genetics exam 4
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
You perform a cell free translation experiment like Nirenberg and Matthaei, but you forget to write down what nucleotides you added to make the mRNA. You precipitate the translated polypeptides and measure the relative amount of radiolabeled amino acids incorporated into them. You get 25% proline, 25% threonine, 12.5% glutamine, 12.5% lysine, 12.5% asparagine, and 12.5% histidine. What nucleotides and in what % did you add to make the mRNA?
50% C and 50% A
The scientist(s) __________ studied patients who had defects in their ability to metabolize certain compounds, particularly the inherited disease alkaptonuria. He/They proposed that a relationship exists between the inheritance of the trait and the inheritance of a defective enzyme
Garrod
where are the ribosomal subunits assembled?
nucleolus
what does elF5 act to recruit during the initiation stage?
The large ribosomal subunit
Kozak's rules for translation are similar to those for transcription in prokaryotes in that they both contain consensus sequences. In prokaryotes, the promoter consensus sequences are at −35 and −10. Where is the consensus sequence for translational initiation according to Kozak's rules?
-6 to +4
in bacteria, the sequence that facilitates the binding of the mRNA to the ribosome is called the
Shine-Dalgarno sequence
what is the least number of tRNAs that can be used to recognize all of the codons of isoleucine, and what is/are anticodon(s)? (in the answer choices, I=inosine)
one - 5’IAU3’
which of the following would be considered an activated amino acid?
amino acid AMP
You are studying the DNA of a person who you know has two defective copies of the gene that encodes phenylalanine hydroxylase. You are surprised to find that this person also carries two defective copies of the gene for homogentisic acid oxidase. What disease symptoms will this person exhibit? (Assume pathway intermediates are not available from sources outside the phenylalanine breakdown pathway.)
this person will exhibit symptoms of phenylketonuria
what level of protein structure is exemplified by α-helices and β-sheets?
secondary structure
The scientist(s) __________ developed the triplet-binding assay. Samples containing ribosomes and a particular RNA triplet were exposed to charged tRNAs with different radiolabeled amino acids. Only the amino acid whose tRNA matched the triplet would bind the ribosome. The triplet-binding assay established relationships between particular triplet sequences and specific amino acids.
Ninenberg and leder
The scientist(s) __________ created a cell-free translation system. An mRNA template was added to a number of tubes, each containing amino acids with a different one radiolabeled. Radiation was measured from the precipitated protein, and this corresponded to the mRNA template that had been added. This was the first experiment that demonstrated the ability to synthesize polypeptides from synthetic mRNA, and revealed a relationship between the two.
Nirenberg and Matthaei
what site on the ribosome is primarily responsible for holding the growing polypeptide?
P
what is the minimal number of tRNAs thata can be used to recognize all of the codons for threonine?
2
which of the following is NOT a stop codon?
UUA
the scientist(s) _____ studied Neurospora mutants that were altered in their nutritional requirements and hypothesized that one gene encodes one enzyme
Beadle and Tatum
which component of the ribosome is part of the peptidyl transferase in the 50S subunit and acts as a ribozyme to catalyze peptide bond formation?
23S rRNA
RF1 and RF2 are active during
termination
Francis Crick proposed the adaptor hypothesis, and later the adaptor was discovered to be ____
tRNA
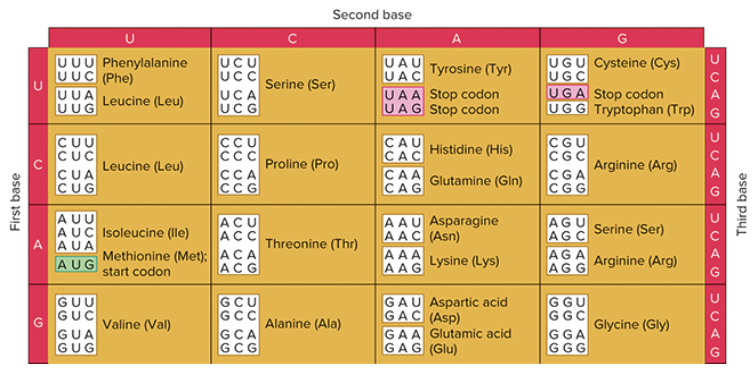
at tRNA’s anticodon is 5’GGC3’. what amino acid is attached to it?
alanine
The scientist(s) __________ developed a novel method to synthesize RNA. Short RNAs of 2 to 4 nucleotides were linked together to create a copolymer. The resulting peptide created after translation revealed the 3-letter code for the amino acids.
