08.10 BIO, HN U8P1 Cell Growth, the Cell Cycle & Mitosis (ALL)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Asexual reproduction (Description)
A type reproduction in which DNA is replicated and two genetically identical daughter cells are reproduced from one parent cell
Sexual reproduction (Description)
A type of reproduction in which DNA from two different gamete cells is recombined to form a genetically different cell
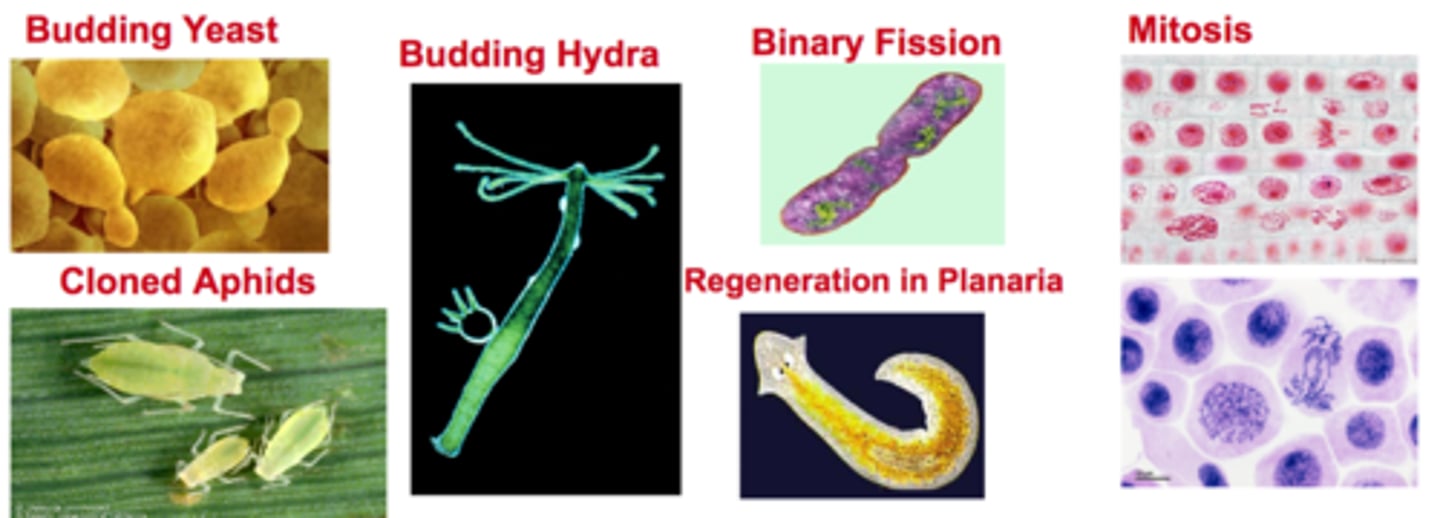
Asexual reproduction (Examples)
Examples include binary fission, budding, regeneration, cloning and mitosis
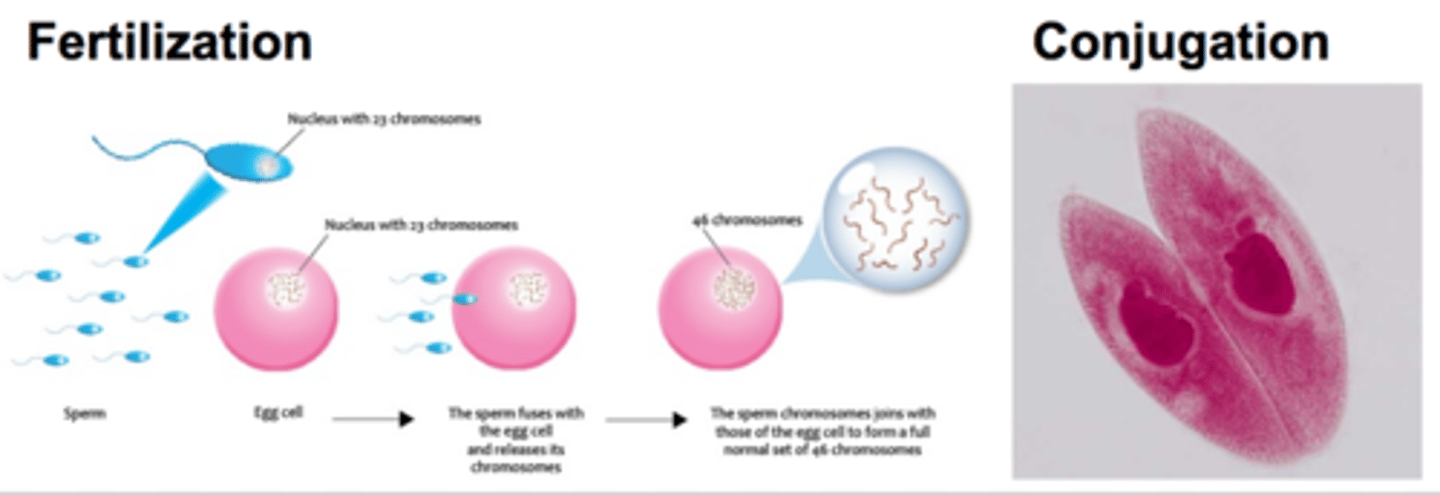
Sexual reproduction (Examples)
Examples include fertilization and conjugation
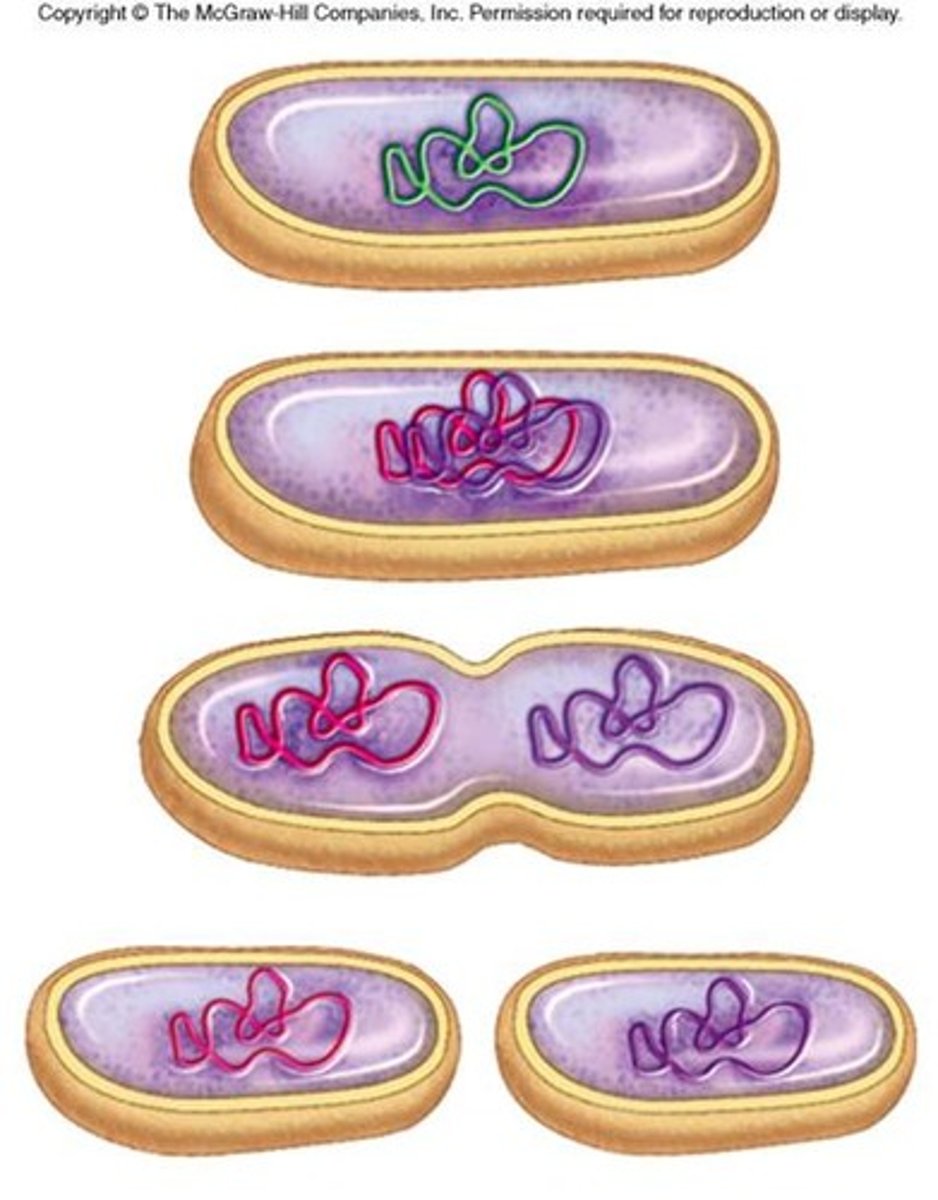
Binary fission
A type of asexual reproduction in which one prokaryotic cell divides to form two identical cells; occurs in bacteria
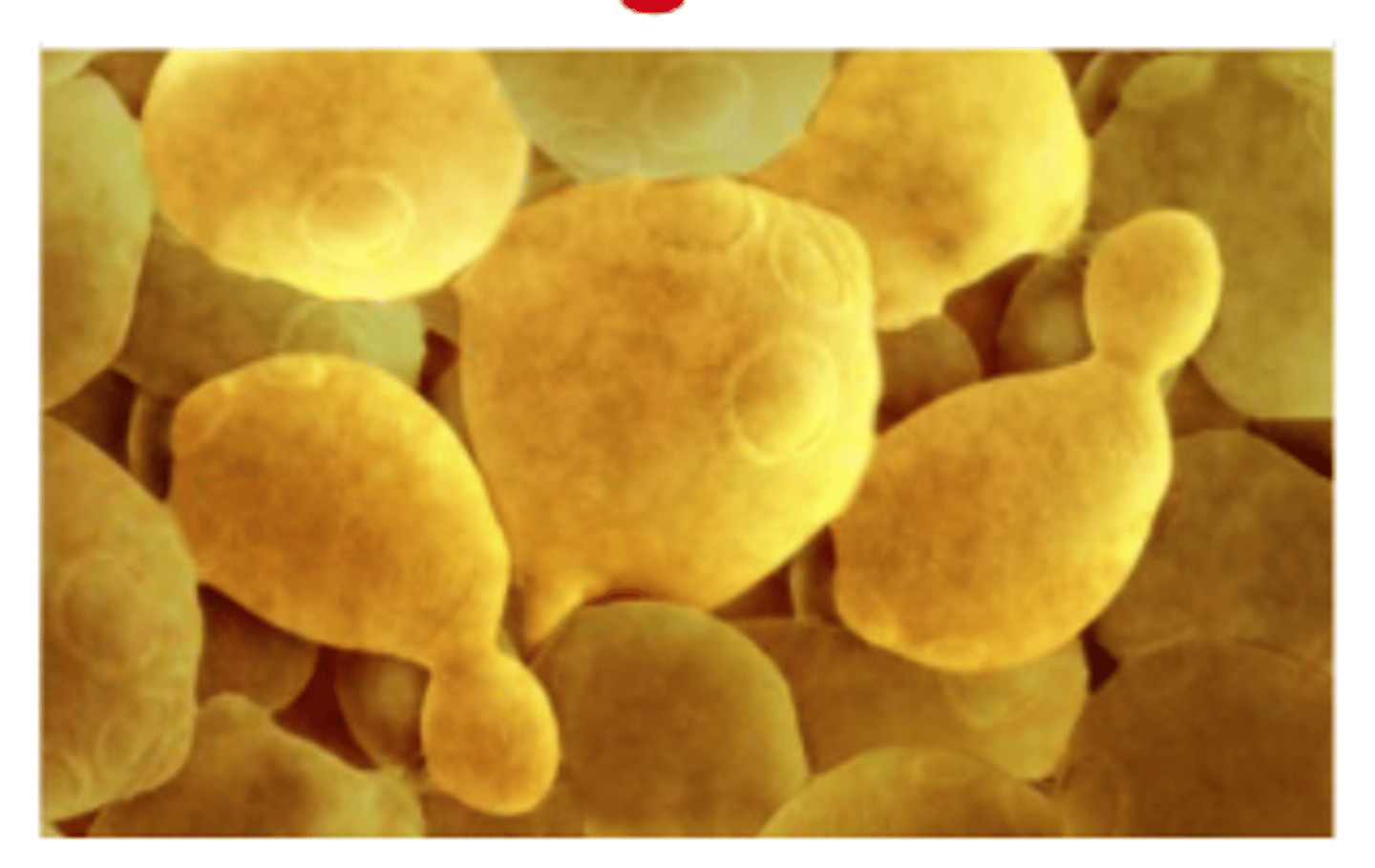
Budding
A type of asexual reproduction in which a part of the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism; occurs in yeast, hydra and many other organism
Regeneration
A type of asexual reproduction in which certain organisms regrow missing body parts; occurs in planaria, starfish and many other organisms
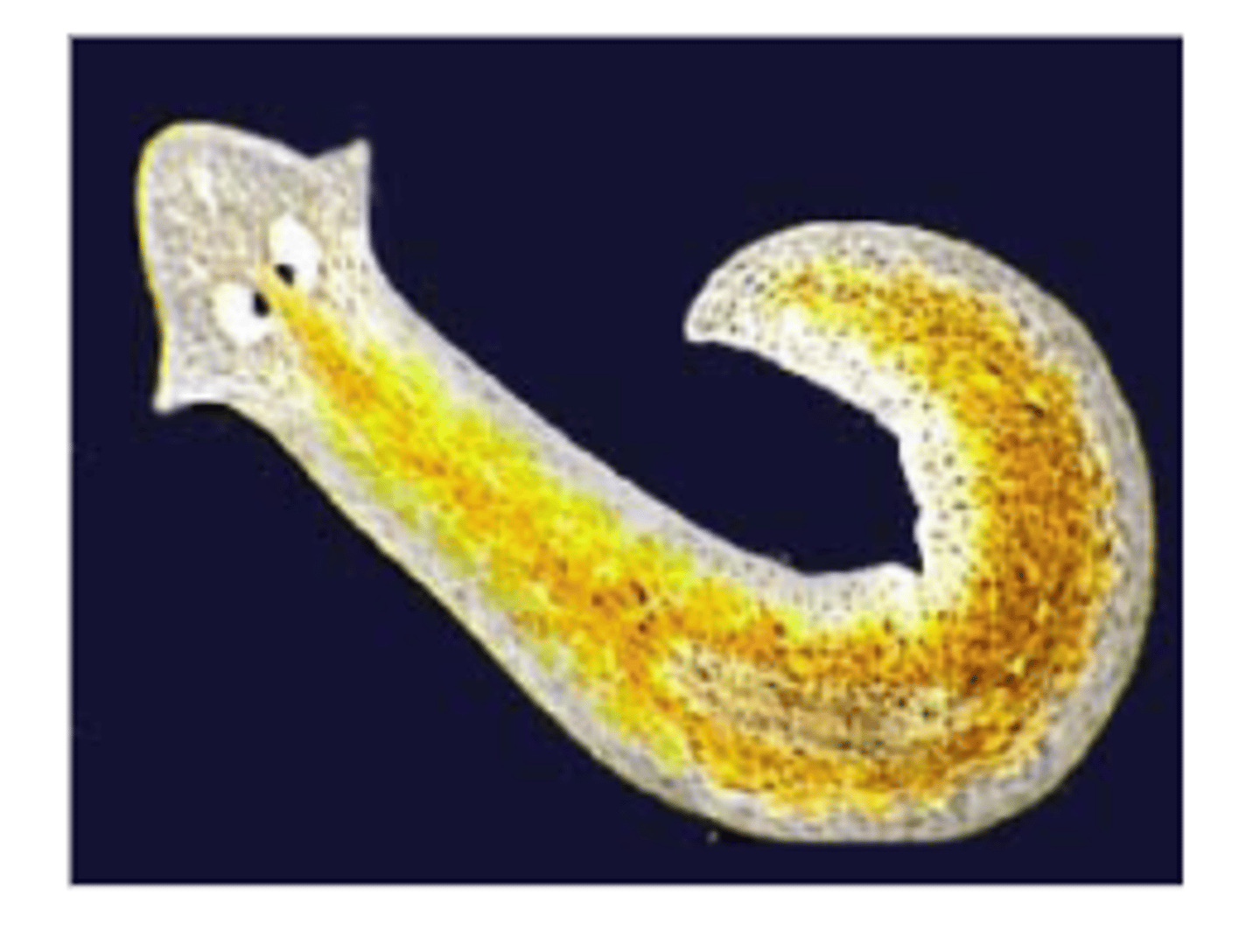
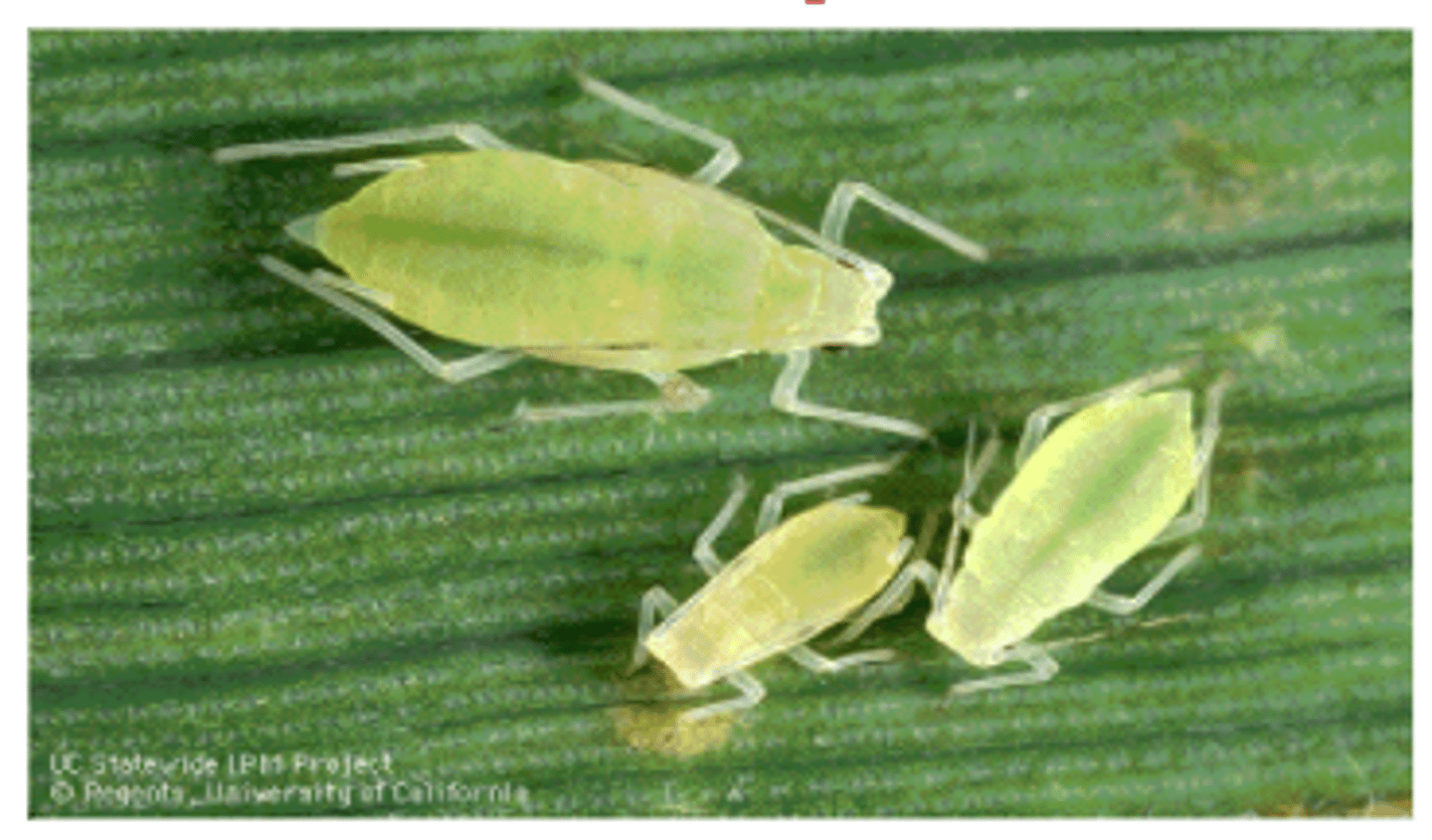
Cloning
A type of asexual reproduction in which a cell or organism is copied from an original source; i.e. aphids

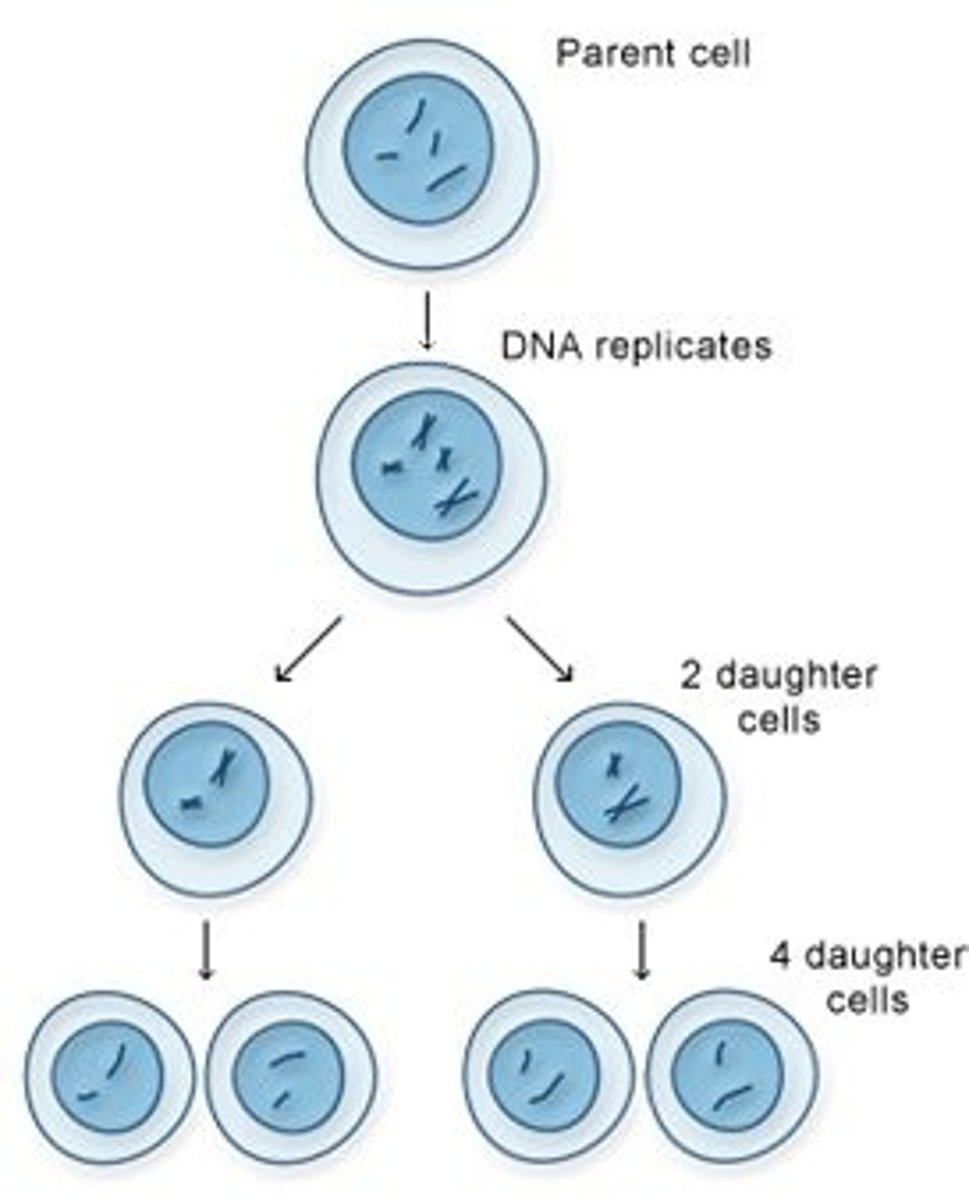
Mitosis
A type of asexual reproduction that occurs in eukaryotes when a parent cell copies the DNA and divides to produce two identical daughter cells typical of ordinary tissue growth and repair
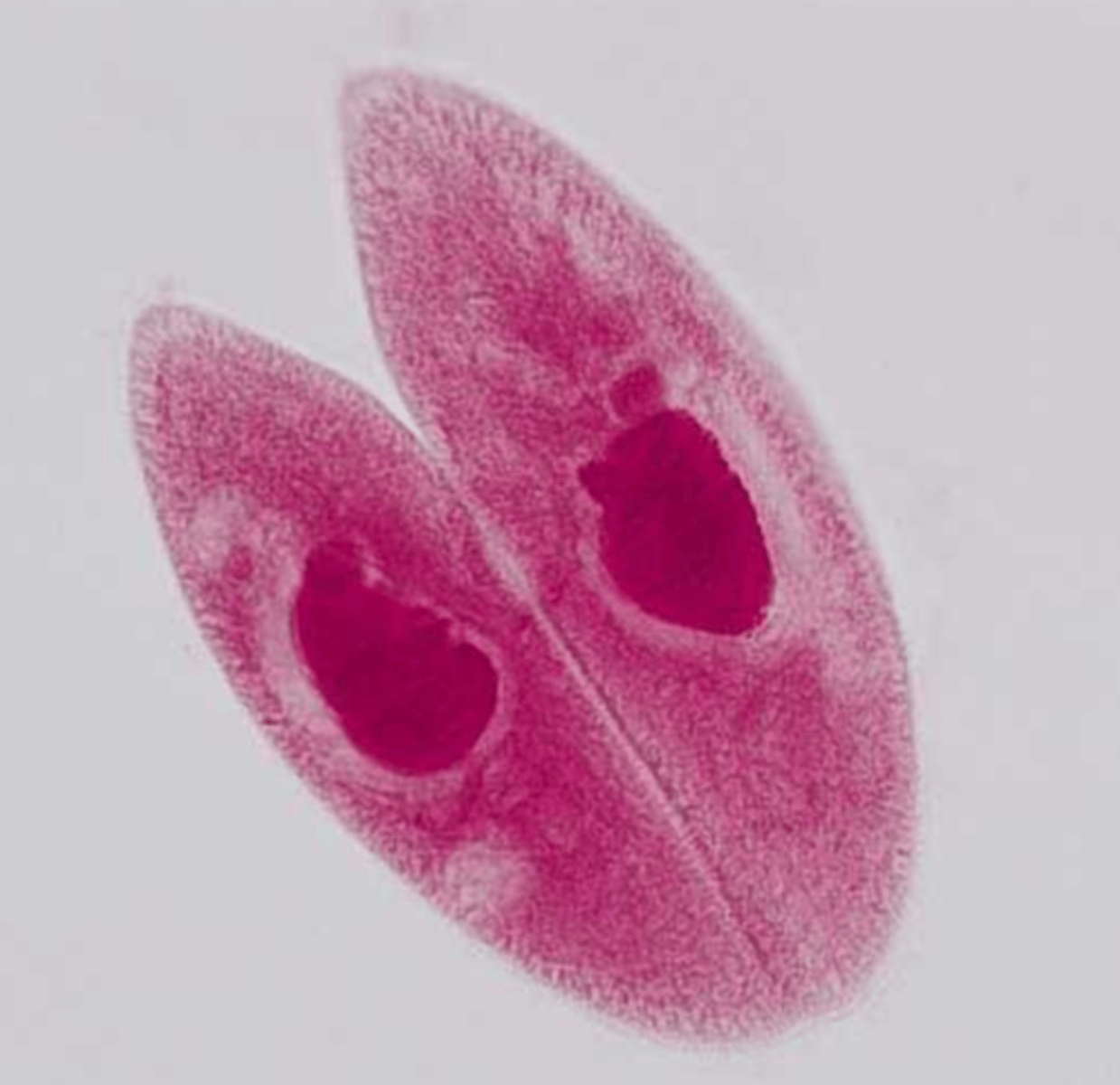
Conjugation (Eukaryotes)
A type of sexual reproduction that occurs when unicellular eukaryotic cells like paramecium join and exchange DNA
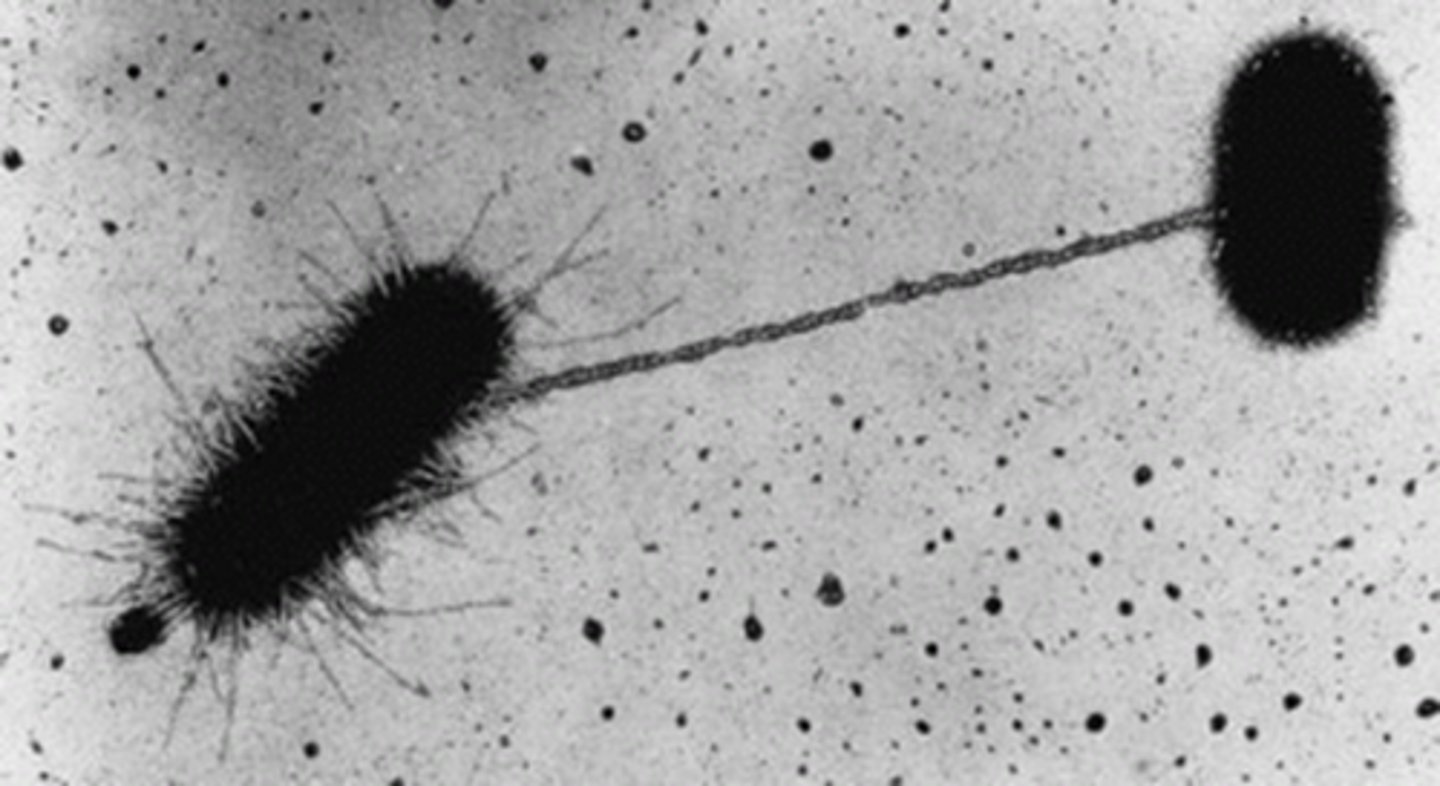
Conjugation (Prokaryotes)
A type of sexual reproduction that occurs when two bacteria join via pili and exchange DNA
