IB Chemistry S2 EOT Review
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Be able to identify properties of transition metals based on melting point,
electrical conductivity, and ductility using high, good, poor and low indicators.
Properties of transition metals typically include high melting points, good electrical conductivity, and high ductility, showcasing their metallic nature.
Know that group 1 and 2 metals produce a basic oxide and a high pH.
Group 1 and 2 metals react with oxygen to form basic oxides that typically exhibit a high pH in solution.

How do you write a formula from a chemical name?
To write a formula from a chemical name, identify the elements present, determine their oxidation states based on the name, and combine them in proportion to balance the charges, using subscripts to indicate the number of atoms.

How do you identify the bonds that are most polar?
To identify the bonds that are most polar, compare the electronegativities of the bonded atoms; the greater the difference in their electronegativities, the more polar the bond will be.
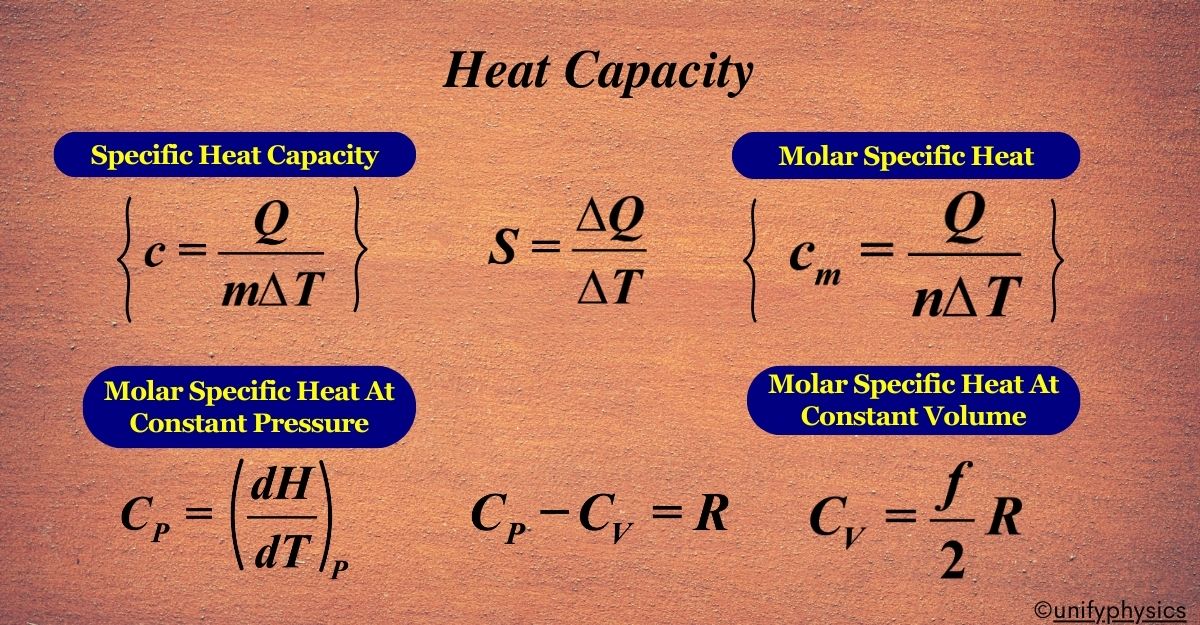
How do you calculate heat capacity?
To calculate heat capacity, use the formula C = q / (ΔT), where C is the heat capacity, q is the heat added, and ΔT is the change in temperature. ΔT Is calculated by T-finale - T-Initial. Also C is most of the time 14.8.

