ap human vocab review
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
words i either need to review, dont know, or i get confused with them. AP EXAM MAY 6TH!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
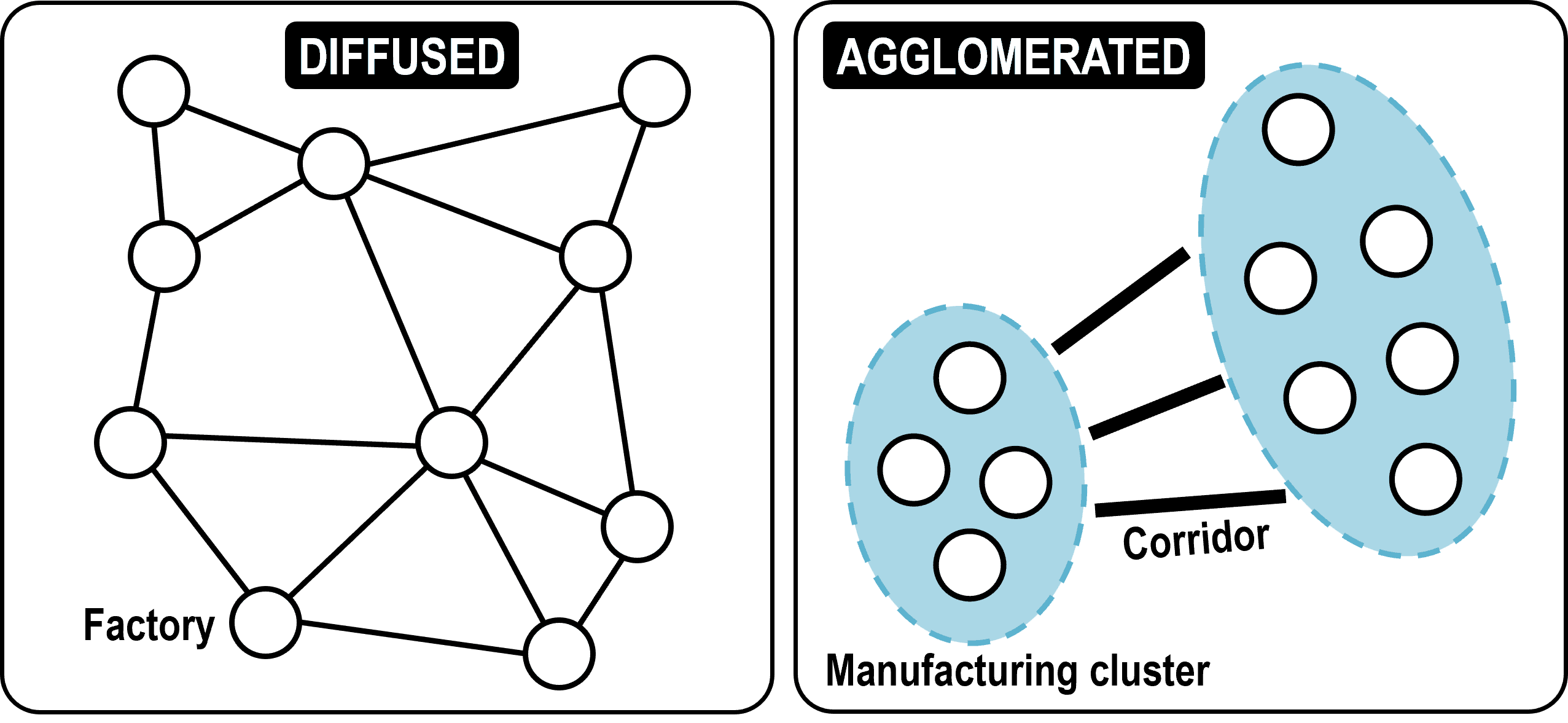
agglomeration
large, densely populated area including its city and suburbs

sustainable development goals
A set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015, aimed at addressing various global challenges including poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace, and justice. (Related to LDC’s)

millennium development goals
A set of 8 international development goals established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, aimed at addressing a range of global issues including poverty, education, gender equality, child mortality, maternal health, disease, environmental sustainability, and global partnerships by 2015. (Related to HDC’s)

export processing zones (EPZs)
Areas in which goods can be landed, handled, manufactured, and re-exported without the intervention of customs authorities, aimed at increasing exports and attracting foreign investment.
