Unit 9 Flashcards
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Albedo
measure of the reflectivity of the earth's surface. Ice, especially with snow on top of it, has a high albedo: most sunlight hitting the surface bounces back towards space.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Organic compounds made up of atoms of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine; found in refrigerators, styrofoam, hairspray, etc. Gaseous CFCs can deplete the ozone layer when they slowly rise into the stratosphere, are broken down by strong ultraviolet radiation, release chlorine atoms, and then react with ozone molecules
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES)
agreement between gov’ts to ensure international trade in wild plants and animals is legal, traceable, and biologically sustainable.
Coral bleaching
corals loose color due to warm water temps
Disease vectors
living organisms that can transmit infectious diseases between humans or from animals to humans. They can include mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, etc.
Domestication
not sure: the process of taming an animal and keeping it as a pet or on a farm.
Edge habitat/edge effect
Edge effects are the boundary between natural habitats and developed or disturbed land.
With the creation of an edge to any natural ecosystem, the area outside the boundary is deeply affected. Examples of the numerous changes are air temperature, vapor pressure deficit, soil moisture and light intensity.
Endangered species
organisms that are at risk of becoming extinct due to various factors such as habitat loss, pollution, or overhunting.
~ Act
a law in the United States that aims to protect and recover endangered and threatened species and their habitats
Extinction
A process in which a species ceases to exist.
Genetic diversity
the biological variation that occurs within species. It makes it possible for species to adapt when the environment changes
Greenhouse Gasses
gases in the earth's atmosphere that trap heat. During the day, the sun shines through the atmosphere, warming the earth's surface. At night the earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air. But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere; CO2, CFCs, Methane, etc.
Greenhouse effect
the process by which energy from the sun is trapped in the form of heat by GHGs.

Habitat corridor
an area of habitat connecting wildlife populations separated by human activities or structures

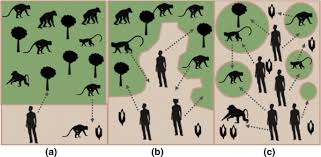
Habitat fragmentation
a process during which a large expanse of habitat is transformed into a number of patches of a smaller total area, isolated from each other by a matrix of habitats unlike the original
HIPPCO
greatest threats to marine biodiversity: Habitat Loss and degradation, Invasive Species, Population Growth, Pollution, Climate Change, Overfishing
Ice cores
They are essentially frozen time capsules that allow scientists to reconstruct climate far into the past
invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced, nonnative organism (disease, parasite, plant, or animal) that begins to spread or expand its range from the site of its original introduction and that has the potential to cause harm to the environment, the economy, or to human health.
IUCN Red List
a critical indicator of the health of the world's biodiversity.
Lacey Act
conservation law in the United States that prohibits trade in wildlife, fish, and plants that have been illegally taken, possessed, transported or sold.
Marine Mammal Protection Act
makes it illegal to "take" marine mammals without a permit