Fertilization
A process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells (gametes) join to form a new cell called a zygote
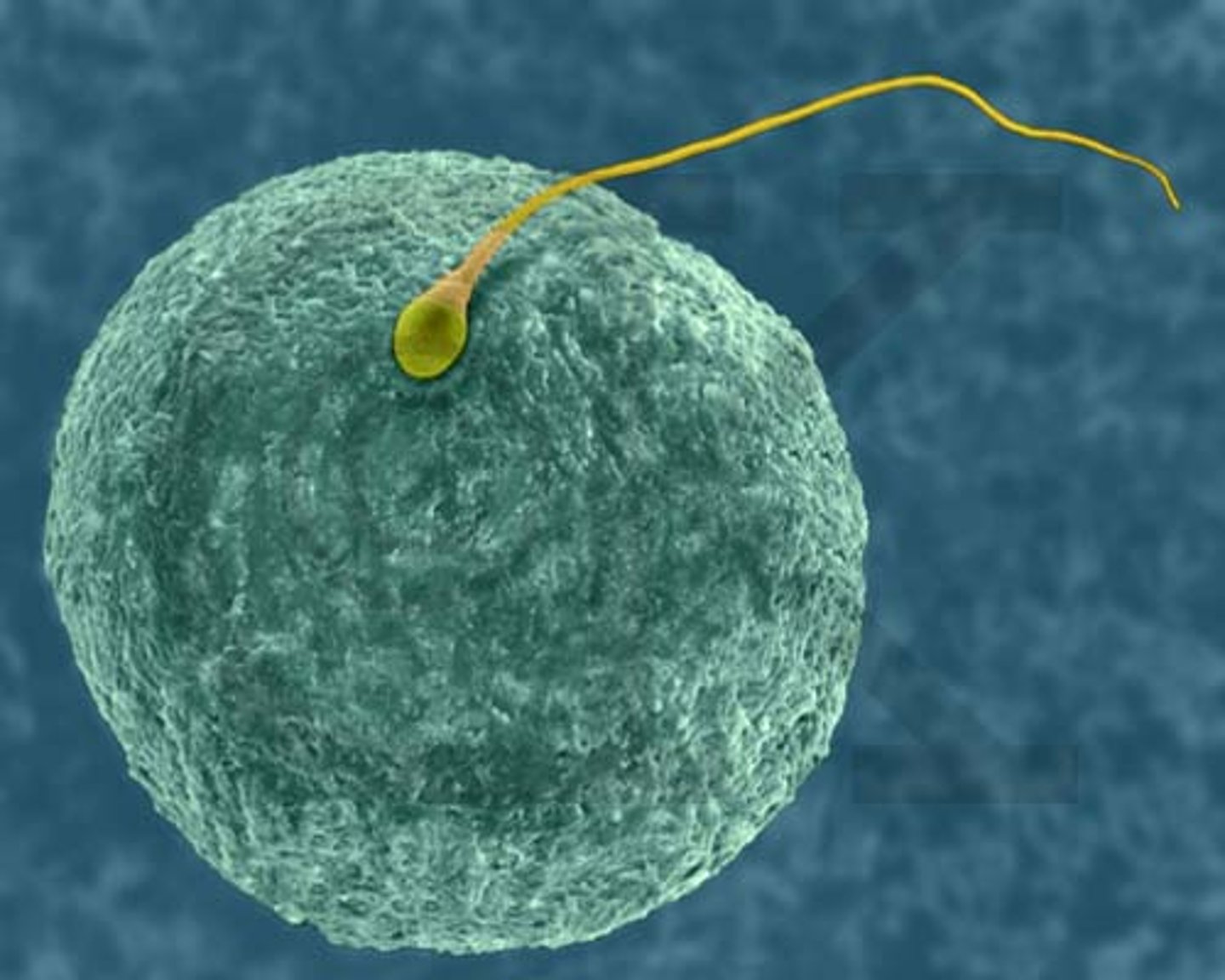
Fertilization (Plants)
A type of sexual reproduction in plants in which the sperm (pollen) and egg fuse to form a genetically unique zygote
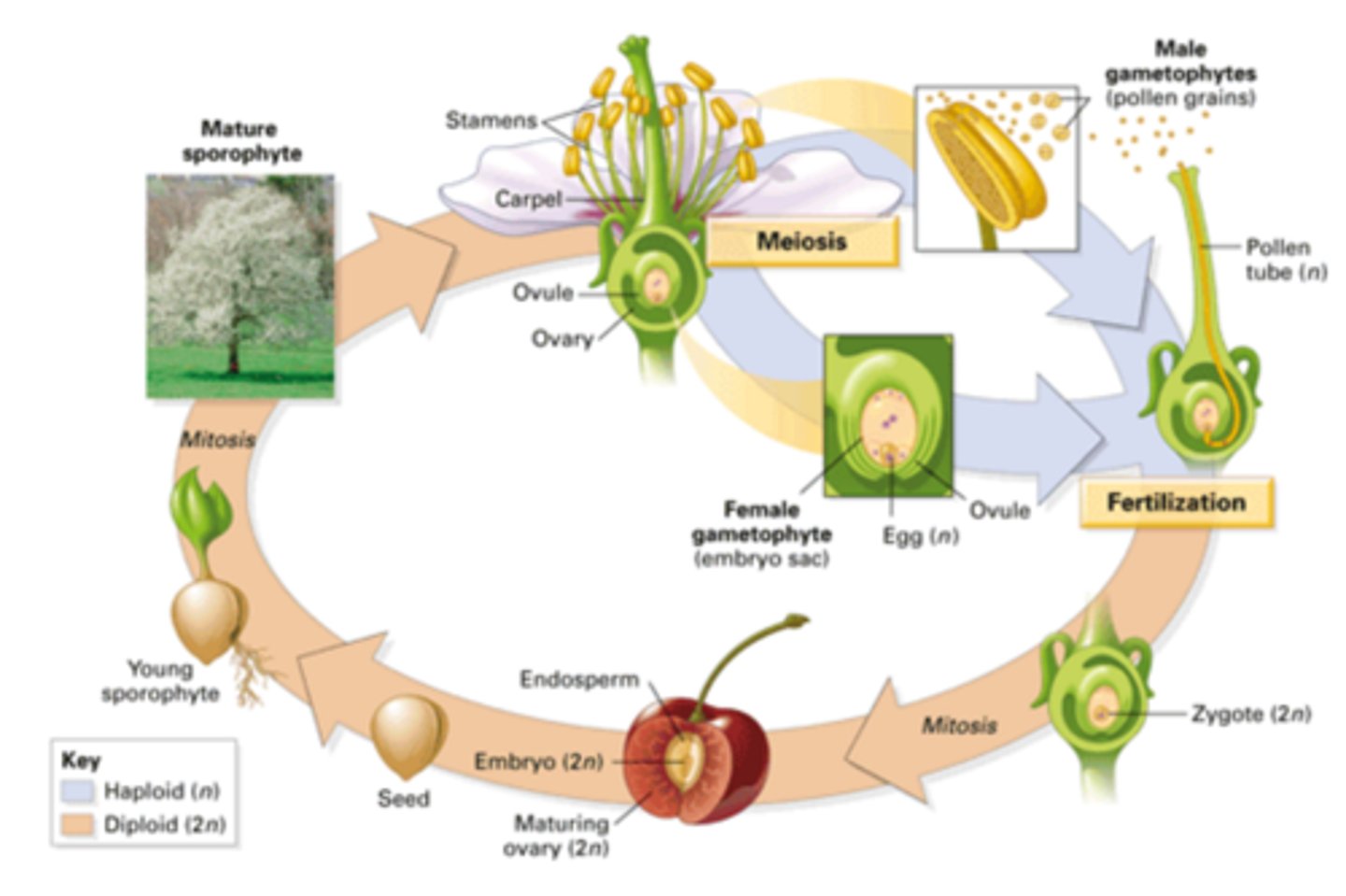
Fertilization (Humans)
A type of sexual reproduction in humans in which a sperm and egg fuse to form a genetically unique zygote
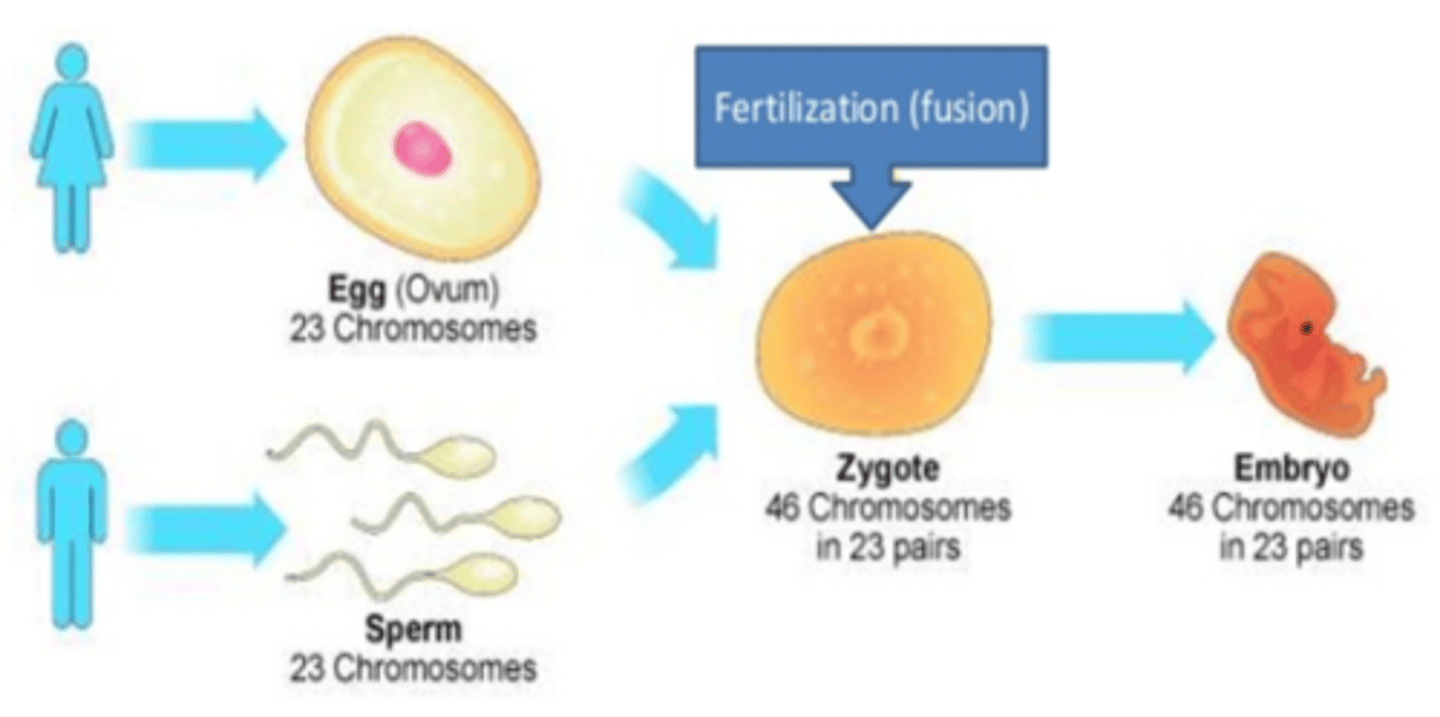
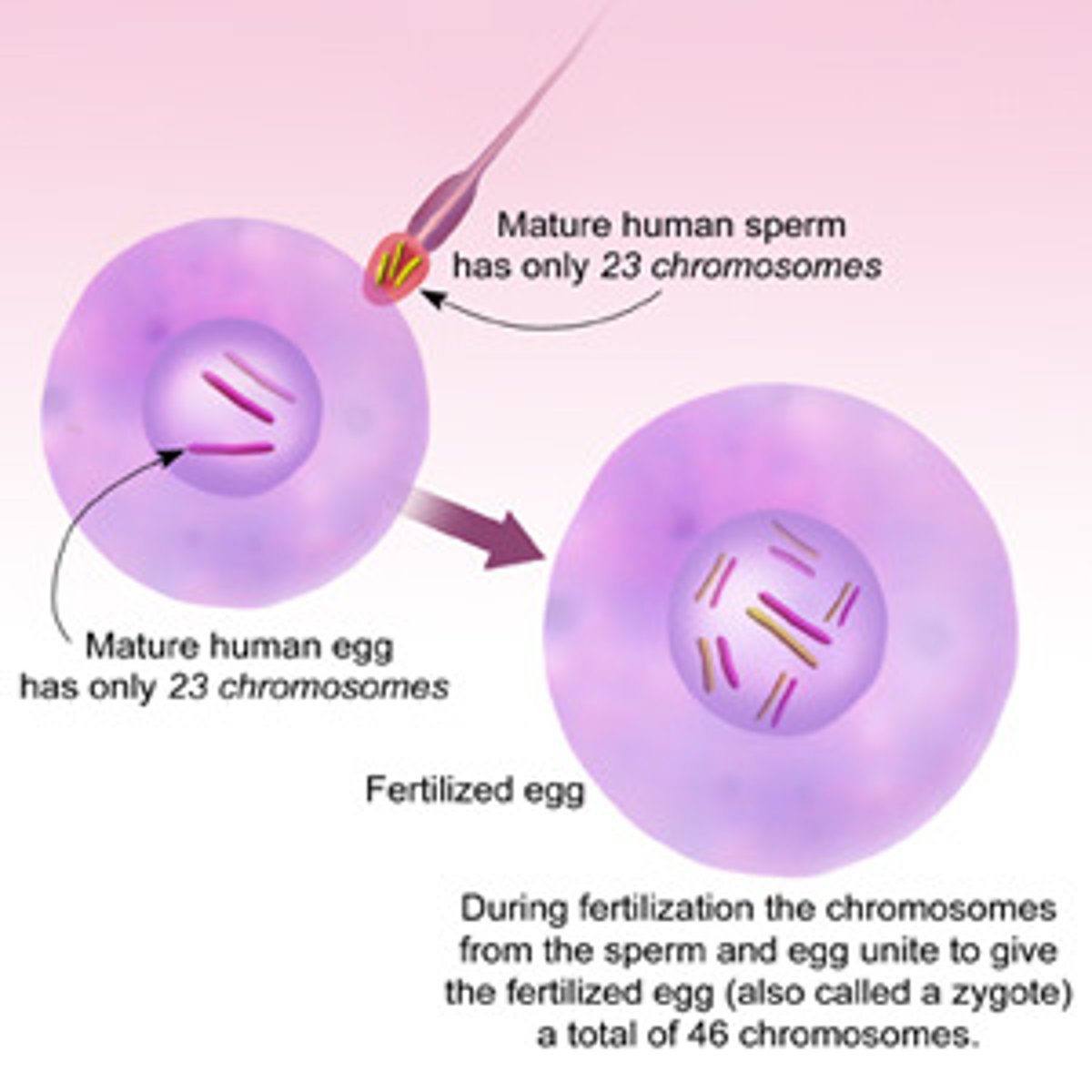
Zygote
The cell formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg
Why do cells divide?
DNA Overload
Exchanging Materials
Surface to Volume Ratio
DNA Overload
The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. Very large cells like muscle cells have many nuclei and are called multinucleate.
Exchange of Materials
Cells must be the appropriate size to exchange nutrients and wastes via diffusion
Surface to Volume Ratio
Cells must have a large surface to volume ratio so that materials can be exchanged via diffusion. The large surface area provides the area for the materials to diffuse across the membrane while the low volume ensure that the materials can travel all the way in and out the cell
Cell division
The process in reproduction and growth by which a cell divides to form daughter cells
Multinucleate
A cell with many nuclei; typical of large cells like muscle cells
Chromatin
Thread-like DNA present when the cells is not dividing; consists of nucleic acid and proteins that are loosely coiled
Genes
Sequences of nucleotides on chromosomes that code for specific traits
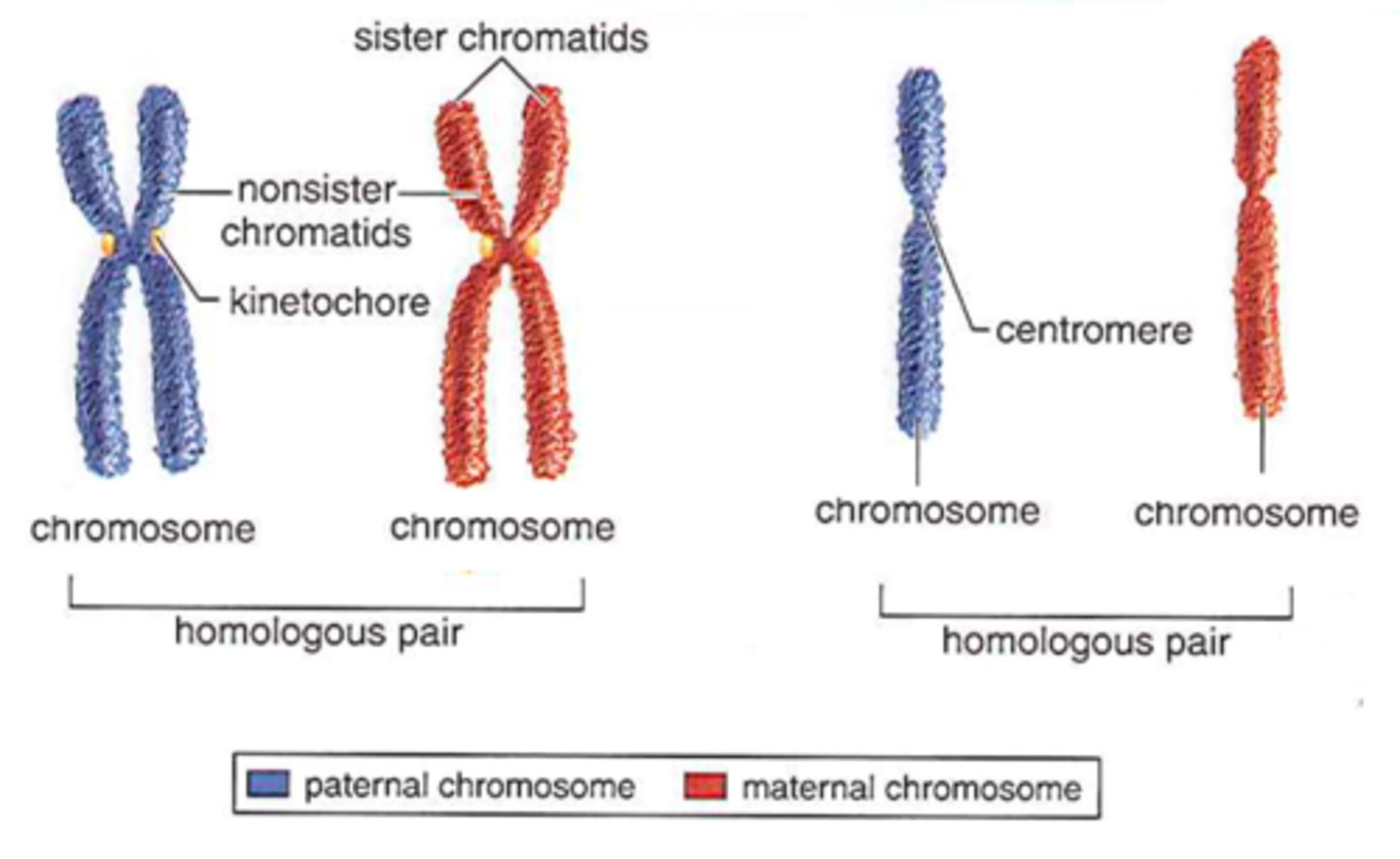
Chromosome
A single piece of coiled DNA and associated proteins found in a linear form in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and circular forms in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells; contains genes that encode traits. Each species has a characteristic number or chromosomes.
