AMS Study Guide - Radar Meteorology
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Radar Meteorology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the WSR-88D?
Stands for Weather Surveillance Radar 88 Doppler
What is the difference between a Doppler Radar and a Dual-Polarization radar?
The Doppler only emits a horizontal signal. Dual Polarization Radar emits a vertical and horizontal pulse to give a better idea of the side of a hydrometer or object the radar beam hits
How often does the radar scan?
Every 4-6 minutes
What do the red and green color son the radars velocity product indicate?
Red shows winds that are going away from the radar, green shows winds going towards the radar site
Base Velocity helps to better detect ________, while storm Relative Velocity helps us to detect _______.
Straight Line Winds; Rotation or Tornadic activity
What is virga?
When we have rain in the upper levels of the atmosphere, but dry air at the surface. Essentially the rain evaporates before it even reaches the ground due to the dry air in place in the atmosphere
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Clear Air Mode with a Radar?
It is very sensitive, but much slower as a result
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Precipitation Mode with a Radar?
It is less sensitive, but much faster
How large is a hydrometer to the radar?
6
What is the “Zero Zone”?
Where the winds are perpendicular to the radar, and the radar velocity is zero
Also known as Zero Isodop
True or False: The resolution of the radar decreases when the distance increases
True
If the radar beam is 1 degree, can it pick up a tornado signature at 120 nm?
No
What is the average Radar Beam?
95 degrees
The Average radar beam can only pick up detailed structures, such as tornadoes, at what distance?
Within 48 nm
If a radar beam is at 0.5-degree tilt, at 120 nm, how far above the ground is the beam?
10,000 to 15,000 feet
Ground clutter picked up by the radar beam may be: Birds, Bugs, Traffic, Building or all of the above
All of the Above
What does red indicate in the velocity product of radar?
Winds moving away from the radar sight
True or False: Radar can detect precise precipitation amounts or Flash Flooding?
False
If rain hits the radome, what does it do: Increases Sensitivity, Decreases sensitivity, or Disrupts the Scan?
Decreases Sensitivity
What is the definition of Velocity Aliasing?
AKA Velocity Folding
Happens when the radar can not measure speeds above a certain limit, so it “wraps” or “folds” the velocity values in the wrong direction or to a lower value.
What is the dispersion of Velocities within the radar sample volume called?
Spectrum Width
Can be used to detect tornado vortex signatures
When the unambiguous range increases, the PRF of the radar (Increases or Decreases)?
Decreases
How can you identify 1 inch + hail on radar?
Three Scale Body
What is the Doppler Dilemma?
Deals with Range vs Velocity with Pulse Frequency (PRF)
LOW PRF means you have a high range, but low velocity
HIGH PRF means you have low range, but high velocity
What is the Marshall Palmer Relationship?
The Relationship between Reflectivity and Rainfall Rate
True or False: A microburst will show divergence on radar
True
How can you identify Divergence (Cyclonic) on Radar?
Winds moving away from radar (red) and towards the radar (green) create a counter clockwise or cyclonic rotation
How can you identify Convergence (Anti-cyclonic) on radar?
Winds moving away from the radar (red) and towards the radar (green) create a clockwise or anti-cyclonic rotation
What is the “Cone of Silence”?
The area directly above the radar
Happens because the radar beam can not extend vertically in the atmosphere, so we have little idea as to what is occurring directly over the radar site.
What is the X-Band on Radar?
They are Sub-bands used by Military, Government & Civil Institutions for Weather Monitoring, Defense Tracking and Speed Detection
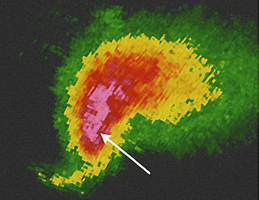
Identify this radar Signature:
Hail Core
Looking for high reflectivity values (pink or purple) located in the main body of a thunderstorm
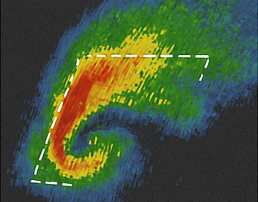
Identify this radar Signature:
Forward Flank
Positioned on the leading edge of the storm. Look for moderately high reflectivity (green and yellow) expecting from the core of the main storm
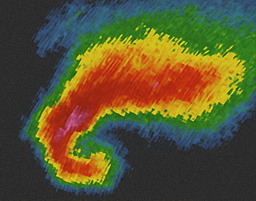
Identify this radar Signature:
Rear Flank
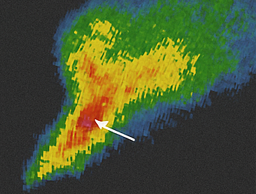
A clear spot or weak echo region on the backside of the storm. Located at the rear. It curves around the back of the storm forming a “hook” with heavy precipitation to the east.
Identify this radar Signature:
Flanking Line
Look for lower reflectivity values (green to yellow) indicating a line of developing cells. Positioned to the southwest of a main supercell. Looking for a linear or stair-step structure of smaller, developing cumulus clouds.
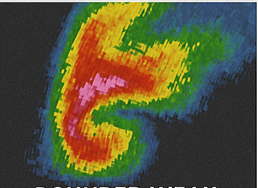
Identify this radar Signature:
Bounded Weak Echo Region
A weak echo region surrounded by high reflectivity. Typically found near the center of a strong thunderstorm of supercell
A donut or hole-like appearance within intense reflectivity, indicating a strong updraft
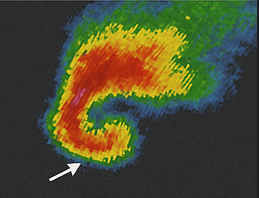
Identify this radar Signature:
Hook Echo
A distinctive, curved or hook-like structure extended from the main storm body. A spiral or “comma” shape, often pointing towards the rear of the storm
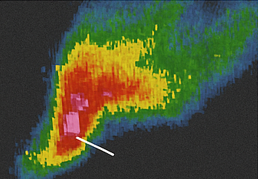
Identify this radar Signature:
V notch or “Flying Eagle”
Strong upper-level winds moving moisture downwind, producing a V shape as precipitation goes outwards on radar
A clear “V’ or wedge shape, indicating strong upper-level divergence
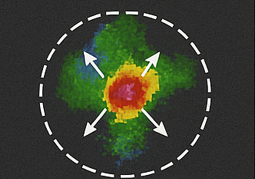
Identify this radar Signature:
Diverging Flow Updraft
Opposing wind directions, typically in the mid-levels of a storm. Look for a clear split in wind directions with a strong gradient
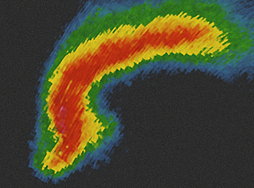
Identify this radar Signature:
Bow Echo
A bow-shaped or arced band of high reflectivity

Identify this radar Signature:
Debris Ball (NEED TO ADD IMAGE)
Extremely high reflectivity (usually pink, purple or white) within the hook echo or a tornadic storm