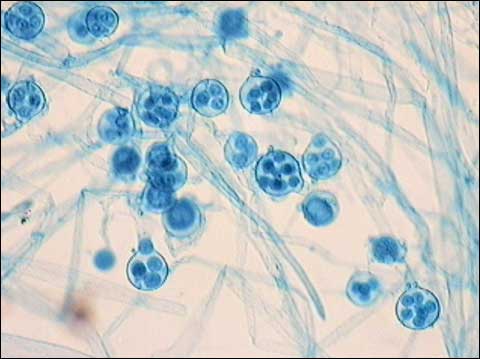
Bot-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 2: Protists
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
kingdom protista
a diverse kingdom of eukaryotic organisms, most of them possessing chlorophyll and other pigments confined to chloroplasts
chlorophyll
green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy
embryophytes
land plants
aquatic/damp habitats
habitat of choice for protists
phytoplankton
comprised mostly of unicellular algae and some cyanobacteria
zooxanthellae
unicellular, golden-brown algae (dinoflagellates) that live either in the water column as plankton or symbiotically inside the tissue of other organisms
asexually
all protists can reproduce _________
Phylum Haptophyta (Coccolithphorids)
primarily unicellular; cells covered with calcium carbonate scales called coccoliths; most available species exist as marine plankton; known to cause white tides
Phylum Bacillariophyta (Diatoms)
primarily unicellular; cells walls are made of silica; can be found in both freshwater and marine habitats; two basic types: centric (radially symmetrical) and pinnate (bilaterally symmetrical); diatomaceous earth
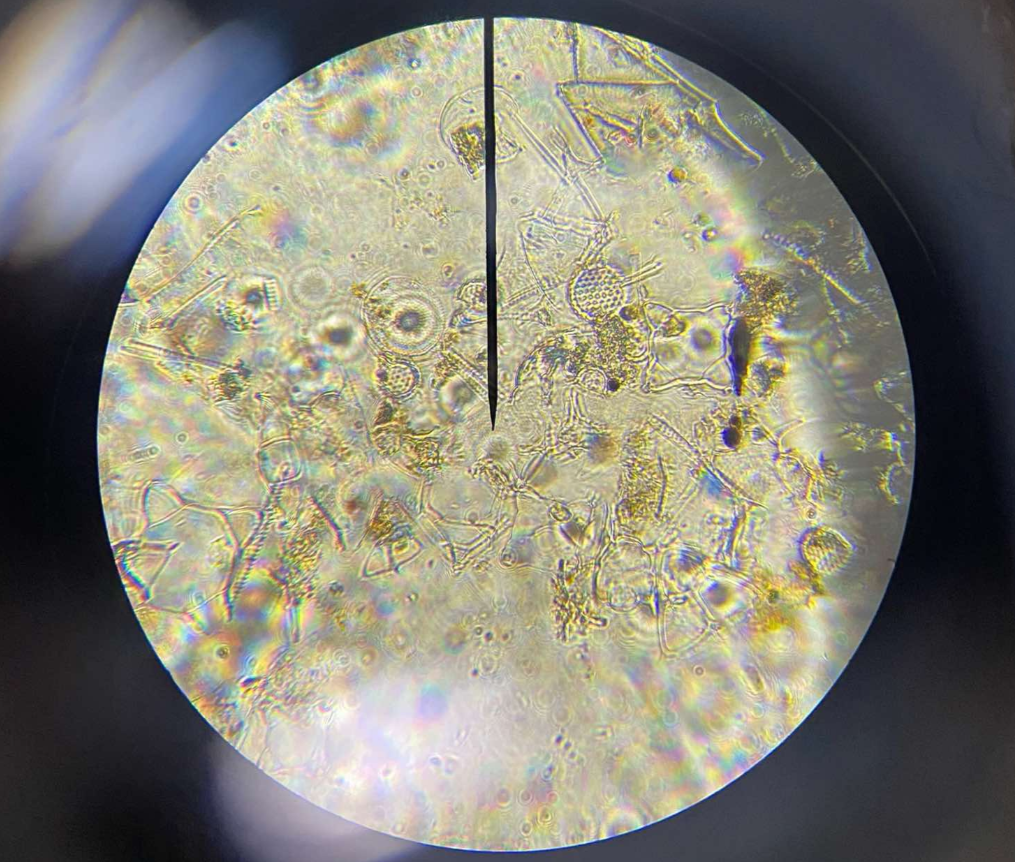
diatomaceous earth
consists of shells of millions of marine diatoms that deposit in the substrate as the cells die
Phylum Dinophyta/Pyrrophyta (Dinoflagellates)
primarily unicellular; cells possess two flagella in the grooves of the cell wall and brownish-gold plastids in the cytoplasm; resistant cell walls composed of overlapping cellulose plates; cause red tides; some are mutualist
plastids
double-membrane bound organelles with their own DNA and ribosomes that are found in photosynthetic organisms like plants and algae; production of energy and storage
Ceratium sp.
