Exam 2 Bio
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Subunit (monomer) of carbs
Monosaccharides (sugar)- one carbon chain
Subunit of proteins
Amino acids
Subunits of lipids
Glycerol/fatty acids
Subunits of nucleic acids (DNA/RNA)
Nucleotides
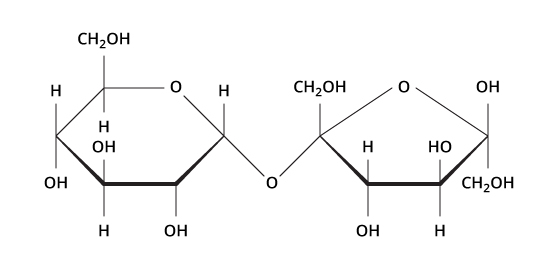
Carbohydrate
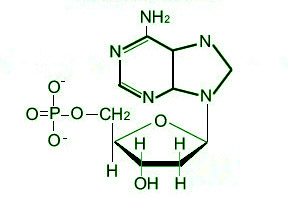
Nucleic Acid
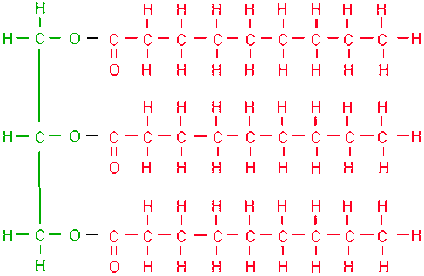
Lipid
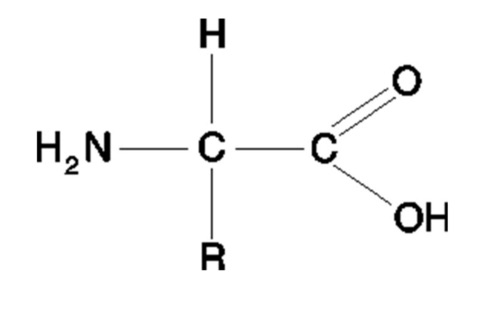
Amino acid
Function of monosaccharides
Quick energy + basic building block for all carbs
Function of disaccharides
Internal carb transport in plants + energy source like monosaccharides
Function of polysaccharides
Energy storage (plants-starch and animals-glycogen)
Structural (plants-cellulose (for cell wall) and animals(like insect shells)-chitin)
Unsaturated
Double bond creates bending
Saturated
All hydrogen filled in fatty acid
Triglycerides
3 fatty acids and glycerol
For energy storage
Phospholipid
Polar head, phosphate group, glycerol, 2 fatty acids
Form the fundamental structure of cell membranes by forming a bilayer
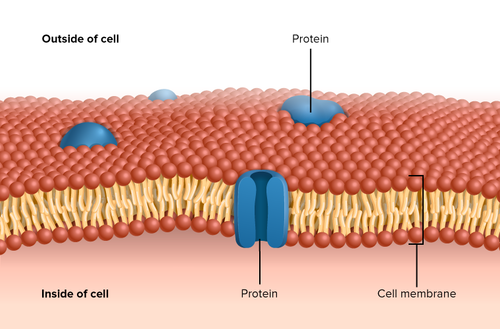
Function of proteins
Structural (keratin-hair)
Regulate body processes (enzymes-insulin-regulates glucose levels)
Transport materials (channel proteins in cell membrane)
How protein is synthesized
Amino acids are bonded dehydration synthesis and form peptide covalent bonds to create polypeptide, polypeptides fold into complex conformation to make protein
Hydrophobic amino acids are
