Chemistry Semester 2 Exam
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/155
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
1
New cards
Reactants
Starting materials of a reaction
2
New cards
Products
Ending materials of a reaction
3
New cards
Yields
→
4
New cards
Heat has been added to the reaction.
^
-→
-→
5
New cards
Reversible Reaction
--→
6
New cards
Catalyst
x
--→
--→
7
New cards
Diatomic elements
Elements that exist in pair when they are not bonded to something else. Br, I, N, O, H, F, Cl,
8
New cards
Chemical Energy
Energy stored in the bonds of chemical compounds. Can change when a substance undergoes a phase change.
9
New cards
Chemical Reaction
Can be indicated by:
\-color change, precipitation (formation of a solid), energy changes (temperature changes), formation of a light, formation of a gas.
\-color change, precipitation (formation of a solid), energy changes (temperature changes), formation of a light, formation of a gas.
10
New cards
Exothermic Reaction
This type of reaction gives off energy and therefore feels hot to the touch. This is usually represented on a graph as a negative, indicating that the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants.
11
New cards
Endothermic Reaction
This reaction absorbs energy and therefore feels cold to the touch. This is usually represented on a graph as a positive slope, indicating that the energy of the products is higher than that of the reactants.
12
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
The amount of mass/atoms is the same on both sides of a chemical equation.
13
New cards
Composition reaction
A reaction that is a combination of two things.
2 reactants and 1 product.
A + B → AB.
All reactions take place except two metals reacting and a noble gas reacting with another element.
2 reactants and 1 product.
A + B → AB.
All reactions take place except two metals reacting and a noble gas reacting with another element.
14
New cards
Decomposition
A reaction that involves one compound breaking down into 2 or more products
1 reactant and 2 products
AB→ A + B
All reactions take place
1 reactant and 2 products
AB→ A + B
All reactions take place
15
New cards
Single Replacement
A reaction that takes place between 1 free element and 1 compound that react to form a new free element and a new compound.
A=metal A+BY→ AY + B
X=nonmetal X+BY→ BX+ Y
This reaction takes place when the reactant free element is more reactive than the product free element.
Remember that free elements have no subscript unless diatomic.
A=metal A+BY→ AY + B
X=nonmetal X+BY→ BX+ Y
This reaction takes place when the reactant free element is more reactive than the product free element.
Remember that free elements have no subscript unless diatomic.
16
New cards
Double Replacement
A reaction that takes place when 2 ionic compounds form 2 new ionic compounds.
AX+BY → AY + BX
\*H2CO3 → H20 + CO2
H2SO3→ H20 +SO2
Takes place if one of the following happens
1) An insoluble solid is formed
2) A gas is formed
3) A molecular substance appears/disappears
\
AX+BY → AY + BX
\*H2CO3 → H20 + CO2
H2SO3→ H20 +SO2
Takes place if one of the following happens
1) An insoluble solid is formed
2) A gas is formed
3) A molecular substance appears/disappears
\
17
New cards
Combustion
A reaction that takes place when a hydrocarbon and oxygen react to form carbon dioxide and water.
C7H14O2→ CO2 +H2O
C7H14O2→ CO2 +H2O
18
New cards
Neutralization
A reaction that takes place when an acid and base form a salt and water.
HX+BOH → BX+ HOH
HX+BOH → BX+ HOH
19
New cards
Chemical Change
A change in which one substance is transformed into a new substance and new molecules are formed.
20
New cards
Physical Change
A usually reversible change in which the form of the matter is altered but is not changed into a different substance.
21
New cards
Chemical Energy
Energy stored in the bonds of molecules that can be released during a chemical reaction.
22
New cards
Phase Energy
Type of energy that is stored or released during a change in the state of matter and in the arrangement of particles Changes in this type of energy result in melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation.
23
New cards
Thermal Energy
The energy that an object possesses due to the motion of its particles. It is directly proportional to the object's temperature and can be transferred through conduction, convection, and radiation.
24
New cards
False, composition reactions don’t occur if there are two metals reacting.
True or false: Li can react with Mg to form Li2Mg.
25
New cards
True
True or false: all combustion reactions occur
26
New cards
False: It is a decomposition reaction.
True or false: 2MgO→2Mg+ O2 is a single replacement reaction.