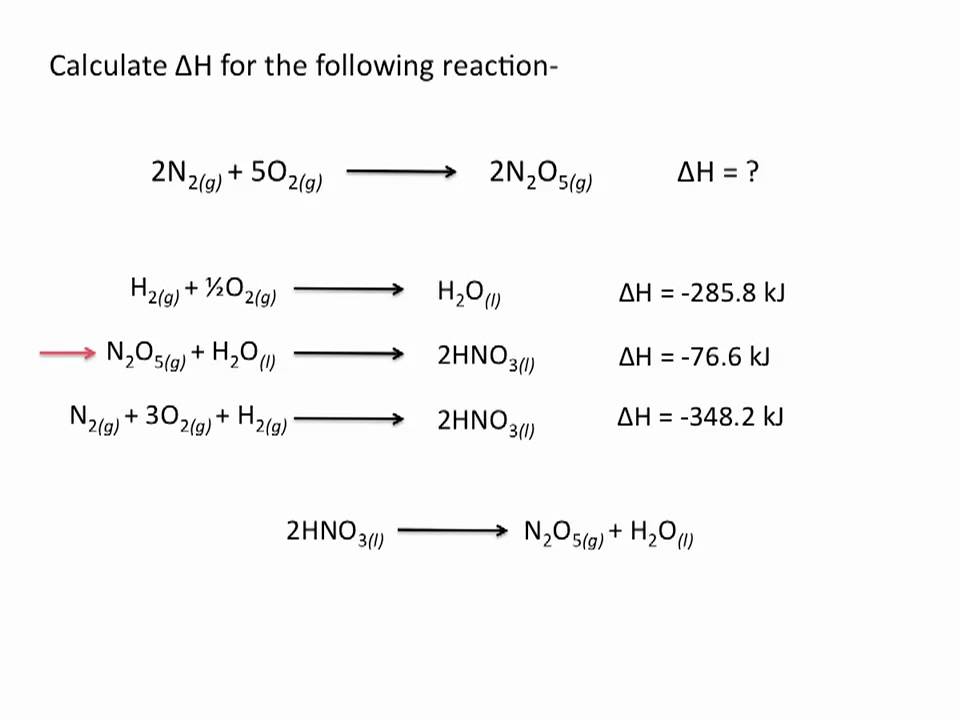
How do you calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction using Hess’ Law.
To calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction using Hess' Law, add the enthalpy changes of individual steps of a reaction pathway. This law states that the total enthalpy change is the same, regardless of the number of stages in the reaction.

Know the formula for calculating enthalpy change of a reaction.
The formula for calculating enthalpy change of a reaction is Delta H = sum Delta H{products} - sum Delta H{reactants}, where Delta H represents the change in enthalpy. Q=mc deltaT.
How would you identify what would decrease the rate of reaction in an experiment?
(hint: diluting the concentration of a reactant)
You can identify factors that decrease the rate of reaction by analyzing how changes to the concentration of reactants, temperature, surface area, or the presence of catalysts affect the reaction speed. For example, diluting the concentration of a reactant typically slows down the reaction rate.
What are the products of complete and incomplete combustion reactions?
The products of complete combustion are carbon dioxide and water, while incomplete combustion produces carbon monoxide and possibly soot, along with water.
How do you write ions in order of increasing ionic radii?
You can write ions in order of increasing ionic radii by comparing their sizes based on their charge and electron configurations. Cations are smaller than their parent atoms, while anions are larger; thus, a sequence can be established by examining the charge and number of electrons.
Explain why metals are malleable.
Metals are malleable because their atomic structure allows layers of atoms to slide over one another without breaking the metallic bond. This property results from the presence of delocalized electrons that can move freely, enabling the metal to deform without fracturing.
How do you identify when liquids are immiscible in one another? (Given a list of liquids)
To identify immiscible liquids, observe whether they form distinct layers rather than mixing completely. Immiscible liquids do not dissolve in each other and will separate based on differences in polarity or density.
Know that products have stronger covalent bonds are exothermic and reactants with stronger bonds are endothermic.
In a chemical reaction, stronger covalent bonds in the products indicate that energy is released, making the reaction exothermic, while stronger bonds in the reactants suggest that energy is absorbed, resulting in an endothermic reaction.
Know that there is a low rate of reaction between two gases at high temperature and high pressure because the bonds in the reactants are strong.
At high temperature and pressure, the strong bonds in gas reactants result in a low rate of reaction due to decreased molecular mobility and energy requirements for bond breaking.
Know electron configuration of d block elements. (remember to fill lowest energy levels first for stability)
The electron configuration of d block elements involves filling the d orbitals after the s orbitals of the preceding energy level. Remember to follow the Aufbau principle, filling lower energy levels first to ensure stability.

