A&P - 9.4 Synovial Joints (anatomy and accessory structures)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
synovial joint - general characteristics
articulating bones are separated by a fluid-filled cavity
joints of limbs
all are diarthrotic
most common type of joint in the body
presence of a joint cavity
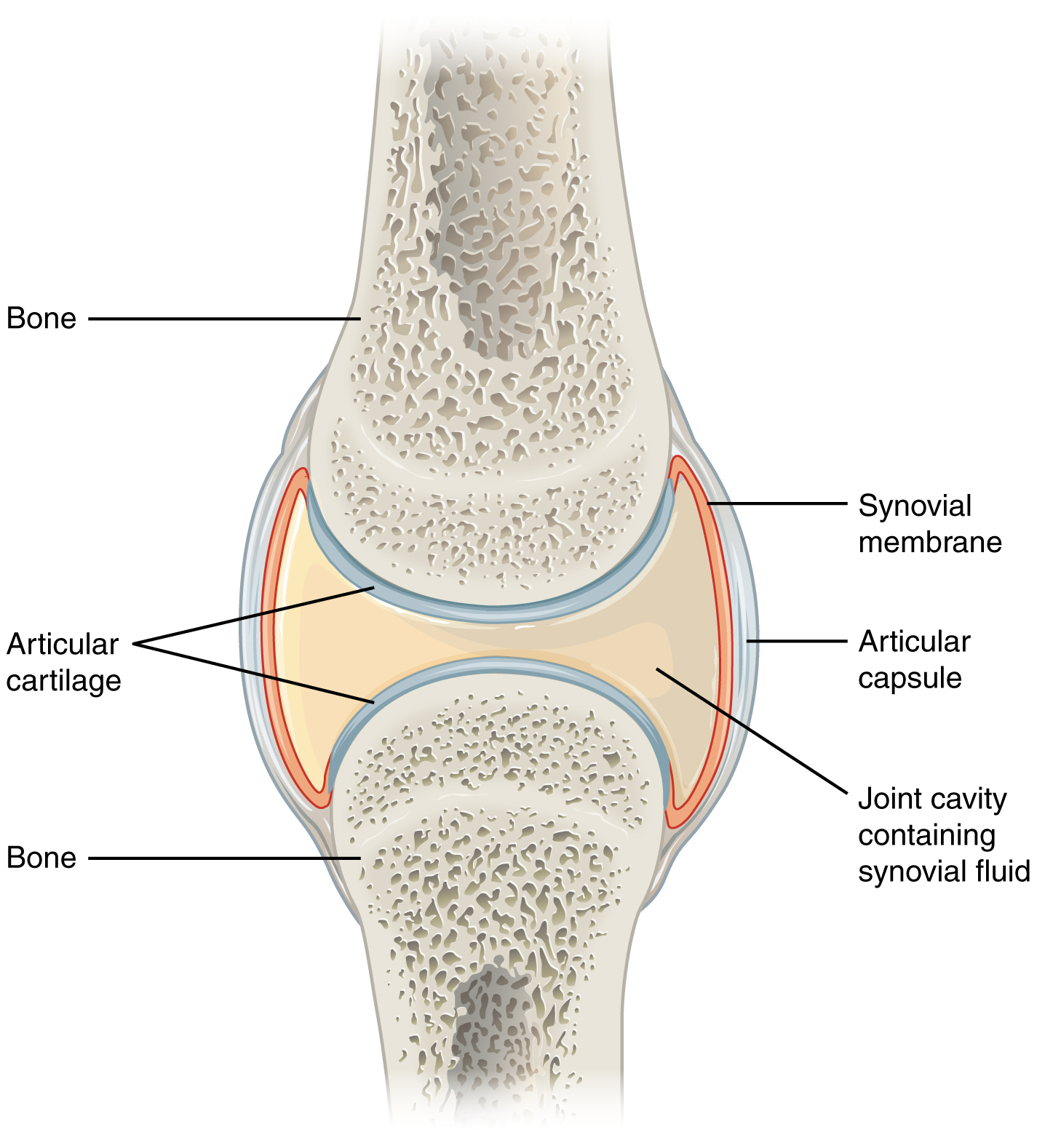
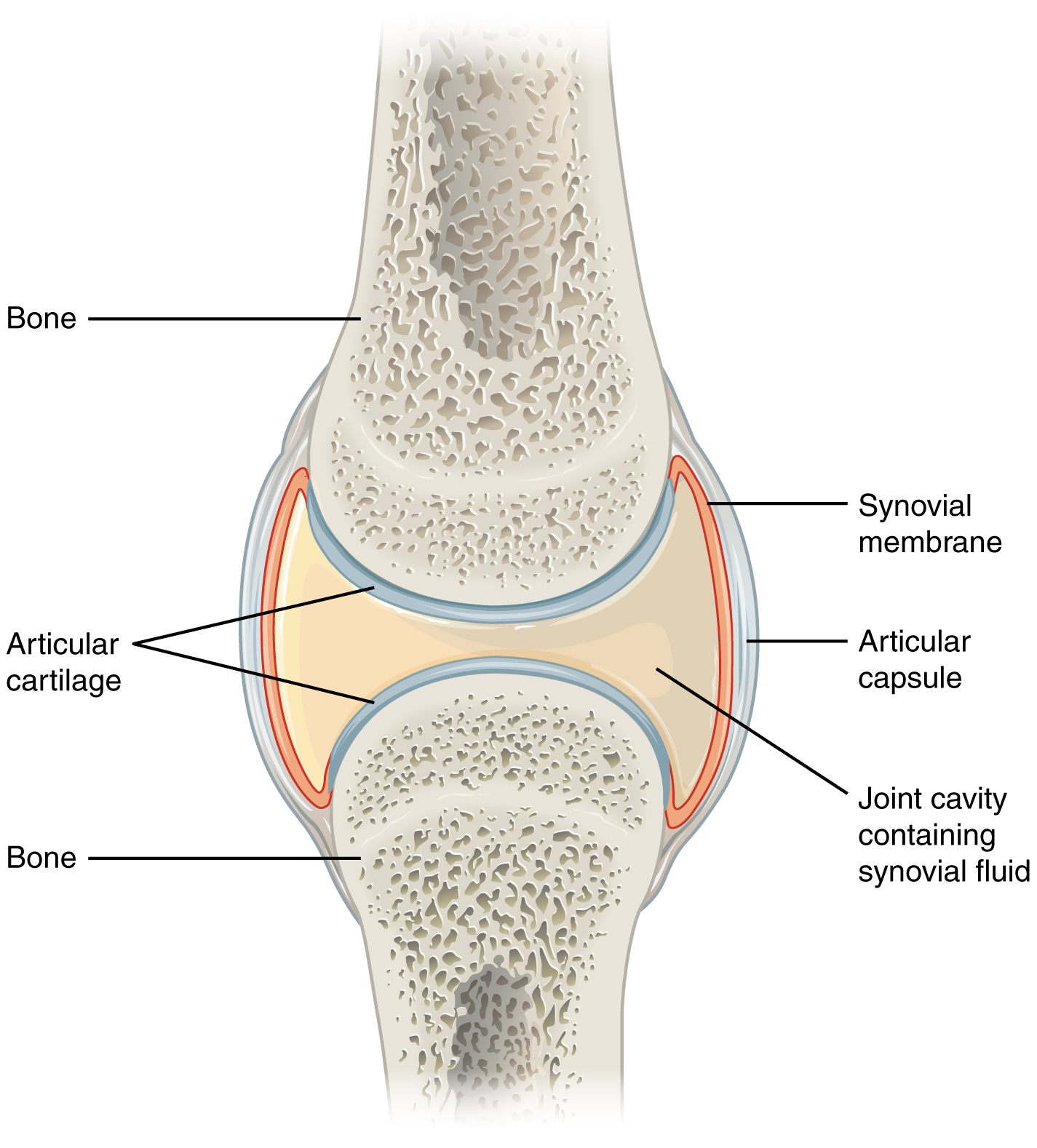
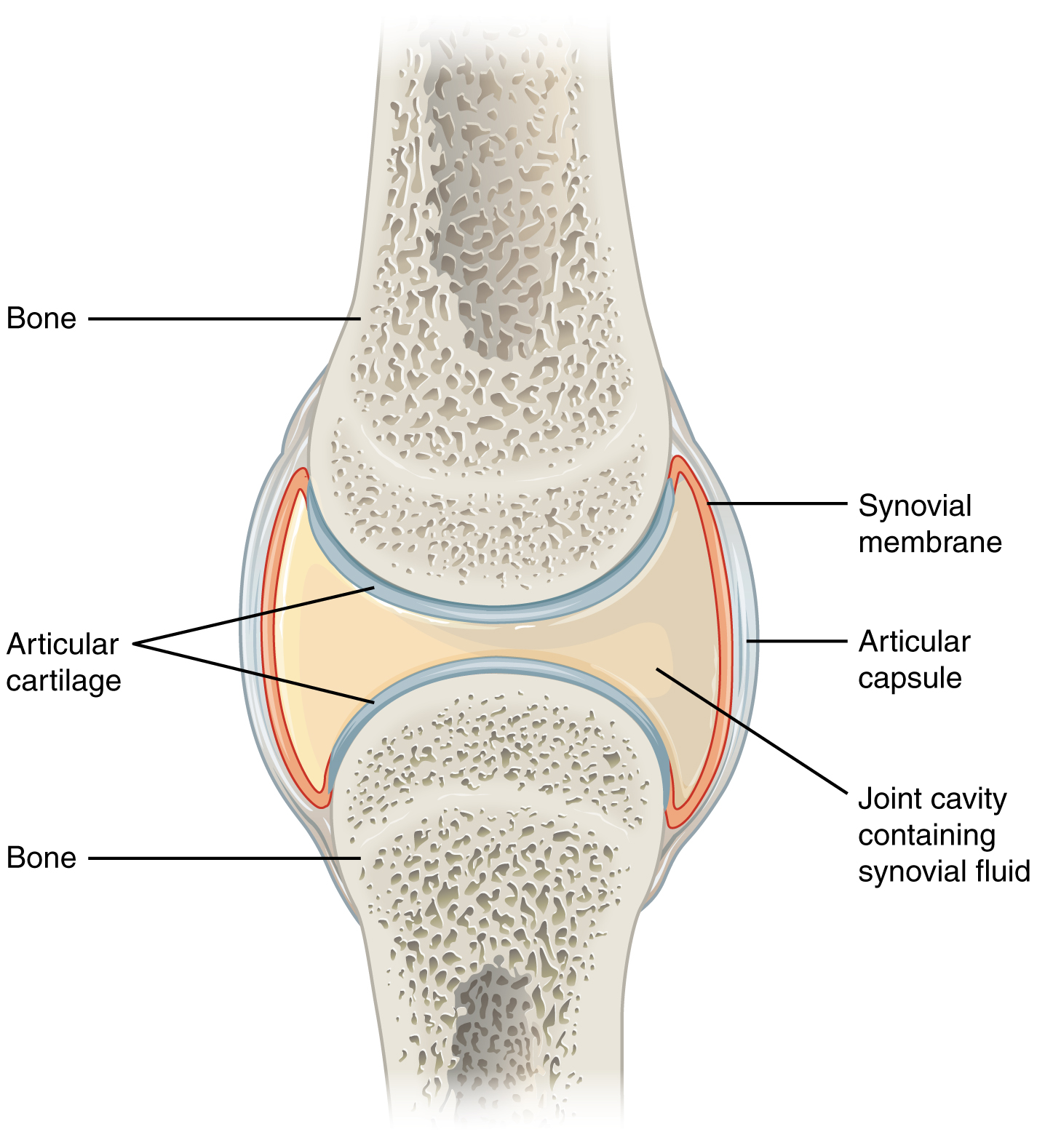
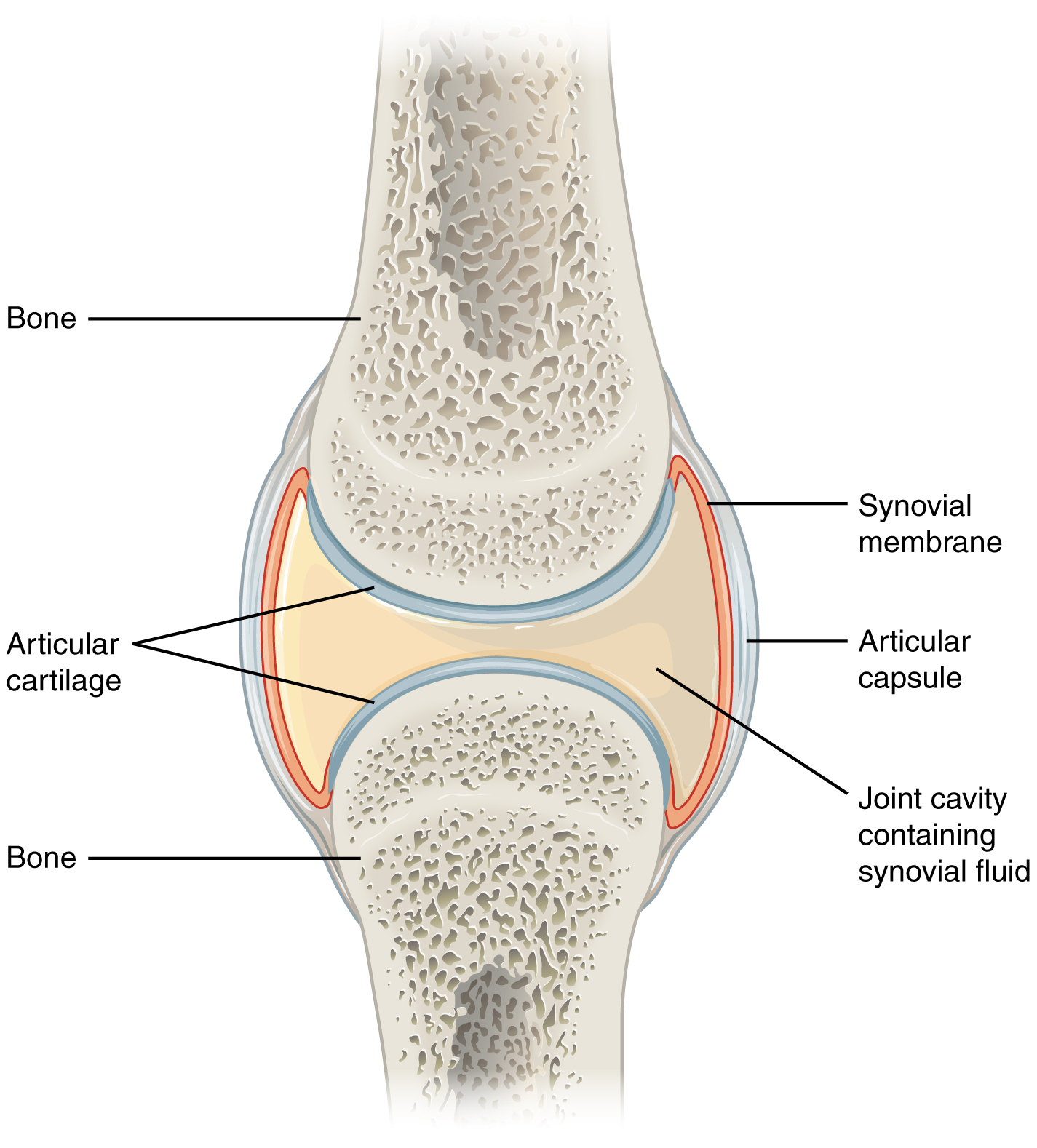
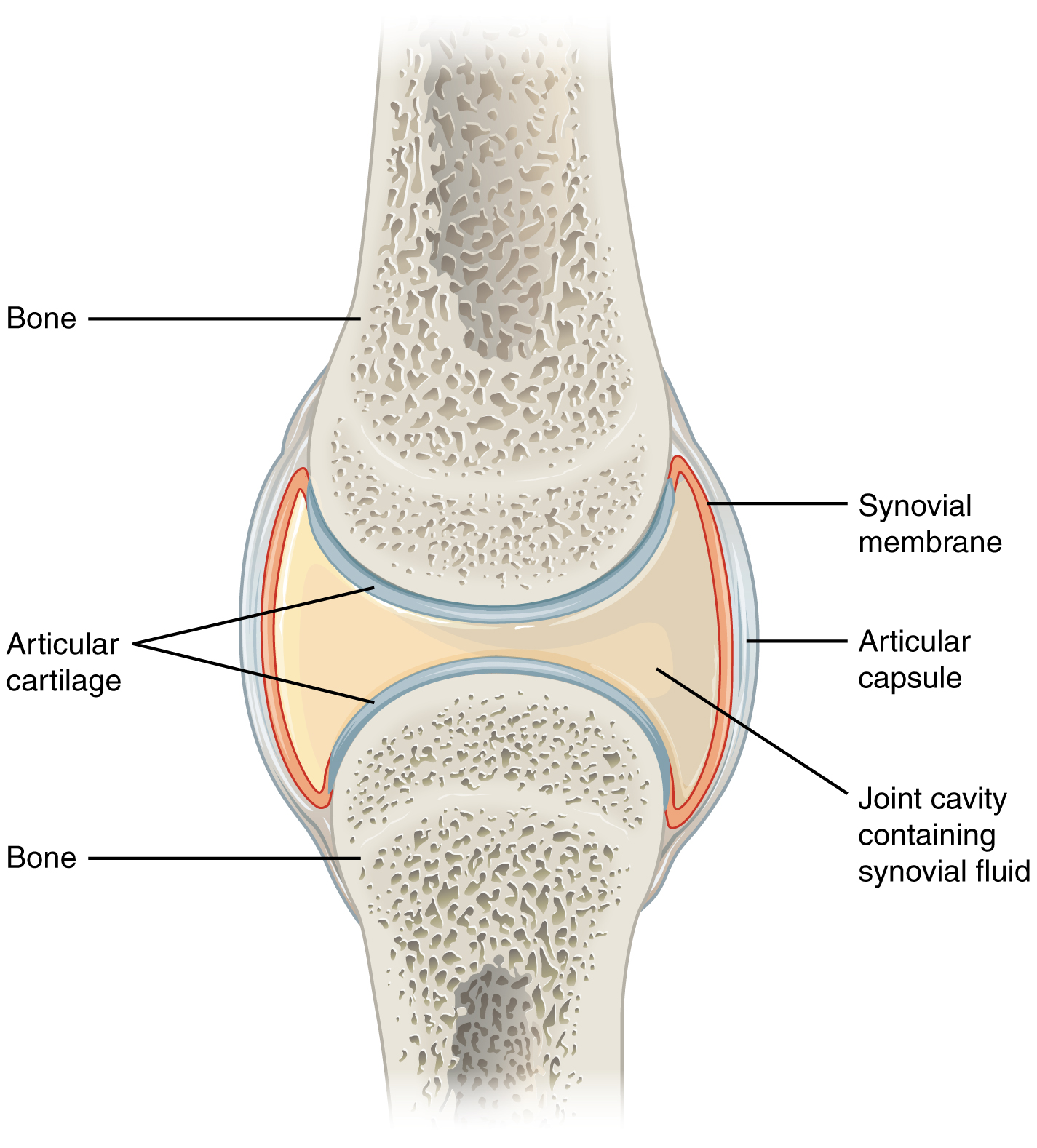
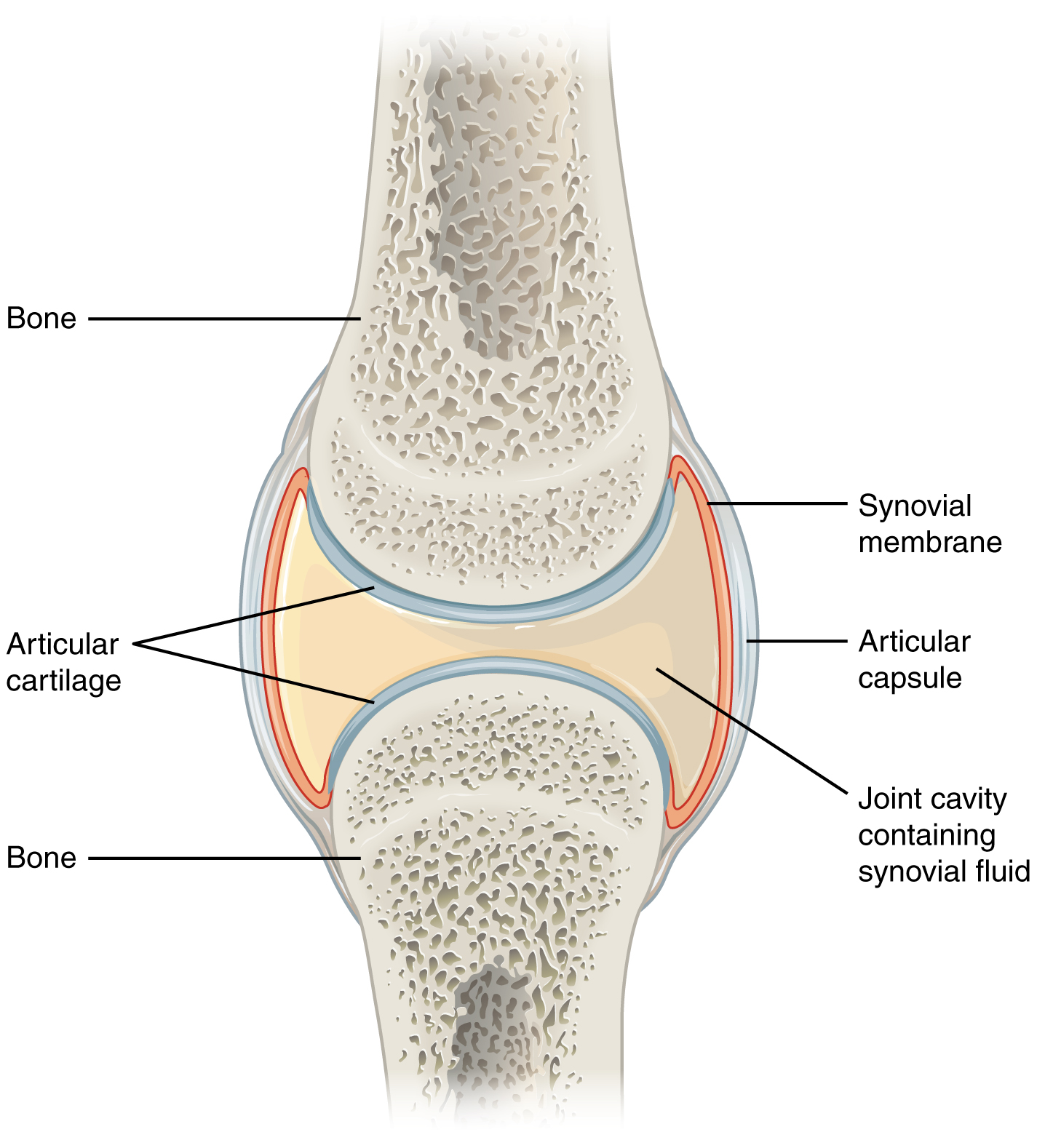
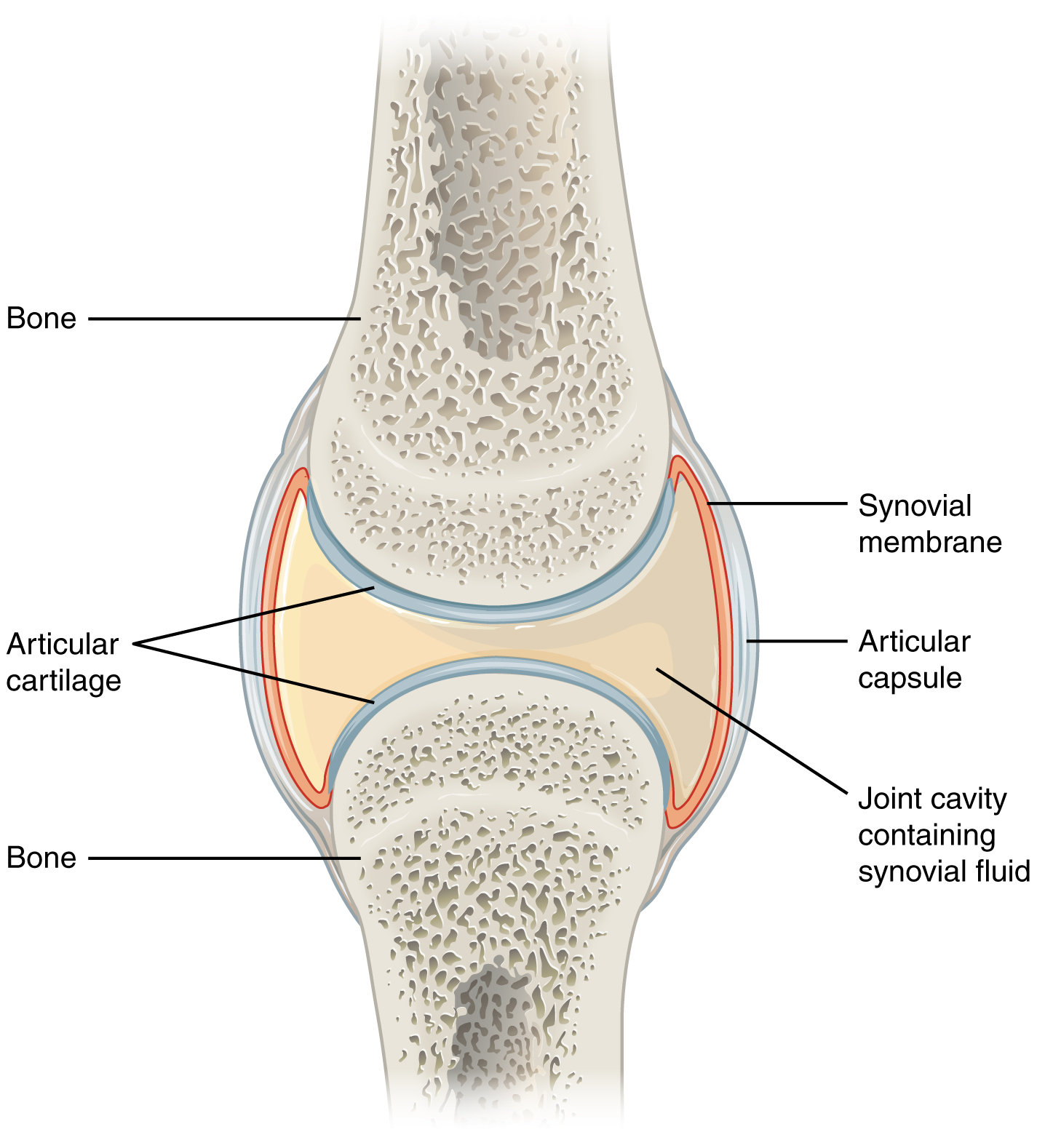
anatomy of a synovial joint
joint cavity
joint capsule
articular capsule
synovial membrane
synovial fluid
articular cartilage
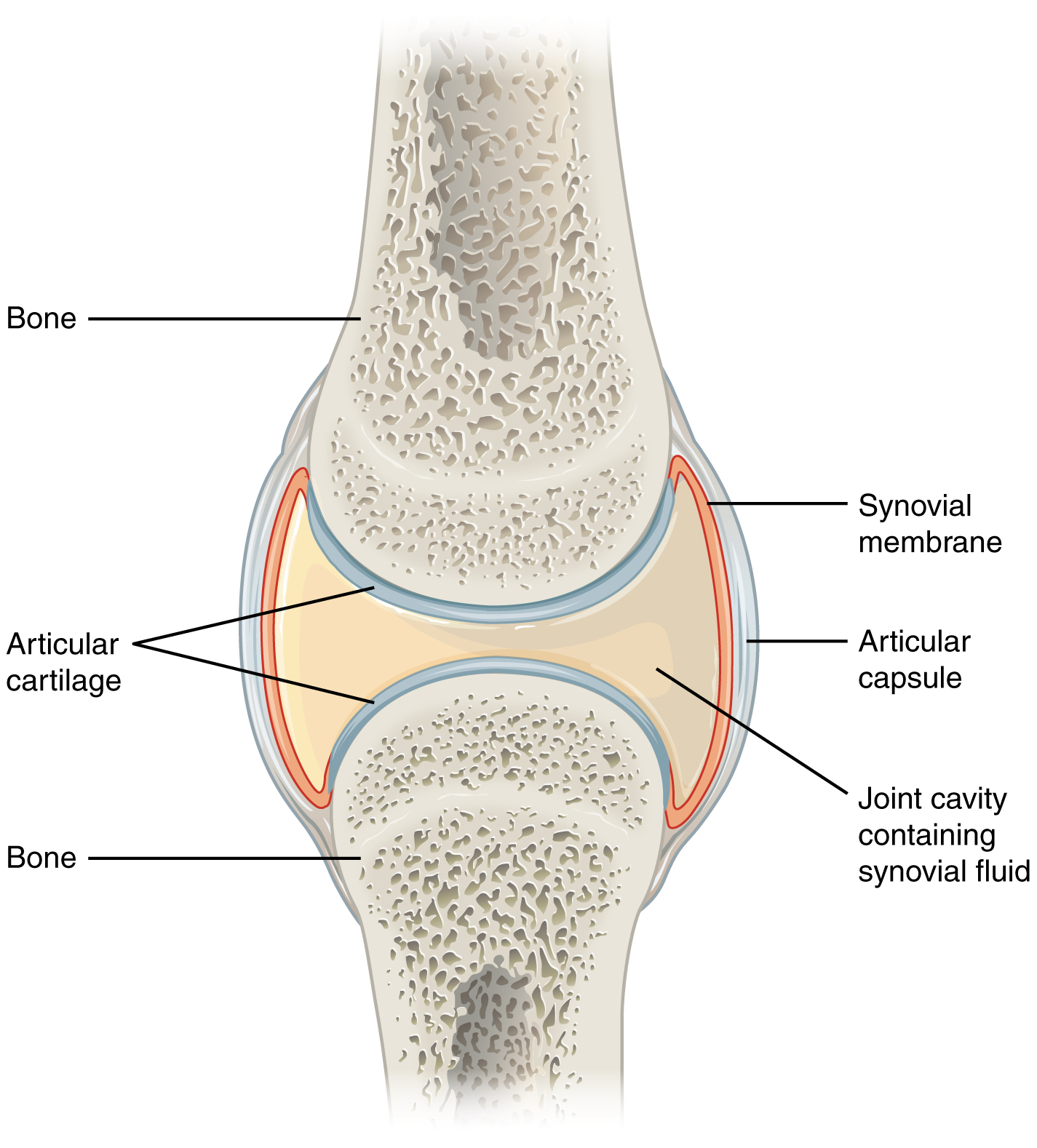
joint cavity
space enclosed by the articular capsule of a synovial joint that is filled with synovial fluid and contains the articulating surfaces of the adjacent bones
the fluid-filled space within the joint capsule
joint capsule