27
New cards
False: The correct reaction is O2+ Li2S--> S + Li2O
True or false: O2+ Li2S--> Li + OS
28
New cards
x=molar mass
1 mole= x grams
29
New cards
x=6.02 \* 10^23
1 mole= x particles
30
New cards
x= 22.4
1 mole= X liters
31
New cards
Stoichiometrey
Using chemical equations to solve problems
32
New cards
Mole Ratio
(coefficient 1/change) = (coefficient 2/change)
33
New cards
Limiting Reagent
The chemical that runs out first and stops the reaction from progressing
34
New cards
Excess Reagent
The chemical that is left over at the end of the reaction.
35
New cards
Molarity
Moles of a solute dissolved in a liter of solution.
36
New cards
Molar
(M) refers to the unit of concentration molarity, which is equal to the number of moles per liter of a solution
37
New cards
Solute
Particles being dissolved in a solution
38
New cards
Solvent
The substance the solute is dissolved in to form a solution.
39
New cards
Concentration
Measure of the amount of a solute that is dissolved in a given quantity of a solvent at a certain temperature.
40
New cards
Dilute
Lots of solvent, little solute, low concentration
41
New cards
Concentration
Lots of solute, little solvent, high concentration.
42
New cards
False: If three cups of sugar are added there will be more than one liter of solution.
True or false: If 3 cups of sugar are added to 1 liter of solvent the molarity would be equal to 3 cups of sugar/1 liter of solvent.
43
New cards
Molarity
moles of solute/liters of solution =
44
New cards
\*Molarity
grams of solute/(molar mass of the solute/liters of solution)= \*
45
New cards
Grams of solute
Molarity\* *Molar Mass* Liters of Solution=*
46
New cards
Dilution
Adding a solvent to a solution to lower the concentration.
47
New cards
Dilution Equation
M1\**V1=M2*V2*
48
New cards
Thompson
He discovered the electron and came up with the plum pudding model of the electron.
49
New cards
Rutherford
He conducted the gold foil experiment where alpha particles were shot at a gold foil. His conclusions were that the atom is mostly empty space and that the center of the atom is positively charged. He discovered the nucleus.
50
New cards
Protons
Subatomic particles with a charge of +1, a mass of 1.673 \* 10^-27, and they are located in the nucleus.
51
New cards
Electron
Subatomic particles with a charge of -1, a mass of 9.109 \* 10^-31, and they are located orbiting the nucleus.
52
New cards
Neutrons
Subatomic particles with a charge of 0, a mass of 1.675 \* 10^-27, and they are located in the nucleus.
53
New cards
\#of electrons
In a neutral atom # of protons is equal to what?
54
New cards
Atomic Number
The number of protons in an atom--found on the periodic table.
55
New cards
Mass Number
The sum of protons and neutrons in an element.
56
New cards
Nuclear symbol
Symbol of an element with the mass# on the top and the atomic # on the bottom
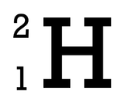
57
New cards
Isotopes
Multiple forms of the sane element that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers because they have a different number of neutrons. THey often have very similar properties
58
New cards
Atomic mass
This is equal to the mass number but measured in amu. THe average atomic mass is the average atomic mass of all of the isotopes of an element and is the same as the molar mass shown on the periodic table.
59
New cards
Natural elements
Elements 1-92
60
New cards
Man Made elements
Elements 93+
61
New cards
Radioactive Decay
Process of which a nucleus spontaneously disintegrated giving off radiation.
62
New cards
Nuclear Decay
Nuclear Reaction in which a nucleus is bombarded or struck by another nuclear particle in a particle accelerator.
63
New cards

\
Alpha particle
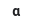
64
New cards
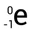
Beta Particle
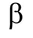
65
New cards
Gamma Particle
66
New cards
Atomic Theory
Must explain: atomic emission spectra, chemical reactivity, and organization of the periodic table.
67
New cards
Bohr’s Theory
Electrons travel in circular orbits, electrons have fixed amounts of energy, ladder theory that energy levels are evenly spaced. His theory was false.
68
New cards
Quantum Mechanical Model
This atomic theory estimates the probable location of an electron and states that energy levels are not evenly spaced but grow closer farther from the nucleus.
69
New cards
(n) Principal Quantum Number
Quantum Mechanical Model # that describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus
70
New cards
2 electrons
How many electrons does the first energy level hold?
71
New cards
8 electrons
How many electrons does the second energy level hold?
72
New cards
18 electrons
How many electrons does the 3rd energy level hold?
73
New cards
32 electrons
How many electrons does the 4th-7th energy level hold?
74
New cards
(l) Orbital Quantum Number
Quantum Mechanical Model # that describes the shape of the orbit.
