Neuroscience II 1005 Quizzes (FINAL) WEEKSA 5 -12 ONLY
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
Which is thought to be the role of the climbing fiber input to the cerebellar cortex?
Provision of a training signal for the parallel fiber synapses onto Purkinje cells
Which structure plays the largest role in cerebellar-cortical "closed loop" circuits?
Dentate nucleus
Which statement about the reeler mutation in mice is false?
a. In reeler mice, the Purkinje, granule, and interneurons are found in incorrect locations in the cerebellum.
b. A “synthetic” reeler mutation was discovered by chance after inserting DNA marker fragments into the mouse genome.
c. The name reeler was given based on the pattern of impaired locomotor abilities it produces.
d. Because of induced genetic abnormalities, it was impossible to determine which chromosome contained the reeler mutation.
e. The mutation appears to interfere with the extracellular matrix in the cerebellum.
d. Because of induced genetic abnormalities, it was impossible to determine which chromosome contained the reeler mutation.
The large size of the cerebral peduncles in the midbrain is related to cerebellar inputs
a. arriving through the middle cerebellar peduncles.
Alcohol-induced damage to the vermis of the cerebellum has been associated with
b. a wide and staggering gait.
The cell bodies that give rise to the largest number of fibers entering the cerebellum are located in the
a. pons.
Which cell type carries the main output from the cerebellar cortex and is considered the prime computational element of the cerebellum?
d. Purkinje
Which part of the cerebellum is highly developed in humans and involved with the planning and execution of complex spatial and temporal sequences?
e. Cerebrocerebellum
Mossy fibers synapse on
d. granule cells and deep cerebellar nuclei.
In the weaver mutant strain of mouse, the defect associated with ataxia, hypotonia, and tremor is
a marked lack of granule cells.
Cerebellar ataxia is characterized by
jerky, imprecise movements.
Which statement about recalibration of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is false?
a. The VOR is precisely recalibrated with each eye movement so that perfect fixation can be maintained during head rotation.
b. The cerebellum is involved in adjusting the VOR when eye movements do not properly compensate for head rotation.
c. The cerebellum integrates visual information, vestibular information, and motor information when performing recalibration.
d. In the absence of the cerebellum, the VOR cannot be recalibrated.
a The VOR is precisely recalibrated with each eye movement so that perfect fixation can be maintained during head rotation.
The axons from the pontine nuclei into the cerebellum are referred to as _______ fibers.
mossy
The _______ make an "inhibitory nest of synapses" with the Purkinje cell bodies.
basket cells
Which part of the cerebellum receives input directly from the spinal cord?
a. Spinocerebellum
Which statement about cerebellar Purkinje cells is false?
a. A Purkinje cell’s dendritic field is oriented parallel to the parallel fibers.
b. A Purkinje cell is contacted by roughly 200,000 granule cells.
c. Purkinje cells inhibit deep cerebellar nuclear cells.
d. Purkinje cells project to the deep cerebellar nuclei.
e. A Purkinje cell’s dendritic field branches in a narrow plane.
a. A Purkinje cell's dendritic field is oriented parallel to the parallel fibers.
During electrical recordings from cerebellar neurons, flipping the wrist back and forth
d. leads to neuronal responses associated with relaxation or contraction of specific muscles and changes in joint position and movement direction.
Which structures receive input from the cerebellar cortex?
Interposed nucleus
Vestibular nucleus
Fastigial nucleus
Dentate nucleus
Which of the following lead to the theory that a proteinaceous agent or prion, and not a virus, causes such diseases as scrapie and “mad cow disease”?
The occurrence of a scrapie-like disease among New Guinea cannibals
Inherited spongiform encephalopathies in humans
Affinity chromatographic purification of the infectious agent, which lacks nucleic acids
Resistance in mice with a null mutation in PrPC (prion protein control)
A patient is having trouble with short-term error correction in his motor behavior. His doctor suspects the patient has a tumor and orders an MRI scan. Where does the doctor expect to find a tumor?
b. Inferior olive
Dopamine is released into the striatum from the substantia nigra pars compacta. Which neural response would you expect to see?
Activation of the frontal cortex by activating the direct pathway and inhibiting the indirect pathway
Focal application of a GABA receptor agonist within the substantia nigra pars reticulata would most likely
result in involuntary saccadic eye movements.
The primary input to the striatum is from
cerebral cortex.