layers of connective tissues that enclose the synovial cavity
fibrous connective tissue structure that surrounds and encloses a joint
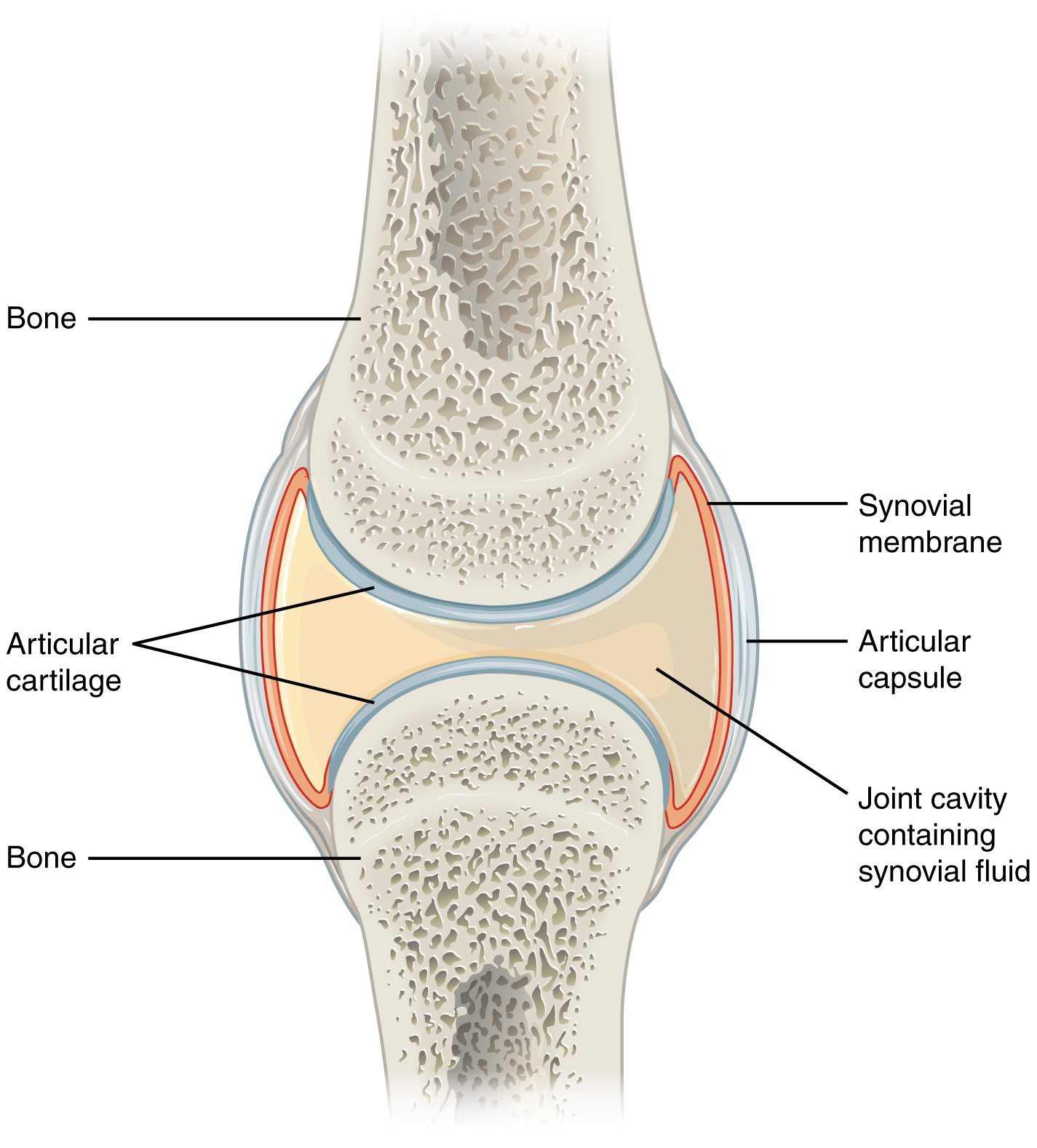
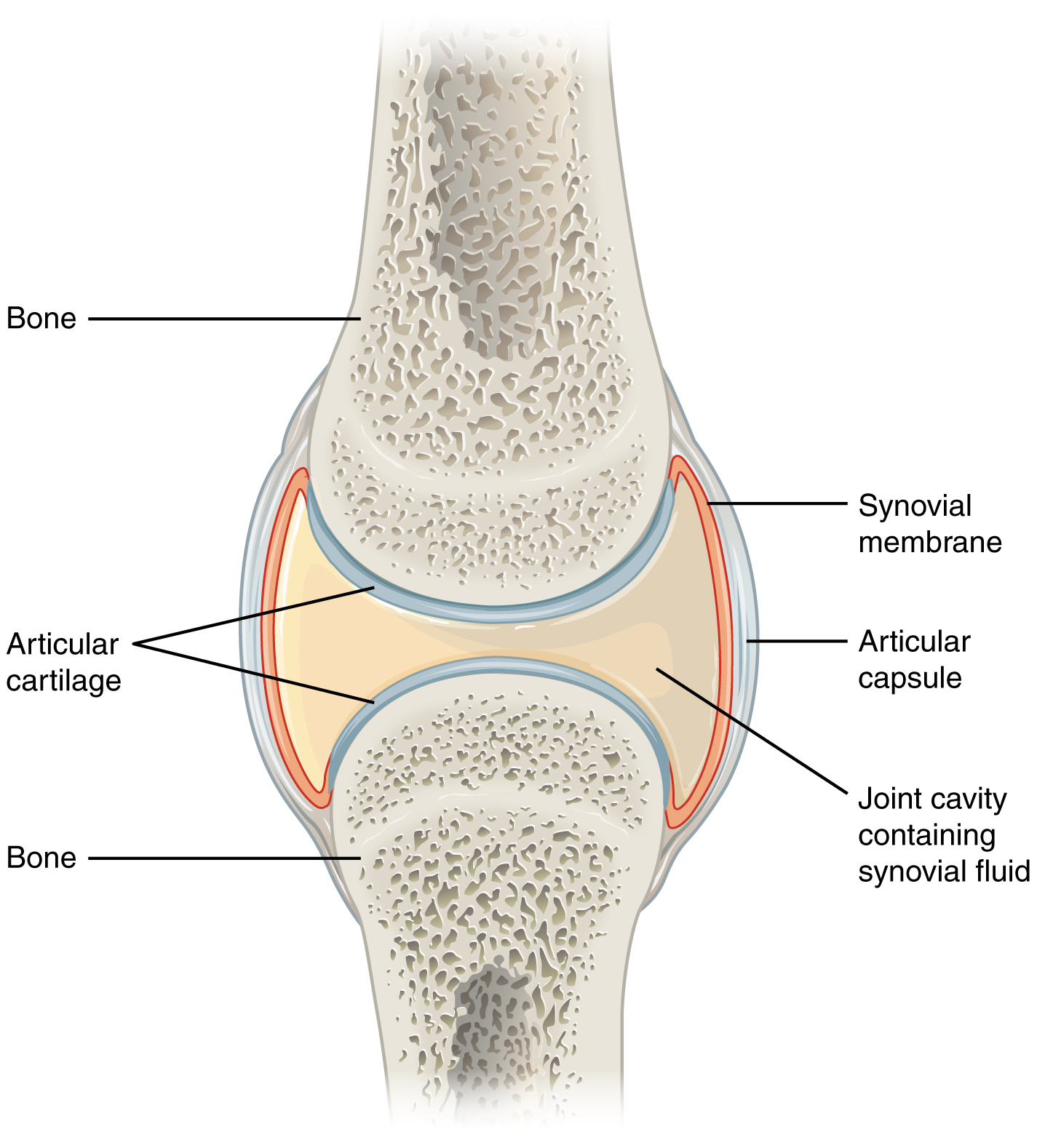
layers of the joint capsule
articular capsule
synovial membrane
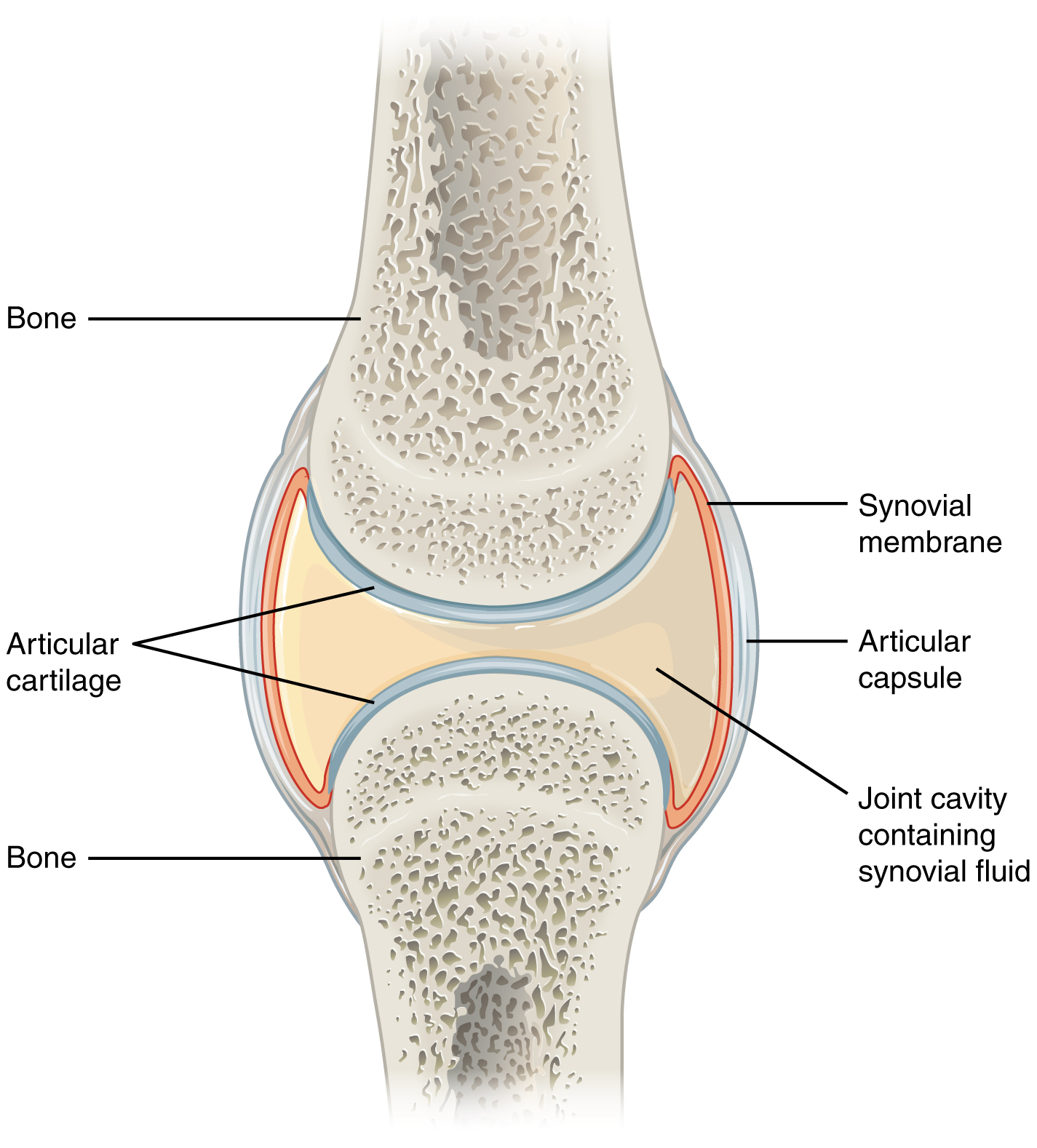
articular capsule
connective tissue structure that encloses the joint cavity of a synovial joint
thick outer layer continuous with the periosteum around the articulating bones
adds strength and helps to stabilize the joint
synovial membrane
thin layer that lines the inner surface of the joint cavity at a synovial joint
inner soft tissue whose network of capillaries leak plasma from the bloodstream to produce the synovial fluid
synovial fluid
thick, lubricating fluid that fills the interior of a synovial joint
functions of synovial fluid
lubrication
nutrient distribution
shock absorption
function of synovial fluid - lubrication:
when part of an articular cartilage is compresses during movement, some of the synovial fluid is squeezed out of the cartilage and into the space between the opposing surfaces
in turn, this thin layer of fluid markedly reduces friction between moving surfaces (weeping lubrication)
function of synovial fluid - nutrient distribution:
synovial fluid in joint must circulate continuously to provide nutrients and waste disposal for the chondrocytes of the articular cartilage
circulates whenever the joint moves, and the repeated compression and expansion of the articular cartilage pumps synovial fluid into and out of the cartilage matrix
function of synovial fluid - shock absorption:
when a joint is subjected to compression, the synovial fluid provides a cushion against the shock
example:
when you jog your knees are severely compressed and the synovial fluid distributes that force evenly across the articular surfaces and outward to the joint capsule
articular cartilage
thin layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the articulating surfaces of bones at a synovial joint
provides a slick, smooth surface to the bones which reduces friction during movement
exercise and articular cartilage
exercise warms synovial fluid
becomes less viscous, more easily absorbed by cartilage
cartilage then swells and provides a more effective cushion
warm-up period before vigorous exercise helps protect cartilage from undue wear and tear
this is why you warm up before exercising and cool down after exercising
repetitive compression of nonvascular cartilage during exercise squeezes fluid and metabolic waster out of the cartilage
when weight removed, cartilage absorbs synovial fluid like a sponge taking in oxygen and nutrients to the chondrocytes
without exercise, cartilage deteriorates more rapidly from inadequate nutrition and waste removal!!
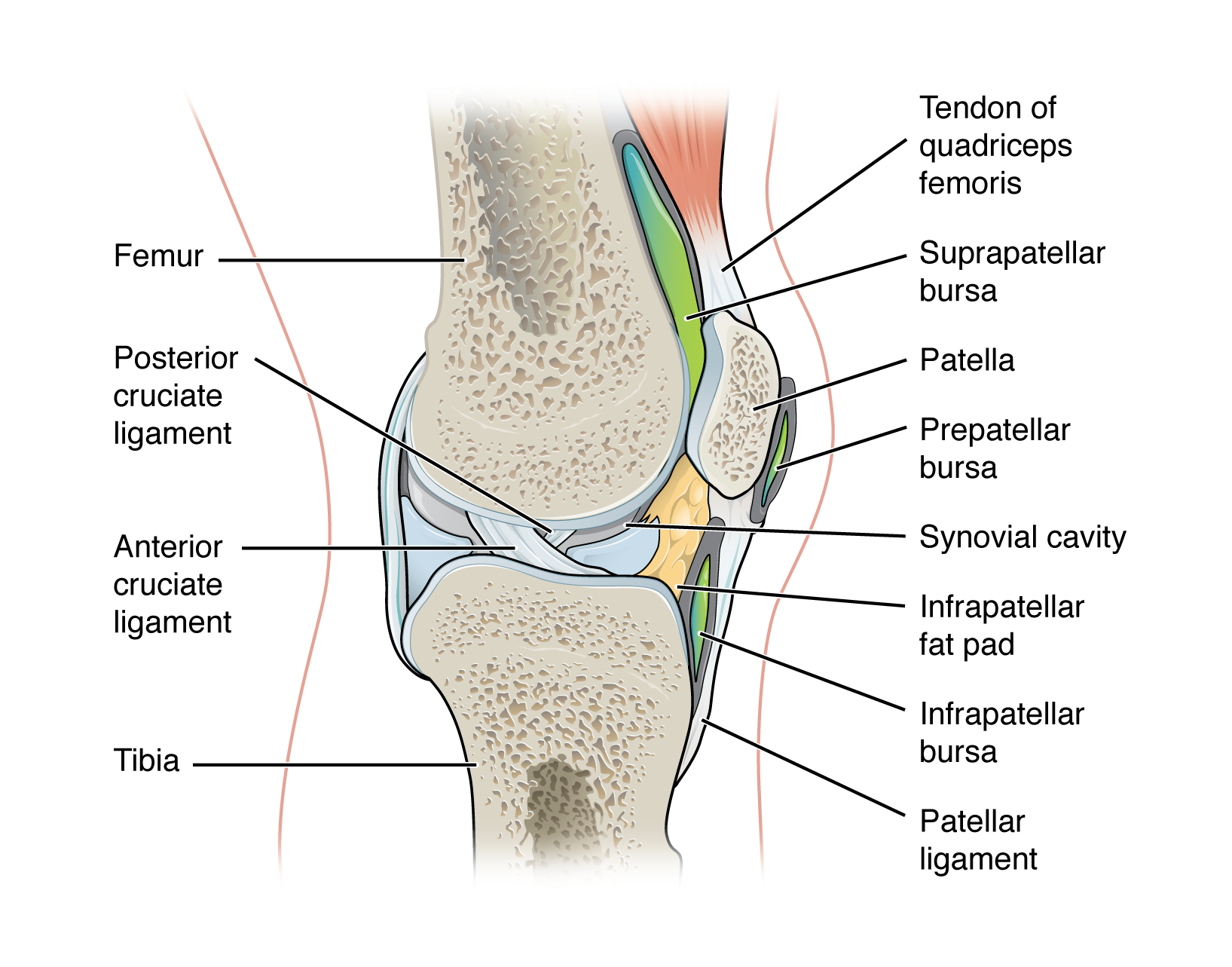
accessory structures of synovial joint
in complex synovial joints, such as the knee, a variety of additional accessory structures provide support and stability