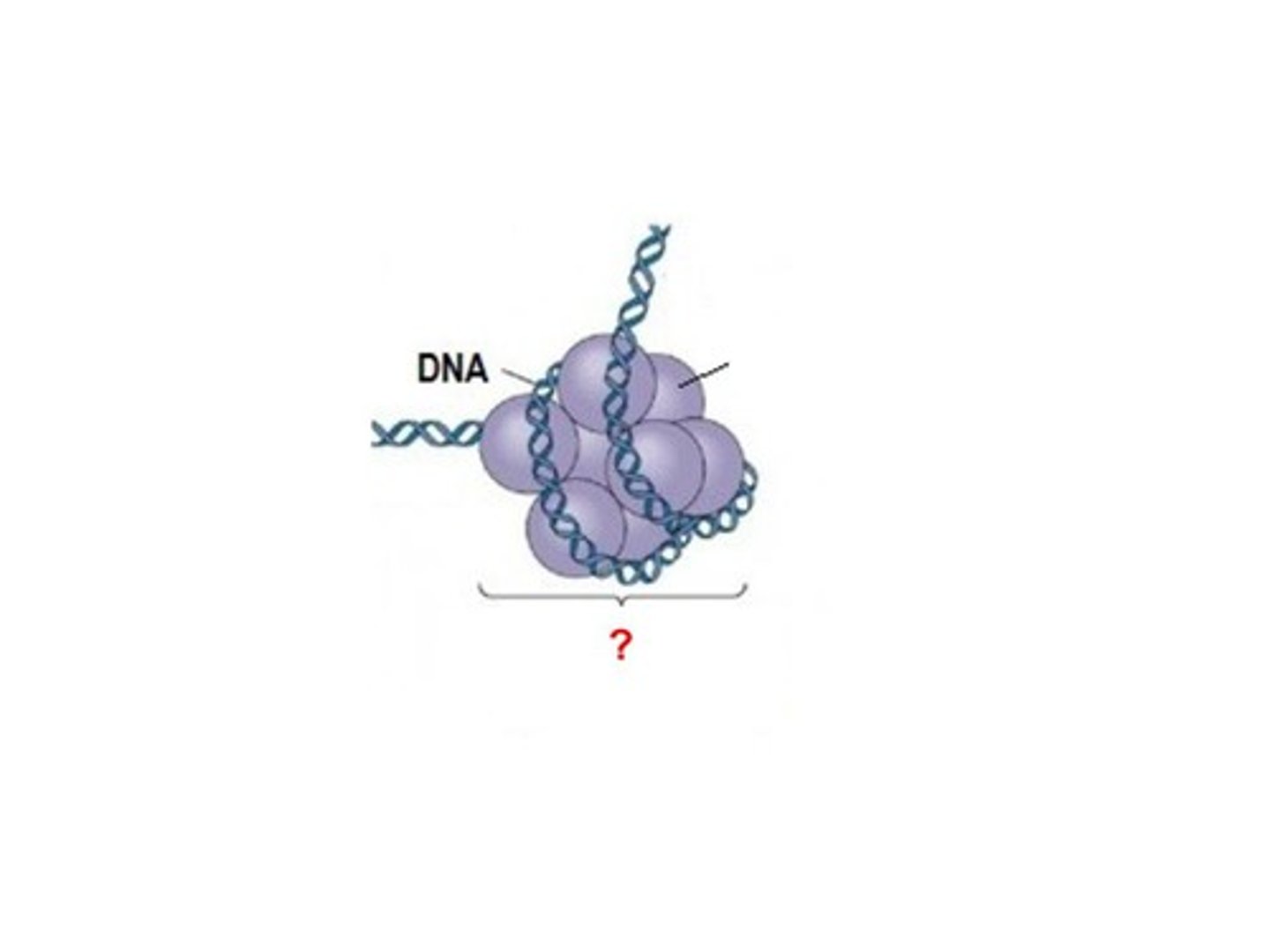
Histones
A globular protein that assists in DNA packaging in eukaryotes when the strand of DNA wraps around it
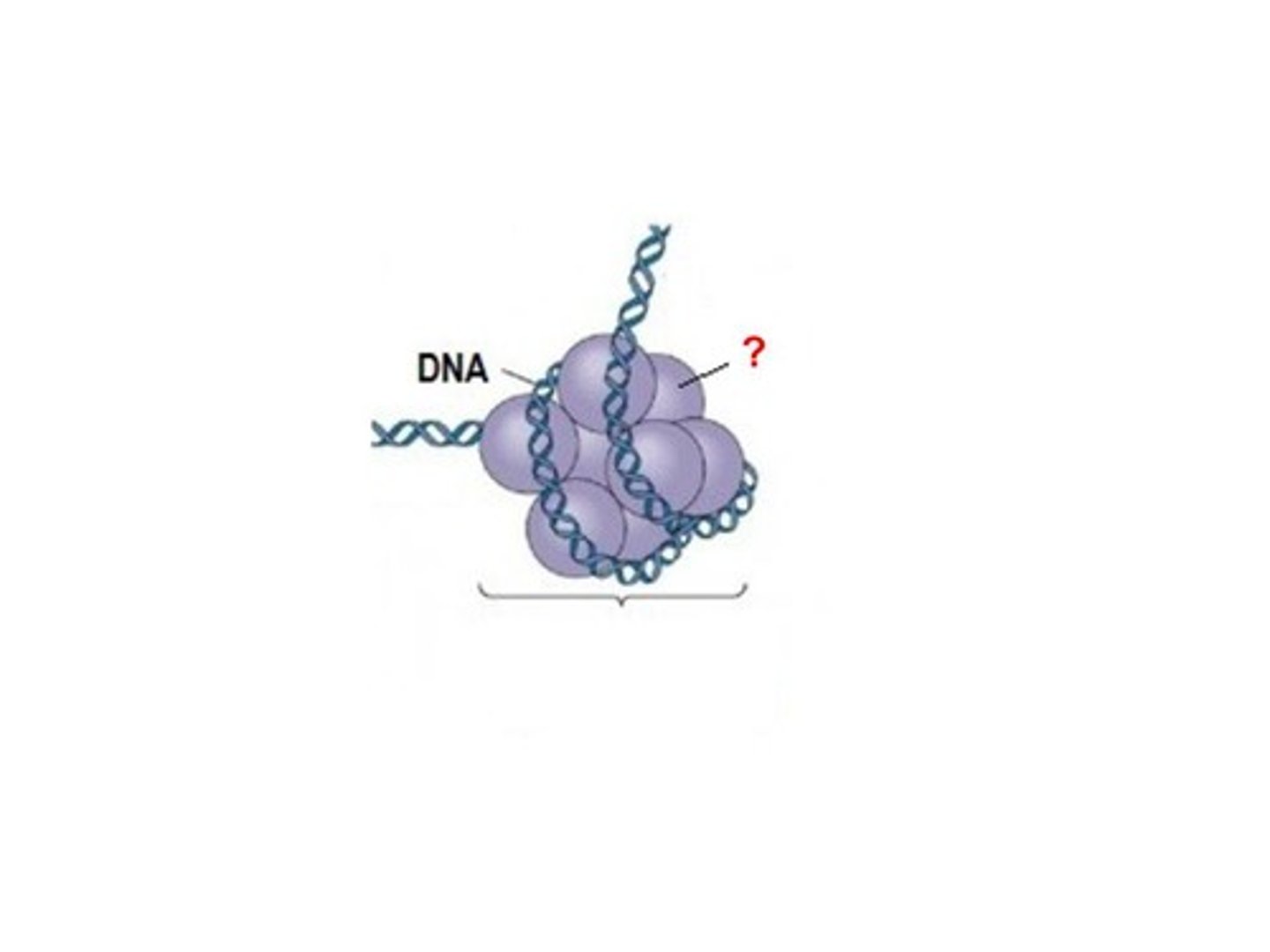
Nucleosomes
The structures formed when DNA is coiled around histones
Mitosis
A type of cell division that occurs in eukaryotes by which the nucleus and duplicated chromosomes of a cell divide and are evenly distributed, forming two daughter nuclei. Makes identical body cells to allow organisms to grow and repair tissue so is considered a type of asexual reproduction.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms; results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell; produces gametes and plant spores
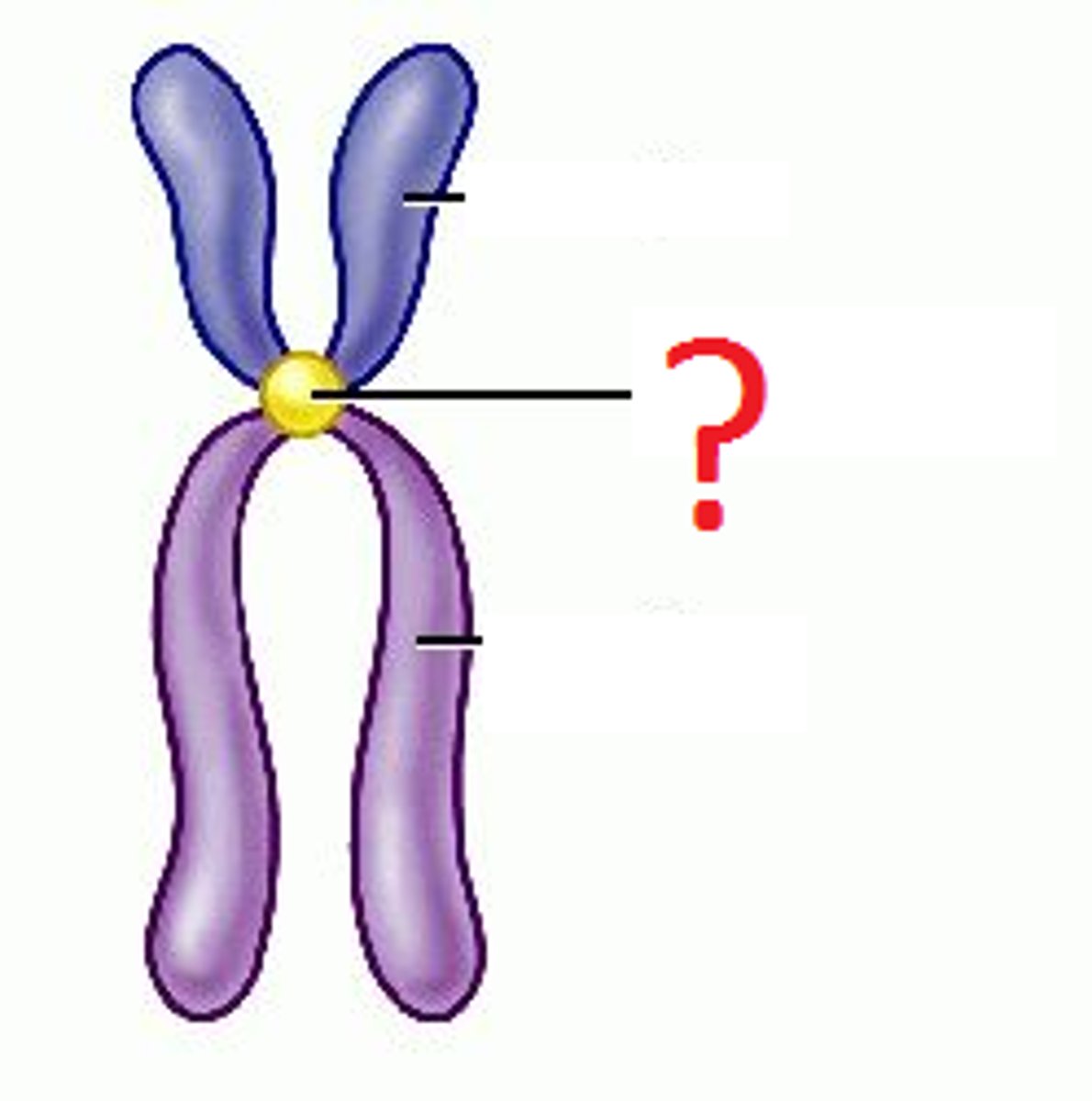
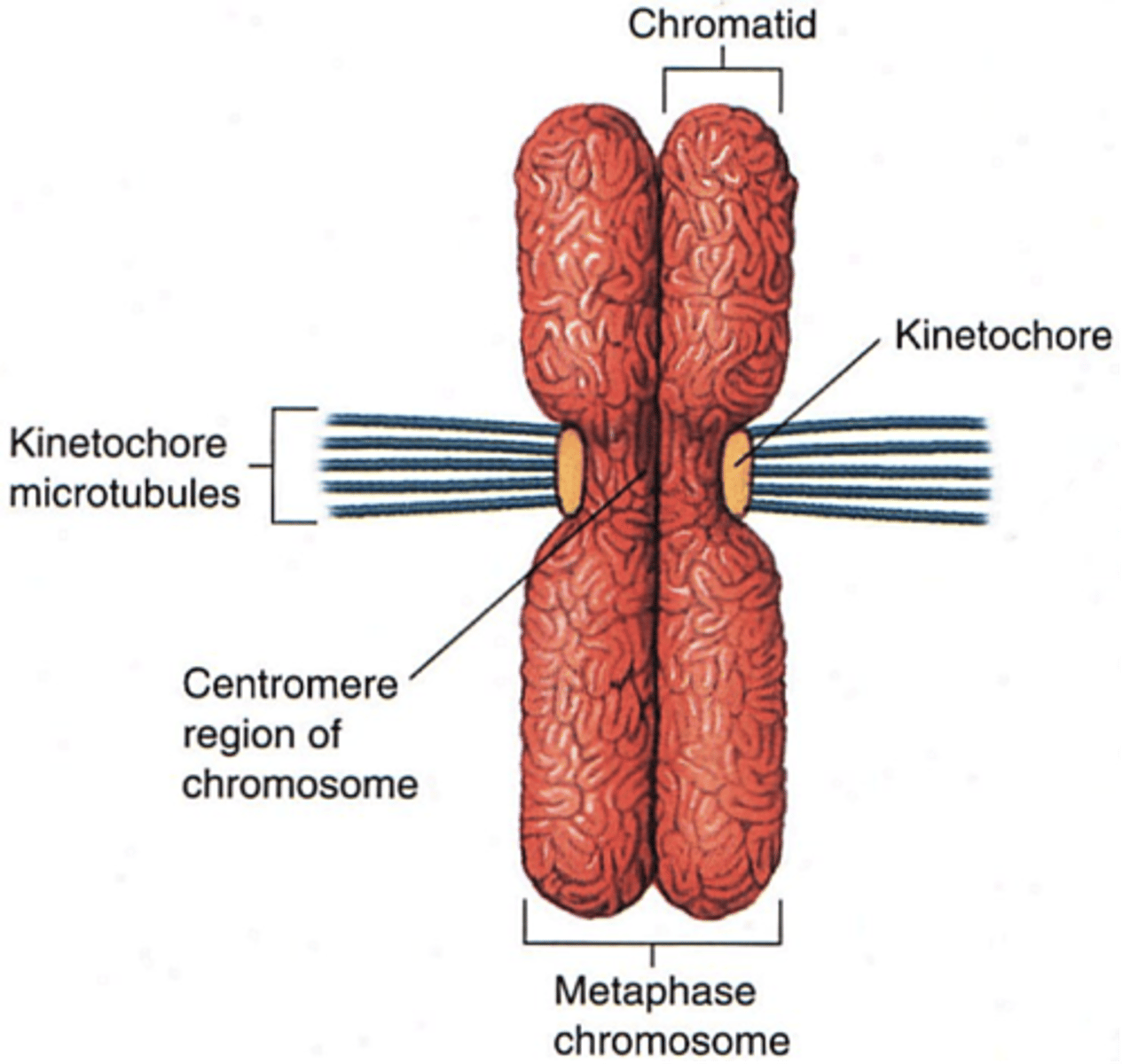
Sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis
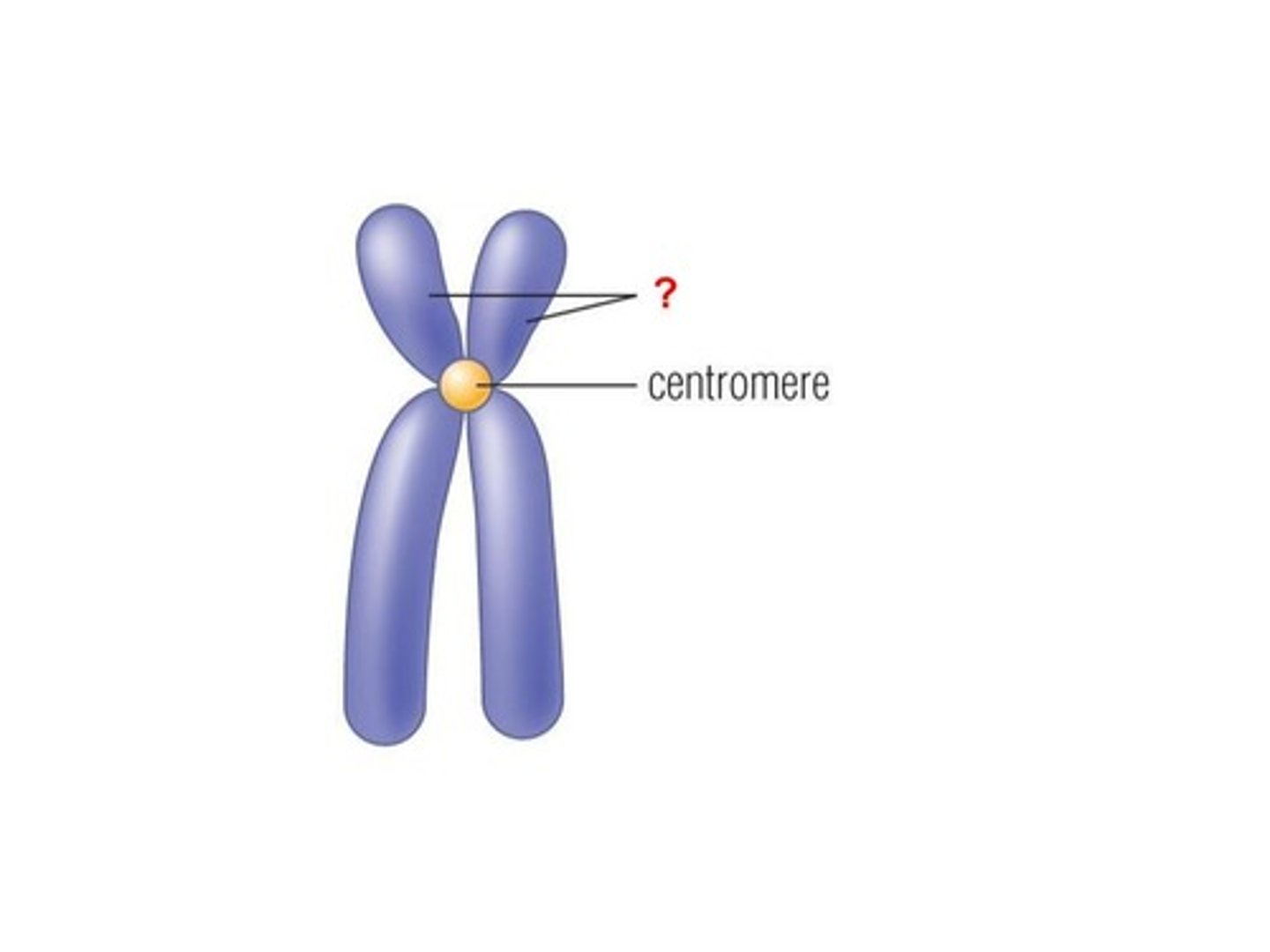
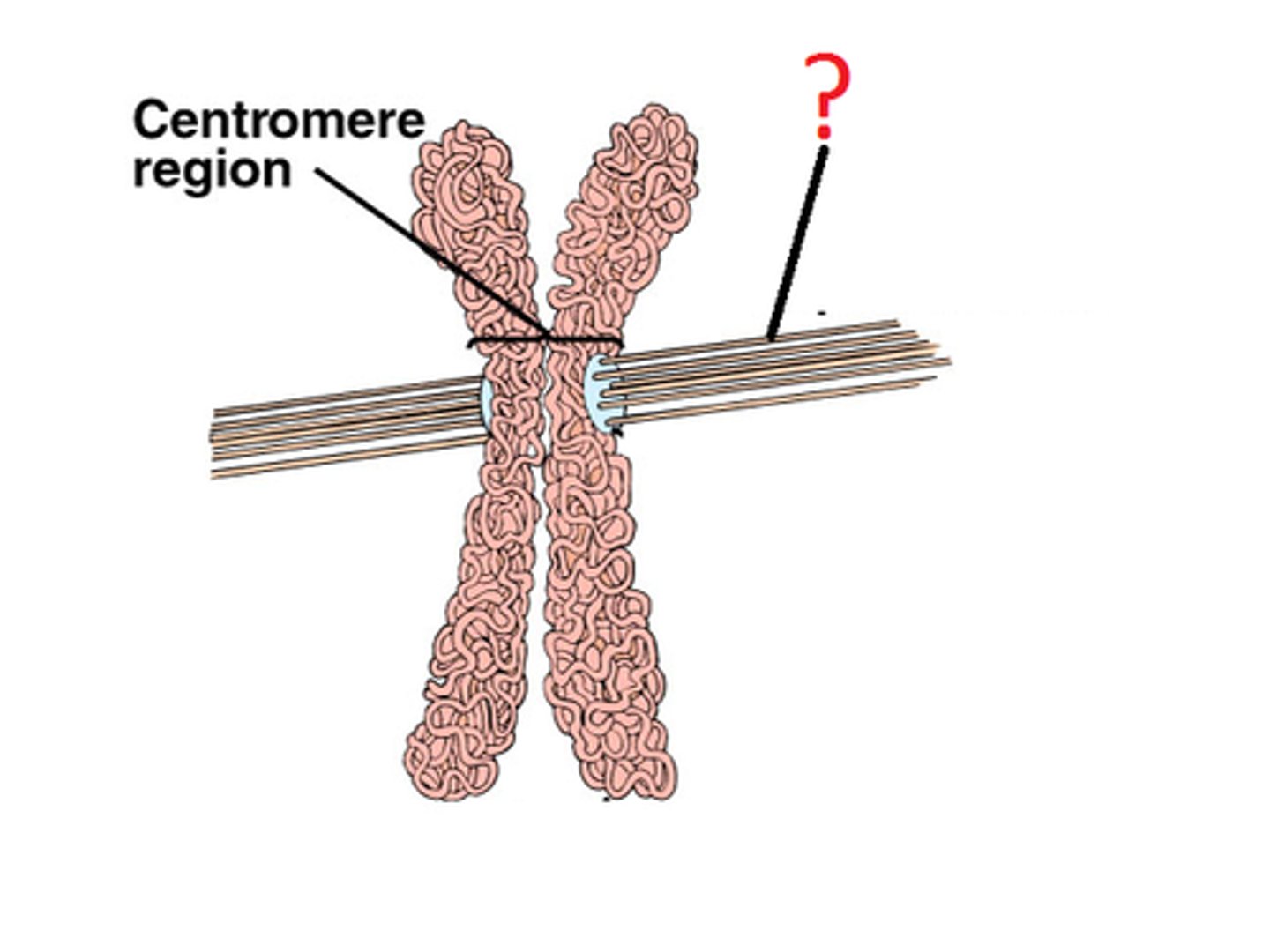
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
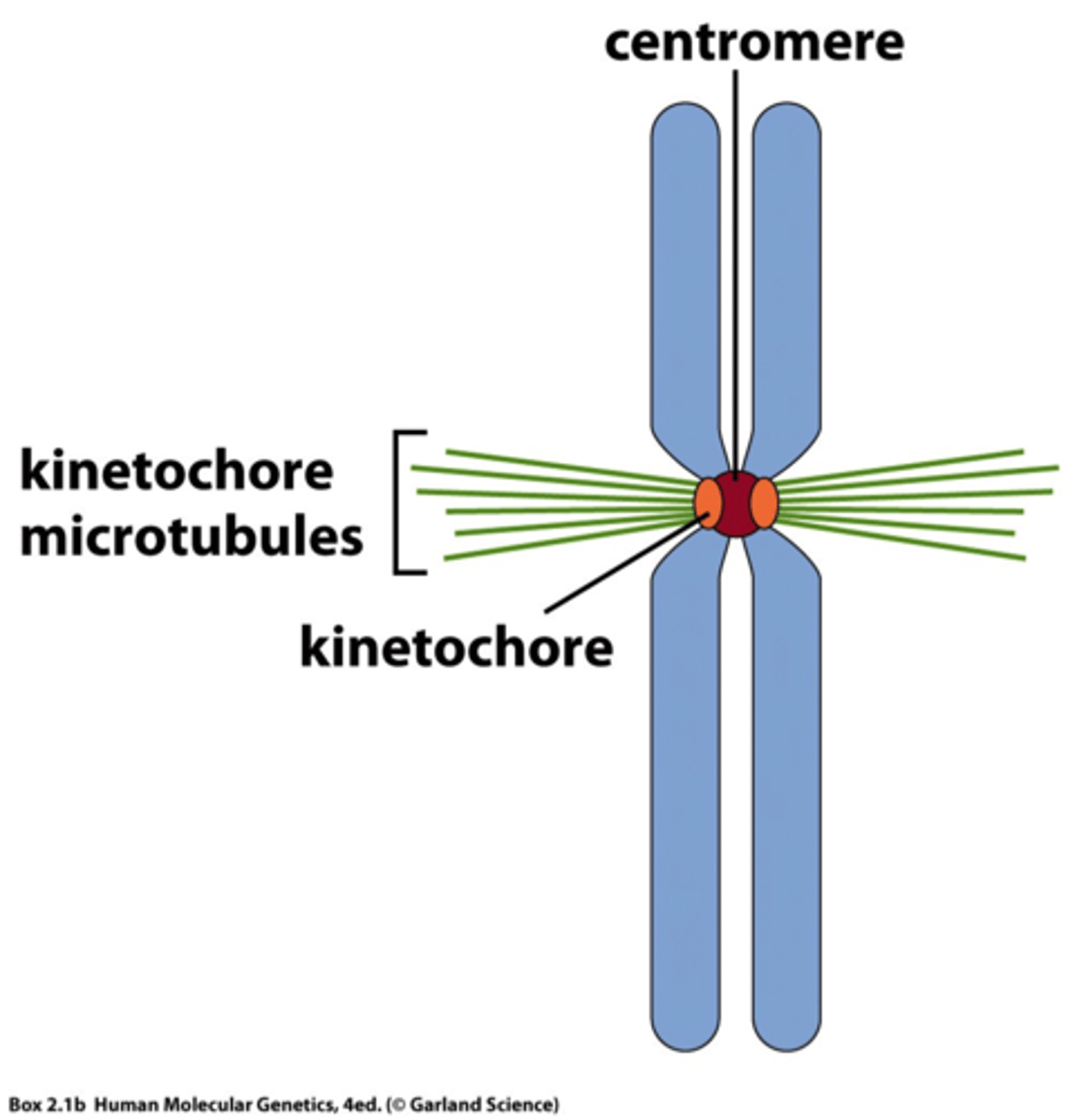
Kinetochore
A disc-shaped protein on the centromere that attaches the chromatid to the mitotic spindle during cell division
The Cell Cycle
The series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
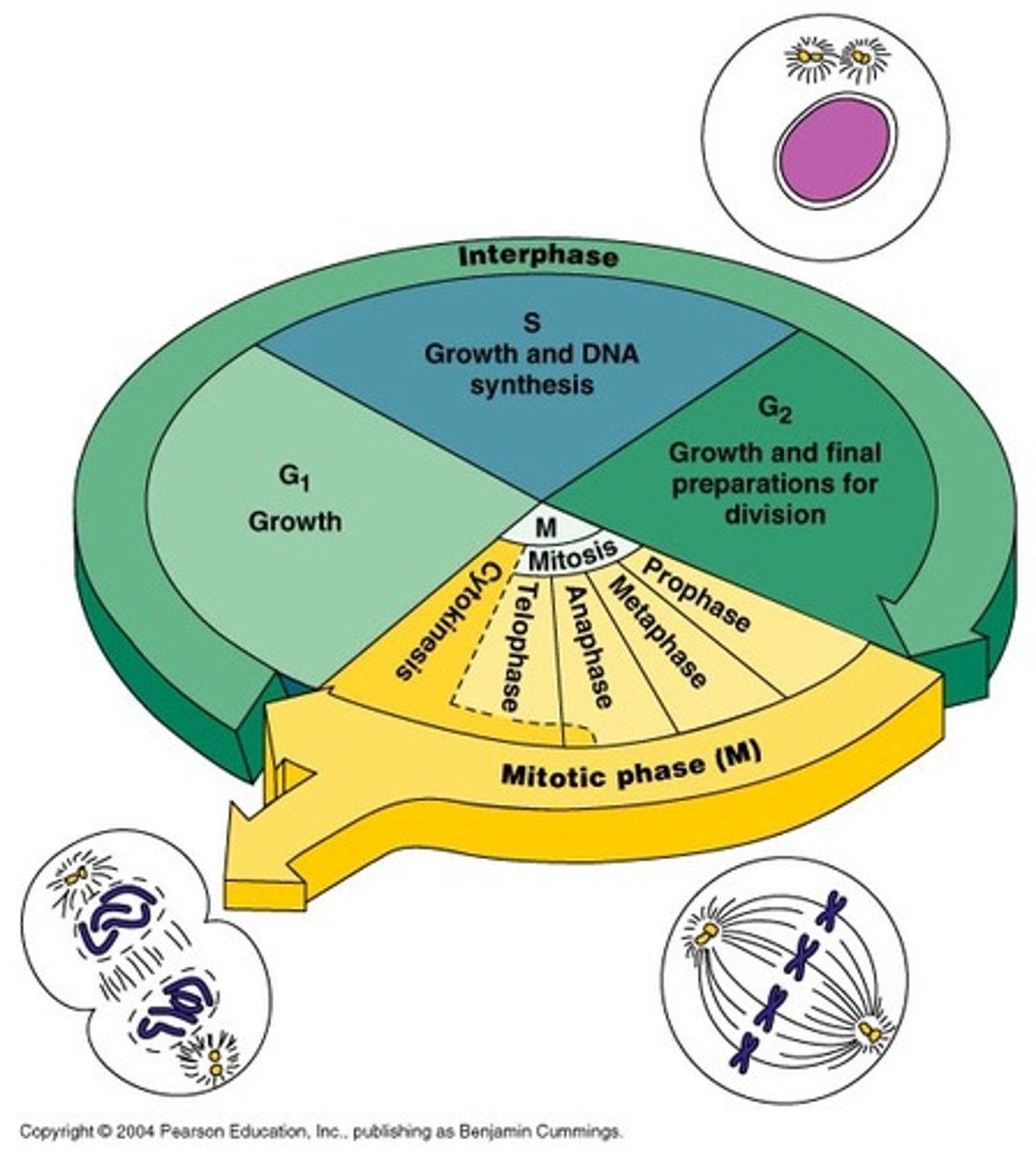
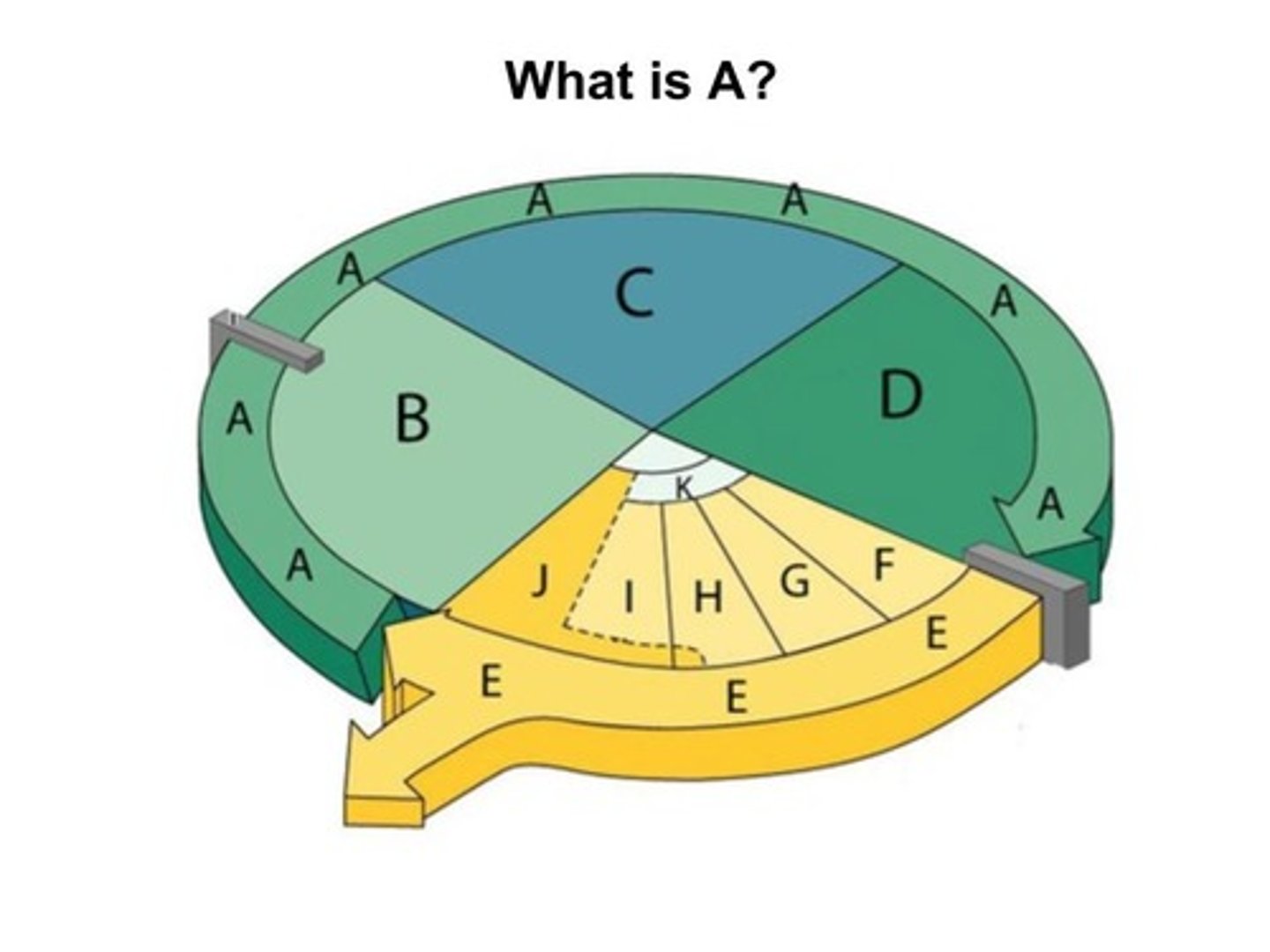
Interphase
The part of the cell cycle where the cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
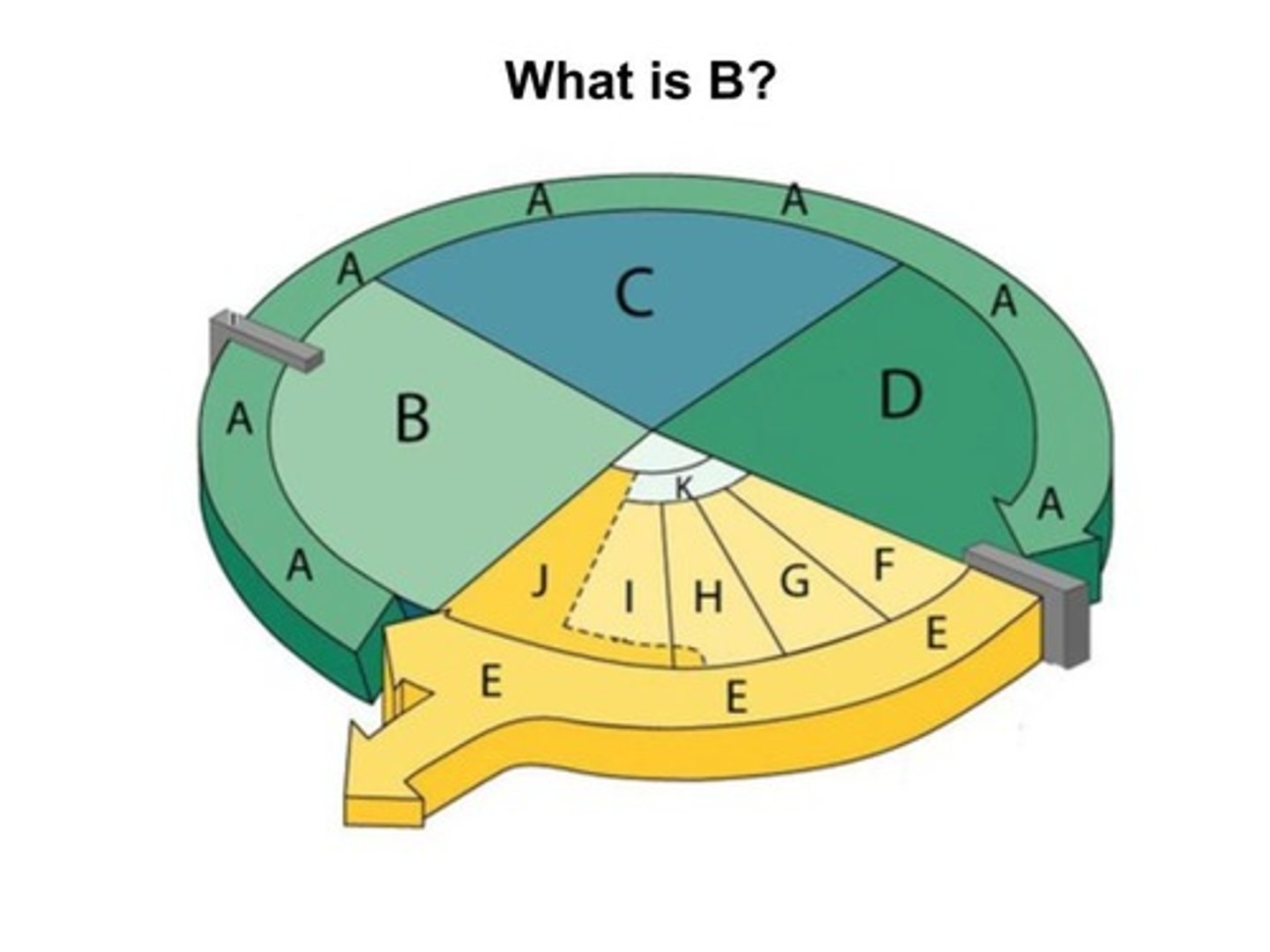
