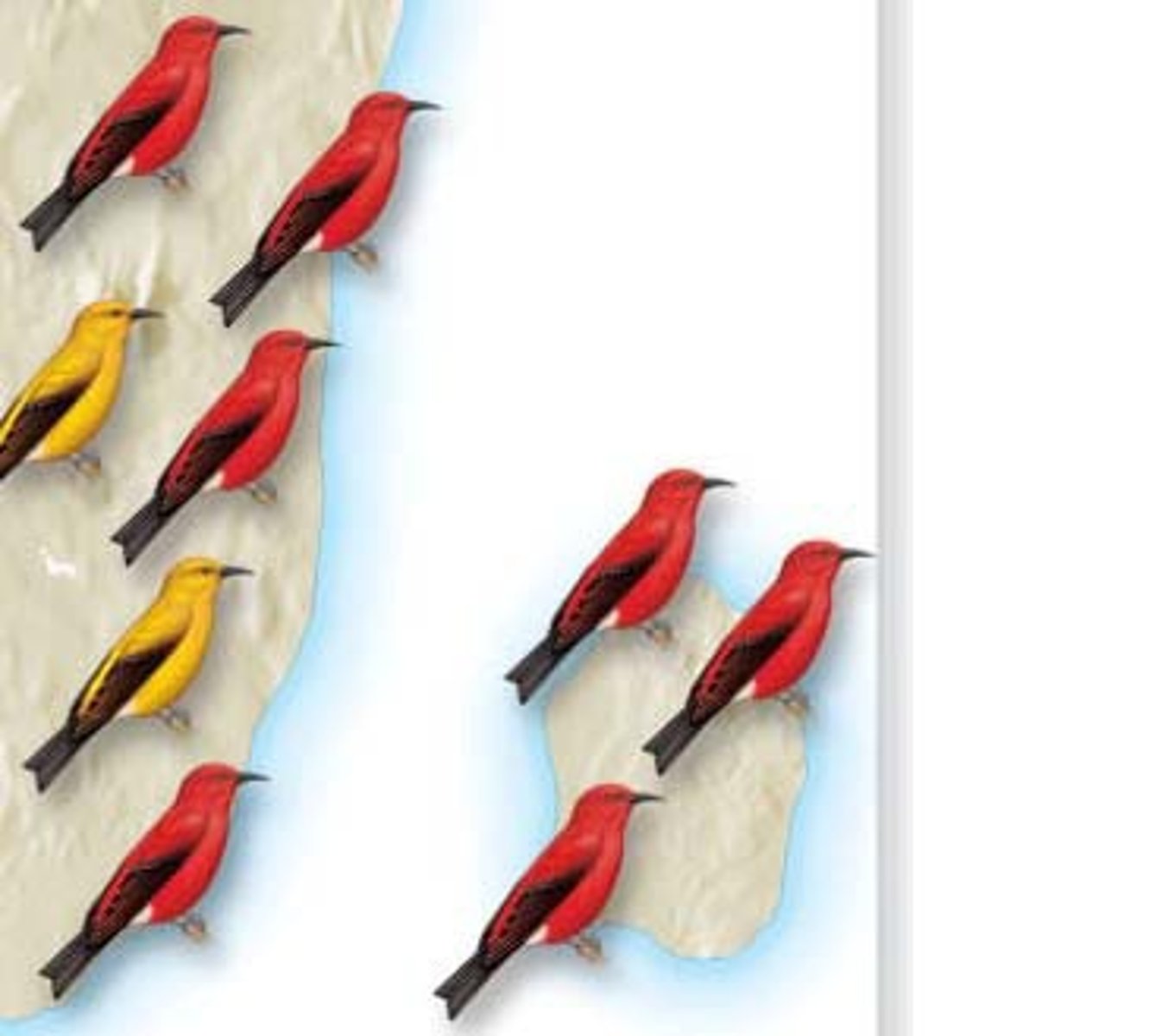
Founder effect
when a new population is created, only some genes are transferred because not all of the population goes.
ex) the red birds making their new group loose the yellow ones that were previous, loosing genes.

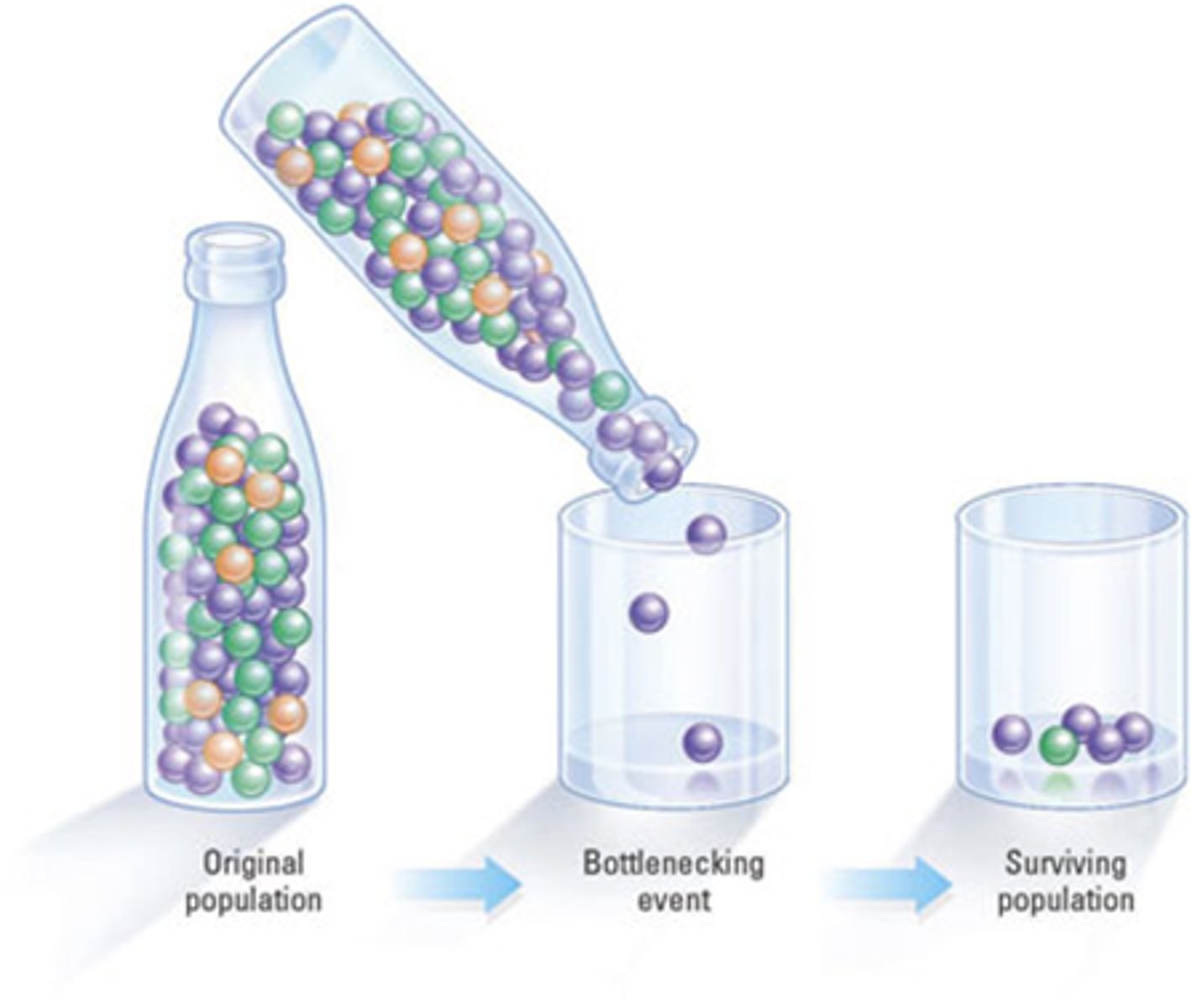
Bottleneck Effect
- loss of genes through die off/ endangered species
- genetic drift can lead to the loss of alleles in isolated populations
ex) a tsunami wipes out almost half of a population because they died
Assortive mating
phenotypically similar individuals mate
Dissortive mating
phenotypically different individuals mate
Hardy-Weinburg Equation
P+q=1 P^2+2pq+q^2=1
P= dominant frequency allele q= Recessive frequency allele
P^2= homozygous dominant q^2= homozygous recessive
2pq= heterozygous
Fitness
individuals with one phenotype leave more surviving offspring in the next generation than individuals with an alternative phenotype.