list of accessory structures of a synovial joint
ligaments:
extrinsic
intrinsic
intracapsular
tendon
tendon sheath
articular disc (meniscus)
fat pad
bursa
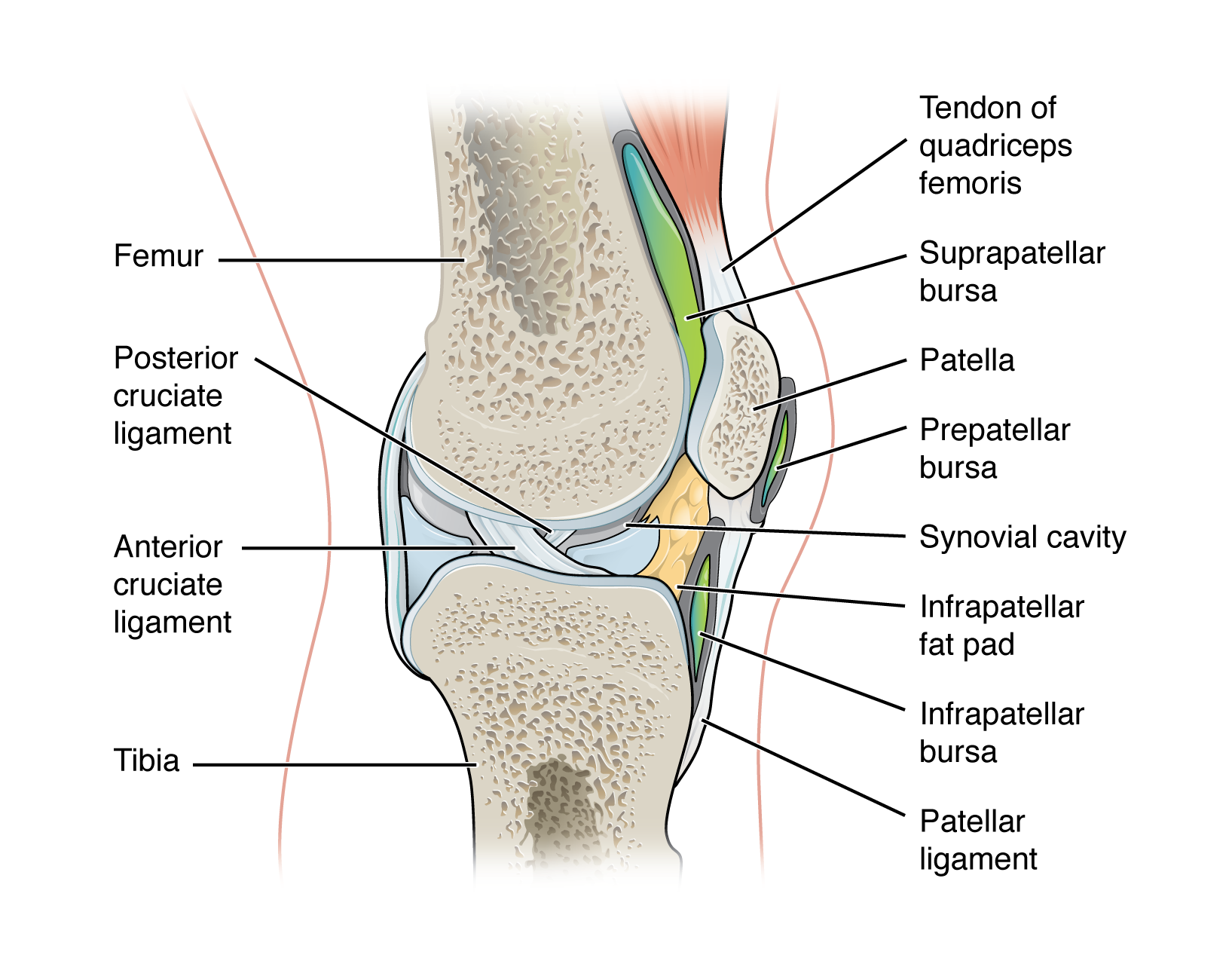
accessory structure of a synovial joint - ligaments:
strong band of dense connective tissue spanning between bones
support, strengthen, and reinforce synovial joints
allow for normal movement of a joint, but limit the range of these motions, thus preventing excessive or abnormal joint movement
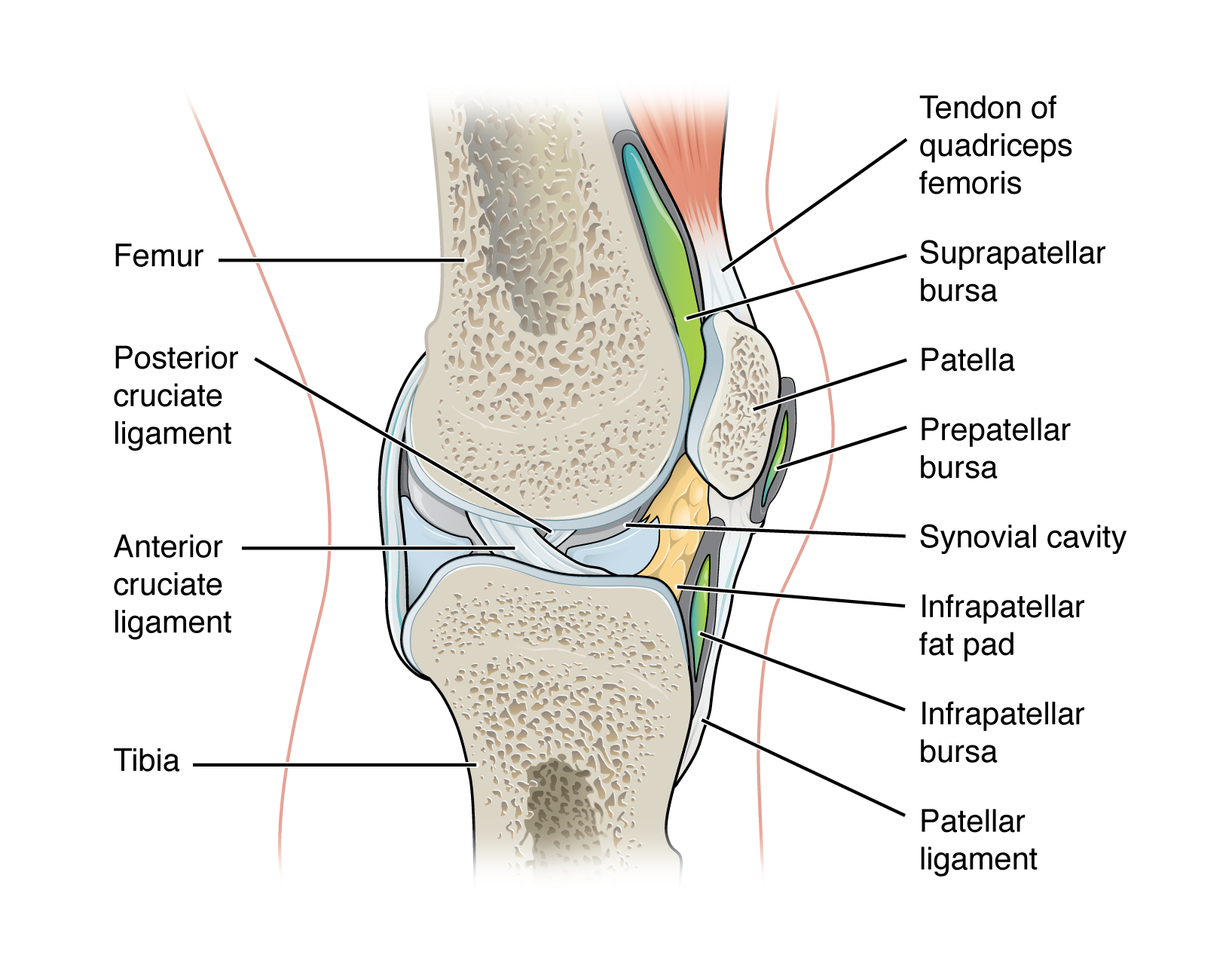
types of ligaments in a synovial joint
classified based on their relationship to the fibrous articular cartilage
extrinsic ligament
extracapsular ligament
intrinsic ligament
intracapsular ligament
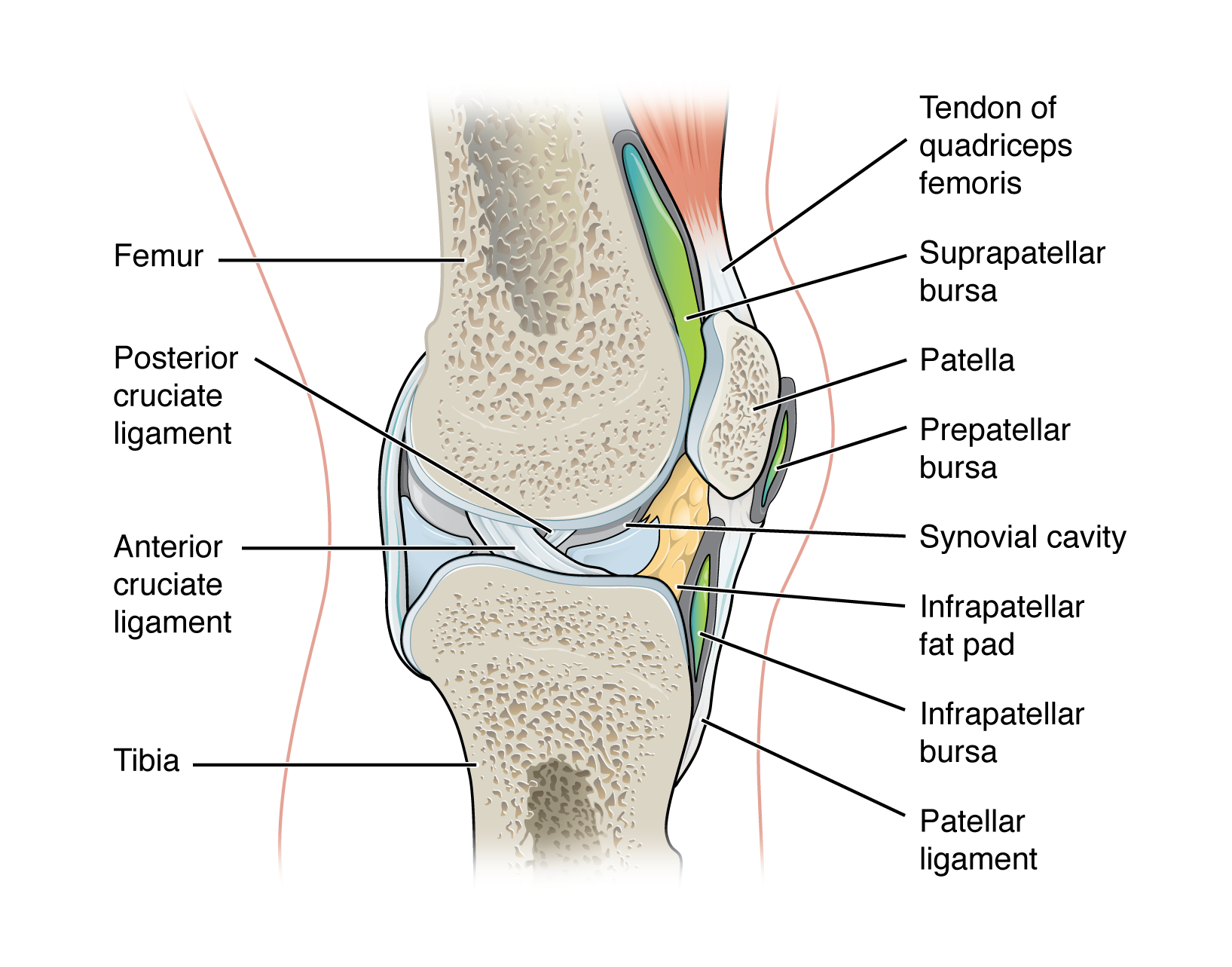
extrinsic ligament
ligament located outside of the articular capsule of a synovial joint
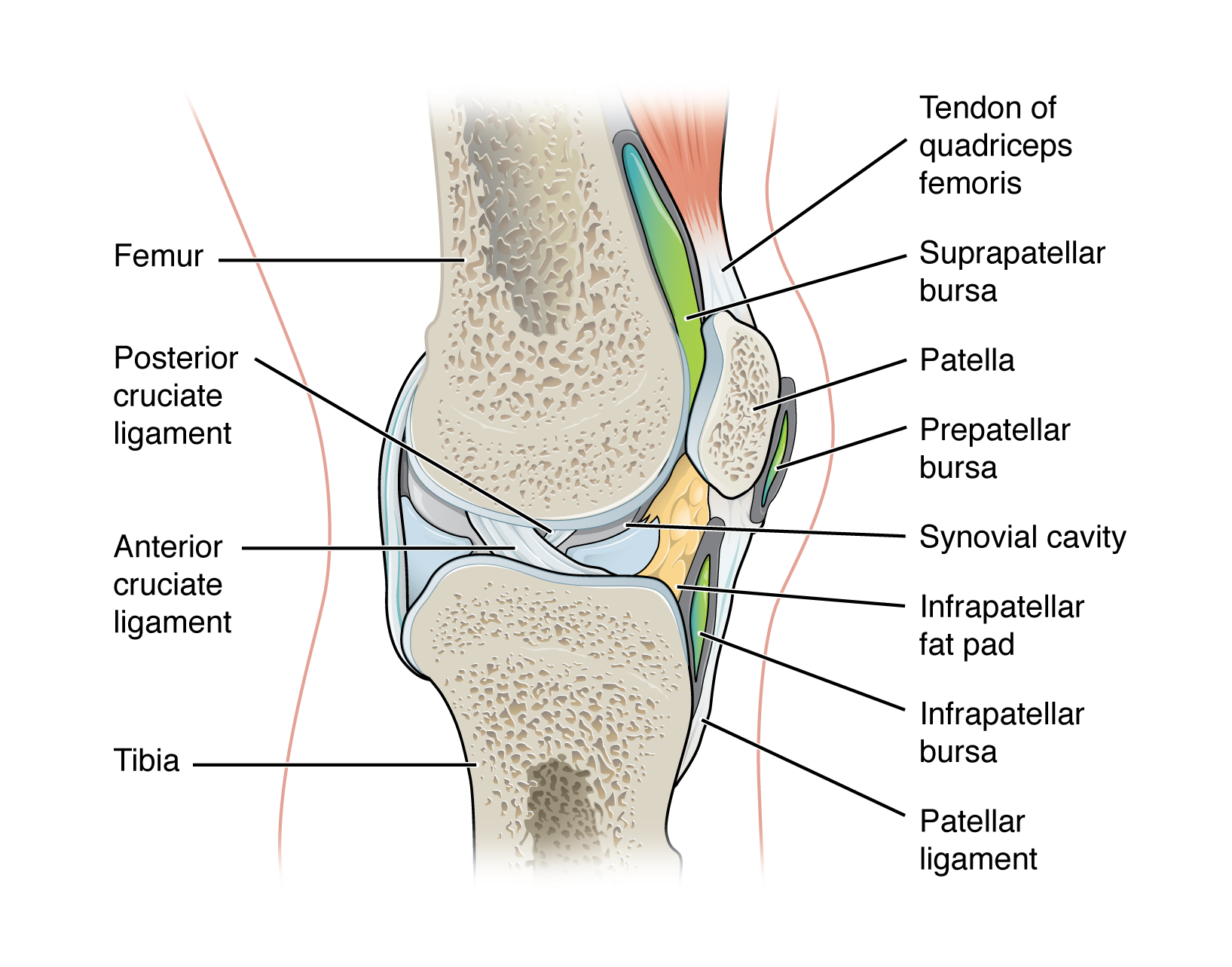
extracapsular ligament
outside the joint capsule
patellar ligament
MCL & LCL