G1 phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins; the cell increases in size and makes new proteins and organelles
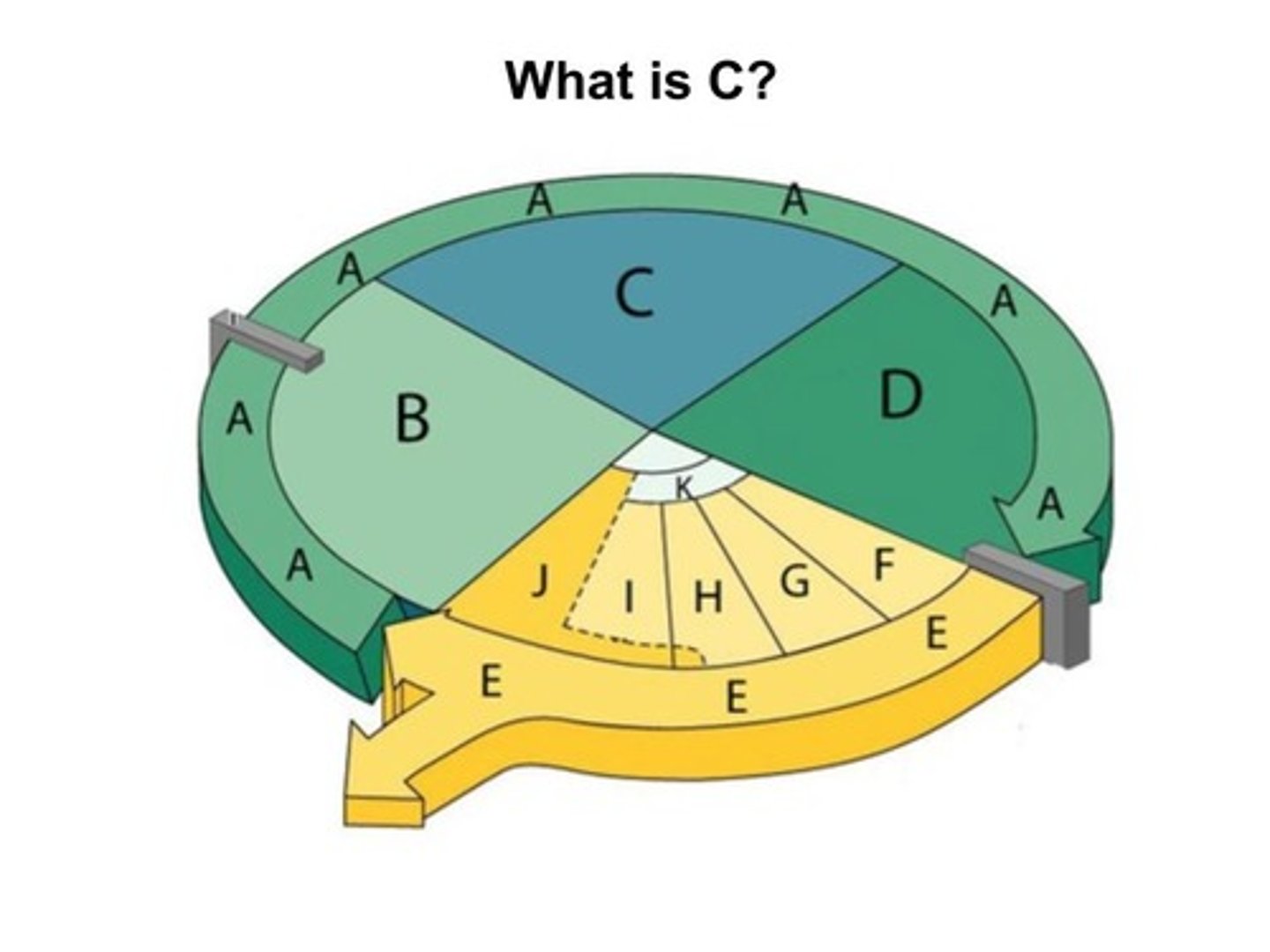
S phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated;
chromosomes are replicated to form sister chromatids attached by centromere
G2 phase
The second gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs; organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced; centrioles replicate and spindle begins to form
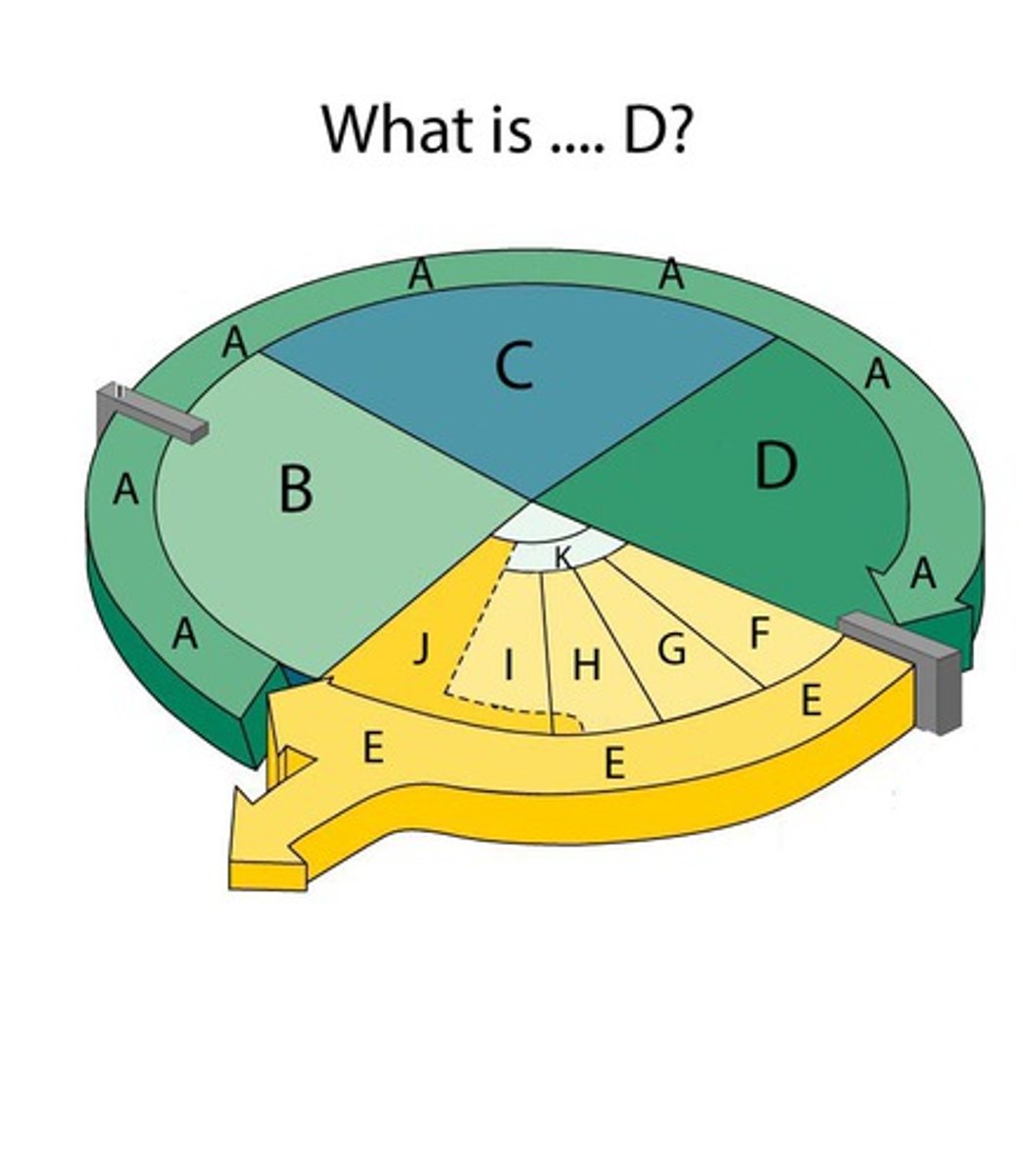
M phase
The phase of the cell cycle that includes mitosis and cytokinesis
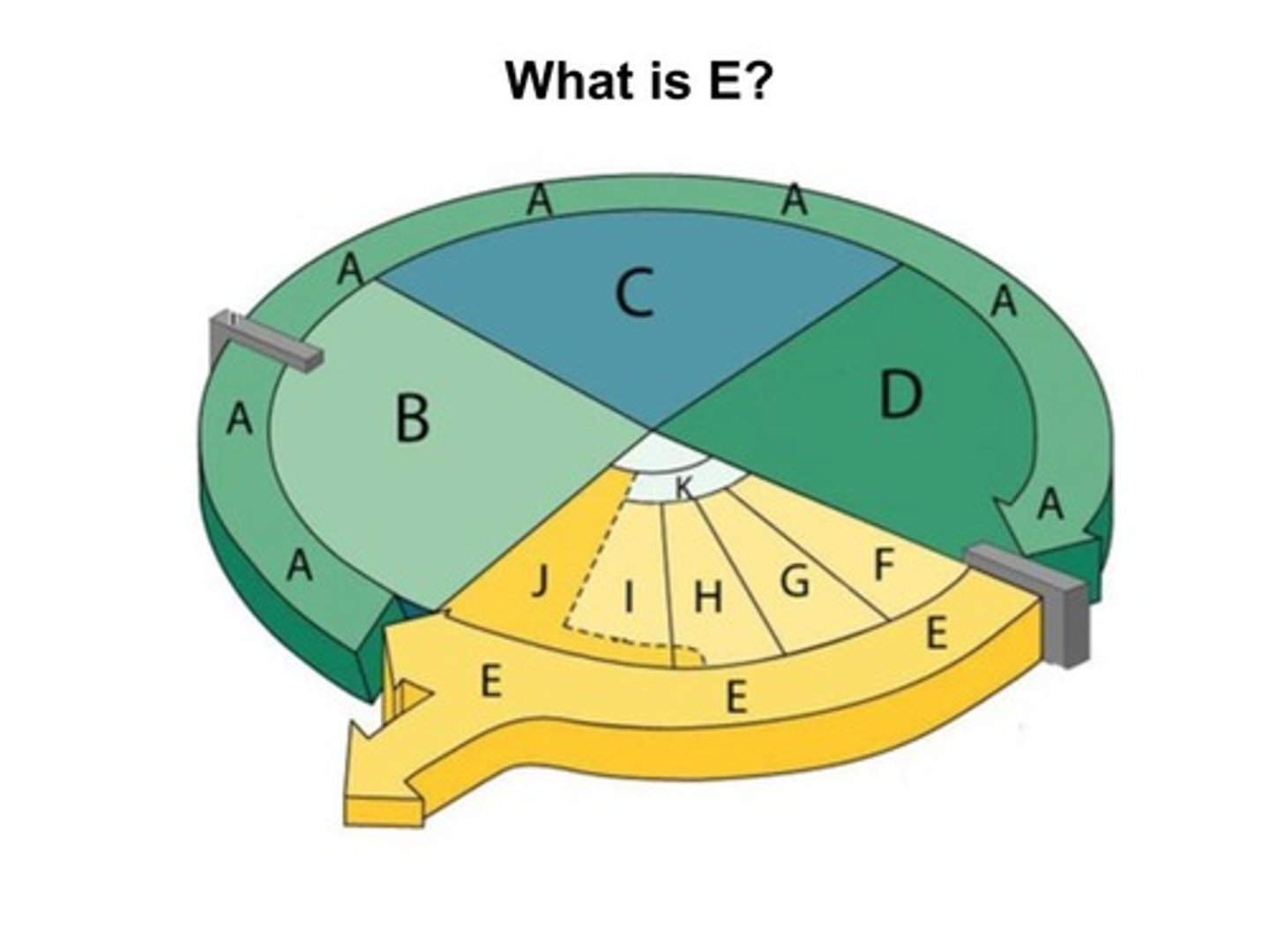
Mitosis
A process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells conventionally divided into four stages - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase; results in the formation of two new nuclei each having the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus
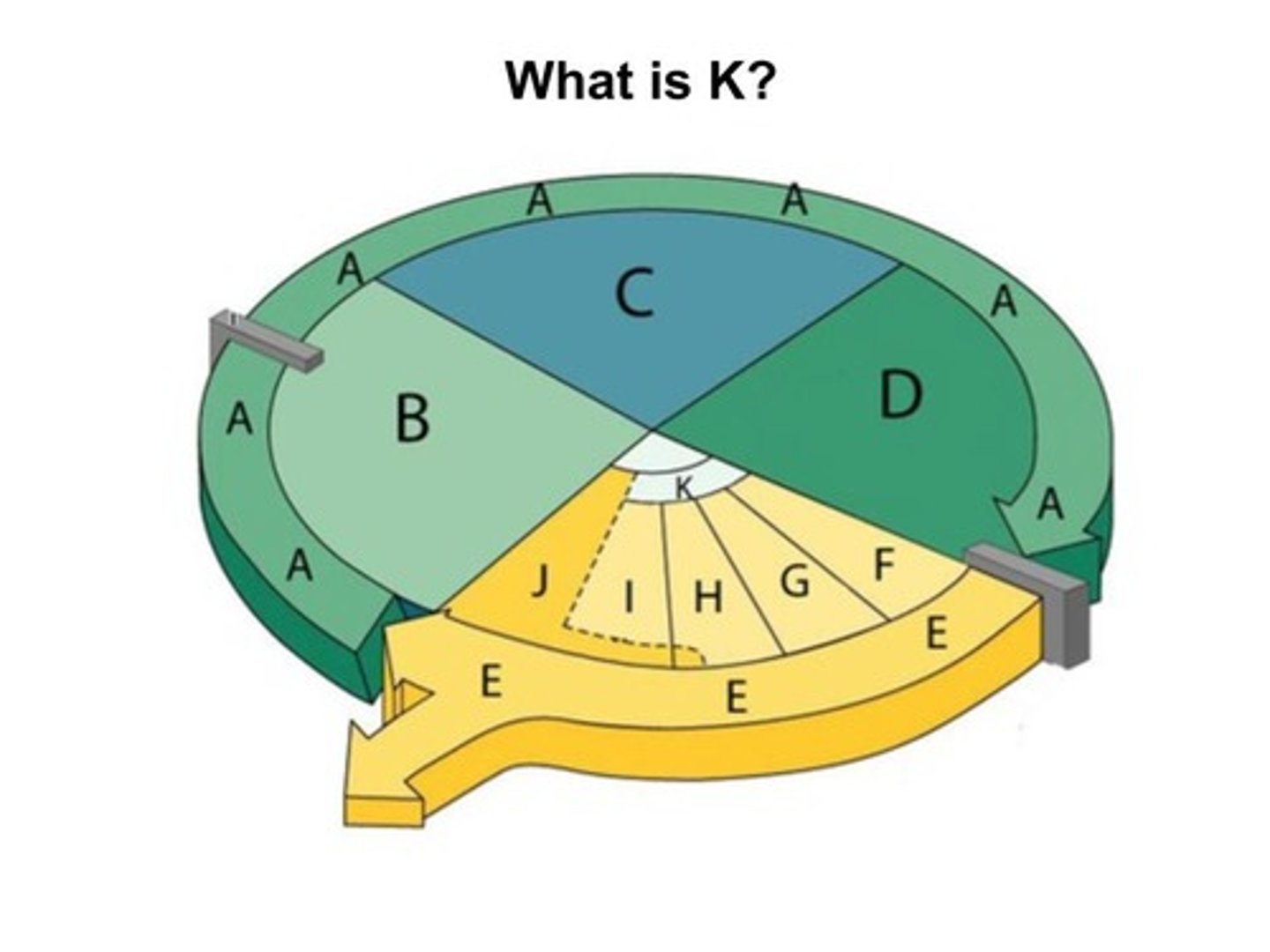
Cytokinesis
The final stage of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells, in which the cell's cytoplasm divides, distributing the organelles into each of the two new daughter cells
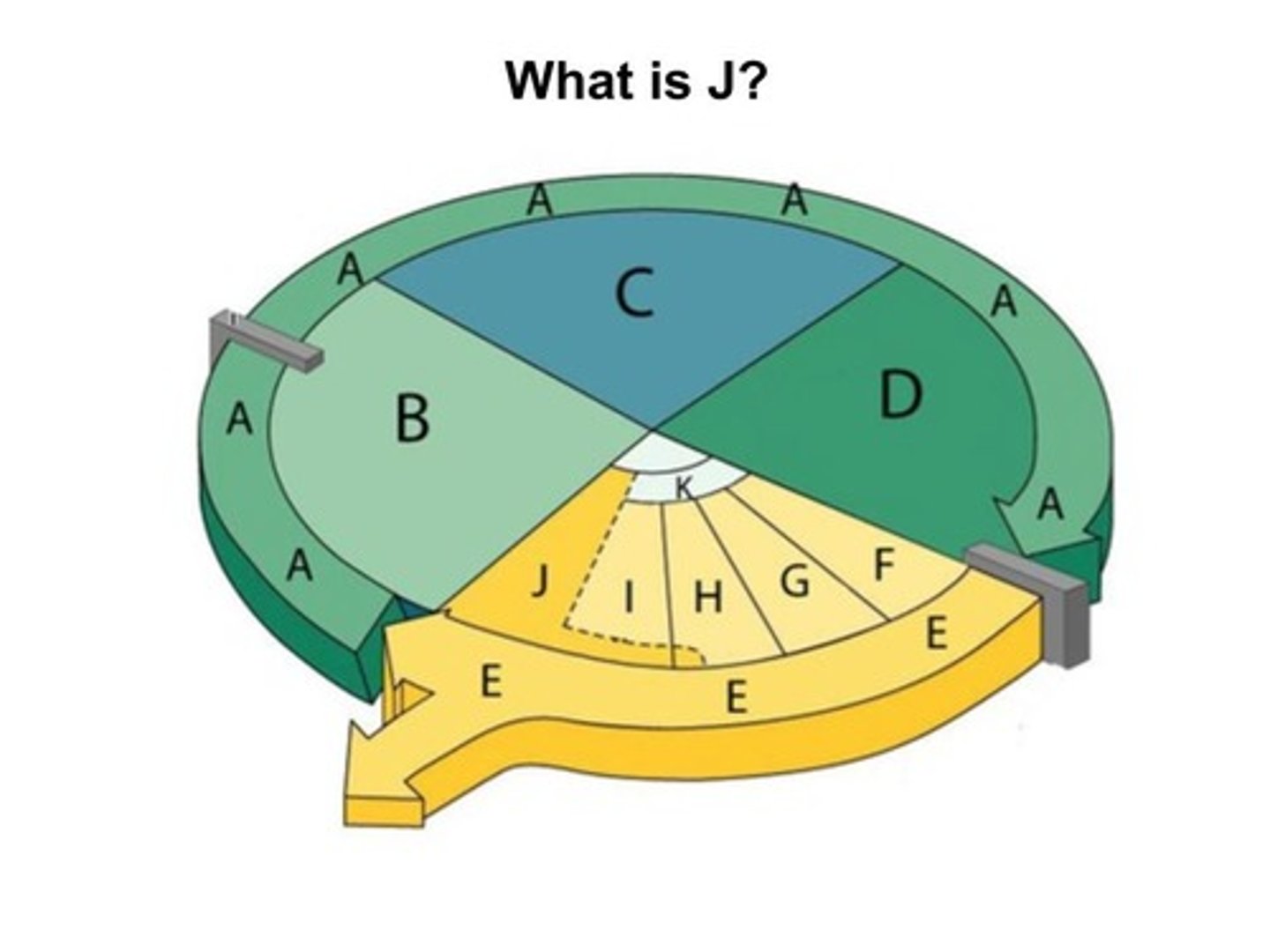
Rate of Mitosis
Cells undergo mitosis at different rates based upon cell type and environmental conditions; some cells like nerve and heart cells only replicate for a short time after birth; other cells, like skin and body linings replicate frequently to repair worn out or damaged cells; prokaryotes like bacteria replicate rapidly about every 20 minutes