ex) brown beetles leave more offspring than yellow beetles
conditions for natural selection to occur
1. Variation must exist among individuals in a population
2. Variation among individuals must result in differences in the number of offspring surviving in the next generation
3. variation must be genetically inherited
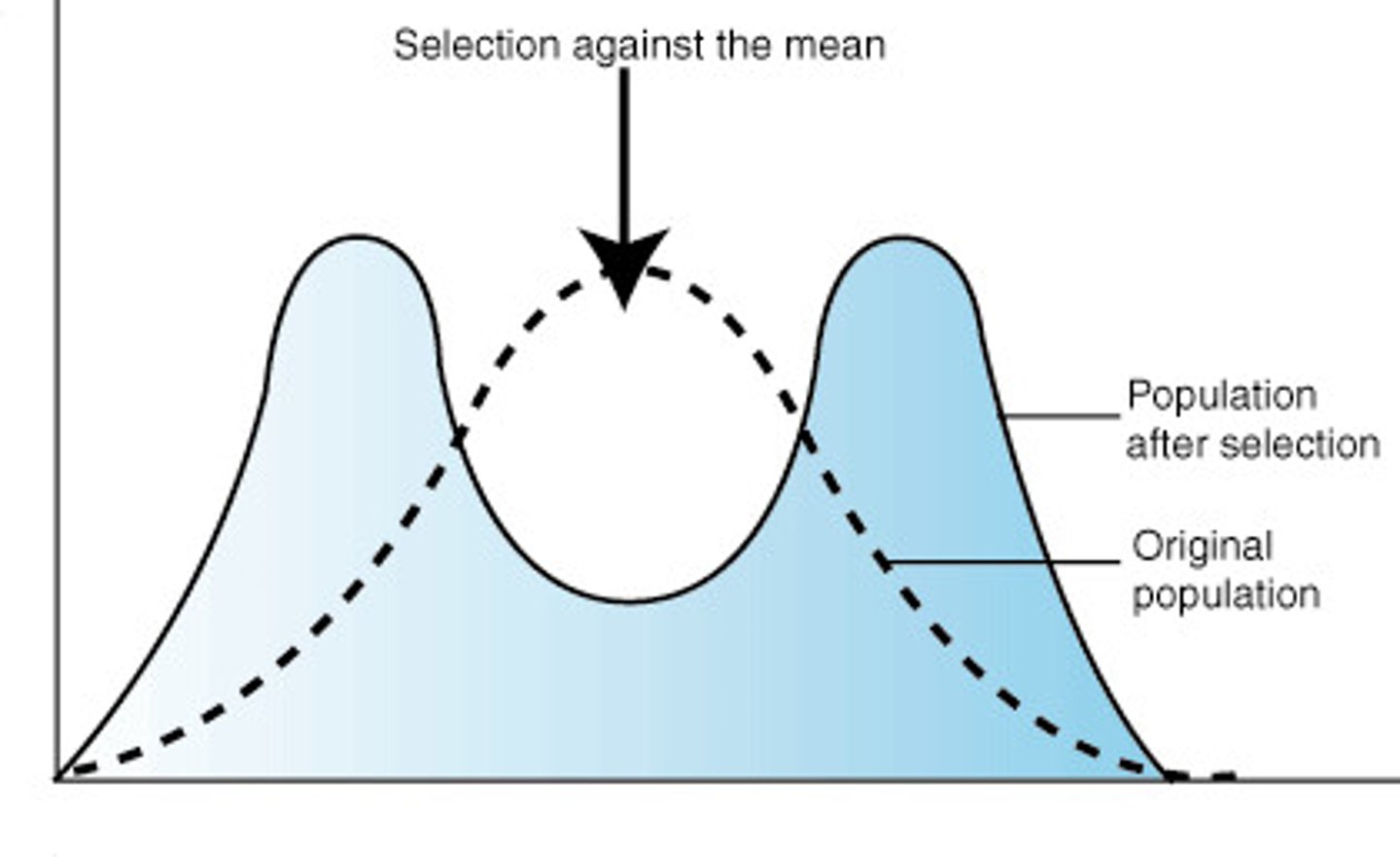
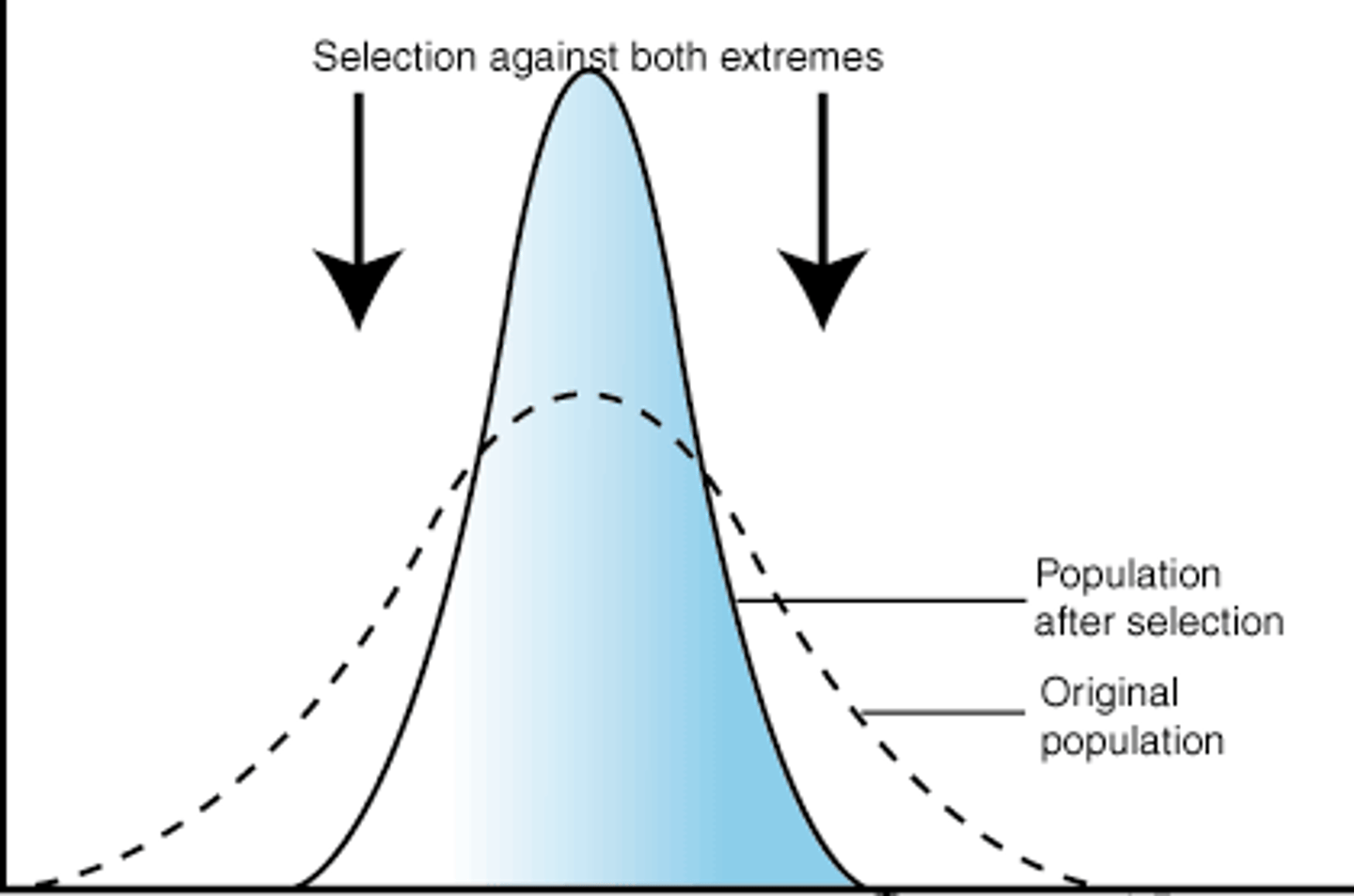
Disruptive selection
acts to eliminate intermediate types
ex) birds with intermediate-sized beaks are at a disadvantage with both seed types- they are unable to open large seeds and too clumsy to efficiently process small seeds.