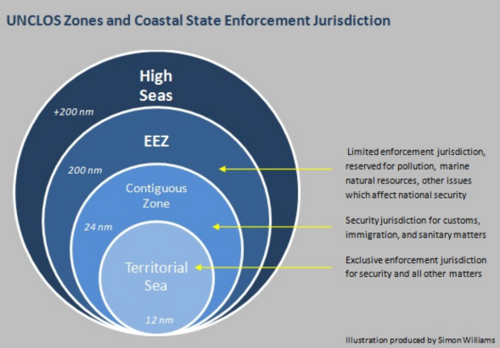
special economic zones (SEZs)
Designated areas within a country that have different economic regulations than the rest of the country to encourage investment and trade. These zones typically feature tax incentives, less stringent labor laws, and streamlined bureaucracy.
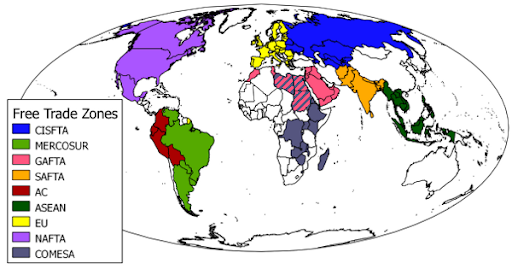
free trade zones (FTZs)
regions where goods can be landed, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured without the intervention of customs authorities.

backwash effect
A negative impact on rural areas caused by urban growth, where resources and jobs are drawn to cities, leaving less for the countryside. (ex. capital of Sierra Leonne in Africa)
ancillary activities
economic activities that support primary (or large scale) industries and enhance overall productivity. Examples being shipping, food-service, and human resource departments.


just in time delivery
A manufacturing strategy where materials and products are delivered exactly when needed in the production process, minimizing inventory costs. (Keep in mind for mcqs and frqs that it reduces waste and increases efficiency.)
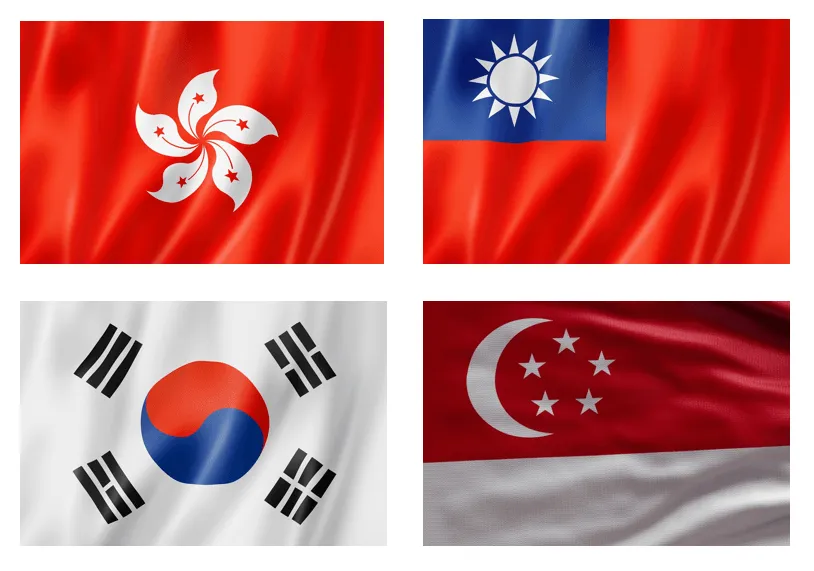
four asian dragons
A term referring to the high-growth economies of Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan, known for their rapid industrialization and economic development. (HSST) These countries are characterized by their strong export-oriented economies and significant investment in technology.

international monetary fund
An organization working to promote global economic stability and growth by providing financial assistance, policy advice, and technical assistance to member countries.
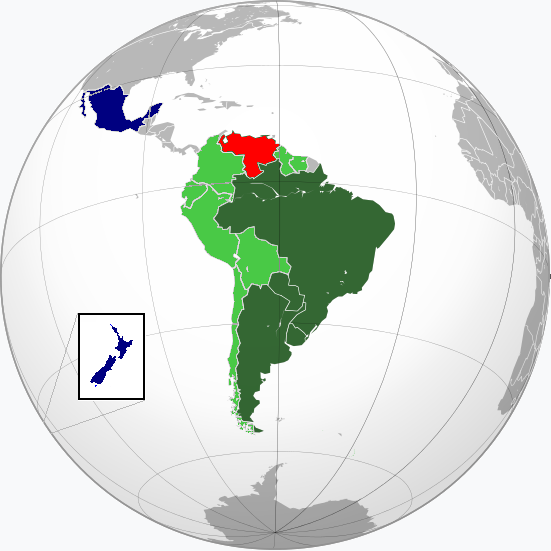
Mercosur
A South American trade bloc that promotes free trade and economic integration among its member countries, primarily Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
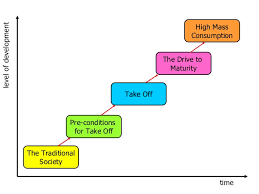
Rostow’s theory stage 1
The traditional society, characterized by subsistence farming, limited technology, and a static social structure.