Which statement about the dopaminergic system associated with the basal ganglia is false?
a. The dopamine cells receive major input from medium spiny neurons.
b. Dopamine exerts excitatory and inhibitory effects on the corpus striatum.
c. Dopamine D1 and D2 receptors are both G-protein-coupled receptors.
d. The primary set of dopamine cells is located in the substantia nigra pars compact.
e. The dopamine cells project to both segments of the globus pallidus.
The dopamine cells project to both segments of the globus pallidus.
Parkinson's disease is associated with loss of
dopamine neurons that project to the striatum, leading to a hypokinetic disorder.
The axons transmitting cortical signals to the basal ganglia
carry information whose nature is poorly understood.
Deep brain stimulation is a potential treatment for advanced Parkinson's disease. Where might a neurosurgeon implant an electrode when using this technique?
Subthalamic nucleus
Which statement about the medium spiny neurons in the caudate and putamen is false?
a. They receive input from dopaminergic neurons.
b. They are GABAergic.
c. They outnumber their target neurons in the globus pallidus by about a factor of 1,000.
d. They are the major output of the striatum.
e. Each one densely innervates 100 to 200 pallidal neurons.
Each one densely innervates 100 to 200 pallidal neurons.
Listed below are the events that occur during basal ganglia functioning.
1. Disinhibition of ventral anterior and ventral lateral thalamic nuclei
2. Inhibition of globus pallidus
3. Excitation of caudate and putamen Which of the following is the correct sequence of these events?
3; 2; 1
Huntington's disease
It is attributable to excessive nucleotide repeats in the responsible gene.
It results in involuntary, choreiform motor acts
It involves atrophy of the striatum
It is attributed to a genetic defect in the huntingtin gene.
The substantia nigra pars reticulata projects to the
superior colliculus.
One of the outputs of the basal ganglia, the substantia nigra pars reticulata, is most similar in its function to the
globus pallidus.
MPTP is a compound that
destroys the substantia nigra of monkeys (and humans).
The basal ganglia are thought to elicit movement via
disinhibition of thalamic neurons (VA/VL).
The basal ganglia's ability to evoke one specific movement pattern out of an almost endless variety of possible movement patterns is best ascribed to which neural coding strategy?
Center-surround style decision making
Which statement about the basal ganglia is false?
a. The striatum includes the caudate and putamen.
b. The pallidum includes the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra pars reticulata.
c. The basal ganglia include the caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus.
d. The striatum receives the bulk of the inputs to the basal ganglia.
e. The major outputs of the basal ganglia are from the putamen.
The major outputs of the basal ganglia are from the putamen.
In addition to their traditional motor program selection and implementation functions, the basal ganglia are also thought to be involved in
drug-seeking behaviors.
mood changes.
initiation and termination of thought patterns related to planning and attention.
disorders such as Tourette's syndrome and schizophrenia.
In monkeys, a decreased latency of saccadic eye movements toward a target object is associated with
the size of the reward received for completing the movement.
The subthalamic nucleus receives input from the
globus pallidus external segment.
In deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson's disease,
stimulation parameters such as pulse width, current amplitudes, and pattern are determined by trial and error.
The longitudinal lanceolate endings do not respond to
pain
Tactile information from the face to the central nervous system follows which pathway?
Cutaneous receptors, cranial nerve V, trigeminal brainstem complex, VPM of thalamus, contralateral cortex
Rapidly adapting fibers are most likely to provide information about the _______ of a stimulus.
movement
Meissner afferents account for about _______ of the mechanosensory innervation of the human hand.
40%
Merkel afferent fibers convey information about which variable(s)?
Shape and texture
Afferent fibers that lack specialized receptors at their terminals detect which type of stimuli?
pain
The axons of the medial lemniscus synapse with neurons of the
thalamus
Which afferents have the highest spatial resolution?
Merkel afferents
The _______ is inversely proportional to the density of the fibers supplying an area.
size of the receptive field
Joint receptors are important to perception of which information?
Finger position near the limits of normal range of motion
Which feature is characteristic of the pseudounipolar neurons of the somatosensory system?
Continuous fibers, with the cell body attached by a single process
A dermatome is an area innervated by
fibers of the cells from a single dorsal root ganglion.
Which afferent fibers have the largest diameter?
Ia sensory afferents from the muscles
Which sensation would be affected if group II sensory afferents in a limb were rendered dysfunctional due to a mutation?
Static position of the limb
Where would the cell body of a sensory neuron that transmits touch information from the cheek to the central nervous system be located?
Ganglion alongside the brainstem
Which type of somatosensory afferents transmit information from touch mechanoreceptors to the central nervous system?
