4.1.7 - balance of payments
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
two types of trade deficit
structural - caused by permanent issues with the economy
cyclical - caused by boom and bust cycle
structural trade deficit reasons
strong currency - imports cheaper (SPICED)
high inflation - exports more expensive for foreign buyers
lack of natural factor endowment - need to import
poor quality domestically - need to import
3 types of policies to reduce deficit
supply side - improve domestic
expenditure switching - protectionism (fix structural deficit)
expenditure reducing - reduce AD (fix cyclical deficit)
they could also just do nothing
good and bad about doing nothing
floating exchange rates are a self correcting mechanism - (over time more imports = currency depreciates = SPICED fixed)
might be other factors that stop the currency from depreciating
could take a long time to self correct
good and bad about supply side
improves quality + quantity of FoPs
lowers costs of production
(exports increase due to both)
long term policies = time lag
involves government spending
good and bad about expenditure switching
(currency depreciation, tariffs, etc)
successfully changes consumer buying habits (from foreign to domestically produced goods)
protectionism = retaliation
what effect can currency depreciation have on fixing a trade deficit
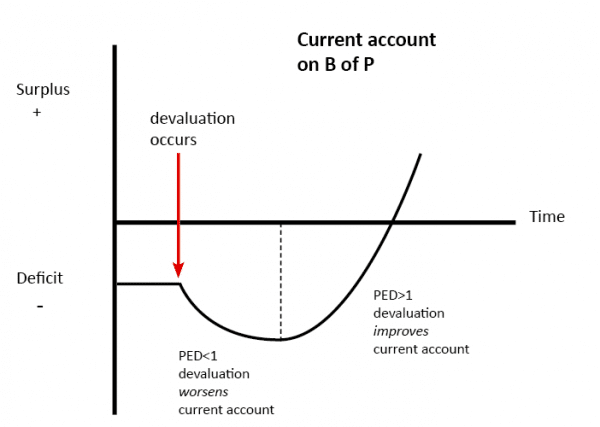
the j-curve effect
show + explain the J-Curve
SHORT-RUN:
TIME taken to substitute or terminate contracts means that:
weak currency = imports expensive = trade deficit worsens (bc it’s about value)
LONG-RUN:
deficit improves
what’s the name of the condition that summarises how the J-Curve works
the Marshall-Lerner condition:
if exports and imports PED adds to 1 or more, then a weaker currency will improve a trade deficit
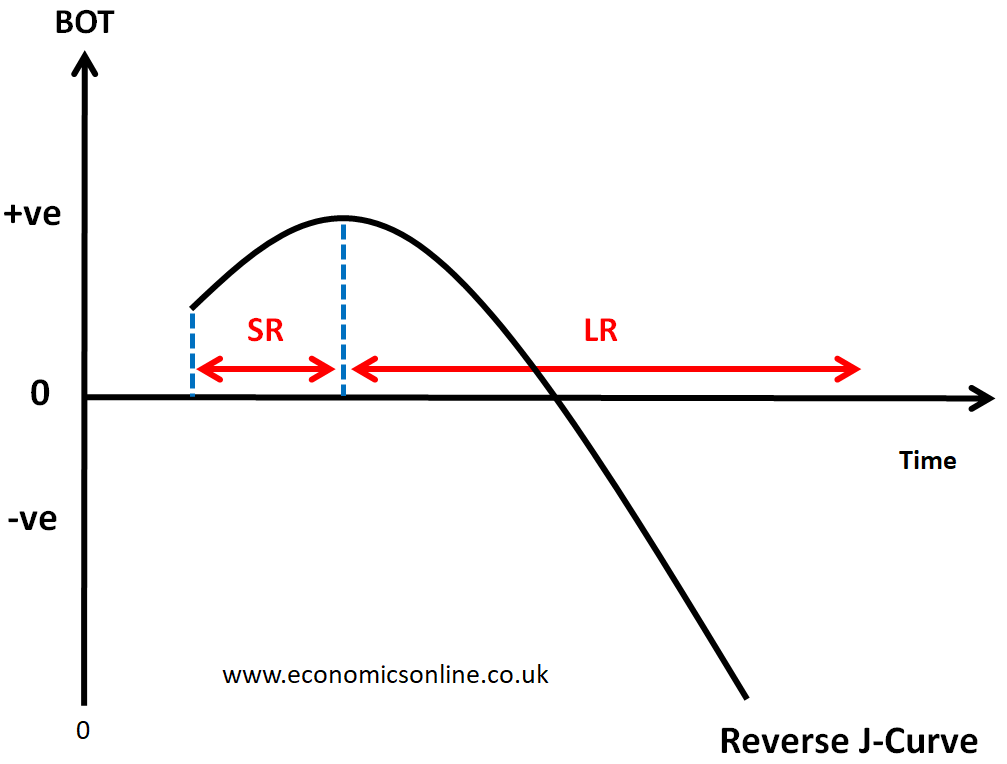
what else can the j curve do
be reverse - to fix a trade surplus
same thing applies but the other way around
good and bad about expenditure reducing
(interest rates, taxes, etc)
fall in discretionary income = demand falls for imported goods
reducing AD = GDP falls, unemployment rises
maths-wise, how does global trade work
NET ZERO - one country’s surplus is another country’s deficit
problems with persistent deficits
loans or FDI required to fund continued imports
—> a country may gradually sell its assets
—> owing money abroad = vulnerable
problems with persistent surpluses
nations resources allocated to meet foreign demand rather than domestic
—> limited availability of g+s localy
—> currency instability if exchange rate is floating