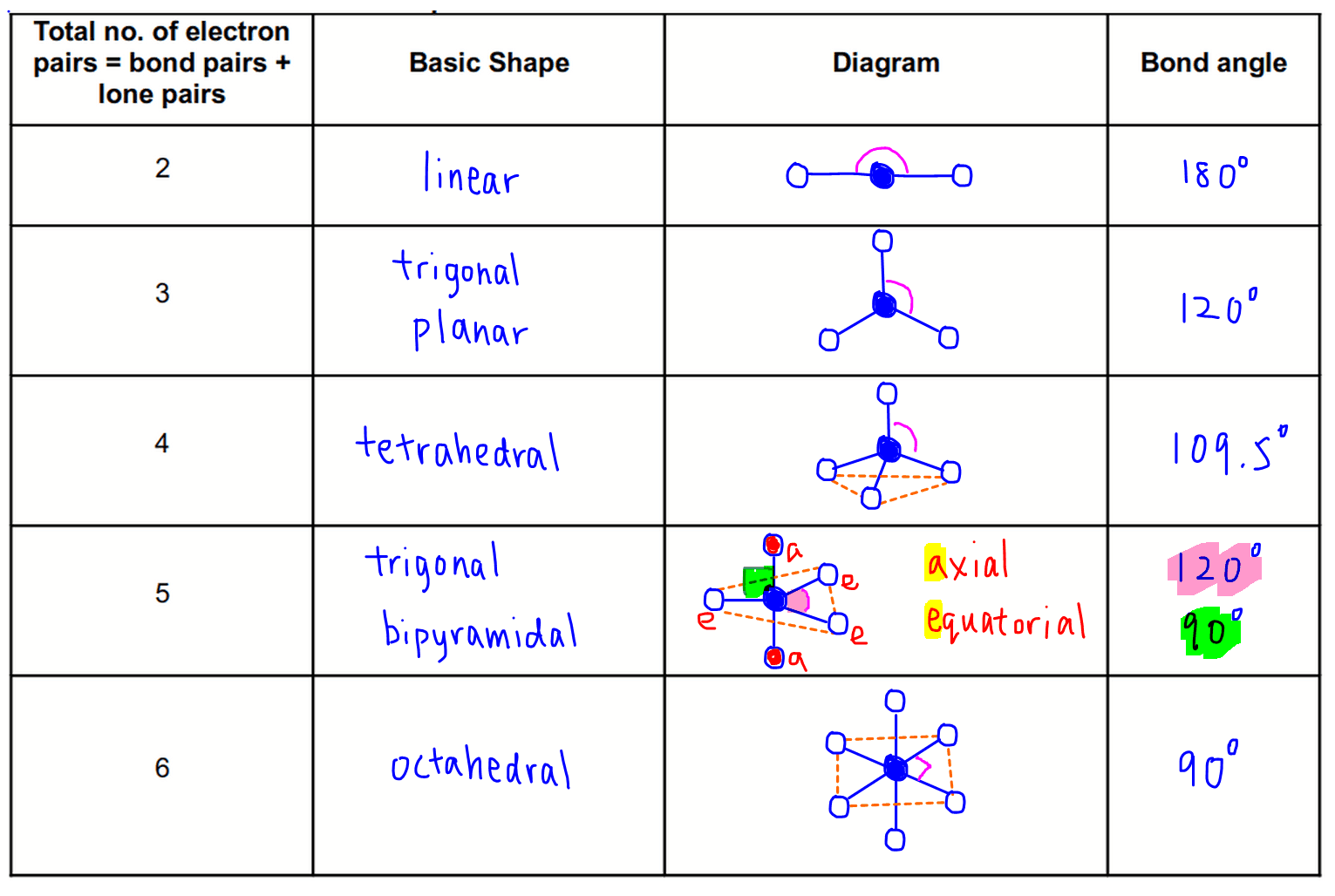
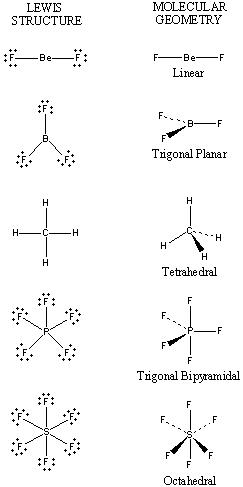
Know electron domain and molecular geometry of a given compound.
Electron domain geometry refers to the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom, while molecular geometry describes the shape formed by the atoms in a molecule. These geometries are determined by the number of bonding and non-bonding electron pairs, as described by the VSEPR theory. It’s the degrees between the bonds.
Identify which reactions release heat.
Reactions that release heat are known as exothermic reactions. In these reactions, the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants, resulting in the release of energy, typically in the form of heat.
