Human Growth and Development Theories Overview
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What is the ID in Freud's theory of personality?
The ID is the amoral, impulsive part of the personality that is ruled by the unconscious and demands immediate gratification, representing drives related to hunger, sex, aggression, and irrational impulses.
How does the superego function in Freud's personality theory?
The superego consists of internalized parental and societal restrictions, acting as a moralistic force that seeks to deny the irrational impulses of the ID, rewarding the ego with self-esteem or punishing it with guilt.
At what age does the superego typically develop?
The superego develops at around 6 to 7 years of age.
What role does the ego play in Freud's personality structure?
The ego is the rational part of the personality that acts as a buffer between the real world and the ID, mediating between the demands of the ID and the restrictions of the superego.
When does the ego typically develop?
The ego develops at around 2 to 3 years of age.
Provide an example of the ID in action.
An example of the ID is a child wanting to eat an entire cake without caring about rules or consequences.
Provide an example of the superego in action.
An example of the superego is a person feeling guilty for wanting to eat a cake that isn't theirs, knowing it is selfish.
Provide an example of the ego in action.
An example of the ego is a person deciding to ask if they can have a small slice of cake instead of taking it without permission.
What is Freud's view on the significance of childhood experiences?
Freud believed that childhood experiences profoundly affect adult life, shaping personality and behavior.
What are the three parts of Freud's personality theory?
The three parts are the ID, the superego, and the ego.
What does Freud mean by the unconscious mind?
The unconscious mind represents the individual's internal wants and desires that are hidden from conscious awareness.
What is the conscious mind according to Freud?
The conscious mind is the part of the mind that allows individuals to choose their actions based on right or wrong, likened to the tip of an iceberg.
What is the preconscious mind?
The preconscious mind contains memories that can be recalled.
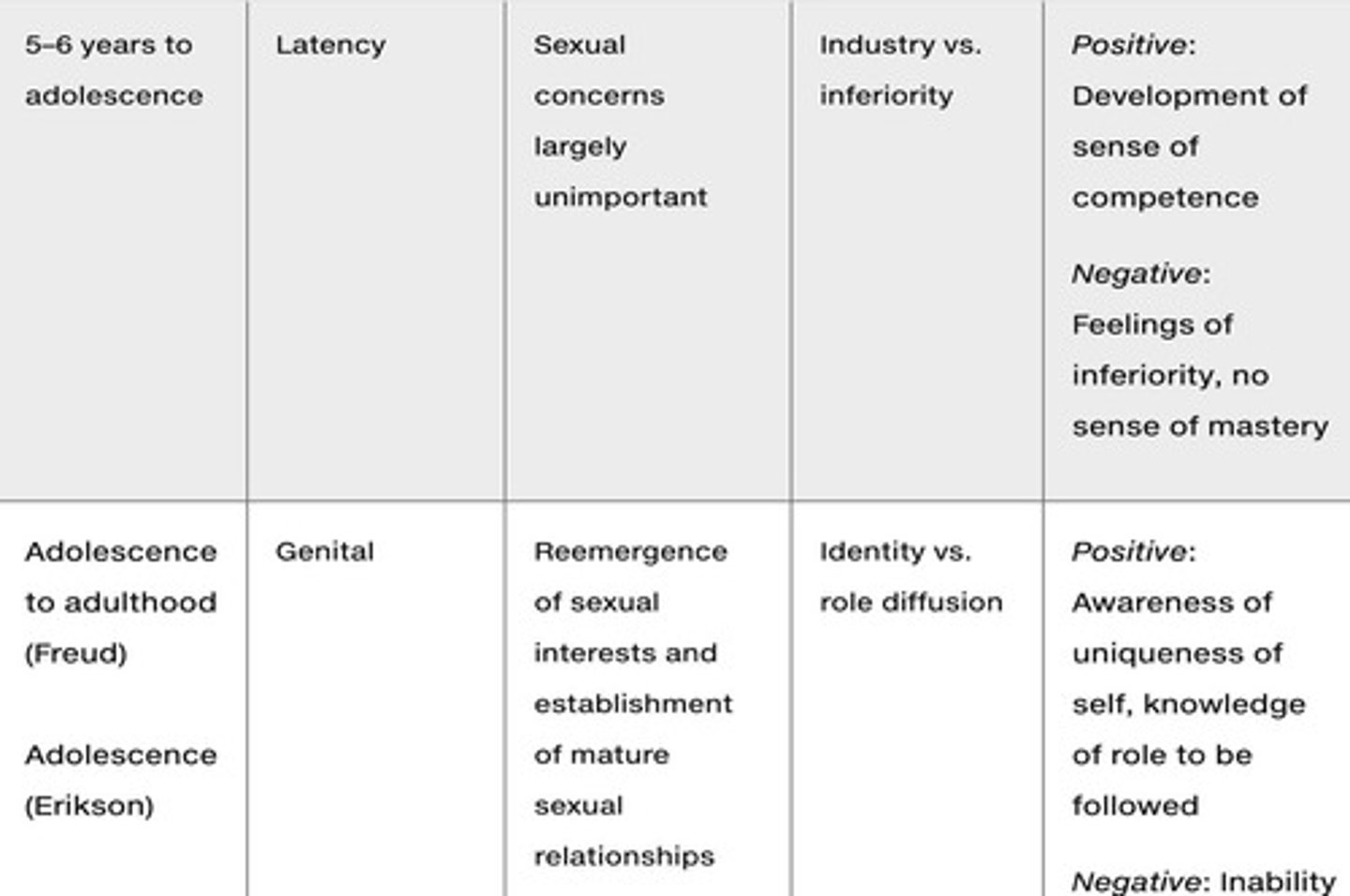
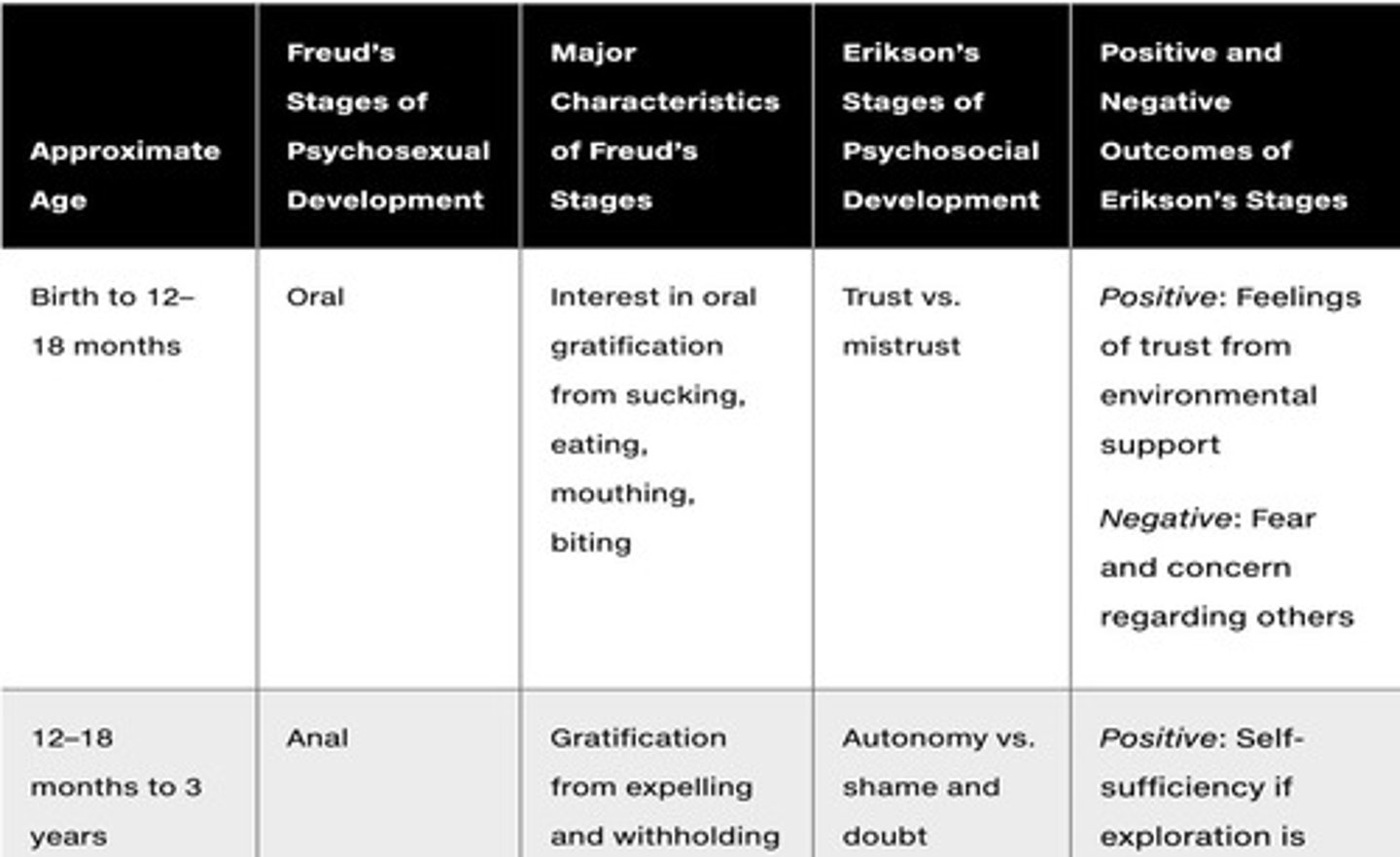
What is Freud's theory of psychosexual development?
Freud's psychosexual development theory posits that personality develops through a series of stages based on the ability to control internal needs and sexual energy, with potential fixation leading to adult behaviors.
What can result from failure to progress through Freud's psychosexual stages?
Failure to progress smoothly through a stage can result in adult behaviors that are fixated on that stage.
What era influenced Freud's views on sexuality?
Freud's views were influenced by the Victorian era, characterized by stifling morality and attitudes toward sexuality.
What is the role of caregivers in Freud's perspective on child development?
Caregivers should be understanding and empathetic towards children's emotional states, as these experiences shape personality.
What does Freud's theory suggest about the relationship between childhood decisions and adult personality?
Freud's theory suggests that decisions made in childhood significantly shape the personality and behavior of teenagers and adults.
How does the ID relate to pleasure-seeking behavior?
The ID seeks immediate gratification and pleasure without regard for rules or consequences.
What metaphor does Freud use to describe the conscious mind?
Freud likens the conscious mind to the tip of an iceberg.
What happens when the superego successfully controls the ego?
When the superego successfully controls the ego, it rewards the ego by building up self-esteem.
What happens when the superego fails to control the ego?
When the superego fails to control the ego, it punishes the ego with a guilty conscience.