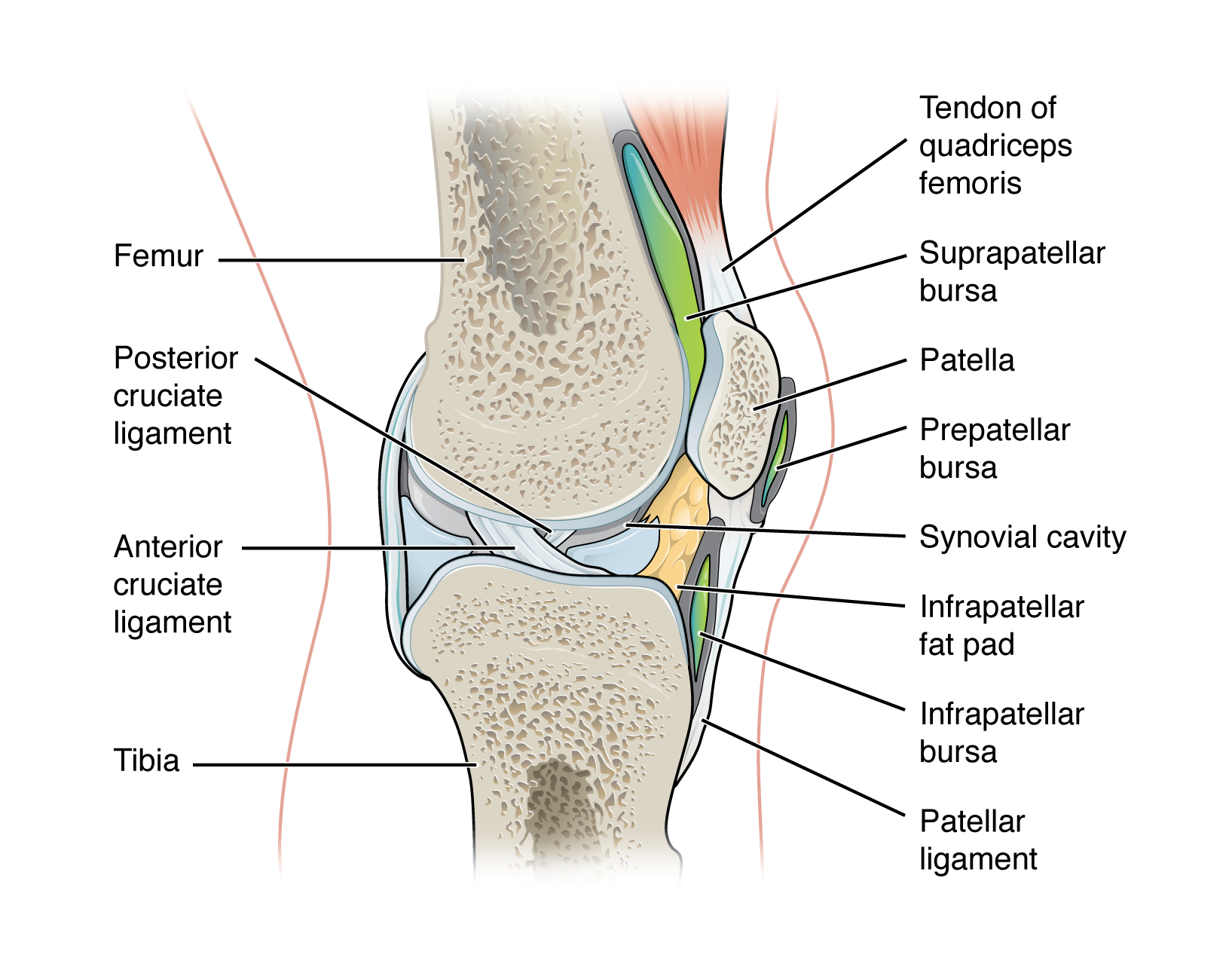
intrinsic ligament
ligament that is fused to or incorporated into the wall of the articular capsule of a synovial joint
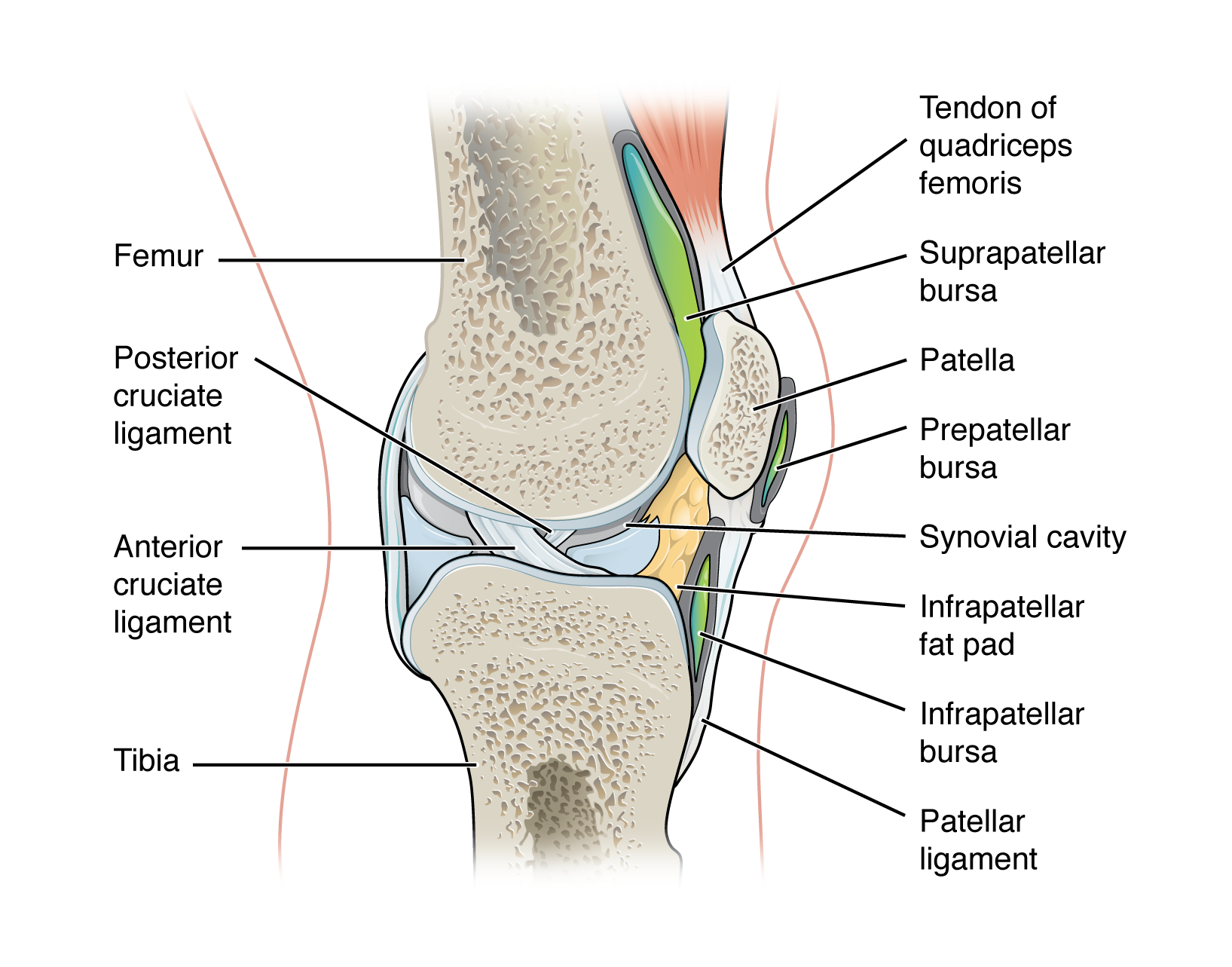
intracapsular ligament
ligament that is located within the articular capsule of a synovial joint
ACL & PCL
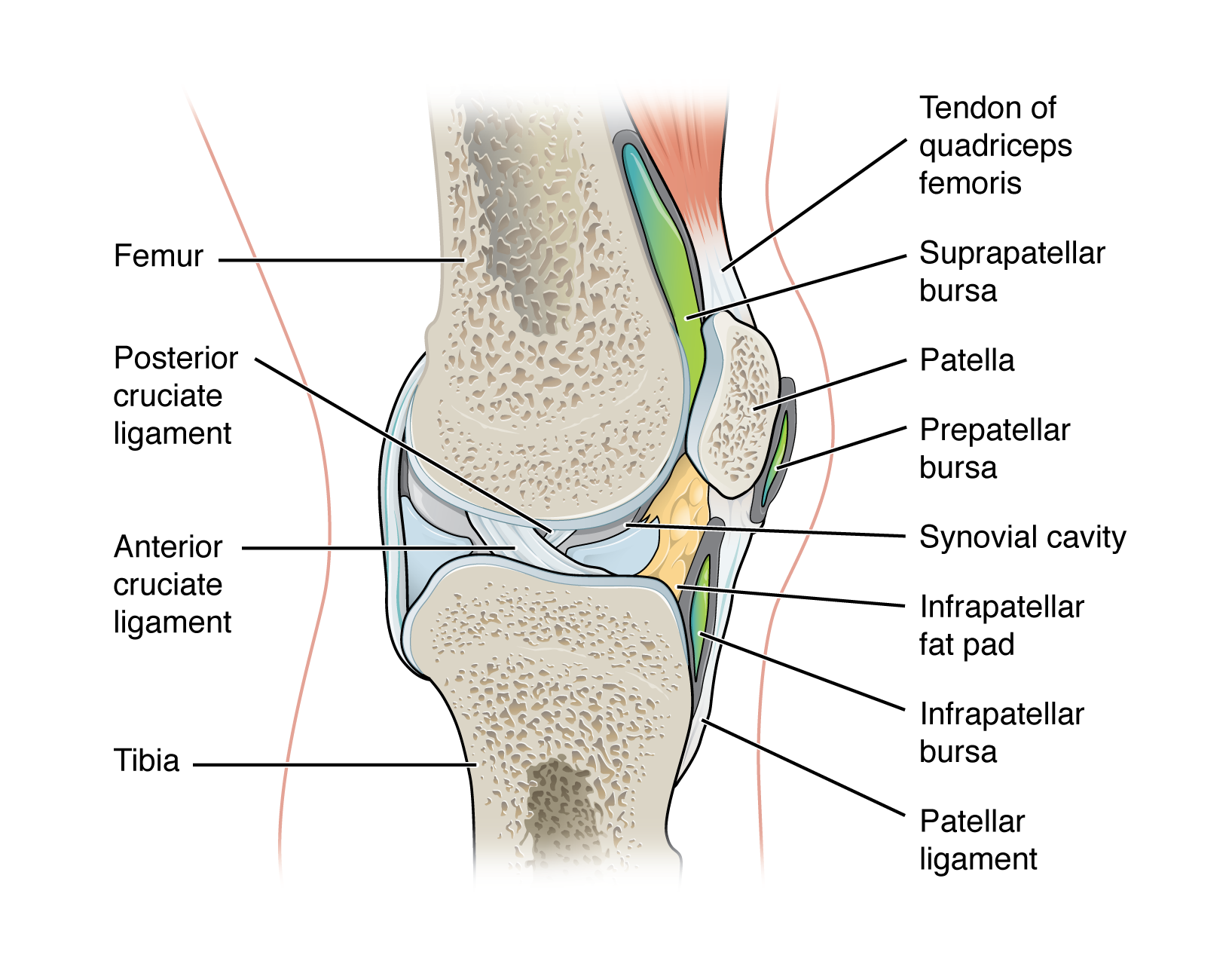
accessory structure of a synovial joint - tendon:
dense connective tissue structure that anchors a muscle to bone
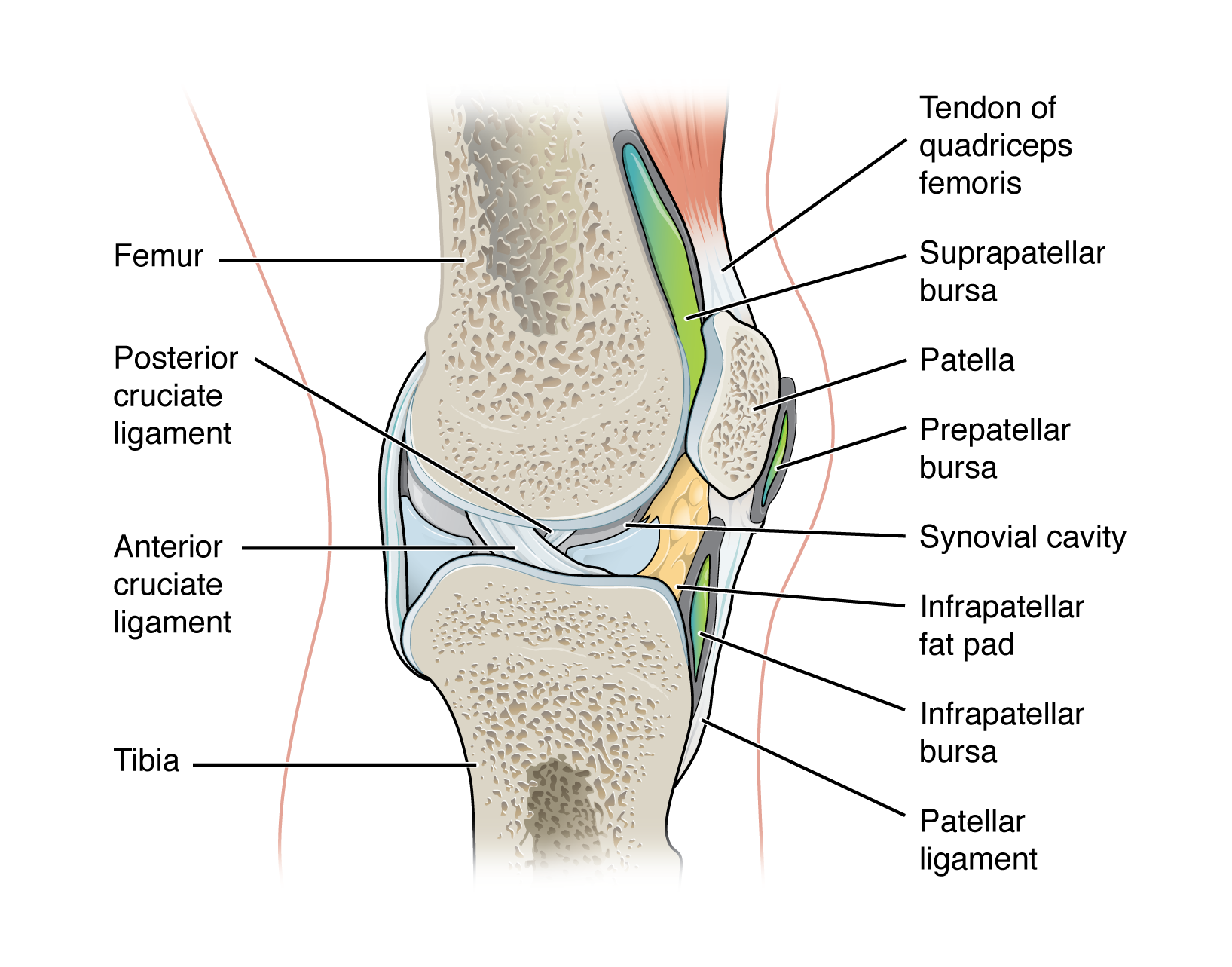
accessory structure of a synovial joint - tendon sheath:
connective tissue sac that surrounds a tendon at places where the tendon crosses a joint
similar in structure to a bursa, but smaller
contains a lubricating fluid to prevent friction and allow smooth movements of the tendon
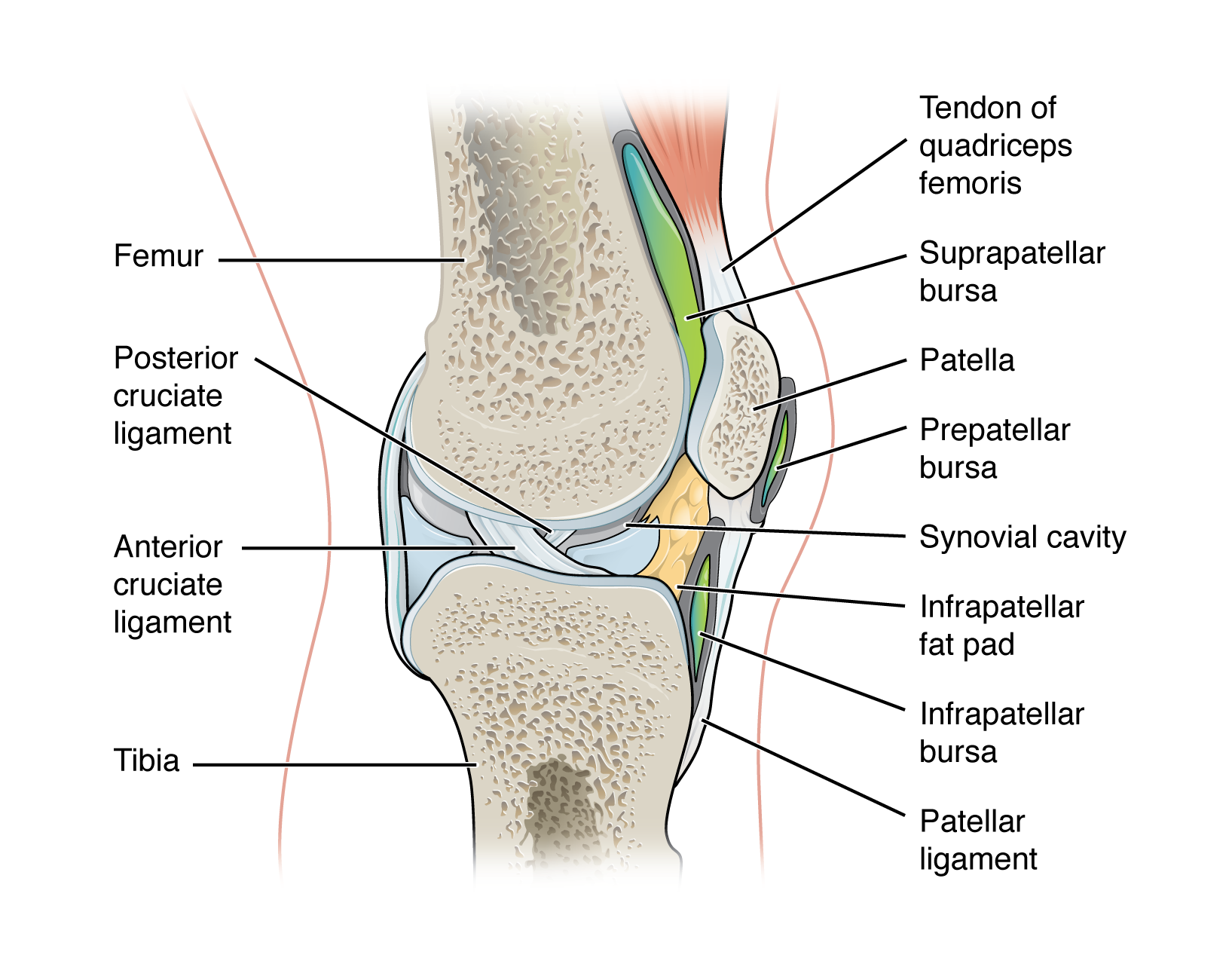
accessory structure of a synovial joint - articular disc (meniscus)
a pad of fibrous cartilage situated between opposing bones within a synovial joint