75
New cards
Sphere (s)
This shape of electron orbit has 1 type, 1 orbit, and holds 2 electrons.
76
New cards
Dumbell (p)
This shape of electron orbit has 3 types, 3 orbits, and holds 6 electrons.
77
New cards
Clover (d)
This shape of electron orbit has 5 types, 5 orbits, and holds 10 electrons.
78
New cards
Undefined (f)
This shape of electron orbit has 7 types, 7 orbits, and holds 14 electrons.
79
New cards
(ml) Magnetic Quantum Number
Quantum Mechanical Model # that describes the electron’s position in space on the x, y, and z axis.
80
New cards
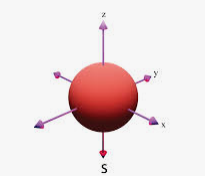
S
ml Sphere
81
New cards
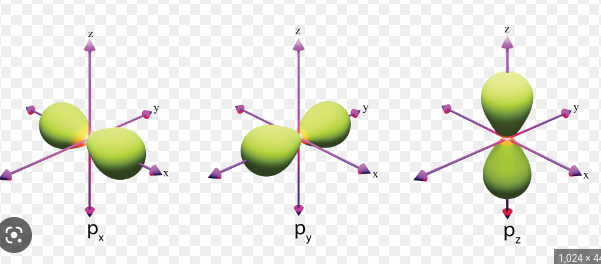
py, px, and pz
ml Dumbell
82
New cards
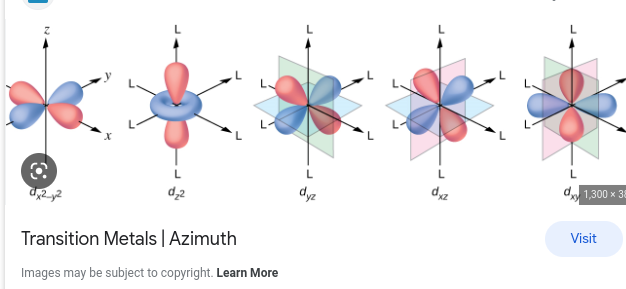
dxy, dxz, dyz, dx2y2, dz2
ml Clover
83
New cards
(ms) Spin Quantum Number
Quantum Mechanical Model # that describes the electron’s spin: up for clockwise, down for counterclockwise.
84
New cards
Light Wave Theory
Light are electromagnetic waves and white lights is all the light in the visible spectrum.
85
New cards
Light Particle Theory
All matter will absorb or release energy and light is particle of energy called photons.
86
New cards
Photon
Particle of light energy
87
New cards
Inverse relationship
Wavelength to frequency relationship
Wavelength to energy relationship
Wavelength to energy relationship
88
New cards
Direct Relationship
Frequency to energy relationship
89
New cards
Atomic Emissions Spectra
Electrons absorb energy and jump to a higher energy level. Electrons lose energy and return to ground state giving off photons/light. The color of light depends on the identity of the element and the energy level of the electron.
3 truths:
\-electrons absorb and released particles of energy as they move up and down energy levels
\-they absorb only particles of a specific frequency
\-they release photons with specific frequency
3 truths:
\-electrons absorb and released particles of energy as they move up and down energy levels
\-they absorb only particles of a specific frequency
\-they release photons with specific frequency
90
New cards
Electron Configurations
Notations for elements that give the location and # of electrons around the nucleus.
91
New cards
True
True or false: electron configuration follows this pattern:
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p
92
New cards
John Newlands
He discovered the law of octaves which states that elements in a row have similar chemical and physical properties and these properties repeat every 8 elements.
93
New cards
Law of octaves
Elements when arranged in a row have similar chemical and physical properties and that repeat every 8 elements.
94
New cards
Dimitri Mendeleev
He made the first periodic table but is was arranged in order of increasing atomic mass.
95
New cards
Mosley
He made the modern periodic table that is arranged in order of increasing atomic number .
96
New cards
Periodic Law
When elements are arranged according to their atomic #s elements with similar properties appear at regular intervals.
97
New cards
Valence Electrons
S and P electrons that are found in the outermost shell of an atom. They determine the atom’s chemical properties and are the only electrons involved in bonding. Elements in the same column have the same number of these explaining why they have similar properties.
98
New cards
Group
A vertical column on the periodic table, elements in this share the same number of valence electrons and therefore have similar properties.
99
New cards
Period
A horizontal row on the periodic table. Elements in this row share the same energy level.
100
New cards
Electron Shielding
When electrons in lower energy levels block the pull of the positively charged nucleus on outer electrons.