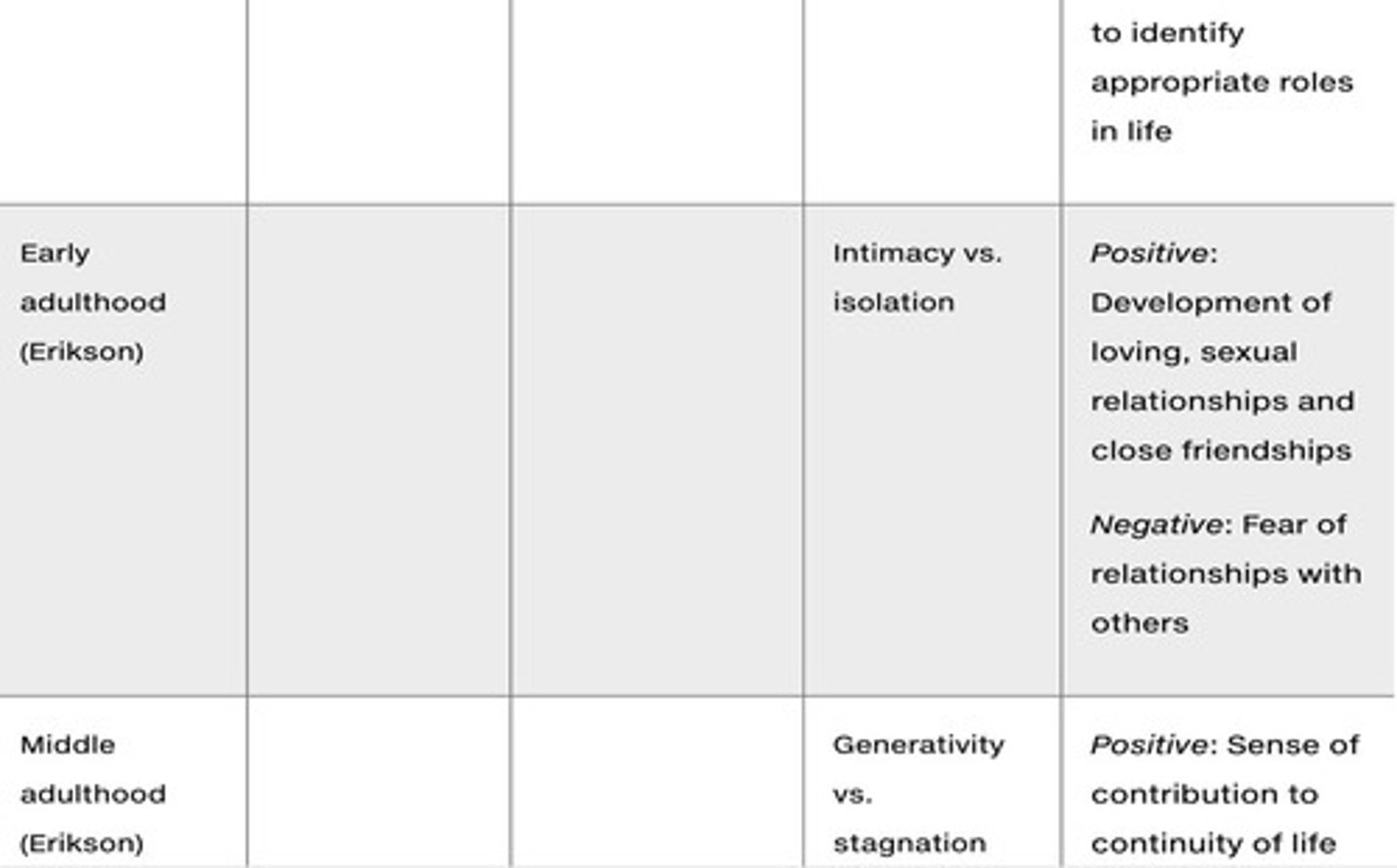
What is the main focus of Erik Erikson's Psychosocial Development theory?
It focuses on personality development through 8 stages, each with a unique psychological crisis influenced by caregivers.