may subdivide a synovial cavity, channel the flow of synovial fluid, or allow for variations in the shapes of the articular surface
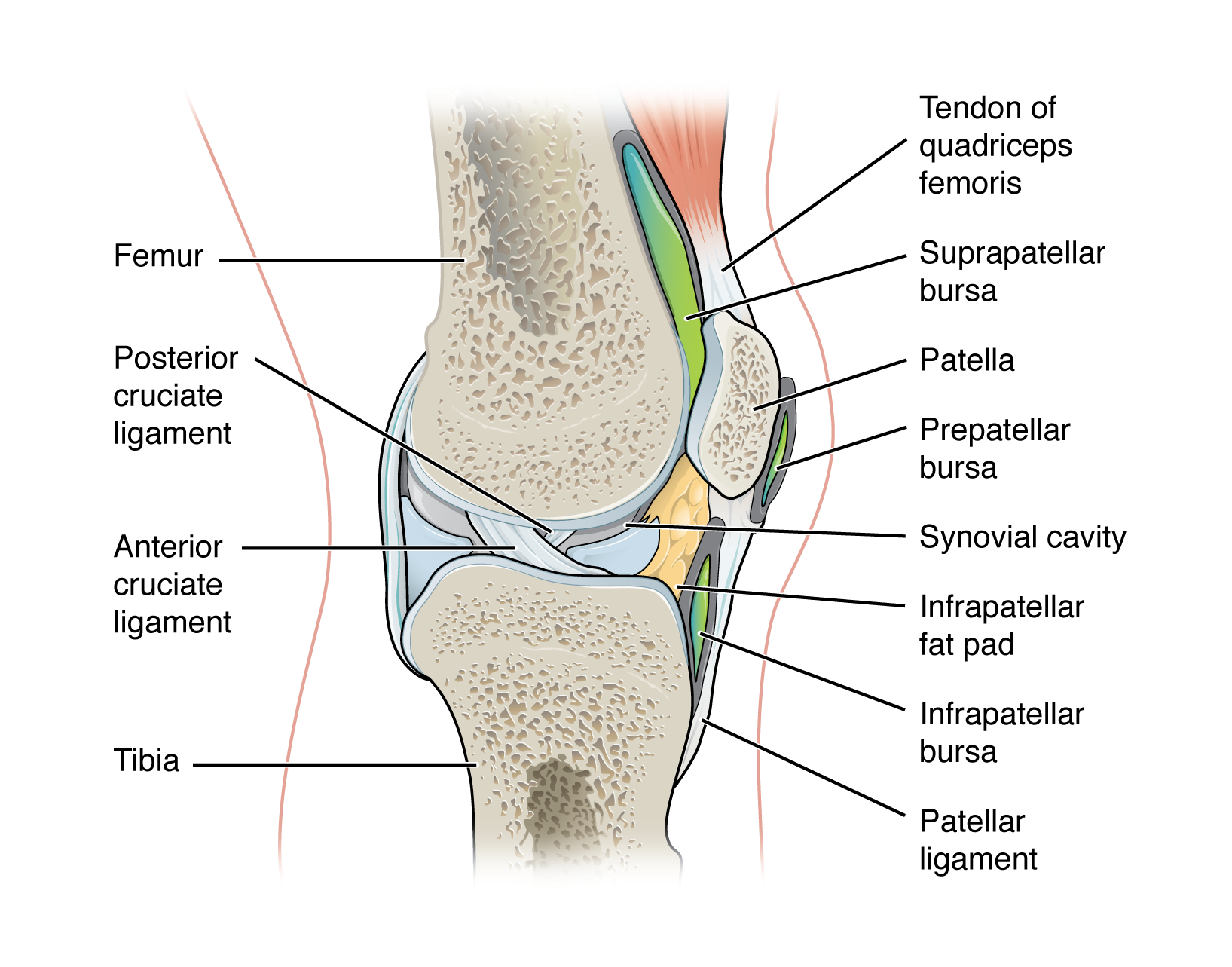
articular disc
fibrocartilage structure found between the bones of some synovial joints
provides padding or smooths movements between the bones
strongly united the bones together
accessory structure of a synovial joint - fat pad:
localized masses of adipose tissue covered by a layer of synovial membrane
commonly superficial to the joint capsule
protect articular cartilages and act as packing material for the joint
serve as a cushion between the bones
when the bones move, the fat pads fill in the spaces created as the joint cavity changes shape
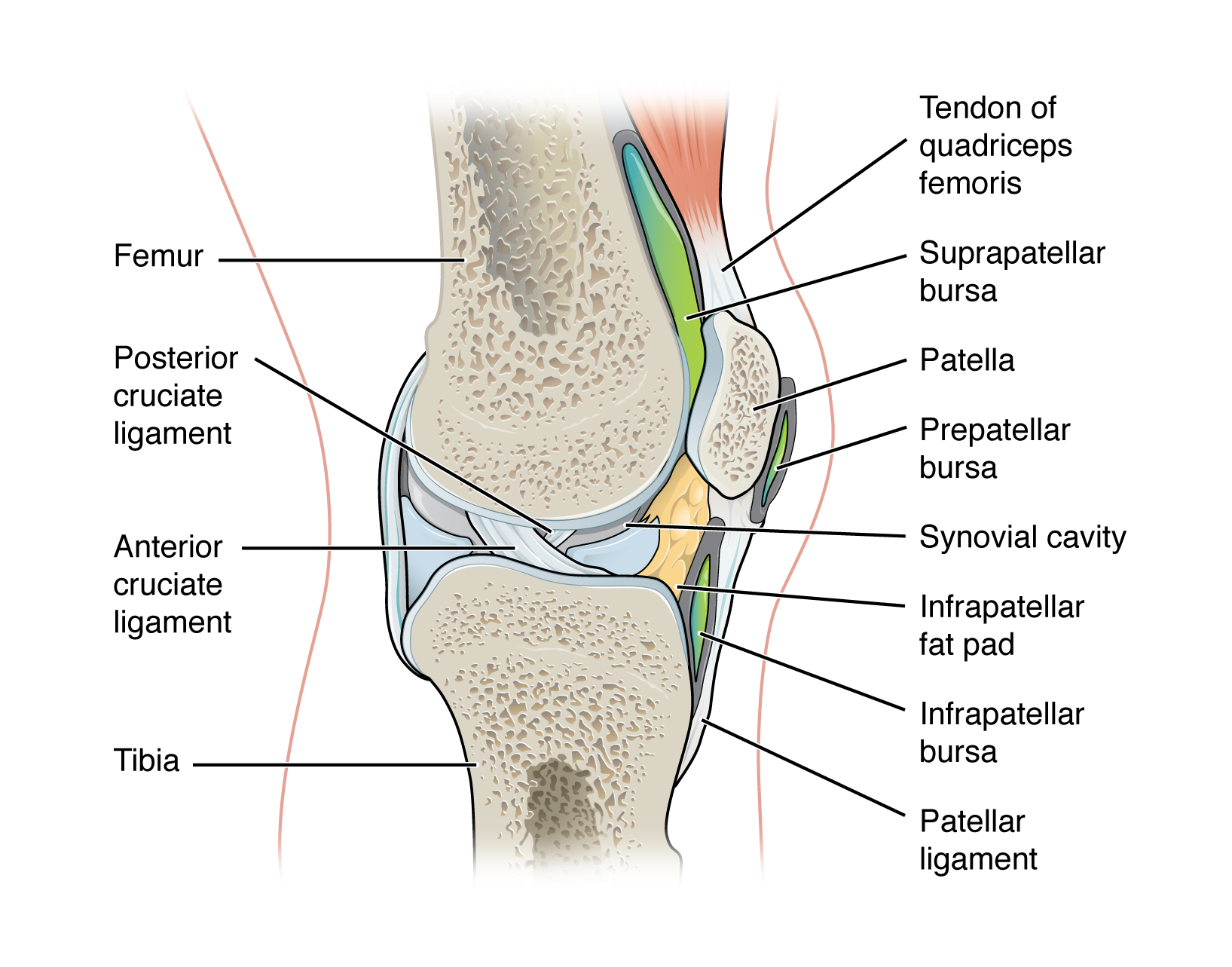
accessory structure of a synovial joint - bursa:
fluid filled lubricating sac that forms in connective tissue
contains synovia fluid and is lined by a synovial membrane
found between moving structures such as skin, muscles, tendons/ligaments usually found near joints