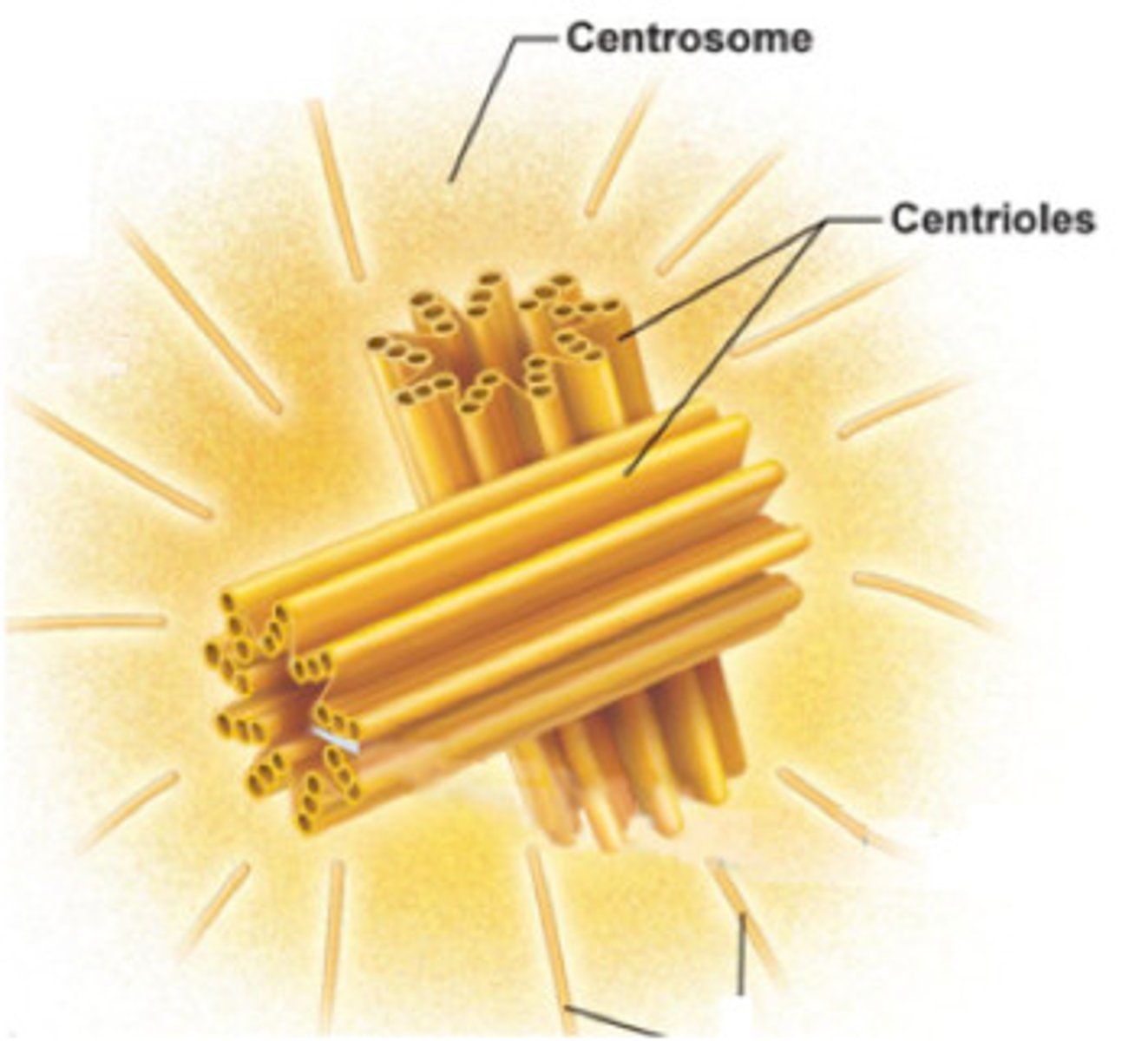
Centrosomes
Microtubule-organizing centers that help to form and organize the mitotic spindle during mitosis
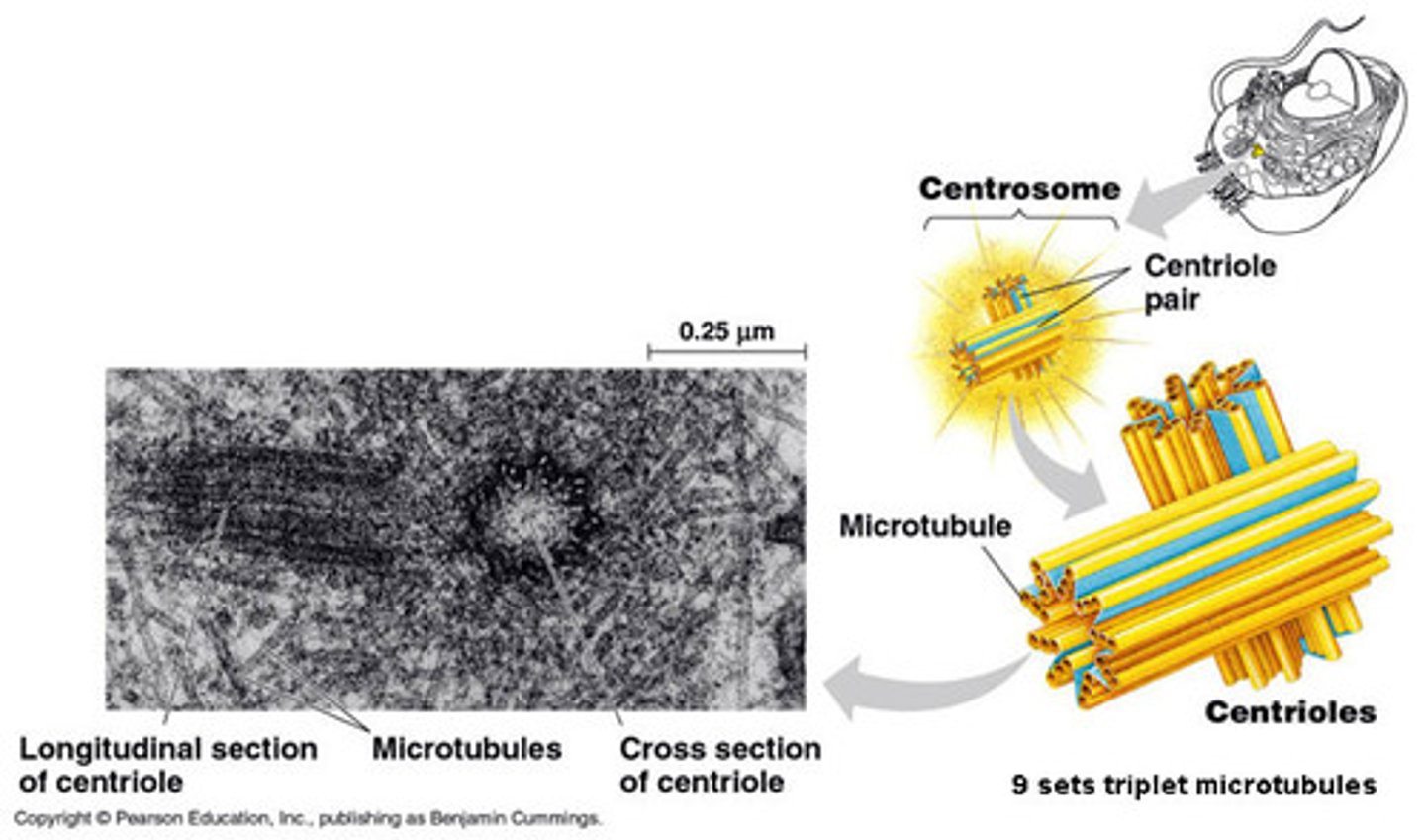
Centrioles
A small, cylindrical cell organelle, seen near the nucleus in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells, that divides during mitosis, the new pair of centrioles moving ahead of the spindle to opposite poles of the cell as the cell divides
Kinetochore
A disc-shaped protein on the centromere that attaches the chromatid to the mitotic spindle during cell division
Microtubules
A hollow rod of the protein tubulin in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells that make up cilia, flagella, spindle fibers, and other cytoskeletal structures of cells
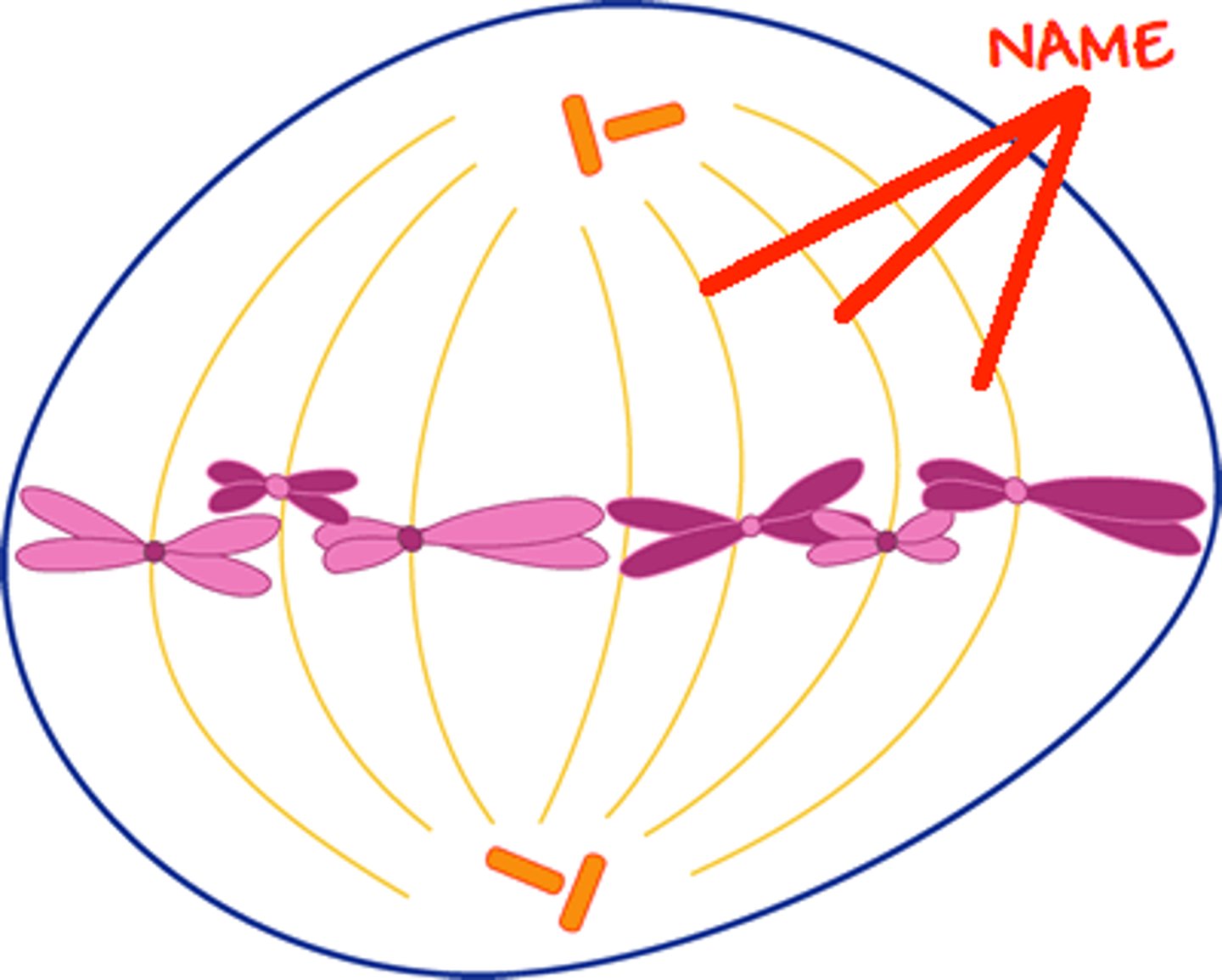
Polar Microtubules
Microtubules that stretch between the poles, lengthening as the cell divides
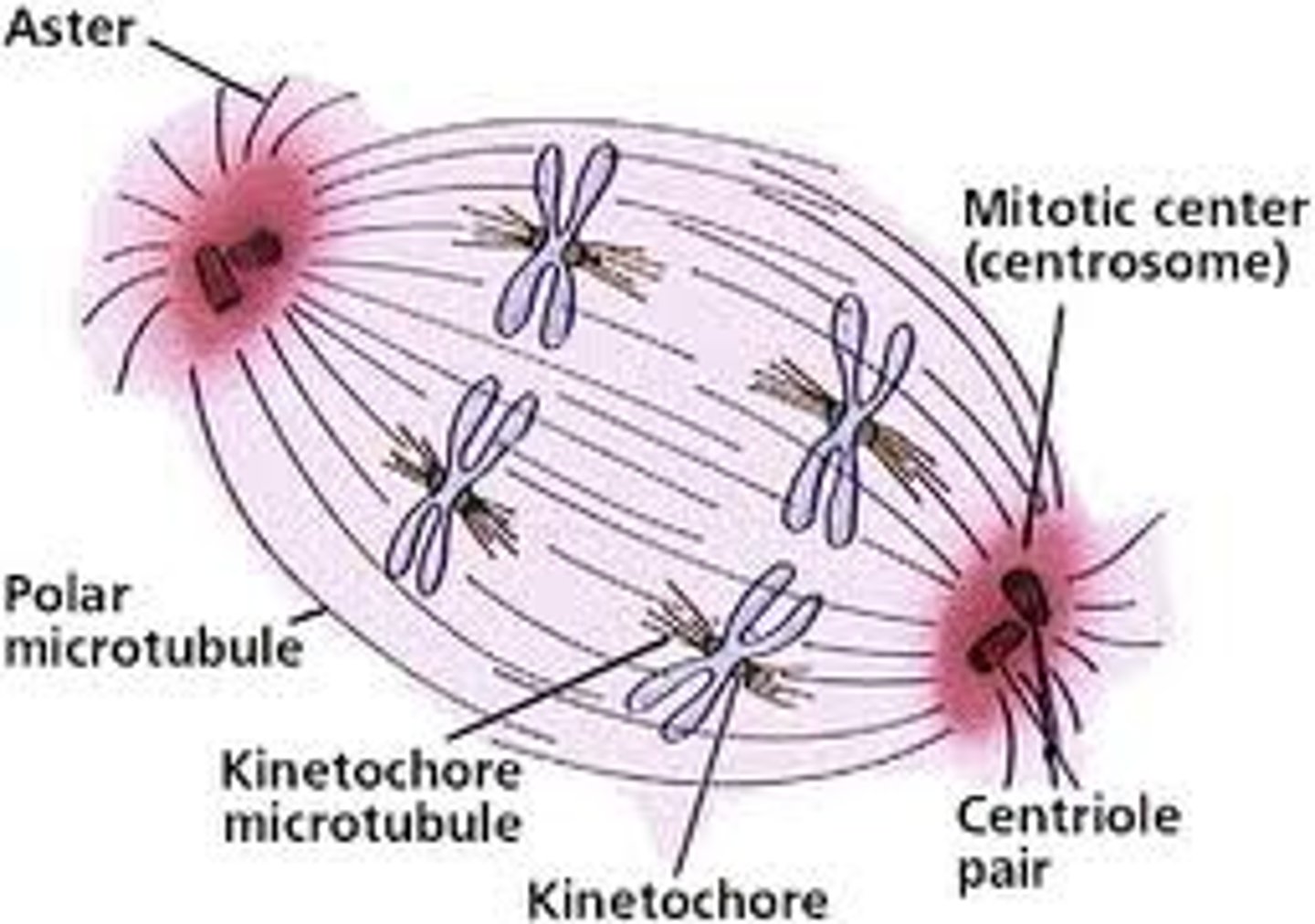
Spindle fibers
Long fibers of microtubules made up of protein that grow out of centrioles during mitosis and meiosis and attach to the centromere of sister chromatids to pull them apart
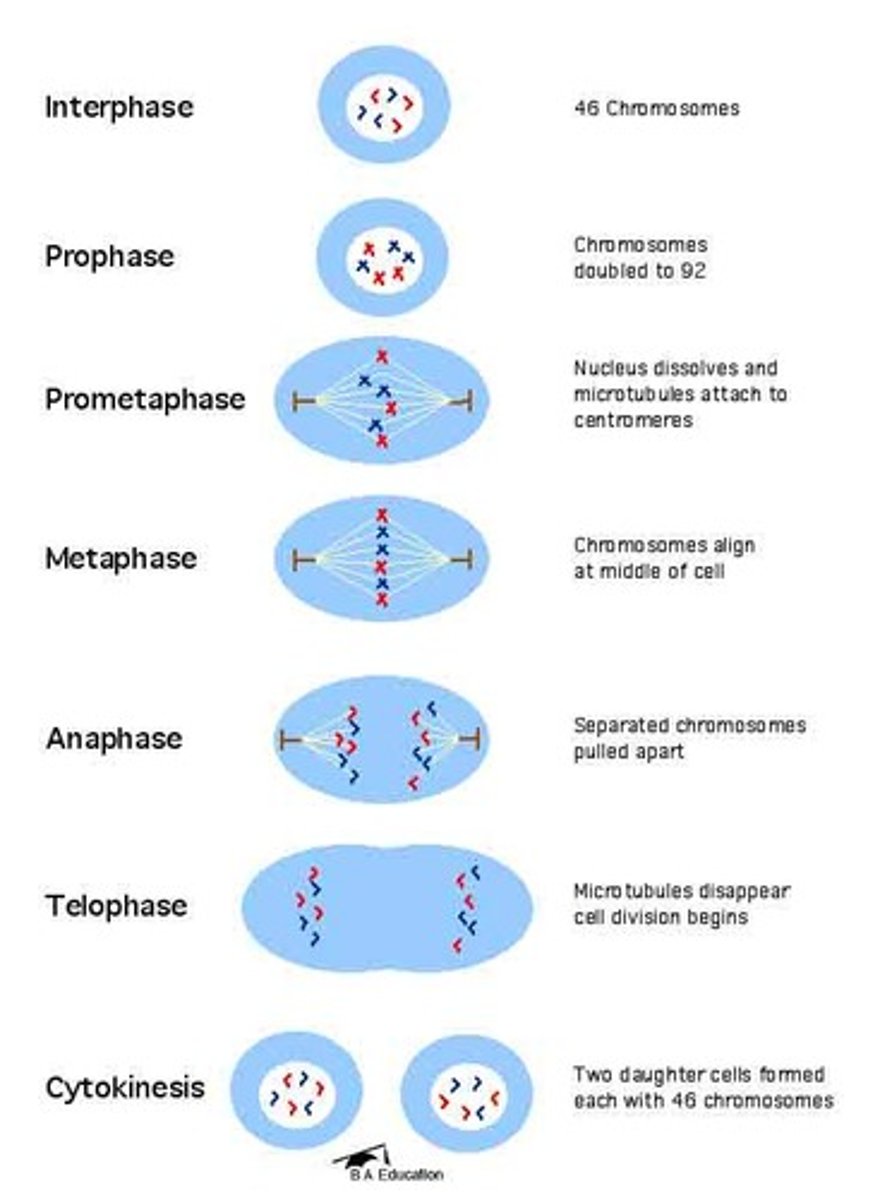
PMAT
The stages of mitosis that include prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase; ("please make a twin")
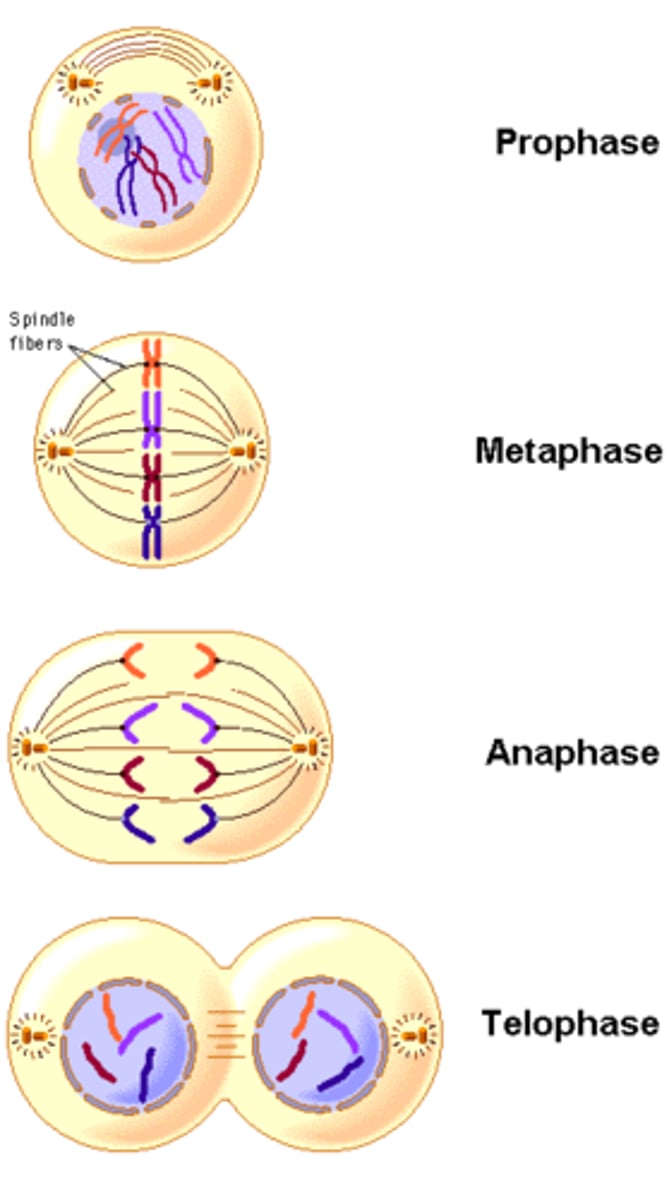
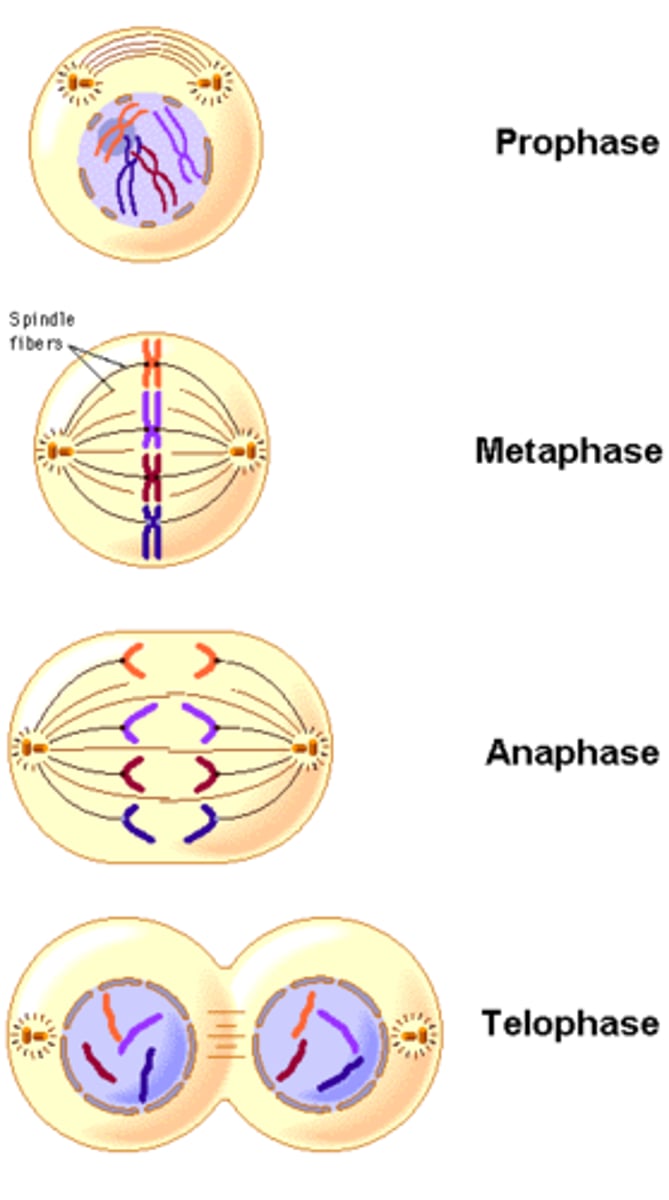
Prophase