Khorana and colleagues
what is responsible for binding the initiator tRNA in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
IF2/ eIF2
which molecule contains an anticodon?
tRNA
you perform a cell free translation experiment like Nirenberg and Matthaei. You start with 60% C and 40% A. what relative amount of radiolabeled proline do you expect in the translated polypeptides?
36%
what site does the initiator tRNA bind to on the ribosome?
P
the primary structure of a protein refers to
the linear sequence of the amino acids
a gene is inducible and under negative control. which of the following pairs will allow expression of this gene?
repressor + inducer
riboswitches have been shown to affect regulation of
transcription and translation
if a bacterium is placed in an environment that contains both glucose and lactose, the regulation of the lac operon will allow which nutrient to be processed first?
glucose
in Jacob, Monod, and Pardee’s experiment, how many functional copies of lacl were there in the merozygote?
1
CAP affects which operon(s)?
the lac operon
what would be the result if the U-rich sequence after the fourth stem loop in the trp operon was replaced by a UG-rich sequence?
attentuation would not occur if tryptophan was high
if the Trp codons in the trpL gene were mutated to encode another amino acid, what would the result be?
the trp operon would never be transcribed
In a particular E. coli strain, a mutation in the thiMD operon results in improper formation of the stem loop secondary structure making it impossible to bind TPP. There are two enzymes encoded by the thiMD operon. How many of the enzymes encoded in the thiMD operon are translated?
two
which of the following is not an example of translational regulation in prokaryotes?
phosphorylation of an enzyme
allosteric regulation is accomplished by
a small molecule that fits into a site on the enzyme that is not the active site
how many promoters are in an operon?
1
which of the following is found in an operon
promoter, terminator, two or more genes, and operator
antisense RNA does which of the following?
binds to a complementary RNA and prevents its translation
enzymes involved in metabolism are most likely regulated via
feedback inhibition
regulation of gene expression may occur at which of the following levels?
transcription, translation, posttranslation
In Jacob, Monod, and Pardee's experiment, what would have been the conclusion if all four tubes produced a yellow color when β-ONPG was added?
expression of the lac operon is constitutive whether lacl is functional or not
if CAP could not bind to its CAP site, then what would be the result? assume lactose is present in each scenario
transcription would be difficult to activate in the absence of glucose
what is the gene responsible for attenuation in the trp operon?
trpL
the regulation of protein function, not gene expression is called ____ regulation
posttranslational
translational regulatory proteins recognize specific areas of what molecule?
mRNA
what stem-loop conformations favor attenuation in the trp operon?
3-4
a deletion in an operon removes the promoter. How will that affect the transcript that is produced from the operon?
the transcript will not be produced
a particular gene has a mutation in its NFR that causes it to bind abnormally tightly to histones. what effect would you expect this mutation has on the expression of this gene?
the expression of the gene would be abnormally low or absent
CpG islands are associated with which of the following?
DNA methylation
which of the following is part of the process of x-chromosome inactivation?
binding of multiple Xist transcripts to Xic on the X chromosome that will be inactivated
what is the difference between the trithorax(TrxG) and polycomb (PcG) complexes of proteins?
TrxG complex proteins activate gene expression by methylating lysine 4 on H3, while PcG complex proteins repress gene expression by methylating lysine 27 on H3
a queen bee is larger than the female worker bees in a hive. the queen develops functional ovaries that allow her to produce up to 2000 eggs a day. what determines which bees become queen bees?
the larvae raised on a diet of royal jelly
regions of chromatin that are more compact are called ____; they are usually found _____ in the nucleus
heterochromatin; at the periphery
which of the following statements are correct?