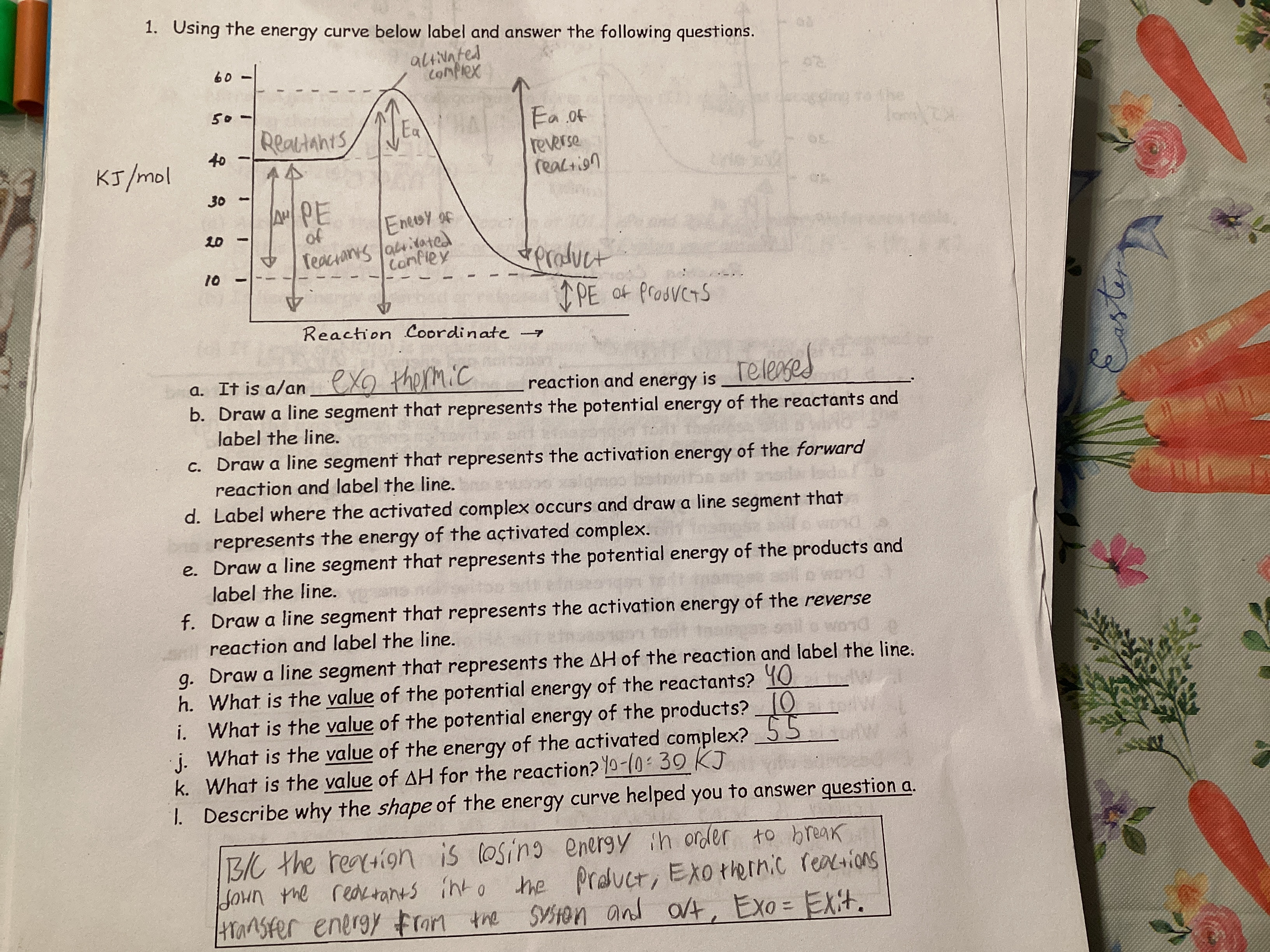
Interpret data from an enthalpy diagram. (i.e. be able to calculate delta H)
Enthalpy diagrams visually represent the energy changes during a chemical reaction. To interpret them, identify the reactants and products, and calculate the change in enthalpy (delta H) by assessing the difference in energy levels between the products and reactants.
Identify the roles a catalyst plays in increasing the rate of reaction.
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. It achieves this by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed, allowing the reaction to occur more easily and quickly.
Identify the compound from a list that would produce equal moles water and carbon dioxide.
To identify the compound from a list that produces equal moles of water and carbon dioxide upon combustion, you need to analyze the carbon and hydrogen ratios in the compound's chemical formula. The compound with an equal number of carbon and hydrogen atoms (a ratio of 1:1) will produce equal moles of carbon dioxide and water.
Identify a polar molecule.