First and longest phase of mitosis; centrioles lie in a region called the centrosome; centrosome helps to organize the spindle - a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes; in animal cells centrioles separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus; the nuclear envelope breaks down; chromosomes continue to condense
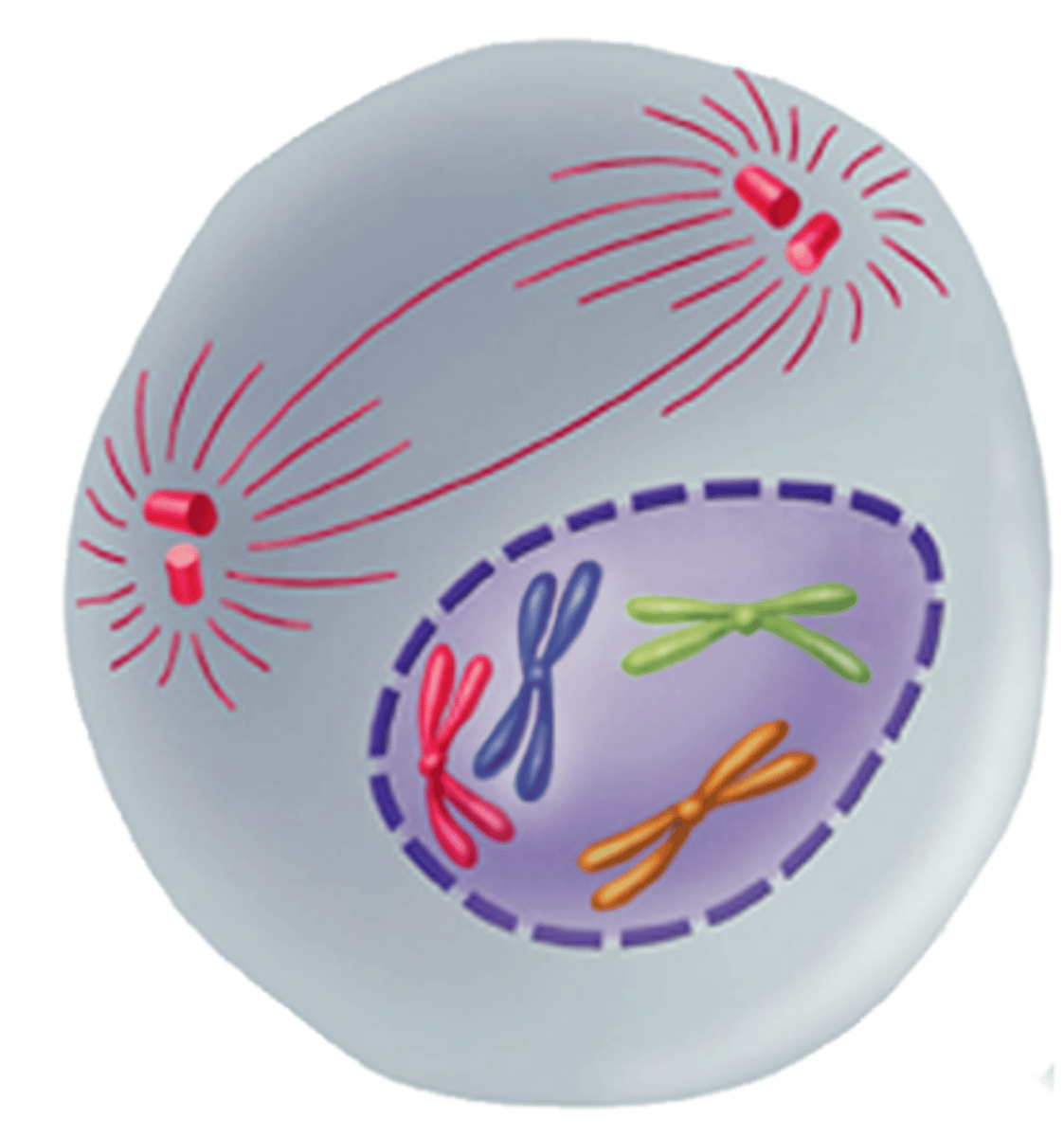
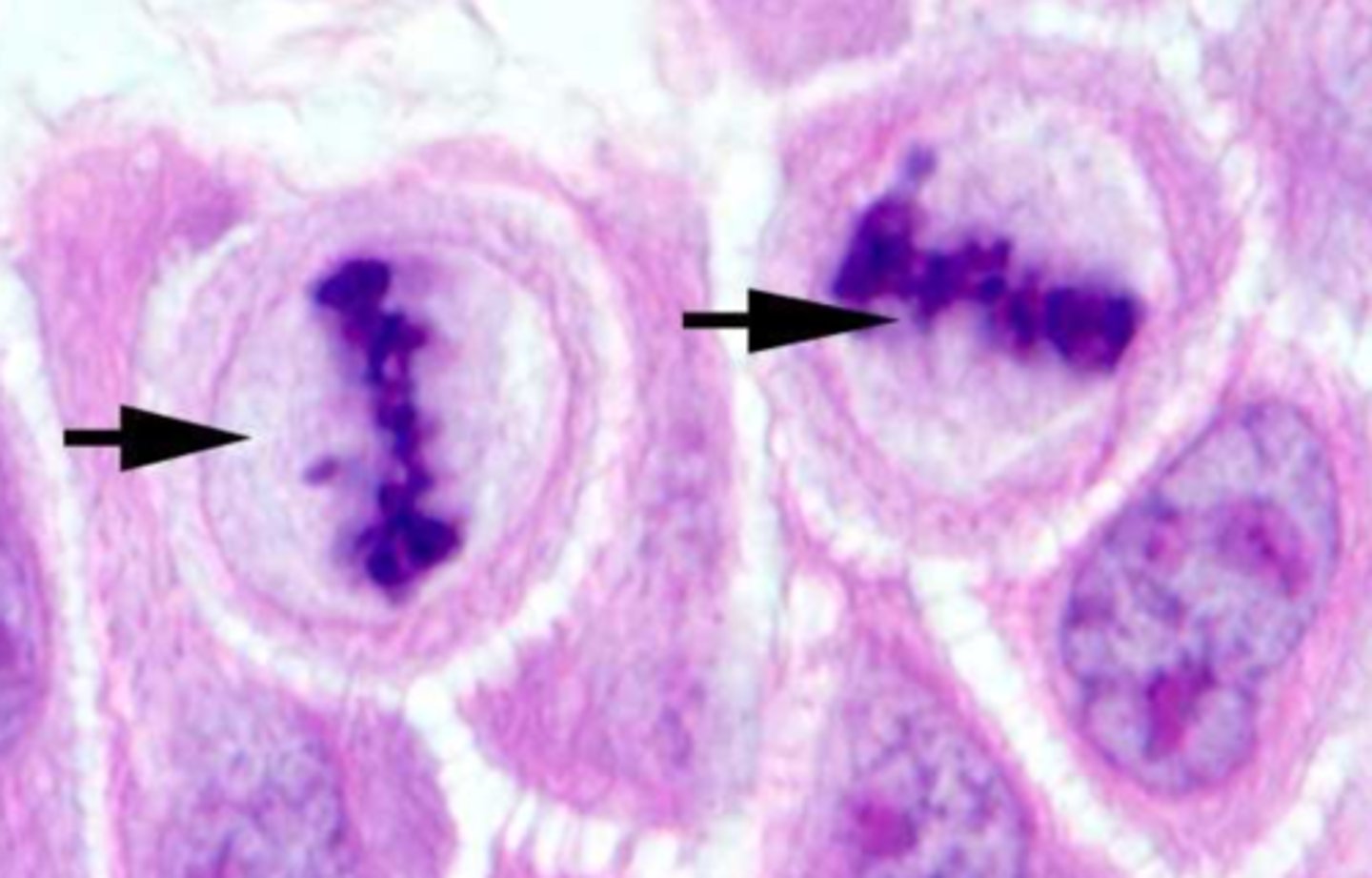
Metaphase
The second phase of mitosis is metaphase; chromosomes line up single file across the center of the cell (equator); kinetochore microtubules connect the centromere of each chromosome to the centrosomes at the poles; polar microtubules connect the centrosomes at each pole to each other
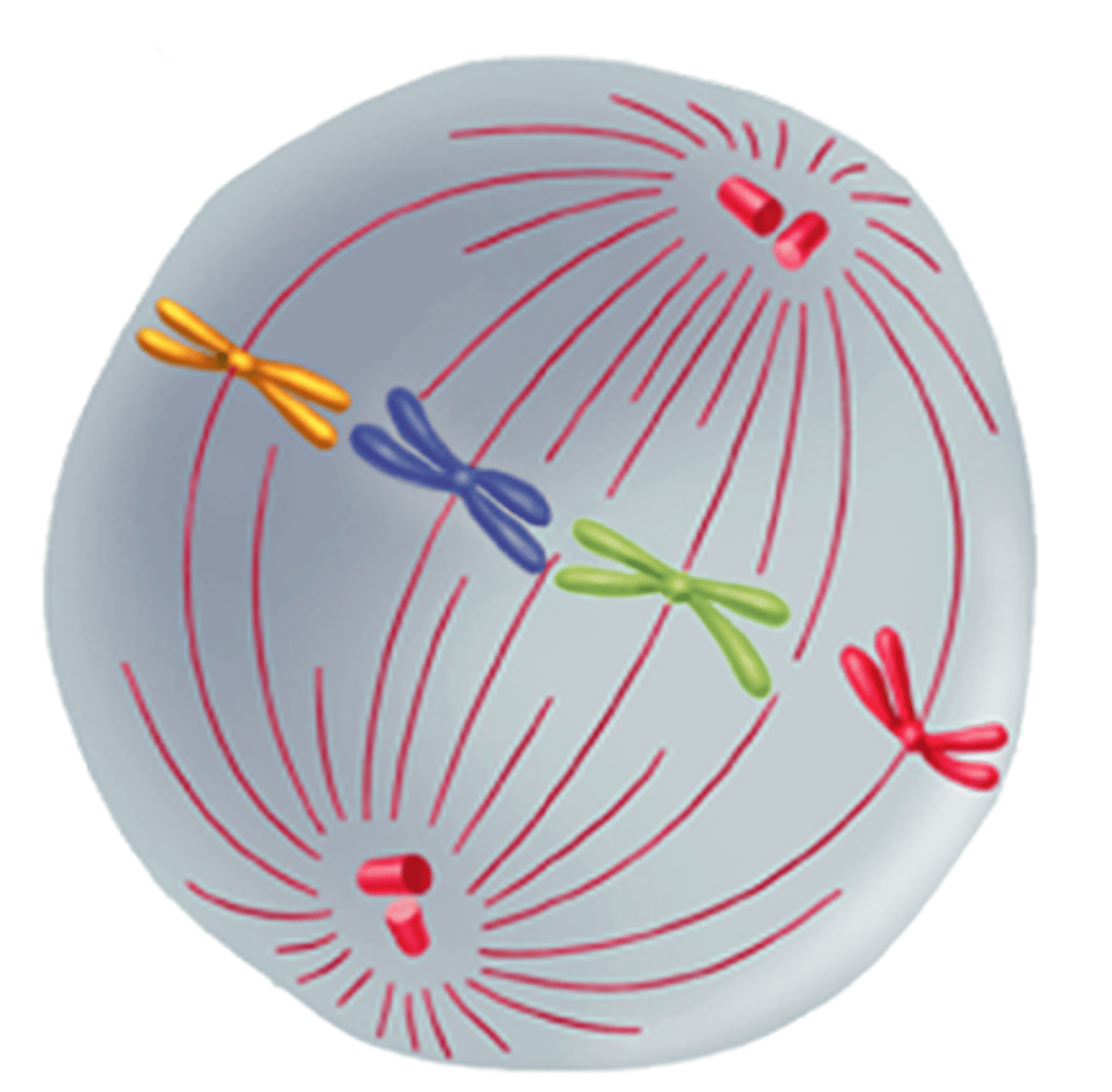
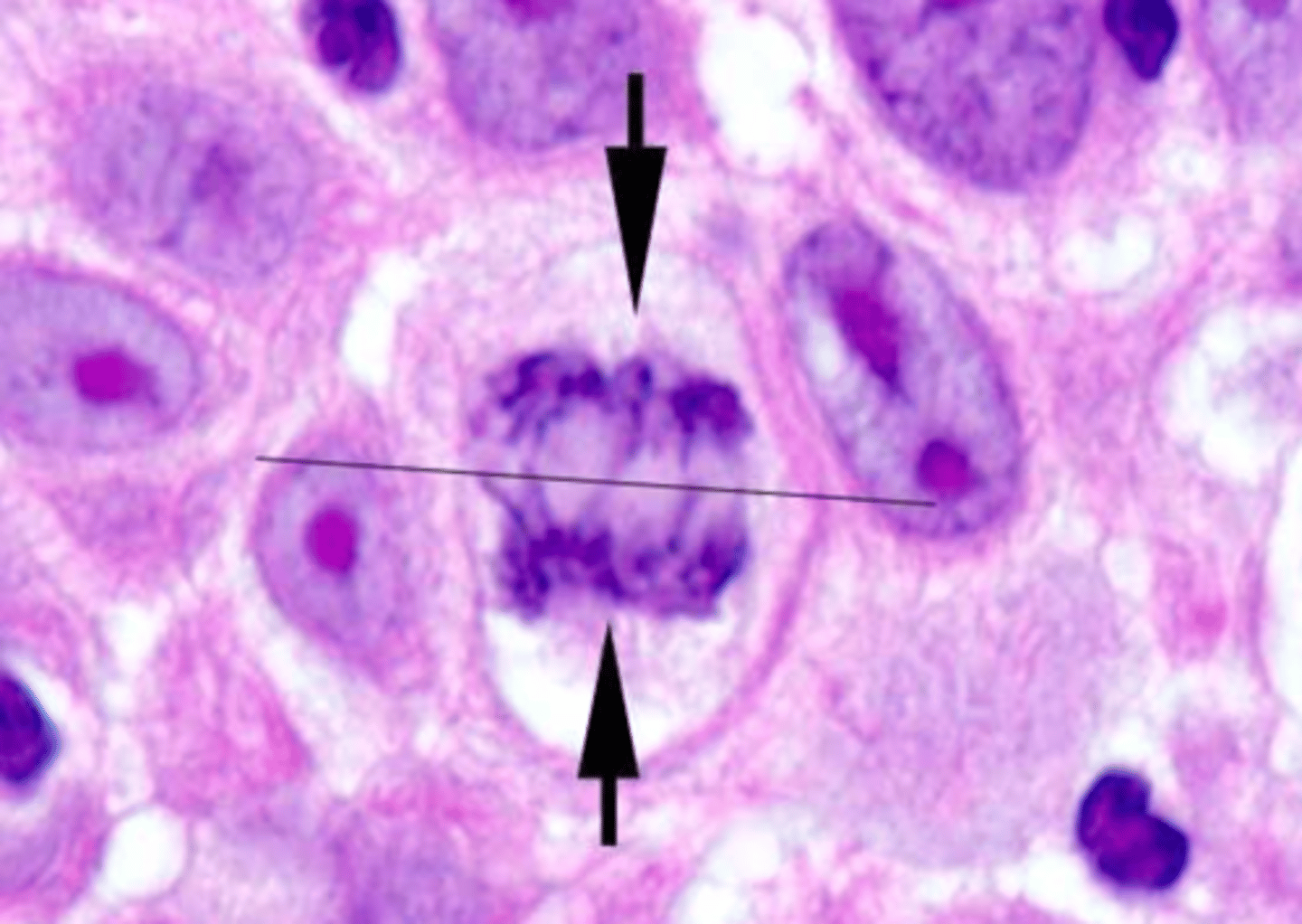
Anaphase
The third phase of mitosis; sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes; the chromosomes continue to move until they have separated into two groups
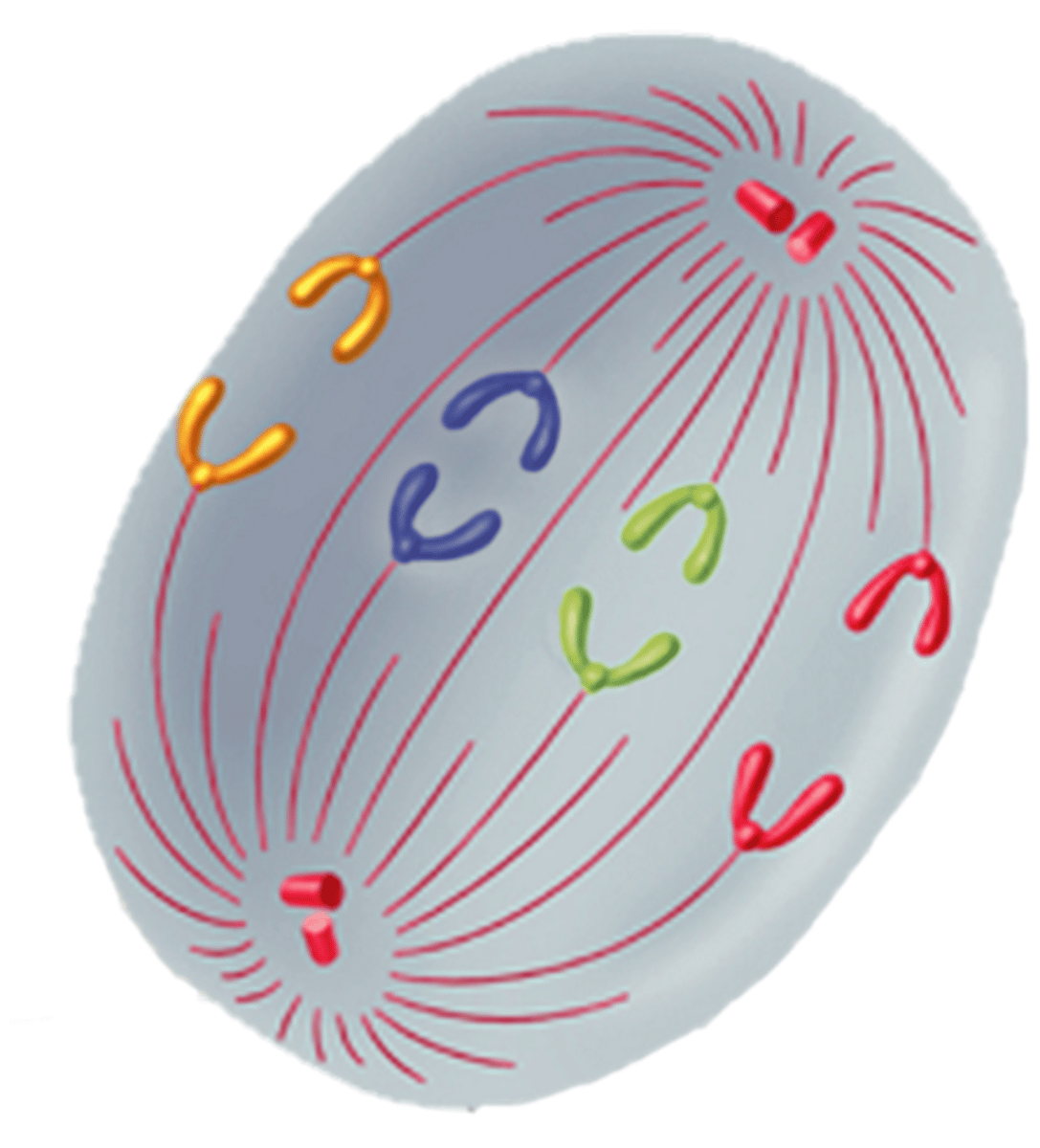
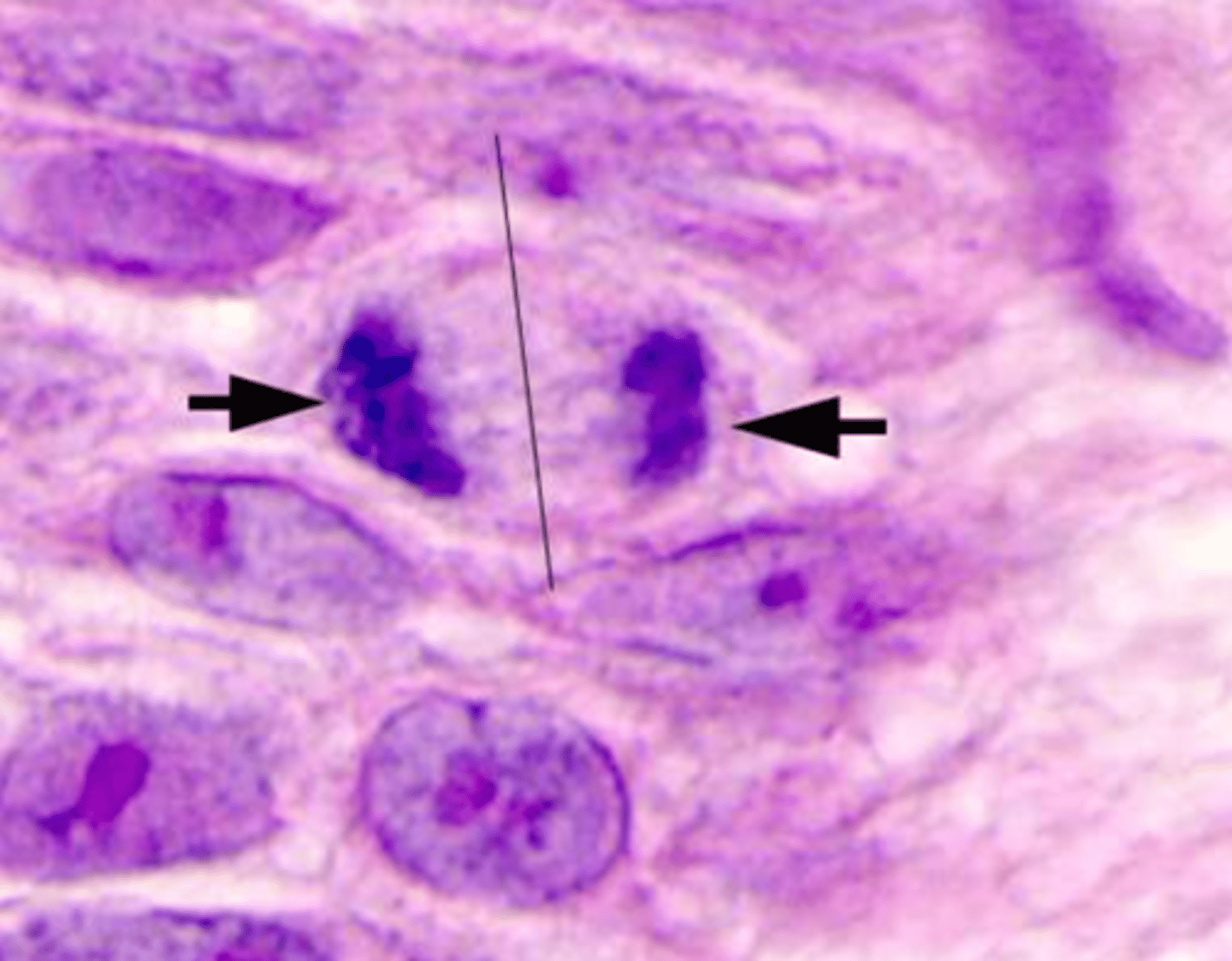
Telophase
The fourth and final phase of mitosis; chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell and lose their distinct shape; a new nuclear envelope forms around each cluster of chromosomes; cleavage furrow starts to form in animal cells and cell plate starts to form in plant cells; centrosomes disappear
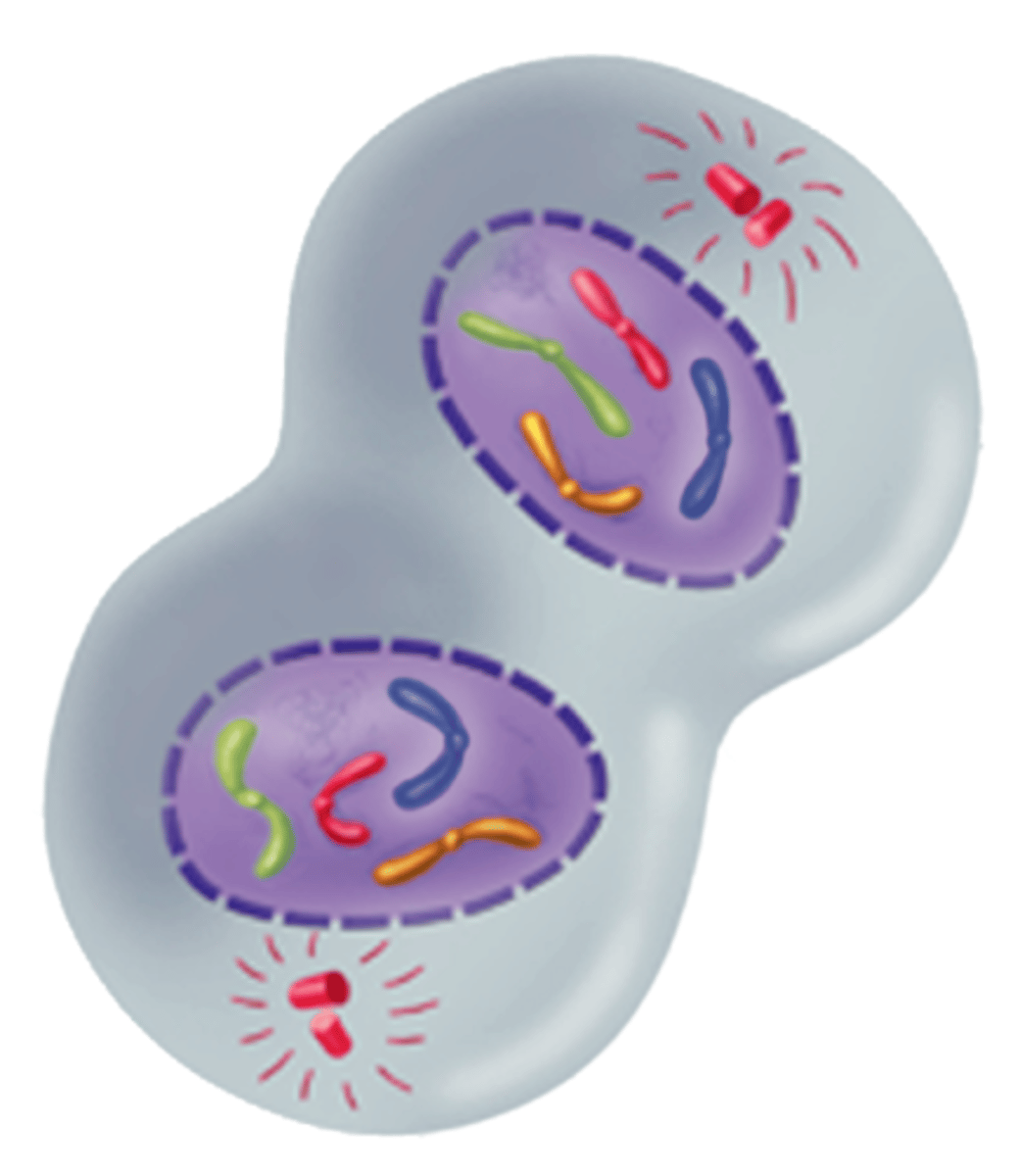
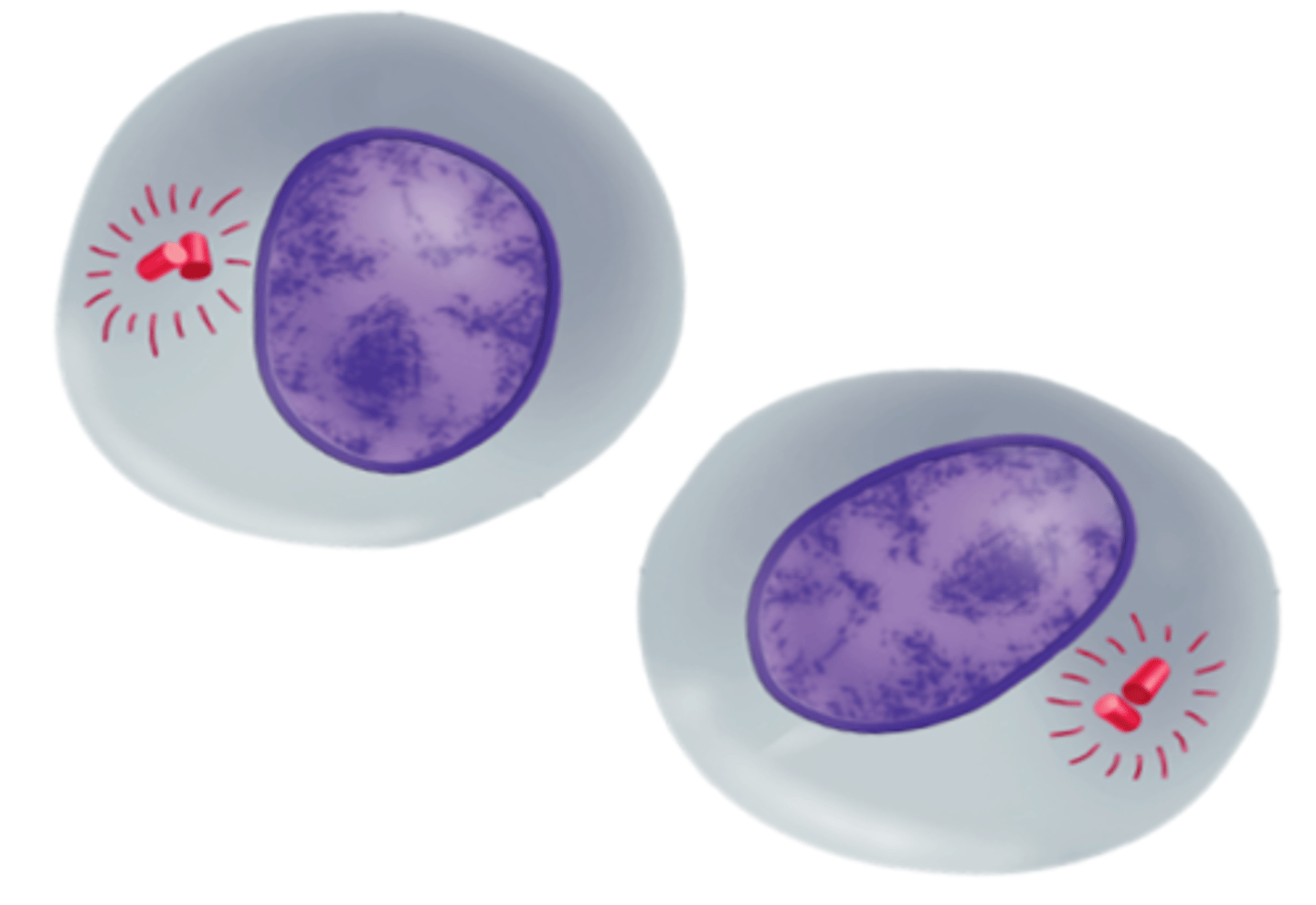
Cytokinesis (Animal Cells)