common freshwater dinoflagellate
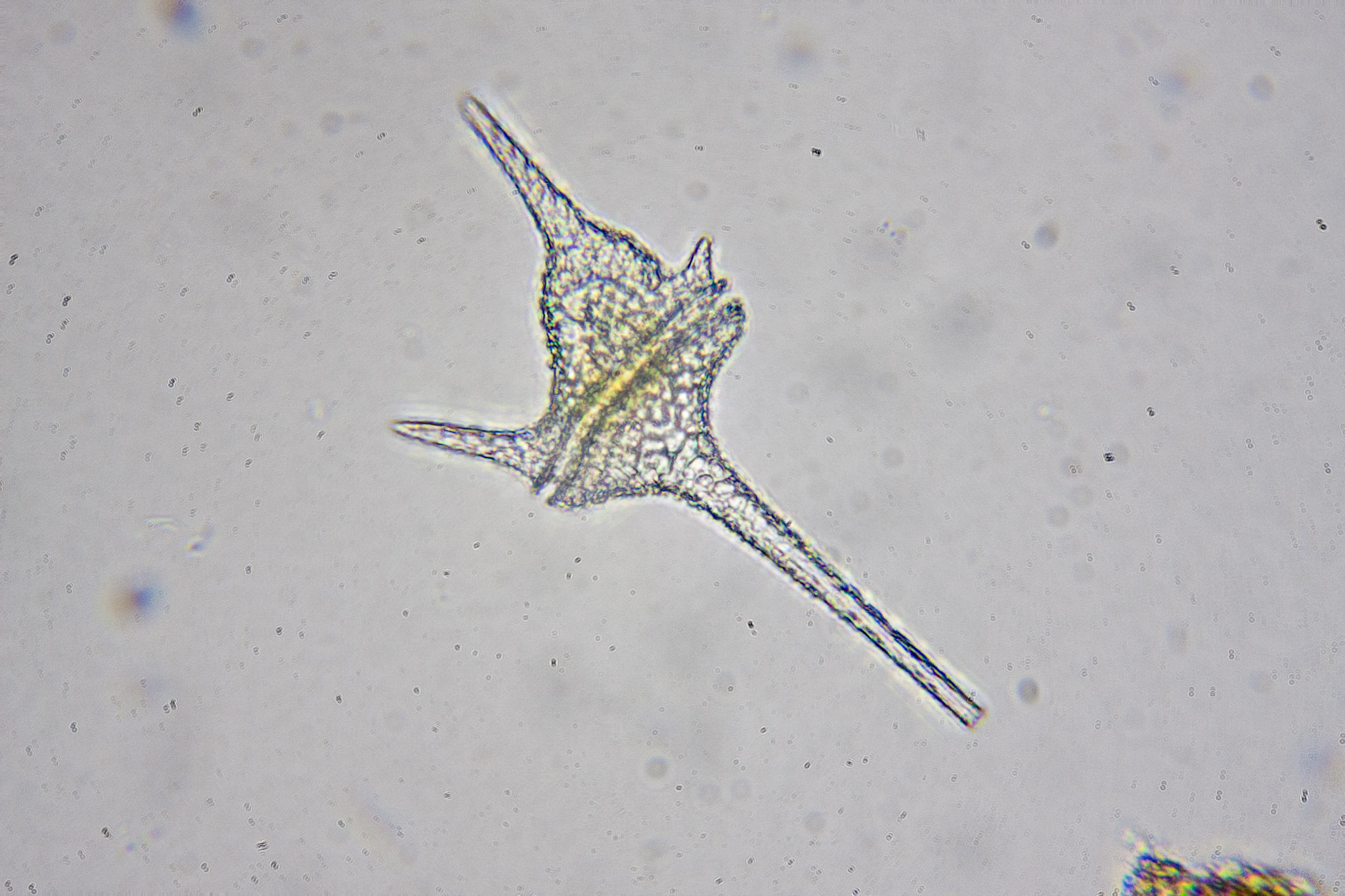
Gymnodinium sp.