A polar molecule is identified by an unequal distribution of electrons, resulting in a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other. This unequal distribution creates a net dipole moment in the molecule. To determine if a molecule is polar, consider electronegativity differences between atoms and the molecule's geometry
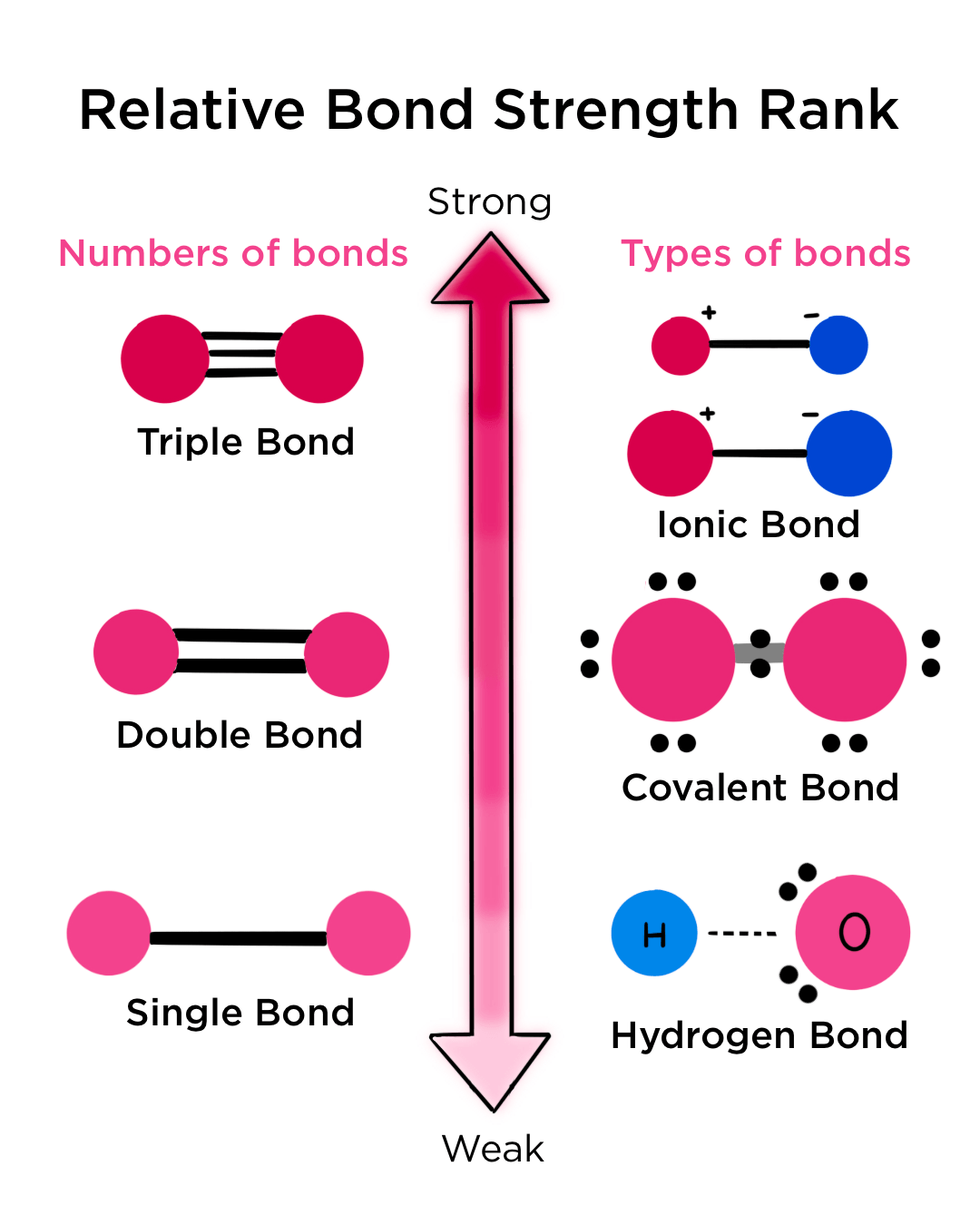
Place bonds in order of increasing bond strength.
Identify the changes that would increase the rate of an exothermic reaction.
To increase the rate of an exothermic reaction, you can increase the concentration of reactants, increase the temperature, increase the surface area of solid reactants, or add a catalyst.
Be able to calculate the relative atomic mass of an element.