A stage of the M phase in which the cytoplasm pinches in half and daughter cells separate from each other; each daughter cell has an identical set of duplicate chromosomes
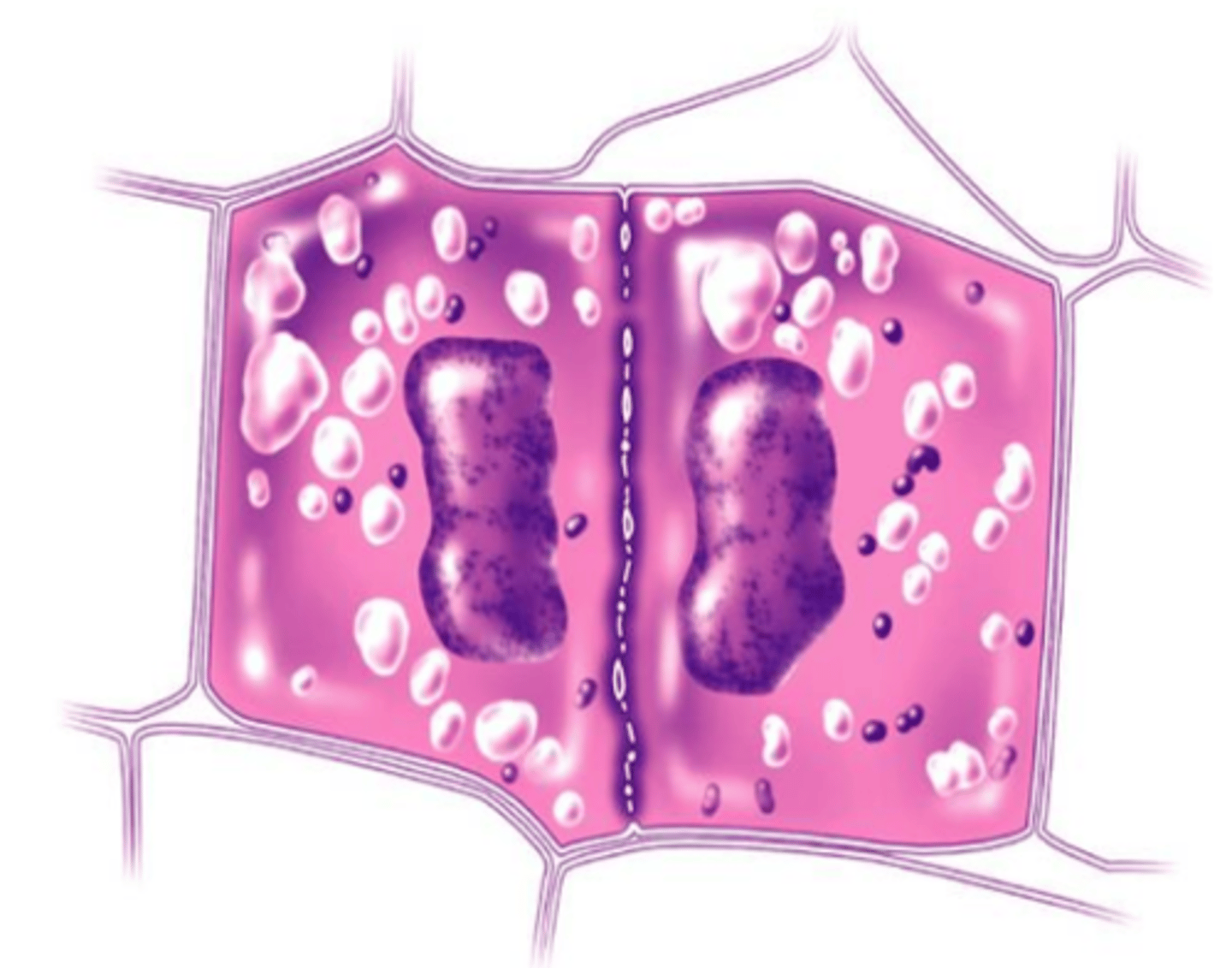
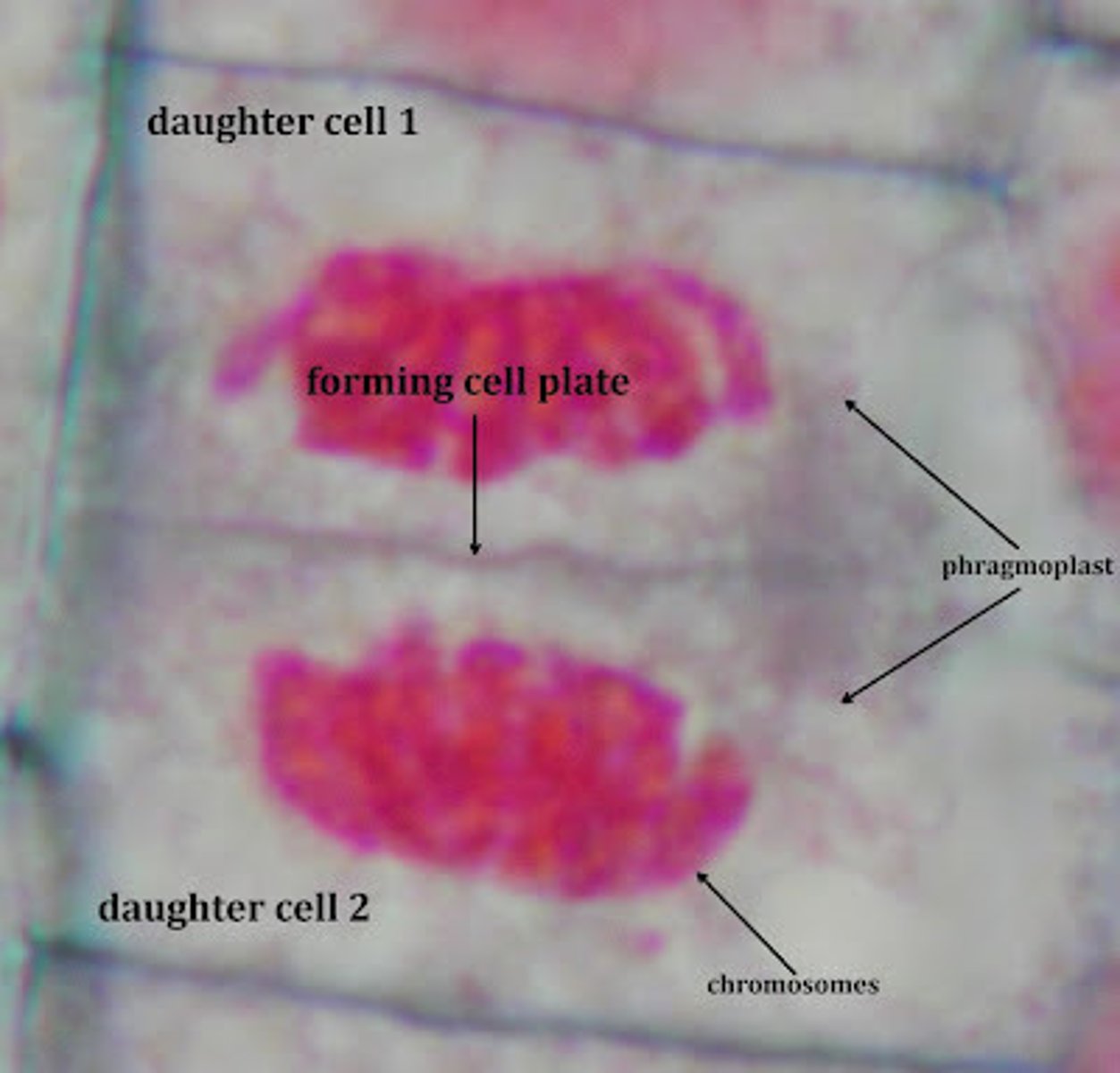
Cytokinesis (Plant Cells)
A stage of the M phase in which a structure known as the cell plate forms midway between the divided nuclei; the cell plate gradually develops into a separating membrane; a cell wall then begins to appear in the cell plate
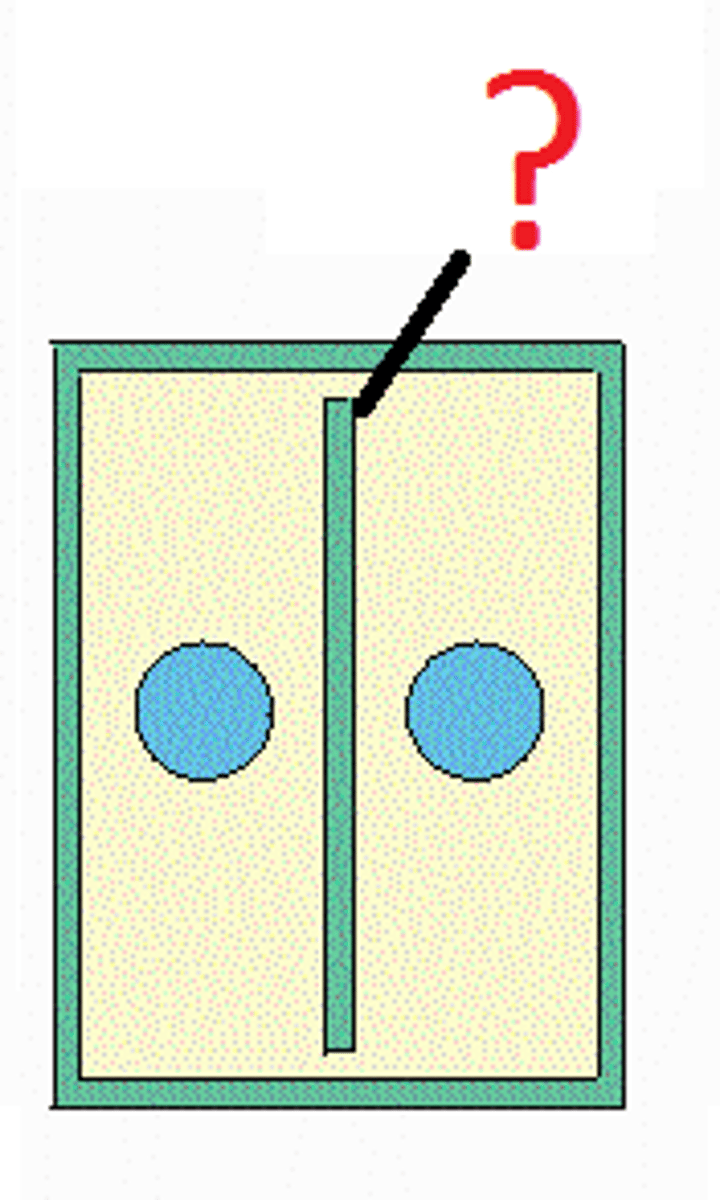
Cell plate
A double membrane across the midline of a dividing plant cell, between which the new cell wall forms during cytokinesis
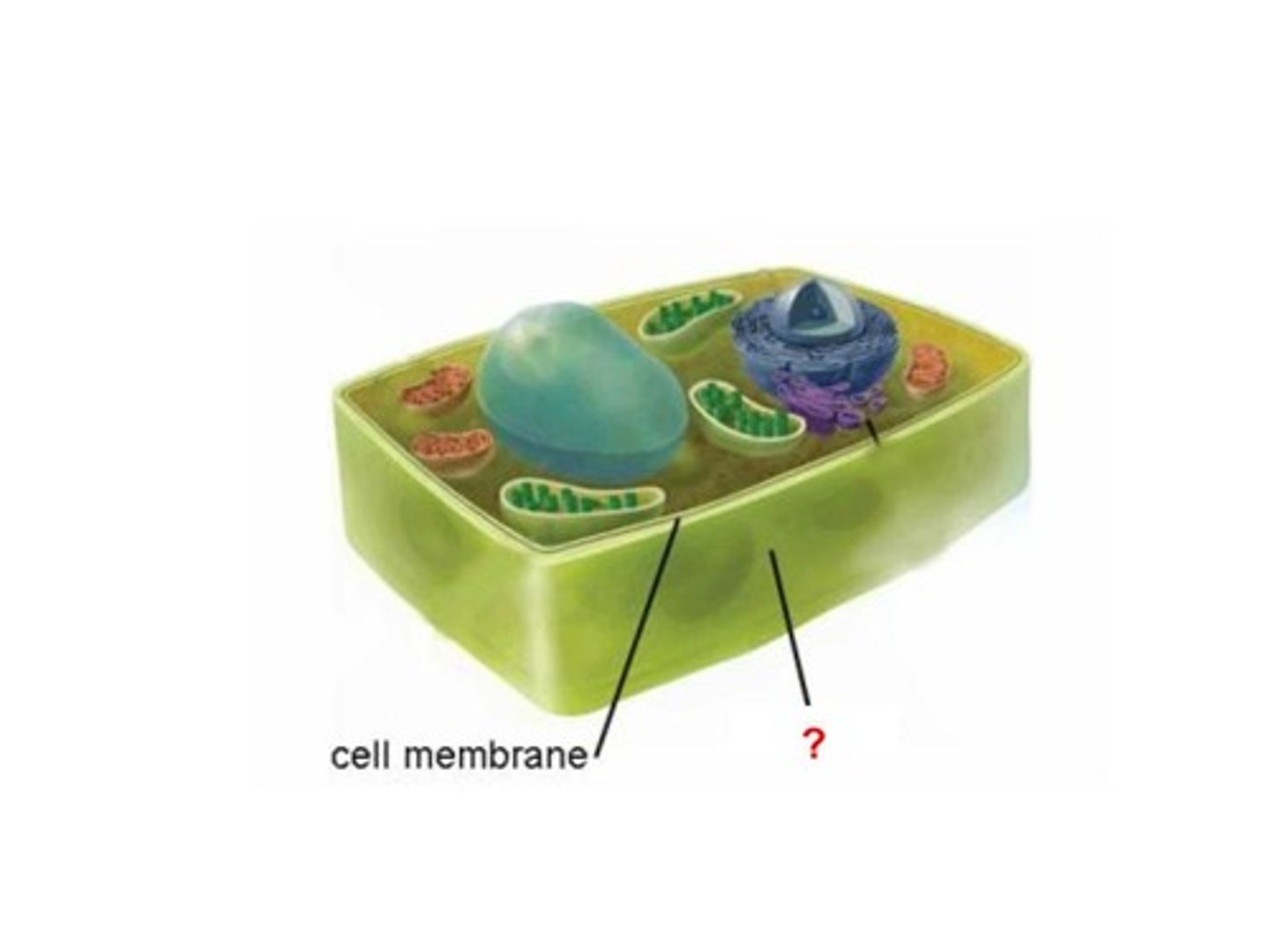
Cell wall
A rough, rigid structure around the outside of the cell membrane in plant cells only; primarily made of cellulose
Prophase (Animal Cell)
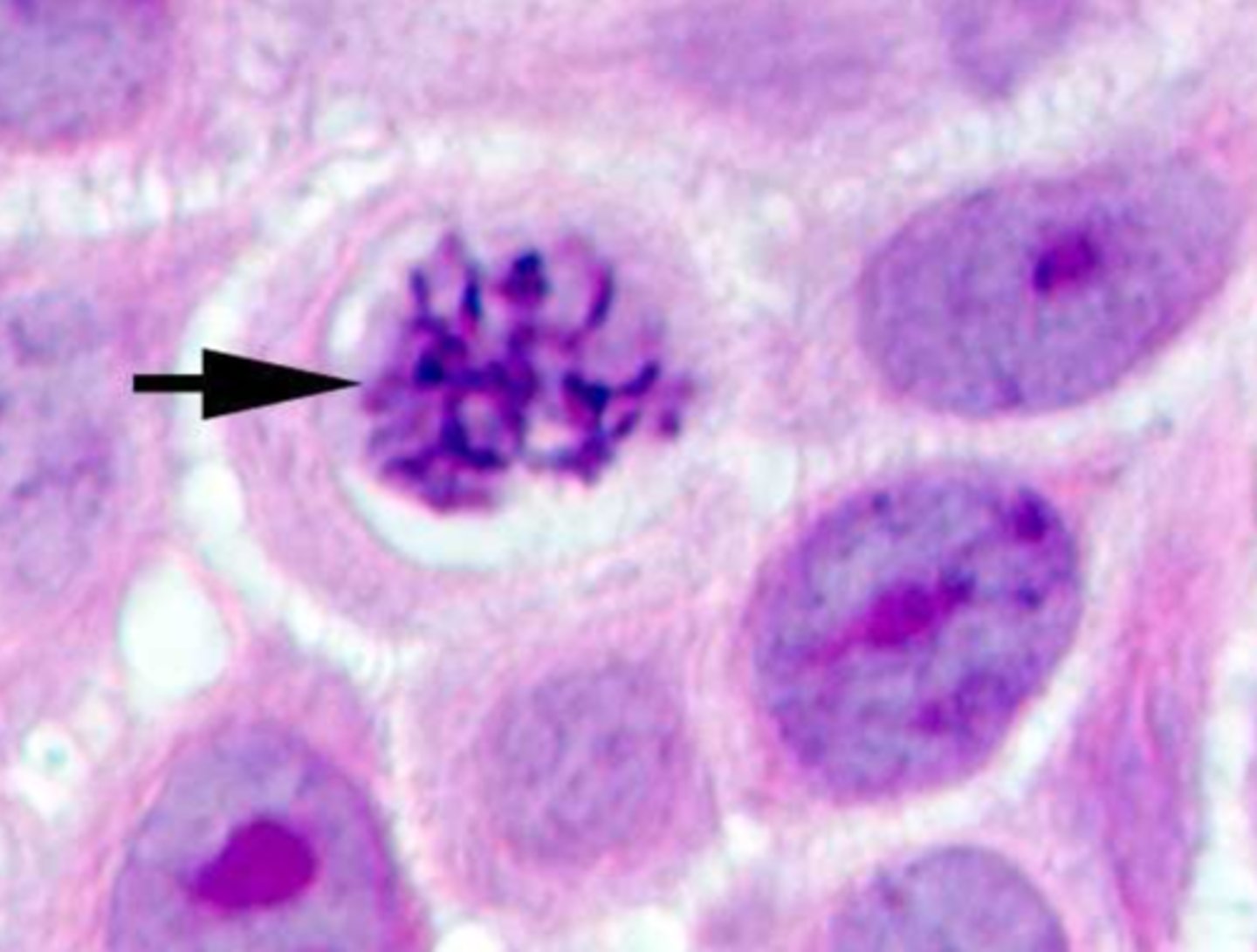
Metaphase (Animal Cell)
Anaphase (Animal Cell)
Telophase (Animal Cell)
Cytokinesis (Animal Cell)
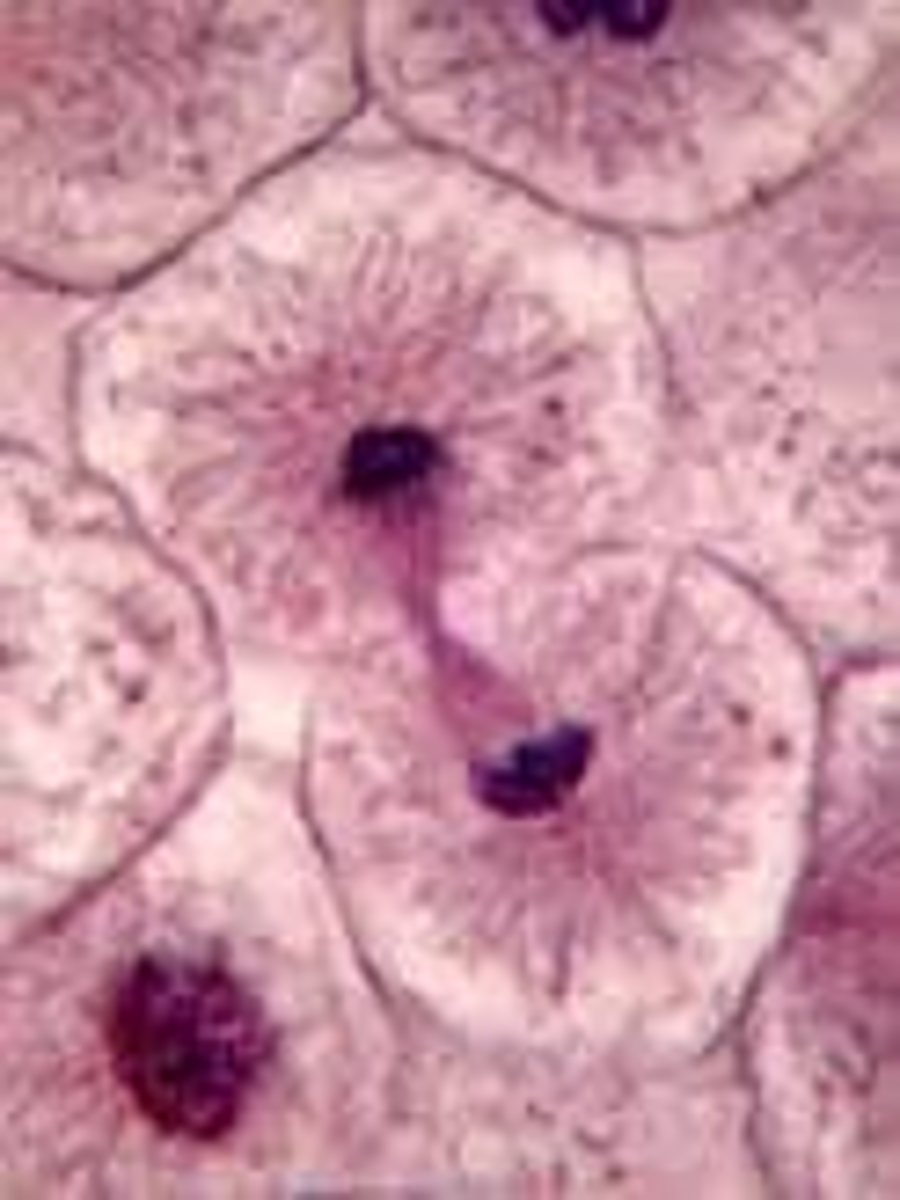
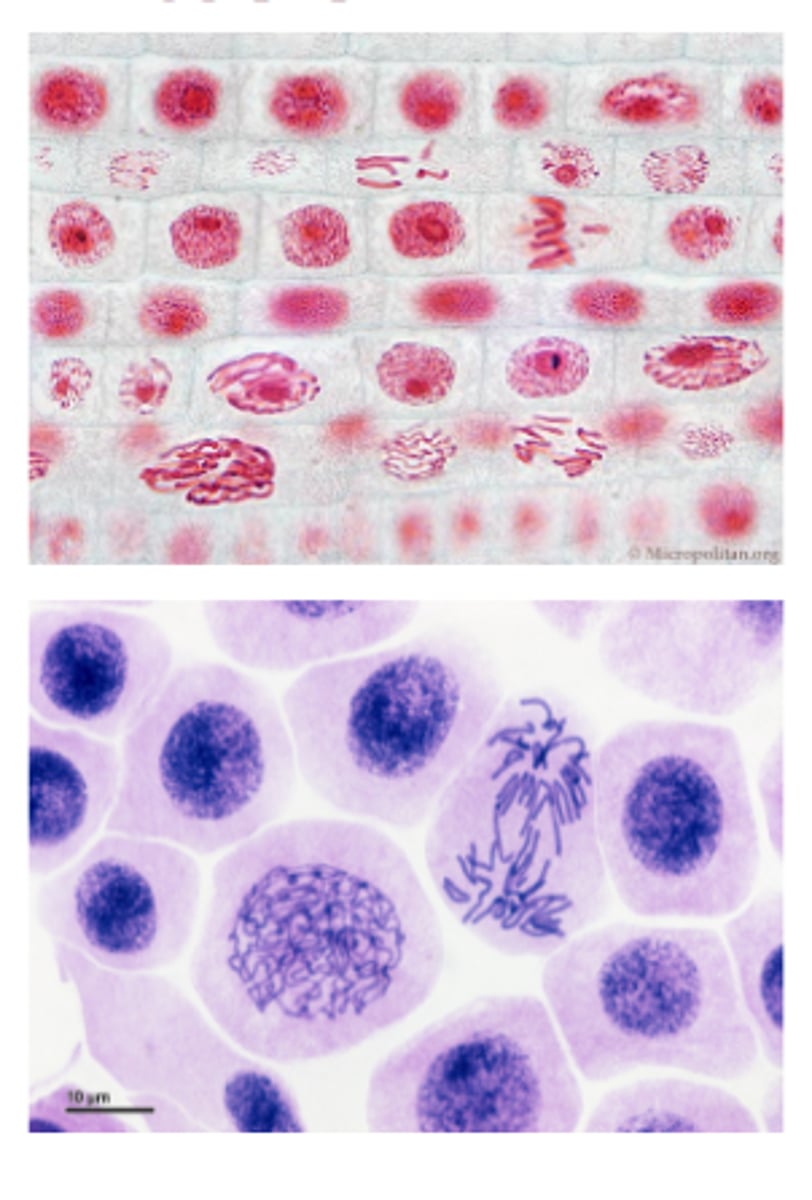
Prophase (Onion Root Tip)
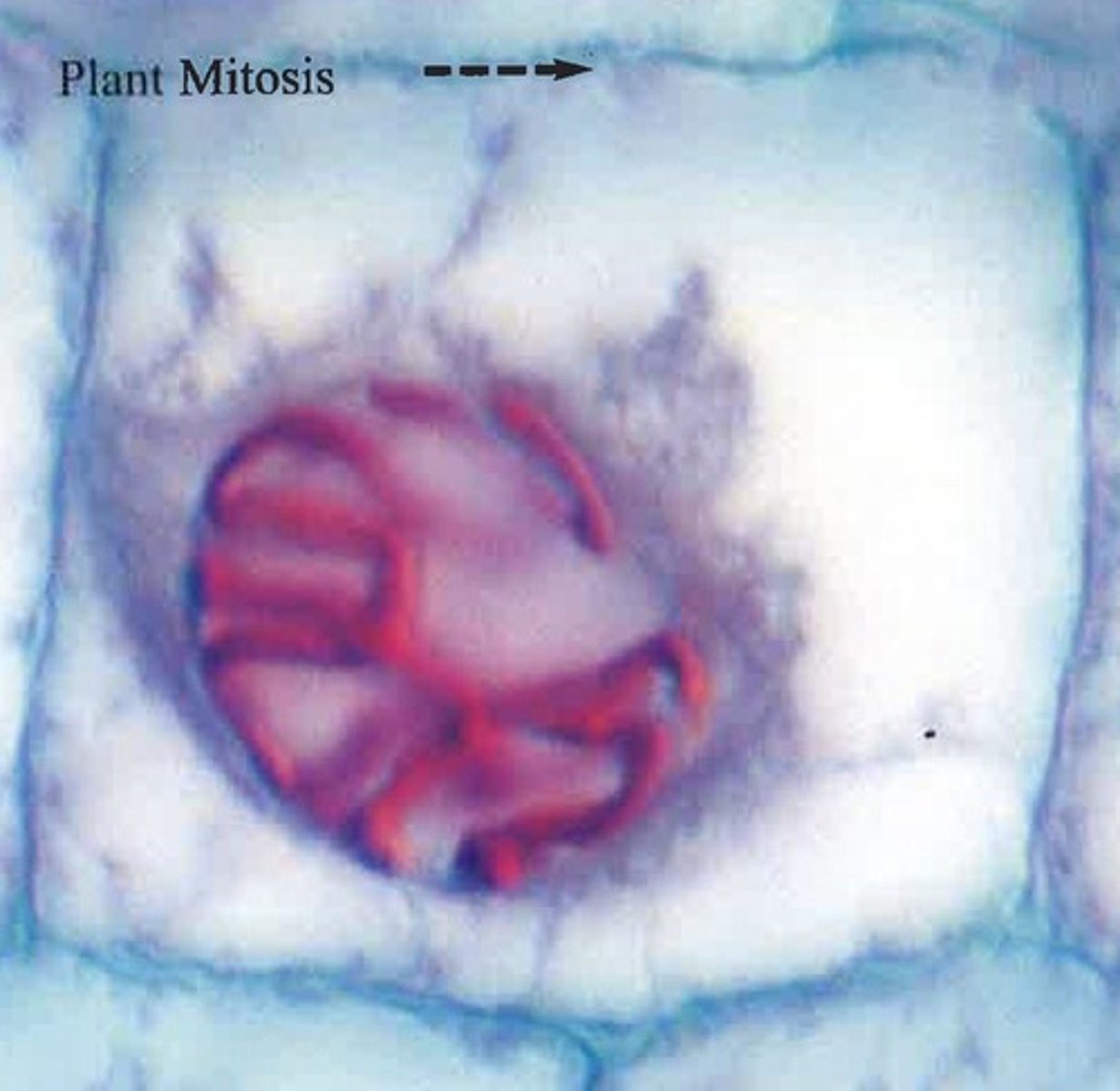
Metaphase (Onion Root Tip)
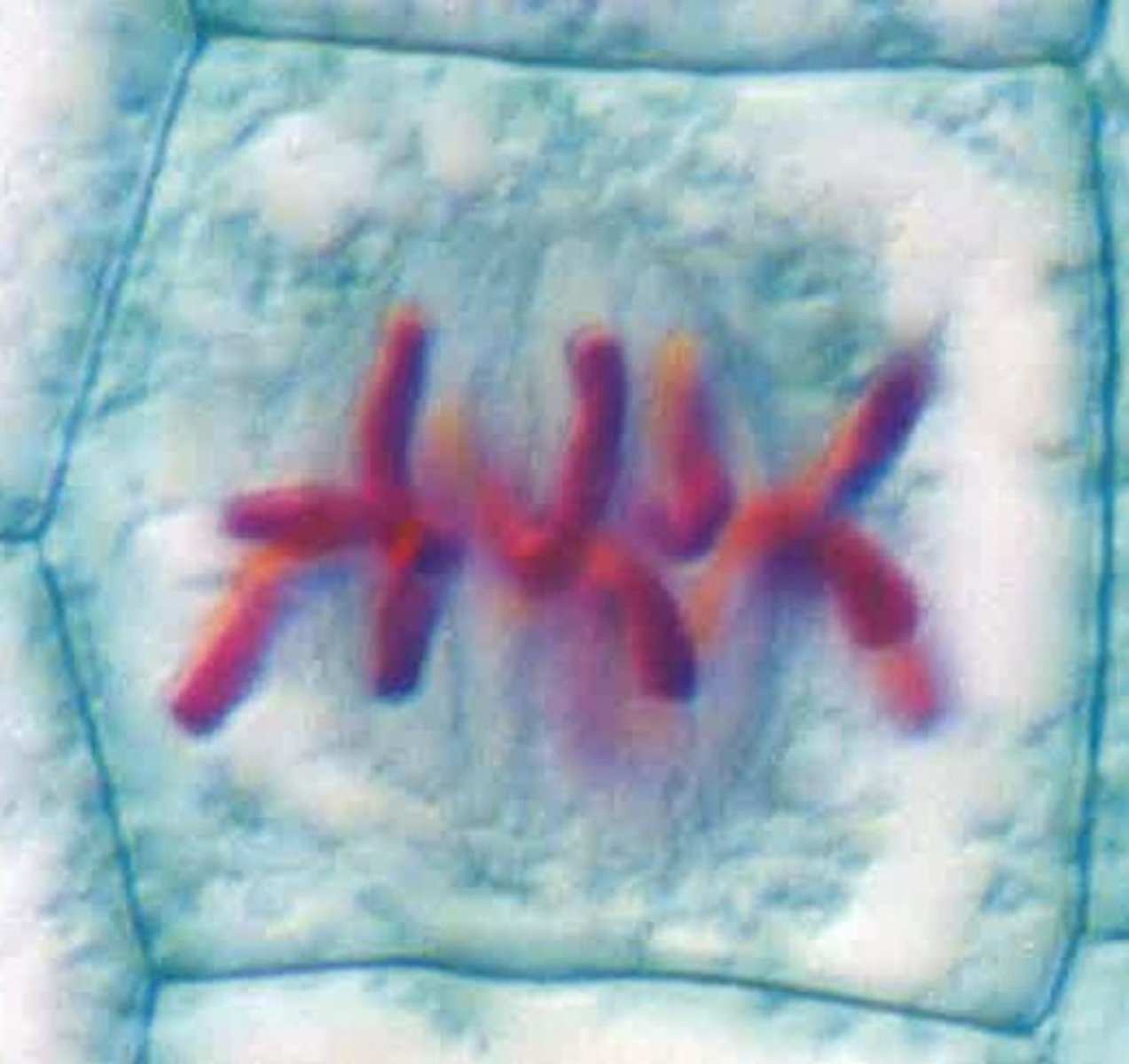
Anaphase (Onion Root Tip)
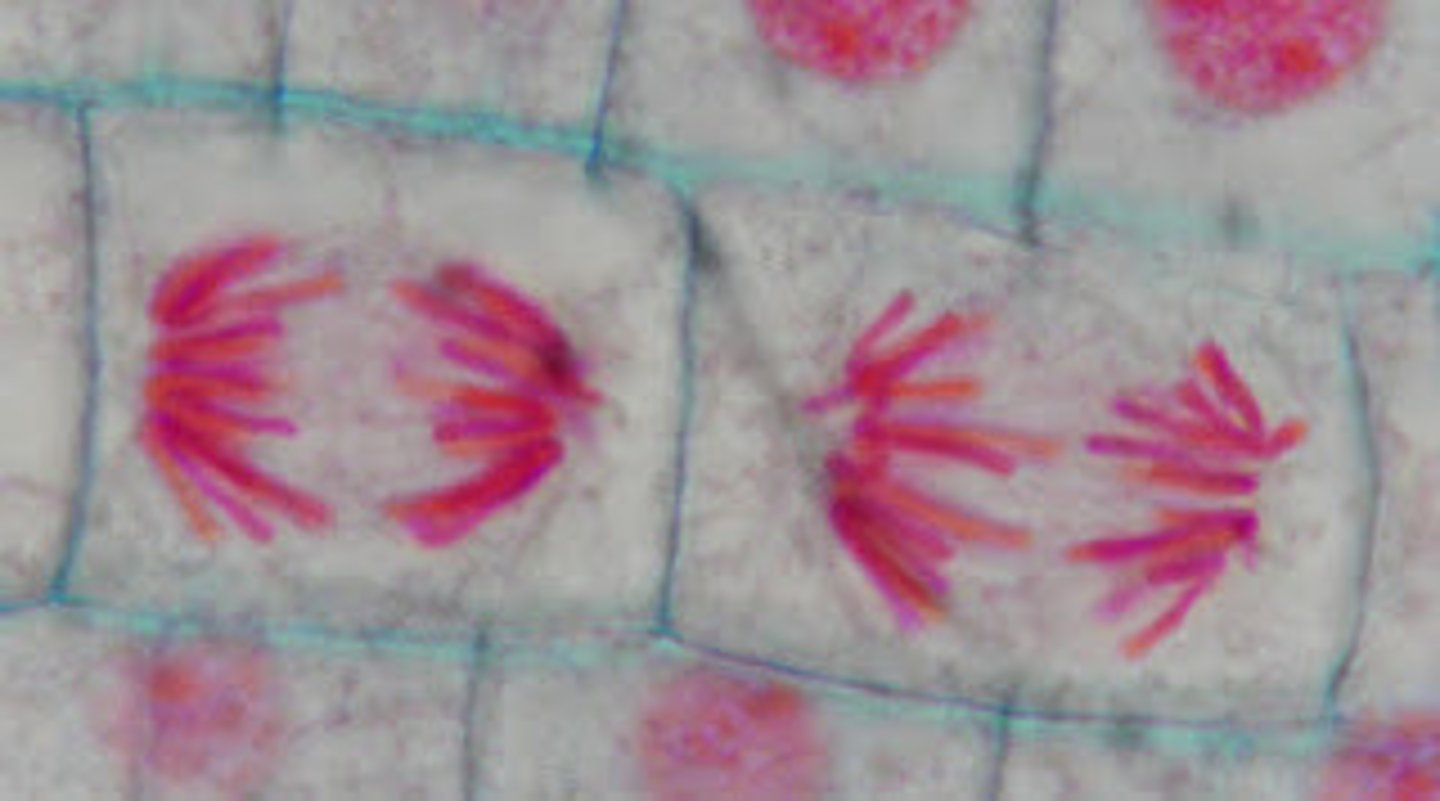
Telophase (Onion Root Tip)
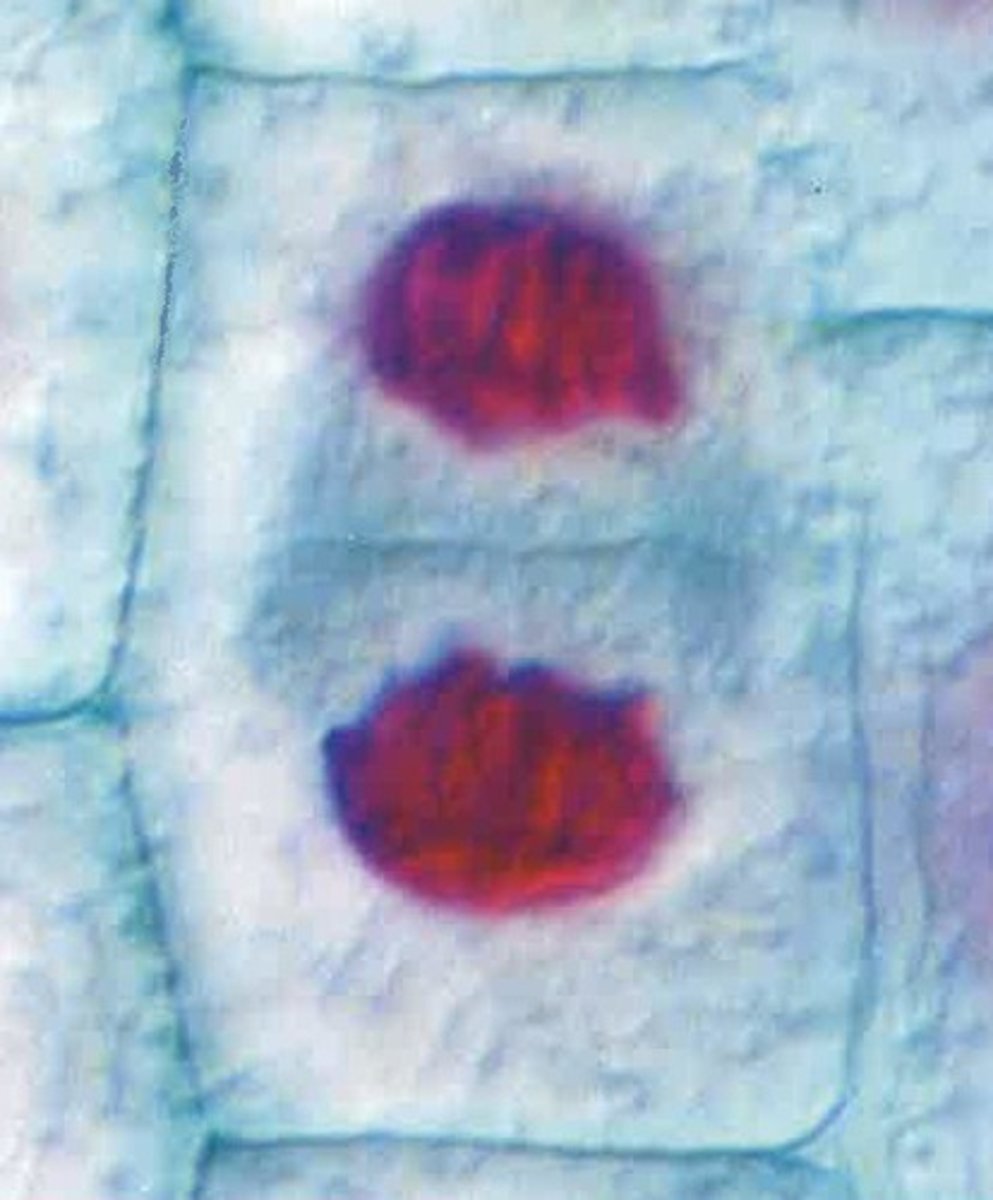
Cytokinesis (Onion Root Tip)
External Regulation of Cell Growth
Contact inhibition
Anchorage dependent inhibition