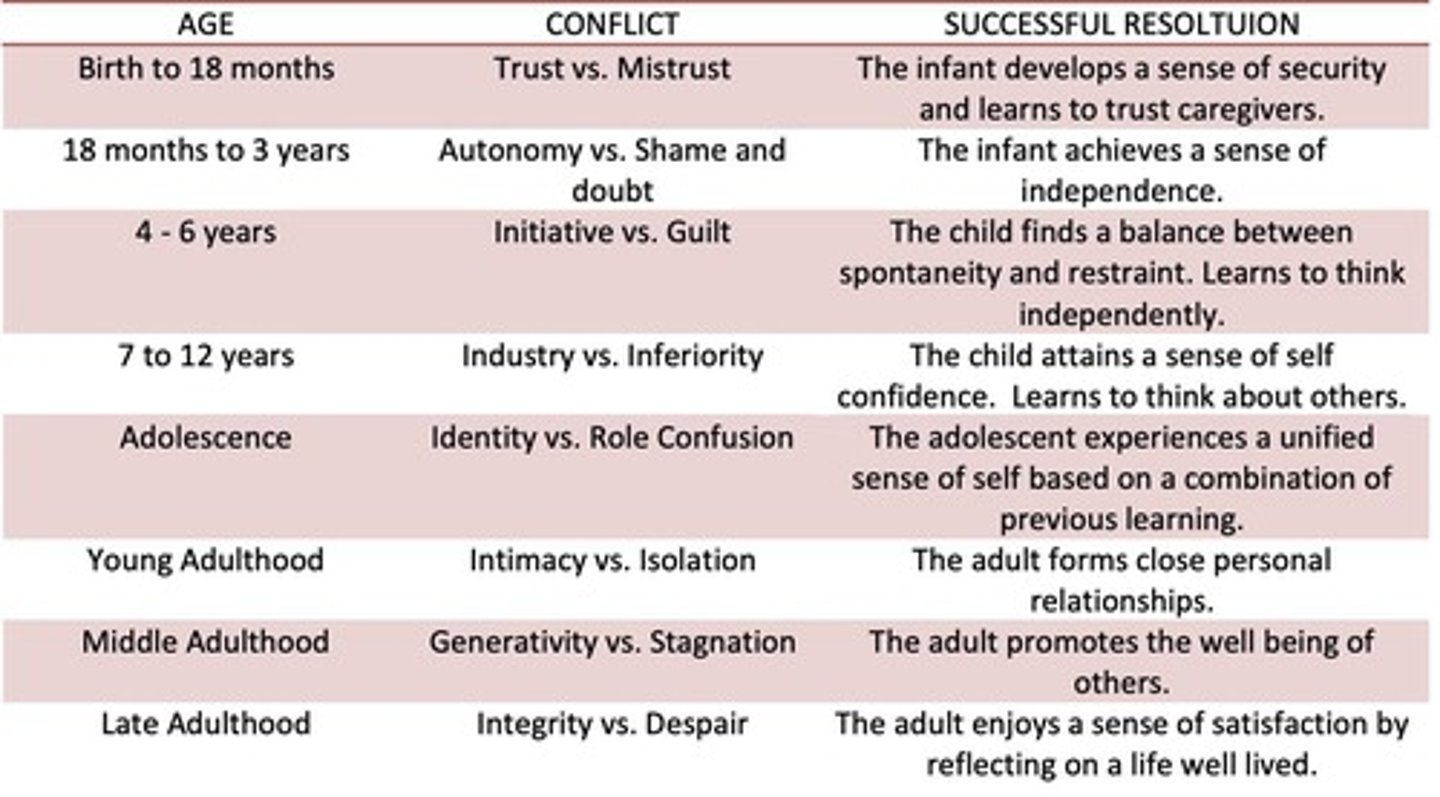
How many stages are there in Erikson's theory of psychosocial development?
Eight stages, starting from infancy and ending with old age.
What happens if a person encounters problems in any of Erikson's stages?
They may develop an identity crisis that affects them later in life.
Why are Erikson's ideas significant for caregivers?
They provide a framework for meeting the emotional needs of children from infancy to adolescence.
What is Jean Piaget known for in the field of intellectual development?
He was the first to study children scientifically, observing their intellectual development through real-life observations.
How many stages are there in Piaget's theory of cognitive development?
Four stages, which children progress through from infancy to adolescence.
What is the Sensorimotor Stage and its age range according to Piaget?
It spans from birth to 2 years, where children understand the world through their senses and actions.