Aβ
Muscles in which region would most likely have the lowest density of muscle spindles?
leg
Which role do γ motor neurons play in the function of a muscle spindle?
They improve the accuracy of the reported sensory information by innervating intrafusal fibers.
Which component of the musculoskeletal system is responsible for force-production?
Extrafusal muscle fiber
On which body part would the two-point discrimination threshold be shortest?
Select one:
a. Thumb
b. Ear
c. Foot
d. Arm
e. Thigh
thumb
Which statement about sensory transduction by hair cells is false?
a. Hair cells are presynaptic to second-order sensory neurons.
b. The firing of action potentials in second-order sensory neurons can be either up- or down-regulated, depending on the direction in which the bundle of cilia (of the afferent hair cell) is bent.
c. The electrical activity initiated by the tip links is transmitted to the vesicular release sites along microtubules that undergo voltage-dependent rearrangements.
d. The hair cell body (basal end) is bathed in perilymph, while the hair cell cilia are bathed in endolymph.
e. Bending of the cilia toward the longest cilium produces depolarization.
The electrical activity initiated by the tip links is transmitted to the vesicular release sites along microtubules that undergo voltage-dependent rearrangements.
Cells with pronounced selectivity for specific combinations of sound frequencies are found in the
medial geniculate complex.
Which statement about lemniscal and collicular sound processing is false?
a. Certain collicular neurons respond preferentially to frequency-modulated sounds.
b. Unlike the physical mapping of the visual world onto the retina, the auditory space map in the inferior colliculus is purely a construct of the brainstem’s processing of auditory information.
c. The different acoustical cell types seen in the inferior colliculus are also present in the cochlear nuclei, but they are not formed into a topographic map at the cochlear level of the pathway.
d. Certain collicular neurons respond preferentially to sounds of a fixed duration.
e. The monaural pathway connects the cochlear nucleus to the midbrain via the nuclei of the lateral lemniscus.
The different acoustical cell types seen in the inferior colliculus are also present in the cochlear nuclei, but they are not formed into a topographic map at the cochlear level of the pathway.
Which function is not an operation of the outer ear?
a. Boosting sound pressure level as it enters the ear
b. Directing different frequencies of sound to specific cochlear locations
c. Optimally transmitting sounds in our range of vocalizations
d. Boosting frequencies by means of passive resonances
e. Filtering sound in an adaptive manner based on source elevation
Directing different frequencies of sound to specific cochlear locations
What quality gives rise to tonotopy along the cochlea?
The changing width and stiffness of the basilar membrane
Which ion and direction of flow is responsible for depolarization of inner hair cells?
Potassium into the cell
In which way is the mechanism of hair-cell transduction distinct from sensory transduction mechanisms that occur outside the ear?
Potassium influx from the endolymph depolarizes the hair cell.
Potassium efflux into the perilymph repolarizes the hair cell.
Calcium and calcium-activated potassium channels contribute to electromechanical resonance.
The two domains of the hair cell operate, in effect, as two distinct compartments, each with its own ionic equilibrium potentials.
Which statement about auditory nerve fibers is false?
a. Afferent fibers receive input from inner hair cells.
b. The higher frequency fibers can respond well to stimuli at frequencies in the 10 to 20 kHz range.
c. The lower frequency fibers have a sharp tuning peak plus a separate extended hump.
d. Efferent fibers innervate the three rows of outer hair cells.
e. The characteristic frequency of the hair cells varies systematically along the cochlear axis.
The lower frequency fibers have a sharp tuning peak plus a separate extended hump.
What is the difference between the endolymph and perilymph?
Endolymph is high in potassium and low in sodium; perilymph is high in sodium and low in potassium.
Which statement about the functioning of cochlear implants (CIs) is false?
a. They are designed to induce electromechanical pressure waves within the cochlear fluid.
b. They provide tonotopic delivery of electrical signals along the length of the cochlea.
c. They require an electrical connection from an implanted stimulator to a cochlear electrode array.
d. They require an auditory signal processing device that decomposes sounds into component frequencies.
e. They electrically stimulate residual hair cells and/or primary auditory afferents.
They are designed to induce electromechanical pressure waves within the cochlear fluid.
In which brain region are the intensities (not the phases) of impinging sound waves compared in order to determine the location of sound sources?