marine dinoflagellate
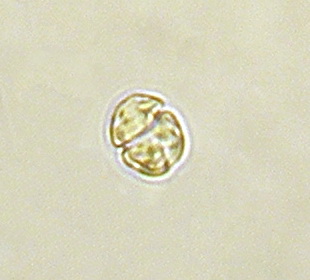
Phylum Chrysophyta (Golden algae)
mainly unicellular freshwater algae; have golden plastids due to the varying chloroplast pigment composition
Phylum Euglenophyta (Euglenoids)
primarily unicellular; flagellates containing chloroplasts; many non-pigmented euglenoids under Protozoa
Protozoa
freshwater organisms that have a flexible cell wall rather than a rigid cell wall in plant cell, meaning they are more animal-like rather than plant-like protists
Euglena sp.
a genus of single cell flagellate eukaryotes; found in fresh water and salt water
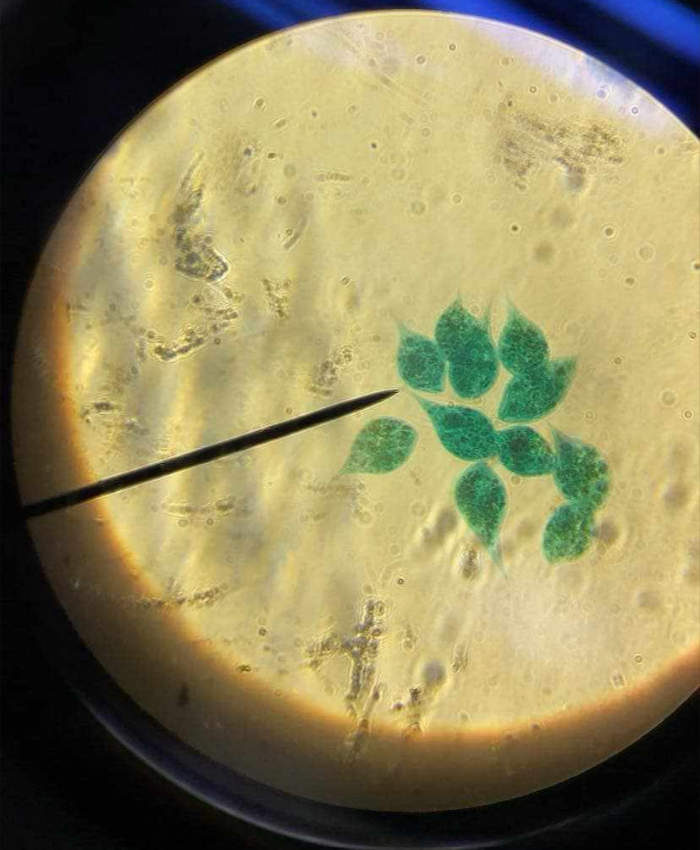
algae
unicellular and primarily multicellular photosynthetic protists; paraphyletic; share a common ancestral origin with fungi, animalia, and the embryophytes (land plants)
Phylum Chlorophyta (Green algae)
universally considered to be the common ancestor of embryophytes/land plants due to starch storage and cellulose content in their walls; could be unicellular, colonial, filamentous, and multicellular platelike forms; found in mostly freshwater, though some are marine; may reproduce sexually or asexually
Ulva sp.
laminar species of green alga; marine multicellular species under Chlorophyta; undergo algal bloom that gives green color to seawater/green tide; diploid sporophyte/haploid gametophyte

Closterium sp.