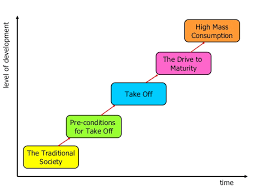
Rostow’s theory stage 2
The pre-conditions for take-off, characterized by the initiation of industrialization, increased investment, and a rise in agricultural productivity.
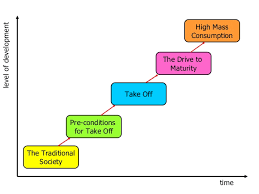
Rostow’s theory stage 3
The stage of economic development where a society begins to industrialize, experiencing rapid growth and urbanization, typically characterized by increased investments and the development of manufacturing industries.
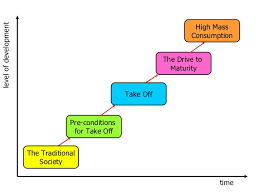
Rostow’s theory stage 4
the stage of development characterized by maturity, where production shifts from reliance on industry to services, leading to high levels of consumer spending.
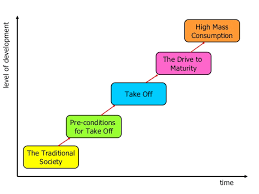
Rostow’s theory stage 5
the final stage of development where the economy is fully developed, focusing on high-value services and further technological advances.
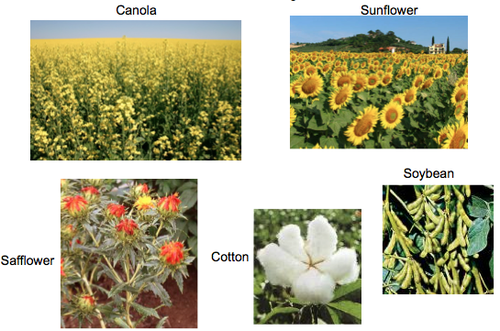
cash crops
crops used to make money ex. cotton

perennial crop
a type of crop that lives for more than two years and can provide harvests multiple times without replanting.

horticulture
the cultivation of plants for food, aesthetics, and medicinal purposes.
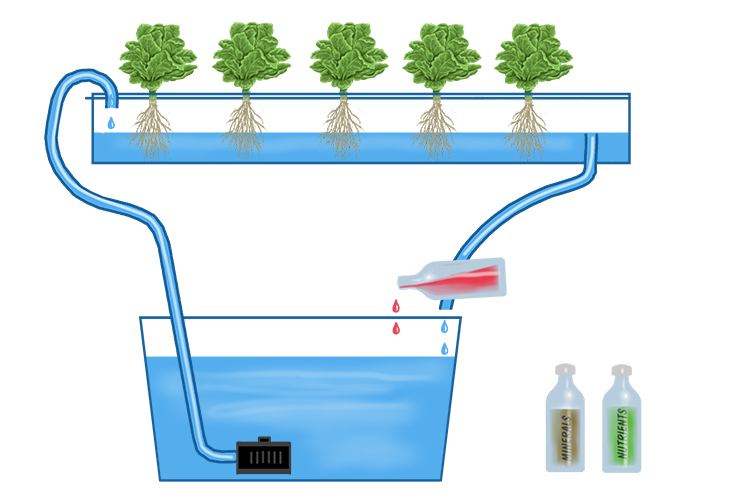
hydroponic
growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution instead of soil. This method allows for efficient use of space and resources, often leading to faster growth and higher yields.