Some dumb formula you can just look at the periodic table
Be able to identify elements as metal, non-metal and metalloids
Look at formula sheet
Know whether the following increase or decrease down a group or across a period (atomic radius, electronegativity, ionic radius, ionization energy)
Look at formula sheet
Be able to interpret a potential energy diagram
Ea is potential energy
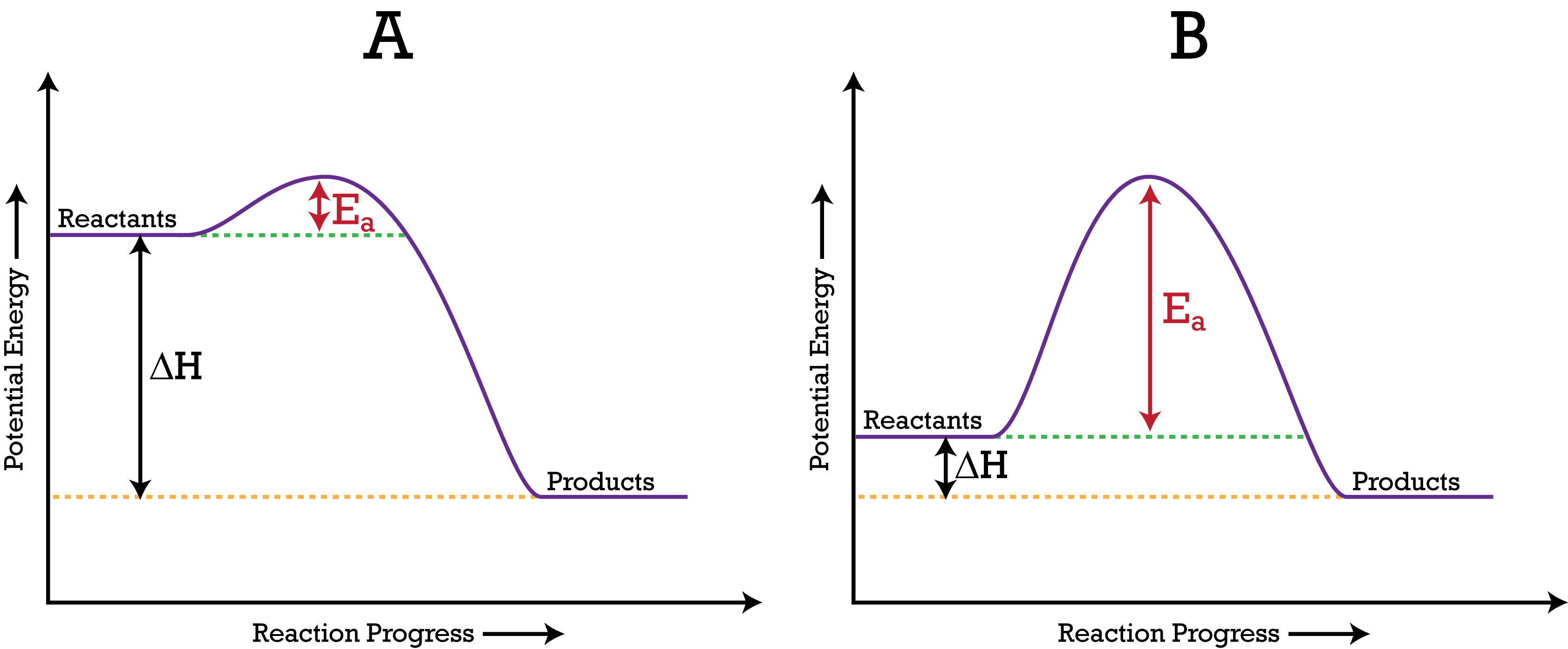
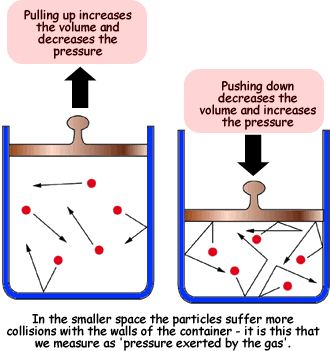
Know why a reaction with gases at a constant temperature occurs faster at a higher pressure.
At a constant temperature, increasing the pressure of a gas-phase reaction speeds it up because higher pressure means more gas molecules are present in a given volume, leading to more frequent collisions and a higher rate of successful reactions.
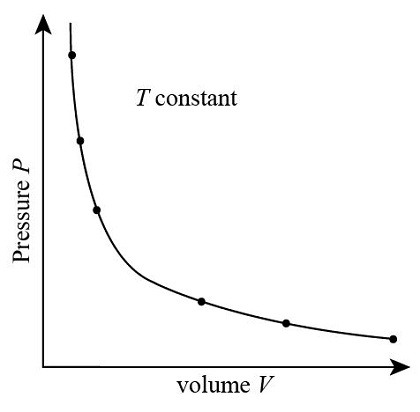
Identify the graph that shows the relationship between pressure and volume of gas at a constant temperature.
Should have a hyperbolas.