green algae/chlorophyta desmid
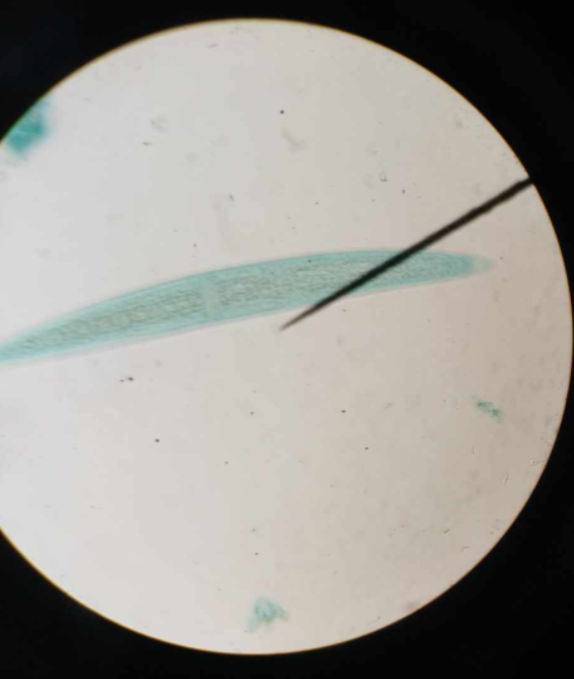
desmids
unicellular freshwater chlorophyta which can reproduce asexually by conjugation
Pandorina sp.
Chlorophyta; common swimming freshwater green alga; simple colony type; compact ball of cells kept together by a gelatinous envelope
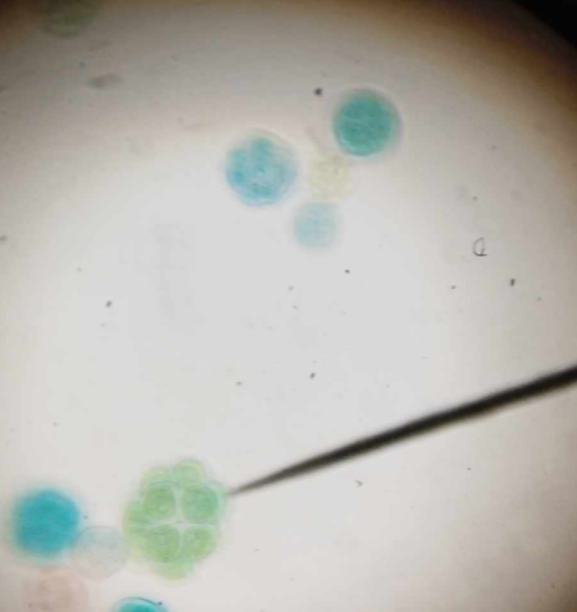
simple colony type
simple aggregation of cells with some degree of coordination among them
Volvox sp.
Chlorophyta; common freshwater chlorophyte which exists also as a colony of green cells but with a more complex organization (single organism could include several daughter colonies)
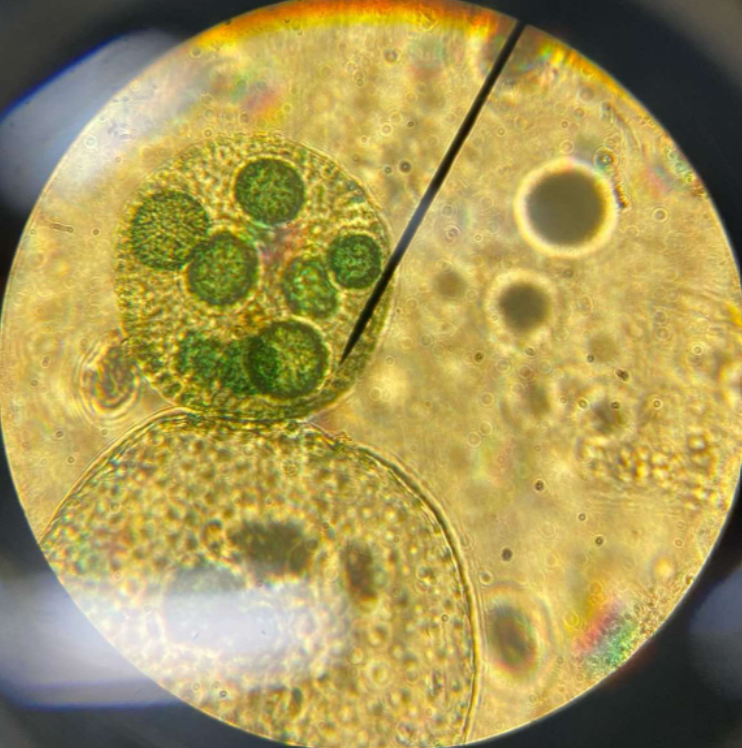
Ulothrix sp.