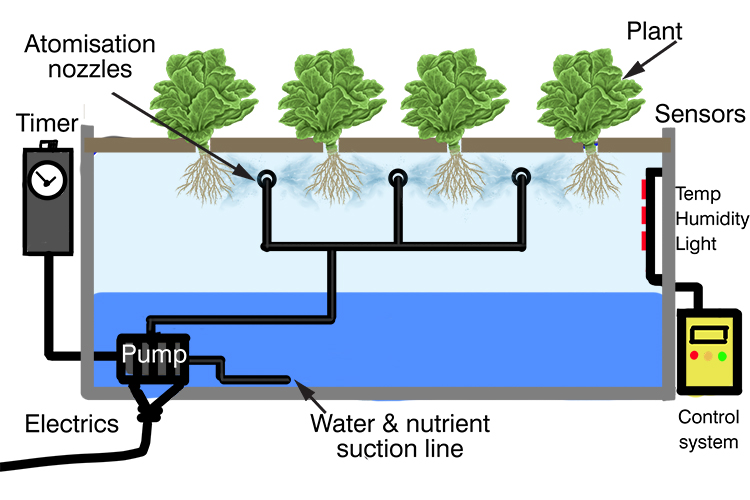
aeroponic
a method of growing plants in an air or mist environment without soil, utilizing a nutrient solution. This technique enhances oxygen exposure to roots, promoting faster growth.
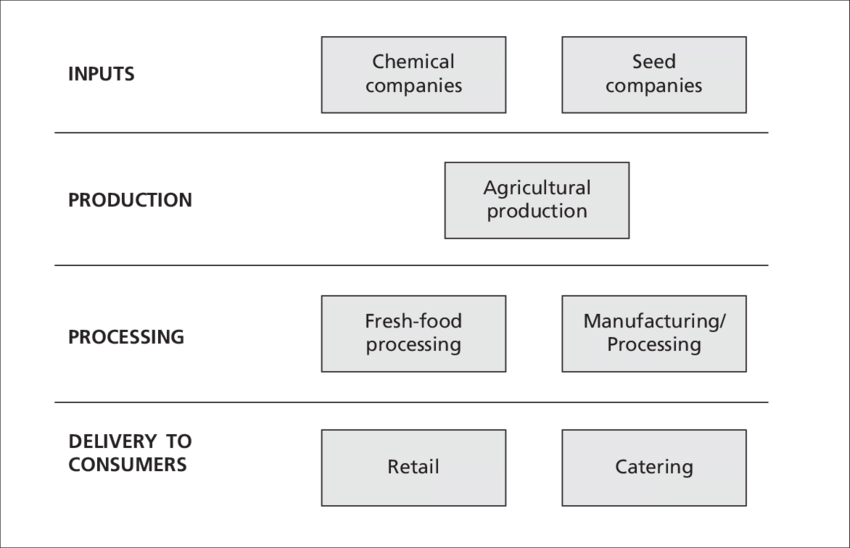
Agribuisness
Refers to the various businesses involved in the production, processing, and distribution of agricultural products. It encompasses everything from farming and seed supply to food processing and retailing.
Outsourcing
The practice of transferring specific business processes or tasks to external service providers, often located in different countries. This can involve the shift of manufacturing jobs from developed countries to developing countries, where labor costs are typically lower.
Knowledge economy
an economic system where growth is primarily driven by the production, distribution, and use of knowledge and information, rather than the traditional means of production such as physical goods. It emphasizes the importance of technology and innovation, prioritizing services over manufacturing.
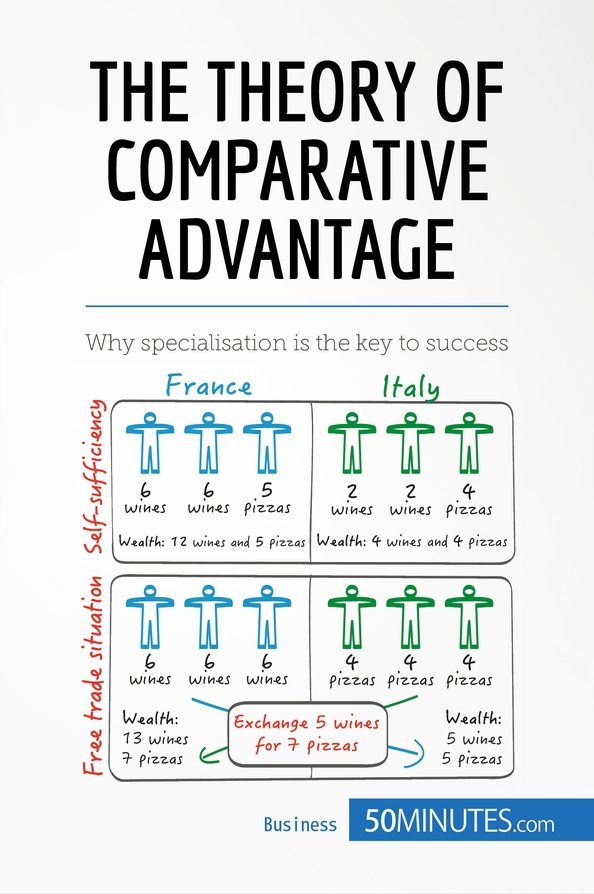
Comparative Advantage
An economic theory that explains how countries can benefit from trade by specializing in the production of goods and services they can produce more efficiently than others. According to this principle, each country should focus on producing goods for which it has a lower opportunity cost relative to other goods.