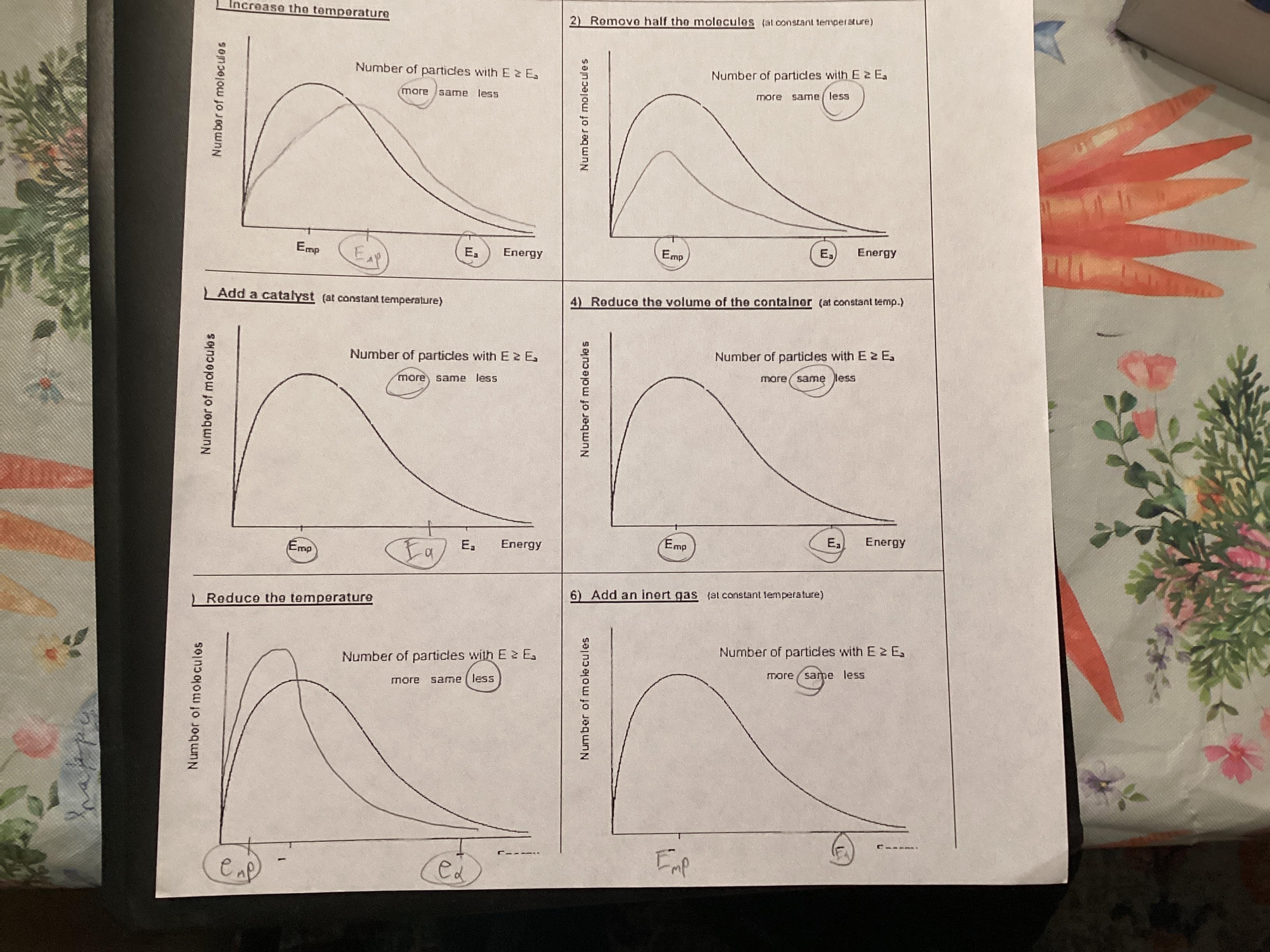
Interpret a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve.
A Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve describes the probability of finding a molecule with a specific speed or energy in a gas at a given temperature. The curve visually represents how the speeds of gas molecules are distributed, showing that not all molecules have the same speed, but rather they are distributed across a range.