Environmental epigenetic changes can vary due to the exposure of the organism to different environmental conditions, while those programmed during development are the result of stimuli generated by the organism itself.
what effect will a mutation in IRP that prevents it from binding to iron have on an individual?
there will be excess transferrin, so iron intake must be lowered
combinatorial factors include activators and repressors as well as
small effector molecules, proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes, and DNA methylation
what is a major difference between the general and regulatory transcription factors?
general transcription factors are essential for any transcription for all genes while regulatory transcription factors regulate transcription of specific genes
a particular cell contains all of the standard histones but lacks several histone variants. which of the following MAT be true of this cell?
the cell will express different sets of genes than other cells in the same organism
genomic imprinting is a result of
DNA methylation
what gene is most responsible for x-chromosome inactivation?
Xist
in imprinting of the lgf2 gene in mice, are the ICR and DMR methylated on the maternal or paternal chromosome? which chromosome expresses lgf2?
paternal, paternal
The Avy allele of the Agouti gene involves the insertion of a transposable element upstream from the normal Agouti promoter. The transposable element carries a promoter that causes the overexpression of the Agouti gene. Mice carrying this allele tend to have coat colors that are more yellow than mice that don’t have this transposable element. If pregnant female mice are fed a diet that contains chemicals that increase DNA methylation, how would you expect that this diet would affect the coat color of offspring carrying the Avy allele?
their fur would be less yellow (darker brown) because the Agouti gene would tend to be under expressed
following mitosis, the two daughter cells usually have ____ pattern of facultative heterochromatin and _____ pattern of constitutive heterochromatin as was present in the mother cell
the same; the same
which of the following is an example of epigenetic inheritance?
expression of the lgf2 gene based on methylation of the ICR and DMR regions
where is the IRE located in the regulation of ferritin translation?
5’ end of mRNA
regulatory transcription factors may influence gene expression in which of the follwoing ways?
recruiting proteins to the promoter that enhance chromatin compaction
Gene methylation can be detected through the use of restriction endonucleases. Usually these are used in pairs where one enzyme will digest only unmethylated DNA in its recognition sequence while the other is insensitive to methylation. Which of the following statements is correct?
the enzyme that insensitive to methylation serves as a control to make sure the inability of the other enzyme to digest DNA is not due to a mutation
imagine all the histone H3 molecules in the cell have a mutation that changes their lysine-9 residue to an alanine. assuming this cell could still live, what would be the result?
the ability of the cell to form heterochromatin would be hindered
what are some types of the molecular changes that underlie epigenetic gene regulation
DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling
which of the following is incorrect regarding the glucocorticoid hormones?
they interact with receptors located in the plasma membrane of the cell
chromatin remodeling complexes alter nucleosomes, this occurs when
complexes of ATP-dependent proteins may reposition, evict, or change nucleosome composition
the differentially methylated region (DMR) is associated with which of the following?
genomic imprinting
epigenetic inheritance may occur at which of the following stages?
oogenesis, spermatogenesis, and embryogenesis
what general transcription factor is most often affected by regulatory transcription factors?
TFIID
which DNA repair process identifies daughter strands by methylation?
mismatch repair
There is a spectrum of syndromes in humans known as Xeroderma pigmentosum. The individuals that have XD most commonly have mutations in their nucleotide excision DNA repair mechanisms that make them particularly susceptible to environmental mutagens such as UV light. Individuals have to be careful with how much sunlight they are exposed to since they have an extremely elevated chance for developing skin cancer. There have been several cell lines that have been established from XD patients that can be studied in tissue culture. In an experiment, several different cell lines of unknown origin were tested for their ability to undergo unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS), an assay for DNA repair. In this essay, the amount of radioactive nucleotides that are incorporated into DNA after the cell sustains a mutagenic event are measured. The amount of radioactivity incorporated is measured by the number of counts per minute (CPM). Below is a table from such an experiment. Which cell line is most likely from XD patient(s)?
ell line | CPM in UDS assay | CPM if no mutagenic event |
A | 2,500 | 2,750 |
B | 300,000 | 5,000 |
C | 45,000 | 25,000 |
D | 275,000 | 50,000 |
Wild-type control | 750,000 | 75,000 |
A
how does position effect influence gene expression?