Lateral superior olive
In order to increase the decibel measurement of a sound, one would have to alter its wave
a. amplitude.
b. form.
c. length.
d. frequency.
amplitude
If efferent axons that travel between the brainstem and cochlea are damaged, leaving the afferent axons intact, which structure would not function properly?
Outer hair cells
Which of the following correctly pairs an auditory pathway location with its input?
a. Medial geniculate complex—axons from ipsilateral superior colliculus
b. Superior olive—ipsilateral auditory nerve
c. Cochlear nuclei—contralateral auditory nerve
d. Inferior colliculus—axons from both cochlear nuclei and contralateral superior olive
e. Nucleus of lateral lemniscus—axons from contralateral cochlear nucleus
Nucleus of lateral lemniscus—axons from contralateral cochlear nucleus
A patient has bilateral damage to the medial longitudinal fasciculus. If she undergoes cold water irrigation in the right ear while unconscious, which oculomotor response would she show?
Slow movement of the right eye toward the right
Squirting cold water into the ear of a reclined person will elicit eye movements
characteristic of different neurological deficits.
The sense of self-motion when, for example, a train adjacent to the one you are sitting on begins moving, is called
vection
The vestibular system is able to detect
translational acceleration in any direction.
rotational acceleration in any direction.
orientation of the head with respect to gravity.
Neural pathways and signals mediating the vestibulospinal reflex
excite extensor muscles
Patients with severe bilateral vestibular damage do not exhibit
a. a permanent deficit in visually fixating while moving.
b. difficulty in visually tracking slow-moving objects.
c. postural instabilities.
d. impaired balance in low-light conditions.
e. difficulty walking on uneven surfaces.
b. difficulty in visually tracking slow-moving objects.
The vestibulo-ocular reflex is a mechanism for
stabilizing gaze during head movement
Which statement about the firing rate in the vestibular afferents when an individual turns her head to the left is accurate?
Firing rate in the afferent from the left horizontal semicircular canal increases.
Which statement about the mechanotransduction mechanism of vestibular hair cells is true?
Transduction is biphasic, in that movements toward and away from the kinocilium can produce increased or decreased firing of vestibular afferents.
_______ convey vestibular signals from the periphery to the CNS.
Cells in Scarpa's ganglion
The semicircular canals are largely insensitive to linear acceleration because
the forces produced by linear acceleration are the same on both sides of the cupula.
Which structure is designed to detect angular acceleration?
semicircular canals
Which mechanism leads to activation of hair cells in the semicircular canals?
Endolymph movement distorts the cupula.
The otoconia-containing organs of the vestibular system signal tilt and linear acceleration by virtue of
their crystals being heavier than surrounding tissue.
You are measuring firing rate from a vestibular axon that innervates a hair cell in the utricle (top left panel, leftmost hair cell). What should happen to the firing rate when the subjects tilt their head forward (right top panel)?
E
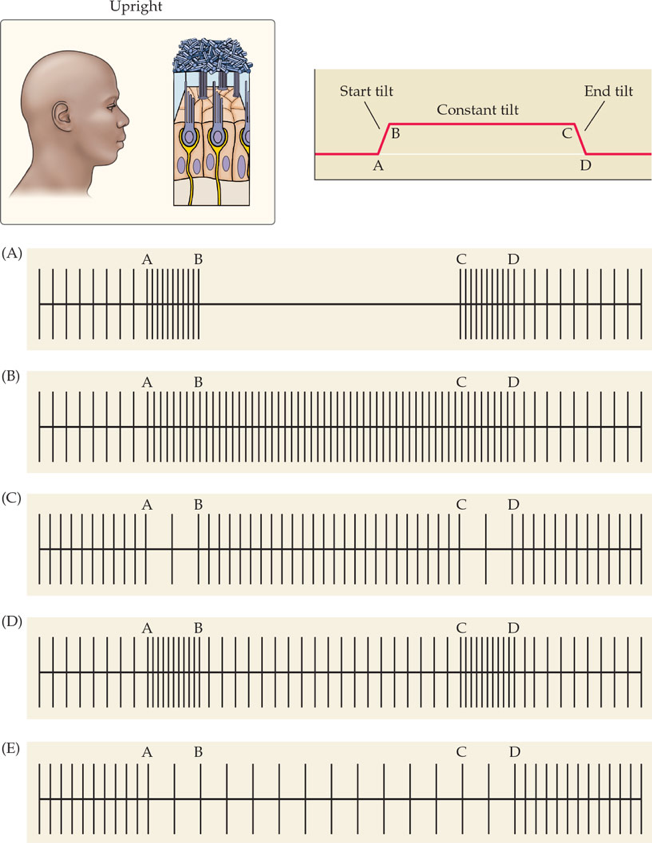
Which organ is most sensitive to horizontal acceleration of the head?