What key concept do children learn during the Sensorimotor Stage?
Object permanence, along with basic shapes and textures.
What characterizes the Preoperational Stage in Piaget's theory?
It occurs from ages 2 to 7, where children understand the world through language and images, but lack logical thinking.
What is egocentrism in the context of Piaget's Preoperational Stage?
The inability to perceive reality from others' points of view.
What abilities develop during the Concrete Operational Stage?
Logical thinking, empathy, understanding patterns, and cause-and-effect relationships.
What is the age range for the Concrete Operational Stage?
From ages 7 to 12 years.
What is the Formal Operations Stage and its age range?
It begins at age 13 and continues into adulthood, characterized by abstract thinking and the ability to understand hypothetical situations.
Why are Piaget's ideas significant for child development?
They emphasize that nurturance should be appropriate for the child's stage of cognitive development.
What did Piaget believe about mastering stages of cognitive development?
A child must master one stage before progressing to the next; failure to do so can hinder their full potential.
What was Erikson's professional background before developing his theory?
He was a German psychologist who later moved to America and studied under Freud.
How did Erikson's theory differ from Freud's?
Erikson refined Freud's ideas by focusing on psychosocial development across the lifespan rather than just psychosexual stages.
What role do caregivers play in Erikson's theory?
Their responses to children's needs at each stage influence the outcomes of psychosocial development.
What is the significance of Piaget's observations of his children?
They provided the basis for his scientific study of intellectual development.
What is the relationship between intellectual development and other aspects of development according to Piaget?
He believed intellectual development controls every other aspect of development.
What does the term 'object conservation' refer to in the context of Piaget's Concrete Operational Stage?
The understanding that objects maintain their properties despite changes in form or appearance.
What is the significance of Piaget's theory in educational settings?
It informs how teaching and learning should be tailored to the cognitive abilities of children at different stages.
What is the main focus of Piaget's theory regarding children's development?
Piaget's theory focuses on how children's thinking develops with age and experience, emphasizing that tasks must be appropriate for their cognitive abilities.
What is a schema according to Piaget?
A schema is a cognitive structure that helps organize mental representations related to particular experiences, allowing children to understand and interact with their environment.
How do infants use schemas when interacting with objects?
Infants experiment with objects by looking at, grasping, sucking, banging, and dropping them, effectively acting as little scientists to discover the best schema for the object.
What are the three processes Piaget describes in cognitive development?
Assimilation, accommodation, and equilibration.
What is assimilation in Piaget's theory?
Assimilation is the process by which infants absorb new information in a way that fits their existing schemas.
What does accommodation mean in the context of Piaget's theory?
Accommodation refers to the changes made in existing cognitive structures to incorporate new stimuli or experiences.
What is equilibration according to Piaget?
Equilibration is the process of balancing assimilation and accommodation to create a stable understanding of new and existing knowledge.
How does Piaget view the development of schemas over time?
Schemas are not fixed; they develop and become more sophisticated and abstract as children grow older.
What did Maria Montessori believe about children's learning?
Montessori believed that children learn best through self-directed exploration using their senses and pursuing their interests.
How did Montessori incorporate Piaget's theories into her educational methods?
Montessori used Piaget's theories as a foundation for her teaching methods, emphasizing the importance of allowing children to learn at their own pace.
What was Montessori's view on children from poverty-stricken areas?
Montessori believed that children from poverty-stricken areas needed better educational opportunities to promote their success.
What role do innate skills and talents play in Montessori's educational philosophy?
Montessori emphasized that children have innate skills and talents that should be nurtured through appropriate educational practices.
What is the significance of self-directed learning in Montessori's approach?
Self-directed learning allows children to engage with their interests and learn in a way that is meaningful to them, rather than being forced into a rigid curriculum.
How does Piaget's theory address the psychological impact of difficult tasks on children?
Piaget suggests that giving children tasks that are too difficult can negatively affect them psychologically and emotionally.