Chlorophyta; common, unbranched, filamentous green alga attached to rocks and pebbles; chloroplast is C-shaped
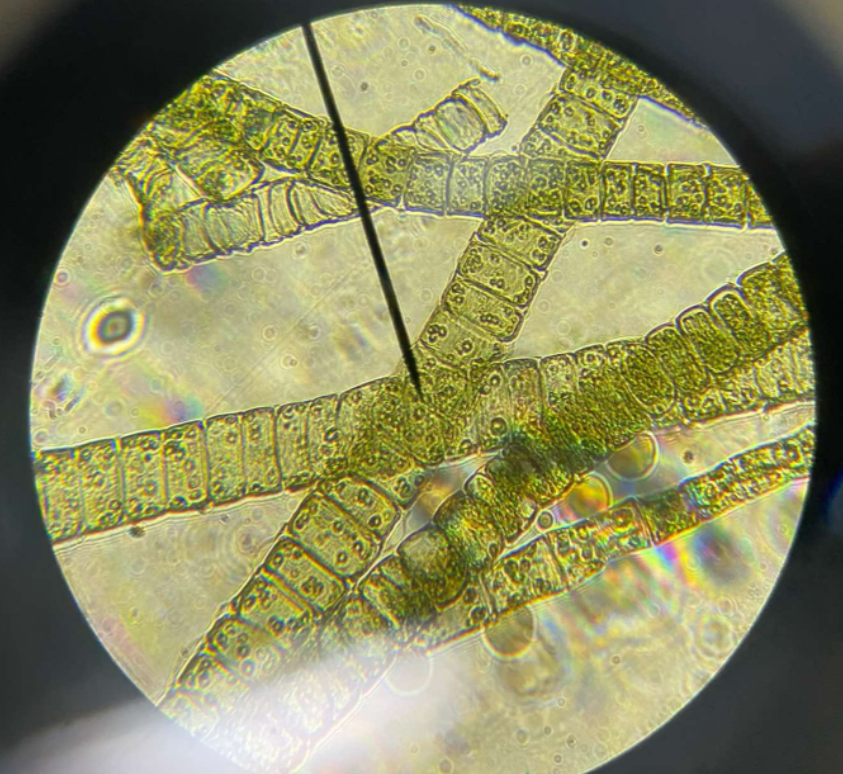

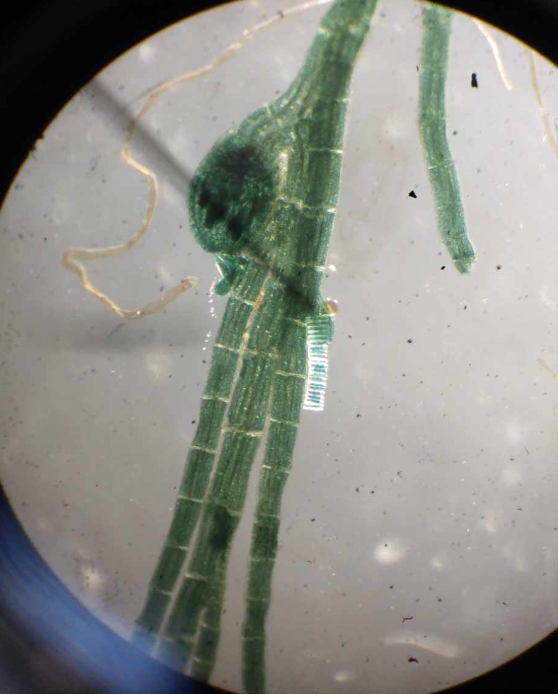
Spirogyra sp.
Chlorophyta; common freshwater filamentous green alga; pondscum organism; form green masses on the surface of ponds and streams; chloroplasts are arranged in a spiral within a cell; conjugation; produces aplanospores
conjugation tube
a slender tube in certain bacteria, algae, and fungi that connects two individuals during conjugation and through which the transfer of genetic material occurs
aplanospores
haploid produced when zygospore undergoes meiosis which germinates into new filaments
Cladophora sp.