Nonpolar
Hydrophilic amino acids are
Polar
Polar acidic amino acids are
Negatively charged
Polar basic amino acids are
Positively charged
Primary strucure is
AA connected through covalent peptide bonds in a chain
Secondary structure is
regions of localized folding formed by hydrogen bonds
Tertiary structure is
3D shape of polypeptides formed by side chain interaction
Quaternary structure is
Proteins with multiple subunits
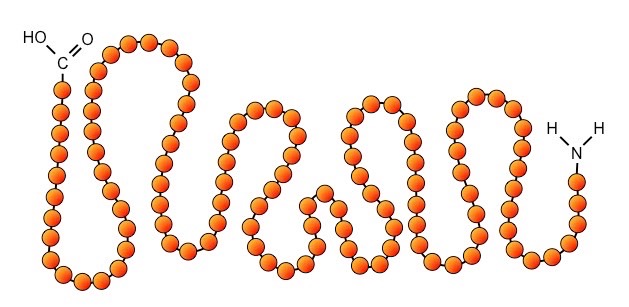
Primary structure

Secondary structure
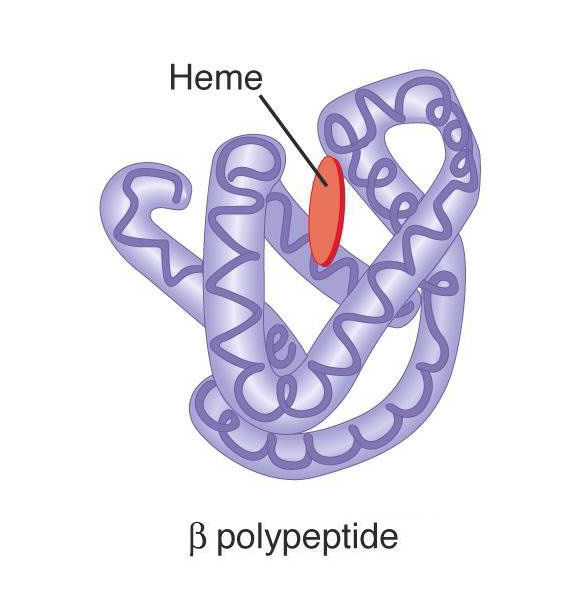
Tertiary structure
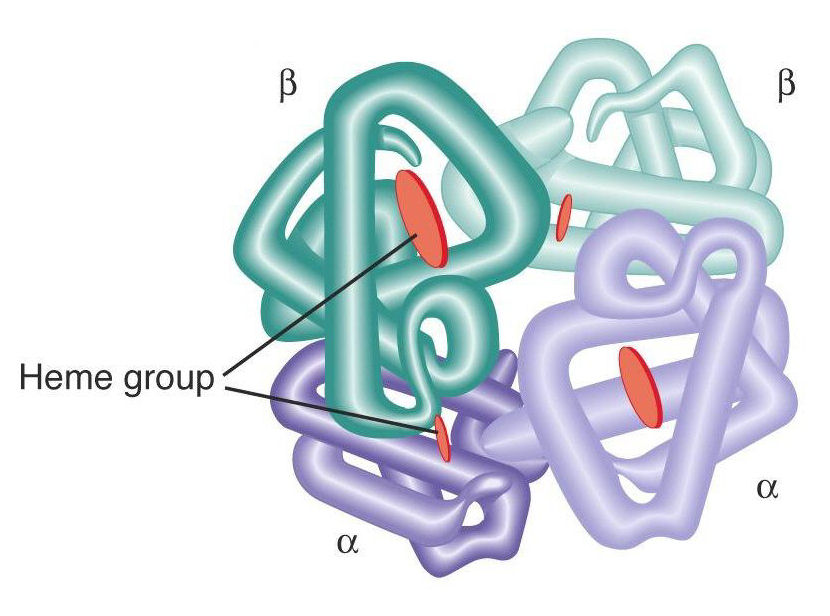
Quaternary structure
Traits of prokaryotic cells
No membrane bound organelles, DNA located in the cytoplasm (eukaryotes have them in nucleus)
Differences between plant and animal cells
Animals=centrosomes and lysosomes
Plants=cell wall, chloroplasts, central vacuole, specialized plastids
Cytoplasm
fluid and organelles within plasma membrane
Cytosol
Fluid component
Nucleus
Stores DNA
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane
Nuclear pores
For ribosomes
Mitochondria
Produce ATP- double membrane
Has own DNA and ribosomes
Performs cellular respiration/breakdown of glucose
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
Has own DNA and ribosomes- double outer membrane
3rd membrane forms thylakoid stacks with stroma (fluid) around it
Chlorophyll
Green, light absorbing pigment
Chloroplasts and mitochondria both have…
Double membrane, free ribosomes, circular DNA, grow and reproduce semi-independently