The movement of the genetic material on the chromosome by inversions or translocations may place a coding sequence near a new regulatory region, thus activating the expression of the gene., The movement of the gene may place it into a region that is highly condensed., The movement of a gene may remove it from its normal promoter, thus silencing the gene. (all of the answers are correct)
which types of mutations are least likely to be subjected to natural selection?
silent
what is an example of a suppressor mutation?
an intragenic mutation that restores protein structure, an intergenic mutation that increases the activity of a protein performing the same function as the mutated protein, an intergenic mutation that alters a transcription factor to activate the expression of a compensating protein (all of the answers)
which environmental agent shown can induce mutations?
UV radiation, x-rays, gamma rays (all of the answers)
after screening a colony of bacteria for a given gene, you discover 100 mutant colonies out of 3 million total colonies. what is the mutation rate for this gene in the population?
3.3 × 10^-5
the results of the replica plating experiments by the Lederbergs supported which of the following theories?
random mutation theory
You are a doctor tasked with diagnosing a patient that comes to you with mental impairment. Upon performing genetic tests, you find he has approximately 300 repeats of GCC in one of his genes. His father and grandfather had similar mental impairment but were never diagnosed with a condition prior to their death. His grandmother, mother, and sisters are unaffected. What disease do you predict that this patient has?
FRAXE
anticipation is associated with which of the following?
TRNE mutations
what process repairs damage form UV radiation?
nucleotide excision repair
in the nucleotide excision repair system, which of the following proteins is responsible for recognizing a thymine dimer to be repaired?
UvrA/UvrB
In the following sequence of DNA, the italicized base has been mutated. What type of mutation is this?
a. 5' - G A T C T C C G A A T T - 3' original strand
5' - G A T C T C C C A A T T - 3' mutated strand
transversion
Consider the following DNA sequence, which codes the first portion of a long protein beginning at the ATG (AUG in mRNA) start codon.
5' ATG CCC CGC AGT AGG GGG TGG AGA 3'
Which of the mutated sequences listed is most likely to be a deleterious mutation?
5' ATG CCC CGC AGT AGG GGG TGA AGA3'
which of the following is an example of a base analog?
5BU
what would be a set of anticipated results from a “Lederberg” experiment?
total number of colonies on a plate: 1500. Total number of resistant colonies on a replica plate with T1: 15
most trinucleotide repeat expansion repeats involve expansion of which of the following?
CAG
which process is used to replicate DNA that contains distortions due to unrepaired DNA damage?
translesion synthesis
which DNA repair process often leads to deletion in chromosome sequence?
nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ)
mutations that change the configuration of a protein at a specific temperature are called ____ mutations
conditional
Beechdrops is a parasitic plant that cannot perform photosynthesis but relies on its host the Beech tree. However, beechdrops still retains many if not all of the genes for photosynthesis. Snapdragons and gladiolas are common garden flowers that rely on their ability to perform photosynthesis. If you were to compare the gene sequences for these three plants for ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) a protein necessary for photosynthesis, what would you predict?
the differences between gladiolas and snapdragons would most likely be silent mutations while those in beechdrops may be silent or missense
translocation and inversion may cause which of the following?
position effect
the complete loss of either a guanine or adenine from DNA is an example of
depurination
which of the following is not a n example of a cause of a spontaneous mutation?
UV light
a translocation that moves a gene from an area of euchromatin to heterochromatin would typically cause ____ in the expression of the gene
a reduction