Internal Regulation of Cell Growth
Cyclins
Stop and Go signals
Contact Inhibition
A mechanism that controls cell growth when cells come into contact with other cells, they respond by not growing; the proteins on the cell membrane surface signals each other
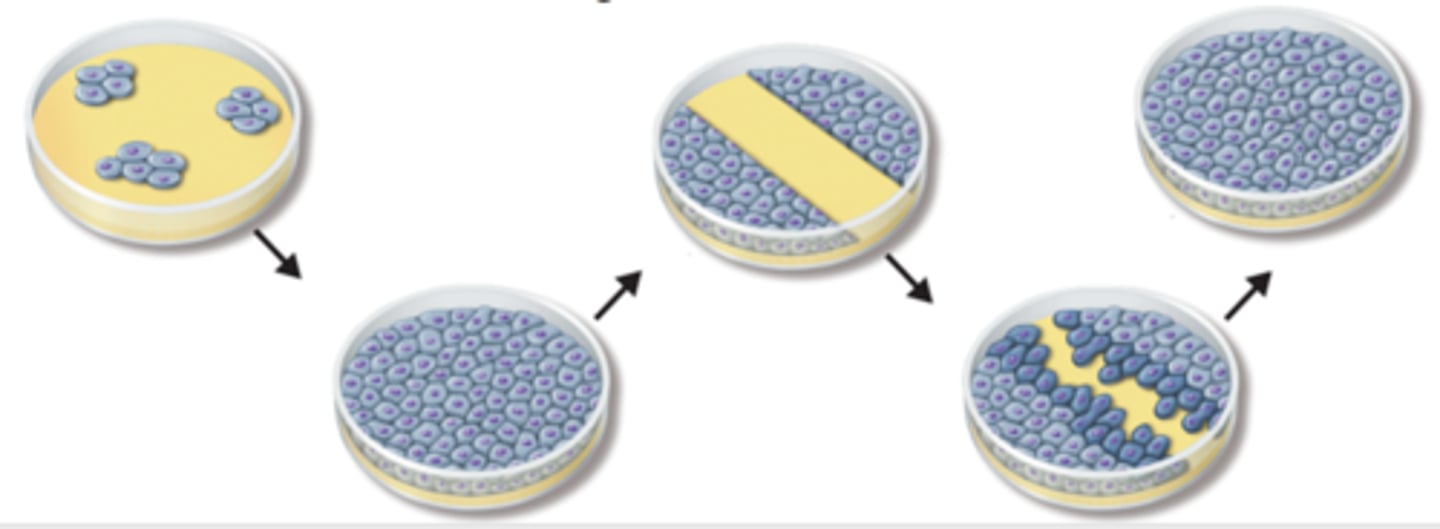
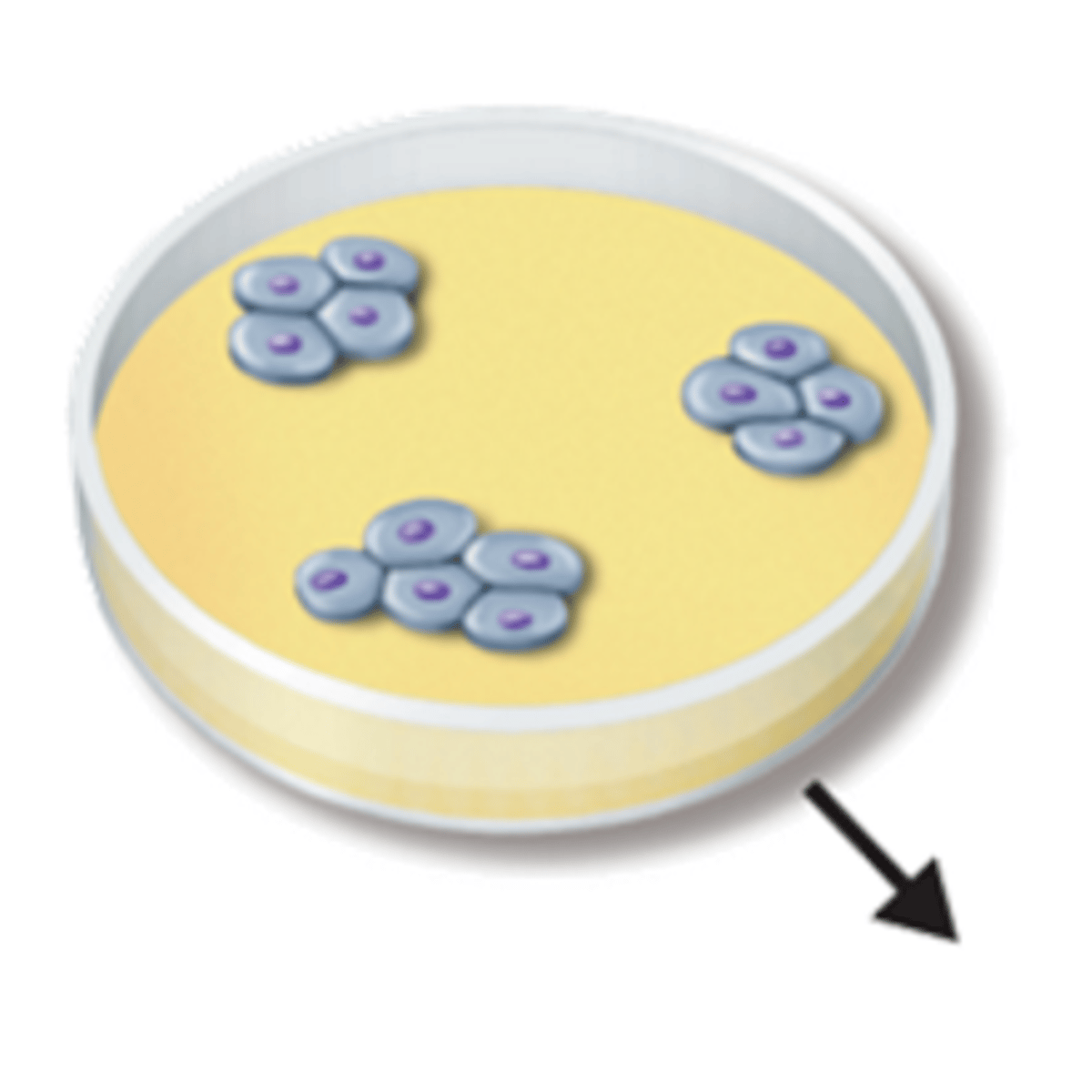
Anchorage Dependent Inhibition
A mechanism that controls cell growth in which cells can only divide when they are anchored to a surface; i.e. inside a culture jar or extracellular matrix of a tissue
Cyclins
A protein that helps regulate the cell cycle
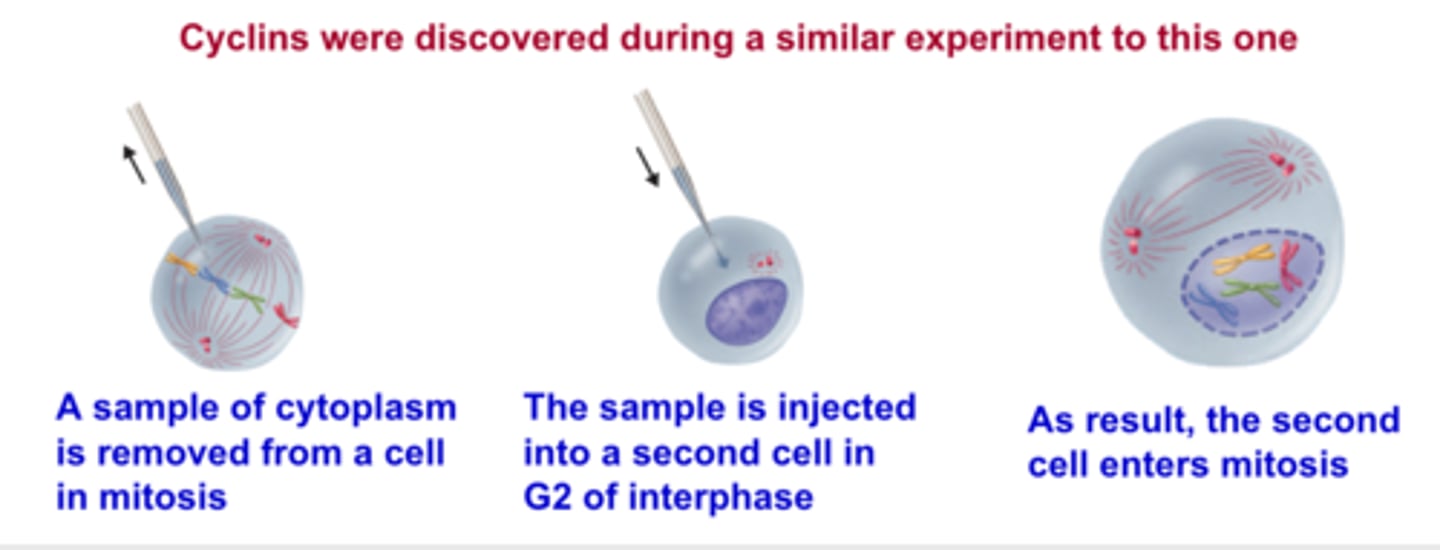
Stop and Go Signals
Certain criteria must be met for a cell to proceed through the process of cell division; for example, if the centromere is not properly attached to spindle microtubules a molecular signal is sent that delays anaphase until they are correctly attached
Cancer
A disorder in which some of the body's own cells lose the ability to control growth
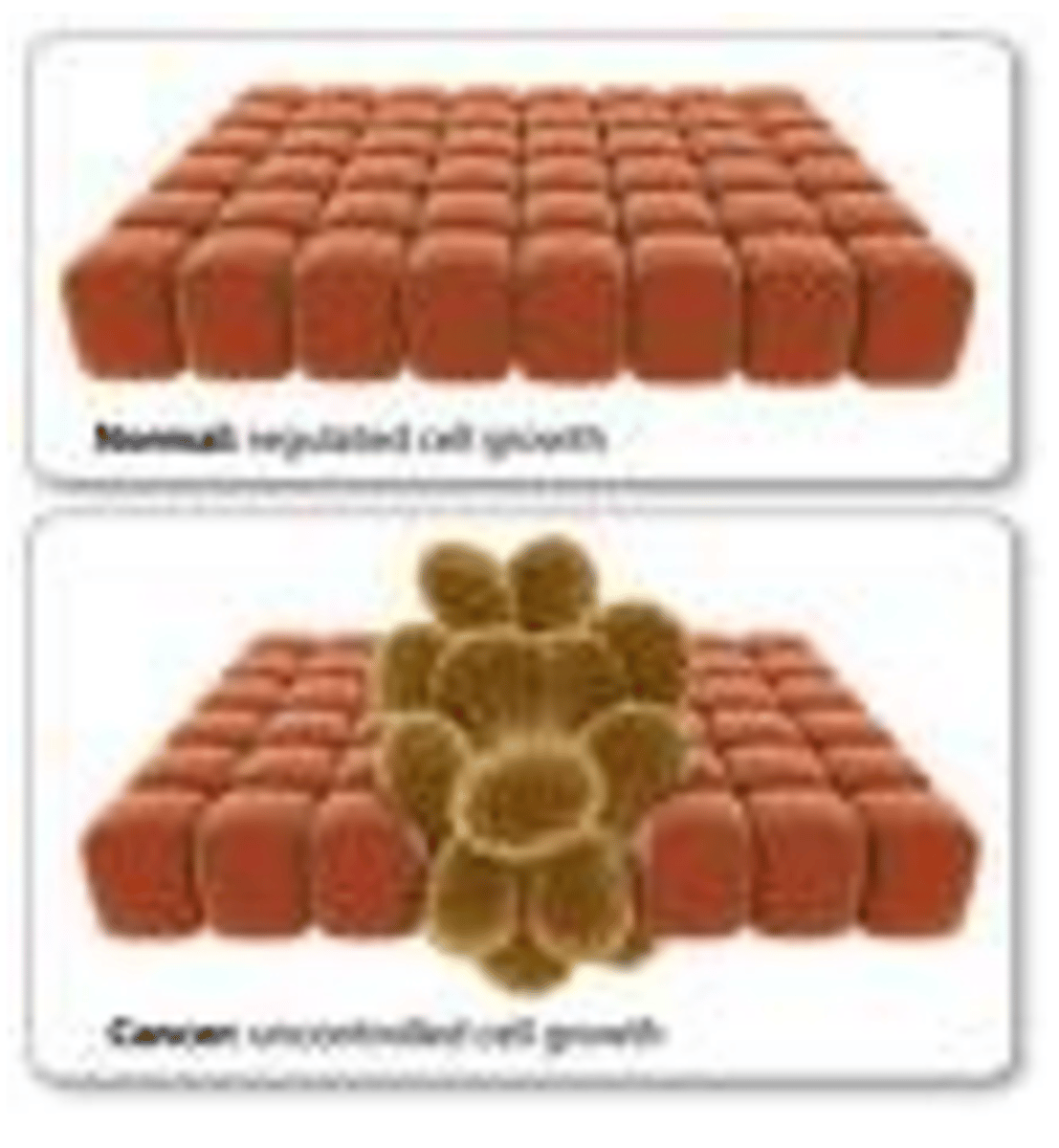
Metastasis
An abnormal mass of cells that is fast growing and spreads beyond their original site in the body; cancerous
Benign tumor
An abnormal mass of cells that is slower growing and remains at its original site in the body; noncancerous tumor
Malignant tumor
An abnormal tissue mass that can spread into neighboring tissue and to other parts of the body; a cancerous tumor
Tumor
A mass of rapidly dividing cells that can damage surrounding tissue