Chlorophyta; branched filamentous green alga; freshwater/marine; diploid sporophyte/haploid gametophyte
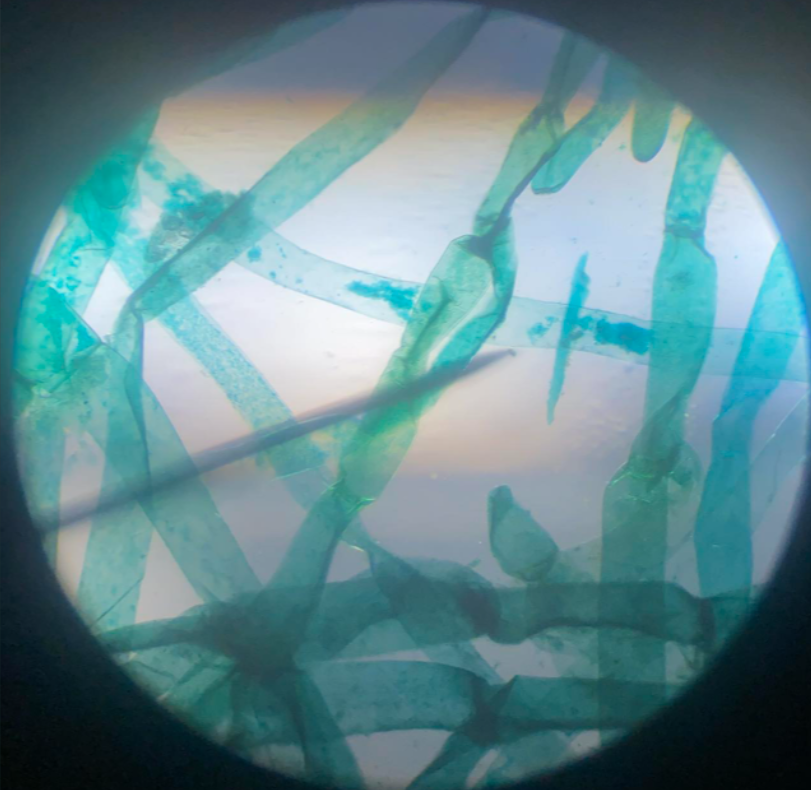

isogametes
gametes that are all alike; fertilize each other to form back the diploid sporophyte
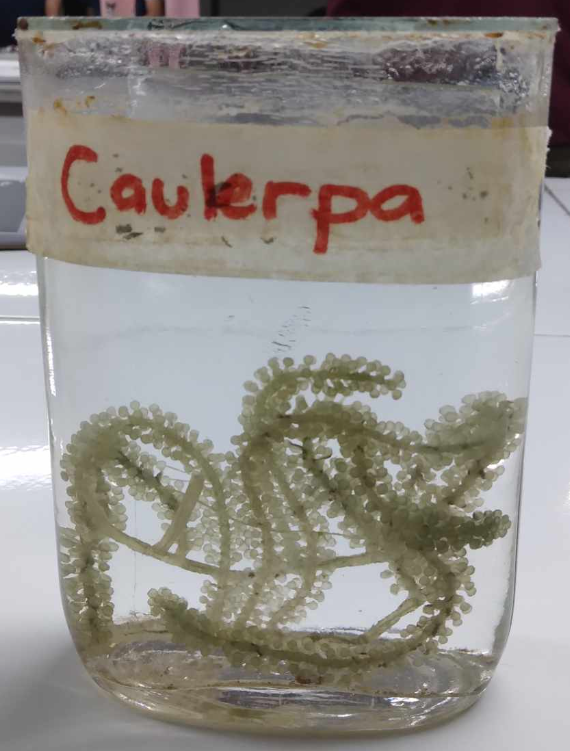
Caulerpa sp.
Chlorophyta; lato; feather algae; economically important green algae; edible algal species

parenchymatous cells
tissue typically composed of living cells that are thin-walled, unspecialized in structure, and therefore adaptable, with differentiation, to various functions
phragmoplast
in dividing plant cells, a structure formed by overlapping microtubules that guide vesicles containing cell wall components to the middle of the cell.