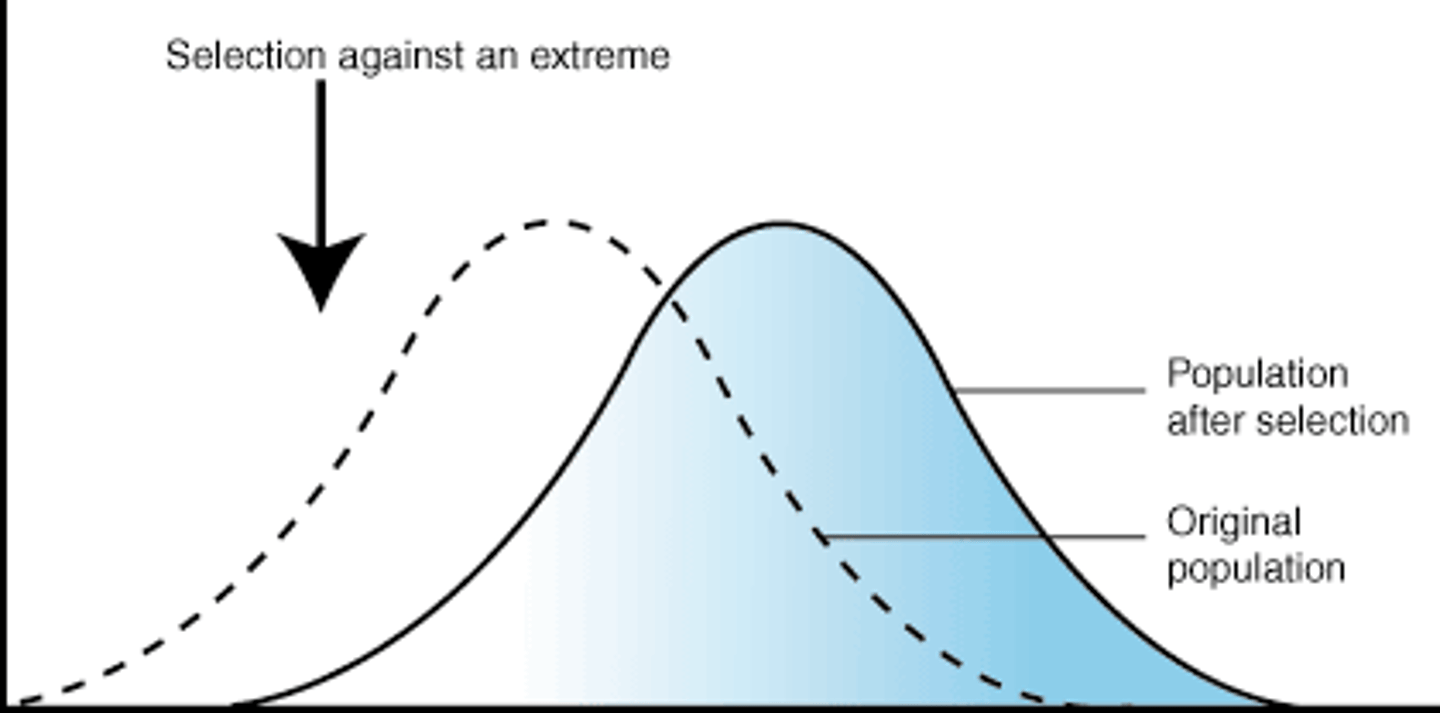
Directional selection
acts to eliminate one extreme
- often occurs in nature when the environment changes
ex) in Drosophila, artificially selected flies that moved toward the light on one side
Stabilizing selection
Acts to eliminate both extremes
ex) in humans, infants with intermediate weight at birth have the highest survival rates
Heterozygote advantage
heterozygotes are favored over homozygotes
works to maintain both alleles in the population
ex) sickle cell anemia

Artificial Selection
Selection by humans for breeding individuals with certain phenotypic traits, so they can pass specific genes to the next generation.