Ribosomes
Read mRNA instructions and synthesize proteins
Made of ribosomal RNA and protein
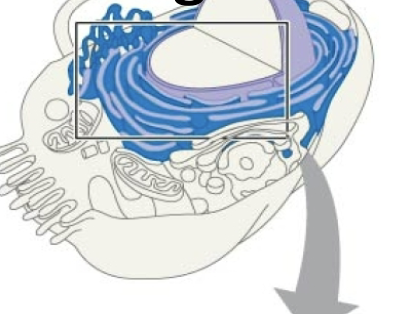
Endomembrane system
Regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions
Endomembrane consists of…
Nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane
Rough ER
Synthesis and export of secretory proteins and glycoproteins
Protein folding
Smooth ER
Synthesize lipids, metabolizes carbs, detoxifies drugs and poisons, stores calcium ions
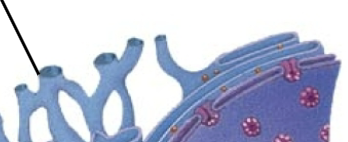
Golgi apparatus
Modifies products of ER, sorts and packages items into transport vesicles
Endosymbiotic theory
Mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from being seperate prokaryotic organisms
Components of cytoskeleton
Microtubule, Intermediate filament, Microfilament
Microtubules
Highway of cell, motor proteins use ATP to walk transport vesicles
Intermediate filaments
Only found in complex, multicellular organisms
Provide physical support and stability to cells
Microtubules (actin filaments)
Local roads of cell, motor proteins can travel on
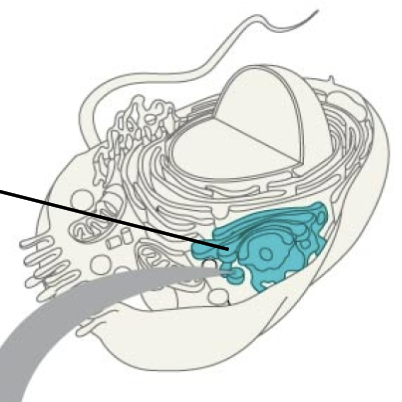
Lysosomes
Organelles that break down molecules, recycling center
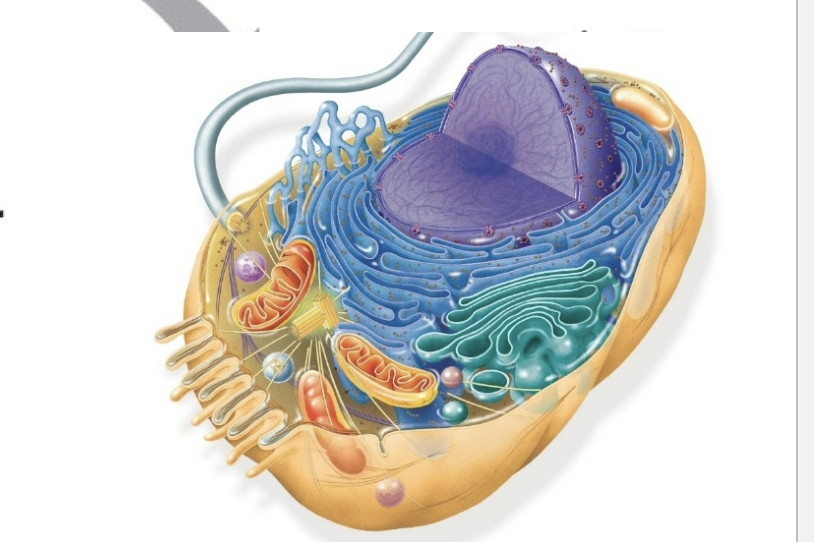
The purple thing in the center is
Nucleus
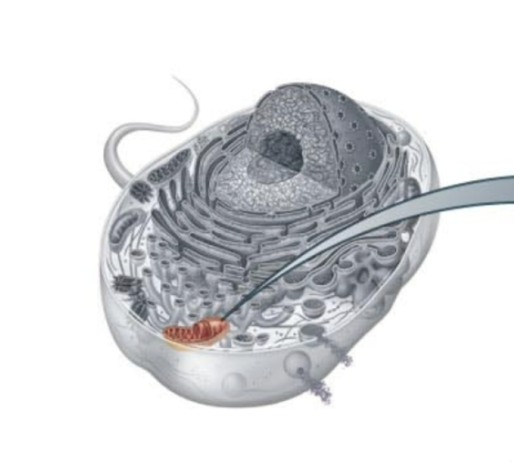
Mitchondria
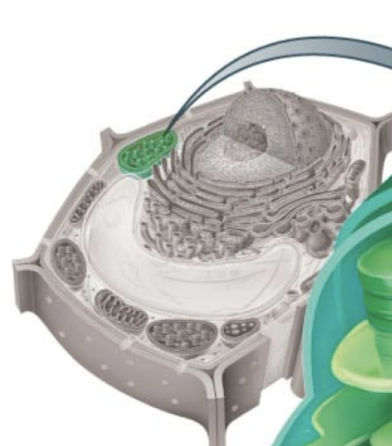
Chloroplast
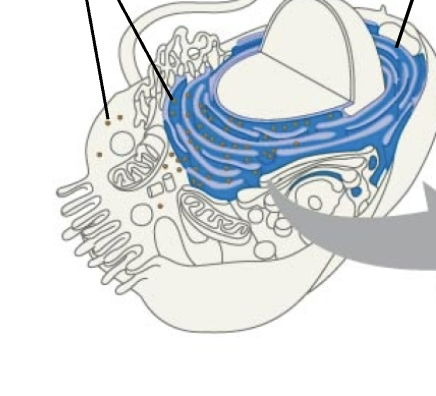
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum
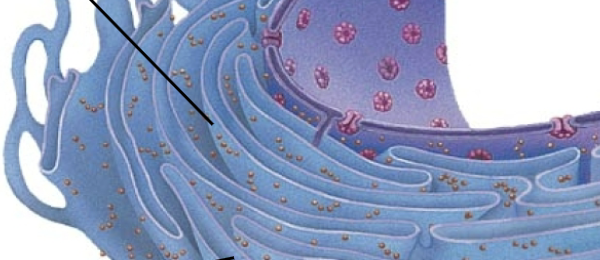
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
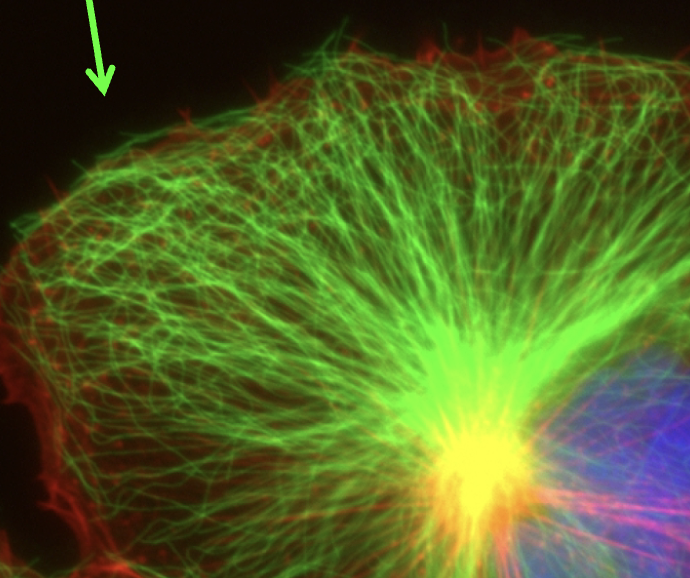
Microtubules
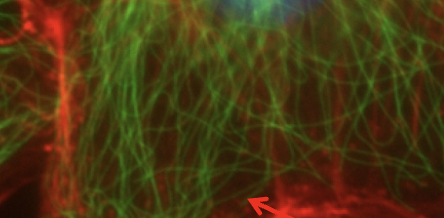
Microfilament/actin
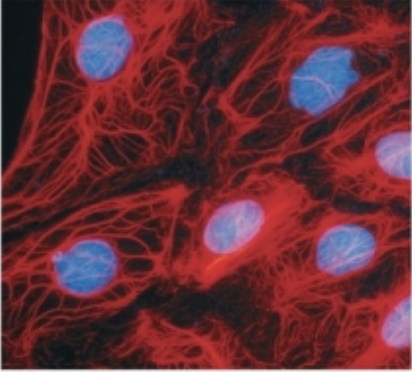
Intermediate filaments
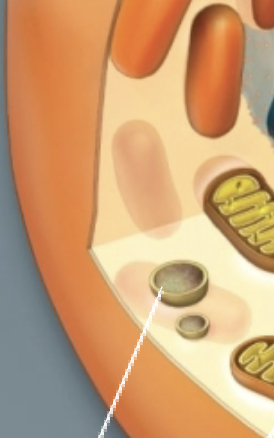
Lysosomes

Vesicle
Purpose of plasma membrane
Provides protection for cell and a fixed environment inside cell
Transport nutrients in and toxins out
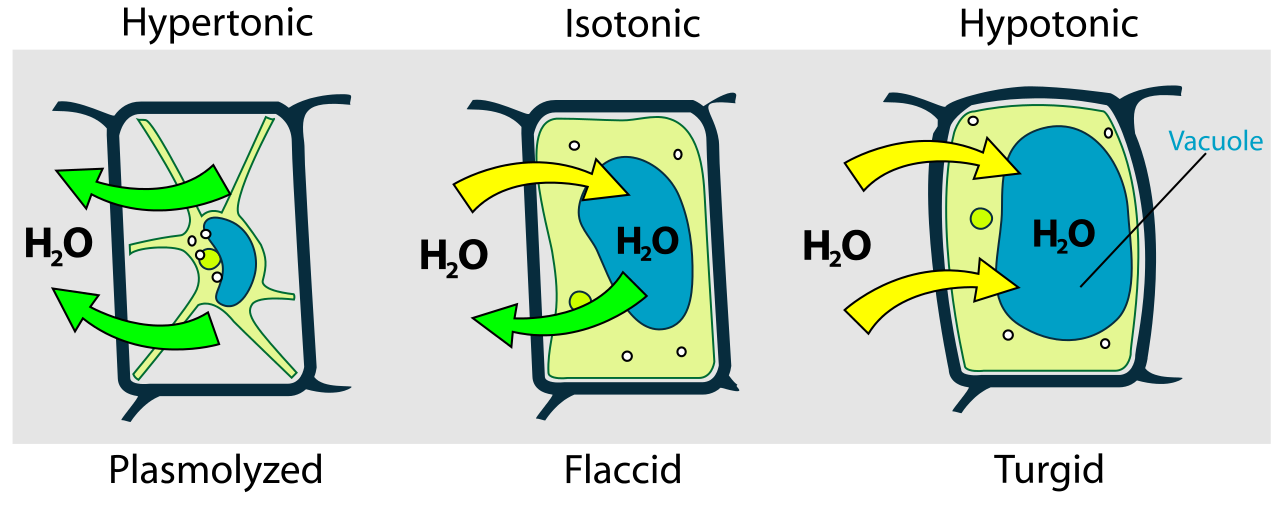
Purpose of cell wall
Provides strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic stress, allows for turgor pressure
First step for path of membrane protein
Protein is put into RER as ribosome makes it
Second step for path of membrane protein
Vesicle carries protein cargo from RER to Golgi where protein is modified
Third step for path of membrane protein
Vesicle carries protein cargo from Golgi to plasma membrane
Fourth step for path of membrane protein
Vesicle fuses to plasma membrane and the protein becomes a part of a membrane (secretory proteins are released through exocytosis)
-OH
Hydroxl, polar, in sugars and amino acids
CH3
Methyl, non polar, fatty acid chains
C=O/-CHO
Carbonyl, polar, sugars, amino acids, nucleotides
-COOH
Carboxyl, polar, amino acids and fatty acids
-NH2/-NH3+
Amino, polar, amino acids and nucleotides
-P
Phosphate, polar, nucleotides, proteins, phospholipids
Polar heads of lipids form what bonds with water
H-bonds
Unsaturation in membrane creates more
fluidity