Utricle
Both the cochlea and the labyrinth
use hair cells in mechanotransduction
Cortical neurons that receive vestibular input via the thalamus
Integrate multimodal sensory information.
Respond to rotation in the dark.
Receive visual and proprioceptive inputs.
Are likely involved with the perception of body orientation in extrapersonal space.
What is mechanotransduction?
Converting mechanical forces into electrical signals
This is different to an AP as it can be graded
What is the difference between dorsal root ganglia and cranial nerve ganglia?
Dorsal root ganglia
Somatosensory afferent fibres
Somatic sensory information (pain, touch, temperature) from the body to the spinal cord
Pseudounipolar
Oval shape in spine
Periphery to CNS
Cranial nerve ganglia
Sensory information from the head and neck
Transmits general and special sensory information (e.g., touch, taste, smell, hearing) to the brain
Cranial nerves
Pseudounipolar
Merkel
Superficial
steady pressure
rapidly adapting
small receptive field = more detail
shape and texture
What is cortical magnification?
Where an area of the brain is represented bigger than its actual part
For example fingers have a large area in the brain as they require fine motor control
Do maps in the somatosensory system exhibit synaptic plasticity?
Repetitive task ➜ Adapt ➜ Move finger ➜ Brain area becomes bigger for fine motor control
Loss of finger ➜ Loss of circuits for finger ➜ Brain uses it as a different area
What are the three main sections of the human ear? Describe one thing that each section does.
Outer ear: Collects sound waves and funnels them into the ear canal toward the eardrum. (pinna and ear canal internal acoustic meatus)
Middle ear: Amplifies and transmits sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear via the ossicles (bones).
Inner ear: Converts sound vibrations into neural signals in the cochlea and maintains balance through the vestibular system.
What is tonotopy?
systematic organisation of sound frequencies along the cochlea in the auditory cortex
Different spatial regions respond best to different frequencies of sound
In the cochlea
The base is sensitive to high frequency sounds
The apex is sensitive to high frequency sounds
This is for frequency distinguation
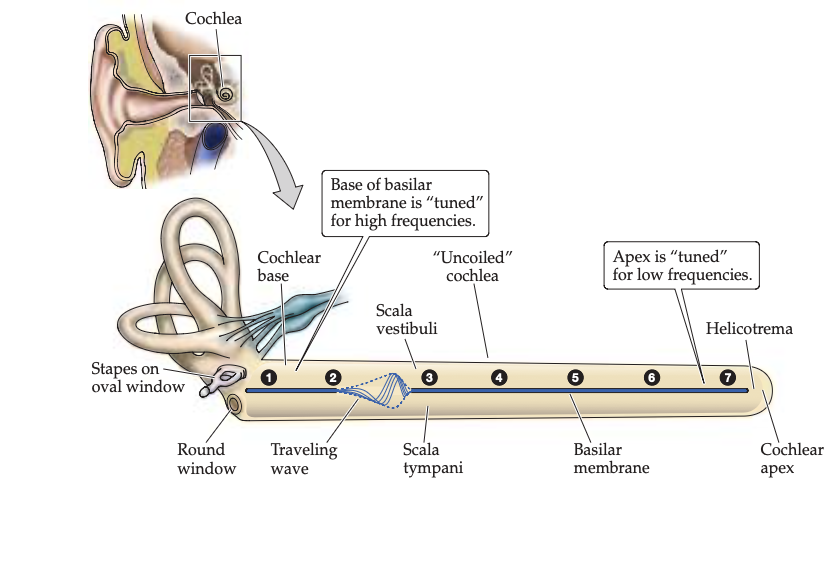
What role do hair cells play in sensory transduction?
Mechanotransduction (sound wave ➜ vibrate in ear ➜ ossicles amplify ➜ oval window ➜ vibrations create waves in cochlea fluid (perilymph and endolymph) ➜ basial membrane moves up and down ➜ hair cells bend
Sound waves and head movements create mechanical forces that cause endolymph fluid in the ear to move
The stereocilia bend and when they bend towards the kinocillium they open K channels and depolarise the cell as K comes in to an generate an receptor potential
This releases NT on afferent nerve fibres increasing their activity
The brain processes these signals to perceive sound (in hearing) or to maintain balance and spatial orientation (in the vestibular system).