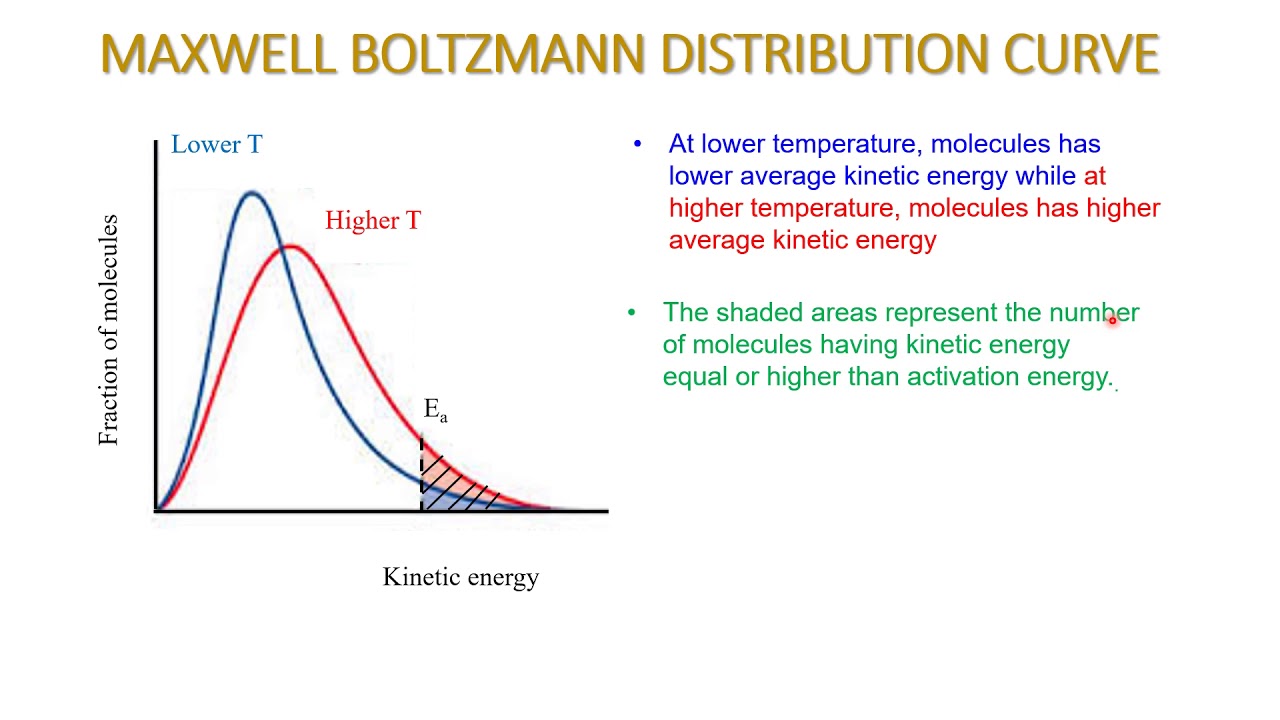
Know that particles energy greater than the activation energy and greater frequency of collisions increases the rate of reaction as temperature increases.
Know what happens to a catalyst in a chemical reaction.
Stays unchanged.
Be able to identify what changes can be made to reactants to increase the initial rate of reaction (i.e. double concentration, use smaller pieces, etc)
To increase the initial rate of a reaction, you can manipulate factors like reactant concentration, physical state (surface area), temperature, and the presence of a catalyst. Increasing the concentration of reactants generally increases the rate of reaction by providing more molecules for collisions. Additionally, increasing the surface area of solid reactants by using smaller pieces or powders allows for more contact points between reactants, leading to more frequent collisions and a faster reaction. Higher temperatures also increase the reaction rate by giving molecules more kinetic energy and increasing the frequency of collisions. Finally, catalysts can provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, speeding up the reaction without being consumed themselves.
Identify properties of strong metallic bonds in terms of charge on the metal ion and radius of ion.
Strong metallic bonds are characterized by a high positive charge on the metal ions (the larger the amount of protons the higher the charge) and a smaller ionic radius. Higher charge leads to a greater attraction between the positively charged ions and the delocalized electrons, while a smaller radius means the ions are closer together, also strengthening the bond. In essence, a metal with a strong metallic bond will have a high melting and boiling point due to the strong attractions between the ions and delocalized electrons.
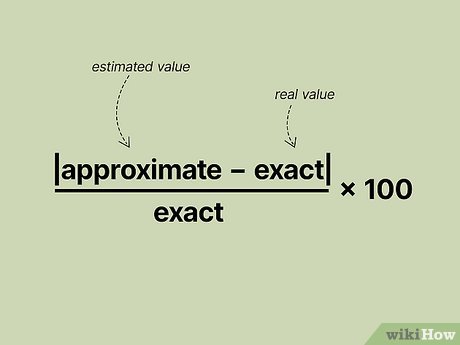
Be able to identify measurements as accurate and precise
% Error = ((Measured Value - Actual Value) / Actual Value) * 100
Be able to calculate density
mass/volume
Be able to identify systemic and random errors.
To differentiate between systematic and random errors, you can use several methods, including analyzing data distributions, comparing measurements against known standards, and examining the source of the error.