charophytes
green algae that are the closest relatives of land plants
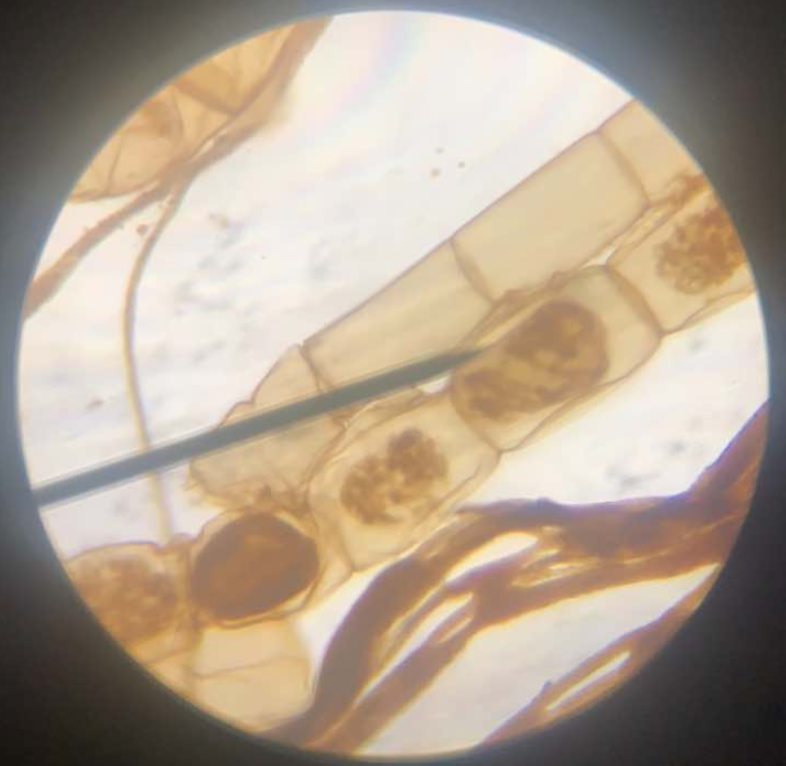
Chara sp.
Charophytic Chlorphyta commonly found in shallow marshes and lakes; maybe more of a plant than alga; microgametangia and megagametangia
megagametangia
archegonia/nodule/female sex organ
microgametangia
antheridia/globule/male sex organ
Phylum Phaeophyta (Brown algae/Giant Kelp)
multicellular organisms; almost exclusively marine, often in the intertidal zone; commonly called seaweeds; differ from green algae and plants because they possess chlorophyll a and c and a variety of xanthophyll pigments; do not produce starch but rather mannitol, fats, and laminarian; undergoes alternation of generations and a more complex body organization
xanthophyll pigments
yellow pigments that occur widely in nature and form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group; the other division is formed by the carotenes
mannitol
a diuretic that helps you make more urine and to lose salt and excess water from your body
laminarin
one of the principal storage products of the brown algae; a polymer of glucose
Fucus sp.
a genus of brown algae found in the intertidal zones of rocky seashores almost throughout the world
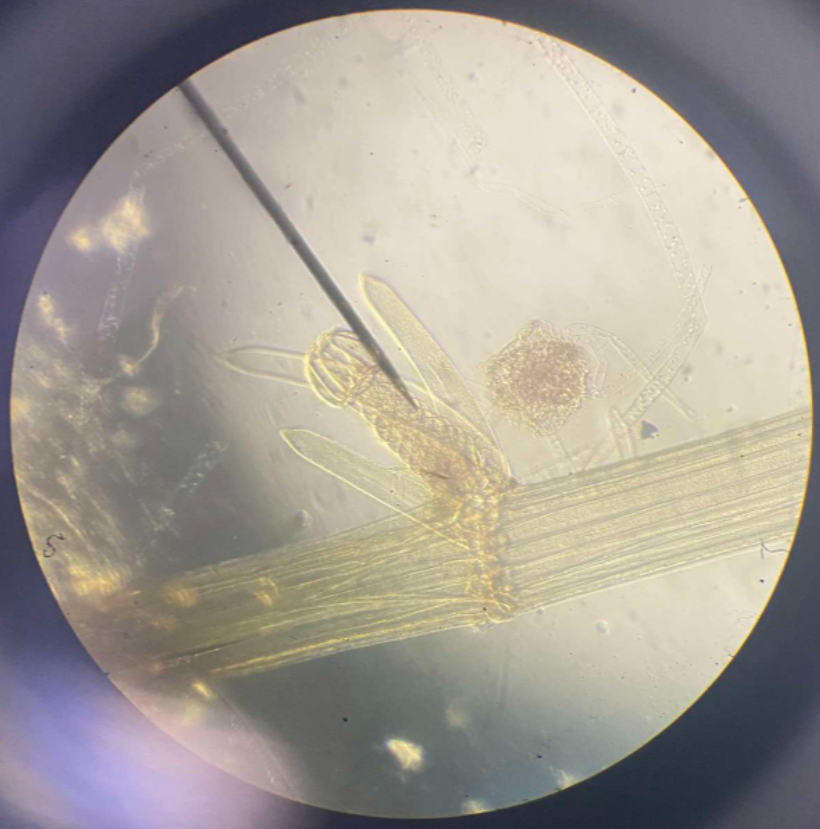
Ectocarpus sp.