Cholesterol makes lipid bilayers
less fluid, filling in the “gaps”
Molecules that can diffuse across membrane without protein-
Non-polar, H2O, some small polar
Molecules that need a protein to cross membrane-
Ions, most polar molecules
Energy is required to produce a chemical gradient, so
the chemical gradient is a form of stored energy
Channel proteins
Let solute cross membrane (H20 or ions) (passive, through diffusion down CG)
Passive/facilitated transport proteins
Allow small polar molecules to cross (passive, through diffusion down CG)
Active transporter proteins
Pump ions or polar molecules across (against CG, needs ATP)
Carrier proteins (must bind to cross)
Active transporters and passive/facilitated transporters
Proteins that move down the CG are
bidirectional
Voltage-gated ion channel
Open in response to change in voltage
Ligand-gated ion channel
Open in response to the binding of small chemical (ligand) to receptor
Mechanically-gated ion channel
Open in response to pressure
Examples of ion channels
Na+, K+
Active transporters are
unidirectional and specific + change in affinity
Example of passive transport protein
GLUT (glucose transporter)
Example of active transport protein
Na+/K+ pump
Really large molecules enter a cell through
Endocytosis (formation of vesicle)
Exocytosis
Exit of cell by vesicle binding to membrane
Primary active transport
Uses ATP
Secondary active transport
Uses electrochemical gradients
Activation energy
Required to begin reaction, slows down reactions