Command economy
An economic system where the government makes all decisions regarding the production and distribution of goods and services.
Market economy
an economic system where decisions about production and consumption are made by individual buyers and sellers in the marketplace.
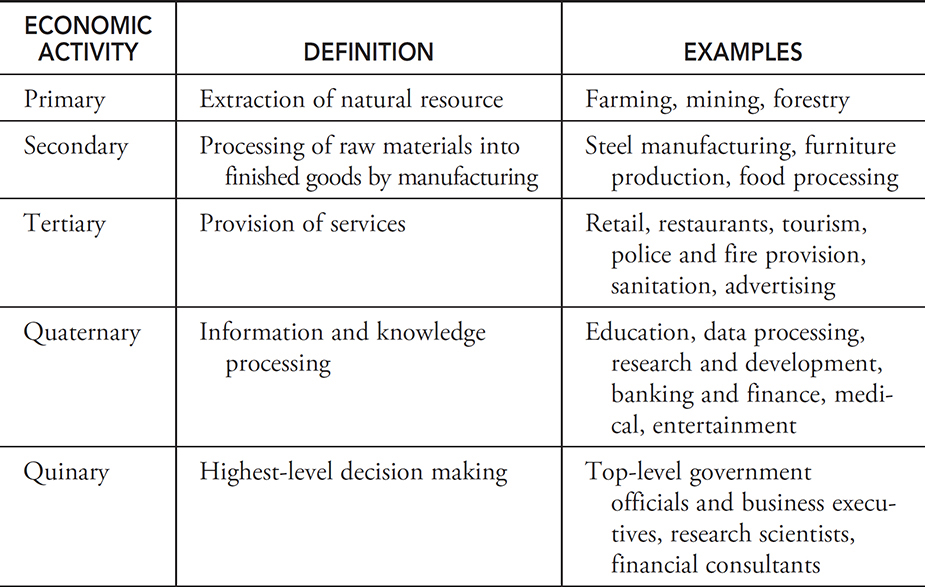
Provision of Services
The provision of services entails delivering critical services such as healthcare, education, and entertainment to fulfill consumer needs and preferences. This process involves the direct supply and maintenance of services to individuals or communities, contributing to their overall well-being and quality of life.
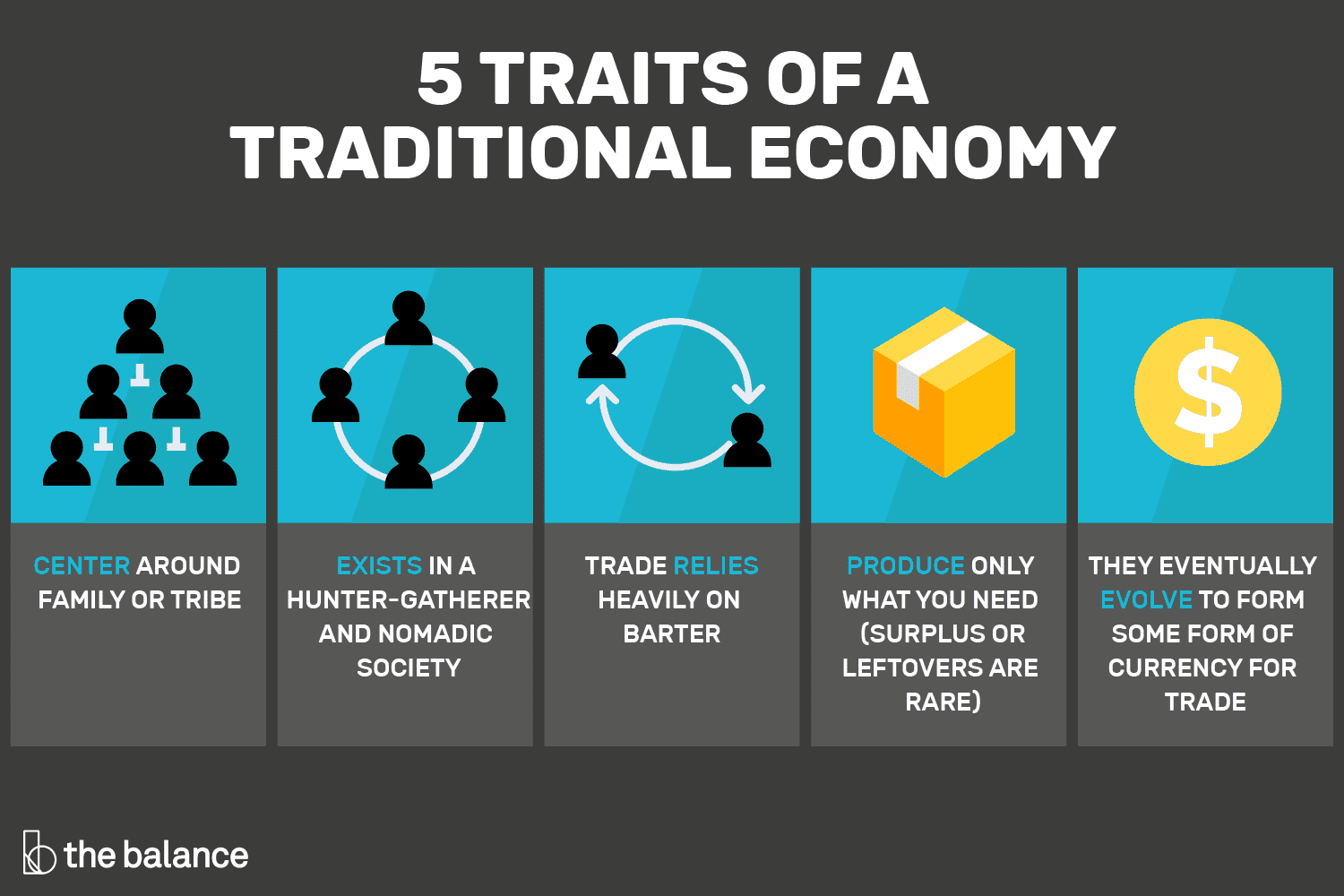
Traditional economy
an economic system that relies on customs and traditions to make decisions about production and distribution, often based on subsistence farming and barter.
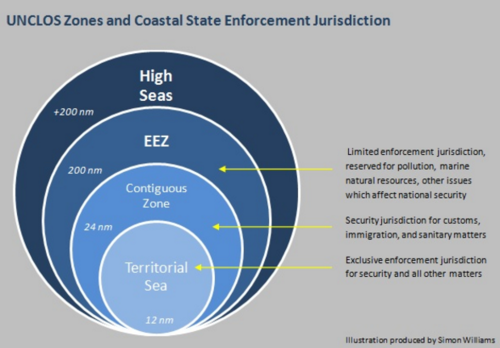
Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZ)
areas of sea where a country has special rights over the exploration and use of marine resources, extending 200 nautical miles from its coastline.
Insourcing
the practice of transferring a business function or process previously performed by an external supplier back to an in-house team, often to improve efficiency or control costs. This method can enhance quality and reduce dependency on outside vendors.
Ecumene
The inhabited or populated areas of the earth, typically referring to regions where human settlement is sustainable. It includes cities, towns, and agricultural lands where people live and work, excluding uninhabitable regions such as deserts and polar areas.
Arithmetic density
The total number of people per unit area of land, often used to understand population distribution. It is calculated by dividing a country's population by its total land area, providing insights into how densely populated a region is.
Physiological density
The number of people per unit area of arable land, indicating the pressure on agricultural resources. It helps to assess the sustainability of food production relative to population size. Total population divided by arable land area.
doubling time
The period of time required for a quantity to double in size or value, often used in the context of population growth. It estimates how long it will take for a population to double based on its current growth rate. (70/NIR)
cultural complex
group of related cultural traits or practices that are interconnected and define a particular cultural
absolute direction
tells distance by using north, east, south, and west (and other combinations)
indigenous culture
traditional cultures of a society pre-colonization or significant migration
traditional culture
practices, beliefs, and customs passed down through generations of a specific community/region
popular culture
collection of beliefs, ideas, behaviors, and trends that are widely accepted and practiced by a large majority of people
cultural hearths
place of origin of a significant cultural trait
built environment
human made physical features that create a landscape
sociofact
structures and organizations of a culture that influence social behavior
reference map
map that shows geographical locations on earths surface like locations of cities or oceans
cartogram
map that distorts the geographic shape of an area in order to show the size of a specific variable.
mercator projection
peters projection
robinson projection
polar projection
goode projection