act to reduce friction
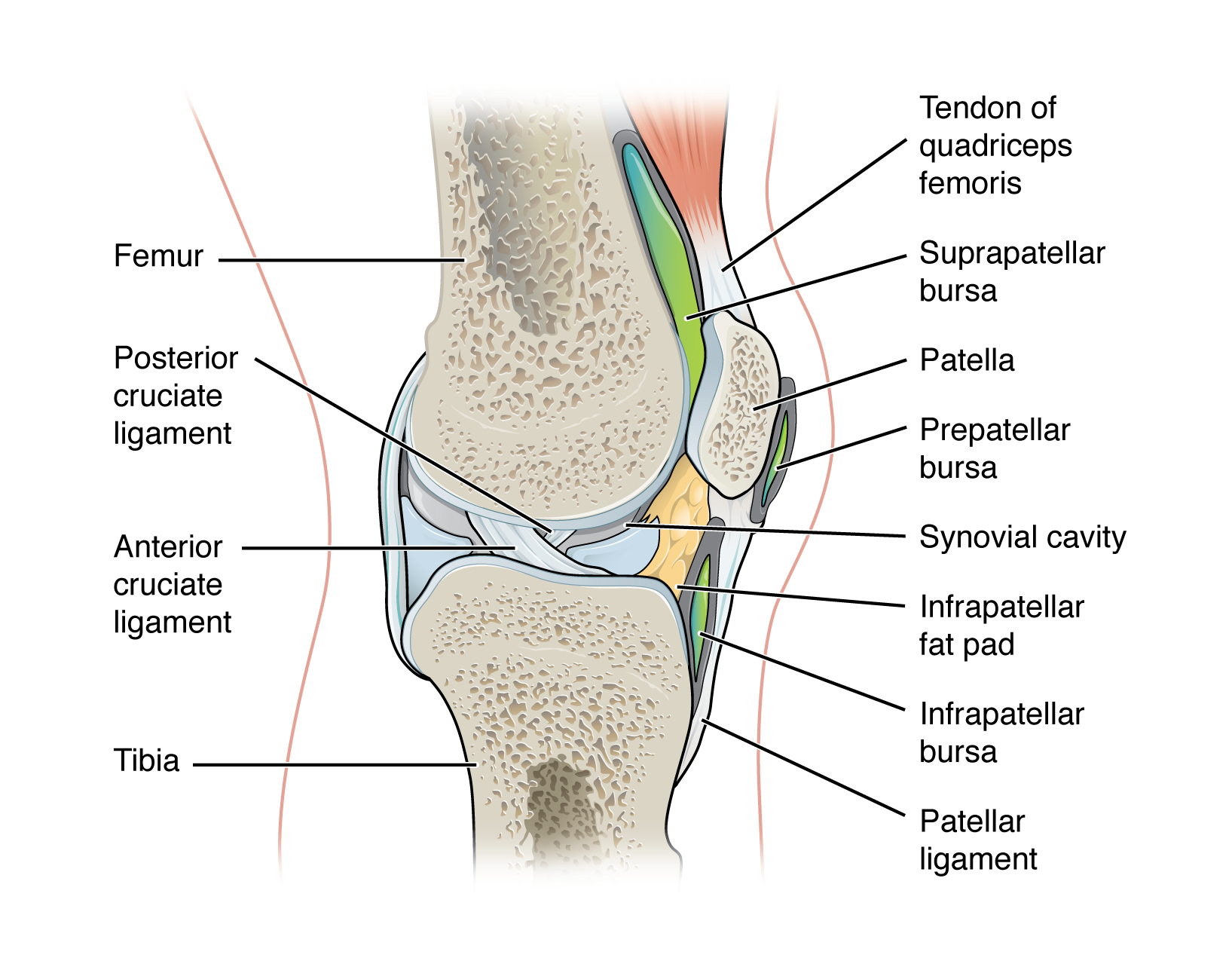
common types of bursae
classified by their location
subcutaneous bursa
submuscular bursa
subtendinous bursa
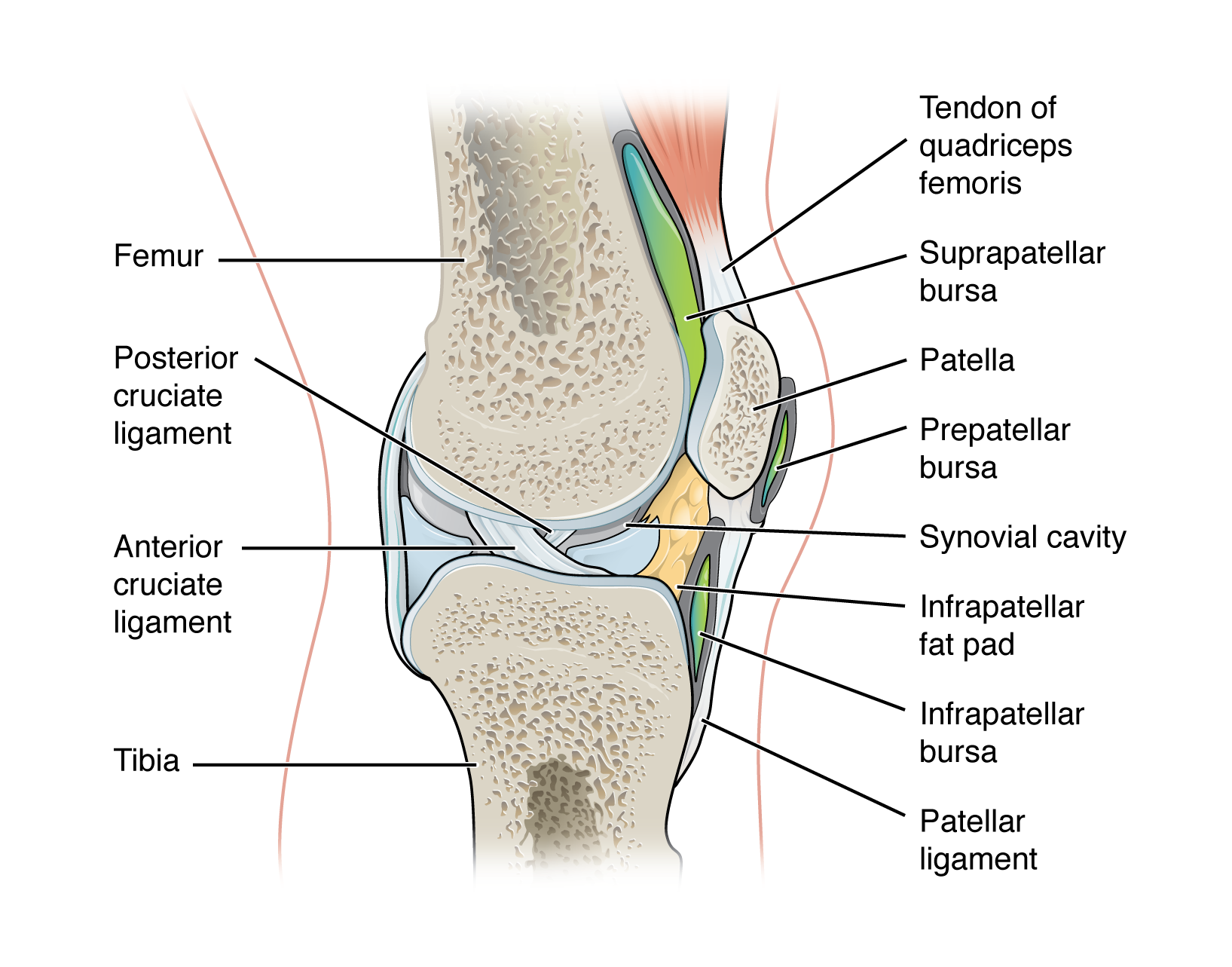
subcutaneous bursa
bursa that prevents friction between skin and underlying bone
examples:
prepatellar bursa - located over the kneecap
olecranon bursa - at the tip of the elbow
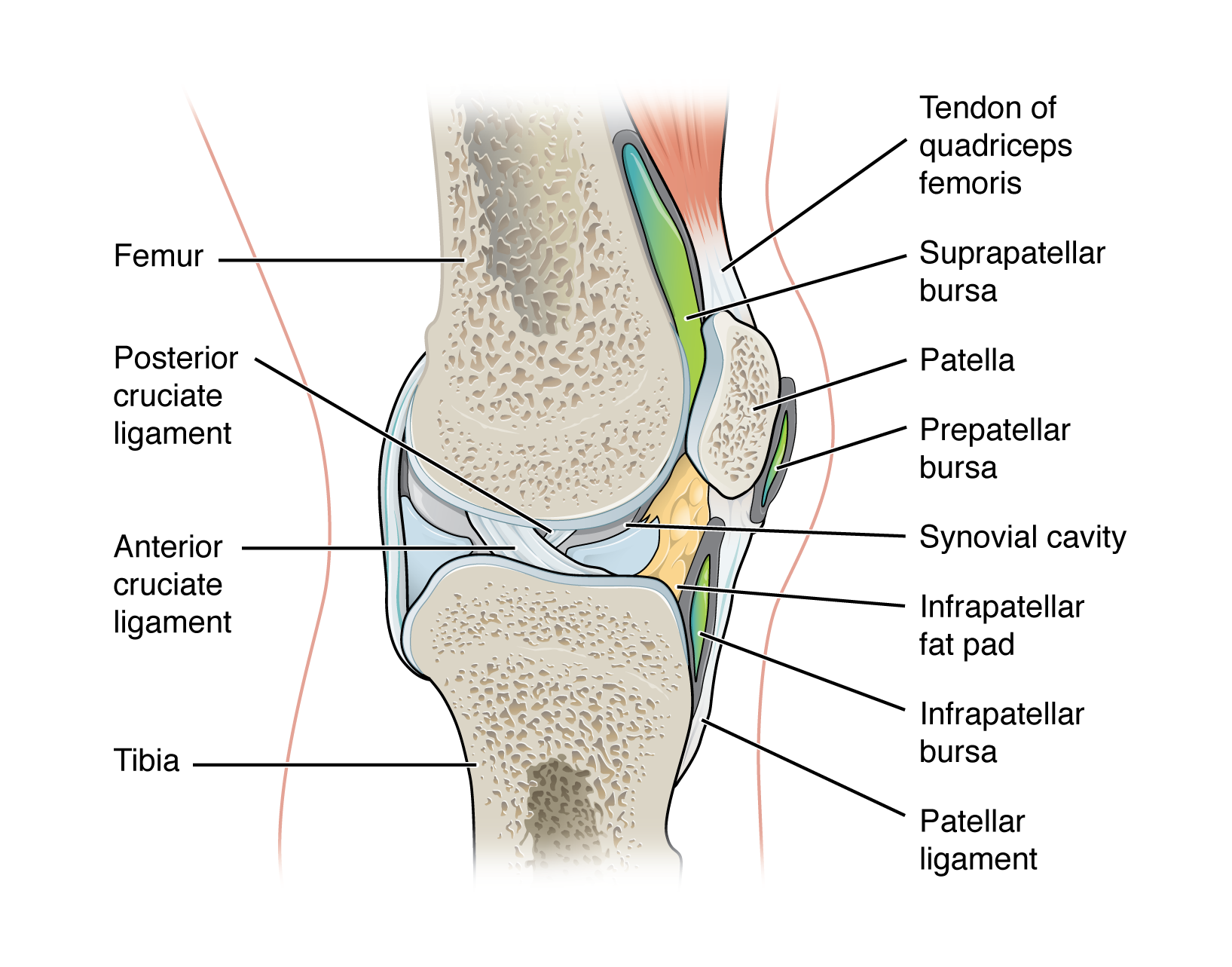
submuscular bursa
bursa that prevents friction between bone and a muscle or between adjacent muscles during movement
examples:
trochanteric bursa - found at the lateral hip, between the greater trochanter of the femur and the overlying gluteus maximus muscle
subtendinous bursa
bursa that prevents friction between bone and a muscle tendon
examples:
suprapatellar bursa - protects the tendon of the large anterior thigh muscle from the distal femur just above the knee
subacromial bursa - protects the tendon of shoulder muscle as it passes under the acromion of the scapula