ex) taking fruit flies with not a lot of abdomen hair and breading another like that until they bread one with no hair.

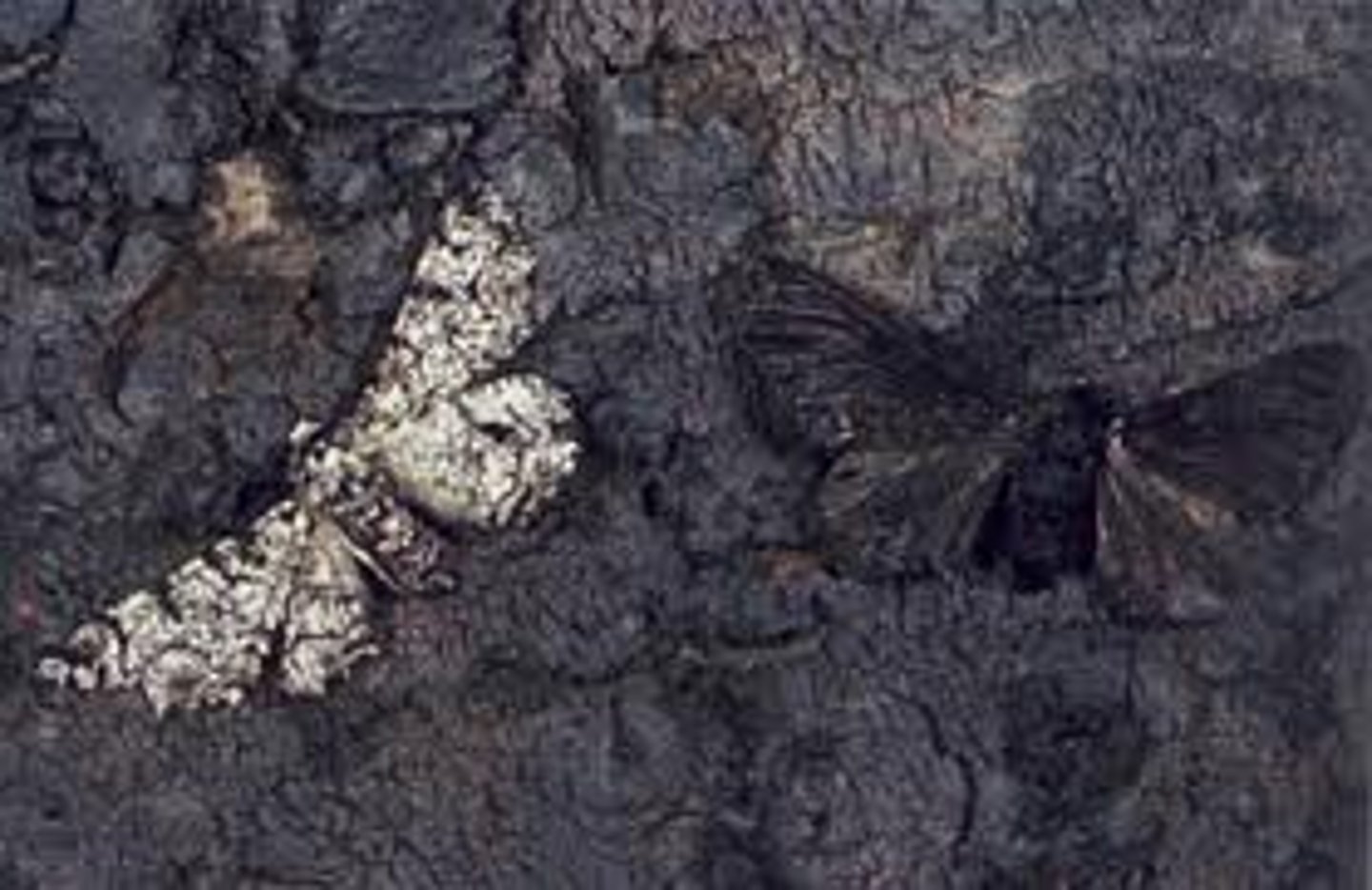
industrial melanism
phenomenon in which darker individuals come to predominate over lighter ones
- pollution control resulted on dark color being lighter again

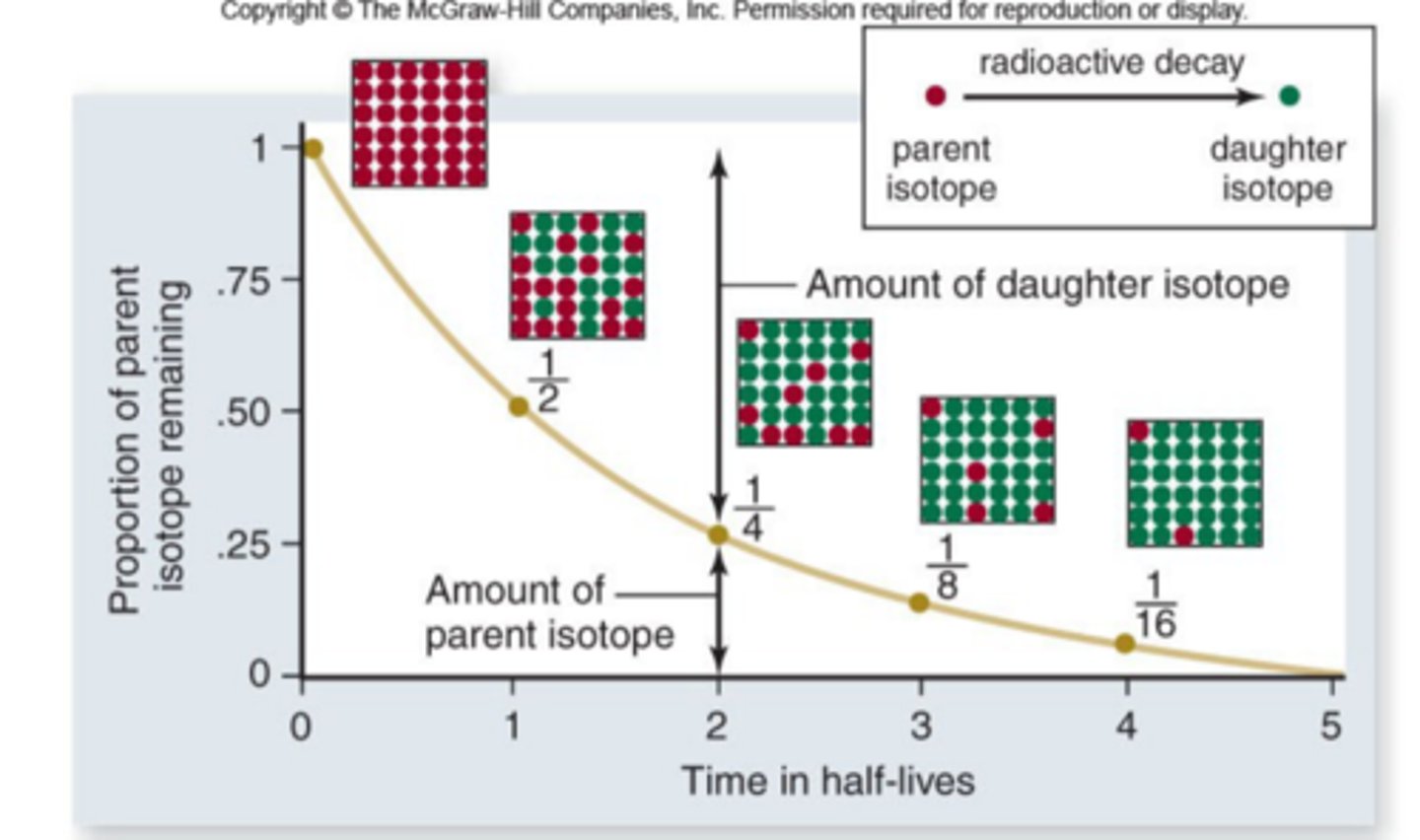
Absolute Dating
age of fossils is estimated by rates of radioactive decay
- rate of decay is known as an isotope's half-life
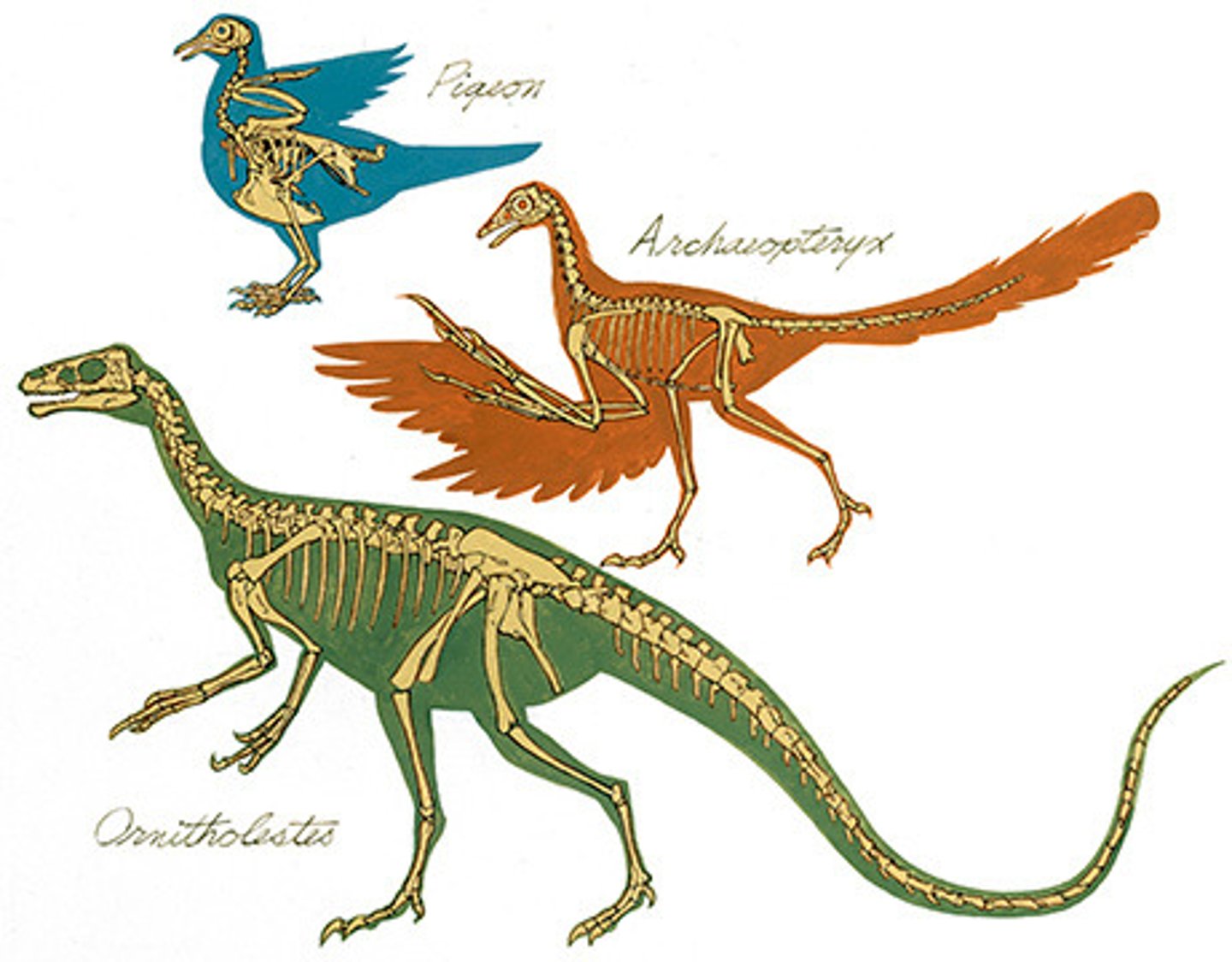
Transitional Fossils
Fossils that provide patterns of evolutionary change from the early ancestors to modern life forms.