a genus of filamentous brown alga that includes a model organism for the genomics of multicellularity; selected for the relatively small size of its mature thallus and the speed with which it completes its life cycle
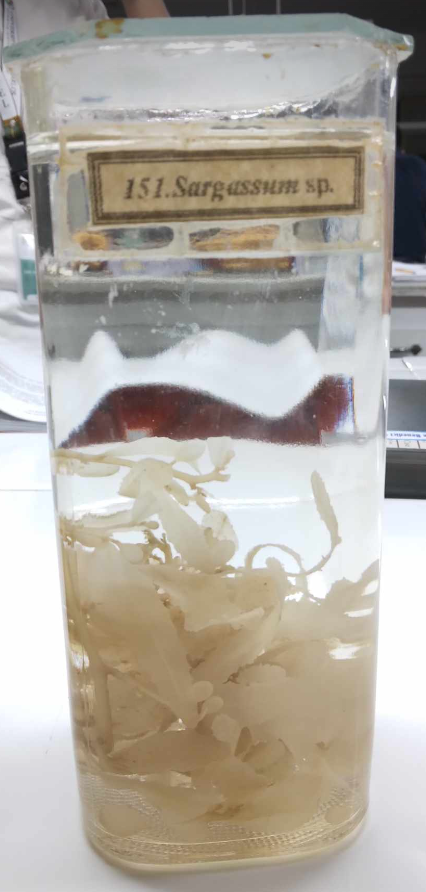
Sargassum sp.
lusay; a genus of brown macroalgae in the order Fucales of the Phaeophyceae class; numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral reefs, and the genus is widely known for its planktonic species

Phylum Rhodophyta (Red algae)
multicellular marine algae that are also referred to as seaweeds (like the brown algae); undergo sexual reproduction without flagellated cells; most also undergo alternation of generations; reddish in color due to phycoerythrin
phycoerythrin
red pigment in red algae
Polysiphonia sp.
known as red hair algae; a genus of filamentous red algae
trichogyne
in the red algae and certain ascomycetes and Basidiomycota, a receptive protuberance of the female gametangium for the conveyance of spermatia
tetrasporophyte
diploid multicellular stage of red algae that produces spores by meiosis
tetraspores
haploid, asexual dispersal cells of red algae
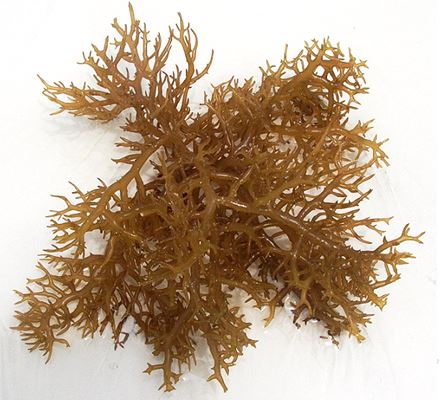
Kappaphycus sp.
among the largest tropical red algae, with a high growth rate; not only edible but also a commercially viable source of agar and carrageenan which are used as thickening and solidifying agents in industry

Gracilaria sp.
also known as irish moss or ogonori, is a genus of red algae; notable for its economic importance as an agarophyte meaning that it is used to make agar, as well as its use as a food for humans and various species of shellfish

slime molds
fungus-like protists that play key roles in recycling organic material
Phylum Myxomycota (Plasmodial slime molds)
multinucleated continuum of cytoplasm without cell membranes; ameboid plasmodium; reproduction can be asexual or by gametes produced by meiosis
ameboid plasmodium
an amoeboid, multinucleate, and naked mass of cytoplasm that contains many diploid nuclei
Stemonitis sp.
distinctive genus of slime molds found throughout the world; they are characterized by the tall brown sporangia, supported on slender stalks, which grow in clusters on rotting wood.
water molds
most are small, single- celled organism. live in water, moist soil, or other organisms
Phylum Oomycota (water molds, white rusts, and downy mildews)
freshwater habitats; generally decomposers but some are parasitic in nature; cell walls are composed of cellulose; reproduction is either by non-motile/flagellated zoospores
Saprolegnia sp.
Oomycota; a genus of water moulds often called cotton moulds because of the characteristic white or grey fibrous patches they form