What is the role of experience in Piaget's theory of cognitive development?
Experience is crucial as it helps children construct their understanding of reality and develop their cognitive abilities.
What is the difference between concrete and abstract schemes in children?
In infants, schemes represent concrete behaviors, while in older children, schemes become more sophisticated and abstract.
How does Piaget's theory relate to the concept of learning readiness?
Piaget's theory implies that children must be developmentally ready to learn certain concepts, as tasks that are too advanced can hinder their progress.
What is the impact of Piaget's theory on educational practices?
Piaget's theory has influenced educational practices by highlighting the importance of age-appropriate learning experiences that align with children's cognitive development.
What is the significance of the 'little scientist' analogy in Piaget's theory?
The 'little scientist' analogy illustrates how children actively explore and experiment with their environment to develop their understanding and schemas.
What is the relationship between schemas and meaning in Piaget's theory?
Schemas provide the basis for understanding, as they allow children to attribute meaning to their experiences.
How did Piaget's theory overlook adult intellectual development?
Piaget's theory primarily focuses on the cognitive development of children and does not extensively address the stages of intellectual development in adults.
What are sensitive periods in child development according to Montessori's philosophy?
Sensitive periods indicate when a child is ready to learn.
How does Montessori's educational philosophy view traditional forms of achievement?
It discourages many traditional forms of achievement such as grades and tests.
What is the role of teachers in a Montessori classroom?
Teachers should provide necessary resources for independent learning and intrude as little as possible.
What is emphasized in Montessori education regarding group lessons?
Group lessons are kept to a minimum, stressing independent exploration.
What types of activities are stressed in Montessori education?
Real-life experiences and hands-on activities.
What happens when age-appropriate learning materials are provided in Montessori education?
Children will take over the learning process.
List the six concepts that describe Montessori's educational theory.
1. Independence - let the child choose; 2. Observation - watch how they enjoy themselves; 3. Following the child - be non-directive; 4. Correcting the child - do not yell for unintentional mistakes; 5. Prepared environment - adult's role is to construct the child's learning environment; 6. Absorbent mind - the child absorbs learning through experience.
Why are Montessori's ideas significant in education?
Montessori emphasized the need for adults to provide resources for children to learn, highlighting the importance of hands-on learning and self-motivation.
Who is Howard Gardner and what is he known for?
Howard Gardner is an American psychologist known for his theory of Multiple Intelligences.
What did Gardner's theory of Multiple Intelligences challenge?
It challenged the idea that humans have a single, fixed intelligence.
How many different intelligences did Gardner propose humans possess?
Initially seven, and later expanded to nine.
What are the types of intelligences identified by Gardner?
Logical-mathematical, linguistic, visual-spatial, musical, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, and intrapersonal intelligence.
What impact did Gardner's ideas have on education?
His theory revolutionized classrooms by encouraging teachers to present material in ways that consider different intelligences.
What did Gardner believe about how individuals approach tasks?
He believed individuals draw on multiple types of intelligence when approaching tasks.
What was Gardner's educational background?
He studied at Harvard University and was tutored by Erik Erikson.
What is a key aspect of Gardner's theory regarding intelligence tests?
He argued that intelligence is multidimensional and cannot be fully measured by traditional intelligence tests.
How did Gardner's work influence teaching practices in North America?
It led to a shift towards recognizing and accommodating various learning styles in educational practices.
What is the significance of hands-on learning in Montessori education?
It is viewed as a form of work that facilitates deeper engagement and understanding.
What does the term 'absorbent mind' refer to in Montessori education?
It refers to the child's ability to absorb learning from a well-prepared environment.
What is the importance of the prepared environment in Montessori education?
It is considered the most important aspect, as it allows children to learn effectively.
How does Montessori suggest correcting a child's mistakes?
By not yelling at the child for unintentional mistakes.
What is the significance of observation in Montessori education?
It helps teachers understand how children enjoy themselves and what they need for learning.