ex) oldest known bird fossil is the archaeopteryx (which was a dinosaur)
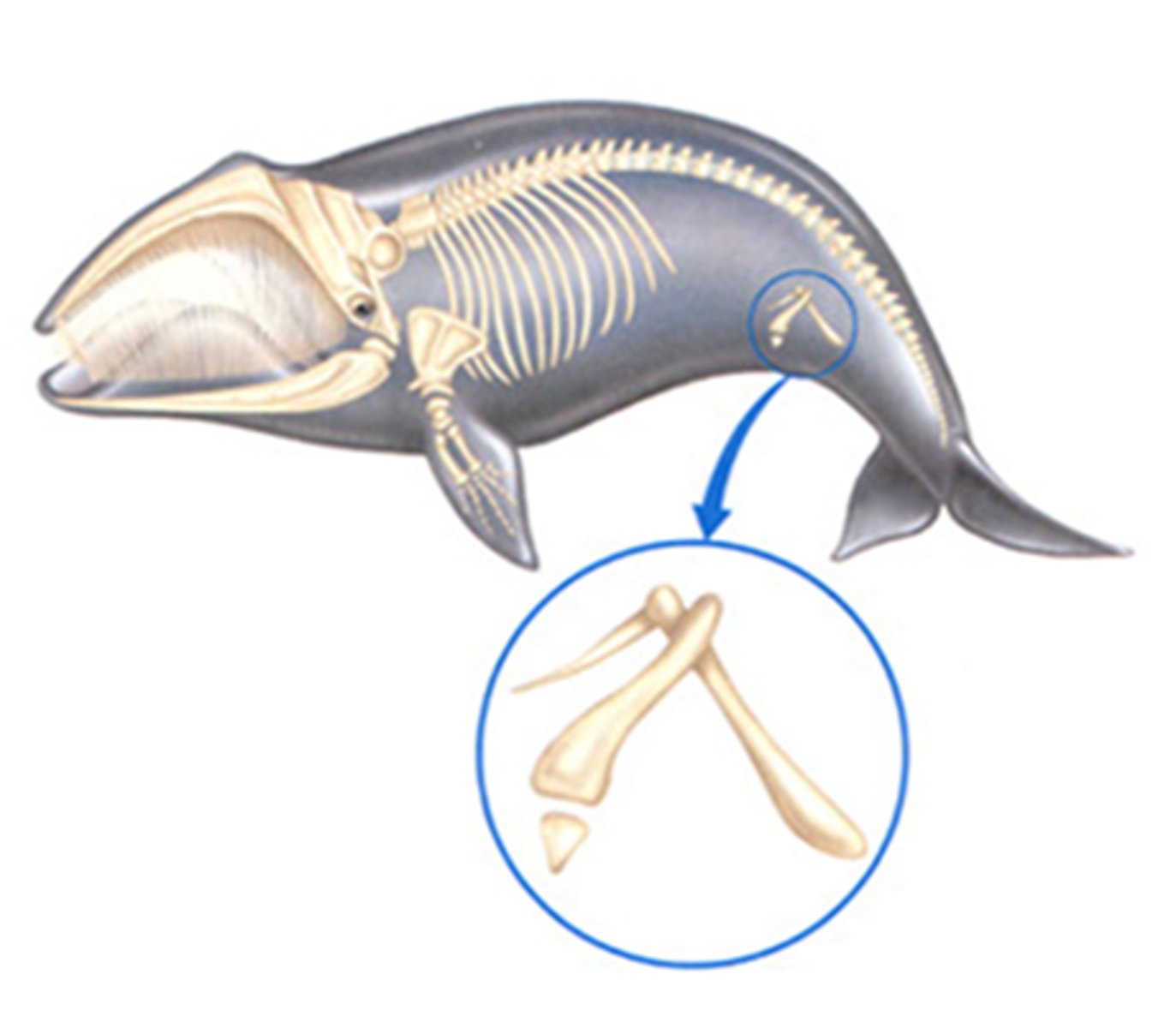
Vestigial Structure
Have no apparent function, but resemble structures their
ancestors possessed
ex) Hip bones in boa constrictors
- Evolutionary relicts
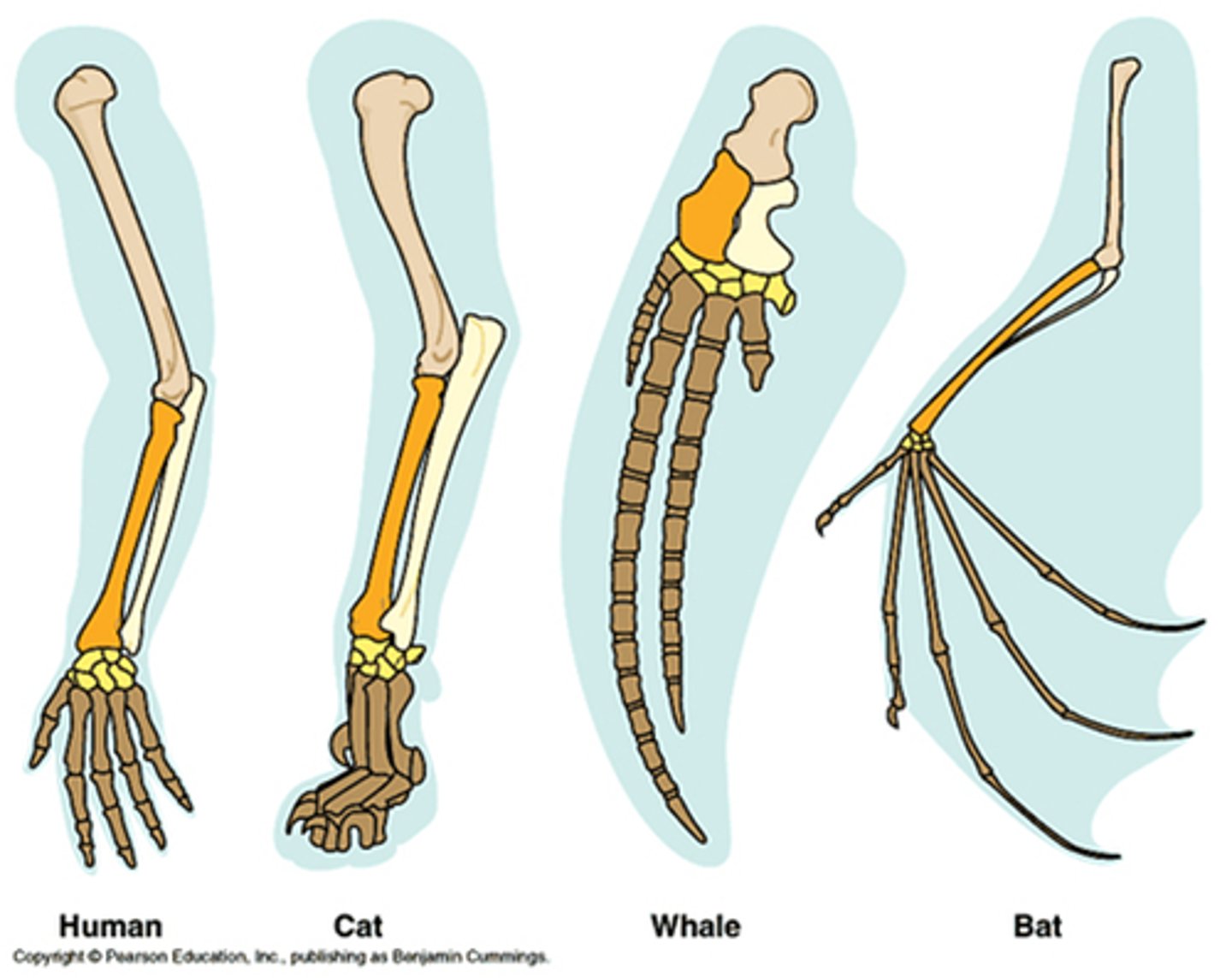
homologous structures
Structures with different appearances and functions that all derived from the same body part in a common ancestor
ex) bones in the forelimb of mammals
- different functions, same ancestor structure
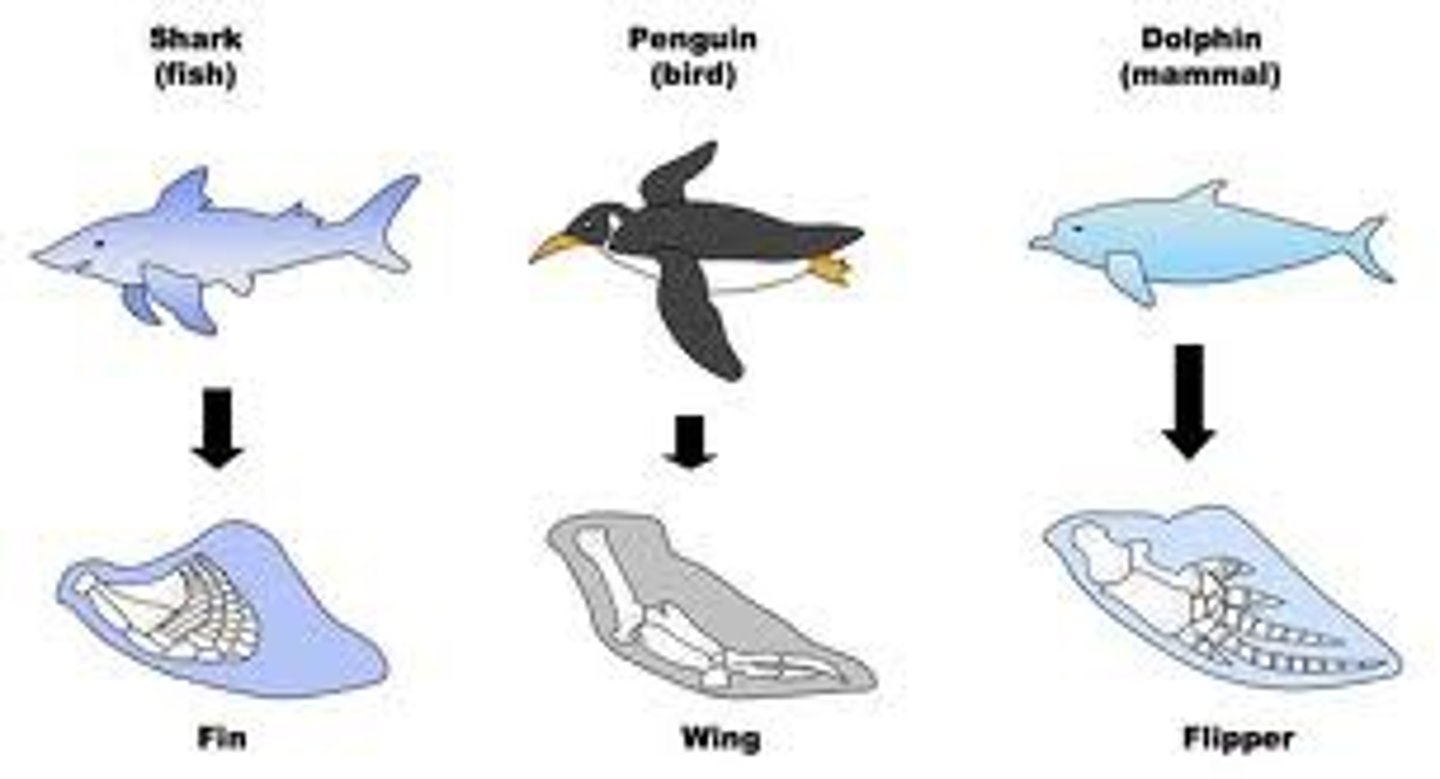
Convergence
Similar forms having evolved in different, isolated areas because of similar selective pressures in similar environments.
