Pedigrees and Modes of Inheritance
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Pedigree
A diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships.
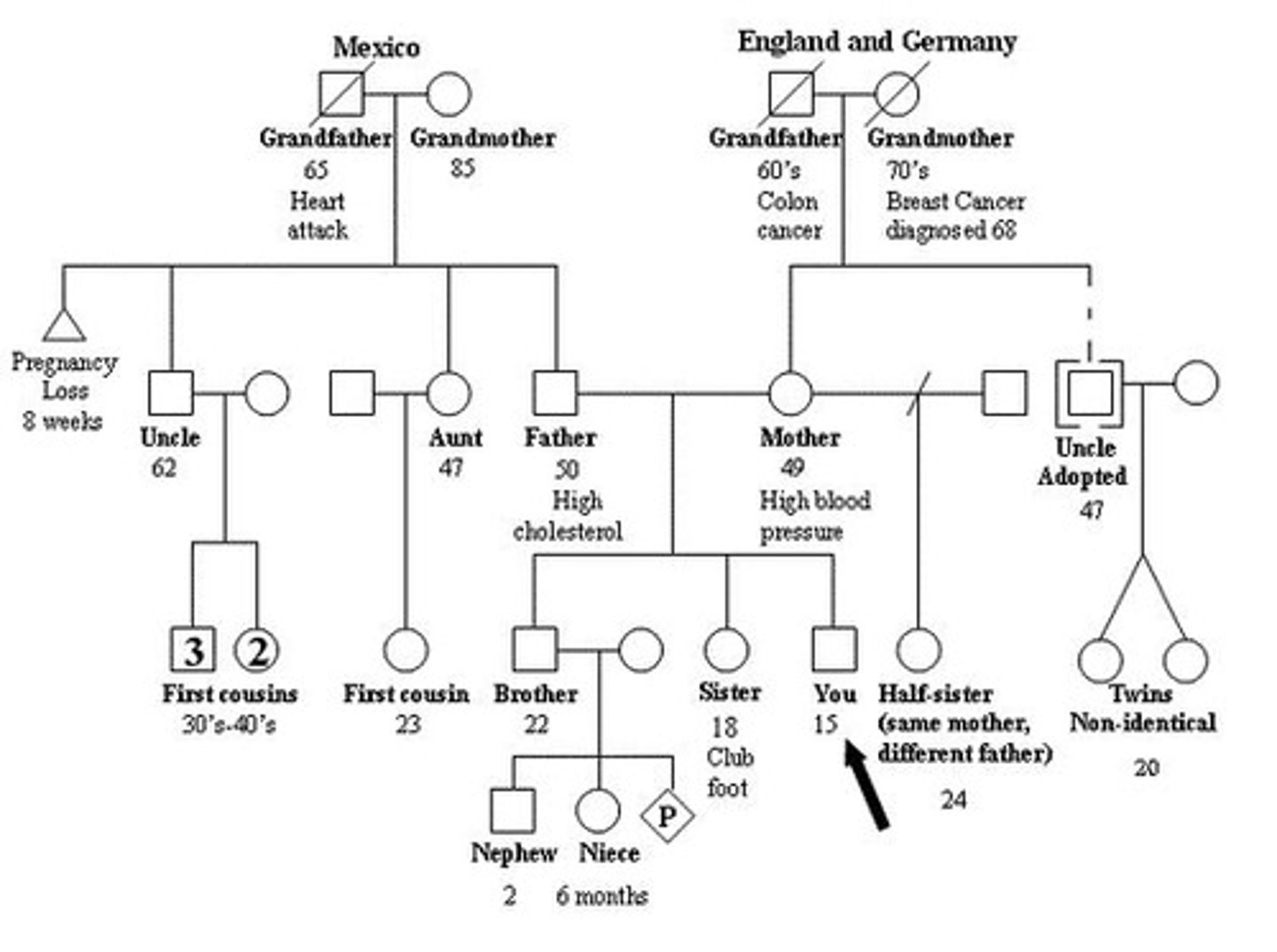
Modes of Inheritance (MOI)
The ways in which traits are passed from parents to offspring.
Autosomal Recessive
A mode of inheritance where traits are passed on from parents to offspring and examples include Cystic fibrosis and Sickle cell anaemia.
Autosomal Dominant
A mode of inheritance where traits are passed on from parents to offspring and examples include Retinoblastoma.
X-Linked Recessive
A mode of inheritance where traits are passed almost exclusively on the X chromosome, with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy as an example.
X-Linked Dominant
A mode of inheritance where traits are passed almost exclusively on the X chromosome, with Rett Syndrome as an example.
Autosomal Traits
Traits that are passed on from parents to offspring independent of the X and Y chromosomes.
X-Linked Traits
Traits that are almost exclusively passed on the X chromosome.
Normal Allele
The allele that does not cause a genetic disease, represented as A+.
Disease Allele
The allele that causes a genetic disease, represented as A-.
Inbreeding
The mating of individuals who are closely related, which can increase the risk of genetic diseases.
Consanguinity
The sharing of blood or genetic material between individuals.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a particular gene.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a particular gene.
Autosomal Dominant Trait
Normal: A-A-, Affected: A+A+ or A+A-.
Autosomal Recessive Trait
Normal: A+A+ or A+A-, Affected: A-A-.
X-Linked Dominant Trait
Normal: XA-XA- or XA-Y, Affected: XA+XA+ or XA+XA- or XA+Y.
X-Linked Recessive Trait
Normal: XA+XA+ or XA+XA- or XA+Y, Affected: XA-XA- or XA-Y.
Male to Male Transmission
Transmission of traits that can only occur through autosomal inheritance.
More than 1 possible MOI
Indicates that additional generations may be needed to determine the correct mode of inheritance.
Obligate Heterozygotes
Individuals who do not show a trait but must carry one allele for it.
Autosomal Hypothesis
A hypothesis that suggests a trait is inherited through autosomal recessive inheritance.
X-Linked Hypothesis
A hypothesis that suggests a trait is inherited through X-linked inheritance.
Albinism
A genetic condition that can be analyzed using all four modes of inheritance.
Pedigree Analysis
The study of family trees to understand the inheritance of traits.
Extra Generation
Additional generations added to a pedigree to clarify modes of inheritance.
Labeling Pedigrees
The process of assigning symbols and explanations to a pedigree.
Research Before Inbreeding
The importance of understanding genetic risks before mating closely related individuals.
Obligate Heterozygote
individual who might be clinically unaffected but must carry the mutant allele based on pedigree analysis
indicates dominance OR indicates recessive:
disease present in every generation.
dominance
indicates dominance OR indicates recessive:
family is outbred
dominance
indicates dominance OR indicates recessive:
family inbred
recessive
indicates dominance OR indicates recessive:
generations skipped
recessive, but data missing