ex) bats and birds both have wings and can fly; however, they evolved these traits seperately
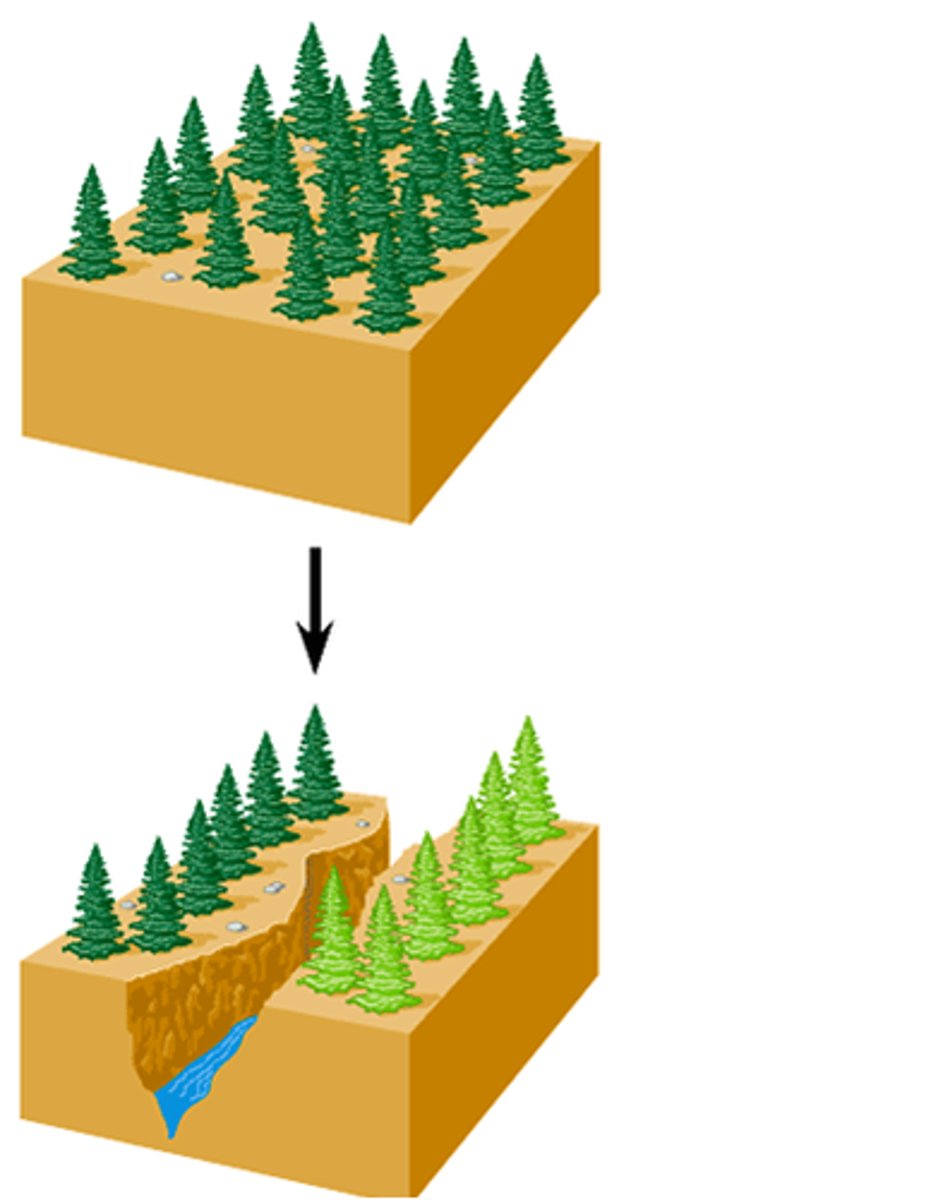
allopatric speciation
geographically separated populations appear much more likely to have evolved substantial differences leading to speciation.
Speciation
the evolution of a new species from an existing species
sympatric speciation
one species splits into two at a single locality, without the two species ever having been geographically separated
Gradualism
accumulation of small changes
standard view for a long time
Prezygotic isolating mechanisms
prevent formation of zygote

Temporal Isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations reproduce at different times
ex) one flower is in early spring and one is in summer
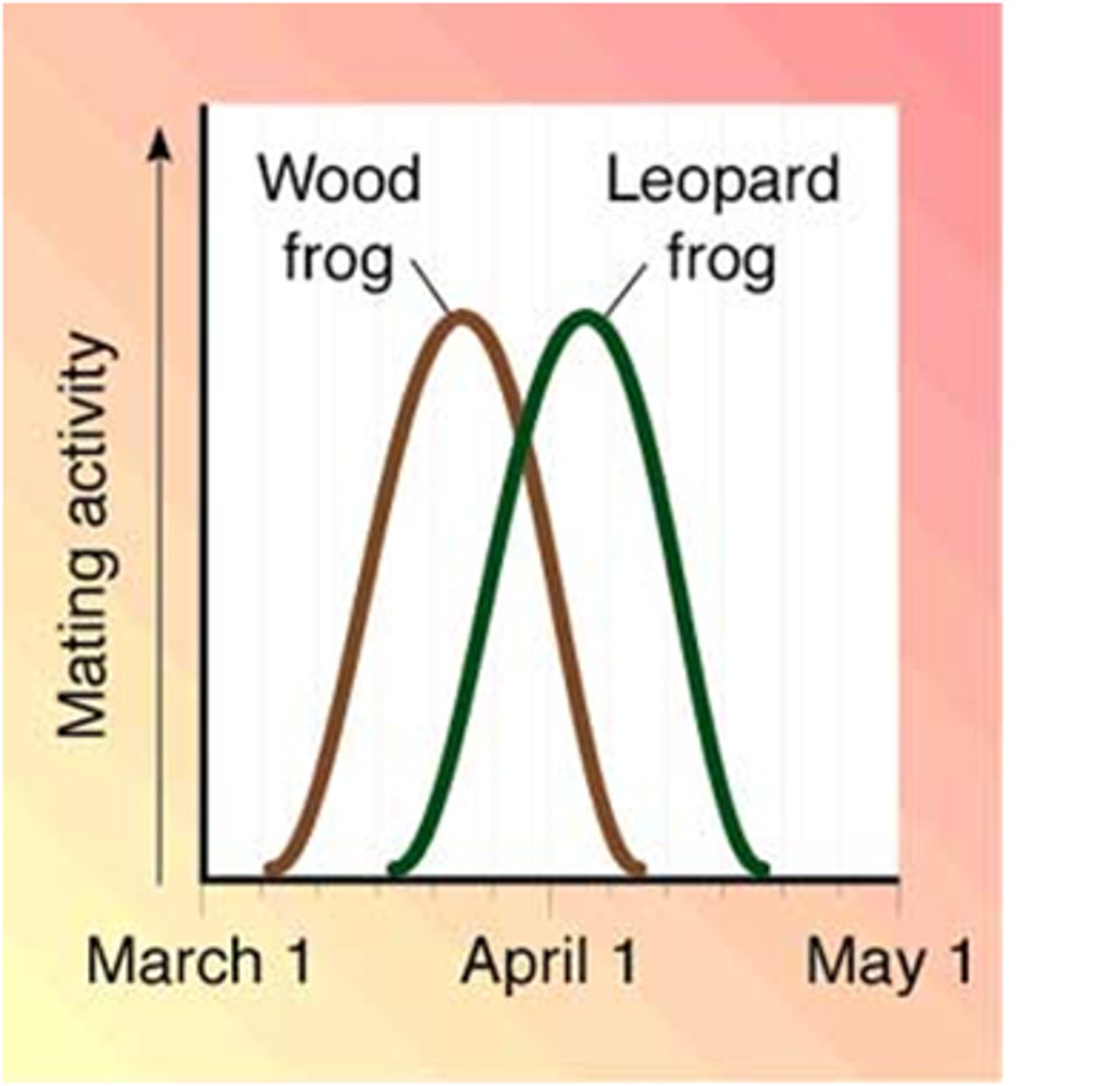
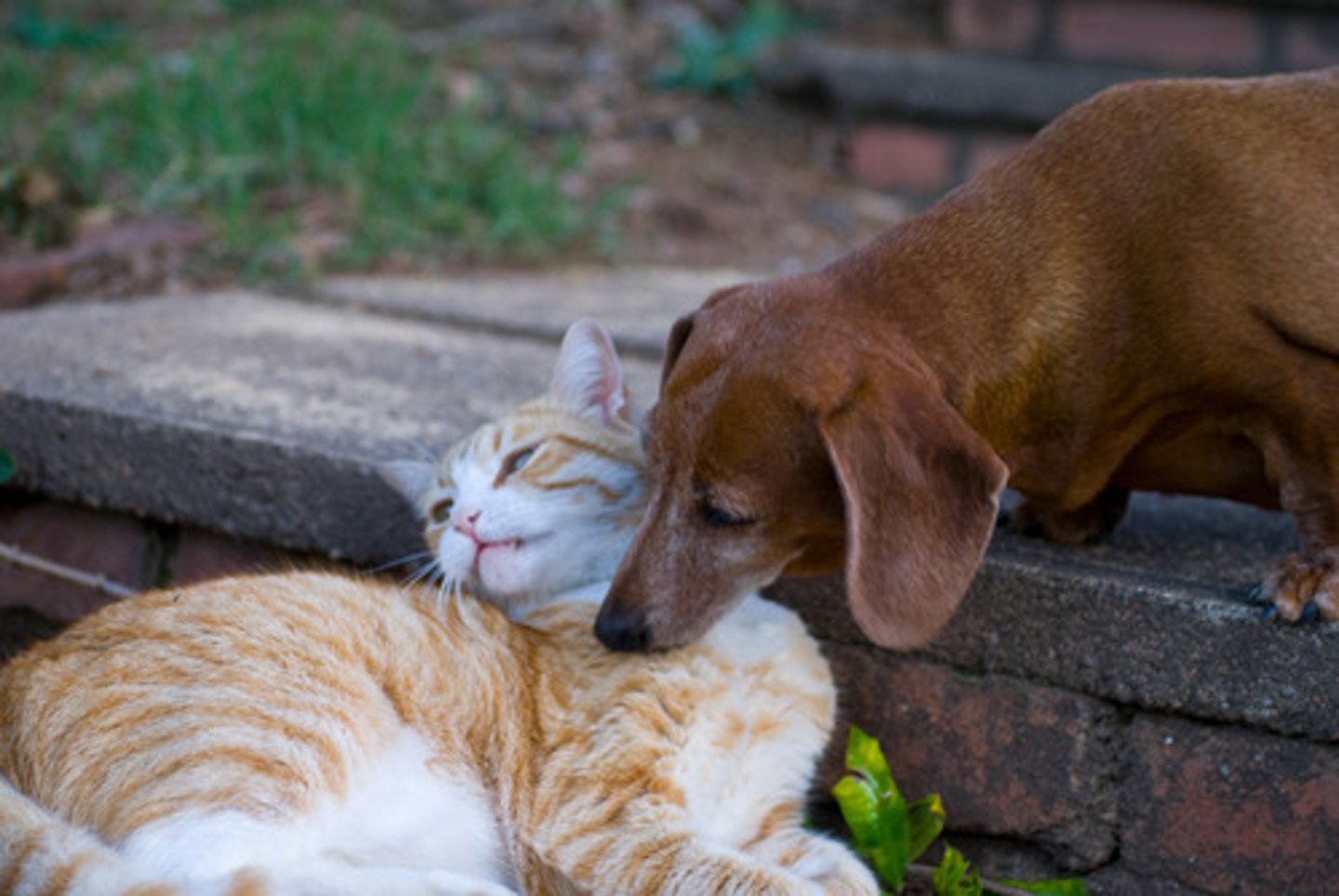
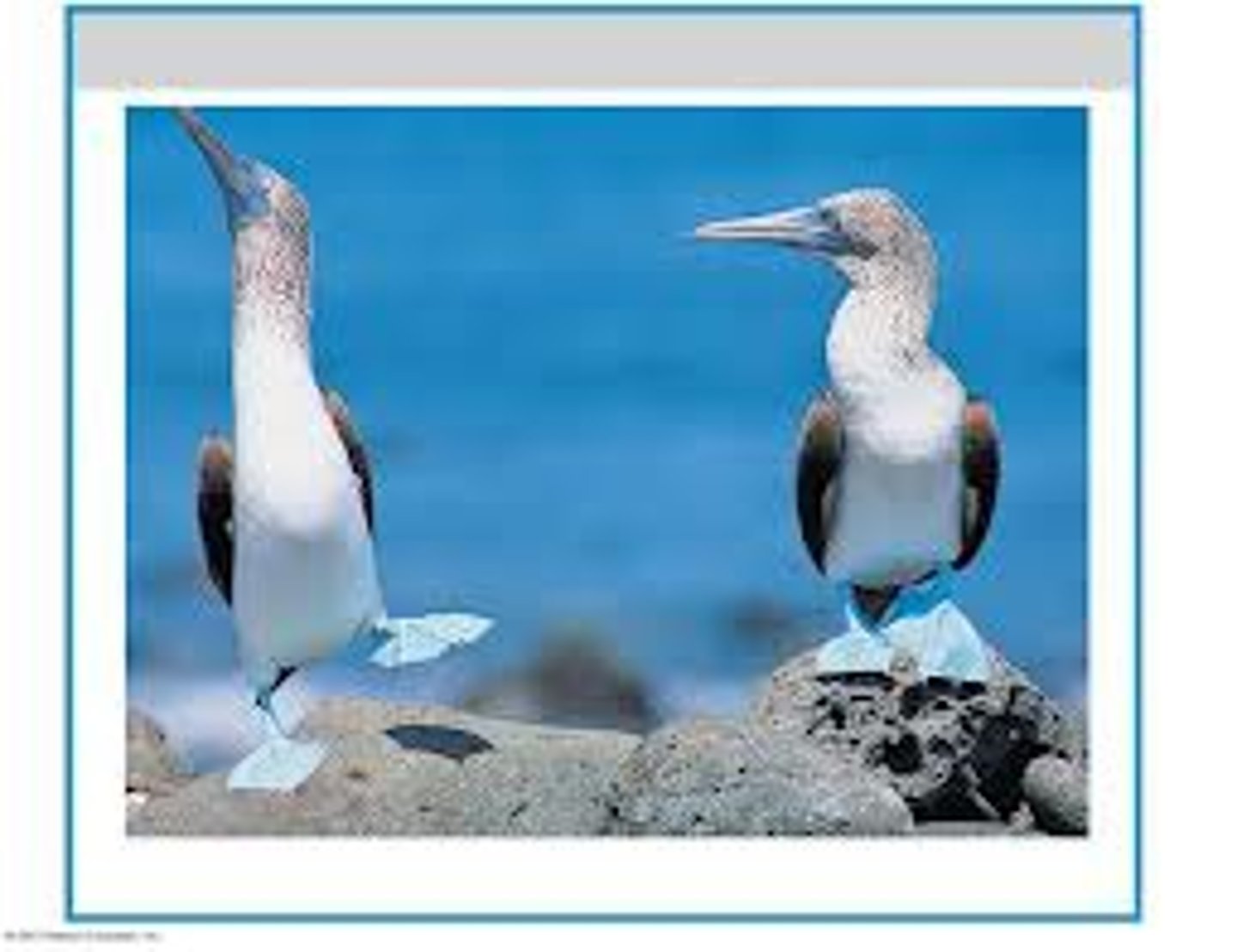
Behavioral Isolation
Form of reproductive isolation in which two populations have differences in courtship rituals or other types of behavior that prevent them from interbreeding
ex) if male boobie doesn't do the write song or dance, the female will not mate with the male

mechanical isolation
structure of the male and female copulatory organs may be incompatible
ex) bees carry pollen that have to release on the receptive structure on flower

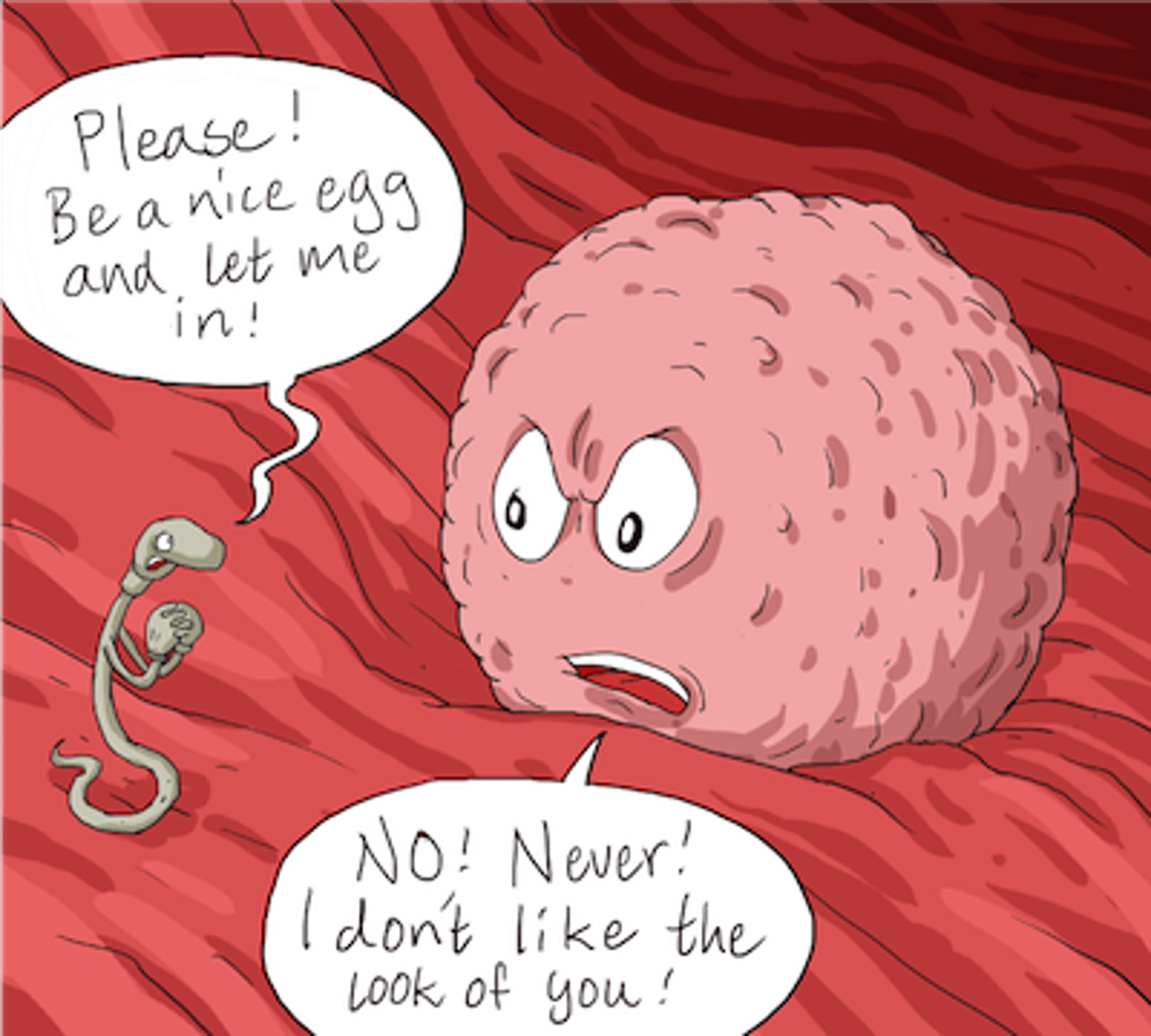
Gamete fusion
In animals that shed gametes directly into water; the eggs and sperm derived from different species may not attract or fuse with one another
postzygotic isolating mechanisms
operate after fertilization has occurred to ensure that the resulting hybrid remains infertile
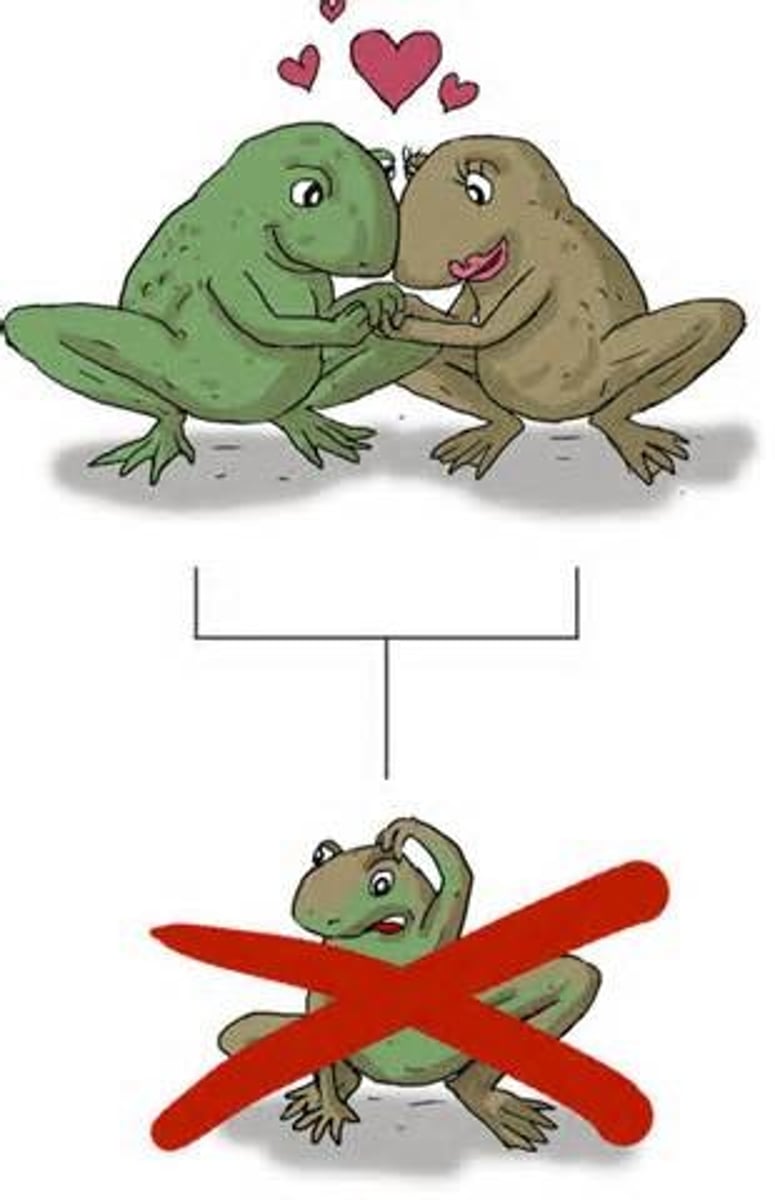
hybrid sterility
hybrids fail to produce functional gametes and have abnormal sex organs
ex) a mule is able to live a healthy life but will not be able to have offspring
Polyploidy
individuals that have more than two sets of chromosomes
Reinforcement
Initially incomplete isolating mechanisms are reinforced by natural selection until they are completely effective
- favor breading within a population
ex) if 2 species of frogs have different mating calls, and hybrids between them are less fit, natural selection will favor frogs that have even more distinct calls making it less likely for interbreeding.
character displacement
Natural selection in each species favors those individuals that use resources not used by the other species
- greater fitness
- species will diverge
ex) a bird eating a specific seed and doesn't have to compete for food because not every bird likes them.